-

 Rare,fantastic retro Guinness advert 42cm x 30cm Limerick Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.”
Rare,fantastic retro Guinness advert 42cm x 30cm Limerick Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.” -

 John Gilroy inspired Guinness For Strength advert 24cm x 37cm Carlingford Co Louth Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.”
John Gilroy inspired Guinness For Strength advert 24cm x 37cm Carlingford Co Louth Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.” -

 24cm x 34cm Ennis Co Clare The Willie Clancy Summer School (Irish Scoil Samhraidh Willie Clancy) is Ireland's largest traditional music summer school held annually since 1973 in memory of the uilleann piper Willie Clancy. During the week, nearly a thousand students from every part of the world attend daily classes taught by experts in Irish music and dance. In addition, a full program of lectures, recitals, dances (céilithe) and exhibitions are run by the summer school. All events happen in the town of Milltown Malbay, in County Clare, on the west coast of Ireland, during the week beginning with the first Saturday of July. The weekly registration includes six classes, all lectures and recitals (except the Saturday concert) and reduced price admission to céilithe. Lectures, recitals, concert and céilithe are open to the public.
24cm x 34cm Ennis Co Clare The Willie Clancy Summer School (Irish Scoil Samhraidh Willie Clancy) is Ireland's largest traditional music summer school held annually since 1973 in memory of the uilleann piper Willie Clancy. During the week, nearly a thousand students from every part of the world attend daily classes taught by experts in Irish music and dance. In addition, a full program of lectures, recitals, dances (céilithe) and exhibitions are run by the summer school. All events happen in the town of Milltown Malbay, in County Clare, on the west coast of Ireland, during the week beginning with the first Saturday of July. The weekly registration includes six classes, all lectures and recitals (except the Saturday concert) and reduced price admission to céilithe. Lectures, recitals, concert and céilithe are open to the public.The school
Founded by a committee of local people, after the death of their friend and neighbour Willie Clancy, at a young age, in early 1973. The group included Paddy McMahon, Paddy Malone, Micheal O Friel, Junior Crehan, Martin Talty, Sean Reid, JC Talty and Jimmy Ward. These were later joined by Muiris Ó Rócháin (moved from Kerry 1971), Peadar O'Loughlin (Kilmaley) and after the first ten years of the school Eamonn McGivney and Harry Hughes. The school has a fine reputation as an event where Irish traditional music can be learned and practised by all. The school was founded with the idea that music could be learned outside of the strictures of competition or borders. Students are children or teenagers as well as adults. All are mixed within classes according to level of musicianship on a particular instrument. It is possible during the week to attend activities as different as reed making workshops for pipes, as well as concertinaclasses, for example. Classes are held in different venues: schools, hotels, and private houses. Depending on the student's wishes, it is possible to change teachers during the week. Teachers are chosen for their expertise and many are renowned exponents of Irish music and song.The craic
Craic agus ceol: "fun and music" in Irish, is a frequent description for the atmosphere. During the week, crowds come to Milltown Malbay solely for informal playing, or to listen to traditional Irish music in all kinds of venues - pubs, kitchens, and streets. This audience does not necessarily attend classes.O -

 35cm x 45cm Ennis Co ClareOnce upon a time, the Lisdoonvarna Folk Festival was the largest and most famous outdoor music festival in Ireland. A total of 150 acts performed at the festival which took place each summer from 1978 to 1983. The festivals were the brainchild of local men, Paddy Doherty & Jim Shannon, with the first festival taking place in 1978, which proved to be a huge success. One Irish newspaper would go on to call these festivals the “Irish Woodstock” and the Irish equivalent to “Glastonbury”! A host of top Irish and international artists graced the stage during the 6 years the festival was held here. They included the likes of Jackson Browne, UB40, The Chieftains, Paul Brady, Loudon Wainwright III, Ralph McTell, The Fureys, De Dannan, Stocktons Wing, EmmyLou Harris, Van Morrison, Rory Gallagher, Panxty, Clannad, to name just a few, and of course the one and only Christy Moore, who wrote the world famous song about the festival, simply called “Lisdoonvarna”. The festivals enjoyed a hugely successful run until 1983 when two very unfortunate events sadly overshadowed the excellent performances on the stage and effectively ended the festival from being held in its original format.
