-
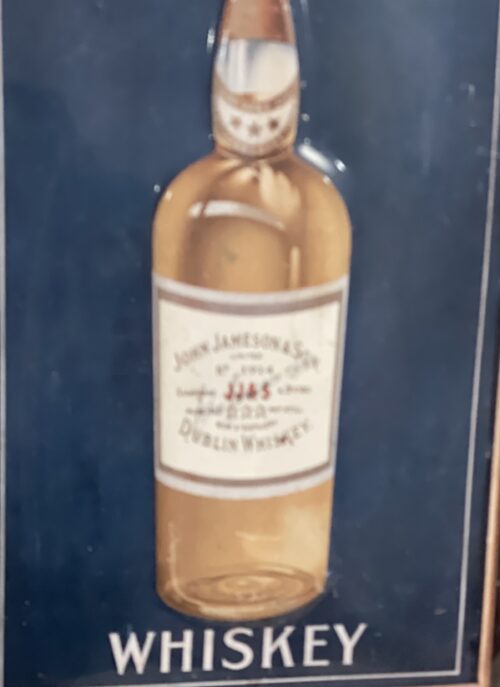
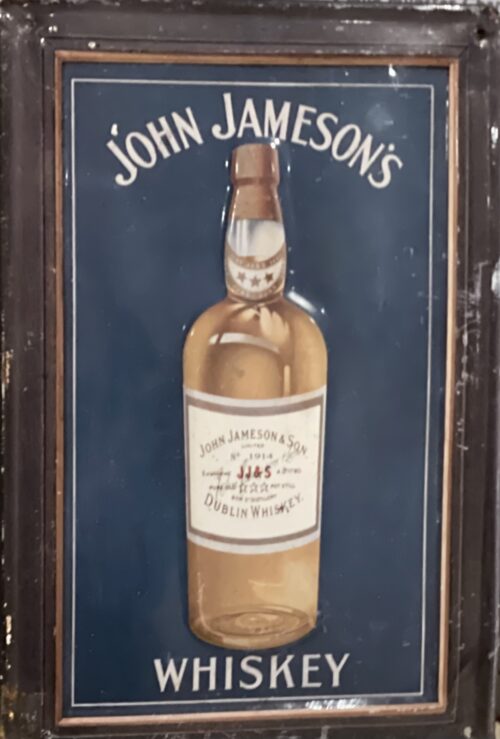
 29cm x 20cm John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it
29cm x 20cm John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it -

 42cm x 68cm Bushmills is officially the worlds oldest whiskey distillery- when in 1608 King James I granted Sir Thomas Phillips,landowner and Governor of Co Antrim,Ireland - a licence to distill.It was in 1784 when Mr Hugh Anderson registered the Old Bushmills Distillery and the Pot Still became its registered trademark, which is still a mark of genuine distinction to this day. The Bushmills area has a long tradition with distillation. According to one story, as far back as 1276, an early settler called Sir Robert Savage of Ards, before defeating the Irish in battle, fortified his troops with "a mighty drop of acqua vitae". In 1608, a licence was granted to Sir Thomas Phillips (Irish adventurer) by King James I to distil whiskey. The Bushmills Old Distillery Company itself was not established until 1784 by Hugh Anderson. Bushmills suffered many lean years with numerous periods of closure with no record of the distillery being in operation in the official records both in 1802 and in 1822. In 1860 a Belfast spirit merchant named Jame McColgan and Patrick Corrigan bought the distillery; in 1880 they formed a limited company. In 1885, the original Bushmills buildings were destroyed by fire but the distillery was swiftly rebuilt. In 1890, a steamship owned and operated by the distillery, SS Bushmills, made its maiden voyage across the Atlantic to deliver Bushmills whiskey to America. It called at Philadelphiaand New York City before heading on to Singapore, Hong Kong, Shanghai and Yokohama.In the early 20th century, the U.S. was a very important market for Bushmills (and other Irish Whiskey producers). American Prohibition in 1920 came as a large blow to the Irish Whiskey industry, but Bushmills managed to survive. Wilson Boyd, Bushmills' director at the time, predicted the end of prohibition and had large stores of whiskey ready to export. After the Second World War, the distillery was bought by Isaac Wolfson, and, in 1972, it was taken over by Irish Distillers, meaning that Irish Distillers controlled the production of all Irish whiskey at the time. In June 1988, Irish Distillers was bought by French liquor group Pernod Ricard.In June 2005, the distillery was bought by Diageo for £200 million. Diageo have also announced a large advertising campaign in order to regain a market share for Bushmills.In May 2008, the Bank of Ireland issued a new series of sterling banknotes in Northern Ireland which all feature an illustration of the Old Bushmills Distillery on the obverse side, replacing the previous notes series which depicted Queen's University of Belfast. In November 2014 it was announced that Diageo had traded the Bushmills brand with Jose Cuervo in exchange for the 50% of the Don Julio brand of tequila that Diageo did not already own.
42cm x 68cm Bushmills is officially the worlds oldest whiskey distillery- when in 1608 King James I granted Sir Thomas Phillips,landowner and Governor of Co Antrim,Ireland - a licence to distill.It was in 1784 when Mr Hugh Anderson registered the Old Bushmills Distillery and the Pot Still became its registered trademark, which is still a mark of genuine distinction to this day. The Bushmills area has a long tradition with distillation. According to one story, as far back as 1276, an early settler called Sir Robert Savage of Ards, before defeating the Irish in battle, fortified his troops with "a mighty drop of acqua vitae". In 1608, a licence was granted to Sir Thomas Phillips (Irish adventurer) by King James I to distil whiskey. The Bushmills Old Distillery Company itself was not established until 1784 by Hugh Anderson. Bushmills suffered many lean years with numerous periods of closure with no record of the distillery being in operation in the official records both in 1802 and in 1822. In 1860 a Belfast spirit merchant named Jame McColgan and Patrick Corrigan bought the distillery; in 1880 they formed a limited company. In 1885, the original Bushmills buildings were destroyed by fire but the distillery was swiftly rebuilt. In 1890, a steamship owned and operated by the distillery, SS Bushmills, made its maiden voyage across the Atlantic to deliver Bushmills whiskey to America. It called at Philadelphiaand New York City before heading on to Singapore, Hong Kong, Shanghai and Yokohama.In the early 20th century, the U.S. was a very important market for Bushmills (and other Irish Whiskey producers). American Prohibition in 1920 came as a large blow to the Irish Whiskey industry, but Bushmills managed to survive. Wilson Boyd, Bushmills' director at the time, predicted the end of prohibition and had large stores of whiskey ready to export. After the Second World War, the distillery was bought by Isaac Wolfson, and, in 1972, it was taken over by Irish Distillers, meaning that Irish Distillers controlled the production of all Irish whiskey at the time. In June 1988, Irish Distillers was bought by French liquor group Pernod Ricard.In June 2005, the distillery was bought by Diageo for £200 million. Diageo have also announced a large advertising campaign in order to regain a market share for Bushmills.In May 2008, the Bank of Ireland issued a new series of sterling banknotes in Northern Ireland which all feature an illustration of the Old Bushmills Distillery on the obverse side, replacing the previous notes series which depicted Queen's University of Belfast. In November 2014 it was announced that Diageo had traded the Bushmills brand with Jose Cuervo in exchange for the 50% of the Don Julio brand of tequila that Diageo did not already own.- Bushmills Original – Irish whiskey blend sometimes called White Bush or Bushmills White Label. The grain whiskey is matured in American oak casks.
- Black Bush – A blend with a significantly greater proportion of malt whiskey than the white label. It features malt whiskey aged in casks previously used for Spanish Oloroso sherry.
- Red Bush – Like the Black Bush, this is a blend with a higher proportion of malt whiskey than the standard bottling, but in contrast the malt whiskey has been matured in ex-bourbon casks.
- Bushmills 10 year single malt – Combines malt whiskeys aged at least 10 years in American bourbon or Oloroso sherry casks.
- Bushmills Distillery Reserve 12 year single malt – exclusively available at the Old Bushmills Distillery, this 12 year aged single malt is matured in oak casks for a rich, complex flavour with notes of sherry, dark chocolate and spices.
- Bushmills 16 year single malt – Malt whiskeys aged at least 16 years in American bourbon barrels or Spanish Oloroso sherry butts are mixed together before finishing in Port pipes for a few months.
- Bushmills 21 year single malt – A limited number of 21 year bottles are made each year. After 19 years, bourbon-barrel-aged and sherry-cask-aged malt whiskeys are combined, which is followed by two years of finishing in Madeira drums.
- Bushmills 1608: Originally released as a special 400th Anniversary whiskey; since 2009 it will be available only in the Whiskey Shop at the distillery and at duty-free shops.
-

