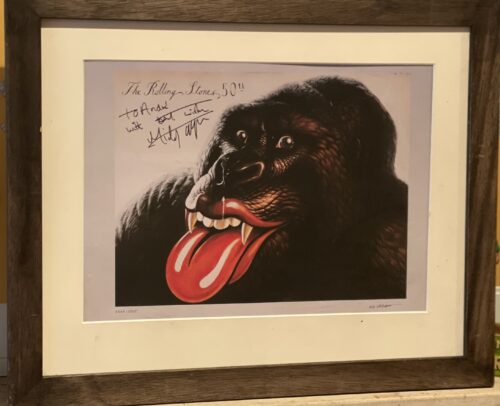
- You cannot add "The Great Montjeu with Mick Kinane riding -The 1999 Irish Derby & Prix de l'Arc de Triomphe Winner" to the cart because the product is out of stock.
-
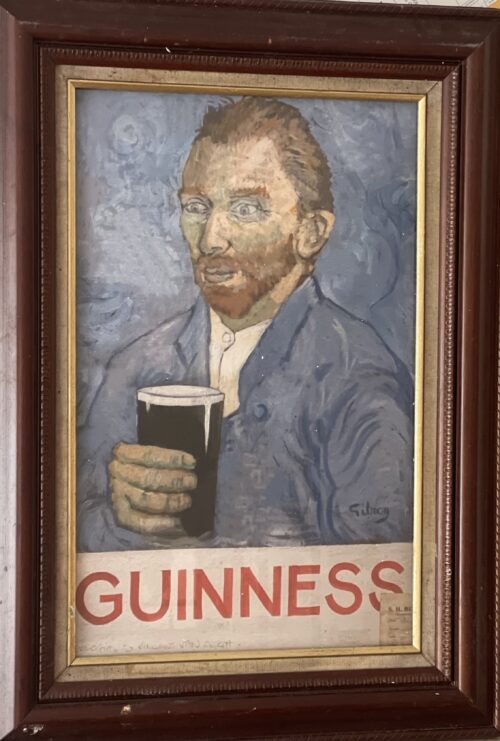
 75cm x 65cmThe biggest cliché in the collecting world is the “discovery” of a previously unknown cache of stuff that’s been hidden away for years until one day, much to everyone’s amazement, the treasure trove is unearthed and the collecting landscape is changed forever. As a corollary to this hoary trope, if you are in the right place at the right time, you can get in on the action before the word gets out.Cliché or not, that’s roughly what happened in 2008 when hundreds of artist John Gilroy’s oil-on-canvas paintings started to appear on the market. The canvases had been painted by Gilroy as final proofs for his iconic Guinness beer posters, the most recognized alcoholic-beverage advertisements of the mid-20th century. Before most collectors of advertising art and breweriana knew what had happened, most of the best pieces had been snapped up by a handful of savvy collectors. In fact, the distribution of the canvases into the hands of private collectors was so swift and stealthy that one prominent member of the Guinness family was forced to get their favorite Gilroys on the secondary market.One of those early collectors, who wishes to remain anonymous, recalls seeing several canvases for the first time at an antiques show. At first, he thought they were posters since that’s what Guinness collectors have come to expect. But after looking at them more closely, and realizing they were all original paintings, he purchased the lot on the spot. “It was quite exciting to stumble upon what appeared to be the unknown original advertising studies for one of the world’s great brands,” he says. But the casualness of that first encounter would not last, as competition for the newly found canvases ramped up among collectors. Today, the collector describes the scramble for these heretofore-unknown pieces as “a Gilroy art scrum.”Among those who were particularly interested in the news of the Gilroy cache was David Hughes, who was a brewer at Guinness for 15 years and has written three books on Guinness advertising art and collectibles, the most recent being “Gilroy Was Good for Guinness,” which reproduces more than 150 of the recently “discovered” paintings. Despite being an expert on the cheery ephemera that was created to sell the dark, bitter stout, Hughes, like a lot of people, only learned of the newly uncovered Gilroy canvases as tantalizing examples from the cache (created for markets as diverse as Russia, Israel, France, and the United States) started to surface in 2008.“Within the Guinness archives itself,” Hughes says of the materials kept at the company’s Dublin headquarters, “they’ve got lots of advertising art, watercolors, and sketches of workups towards the final version of the posters. But they never had a single oil painting. Until the paintings started turning up in the United States, where Guinness memorabilia is quite collectible, it wasn’t fully understood that the posters were based on oils. All of the canvases will be in collections within a year,” Hughes adds. For would-be Gilroy collectors, that means the clock is ticking.As it turns out, Gilroy’s entire artistic process was a prelude to the oils. “The first thing he’d usually do was a pencil sketch,” says Hughes. “Then he’d paint a watercolor over the top of the pencil sketch to get the color balance right. Once that was settled and all the approvals were in, he’d sit down and paint the oil. The proof version that went to Guinness for approval, it seems, was always an oil painting.”Based on what we know of John Gilroy’s work as an artist, that makes sense. For almost half a century, Gilroy was regarded not only as one of England’s premier commercial illustrators, but also as one of its best portraitists. “He painted the Queen three times,” says Hughes, “Lord Mountbatten about four times. In 1942, he did a pencil-and-crayon sketch of Churchill in a London bunker.” According to Hughes, Churchill gave that portrait to Russian leader Joseph Stalin at the Yalta Conference with Franklin Delano Roosevelt, which may mean that somewhere in the bowels of the Kremlin, there’s a portrait of Winnie by the same guy who made a living drawing cartoons of flying toucans balancing pints of Guinness on their beaks.For those who collect advertising art and breweriana, Gilroy is revered for the numerous campaigns he conceived as an illustrator for S.H. Benson, the venerable British ad agency, which was founded in 1893. Though most famous for the Guinness toucan, which has been the internationally recognized mascot of Guinness since 1935, Gilroy’s first campaign with S.H. Benson was for a yeast extract called Bovril. “Do you have Bovril in the U.S.?” Hughes asks. “It’s a rather dark, pungent, savory spread that goes on toast or bread. It’s full of vitamins, quite a traditional product. He also did a lot of work on campaigns for Colman’s mustard and Macleans toothpaste.”pparently Gilroy’s work caught the eye of Guinness, which wanted something distinctive for its stout. “A black beer is a unique product,” says Hughes. “There weren’t many on the market then, and there are even fewer now. So they wanted their advertising to be well thought of and agreeable to the public.” For example, in the early 1930s, Benson already had an ad featuring a glass of Guinness with a nice foamy head on top. “Gilroy put a smiling face in the foam,” says Hughes. Collectors often refer to this charming drawing as the “anthropomorphic glass.”That made the black beer friendly. To ensure that it would be appealing to the common man, Benson launched its “Guinness for Strength” campaign, whose most famous image is the 1934 Gilroy illustration of a muscular workman effortlessly balancing an enormous steel girder on one arm and his head.Another early campaign put Guinness beer in the world of Lewis Carroll’s “Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland.” “Guinness and oysters were a big thing,” says Hughes. In one ad, “Gilroy drew all the oysters from the poem ‘The Walrus and the Carpenter’ sipping glasses of Guinness.”nd then there were the animals, of which the toucan is only the most recognized, and not even the first (that honor goes to a seal). “He had the lion and the ostrich and the bear up the pole,” Hughes says. “There was a whole menagerie of them. The animals kept going for 30 years. It’s probably the longest running campaign in advertising history.”Most of Gilroy’s animals lived in a zoo, so a central character of the animal advertisements was a zookeeper, who was a caricature of the artist himself. “That’s what Gilroy looked like,” says Hughes. “Gilroy was a chubby, little man with a little moustache. As a younger man, he drew himself into the advert, and he became the zookeeper.”Gilroy’s animals good-naturedly tormented their zookeeper by stealing his precious Guinness: An ostrich swallows his glass pint whole, whose bulging outline can be seen in its slender throat; a seal balances a pint on its nose; a kangaroo swaps her “joey” for the zookeeper’s brown bottle. Often the zookeeper is so taken aback by these circumstances his hat has popped off his head.In fact, Gilroy spent a lot of time at the London Zoo to make sure he captured the essence of his animals accurately. “In the archives at Guinness,” says Hughes, “there are a lot of sketches of tortoises, emus, ostriches, and the rest. He perfected the drawing of the animals by going to the zoo, then he adapted them for the adverts.” As a result, a Gilroy bear really looked like a bear, albeit one with a smile on its face.During World War II, Gilroy’s Guinness ads managed to keep their sense of humor (eg: two sailors painting the hull of an aircraft carrier, each wishing the other was a Guinness), and in the 1950s and early ’60s, Gilroy’s famous pint-toting toucans flew