35cm x 45cm Ennis Co ClareOnce upon a time, the Lisdoonvarna Folk Festival was the largest and most famous outdoor music festival in Ireland. A total of 150 acts performed at the festival which took place each summer from 1978 to 1983. The festivals were the brainchild of local men, Paddy Doherty & Jim Shannon, with the first festival taking place in 1978, which proved to be a huge success. One Irish newspaper would go on to call these festivals the “Irish Woodstock” and the Irish equivalent to “Glastonbury”! A host of top Irish and international artists graced the stage during the 6 years the festival was held here. They included the likes of Jackson Browne, UB40, The Chieftains, Paul Brady, Loudon Wainwright III, Ralph McTell, The Fureys, De Dannan, Stocktons Wing, EmmyLou Harris, Van Morrison, Rory Gallagher, Panxty, Clannad, to name just a few, and of course the one and only Christy Moore, who wrote the world famous song about the festival, simply called “Lisdoonvarna”. The festivals enjoyed a hugely successful run until 1983 when two very unfortunate events sadly overshadowed the excellent performances on the stage and effectively ended the festival from being held in its original format.
-

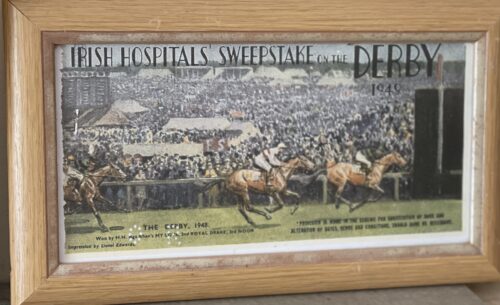 Vintage ticket for the Irish Hospital Sweepstakes 1949 Epsom Derby Dublin 35cm x 20cm The Irish Hospital Sweepstake was a lottery established in the Irish Free State in 1930 as the Irish Free State Hospitals' Sweepstake to finance hospitals. It is generally referred to as the Irish Sweepstake, frequently abbreviated to Irish Sweeps or Irish Sweep. The Public Charitable Hospitals (Temporary Provisions) Act, 1930 was the act that established the lottery; as this act expired in 1934, in accordance with its terms, the Public Hospitals Acts were the legislative basis for the scheme thereafter. The main organisers were Richard Duggan, Captain Spencer Freeman and Joe McGrath. Duggan was a well known Dublin bookmaker who had organised a number of sweepstakes in the decade prior to setting up the Hospitals' Sweepstake. Captain Freeman was a Welsh-born engineer and former captain in the British Army. After the Constitution of Ireland was enacted in 1937, the name Irish Hospitals' Sweepstake was adopted. The sweepstake was established because there was a need for investment in hospitals and medical services and the public finances were unable to meet this expense at the time. As the people of Ireland were unable to raise sufficient funds, because of the low population, a significant amount of the funds were raised in the United Kingdom and United States, often among the emigrant Irish. Potentially winning tickets were drawn from rotating drums, usually by nurses in uniform. Each such ticket was assigned to a horse expected to run in one of several horse races, including the Cambridgeshire Handicap, Derby and Grand National. Tickets that drew the favourite horses thus stood a higher likelihood of winning and a series of winning horses had to be chosen on the accumulator system, allowing for enormous prizes. The original sweepstake draws were held at The Mansion House, Dublin on 19 May 1939 under the supervision of the Chief Commissioner of Police, and were moved to the more permanent fixture at the Royal Dublin Society (RDS) in Ballsbridge later in 1940. The Adelaide Hospital in Dublin was the only hospital at the time not to accept money from the Hospitals Trust, as the governors disapproved of sweepstakes. From the 1960s onwards, revenues declined. The offices were moved to Lotamore House in Cork. Although giving the appearance of a public charitable lottery, with nurses featured prominently in the advertising and drawings, the Sweepstake was in fact a private for-profit lottery company, and the owners were paid substantial dividends from the profits. Fortune Magazine described it as "a private company run for profit and its handful of stockholders have used their earnings from the sweepstakes to build a group of industrial enterprises that loom quite large in the modest Irish economy. Waterford Glass, Irish Glass Bottle Company and many other new Irish companies were financed by money from this enterprise and up to 5,000 people were given jobs."