 58cm x 58cm Jameson did not bottle our own whiskey until 1963. The first Jameson whiskey bottled at Bow Street was launched as Crested Ten. Back then, Jameson was available in 68 markets worldwide, exporting 15,000 cases annually to the United States. During the 19th century Irish distillers did not bottle and sell their own whiskey. They simply produced the spirit, put it in casks and then sold it on to retailers directly, who would then supply the public as they wished. These spirits merchants were known as bonders, from the practice of holding whiskey “in bond” (i.e. without duties paid on it) in their specialised bonded warehouses. Many pubs also doubled as bonders, which meant they could, supply their patrons with whiskey of which they were assured the provenance. Provenance and dishonesty were the main problem with this system as distilleries had no control over what happened to their whiskey after it left their premises. This lead some of the more unscrupulous proprietors to adulterate the whiskey coming from the cask or lie about how old it was, meaning that a distillery might end up with a bad name for their product through no fault of their own. However, some whiskey bonders of the era were renowned for their dedication to the art of maturing and blending, such that their names and products have today become some of the most important in Irish whiskey.Though beginning life in 1805 as a tea shop and confectionary business, it was in 1887 that the Mitchell family made their mark on Irish spirit history. That was the year they decided to go into the whiskey bonding, following a period as solely wine merchants. The ingenious idea must have seemed quite obvious, they had lots of empty wine and sherry casks so why not send them across the river to Jameson’s Bow Street distillery to be filled with new make single pot still whiskey. Once in the bonded warehouse the casks were given a coloured dash or spot, depending on how long they were due to be aged for, blue for seven years, green for 10, yellow for 12 and red for 15. This led to its renown as “Spot Whiskey” which became hugely popular with the high society of the time and had no lesser proponent than Samuel Beckett, who would order casks to be delivered to his Parisian literary atelier. Thankfully, Mitchell and Son are still going strong, and aged single pot still whiskey from Midleton, in the form of Green and Yellow Spot is widely available. John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it
58cm x 58cm Jameson did not bottle our own whiskey until 1963. The first Jameson whiskey bottled at Bow Street was launched as Crested Ten. Back then, Jameson was available in 68 markets worldwide, exporting 15,000 cases annually to the United States. During the 19th century Irish distillers did not bottle and sell their own whiskey. They simply produced the spirit, put it in casks and then sold it on to retailers directly, who would then supply the public as they wished. These spirits merchants were known as bonders, from the practice of holding whiskey “in bond” (i.e. without duties paid on it) in their specialised bonded warehouses. Many pubs also doubled as bonders, which meant they could, supply their patrons with whiskey of which they were assured the provenance. Provenance and dishonesty were the main problem with this system as distilleries had no control over what happened to their whiskey after it left their premises. This lead some of the more unscrupulous proprietors to adulterate the whiskey coming from the cask or lie about how old it was, meaning that a distillery might end up with a bad name for their product through no fault of their own. However, some whiskey bonders of the era were renowned for their dedication to the art of maturing and blending, such that their names and products have today become some of the most important in Irish whiskey.Though beginning life in 1805 as a tea shop and confectionary business, it was in 1887 that the Mitchell family made their mark on Irish spirit history. That was the year they decided to go into the whiskey bonding, following a period as solely wine merchants. The ingenious idea must have seemed quite obvious, they had lots of empty wine and sherry casks so why not send them across the river to Jameson’s Bow Street distillery to be filled with new make single pot still whiskey. Once in the bonded warehouse the casks were given a coloured dash or spot, depending on how long they were due to be aged for, blue for seven years, green for 10, yellow for 12 and red for 15. This led to its renown as “Spot Whiskey” which became hugely popular with the high society of the time and had no lesser proponent than Samuel Beckett, who would order casks to be delivered to his Parisian literary atelier. Thankfully, Mitchell and Son are still going strong, and aged single pot still whiskey from Midleton, in the form of Green and Yellow Spot is widely available. John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it -