all over the world for Guinness, in front of the Kremlin as well as Mt. Rushmore, the Leaning Tower of Pisa, and the Statue of Liberty, although some of these paintings never made it to the campaign stage.Gilroy’s work on the Guinness account ended in 1962, and in 1971, Benson was gobbled up by the Madison Avenue advertising firm of Ogilvy & Mather. By then, says Hughes, Gilroy’s work for Guinness was considered the pinnacle of poster design in the U.K., and quite collectible. “The posters were made by a lithographic process. In the 1930s, the canvases were re-created on stone by a print maker, but eventually the paintings were transferred via photolithography onto metal sheets. Some of the biggest posters were made for billboards. Those used 64 different sheets that you’d give to the guy with the bucket of wheat paste and a mop to put up in the right order to create the completed picture.”In terms of single-sheet posters, Hughes says the biggest ones were probably 4 by 3 feet. Benson’s had an archive of it all, but “when Benson’s shut down in ’71, when they were taken over, they cleaned out their stockroom of hundreds of posters and gave them to the British Museum and the Victoria and Albert Museum in London. Today, both have collections of the original posters, including the 64-sheets piled into these packets, which were wrapped in brown paper and tied up with string. They’re extremely difficult to handle; you can’t display them, really.”At least the paper got a good home. As for the canvases? Well, their history can only be pieced together based on conjecture, but here’s what Hughes thinks he knows.Sometime in the 1970s, a single collector whose name remains a mystery appears to have purchased as many as 700 to 900 Gilroy paintings that had been in the archives. “The guy who bought the whole archive was an American millionaire,” Hughes says. “He’s a secretive character who doesn’t want to be identified. I don’t blame him. He doesn’t want any publicity about how he bought the collection or its subsequent sale.”air enough. What we do know for sure is that the years were not kind to Gilroy’s canvases while in storage at Benson’s. In fact, it’s believed that more than half of the cache did not survive the decades and were probably destroyed by the mystery collector who bought them because of their extremely deteriorated condition (torn canvases, images blackened by mildew, etc.). After all, when Gilroy’s canvases were put away, no one at Benson’s thought they’d be regarded in the future as masterpieces.“A lot of the rolled-up canvases were stuck together,” says Hughes. “Oil takes a long while to dry. Gilroy diluted his oils with what’s called Japan drier, which is a sort of oil thinner that allows you to put the oil on the canvas in a much thinner texture, and then roll them up afterwards. The painted canvas becomes reasonably flexible. The problem is that even with a drier, they still took a long time to dry. And if someone had packed them tightly together and put weight on them, which is what must have happened while the Gilroy paintings were in storage at Benson’s, they’d just stick together. Some of the canvases were 80 years old, dating from 1930.”For diehard Guinness-advertising fans, though, it’s not all bad news. After all, almost half of the cache was saved, “and it’s beautiful,” says Hughes. “I’ve just come back from Boston to look at a lot of these canvases out there, and they are superb. The guy who’s selling the canvases I saw had about 40 or 50 with him. They’re absolutely fabulous.”Although he has no proof, Hughes believes the person who bought the cache in the 1970s also oversaw its preservation. Importantly to many collectors, all of the Gilroy canvases are in their found condition, stabilized but essentially unchanged. Even areas in the paint that show evidence of rubbing from adjacent canvases remain as they were found. “I think the preservation has been done by the owner,” Hughes says. “I don’t think the dealers did it. It’s my understanding that they were supplied with fully stabilized canvases from the original buyer. It appears that they were shipped from the U.K., so that’s interesting in itself.” Which suggests they never left the United Kingdom after being purchased by the mysterious American millionaire.collectors of the approval process at Benson. Gilroy painted his canvases on stretchers, and in the bottom corner of each canvas was a small tag identifying the artist, account code, and action to be taken (“Re-draw,” “Revise,” “Hold,” “Print,” and, during World War II, “Submit to censor”). “They would’ve been shown to Guinness on a wooden stretcher,” Hughes says. “Before they went into storage, somebody removed the stretchers and either laid them flat or rolled them up.”Without exception, the canvases Hughes has seen, which were photographed exclusively for his book, are in fine shape and retain their mounting holes for the stretchers and Benson agency tags. “The colors are good,” he says. “They haven’t been in sunlight. They’ll keep for years and years and years.” One collector notes that you can even see the ruby highlights in Gilroy’s paintings of glasses of the stout. “When a pint of Guinness is backlit by a very strong light, the liquid has a deep ruby color,” this collector says. “Gilroy was very careful to include this effect when he painted beer in clear pint glasses.”Finally, for Guinness, breweriana, and advertising-art collectors, the Gilroy canvases also offer a peek of what might have been. “I would say about half the images were never commercially used, so they are absolutely brand new, never been seen before,” says Hughes. “They’re going to blow people away.” Of particular interest to collectors in the United States are the Gilroy paintings of classic cars that were created for an aborted, early 1950s campaign to coincide with the brewing of Guinness on Long Island.Still, it’s the medium that continues to amaze Hughes. “The idea of the canvases, none of us expected that,” he says. “As a Guinness collector, I’ve always collected their adverts, but they’re prints. They never touched Gilroy, he was never anywhere near the printing process. I had acquired a pencil drawing, which I was delighted with. Then these oils started turning up,” he Naturally, Hughes the Guinness scholar has seen a few oils that Hughes the Guinness collector would very much like to own. “If I had a magic wand? Well, I saw one this weekend that I really liked. It’s one of the animal ones. But it’s an animal that was not used commercially. It’s of a rhinoceros sitting on the ground with the zookeeper’s Guinness between his legs. The rhinoceros is looking at the zookeeper, and the zookeeper’s looking around the corner holding his broom. It’s just a great image, and it’s probably the only one of that advert that exists. So if I could wave my magic wand, I think that’s what I’d get. But I’d need $10,000With those kinds of prices and that kind of buzz, you might think that whoever is handling the Guinness advertising account today might be tempted to just re-run the campaign. But Hughes is realistic about the likelihood of that. “Advertising moves on,” he says. “Gilroy’s jokey, humorous, cartoon-like poster design is quintessentially 1930s, ’40s, and ’50s. It is a bit quaint, maybe even a little juvenile for today’s audiences. But it’s still amusing. The other day I showed the draft of my book to my mother, who’s 84. She sat in the kitchen, just giggling at the pictures.”That sums up Gilroy to Hughes; not that it’s only appealing to people in their 80s, but that his work is ultimately about making people happy, which is why his advertising images connected so honestly with viewers. “Gilroy had a tremendous sense of humor,” Hughes says. “He always saw the funny side of things. He was apparently a chap who, if you were feeling a little down and out, you’d spend a couple of hours with him and he’d just lift your spirits.” You know, in much the same way as a lot of us feel after a nice pint of Guinness.