[3] By his death in 1966, Joe McGrath had interests in the racing industry, and held the Renault dealership for Ireland besides large financial and property assets. He was known throughout Ireland for his tough business attitude but also by his generous spirit.At that time, Ireland was still one of the poorer countries in Europe; he believed in investment in Ireland. His home, Cabinteely House, was donated to the state in 1986. The house and the surrounding park are now in the ownership of Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown County Council who have invested in restoring and maintaining the house and grounds as a public park. In 1986, the Irish government created a new public lottery, and the company failed to secure the new contract to manage it. The final sweepstake was held in January 1986 and the company was unsuccessful for a licence bid for the Irish National Lottery, which was won by An Post later that year. The company went into voluntary liquidation in March 1987. The majority of workers did not have a pension scheme but the sweepstake had fed many families during lean times and was regarded as a safe job.The Public Hospitals (Amendment) Act, 1990 was enacted for the orderly winding up of the scheme which had by then almost £500,000 in unclaimed prizes and accrued interest. A collection of advertising material relating to the Irish Hospitals' Sweepstakes is among the Special Collections of National Irish Visual Arts Library. At the time of the Sweepstake's inception, lotteries were generally illegal in the United Kingdom, the United States and Canada. In the absence of other readily available lotteries, the Irish Sweeps became popular. Even though tickets were illegal outside Ireland, millions were sold in the US and Great Britain. How many of these tickets failed to make it back for the drawing is unknown. The United States Customs Service alone confiscated and destroyed several million counterfoils from shipments being returned to Ireland. In the UK, the sweepstakes caused some strain in Anglo-Irish relations, and the Betting and Lotteries Act 1934 was passed by the parliament of the UK to prevent export and import of lottery related materials. The United States Congress had outlawed the use of the US Postal Service for lottery purposes in 1890. A thriving black market sprang up for tickets in both jurisdictions. From the 1950s onwards, as the American, British and Canadian governments relaxed their attitudes towards this form of gambling, and went into the lottery business themselves, the Irish Sweeps, never legal in the United States,declined in popularity. Origins: Co Galway Dimensions :39cm x 31cm
Vintage ticket for the Irish Hospital Sweepstakes 1949 Epsom Derby Dublin 35cm x 20cm The Irish Hospital Sweepstake was a lottery established in the Irish Free State in 1930 as the Irish Free State Hospitals' Sweepstake to finance hospitals. It is generally referred to as the Irish Sweepstake, frequently abbreviated to Irish Sweeps or Irish Sweep. The Public Charitable Hospitals (Temporary Provisions) Act, 1930 was the act that established the lottery; as this act expired in 1934, in accordance with its terms, the Public Hospitals Acts were the legislative basis for the scheme thereafter. The main organisers were Richard Duggan, Captain Spencer Freeman and Joe McGrath. Duggan was a well known Dublin bookmaker who had organised a number of sweepstakes in the decade prior to setting up the Hospitals' Sweepstake. Captain Freeman was a Welsh-born engineer and former captain in the British Army. After the Constitution of Ireland was enacted in 1937, the name Irish Hospitals' Sweepstake was adopted. The sweepstake was established because there was a need for investment in hospitals and medical services and the public finances were unable to meet this expense at the time. As the people of Ireland were unable to raise sufficient funds, because of the low population, a significant amount of the funds were raised in the United Kingdom and United States, often among the emigrant Irish. Potentially winning tickets were drawn from rotating drums, usually by nurses in uniform. Each such ticket was assigned to a horse expected to run in one of several horse races, including the Cambridgeshire Handicap, Derby and Grand National. Tickets that drew the favourite horses thus stood a higher likelihood of winning and a series of winning horses had to be chosen on the accumulator system, allowing for enormous prizes. The original sweepstake draws were held at The Mansion House, Dublin on 19 May 1939 under the supervision of the Chief Commissioner of Police, and were moved to the more permanent fixture at the Royal