 67cm x 56cm This historic brand of whiskey has now been revived by the Cooley Distillery (which is now part of Beam Suntory).The brand was previously owned by the Watt Distillery, which (according to the company) dates back to 1762. The Tyrconnell was their flagship brand, and was named after a racehorse owned by Andrew Alexander Watt. The horse was a chestnut colt that won at 100 to 1 odds in 1876 in the Irish horse race called The National Produce Stakes.The actual horse race is depicted on the label. Tír Chonaill in the Irish Language comes from Tír meaning “Land of” and Chonaill which was the name of an ancient 5th Century High King of the North West of Ireland in the 5th century who was a son of the famous Niall of the Nine Hostages. Tyrconnell was therefore the name of this ancient North West Irish Kingdom and is still to this day used as the Irish language name of Donegal in the North West of Ireland. Tír Chonaill would have encompassed the modern county of Donegal and much of her neighbouring counties of Sligo, Leitrim, Fermanagh and Tyrone. The Kingdom survived until 1601. In 1876, the Donegal – Derry based Watt family who owned one of the largest whiskey distilleries in Ireland entered a racehorse called “Tyrconnell” (after the local ancient kingdom) in the Irish Classic “National Produce Stakes” where it won against all the odds at an incredible 100 to 1. This spectacular achievement inspired the Watt whiskey distillery in Derry to celebrate the occasion with a special commemorative Tyrconnell Irish whiskey label. The Tyrconnell was, before American prohibition, one of the biggest selling whiskey brands in the United States. Pre-prohibition photos taken in Yankee Stadium in New York show Tyrconnell Irish Whiskey billboards in positions of prominence at the venue. All three of the company’s whiskey brands enjoyed great success in the export sector. Sales in England, Canada, Australia, Nigeria and the West Indies and the U.S. put Derry on the commercial map as never before. Unfortunately, with the decline of Irish Whiskey after prohibition, Watts distillery and Tyrconnell whiskey faded and died like the majority of Irish whiskey distilleries and brands of the time. When the Cooley Irish Whiskey Distillery was recommissioned by Dr. John Teeling a few years ago, Tyrconnell was one of the old iconic Irish whiskey brands that Cooley brought back to life. Cooley Distillery and the Cooley Irish Whiskey brands are now owned by the Japanese – American whiskey giant Beam Suntory. Today, Tyrconnell whiskey is available as a standard 10 Year Old Cooley Single Malt and is also available through the Tyrconnell Irish Whiskey Finishes Collection in Port Pipe, Madeira Cask and Sherry Butt finishes at 46% abv as well as a 15 Year Old Single Cask expression. Andrew Watt (4 November 1853 – 11 October 1928) was an Anglo-Irish businessman with a net worth of over £900,000 at his death in 1928, worth £51.8 million in 2016.He was born in 1853 to Samuel Watt of Thornhill and his wife Jane Newman, daughter of Captain Robert Newman, R.N.. He was educated at Foyle College and then at home by tutors. His family were gentry who had arrived at Claragh in County Donegal during one of the Ulster Plantations.He was the owner of Watt’s Distillery, one of the largest distilleries in Ireland, and the creator of many whiskies including the famous Tyrconnell,which he named after his racehorse that won the National Produce Stakes against the odds of 100 to 1. During industrial unrest of 1921, brought about by prohibition in the United States and the First World War, Watt’s workers at the distillery were made redundant after challenging his authority. Watt is said to have stood on a barrel outside the gates to his distillery in Bogside, whilst the workers were on strike, and shouted, ‘Well men, I shall put it to you like this …what is it to be? Will you open the gates?’ To which the workers retorted, ‘The gates stay shut!’ This prompted Watt to reply, ‘Shut they are, and shut they shall remain!’ Watt subsequently closed down the distillery at great economic expense. On 7 October 1895, he married Violet Flora de Burgh, daughter of George de Burgh and Constance Matthews, with whom he had 4 sons and 2 daughters.He served as High Sheriff of County Londonderry from 1886 to 1887.He was a member of Boodle’s. He died at Easton Hall, where he lived in England after he left Ireland. Below is an additional and very interesting article from the Derry Historical Journal chronicling the rise and fall, like so many other Irish Whiskey distilleries, of the once all conquering Watts “Tyrconnell” brand.
67cm x 56cm This historic brand of whiskey has now been revived by the Cooley Distillery (which is now part of Beam Suntory).The brand was previously owned by the Watt Distillery, which (according to the company) dates back to 1762. The Tyrconnell was their flagship brand, and was named after a racehorse owned by Andrew Alexander Watt. The horse was a chestnut colt that won at 100 to 1 odds in 1876 in the Irish horse race called The National Produce Stakes.The actual horse race is depicted on the label. Tír Chonaill in the Irish Language comes from Tír meaning “Land of” and Chonaill which was the name of an ancient 5th Century High King of the North West of Ireland in the 5th century who was a son of the famous Niall of the Nine Hostages. Tyrconnell was therefore the name of this ancient North West Irish Kingdom and is still to this day used as the Irish language name of Donegal in the North West of Ireland. Tír Chonaill would have encompassed the modern county of Donegal and much of her neighbouring counties of Sligo, Leitrim, Fermanagh and Tyrone. The Kingdom survived until 1601. In 1876, the Donegal – Derry based Watt family who owned one of the largest whiskey distilleries in Ireland entered a racehorse called “Tyrconnell” (after the local ancient kingdom) in the Irish Classic “National Produce Stakes” where it won against all the odds at an incredible 100 to 1. This spectacular achievement inspired the Watt whiskey distillery in Derry to celebrate the occasion with a special commemorative Tyrconnell Irish whiskey label. The Tyrconnell was, before American prohibition, one of the biggest selling whiskey brands in the United States. Pre-prohibition photos taken in Yankee Stadium in New York show Tyrconnell Irish Whiskey billboards in positions of prominence at the venue. All three of the company’s whiskey brands enjoyed great success in the export sector. Sales in England, Canada, Australia, Nigeria and the West Indies and the U.S. put Derry on the commercial map as never before. Unfortunately, with the decline of Irish Whiskey after prohibition, Watts distillery and Tyrconnell whiskey faded and died like the majority of Irish whiskey distilleries and brands of the time. When the Cooley Irish Whiskey Distillery was recommissioned by Dr. John Teeling a few years ago, Tyrconnell was one of the old iconic Irish whiskey brands that Cooley brought back to life. Cooley Distillery and the Cooley Irish Whiskey brands are now owned by the Japanese – American whiskey giant Beam Suntory. Today, Tyrconnell whiskey is available as a standard 10 Year Old Cooley Single Malt and is also available through the Tyrconnell Irish Whiskey Finishes Collection in Port Pipe, Madeira Cask and Sherry Butt finishes at 46% abv as well as a 15 Year Old Single Cask expression. Andrew Watt (4 November 1853 – 11 October 1928) was an Anglo-Irish businessman with a net worth of over £900,000 at his death in 1928, worth £51.8 million in 2016.He was born in 1853 to Samuel Watt of Thornhill and his wife Jane Newman, daughter of Captain Robert Newman, R.N.. He was educated at Foyle College and then at home by tutors. His family were gentry who had arrived at Claragh in County Donegal during one of the Ulster Plantations.He was the owner of Watt’s Distillery, one of the largest distilleries in Ireland, and the creator of many whiskies including the famous Tyrconnell,which he named after his racehorse that won the National Produce Stakes against the odds of 100 to 1. During industrial unrest of 1921, brought about by prohibition in the United States and the First World War, Watt’s workers at the distillery were made redundant after challenging his authority. Watt is said to have stood on a barrel outside the gates to his distillery in Bogside, whilst the workers were on strike, and shouted, ‘Well men, I shall put it to you like this …what is it to be? Will you open the gates?’ To which the workers retorted, ‘The gates stay shut!’ This prompted Watt to reply, ‘Shut they are, and shut they shall remain!’ Watt subsequently closed down the distillery at great economic expense. On 7 October 1895, he married Violet Flora de Burgh, daughter of George de Burgh and Constance Matthews, with whom he had 4 sons and 2 daughters.He served as High Sheriff of County Londonderry from 1886 to 1887.He was a member of Boodle’s. He died at Easton Hall, where he lived in England after he left Ireland. Below is an additional and very interesting article from the Derry Historical Journal chronicling the rise and fall, like so many other Irish Whiskey distilleries, of the once all conquering Watts “Tyrconnell” brand.When Bogside whiskey was the toast of the world
 By 1887 Watts Distillery at Abbey Street was the largest in Ireland and had become a world leader in whiskey production. The massive city centre plant covered eight acres, which included Abbey Street, Fahan Street and adjoining thoroughfares.
By 1887 Watts Distillery at Abbey Street was the largest in Ireland and had become a world leader in whiskey production. The massive city centre plant covered eight acres, which included Abbey Street, Fahan Street and adjoining thoroughfares. At that time the company’s director, David Watt, installed a second Coffey still – an invention by Aeneas Coffey which revolutionised the whiskey industry – to boost output to an incredible two million gallons a year.The firm developed three major brands, Tyrconnell, Favourite and Innishowen. In 1876, Andrew Alexander Watt entered a racehorse called “Tyrconnell” in the Irish Classic ‘National Produce Stakes’ and it won against all the odds at an incredible 100 to 1. This spectacular achievement inspired the Watt distillery to celebrate the occasion with a special commemorative Tyrconnell label. The Tyrconnell was, before prohibition, one of the biggest selling whiskey brands in the United States. Pre-prohibition photos of Yankee Stadium in New York show Tyrconnell billboards in positions of prominence at the venue. All three of the company’s brand names enjoyed great success in the export sector. Sales in England, Canada, Australia, Nigeria and the West Indies and the US put Derry on the commercial map as never before. Water used in the distillery came from the surrounding Derry hills and was stored in reservoirs on site. The wheat and maize stores were immense. At any one time, the warehouses, ranging in size from two to four storeys in height, contained 2,000 tons of wheat and barley; 1,000 tons of maize; 1,600 tons of barley, oats and maize. Attached to these buildings were two large “Malakoff’ dry-corn kilns, capable of drying 30 tons of corn every 24 hours, while in each of the two malting houses, 16 tons of grain were malted in a steep (50 ft in length by 9 ft wide) four times a week. The Coffey stills – the revolutionary inventions designed by Aeneas Coffey – were located in a still house which was seven storeys high, the tallest building in the city apart from the Cathedral. After dilution