75cm x 65cmThe biggest cliché in the collecting world is the “discovery” of a previously unknown cache of stuff that’s been hidden away for years until one day, much to everyone’s amazement, the treasure trove is unearthed and the collecting landscape is changed forever. As a corollary to this hoary trope, if you are in the right place at the right time, you can get in on the action before the word gets out.Cliché or not, that’s roughly what happened in 2008 when hundreds of artist John Gilroy’s oil-on-canvas paintings started to appear on the market. The canvases had been painted by Gilroy as final proofs for his iconic Guinness beer posters, the most recognized alcoholic-beverage advertisements of the mid-20th century. Before most collectors of advertising art and breweriana knew what had happened, most of the best pieces had been snapped up by a handful of savvy collectors. In fact, the distribution of the canvases into the hands of private collectors was so swift and stealthy that one prominent member of the Guinness family was forced to get their favorite Gilroys on the secondary market.One of those early collectors, who wishes to remain anonymous, recalls seeing several canvases for the first time at an antiques show. At first, he thought they were posters since that’s what Guinness collectors have come to expect. But after looking at them more closely, and realizing they were all original paintings, he purchased the lot on the spot. “It was quite exciting to stumble upon what appeared to be the unknown original advertising studies for one of the world’s great brands,” he says. But the casualness of that first encounter would not last, as competition for the newly found canvases ramped up among collectors. Today, the collector describes the scramble for these heretofore-unknown pieces as “a Gilroy art scrum.”Among those who were particularly interested in the news of the Gilroy cache was David Hughes, who was a brewer at Guinness for 15 years and has written three books on Guinness advertising art and collectibles, the most recent being “Gilroy Was Good for Guinness,” which reproduces more than 150 of the recently “discovered” paintings. Despite being an expert on the cheery ephemera that was created to sell the dark, bitter stout, Hughes, like a lot of people, only learned of the newly uncovered Gilroy canvases as tantalizing examples from the cache (created for markets as diverse as Russia, Israel, France, and the United States) started to surface in 2008.“Within the Guinness archives itself,” Hughes says of the materials kept at the company’s Dublin headquarters, “they’ve got lots of advertising art, watercolors, and sketches of workups towards the final version of the posters. But they never had a single oil painting. Until the paintings started turning up in the United States, where Guinness memorabilia is quite collectible, it wasn’t fully understood that the posters were based on oils. All of the canvases will be in collections within a year,” Hughes adds. For would-be Gilroy collectors, that means the clock is ticking.As it turns out, Gilroy’s entire artistic process was a prelude to the oils. “The first thing he’d usually do was a pencil sketch,” says Hughes. “Then he’d paint a watercolor over the top of the pencil sketch to get the color balance right. Once that was settled and all the approvals were in, he’d sit down and paint the oil. The proof version that went to Guinness for approval, it seems, was always an oil painting.”Based on what we know of John Gilroy’s work as an artist, that makes sense. For almost half a century, Gilroy was regarded not only as one of England’s premier commercial illustrators, but also as one of its best portraitists. “He painted the Queen three times,” says Hughes, “Lord Mountbatten about four times. In 1942, he did a pencil-and-crayon sketch of Churchill in a London bunker.” According to Hughes, Churchill gave that portrait to Russian leader Joseph Stalin at the Yalta Conference with Franklin Delano Roosevelt, which may mean that somewhere in the bowels of the Kremlin, there’s a portrait of Winnie by the same guy who made a living drawing cartoons of flying toucans balancing pints of Guinness on their beaks.For those who collect advertising art and breweriana, Gilroy is revered for the numerous campaigns he conceived as an illustrator for S.H. Benson, the venerable British ad agency, which was founded in 1893. Though most famous for the Guinness toucan, which has been the internationally recognized mascot of Guinness since 1935, Gilroy’s first campaign with S.H. Benson was for a yeast extract called Bovril. “Do you have Bovril in the U.S.?” Hughes asks. “It’s a rather dark, pungent, savory spread that goes on toast or bread. It’s full of vitamins, quite a traditional product. He also did a lot of work on campaigns for Colman’s mustard and Macleans toothpaste.”pparently Gilroy’s work caught the eye of Guinness, which wanted something distinctive for its stout. “A black beer is a unique product,” says Hughes. “There weren’t many on the market then, and there are even fewer now. So they wanted their advertising to be well thought of and agreeable to the public.” For example, in the early 1930s, Benson already had an ad featuring a glass of Guinness with a nice foamy head on top. “Gilroy put a smiling face in the foam,” says Hughes. Collectors often refer to this charming drawing as the “anthropomorphic glass.”That made the black beer friendly. To ensure that it would be appealing to the common man, Benson launched its “Guinness for Strength” campaign, whose most famous image is the 1934 Gilroy illustration of a muscular workman effortlessly balancing an enormous steel girder on one arm and his head.Another early campaign put Guinness beer in the world of Lewis Carroll’s “Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland.” “Guinness and oysters were a big thing,” says Hughes. In one ad, “Gilroy drew all the oysters from the poem ‘The Walrus and the Carpenter’ sipping glasses of Guinness.”nd then there were the animals, of which the toucan is only the most recognized, and not even the first (that honor goes to a seal). “He had the lion and the ostrich and the bear up the pole,” Hughes says. “There was a whole menagerie of them. The animals kept going for 30 years. It’s probably the longest running campaign in advertising history.”Most of Gilroy’s animals lived in a zoo, so a central character of the animal advertisements was a zookeeper, who was a caricature of the artist himself. “That’s what Gilroy looked like,” says Hughes. “Gilroy was a chubby, little man with a little moustache. As a younger man, he drew himself into the advert, and he became the zookeeper.”Gilroy’s animals good-naturedly tormented their zookeeper by stealing his precious Guinness: An ostrich swallows his glass pint whole, whose bulging outline can be seen in its slender throat; a seal balances a pint on its nose; a kangaroo swaps her “joey” for the zookeeper’s brown bottle. Often the zookeeper is so taken aback by these circumstances his hat has popped off his head.In fact, Gilroy spent a lot of time at the London Zoo to make sure he captured the essence of his animals accurately. “In the archives at Guinness,” says Hughes, “there are a lot of sketches of tortoises, emus, ostriches, and the rest. He perfected the drawing of the animals by going to the zoo, then he adapted them for the adverts.” As a result, a Gilroy bear really looked like a bear, albeit one with a smile on its face.During World War II, Gilroy’s Guinness ads managed to keep their sense of humor (eg: two sailors painting the hull of an aircraft carrier, each wishing the other was a Guinness), and in the 1950s and early ’60s, Gilroy’s famous pint-toting toucans flew all over the world for Guinness, in front of the Kremlin as well as Mt. Rushmore, the Leaning Tower of Pisa, and the Statue of Liberty, although some of these paintings never made it to the campaign stage.Gilroy’s work on the Guinness account ended in 1962, and in 1971, Benson was gobbled up by the Madison Avenue advertising firm of Ogilvy & Mather. By then, says Hughes, Gilroy’s work for Guinness was considered the pinnacle of poster design in the U.K., and quite collectible. “The posters were made by a lithographic process. In the 1930s, the canvases were re-created on stone by a print maker, but eventually