Dublin Society (RDS) in Ballsbridge later in 1940. The Adelaide Hospital in Dublin was the only hospital at the time not to accept money from the Hospitals Trust, as the governors disapproved of sweepstakes. From the 1960s onwards, revenues declined. The offices were moved to Lotamore House in Cork. Although giving the appearance of a public charitable lottery, with nurses featured prominently in the advertising and drawings, the Sweepstake was in fact a private for-profit lottery company, and the owners were paid substantial dividends from the profits. Fortune Magazine described it as "a private company run for profit and its handful of stockholders have used their earnings from the sweepstakes to build a group of industrial enterprises that loom quite large in the modest Irish economy. Waterford Glass, Irish Glass Bottle Company and many other new Irish companies were financed by money from this enterprise and up to 5,000 people were given jobs."[3] By his death in 1966, Joe McGrath had interests in the racing industry, and held the Renault dealership for Ireland besides large financial and property assets. He was known throughout Ireland for his tough business attitude but also by his generous spirit.At that time, Ireland was still one of the poorer countries in Europe; he believed in investment in Ireland. His home, Cabinteely House, was donated to the state in 1986. The house and the surrounding park are now in the ownership of Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown County Council who have invested in restoring and maintaining the house and grounds as a public park. In 1986, the Irish government created a new public lottery, and the company failed to secure the new contract to manage it. The final sweepstake was held in January 1986 and the company was unsuccessful for a licence bid for the Irish National Lottery, which was won by An Post later that year. The company went into voluntary liquidation in March 1987. The majority of workers did not have a pension scheme but the sweepstake had fed many families during lean times and was regarded as a safe job.The Public Hospitals (Amendment) Act, 1990 was enacted for the orderly winding up of the scheme which had by then almost £500,000 in unclaimed prizes and accrued interest. A collection of advertising material relating to the Irish Hospitals' Sweepstakes is among the Special Collections of National Irish Visual Arts Library. At the time of the Sweepstake's inception, lotteries were generally illegal in the United Kingdom, the United States and Canada. In the absence of other readily available lotteries, the Irish Sweeps became popular. Even though tickets were illegal outside Ireland, millions were sold in the US and Great Britain. How many of these tickets failed to make it back for the drawing is unknown. The United States Customs Service alone confiscated and destroyed several million counterfoils from shipments being returned to Ireland. In the UK, the sweepstakes caused some strain in Anglo-Irish relations, and the Betting and Lotteries Act 1934 was passed by the parliament of the UK to prevent export and import of lottery related materials. The United States Congress had outlawed the use of the US Postal Service for lottery purposes in 1890. A thriving black market sprang up for tickets in both jurisdictions. From the 1950s onwards, as the American, British and Canadian governments relaxed their attitudes towards this form of gambling, and went into the lottery business themselves, the Irish Sweeps, never legal in the United States,declined in popularity. Origins: Co Galway Dimensions :39cm x 31cmThe Irish Hospitals Sweepstake was established because there was a need for investment in hospitals and medical services and the public finances were unable to meet this expense at the time. As the people of Ireland were unable to raise sufficient funds, because of the low population, a significant amount of the funds were raised in the United Kingdom and United States, often among the emigrant Irish. Potentially winning tickets were drawn from rotating drums, usually by nurses in uniform. Each such ticket was assigned to a horse expected to run in one of several horse races, including the Cambridgeshire Handicap, Derby and Grand National. Tickets that drew the favourite horses thus stood a higher likelihood of winning and a series of winning horses had to be chosen on the accumulator system, allowing for enormous prizes.