and casking, the barrels were taken to one of the five warehouses by an overhead railway pulled by a small steam engine. An advantage by-product from the Coffey stills was fusel oil which was used to light the distillery. It had a distinctive all pervading spirituous smell that the men carried home with them in their clothes. The Abbey Street site had many distinctive features notably two massive chimneys, one 160 feet and the other 130 feet high.Around 1820, James Robinson started distilling in the Waterside with a simple 76-gallon still. The operation was later acquired by the Meehan family who built a street in the Waterside called Meehan’s Row to accommodate the distillery workers. By the early 1830’s, the Watt family purchased the business and set out on a planned, systematic expansion of the site. Despite being successful, the Waterside operation always laboured in the shadow of the Abbey street distillery. In the 1880s, Abbey Street had the capacity to produce two million gallons of whiskey a year; the Waterside’s maximum output was 200,000 gallons. It is possible that the geographical location inhibited major expansion as the premises were situated on a steep hill and were flanked by two major thoroughfares. The decision was taken in 1902-03 by the Watt family to merge with two Belfast distilleries, the small Avoniel, owned by William Higgins and the Irish Distillery Ltd., Connswater, to form the United Distilleries Company Limited (UDC). Andrew Watt would chair the new consortium that had the capability to produce the six million gallons of grain whiskey per year. The operation would have several Coffey stills and would exert great influence within the industry becoming a major supplier of grain whiskey to blenders in both Scotland and England. Things worked perfectly at first but around 1908 and 1910, conflict arose between the UDC group and Scottish giants DCL based in Edinburgh. A series of further complicated deals between them served only to undermine confidence in both organisations. This was to be the beginning of the end for the huge Derry operation and company head, Andrew Alexander Watt closed the business after the strike of 1921. Watt himself died at his English estate in Easton Hall near Grantham in October 1928 at the age of 75. Derry Auther Ken McCormick describes the last encounter of AA Watt with his employees in a wonderful account ‘The Folly of Andrew Watt’ in his book ‘Ken McCormick’s Derry – Heroes, Villains and Ghosts’.“A gleaming yellow Rolls Royce slowly making its way through the gloom of a cold foggy morning in the Bogside in the year 1921. The air is tense and there are huddles of men everywhere – unbelievably, the workers of Watt’s Distillery are on strike. The eight-acre site, normally humming with activity round the clock, is as silent as the grave. But in the approaching vehicle is 68 year – old Andrew Alexander Watt, and he’s intent on a showdown . . . “Andrew Watt asked to be helped up on to one of his own whiskey barrels and from there he addressed the crowd with the menacing words – ‘Well men, I shall put it to you like this . . . what is it to be? Will you open the gates?’ The workers retorted angrily- ‘The gates stay shut!’ ‘Very well!’ exclaimed Watt bluntly. ‘Shut they are, and shut they shall remain!’ “In that bleak instant the Watt’s whiskey enterprise disappeared from Derry forever. Over 300 jobs were lost, including the talents of some of Ireland’s finest whiskey blenders. Also left jobless were coopers, carpenters and a host of other tradesfolk and office staff, many of whose parents and grandparents had worked for Watts for generations.“As for A A Watt, he left the city never to return. In doing so he turned his back on what would be a multi-million pound business in today’s world. Looking back, the outcome can only be viewed as a total disaster.” It ranks as one of the bleakest days in Derry’s industrial history and marked the end the city’s reputation as a world leader in whiskey production. Mr McCormick adds: “The loss was staggering.” The tensions created by the War of Independents and the Civil War and the introduction of new laws demanding that grain whiskey be laid down for three years before it could be sold may have had a bearing on Watt’s decision to shut up shop, although many agree that it was his expansionist tendency’s which were as Mr McCormick put it “his folly”. “Quite simply he bit off more than he could chew and left his whole operation vulnerable to a take-over,” he adds. Meanwhile some people maintained that a fire – in which several employees died – at the Abbey St distillery in 1915 was the beginning of the end for the Watts. According to Mr McCormick: “The vats had to be opened and it seems whiskey flowed along the gutters – much to the delight of the locals, it must be said, for they were able to collect bucketfuls of the precious spirit!”
At that time the company’s director, David Watt, installed a second Coffey still – an invention by Aeneas Coffey which revolutionised the whiskey industry – to boost output to an incredible two million gallons a year.The firm developed three major brands, Tyrconnell, Favourite and Innishowen. In 1876, Andrew Alexander Watt entered a racehorse called “Tyrconnell” in the Irish Classic ‘National Produce Stakes’ and it won against all the odds at an incredible 100 to 1. This spectacular achievement inspired the Watt distillery to celebrate the occasion with a special commemorative Tyrconnell label. The Tyrconnell was, before prohibition, one of the biggest selling whiskey brands in the United States. Pre-prohibition photos of Yankee Stadium in New York show Tyrconnell billboards in positions of prominence at the venue. All three of the company’s brand names enjoyed great success in the export sector. Sales in England, Canada, Australia, Nigeria and the West Indies and the US put Derry on the commercial map as never before. Water used in the distillery came from the surrounding Derry hills and was stored in reservoirs on site. The wheat and maize stores were immense. At any one time, the warehouses, ranging in size from two to four storeys in height, contained 2,000 tons of wheat and barley; 1,000 tons of maize; 1,600 tons of barley, oats and maize. Attached to these buildings were two large “Malakoff’ dry-corn kilns, capable of drying 30 tons of corn every 24 hours, while in each of the two malting houses, 16 tons of grain were malted in a steep (50 ft in length by 9 ft wide) four times a week. The Coffey stills – the revolutionary inventions designed by Aeneas Coffey – were located in a still house which was seven storeys high, the tallest building in the city apart from the Cathedral. After dilution and casking, the barrels were taken to one of the five warehouses by an overhead railway pulled by a small steam engine. An advantage by-product from the Coffey stills was fusel oil which was used to light the distillery. It had a distinctive all pervading spirituous smell that the men carried home with them in their clothes. The Abbey Street site had many distinctive features notably two massive chimneys, one 160 feet and the other 130 feet high.Around 1820, James Robinson started distilling in the Waterside with a simple 76-gallon still. The operation was later acquired by the Meehan family who built a street in the Waterside called Meehan’s Row to accommodate the distillery workers. By the early 1830’s, the Watt family purchased the business and set out on a planned, systematic expansion of the site. Despite being successful, the Waterside operation always laboured in the shadow of the Abbey street distillery. In the 1880s, Abbey Street had the capacity to produce two million gallons of whiskey a year; the Waterside’s maximum output was 200,000 gallons. It is possible that the geographical location inhibited major expansion as the premises were situated on a steep hill and were flanked by two major thoroughfares. The decision was taken in 1902-03 by the Watt family to merge with two Belfast distilleries, the small Avoniel, owned by William Higgins and the Irish Distillery Ltd., Connswater, to form the United Distilleries Company Limited (UDC). Andrew Watt would chair the new consortium that had the capability to produce the six million gallons of grain whiskey per year. The operation would have several Coffey stills and would exert great influence within the industry becoming a major supplier of grain whiskey to blenders in both Scotland and England. Things worked perfectly at first but around 1908 and 1910, conflict arose between the UDC group and Scottish giants DCL based in Edinburgh. A series of further complicated deals between them served only to undermine confidence in both organisations. This was to be the beginning of the end for the huge Derry operation and company head, Andrew Alexander Watt closed the business after the strike of 1921. Watt himself died at his English estate in Easton Hall near Grantham in October 1928 at the age of 75. Derry Auther Ken McCormick describes the last encounter of AA Watt with his employees in a wonderful account ‘The Folly of Andrew Watt’ in his book ‘Ken McCormick’s Derry – Heroes, Villains and Ghosts’.“A gleaming yellow Rolls Royce slowly making its way through the gloom of a cold foggy morning in the Bogside in the year 1921. The air is tense and there are huddles of men everywhere – unbelievably, the workers of Watt’s Distillery are on strike. The eight-acre site, normally humming with activity round the clock, is as silent as the grave. But in the approaching vehicle is 68 year – old Andrew Alexander Watt, and he’s intent on a showdown . . . “Andrew Watt asked to be helped up on to one of his own whiskey barrels and from there he addressed the crowd with the menacing words – ‘Well men, I shall put it to you like this . . . what is it to be? Will you open the gates?’ The workers retorted angrily- ‘The gates stay shut!’ ‘Very well!’ exclaimed Watt bluntly. ‘Shut they are, and shut they shall remain!’ “In that bleak instant the Watt’s whiskey enterprise disappeared from Derry forever. Over 300 jobs were lost, including the talents of some of Ireland’s finest whiskey blenders. Also left jobless were coopers, carpenters and a host of other tradesfolk and office staff, many of whose parents and grandparents had worked for Watts for generations.“As for A A Watt, he left the city never to return. In doing so he turned his back on what would be a multi-million pound business in today’s world. Looking back, the outcome can only be viewed as a total disaster.” It ranks as one of the bleakest days in Derry’s industrial history and marked the end the city’s reputation as a world leader in whiskey production. Mr McCormick adds: “The loss was staggering.” The tensions created by the War of Independents and the Civil War and the introduction of new laws demanding that grain whiskey be laid down for three years before it could be sold may have had a bearing on Watt’s decision to shut up shop, although many agree that it was his expansionist tendency’s which were as Mr McCormick put it “his folly”. “Quite simply he bit off more than he could chew and left his whole operation vulnerable to a take-over,” he adds. Meanwhile some people maintained that a fire – in which several employees died – at the Abbey St distillery in 1915 was the beginning of the end for the Watts. According to Mr McCormick: “The vats had to be opened and it seems whiskey flowed along the gutters – much to the delight of the locals, it must be said, for they were able to collect bucketfuls of the precious spirit!” -