the paintings were transferred via photolithography onto metal sheets. Some of the biggest posters were made for billboards. Those used 64 different sheets that you’d give to the guy with the bucket of wheat paste and a mop to put up in the right order to create the completed picture.”In terms of single-sheet posters, Hughes says the biggest ones were probably 4 by 3 feet. Benson’s had an archive of it all, but “when Benson’s shut down in ’71, when they were taken over, they cleaned out their stockroom of hundreds of posters and gave them to the British Museum and the Victoria and Albert Museum in London. Today, both have collections of the original posters, including the 64-sheets piled into these packets, which were wrapped in brown paper and tied up with string. They’re extremely difficult to handle; you can’t display them, really.”At least the paper got a good home. As for the canvases? Well, their history can only be pieced together based on conjecture, but here’s what Hughes thinks he knows.Sometime in the 1970s, a single collector whose name remains a mystery appears to have purchased as many as 700 to 900 Gilroy paintings that had been in the archives. “The guy who bought the whole archive was an American millionaire,” Hughes says. “He’s a secretive character who doesn’t want to be identified. I don’t blame him. He doesn’t want any publicity about how he bought the collection or its subsequent sale.”air enough. What we do know for sure is that the years were not kind to Gilroy’s canvases while in storage at Benson’s. In fact, it’s believed that more than half of the cache did not survive the decades and were probably destroyed by the mystery collector who bought them because of their extremely deteriorated condition (torn canvases, images blackened by mildew, etc.). After all, when Gilroy’s canvases were put away, no one at Benson’s thought they’d be regarded in the future as masterpieces.“A lot of the rolled-up canvases were stuck together,” says Hughes. “Oil takes a long while to dry. Gilroy diluted his oils with what’s called Japan drier, which is a sort of oil thinner that allows you to put the oil on the canvas in a much thinner texture, and then roll them up afterwards. The painted canvas becomes reasonably flexible. The problem is that even with a drier, they still took a long time to dry. And if someone had packed them tightly together and put weight on them, which is what must have happened while the Gilroy paintings were in storage at Benson’s, they’d just stick together. Some of the canvases were 80 years old, dating from 1930.”For diehard Guinness-advertising fans, though, it’s not all bad news. After all, almost half of the cache was saved, “and it’s beautiful,” says Hughes. “I’ve just come back from Boston to look at a lot of these canvases out there, and they are superb. The guy who’s selling the canvases I saw had about 40 or 50 with him. They’re absolutely fabulous.”Although he has no proof, Hughes believes the person who bought the cache in the 1970s also oversaw its preservation. Importantly to many collectors, all of the Gilroy canvases are in their found condition, stabilized but essentially unchanged. Even areas in the paint that show evidence of rubbing from adjacent canvases remain as they were found. “I think the preservation has been done by the owner,” Hughes says. “I don’t think the dealers did it. It’s my understanding that they were supplied with fully stabilized canvases from the original buyer. It appears that they were shipped from the U.K., so that’s interesting in itself.” Which suggests they never left the United Kingdom after being purchased by the mysterious American millionaire.collectors of the approval process at Benson. Gilroy painted his canvases on stretchers, and in the bottom corner of each canvas was a small tag identifying the artist, account code, and action to be taken (“Re-draw,” “Revise,” “Hold,” “Print,” and, during World War II, “Submit to censor”). “They would’ve been shown to Guinness on a wooden stretcher,” Hughes says. “Before they went into storage, somebody removed the stretchers and either laid them flat or rolled them up.”Without exception, the canvases Hughes has seen, which were photographed exclusively for his book, are in fine shape and retain their mounting holes for the stretchers and Benson agency tags. “The colors are good,” he says. “They haven’t been in sunlight. They’ll keep for years and years and years.” One collector notes that you can even see the ruby highlights in Gilroy’s paintings of glasses of the stout. “When a pint of Guinness is backlit by a very strong light, the liquid has a deep ruby color,” this collector says. “Gilroy was very careful to include this effect when he painted beer in clear pint glasses.”Finally, for Guinness, breweriana, and advertising-art collectors, the Gilroy canvases also offer a peek of what might have been. “I would say about half the images were never commercially used, so they are absolutely brand new, never been seen before,” says Hughes. “They’re going to blow people away.” Of particular interest to collectors in the United States are the Gilroy paintings of classic cars that were created for an aborted, early 1950s campaign to coincide with the brewing of Guinness on Long Island.Still, it’s the medium that continues to amaze Hughes. “The idea of the canvases, none of us expected that,” he says. “As a Guinness collector, I’ve always collected their adverts, but they’re prints. They never touched Gilroy, he was never anywhere near the printing process. I had acquired a pencil drawing, which I was delighted with. Then these oils started turning up,” he Naturally, Hughes the Guinness scholar has seen a few oils that Hughes the Guinness collector would very much like to own. “If I had a magic wand? Well, I saw one this weekend that I really liked. It’s one of the animal ones. But it’s an animal that was not used commercially. It’s of a rhinoceros sitting on the ground with the zookeeper’s Guinness between his legs. The rhinoceros is looking at the zookeeper, and the zookeeper’s looking around the corner holding his broom. It’s just a great image, and it’s probably the only one of that advert that exists. So if I could wave my magic wand, I think that’s what I’d get. But I’d need $10,000With those kinds of prices and that kind of buzz, you might think that whoever is handling the Guinness advertising account today might be tempted to just re-run the campaign. But Hughes is realistic about the likelihood of that. “Advertising moves on,” he says. “Gilroy’s jokey, humorous, cartoon-like poster design is quintessentially 1930s, ’40s, and ’50s. It is a bit quaint, maybe even a little juvenile for today’s audiences. But it’s still amusing. The other day I showed the draft of my book to my mother, who’s 84. She sat in the kitchen, just giggling at the pictures.”That sums up Gilroy to Hughes; not that it’s only appealing to people in their 80s, but that his work is ultimately about making people happy, which is why his advertising images connected so honestly with viewers. “Gilroy had a tremendous sense of humor,” Hughes says. “He always saw the funny side of things. He was apparently a chap who, if you were feeling a little down and out, you’d spend a couple of hours with him and he’d just lift your spirits.” You know, in much the same way as a lot of us feel after a nice pint of Guinness. -
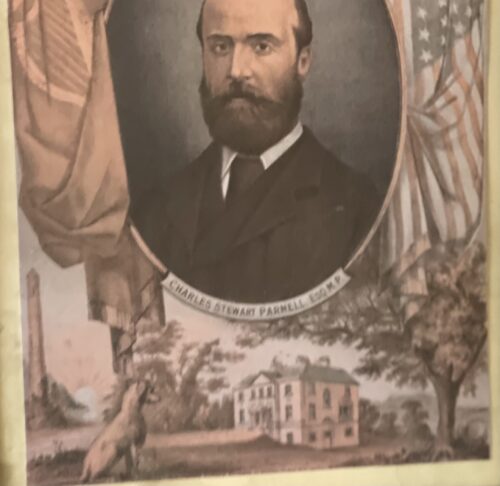
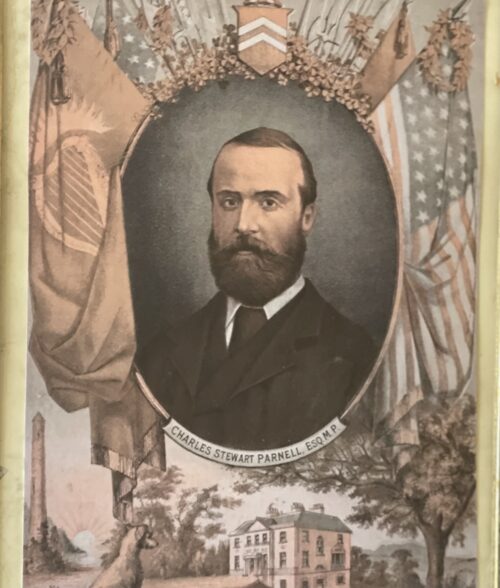
 32cm x 25cm Charles Stewart Parnell (1846-1891) will be remembered as one of the most iconic and indeed controversial politicians in Irish history.MP and Leader of the Irish Parliamentary or Home Rule Party from1882 to 1891 until revelations of his adulterous love affair with Kitty O'Shea forced his resignation.He died shortly afterwards from pneumonia in the arms of his newly divorced and remarried wife Katherine.His death was considered to be a direct result of the stresses he endured because of the Victorian era scandal and his subsequent funeral at Glasnevin Cemetery in Dublin was attended by more than 200000 people.His notability was such that his gravestone of unhewn Wicklow granite, erected in 1940,reads only Parnell. This faithful portrayal of Parnell,well over 130 years old, by the artist JG Wills dates to 1884 and is a beautiful homage to the "uncrowned king of Ireland".