The original sweepstake draws were held at The Mansion House, Dublin on 19 May 1939 under the supervision of the Chief Commissioner of Police, and were moved to the more permanent fixture at the Royal Dublin Society (RDS) in Ballsbridge later in 1940. The Adelaide Hospital in Dublin was the only hospital at the time not to accept money from the Hospitals Trust, as the governors disapproved of sweepstakes. From the 1960s onwards, revenues declined. The offices were moved to Lotamore House in Cork. Although giving the appearance of a public charitable lottery, with nurses featured prominently in the advertising and drawings, the Sweepstake was in fact a private for-profit lottery company, and the owners were paid substantial dividends from the profits. Fortune Magazine described it as "a private company run for profit and its handful of stockholders have used their earnings from the sweepstakes to build a group of industrial enterprises that loom quite large in the modest Irish economy. Waterford Glass, Irish Glass Bottle Company and many other new Irish companies were financed by money from this enterprise and up to 5,000 people were given jobs."By his death in 1966, Joe McGrath had interests in the racing industry, and held the Renault dealership for Ireland besides large financial and property assets. He was known throughout Ireland for his tough business attitude but also by his generous spirit. At that time, Ireland was still one of the poorer countries in Europe; he believed in investment in Ireland. His home, Cabinteely House, was donated to the state in 1986. The house and the surrounding park are now in the ownership of Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown County Council who have invested in restoring and maintaining the house and grounds as a public park. In 1986, the Irish government created a new public lottery, and the company failed to secure the new contract to manage it. The final sweepstake was held in January 1986 and the company was unsuccessful for a licence bid for the Irish National Lottery, which was won by An Post later that year. The company went into voluntary liquidation in March 1987. The majority of workers did not have a pension scheme but the sweepstake had fed many families during lean times and was regarded as a safe job.The Public Hospitals (Amendment) Act, 1990 was enacted for the orderly winding up of the scheme,which had by then almost £500,000 in unclaimed prizes and accrued interest. A collection of advertising material relating to the Irish Hospitals' Sweepstakes is among the Special Collections of National Irish Visual Arts Library.In the United Kingdom and North America[edit]
At the time of the Sweepstake's inception, lotteries were generally illegal in the United Kingdom, the United States and Canada. In the absence of other readily available lotteries, the Irish Sweeps became popular. Even though tickets were illegal outside Ireland, millions were sold in the US and Great Britain. How many of these tickets failed to make it back for the drawing is unknown. The United States Customs Service alone confiscated and destroyed several million counterfoils from shipments being returned to Ireland. In the UK, the sweepstakes caused some strain in Anglo-Irish relations, and the Betting and Lotteries Act 1934 was passed by the parliament of the UK to prevent export and import of lottery related materials.[6][7] The United States Congress had outlawed the use of the US Postal Service for lottery purposes in 1890. A thriving black market sprang up for tickets in both jurisdictions. From the 1950s onwards, as the American, British and Canadian governments relaxed their attitudes towards this form of gambling, and went into the lottery business themselves, the Irish Sweeps, never legal in the United States,[8]:227 declined in popularity. -

 25cm x 30cm Glasgow
25cm x 30cm GlasgowThe Troubles, also called Northern Ireland conflict, violent sectarian conflict from about 1968 to 1998 in Northern Irelandbetween the overwhelmingly Protestantunionists (loyalists), who desired the province to remain part of the United Kingdom, and the overwhelmingly Roman Catholic nationalists (republicans), who wanted Northern Ireland to become part of the republic of Ireland. The other major players in the conflict were the British army, Royal Ulster Constabulary (RUC), and Ulster Defence Regiment (UDR; from 1992 called the Royal Irish Regiment), and their avowed purpose was to play a peacekeeping role, most prominently between the nationalist Irish Republican Army(IRA), which viewed the conflict as a guerrilla war for national independence, and the unionist paramilitary forces, which characterized the IRA’s aggression as terrorism. Marked by street fighting, sensational bombings, sniper attacks, roadblocks, and internment without trial, the confrontation had the characteristics of a civil war, notwithstanding its textbook categorization as a “low-intensity conflict.” Some 3,600 people were killed and more than 30,000 more were wounded before a peaceful solution, which involved the governments of both the United Kingdom and Ireland, was effectively reached in 1998, leading to a power-sharing arrangement in the Northern Ireland Assembly at Stormont.
Deep origins
The story of the Troubles is inextricably entwined with the history of Ireland as whole and, as such, can be seen as stemming from the first British incursion on the island, the Anglo-Norman invasion of the late 12th century, which left a wave of settlers whose descendants became known as the “Old English.” Thereafter, for nearly eight centuries, England and then Great Britain as a whole would dominate affairs in Ireland. Colonizing British landlords widely displaced Irish landholders. The most successful of these “plantations” began taking hold in the early 17th century in Ulster, the northernmost of Ireland’s four traditional provinces, previously a centre of rebellion, where the planters included English and Scottish tenants as well as British landlords. Because of the plantation of Ulster, as Irish history unfolded—with the struggle for the emancipation of the island’s Catholic majority under the supremacy of the Protestant ascendancy, along with the Irish nationalist pursuit of Home Rule and then independence after the island’s formal union with Great Britain in 1801—Ulster developed as a region where the Protestant settlers outnumbered the indigenousIrish. Unlike earlier English settlers, most of the 17th-century English and Scottish settlers and their descendants did not assimilate with the Irish. Instead, they held on tightly to British identity and remained steadfastly loyal to the British crown.