 68cm x 56cmWith a history dating back generations it is inevitable that many myths and legends about Kinahans whiskey steeped into storytelling. But the origins of the L.L. mark have been well documented. In 1807, the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland (the head of state), Charles Lennox, was so impressed with the whiskeys made by Kinahans that he ordered all stocks at the Kinahans Dublin vaults to be taken exclusively for his private use, marking each cask with “L.L.”. The news, which were highly advertised, led to Kinahans becoming one of the most sought after whiskeys both, domestically and in neighbouring countries.In 1819, the popularity of the Kinahans brand allowed to set up its own four story headquarters, at the corner of Burgh Quay and D’Olier Street, Dublin, Named the Carlisle Building, to resonate with nearby Carlisle Bridge, the premises were built as part of the re-development of the city being overseen by the city's Wide Street Commissioners. By the middle of 20th Century the historic building has been taken down.As Kinahans popularity grew, London became a natural base for the company in 1800s wishing to expand into international markets. On 31 December 1841, Kinahans appointed Mr. George Smyth as its first agent in the city of London, with an address at no.1 White Hart Court, London, UK. For over half a century the company's London base has formed the centre of a great volume of export trade to the Continent, China, India, Australia and all the foreign markets.
68cm x 56cmWith a history dating back generations it is inevitable that many myths and legends about Kinahans whiskey steeped into storytelling. But the origins of the L.L. mark have been well documented. In 1807, the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland (the head of state), Charles Lennox, was so impressed with the whiskeys made by Kinahans that he ordered all stocks at the Kinahans Dublin vaults to be taken exclusively for his private use, marking each cask with “L.L.”. The news, which were highly advertised, led to Kinahans becoming one of the most sought after whiskeys both, domestically and in neighbouring countries.In 1819, the popularity of the Kinahans brand allowed to set up its own four story headquarters, at the corner of Burgh Quay and D’Olier Street, Dublin, Named the Carlisle Building, to resonate with nearby Carlisle Bridge, the premises were built as part of the re-development of the city being overseen by the city's Wide Street Commissioners. By the middle of 20th Century the historic building has been taken down.As Kinahans popularity grew, London became a natural base for the company in 1800s wishing to expand into international markets. On 31 December 1841, Kinahans appointed Mr. George Smyth as its first agent in the city of London, with an address at no.1 White Hart Court, London, UK. For over half a century the company's London base has formed the centre of a great volume of export trade to the Continent, China, India, Australia and all the foreign markets.
The Royal Warrants