32cm x 25cm Charles Stewart Parnell (1846-1891) will be remembered as one of the most iconic and indeed controversial politicians in Irish history.MP and Leader of the Irish Parliamentary or Home Rule Party from1882 to 1891 until revelations of his adulterous love affair with Kitty O'Shea forced his resignation.He died shortly afterwards from pneumonia in the arms of his newly divorced and remarried wife Katherine.His death was considered to be a direct result of the stresses he endured because of the Victorian era scandal and his subsequent funeral at Glasnevin Cemetery in Dublin was attended by more than 200000 people.His notability was such that his gravestone of unhewn Wicklow granite, erected in 1940,reads only Parnell. This faithful portrayal of Parnell,well over 130 years old, by the artist JG Wills dates to 1884 and is a beautiful homage to the "uncrowned king of Ireland". -

 32cm x 27cm
32cm x 27cmDaniel O’Connnell Jr. had famously acquired the Phoenix Brewery in James’s street in 1831, which produced O’Connell’s Ale. It should be noted that O’Connell and the Guinness family were at times political rivals, something best captured by the 1841 ‘Repeal Election’, where O’Connell had stood against and defeated Arthur Guinness Jr. This period would see a sizeable boycott of Guinness, dubbed “Protestant Porter” by sections of the populace, though this was against the wishes of O’Connell himself.
John D’Arcy continued to brew O’Connell Ale after the family had ceased their role in brewing, and in time production moved to the Anchor Brewery in Usher Street. Watkins eventually took up the brewing of O’Connell Ale, and this advertisement was placed by them in the pages of leading newspapers in the 1930s.
While Arthur had failed to defeat O’Connell at the Ballot Box, I always wonder what O’Connell would think of the Guinness Empire today every time I see a Diaego truck pass his statue.
-

 75cm x 65cmThe biggest cliché in the collecting world is the “discovery” of a previously unknown cache of stuff that’s been hidden away for years until one day, much to everyone’s amazement, the treasure trove is unearthed and the collecting landscape is changed forever. As a corollary to this hoary trope, if you are in the right place at the right time, you can get in on the action before the word gets out.
75cm x 65cmThe biggest cliché in the collecting world is the “discovery” of a previously unknown cache of stuff that’s been hidden away for years until one day, much to everyone’s amazement, the treasure trove is unearthed and the collecting landscape is changed forever. As a corollary to this hoary trope, if you are in the right place at the right time, you can get in on the action before the word gets out.“Some of the canvases were 80 years old, dating from 1930.”
Cliché or not, that’s roughly what happened in 2008 when hundreds of artist John Gilroy’s oil-on-canvas paintings started to appear on the market. The canvases had been painted by Gilroy as final proofs for his iconic Guinness beer posters, the most recognized alcoholic-beverage advertisements of the mid-20th century. Before most collectors of advertising art and breweriana knew what had happened, most of the best pieces had been snapped up by a handful of savvy collectors. In fact, the distribution of the canvases into the hands of private collectors was so swift and stealthy that one prominent member of the Guinness family was forced to get their favorite Gilroys on the secondary market.One of those early collectors, who wishes to remain anonymous, recalls seeing several canvases for the first time at an antiques show. At first, he thought they were posters since that’s what Guinness collectors have come to expect. But after looking at them more closely, and realizing they were all original paintings, he purchased the lot on the spot. “It was quite exciting to stumble upon what appeared to be the unknown original advertising studies for one of the world’s great brands,” he says. But the casualness of that first encounter would not last, as competition for the newly found canvases ramped up among collectors. Today, the collector describes the scramble for these heretofore-unknown pieces as “a Gilroy art scrum.”Among those who were particularly interested in the news of the Gilroy cache was David Hughes, who was a brewer at Guinness for 15 years and has written three books on Guinness advertising art and collectibles, the most recent being “Gilroy Was Good for Guinness,” which reproduces more than 150 of the recently “discovered” paintings. Despite being an expert on the cheery ephemera that was created to sell the dark, bitter stout, Hughes, like a lot of people, only learned of the newly uncovered Gilroy canvases as tantalizing examples from the cache (created for markets as diverse as Russia, Israel, France, and the United States) started to surface in 2008.“Within the Guinness archives itself,” Hughes says of the materials kept at the company’s Dublin headquarters, “they’ve got lots of advertising art, watercolors, and sketches of workups towards the final version of the posters. But they never had a single oil painting. Until the paintings started turning up in the United States, where Guinness memorabilia is quite collectible, it wasn’t fully understood that the posters were based on oils. All of the canvases will be in collections within a year,” Hughes adds. For would-be Gilroy collectors, that means the clock is ticking.As it turns out, Gilroy’s entire artistic process was a prelude to the oils. “The first thing he’d usually do was a pencil sketch,” says Hughes. “Then he’d paint a watercolor over the top of the pencil sketch to get the color balance right. Once that was settled and all the approvals were in, he’d sit down and paint the oil. The proof version that went to Guinness for approval, it seems, was always an oil painting.”Based on what we know of John Gilroy’s work as an artist, that makes sense. For almost half a century, Gilroy was regarded not only as one of England’s premier commercial illustrators, but also as one of its best portraitists. “He painted the Queen three times,” says Hughes, “Lord Mountbatten about four times. In 1942, he did a pencil-and-crayon sketch of Churchill in a London bunker.” According to Hughes, Churchill gave that portrait to Russian leader Joseph Stalin at the Yalta Conference with Franklin Delano Roosevelt, which may mean that somewhere in the bowels of the Kremlin, there’s a portrait of Winnie by the same guy who made a living drawing cartoons of flying toucans balancing pints of Guinness on their beaks.For those who collect advertising art and breweriana, Gilroy is revered for the numerous campaigns he conceived as an illustrator for S.H. Benson, the venerable British ad agency, which was founded in 1893. Though most famous for the Guinness toucan, which has been the internationally recognized mascot of Guinness since 1935, Gilroy’s first campaign with S.H. Benson was for a yeast extract called Bovril. “Do you have Bovril in the U.S.?” Hughes asks. “It’s a rather dark, pungent, savory spread that goes on toast or bread. It’s full of vitamins, quite a traditional product. He also did a lot of work on campaigns for Colman’s mustard and Macleans toothpaste.”pparently Gilroy’s work caught the eye of Guinness, which wanted something distinctive for its stout. “A black beer is a unique product,” says Hughes. “There weren’t many on the market then, and there are even fewer now. So they wanted their advertising to be well thought of and agreeable to the public.” For example, in the early 1930s, Benson already had an ad featuring a glass of Guinness with a nice foamy head on top. “Gilroy put a smiling face in the foam,” says Hughes. Collectors often refer to this charming drawing as the “anthropomorphic glass.”That made the black beer friendly. To ensure that it would be appealing to the common man, Benson launched its “Guinness for Strength” campaign, whose most famous image is the 1934 Gilroy illustration of a muscular workman effortlessly balancing an enormous steel girder on one arm and his head.Another early campaign put Guinness beer in the world of Lewis Carroll’s “Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland.” “Guinness and oysters were a big thing,” says Hughes. In one ad, “Gilroy drew all the oysters from the poem ‘The Walrus and the Carpenter’ sipping glasses of Guinness.”nd then there were the animals, of which the toucan is only the most recognized, and not even the first (that honor goes to a seal). “He had the lion and the ostrich and the bear up the pole,” Hughes says. “There was a whole menagerie of them. The animals kept going for 30 years. It’s probably the longest running campaign in advertising history.”Most of Gilroy’s animals lived in a zoo, so a central character of the animal advertisements was a zookeeper, who was a caricature of the artist himself. “That’s what Gilroy looked like,” says Hughes. “Gilroy was a chubby, little man with a little moustache. As a younger man, he drew himself into the advert, and he became the zookeeper.”Gilroy’s animals good-naturedly tormented their zookeeper by stealing his precious Guinness: An ostrich swallows his glass pint whole, whose bulging outline can be seen in its slender throat; a seal balances a pint on its nose; a kangaroo swaps her “joey” for the zookeeper’s brown bottle. Often the