The formation of Northern Ireland, Catholic grievances, and the leadership of Terence O’Neill
Of the nine modern counties that constituted Ulster in the early 20th century, four—Antrim, Down, Armagh, and Londonderry (Derry)—had significant Protestant loyalist majorities; two—Fermanagh and Tyrone—had small Catholic nationalist majorities; and three—Donegal, Cavan, and Monaghan—had significant Catholic nationalist majorities. In 1920, during the Irish War of Independence (1919–21), the British Parliament, responding largely to the wishes of Ulster loyalists, enacted the Government of Ireland Act , which divided the island into two self-governing areas with devolved Home Rule-like powers. What would come to be known as Northern Ireland was formed by Ulster’s four majority loyalist counties along with Fermanagh and Tyrone. Donegal, Cavan, and Monaghan were combined with the island’s remaining 23 counties to form southern Ireland. The Anglo-Irish Treaty that ended the War of Independence then created the Irish Free State in the south, giving it dominion status within the British Empire. It also allowed Northern Ireland the option of remaining outside of the Free State, which it unsurprisingly chose to do.
Thus, in 1922 Northern Ireland began functioning as a self-governing region of the United Kingdom. Two-thirds of its population (about one million people) was Protestant and about one-third (roughly 500,000 people) was Catholic. Well before partition, Northern Ireland, particularly Belfast, had attracted economic migrants from elsewhere in Ireland seeking employment in its flourishing linen-making and shipbuilding industries. The best jobs had gone to Protestants, but the humming local economy still provided work for Catholics. Over and above the long-standing dominance of Northern Ireland politics that resulted for the Ulster Unionist Party (UUP) by virtue of the Protestants’ sheer numerical advantage, loyalist control of local politics was ensured by the gerrymandering of electoral districts that concentrated and minimized Catholic representation. Moreover, by restricting the franchise to ratepayers (the taxpaying heads of households) and their spouses, representation was further limited for Catholic households, which tended to be larger (and more likely to include unemployed adult children) than their Protestant counterparts. Those who paid rates for more than one residence (more likely to be Protestants) were granted an additional vote for each ward in which they held property (up to six votes). Catholics argued that they were discriminated against when it came to the allocation of public housing, appointments to public service jobs, and government investment in neighbourhoods. They were also more likely to be the subjects of police harassment by the almost exclusively Protestant RUC and Ulster Special Constabulary (B Specials).
The divide between Catholics and Protestants in Northern Ireland had little to do with theological differences but instead was grounded in culture and politics. Neither Irish history nor the Irish language was taught in schools in Northern Ireland, it was illegal to fly the flag of the Irish republic, and from 1956 to 1974 Sinn Féin, the party of Irish republicanism, also was banned in Northern Ireland. Catholics by and large identified as Irish and sought the incorporation of Northern Ireland into the Irish state. The great bulk of Protestants saw themselves as British and feared that they would lose their culture and privilege if Northern Ireland were subsumed by the republic. They expressed their partisan solidarity through involvement with Protestant unionist fraternal organizations such as the Orange Order, which found its inspiration in the victory of King William III (William of Orange) at the Battle of the Boyne in 1690 over his deposed Catholic predecessor, James II, whose siege of the Protestant community of Londonderry had earlier been broken by William. Despite these tensions, for 40 or so years after partition the status of unionist-dominated Northern Ireland was relatively stable.
IRA graffiti “IRA” spray-painted on a container, Derry (Londonderry), Northern Ireland.© Attila Jandi/Dreamstime.comRecognizing that any attempt to reinvigorate Northern Ireland’s declining industrial economy in the early 1960s would also need to address the province’s percolatingpolitical and social tensions, the newly elected prime minister of Northern Ireland, Terence O’Neill, not only reached out to the nationalist community but also, in early 1965, exchanged visits with Irish Taoiseach (Prime Minister) Seán Lemass—a radical step, given that the republic’s constitution included an assertion of sovereignty over the whole island. Nevertheless, O’Neill’s efforts were seen as inadequate by nationalists and as too conciliatory by loyalists, including the Rev. Ian Paisley, who became one of the most vehement and influential representatives of unionist reaction.