1845
Throughout 1800s Kinahans continued to offer the highest level of differentiated taste and craftsmanship, for which Queen Victoria awarded it a Royal Warrant in 1845. With major accolades in hand, the recruitment of the agents and retail outlets continued.
The Preferred Whiskey Of Jerry Thomas

1862
With popularity in the British Isles, by the middle of 19th century Kinahans whiskey came to be the notice of many American authors and connoisseurs. In 1860s Kinahans came to the attention of the legendary Jerry Thomas. Also known as "the father of American mixology", Jerry Thomas was a revolutionary character, who due to his creativity and showmanship transformed the image of the bartender as a creative professional. In his 1862 "Guide on How to Mix Drinks", Jerry Thomas featured Kinahans in one of his book's recipes. The Bartender's "Guide on How to Mix Drinks" was the first drinks and mixology book ever published in the United States and can be counted amongst very few most influential drinks publications to date.
Protected Trademark

1863
Since its rise to popularity Kinahans faced hazardous times. Because of the brand's accolades, unscrupulous merchants publicans and others were restless in using the Kinahans bottles, labels and brand marks in order to sell their own products. In 1863, the activities of William Bolton, a grocer in Dublin's Westmoreland Street, led to the final and landmark case of legal redress. In the Irish case of Kinahan v. Bolton, the Irish Courts granted an injunction to restrain others from invading the Kinahans L.L. mark.
A Household Name

1881
The terms “Kinahans” and “Kinahans L.L.” is by 1881 a household name, becoming widely accepted as shorthand for a whisky of a specific price, quality and reputation. Confirmation for this is found in the 1881 Edition of Brewer's Dictionary of Phrases and Fables, in which the origin of L.L. trademark is also described. It is against this background that familiarity with the Kinahans brand name found expression in books written by countless British and American authors.
Decline Of The Irish Whiskey Industry

1902-1911
The new century began favourably. However, nothing could shield the company from the tribulations that were about to unfold. One of the key family members, George Kinahan died in 1903 and with him ended the family's long association with Dublin civic life as well as the prestige and opportunities which would have created. As the longest serving director, he took with him an intimate knowledge of the company's history as well as a wealth of practical business experience. Additionally, his long directorship at the Bank of Ireland would also have been of great practical value, not least because at various times his fellow directors at the bank included senior members of the Jameson whiskey family. On top of the departure of George Kinahan, the company had to cope with changing and more difficult economy in Ireland. Overall Irish whiskey exports declined spectacularly between 1900 and 1914. In Ireland itself both consumption and production fell, aided by increase of almost a third in spirit duty, as proposed by Lloyd George in his 1909 budget.
Transfer Of The Brand
 In June 1911 Kinahans business operations were being transferred to Bagot & Hutton, another long established Dublin wine and spirit enterprise. This company bottled and distributed Kinahans L.L. whiskey up until the time of Prohibition in the United States in 1920.In November 1920, following the Prohibition in the United States, an economic decline and a forthcoming Civil War in Ireland, the two spirit houses combined and were registered as Bagot Hutton & Kinahan. This arrangement continued until October 1988, when the shareholders decided to take a long break for one of Dublin's most prominent business houses, until better times.
In June 1911 Kinahans business operations were being transferred to Bagot & Hutton, another long established Dublin wine and spirit enterprise. This company bottled and distributed Kinahans L.L. whiskey up until the time of Prohibition in the United States in 1920.In November 1920, following the Prohibition in the United States, an economic decline and a forthcoming Civil War in Ireland, the two spirit houses combined and were registered as Bagot Hutton & Kinahan. This arrangement continued until October 1988, when the shareholders decided to take a long break for one of Dublin's most prominent business houses, until better times. -

 74cm x 52cm ANOTHER great industry on the Scotch Hall site was the brewing firm of Cairnes Ltd, one of the original firms of Irish brewers dating back to 1772 with the foundation of the Castlebellingham Brewery at the picturesque Co Louth village of that name.In 1825, William Cairnes, who was related by marriage to the owners of the ’Bellingham brewery, founded the brewery at Marsh Road, Drogheda, which, for over 150 years, gave employment to almost 200 workers and the firm was famous for its ales and stout. In 1889 the interests of the two breweries were pooled, a public company being formed under the title of the Castlebellingham and Drogheda Breweries Ltd. This title was changed for brevity in 1933 to Cairnes Ltd. For a good many years subsequent to the merger, the breweries were worked independently, each supplying its own customers throughout Ireland and abroad. However, in 1923, it was considered advisable to concentrate brewing in Drogheda, owing to the more advantageous position of the town, and the brewing plant and premises there, were more extensive. Actually the plant at Drogheda was one of the most up-to-date in Ireland and compared very favourably with that of breweries in England and Wales. The supply of brewing water was obtained from a 400ft deep artesian well on the company’s premises. (I wonder if it is still there) and this water was used with the choicest hops and malt made from the best Irish barley obtainable. The hops used came chiefly from Kent and when obtainable, a percentage came from the USA. The process through which the barley went from its arrival in the brewery until it emerged as ale or stout, was extremely interesting and quaint. The barley was first dried to a consistent level of moisture content and then stored for a few weeks before being steeped. It was then ‘floored’ on lots which the brewery had, as well as lofts in Dominic Street and Wellington Quay. These have, in recent years, been converted into shops and a high rise apartment block. Here on these lofts the growing process of the barley in the ground was artificially repeated, the growth however being terminated at the desired stage. The barley was then kilned and cured before being ground and mashed with hot water and the liquid was drawn off. It was then run to built-in coppers, where hops was added, then boiled, the wort, as it was called, being subsequently strained from the hops, cooled and fermented. The final stage was when the beer was casked (in wooden barrels) and matured. Altogether there were approximately 200 people employed in the industry, for apart from the actual brewing of the beer there was a tremendous amount of activity, and the transport department built up a fine fleet of steam lorries, (I remember seeing Gerry McConville driving one of these down the Marsh Road), motor lorries and carts and Jemmy Early was in charge of town deliveries in a horse drawn wagon, from which he rolled the barrells into the pub. While catering for an extensive home market, Cairnes Ltd had, since May 1951, been engaged in the export of bottled stout to America. This stout was much stronger than anything of its kind on sale in Ireland and the venture steadily expanded in the new market. The metal caps of the export bottles had the imprint of the Star and Crescent, which is part of the Drogheda Coat of Arms, while the label carried three reproductions of miniature photographs of St Laurence Gate. And so one of Drogheda’s oldest industries was carrying the name of the town across the world. In Millmount museum there is a permanent exhibition of artifacts from Cairnes Brewery which were literally ‘rescued’ before and during the closing down of the brewery in 1965 when Guinness started buying out their competitors.Showcased are the various bottles with their beer labels – the famous ‘Stingo’, a most favoured ale at the time. There are also the large enamel advertising signs with ‘W Cairnes and Son. X Porter’ showing the brewery in its heyday, and a complete set of tools which were used by the cooper (wooden barrel maker), with a mythology of names like, the adze, draw knife, the buzz, the auger and chisel, the spokeshave and the coopers anvil. Note: A recent informant who wishes to remain anonymous, wrote the following about Cairnes Brewery: ‘The last brew was carried out in October 1960. The brew was mashed by Joseph Oliver Roche, head brewer and declared by Patrick (Paddy) Weldon. ‘In the break-up of the Brewery by Guinness, Roche was sent to Waterford, while Weldon was sent to Dundalk. Kevin Beatty was also sent to New Ross or was it Enniscorthy?’
74cm x 52cm ANOTHER great industry on the Scotch Hall site was the brewing firm of Cairnes Ltd, one of the original firms of Irish brewers dating back to 1772 with the foundation of the Castlebellingham Brewery at the picturesque Co Louth village of that name.In 1825, William Cairnes, who was related by marriage to the owners of the ’Bellingham brewery, founded the brewery at Marsh Road, Drogheda, which, for over 150 years, gave employment to almost 200 workers and the firm was famous for its ales and stout. In 1889 the interests of the two breweries were pooled, a public company being formed under the title of the Castlebellingham and Drogheda Breweries Ltd. This title was changed for brevity in 1933 to Cairnes Ltd. For a good many years subsequent to the merger, the breweries were worked independently, each supplying its own customers throughout Ireland and abroad. However, in 1923, it was considered advisable to concentrate brewing in Drogheda, owing to the more advantageous position of the town, and the brewing plant and premises there, were more extensive. Actually the plant at Drogheda was one of the most up-to-date in Ireland and compared very favourably with that of breweries in England and Wales. The supply of brewing water was obtained from a 400ft deep artesian well on the company’s premises. (I wonder if it is still there) and this water was used with the choicest hops and malt made from the best Irish barley obtainable. The hops used came chiefly from Kent and when obtainable, a percentage came from the USA. The process through which the barley went from its arrival in the brewery until it emerged as ale or stout, was extremely interesting and quaint. The barley was first dried to a consistent level of moisture content and then stored for a few weeks before being steeped. It was then ‘floored’ on lots which the brewery had, as well as lofts in Dominic Street and Wellington Quay. These have, in recent years, been converted into shops and a high rise apartment block. Here on these lofts the growing process of the barley in the ground was artificially repeated, the growth however being terminated at the desired stage. The barley was then kilned and cured before being ground and mashed with hot water and the liquid was drawn off. It was then run to built-in coppers, where hops was added, then boiled, the wort, as it was called, being subsequently strained from the hops, cooled and fermented. The final stage was when the beer was casked (in wooden barrels) and matured. Altogether there were approximately 200 people employed in the industry, for apart from the actual brewing of the beer there was a tremendous amount of activity, and the transport department built up a fine fleet of steam lorries, (I remember seeing Gerry McConville driving one of these down the Marsh Road), motor lorries and carts and Jemmy Early was in charge of town deliveries in a horse drawn wagon, from which he rolled the barrells into the pub. While catering for an extensive home market, Cairnes Ltd had, since May 1951, been engaged in the export of bottled stout to America. This stout was much stronger than anything of its kind on sale in Ireland and the venture steadily expanded in the new market. The metal caps of the export bottles had the imprint of the Star and Crescent, which is part of the Drogheda Coat of Arms, while the label carried three reproductions of miniature photographs of St Laurence Gate. And so one of Drogheda’s oldest industries was carrying the name of the town across the world. In Millmount museum there is a permanent exhibition of artifacts from Cairnes Brewery which were literally ‘rescued’ before and during the closing down of the brewery in 1965 when Guinness started buying out their competitors.Showcased are the various bottles with their beer labels – the famous ‘Stingo’, a most favoured ale at the time. There are also the large enamel advertising signs with ‘W Cairnes and Son. X Porter’ showing the brewery in its heyday, and a complete set of tools which were used by the cooper (wooden barrel maker), with a mythology of names like, the adze, draw knife, the buzz, the auger and chisel, the spokeshave and the coopers anvil. Note: A recent informant who wishes to remain anonymous, wrote the following about Cairnes Brewery: ‘The last brew was carried out in October 1960. The brew was mashed by Joseph Oliver Roche, head brewer and declared by Patrick (Paddy) Weldon. ‘In the break-up of the Brewery by Guinness, Roche was sent to Waterford, while Weldon was sent to Dundalk. Kevin Beatty was also sent to New Ross or was it Enniscorthy?’ -