zookeeper is so taken aback by these circumstances his hat has popped off his head.In fact, Gilroy spent a lot of time at the London Zoo to make sure he captured the essence of his animals accurately. “In the archives at Guinness,” says Hughes, “there are a lot of sketches of tortoises, emus, ostriches, and the rest. He perfected the drawing of the animals by going to the zoo, then he adapted them for the adverts.” As a result, a Gilroy bear really looked like a bear, albeit one with a smile on its face.During World War II, Gilroy’s Guinness ads managed to keep their sense of humor (eg: two sailors painting the hull of an aircraft carrier, each wishing the other was a Guinness), and in the 1950s and early ’60s, Gilroy’s famous pint-toting toucans flew all over the world for Guinness, in front of the Kremlin as well as Mt. Rushmore, the Leaning Tower of Pisa, and the Statue of Liberty, although some of these paintings never made it to the campaign stage.Gilroy’s work on the Guinness account ended in 1962, and in 1971, Benson was gobbled up by the Madison Avenue advertising firm of Ogilvy & Mather. By then, says Hughes, Gilroy’s work for Guinness was considered the pinnacle of poster design in the U.K., and quite collectible. “The posters were made by a lithographic process. In the 1930s, the canvases were re-created on stone by a print maker, but eventually the paintings were transferred via photolithography onto metal sheets. Some of the biggest posters were made for billboards. Those used 64 different sheets that you’d give to the guy with the bucket of wheat paste and a mop to put up in the right order to create the completed picture.”In terms of single-sheet posters, Hughes says the biggest ones were probably 4 by 3 feet. Benson’s had an archive of it all, but “when Benson’s shut down in ’71, when they were taken over, they cleaned out their stockroom of hundreds of posters and gave them to the British Museum and the Victoria and Albert Museum in London. Today, both have collections of the original posters, including the 64-sheets piled into these packets, which were wrapped in brown paper and tied up with string. They’re extremely difficult to handle; you can’t display them, really.”At least the paper got a good home. As for the canvases? Well, their history can only be pieced together based on conjecture, but here’s what Hughes thinks he knows.Sometime in the 1970s, a single collector whose name remains a mystery appears to have purchased as many as 700 to 900 Gilroy paintings that had been in the archives. “The guy who bought the whole archive was an American millionaire,” Hughes says. “He’s a secretive character who doesn’t want to be identified. I don’t blame him. He doesn’t want any publicity about how he bought the collection or its subsequent sale.”air enough. What we do know for sure is that the years were not kind to Gilroy’s canvases while in storage at Benson’s. In fact, it’s believed that more than half of the cache did not survive the decades and were probably destroyed by the mystery collector who bought them because of their extremely deteriorated condition (torn canvases, images blackened by mildew, etc.). After all, when Gilroy’s canvases were put away, no one at Benson’s thought they’d be regarded in the future as masterpieces.“A lot of the rolled-up canvases were stuck together,” says Hughes. “Oil takes a long while to dry. Gilroy diluted his oils with what’s called Japan drier, which is a sort of oil thinner that allows you to put the oil on the canvas in a much thinner texture, and then roll them up afterwards. The painted canvas becomes reasonably flexible. The problem is that even with a drier, they still took a long time to dry. And if someone had packed them tightly together and put weight on them, which is what must have happened while the Gilroy paintings were in storage at Benson’s, they’d just stick together. Some of the canvases were 80 years old, dating from 1930.”For diehard Guinness-advertising fans, though, it’s not all bad news. After all, almost half of the cache was saved, “and it’s beautiful,” says Hughes. “I’ve just come back from Boston to look at a lot of these canvases out there, and they are superb. The guy who’s selling the canvases I saw had about 40 or 50 with him. They’re absolutely fabulous.”Although he has no proof, Hughes believes the person who bought the cache in the 1970s also oversaw its preservation. Importantly to many collectors, all of the Gilroy canvases are in their found condition, stabilized but essentially unchanged. Even areas in the paint that show evidence of rubbing from adjacent canvases remain as they were found. “I think the preservation has been done by the owner,” Hughes says. “I don’t think the dealers did it. It’s my understanding that they were supplied with fully stabilized canvases from the original buyer. It appears that they were shipped from the U.K., so that’s interesting in itself.” Which suggests they never left the United Kingdom after being purchased by the mysterious American millionaire.collectors of the approval process at Benson. Gilroy painted his canvases on stretchers, and in the bottom corner of each canvas was a small tag identifying the artist, account code, and action to be taken (“Re-draw,” “Revise,” “Hold,” “Print,” and, during World War II, “Submit to censor”). “They would’ve been shown to Guinness on a wooden stretcher,” Hughes says. “Before they went into storage, somebody removed the stretchers and either laid them flat or rolled them up.”“As a younger man, he drew himself into the advert, and he became the zookeeper.”
Without exception, the canvases Hughes has seen, which were photographed exclusively for his book, are in fine shape and retain their mounting holes for the stretchers and Benson agency tags. “The colors are good,” he says. “They haven’t been in sunlight. They’ll keep for years and years and years.” One collector notes that you can even see the ruby highlights in Gilroy’s paintings of glasses of the stout. “When a pint of Guinness is backlit by a very strong light, the liquid has a deep ruby color,” this collector says. “Gilroy was very careful to include this effect when he painted beer in clear pint glasses.”Finally, for Guinness, breweriana, and advertising-art collectors, the Gilroy canvases also offer a peek of what might have been. “I would say about half the images were never commercially used, so they are absolutely brand new, never been seen before,” says Hughes. “They’re going to blow people away.” Of particular interest to collectors in the United States are the Gilroy paintings of classic cars that were created for an aborted, early 1950s campaign to coincide with the brewing of Guinness on Long Island.Still, it’s the medium that continues to amaze Hughes. “The idea of the canvases, none of us expected that,” he says. “As a Guinness collector, I’ve always collected their adverts, but they’re prints. They never touched Gilroy, he was never anywhere near the printing process. I had acquired a pencil drawing, which I was delighted with. Then these oils started turning up,” he Naturally, Hughes the Guinness scholar has seen a few oils that Hughes the Guinness collector would very much like to own. “If I had a magic wand? Well, I saw one this weekend that I really liked. It’s one of the animal ones. But it’s an animal that was not used commercially. It’s of a rhinoceros sitting on the ground with the zookeeper’s Guinness between his legs. The rhinoceros is looking at the zookeeper, and the zookeeper’s looking around the corner holding his broom. It’s just a great image, and it’s probably the only one of that advert that exists. So if I could wave my magic wand, I think that’s what I’d get. But I’d need $10,000With those kinds of prices and that kind of buzz, you might think that whoever is handling the Guinness advertising account today might be tempted to just re-run the campaign. But Hughes is realistic about the likelihood of that. “Advertising moves on,” he says. “Gilroy’s jokey, humorous, cartoon-like poster design is quintessentially 1930s, ’40s, and ’50s. It is a bit quaint, maybe even a little juvenile for today’s audiences. But it’s still amusing. The other day I showed the draft of my book to my mother, who’s 84. She sat in the kitchen, just giggling at the pictures.”That sums up Gilroy to Hughes; not that it’s only appealing to people in their 80s, but that his work is ultimately about making people happy, which is why his advertising images connected so honestly with viewers. “Gilroy had a tremendous sense of humor,” Hughes says. “He always saw the funny side of things. He was apparently a chap who, if you were feeling a little down and out, you’d spend a couple of hours with him and he’d just lift your spirits.” You know, in much the same way as a lot of us feel after a nice pint of Guinness. -
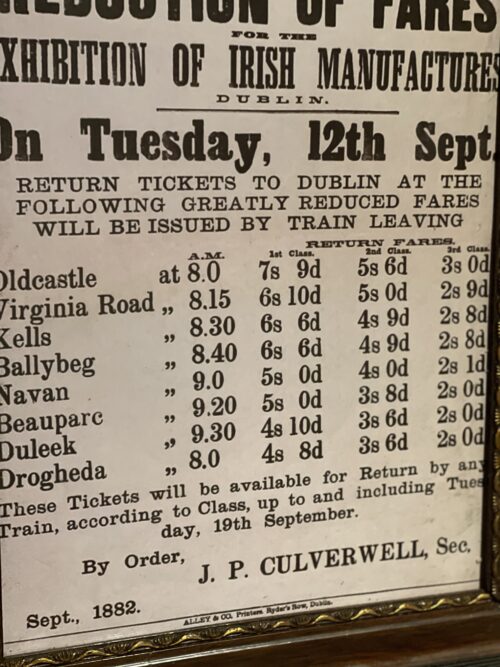
 47cm x 38cm The Great Northern Railway (Ireland) (GNR(I) or GNRI) was an Irish gauge (1,600 mm (5 ft 3 in)) railway company in Ireland. It was formed in 1876 by a merger of the Irish North Western Railway (INW), Northern Railway of Ireland, and Ulster Railway. The governments of Ireland and Northern Ireland jointly nationalised the company in 1953, and the company was liquidated in 1958: assets were split on national lines between the Ulster Transport Authority and Córas Iompair Éireann.
47cm x 38cm The Great Northern Railway (Ireland) (GNR(I) or GNRI) was an Irish gauge (1,600 mm (5 ft 3 in)) railway company in Ireland. It was formed in 1876 by a merger of the Irish North Western Railway (INW), Northern Railway of Ireland, and Ulster Railway. The governments of Ireland and Northern Ireland jointly nationalised the company in 1953, and the company was liquidated in 1958: assets were split on national lines between the Ulster Transport Authority and Córas Iompair Éireann.Foundation
The Ulster, D&D and D&BJct railways together formed the main line between Dublin and Belfast, with the D&BJct completing the final section in 1852 to join the Ulster at Portadown. The GNRI's other main lines were between Derry and Dundalk and between Omagh and Portadown. The Portadown, Dungannon and Omagh Junction Railway together with the Londonderry and Enniskillen Railway enabled GNRI trains between Derry and Belfast to compete with the Belfast and Northern Counties Railway, and both this and the Dundalk route gave connections between Derry and Dublin. These main lines supported the development of an extensive branch network serving the southwest half of Ulster and northern counties of Leinster. The GNRI became Ireland's most prosperous railway company and second largest railway network. In its early years the GNR(I) closely imitated the image of its English namesake, adopting an apple green livery for its steam locomotives and a varnished teak finish for its passenger coaches. Later the company adopted its famous pale blue livery for locomotives (from 1932), with the frames and running gear picked out in scarlet. Passenger vehicles were painted brown, instead of varnished. On 12 June 1889, a significant rail accident occurred when a passenger train stalled between Armagh and Newry. The train was divided, but during the uncoupling operation ten carriages ran away and collided with another passenger train. A total of 80 people were killed and 260 were injured in what was then the deadliest railway accident to have occurred in Europe. The accident remains the deadliest ever to have occurred on the island of Ireland.Growth and partition
In the early 20th century increasing traffic led the GNRI to consider introducing larger locomotives. The Great Southern & Western Railway had introduced express passenger locomotives with a 4-6-0 wheel arrangement, and the GNRI wanted to do the same. However, the lifting shop in the GNRI Dundalk works was too short to build or overhaul a 4-6-0, so the company persisted with 4-4-0 locomotives for even the heaviest and fastest passenger trains. This led to the GNRI to order a very modern and powerful class of 4-4-0's, the Class V three cylinder compound locomotives built by Beyer, Peacock & Company in 1932. This class has been compared with another notable V class, that introduced by the Southern Railway in England in 1930. The Partition of Ireland in 1921 created a border through the GNRI's territory. The new border crossed all three of its main lines and some of its secondary lines. The imposition of border controls caused some service disruption, with main line trains having to stop at both Dundalk and Goraghwood stations. This was not eased until 1947 when customs and immigration facilities for Dublin–Belfast expresses were opened at Dublin Amiens Street and Belfast Great Victoria Street stations.Nationalisation and division
A combination of the increasing road competition facing all railways and a change in patterns of economic activity caused by the Partition of Ireland reduced the GNRI's prosperity. The company modernised and reduced its costs by introducing modern diesel multiple units on an increasing number of services in the 1940s and 1950s and by making Dublin–Belfast expresses non-stop from 1948. In Dundalk at the GNR Works the railway engineers developed railbuses for use on sections of the rural network. Nevertheless, by the 1950s the GNRI had ceased to be profitable and in 1953 the company was jointly nationalised by the governments of the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland. The two governments ran the railway jointly under a Great Northern Railway Board until 1958.In May 1958, the Government of Northern Ireland's wish to close many lines led to the GNR(I) Board being dissolved and the assets divided between the two territories. At midnight on 30 September 1958, all lines entirely within Northern Ireland were transferred to the (nationalised) Ulster Transport Authority (UTA) and all lines entirely within the Republic of Ireland were transferred to Córas Iompair Éireann (CIÉ). CIÉ had been formed as a private company in 1945 but had been nationalised in 1950. In an attempt at fairness, all classes of locomotive and rolling stock were also divided equally between the transport operators of the two new owners.: 184–185 Most classes of GNRI locomotive had been built in small classes, so this division left both railways with an operational and maintenance difficulty of many different designs all in small numbers. The Government of Northern Ireland, which had a very anti-rail policy, rapidly closed most of the GNR(I) lines in Northern Ireland.Exceptions were the Belfast–Dundalk and Portadown–Derry main lines and the Newry–Warrenpoint and Lisburn–Antrim branches. It made the Lisburn–Antrim branch freight-only from 1960 and closed the Portadown–Derry and Newry–Warrenpoint lines to all traffic in 1965.The Republic of Ireland government tried briefly to maintain services on lines closed at the border by the Northern Ireland government, but this was impractical, and the Republic had to follow suit in closing most GNR(I) lines within the Republic. Since 1963, the Drogheda–Navan branch has survived for freight traffic only. The GNR's north western main line between Dundalk and Derry bypassed the small County Tyrone town of Fintona, which was instead served by a 1 mile (1.6 km) branch line from Fintona Junction station. The service was operated by the double-deck Fintona horse tram until the line's closure in 1957. CIÉ also acquired the Hill of Howth Tramway, in the northern suburbs of Dublin, in the 1958 dissolution of the GNRI Board. CIÉ closed the tramway about a year later. Today, the GNR routes remaining consist of the main line from Dublin to Belfast, the Howth branch, electrified for Dublin commuter services since 1984, the Drogheda - Navan (Tara Mines) line, which carries only freight traffic associated with that mine, passenger traffic having ceased with the closure of the line beyond there to Oldcastle in 1963, and the Lisburn to Antrim branch, now mothballed but retained in operational order for the time being. Preserved GNRI Class S no. 171 Slieve Gullion at Lisburn
Preserved GNRI Class S no. 171 Slieve Gullion at LisburnPreservation
Rolling stock
 No.85 taking on water on the former Northern Counties Committee line at Ballymena railway station.
No.85 taking on water on the former Northern Counties Committee line at Ballymena railway station. -

 45cm x 38cm The Sunday Press was a weekly newspaper published in Ireland from 1949 until 1995. It was launched by Éamon de Valera's Irish Press group following the defeat of his Fianna Fáil party in the 1948 Irish general election. Like its sister newspaper, the daily The Irish Press, politically the paper loyally supported Fianna Fáil. The future Taoiseach Seán Lemass was the managing editor of the Irish Press who spearheaded the launch of the Sunday paper, with the first editor Colonel Matt Feehan. Many of the Irish Press journalists contributed to the paper. 'When I open the pages, I duck' was Brendan Behan's description of reading The Sunday Press, for the habit of published memoirs of veterans (usually those aligned to Fianna Fáil) of the Irish War of Independence. It soon built up a large readership, and overtook its main competitor the Sunday Independent, which tended to support Fine Gael. At its peak The Sunday Press sold up to 475,000 copies every week, and had a readership of over one million, around one third of the Irish population. Like the Evening Press, the paper's readership held up better over the years than that of the flagship title in the group, The Irish Press, and it might have survived as a stand-alone title had it been sold. However, with the collapse of the Irish Press Newspapers group in May 1995, all three titles ceased publication immediately. The launch of Ireland on Sunday in 1997 was initially interpreted by many observers as an attempt to appeal to the former readership of The Sunday Press, seen as generally rural, fairly conservative Catholic, and with a traditional Irish nationalist political outlook. When Christmas Day fell on Sunday in 1949, 1955, 1960, 1966, 1977, 1983, 1988 and 1994 the paper came out on the Saturday. Vincent Jennings at the age of 31 became editor of The Sunday Press in 1968, serving until December 1986, when he became manager of the Irish Press Group. Journalists who worked at the press include Stephen Collins served as political editor his father Willie Collins was deputy editor and Michael Carwood became sports editor of The Sunday Press in 1988 until its closure in 1995.