 67cm x 56cm
67cm x 56cmDaniel O’Connnell Jr. had famously acquired the Phoenix Brewery in James’s street in 1831, which produced O’Connell’s Ale. It should be noted that O’Connell and the Guinness family were at times political rivals, something best captured by the 1841 ‘Repeal Election’, where O’Connell had stood against and defeated Arthur Guinness Jr. This period would see a sizeable boycott of Guinness, dubbed “Protestant Porter” by sections of the populace, though this was against the wishes of O’Connell himself.
John D’Arcy continued to brew O’Connell Ale after the family had ceased their role in brewing, and in time production moved to the Anchor Brewery in Usher Street. Watkins eventually took up the brewing of O’Connell Ale, and this advertisement was placed by them in the pages of leading newspapers in the 1930s.
While Arthur had failed to defeat O’Connell at the Ballot Box, I always wonder what O’Connell would think of the Guinness Empire today every time I see a Diaego truck pass his statue.
-

 67cm x 56cm
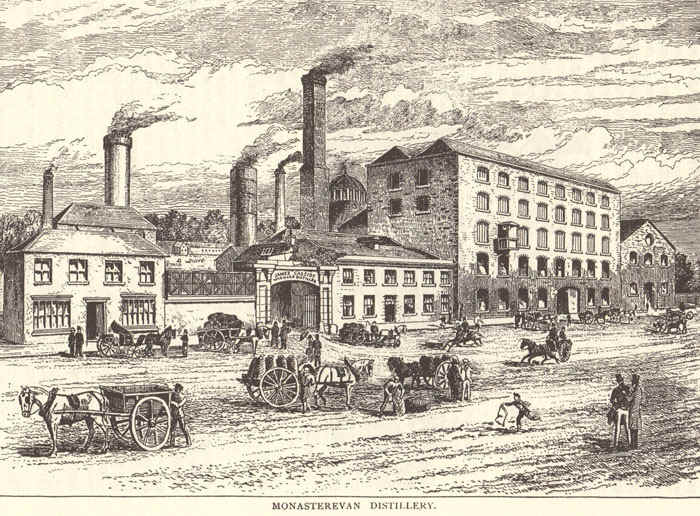
67cm x 56cmIn 1784 Monasterevin Distillery was opened by Mr. John Cassidy. A hundred years later, in 1884 the distillery was making 250,000 gallons of whiskey a year. It was said that the "Cassidy whiskey was the best whiskey in the country".
Some of the whiskey was exported to London. It was transported to Dublin on canal boats and then shipped to England from Dublin Port. A brewery for making beer was later opened in 1860. Cassidy's Distillery and Brewery closed in 1934.
The Cassidy Family lived in Monasterevin House. They were friendly with Gerard Manley Hopkins, the famous poet. He stayed with them when he visited Monasterevin.