45cm x 38cm The Sunday Press was a weekly newspaper published in Ireland from 1949 until 1995. It was launched by Éamon de Valera's Irish Press group following the defeat of his Fianna Fáil party in the 1948 Irish general election. Like its sister newspaper, the daily The Irish Press, politically the paper loyally supported Fianna Fáil. The future Taoiseach Seán Lemass was the managing editor of the Irish Press who spearheaded the launch of the Sunday paper, with the first editor Colonel Matt Feehan. Many of the Irish Press journalists contributed to the paper. 'When I open the pages, I duck' was Brendan Behan's description of reading The Sunday Press, for the habit of published memoirs of veterans (usually those aligned to Fianna Fáil) of the Irish War of Independence. It soon built up a large readership, and overtook its main competitor the Sunday Independent, which tended to support Fine Gael. At its peak The Sunday Press sold up to 475,000 copies every week, and had a readership of over one million, around one third of the Irish population. Like the Evening Press, the paper's readership held up better over the years than that of the flagship title in the group, The Irish Press, and it might have survived as a stand-alone title had it been sold. However, with the collapse of the Irish Press Newspapers group in May 1995, all three titles ceased publication immediately. The launch of Ireland on Sunday in 1997 was initially interpreted by many observers as an attempt to appeal to the former readership of The Sunday Press, seen as generally rural, fairly conservative Catholic, and with a traditional Irish nationalist political outlook. When Christmas Day fell on Sunday in 1949, 1955, 1960, 1966, 1977, 1983, 1988 and 1994 the paper came out on the Saturday. Vincent Jennings at the age of 31 became editor of The Sunday Press in 1968, serving until December 1986, when he became manager of the Irish Press Group. Journalists who worked at the press include Stephen Collins served as political editor his father Willie Collins was deputy editor and Michael Carwood became sports editor of The Sunday Press in 1988 until its closure in 1995. -

 62cm x 42cm John Patrick Healy (9 March 1931 – 5 December 2014), known as Jackie Healy-Rae, was an Irish Independent politician who served as a Teachta Dála (TD) for the Kerry South constituency from 1997 to 2011.
62cm x 42cm John Patrick Healy (9 March 1931 – 5 December 2014), known as Jackie Healy-Rae, was an Irish Independent politician who served as a Teachta Dála (TD) for the Kerry South constituency from 1997 to 2011.Early and private life
Healy-Rae was the first of six children born to Daniel and Mary Healy, and grew up on his family's farm at the foot of Mangerton Mountain, near Kilgarvan in County Kerry. The Rae part of his surname came from the name of the Healys' farm, Reacashlagh. He was educated at the local National School in Kilgarvan. He emigrated to the United States in 1953 but soon returned to Ireland. He played for the local hurling and Gaelic football teams in Kilgarvan, where he won two senior county hurling titles with the club in 1956 and 1958. Healy-Rae was also a saxophone player with the Kilgarvan Dance Band. By the 1960s, he was well established in the plant hire business in south Kerry. In 1969, he became a publican when he purchased an old premises that had been closed for some time in Kilgarvan. The family pub is now run by his son, Danny. Healy-Rae was married to Julie Healy, but the couple separated in 1977.Two sons, Danny and Michael were members of Kerry County Council for the Killarney and Killorglin local electoral areas respectively before becoming TDs. His eldest daughter Joan (Mrs. Larkin) teaches in a Catholic Schoolin New York. His other daughter, Rosemary, is a barrister-at-law. She was appointed to a paid position on the Criminal Injuries Compensation Tribunal in 2007. She was re-appointed, for three further years, by Justice Minister Dermot Ahern on 11 November 2010.A son, Denis, runs his own business, and another son, John Healy (he does not use Rae), is a full-time official with and former President of the Garda Representative Association.Political career
Early involvement
Healy-Rae first became involved in politics in the 1960s. He headed several Fianna Fáil by-election campaigns, most notably the election of John O'Leary to the Dáil in 1966. O'Leary retained the seat for thirty-one years. Healy-Rae later lent his services to several other Fianna Fáil election campaigns in County Limerick, County Cork and County Galway. In 1973, Healy-Rae was first co-opted to Kerry County Council as a Fianna Fáil member, following the death of sitting Kerry County Councillor Michael Doherty. He was elected to the council in his own right in 1974 and re-elected in every subsequent election. Healy-Rae served on the council for 30 years, until he had to resign his seat because of the abolition of the dual mandate in 2003. During the 1970s and 1980s, Healy-Rae served three times as Fianna Fáil's director of elections in Kerry South. In this capacity he was given the task of delivering two of the three seats for the Fianna Fáil Party.Election to Dáil Éireann Healy-Rae broke from Fianna Fáil in controversial circumstances prior to the 1997 general election. When the party refused to nominate him as a candidate in Kerry South, he decided to run as an Independent candidate. This move surprised the party, with many commentators giving him little chance of getting elected. However, Healy-Rae took a seat and denied Fianna Fáil the chance of taking a second seat in the constituency.
After the election, the Fianna Fáil and Progressive Democrats prospective government was still short of an overall majority. Healy-Rae was one of four Independent TDs (the others were Harry Blaney, Tom Gildea and Mildred Fox) who supported the government throughout its five-year term and rejected the opposition Fine Gael. In return for this support he secured funding for projects in his constituency and chairmanship of the Environment committee. His policy approach could be defined as populist, primarily driven by his rural background and constituency, and he frequently demanded upgrades to public services such as schools and roads in his constituency as the price of his support for the government. Healy-Rae contested the 2002 general election and although his seat looked in doubt at some stages of the campaign and he received only the fourth-highest number of first-preference votes, he was narrowly re-elected, winning the third seat. He sat through fewer than half the meetings of an Oireachtas committee tasked with dealing with social welfare he received €20,000 a year to chair. He got up and left during 25pc of the meetings of the committee leaving the vice-chairman, Charlie O'Connor, to oversee the meetings and absented himself entirely from a further 25pc of meetings, despite a convention that chairmen appointed by the government should fully chair all meetings.External support for Fianna Fáil
He was again re-elected to the Dáil at the 2007 general election and signed a confidence and supply deal with Fianna Fáil. Promising to support the government in return for investment in the Kerry South constituency. The details of this deal were not made public. Healy-Rae has been criticised for not making the details of the deal public and for supporting the government over highly controversial cutbacks (in contrast to Finian McGrath who made the details public by entering his deal into the Dáil record and who withdrew his support from the government in 2008, over cutbacks in the health sector). He was confronted publicly by members of the Kerry Public Sector Workers Alliance about his continual support for cutbacks and for the Irish bank bailout. Healy-Rae said he was powerless as he had only one vote and that they "should talk to the Green Party that are making the big changes".Retirement
On 26 June 2008, Healy-Rae announced that he intended to retire at the next general election. His son Michael Healy-Rae was selected as a candidate by the Healy-Rae organisation on 28 October 2010,and was elected at the 2011 general election.Death
Healy-Rae died on 5 December 2014, at Kerry General Hospital in Tralee after a long illness.