-

 65cm x 45cm Nun's Island Distillery was an Irish whiskey distillery which operated in Galway, Ireland, from at least 1815, and possibly as early as the late 1700s, until circa 1908. At its peak, in the late 1800s, output at the distillery reached 400,000 gallons per annum, and with a workforce of over 100, the distillery was one of the largest local employers. Owned by the Persse family from the 1840s onwards, the distillery produced single pot still whiskey known as Persse's Galway Whiskey. The whiskey was sold locally in Connacht, where for much of the 1800s, Nun's Island was the only licensed distillery.However, it was also exported, and is said to have been a sold to the British House of Commons, a fact proudly noted on their labels. Production at the distillery ceased circa 1908, with the remaining stocks wound down off over several few years. A bottle of Persse's whiskey was placed for auction in 2002 with a reserve price of £100,000 - however, it failed to sell. The bottle later sold for £3,300 in 2014.
65cm x 45cm Nun's Island Distillery was an Irish whiskey distillery which operated in Galway, Ireland, from at least 1815, and possibly as early as the late 1700s, until circa 1908. At its peak, in the late 1800s, output at the distillery reached 400,000 gallons per annum, and with a workforce of over 100, the distillery was one of the largest local employers. Owned by the Persse family from the 1840s onwards, the distillery produced single pot still whiskey known as Persse's Galway Whiskey. The whiskey was sold locally in Connacht, where for much of the 1800s, Nun's Island was the only licensed distillery.However, it was also exported, and is said to have been a sold to the British House of Commons, a fact proudly noted on their labels. Production at the distillery ceased circa 1908, with the remaining stocks wound down off over several few years. A bottle of Persse's whiskey was placed for auction in 2002 with a reserve price of £100,000 - however, it failed to sell. The bottle later sold for £3,300 in 2014.History
The early history of the distillery is somewhat difficult to piece together.It is known that a distillery on Nun's Island was being operated on by a John Joyce in the late 1700s.This distillery, which was subsequently taken over by Patrick Joyce, is thought to have ceased operations in 1807. A Patrick Joyce is recorded as running a small distillery on Nun's Island again in 1823. Therefore, it is possible that the closure was temporary. By 1828, output at the distillery had increased to 130,000 proof gallons per annum. There are claims that the distillery ceased operations again in the late 1830s.However, a newspaper advertisement from 1841 reports that a distillery "lately occupied and worked" by Messrs. James and Patrick Joyce was to be sold on 4 February 1841. The advertisement noted that the distillery was held under a 300-year lease, which had commenced in August 1815.This tallies with Alfred Barnard's 1887 report that Joyce's owned the distillery from 1815 to 1840. In about 1840 or 1841, the distillery was purchased by the Persses, a local family who ran several other distilleries in the area.There is some conflicting information with regard to the precise and nature of the sale date. Barnard reported that the distillery was sold by the Encumbered Claims Courts in 1840.However, a newspaper article from the era reports that the distillery was to be sold by private contract in February 1841. As Barnard mentions that the Persses enlarged the original operation, the confusion may be due to piecemeal purchases of different sections of the site, or delays in finalising the sale as the distillery had been repeatedly advertised for sale beginning in at least early 1840. Initially the Persses converted the distillery to a woollen mill, which was known for producing excellent friezes. However, when their lease on the nearby Newcastle Distillery expired in 1846, they moved their distilling operations at the Nun's Island complex, and re-established the site as a distillery. In 1886, the distillery was visited by British historian Alfred Barnard, as recounted in his seminal publication "The Whiskey Distilleries of the United Kingdom". Barnard noted that at the time of his visit Nun's Island was the sole distillery operating in Connacht, and had an output of about 400,000 gallons per annum. In addition to offices, workshops, stables, and storehouses, the distillery buildings included two lofty Maltings and Corn stores built of stone, five storeys of which were devoted to the storing of corn, and two to malting purposes; an elegant brew house equal to any in Ireland; a back house containing thirteen washbacks, each with a capacity of about 18,000 gallons; a still house containing a 16,000 gallon wash still, a 10,000 gallon spirit still, and a 6,000 gallon low-wines still; a spirit store occupied by a 12,000 gallon vat; and five warehouses, holding a total of about 5,000 casks at the time. Like many other Irish distilleries, Nun's Island encountered financial difficulties during the early part of the 20th Century, is thought to have closed shortly before World War I. Since closing, some of the distillery complex has been demolished. However, several of the main distillery buildings, notably the large riverside warehouse, are still extant. -

 72cm x 46cm The original J. H. Ireland Grill Room opened in Chicago in 1906, and was one of the windy city's best loved restaurants. Proprietor Jim Ireland expanded the property over two decades, adding a Lobster Grotto, a Marine Room and a banqueting hall modeled after the saloon of a passenger ship. The infamous gangster John Dillinger often dined at J. H. Ireland - he liked the frog legs - and famed attorney Clarence Darrow ate a victory dinner at the restaurant at the end of the famous Leopold and Loeb murder trial. This 1940s menu cover by folk artist Charles Jerred, in wonderfully vibrant shades of green and red, showcases what was one of Chicago's best loved restaurants and is a Love Menu Art best seller.
72cm x 46cm The original J. H. Ireland Grill Room opened in Chicago in 1906, and was one of the windy city's best loved restaurants. Proprietor Jim Ireland expanded the property over two decades, adding a Lobster Grotto, a Marine Room and a banqueting hall modeled after the saloon of a passenger ship. The infamous gangster John Dillinger often dined at J. H. Ireland - he liked the frog legs - and famed attorney Clarence Darrow ate a victory dinner at the restaurant at the end of the famous Leopold and Loeb murder trial. This 1940s menu cover by folk artist Charles Jerred, in wonderfully vibrant shades of green and red, showcases what was one of Chicago's best loved restaurants and is a Love Menu Art best seller. -
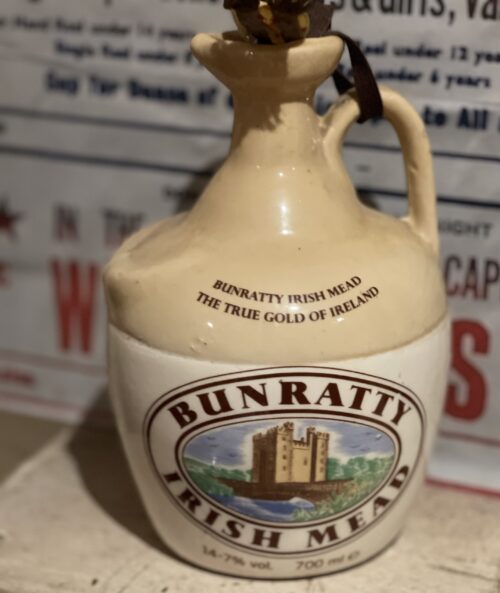
 26cm (empty)
26cm (empty)Bunratty Mead is a traditional wine, produced from an ancient Irish recipe of pure honey, fruit of the vine and natural herbs. It's a medium sweet wine, with a wide taste appeal, and suitable for all important occasions. As the drink of the ancient Celts, Mead derives much of its appeal through Irish Folklore, which is legendary of this mystical drink with strong attachments to Ireland.
In the days of old when knights were bold, the drink of choice was mead. Much more than an extraordinary legendary drink with strong attachments to Ireland, mead can be traced back as many centuries before Christ. It became the chief drink of the Irish and was often referred to in Gaelic poetry. Mead's influence was so great that the halls of Tara, where the High Kings of Ireland ruled, were called the house of the Mead Circle. Its fame spread quickly and soon a medieval banquet was not complete without it.


Even the church recognised the value of this fabulous drink. Legend has it that St. Finian lived for six days a week on bread and water, but on Sundays ate salmon and drank a full sup of mead. In addition, St. Bridget performed a miracle when mead could not be located for the king of Leinster. She blessed an empty vessel, which miraculously filled with Mead.