Civil rights activism, the Battle of Bogside, and the arrival of the British army
Contrary to the policies of UUP governments that disadvantaged Catholics, the Education Act that the Northern Ireland Parliament passed into law in 1947 increased educational opportunities for all citizens of the province. As a result, the generation of well-educated Catholics who came of age in the 1960s had new expectations for more equitable treatment. At a time when political activism was on the rise in Europe—from the events of May 1968 in France to the Prague Spring—and when the American civil rights movement was making great strides, Catholic activists in Northern Ireland such as John Humeand Bernadette Devlin came together to form civil rightsgroups such as the Northern Ireland Civil Rights Association (NICRA).
Although more than one violently disrupted political march has been pointed to as the starting point of the Troubles, it can be argued that the catalyzing event occurred on October 5, 1968, in Derry, where a march had been organized by the NICRA to protest discrimination and gerrymandering. The march was banned when unionists announced that they would be staging a counterdemonstration, but the NICRA decided to carry out their protest anyway. Rioting then erupted after the RUC violently suppressed the marchers with batons and a water cannon.
Similarly inflammatory were the events surrounding a march held by loyalists in Londonderry on August 12, 1969. Two days of rioting that became known as the Battle of Bogside (after the Catholic area in which the confrontation occurred) stemmed from the escalating clash between nationalists and the RUC, which was acting as a buffer between loyalist marchers and Catholic residents of the area. Rioting in support of the nationalists then erupted in Belfast and elsewhere, and the British army was dispatched to restore calm. Thereafter, violent confrontation only escalated, and the Troubles (a name that neither characterized the nature of the conflict nor assigned blame for it to one side or the other) had clearly begun.
The emergence of the Provisional IRA and the loyalist paramilitaries
Initially, the nationalists welcomed the British army as protectors and as a balance for the Protestant-leaning RUC. In time, however, the army would be viewed by nationalists as another version of the enemy, especially after its aggressive efforts to disarm republican paramilitaries. In the process, the Irish Republican Army (IRA) became the defender of the nationalist cause. From its base in Ireland(which had formally left the Commonwealth in 1949), the IRA had mounted an ineffectual guerrilla effort in support of Northern Ireland’s nationalists from 1956 to 1962, but, as the 1960s progressed, the IRA became less concerned with affairs in the north than with advancing a Marxist political agenda. As a result, a splinter group, the Provisional Irish Republican Army (Provos), which was prepared to use force to bring about unification, emerged as the champion of Northern Ireland’s nationalists. (The Official IRA would conduct operations in support of the republicans in Northern Ireland until undertaking a cease-fire in 1972, after which it effectively ceded the title of the IRA in the north to the Provos.) Believing that their fight was a continuation of the Irish War of Independence, the Provos adopted the tactics of guerrilla warfare, financed partly by members of the Irish diaspora in the United States and later supplied with arms and munitions by the government of Libyan strongman Muammar al-Qaddafi. Unionists also took up arms, swelling the numbers of loyalist paramilitary organizations, most notably the Ulster Volunteer Force (UVF) and Ulster Defence Association UDA).
British soldier in Northern Ireland Local people walking past a British soldier on guard in Northern Ireland, August 1969.Peter Kemp—AP/Shutterstock.comInternment, “peace walls,” and “Bloody Sunday”
In an attempt to address nationalist grievances, electoral boundaries were redrawn more fairly, efforts were made to rectify discrimination in housing and public employment, and the B Specials were decommissioned. At the same time, the government of Northern Ireland responded to the growing unrest by introducing increasingly stringent security measures, including internment (detention without trial). The overwhelming majority of those arrested, however, were nationalists.
As the 1970s progressed, rioting became more common in Belfast and Derry, bombings of public places (by both loyalists and republicans) increased, and both sides of the conflict perpetrated violent, deadly atrocities. Barbed wire laid by British soldiers to separate the sectarian communitiesevolved into brick and steel “peace walls,” some of which stood 45 feet (14 metres) high, segregating loyalist and republican enclaves, most famously the Falls Road Catholic community and the Shankill Protestant community of Belfast.
On January 30, 1972, the conflict reached a new level of intensity when British paratroopers fired on Catholic civil rights demonstrators in Londonderry, killing 13 and injuring 14 others (one of whom later died). The incident, which became known as “Bloody Sunday,” contributed to a spike in Provos recruitment and would remain controversial for decades, hinging on the question of which side fired first. In 2010 the Saville Report , the final pronouncement of a British government inquiry into the event, concluded that none of the victims had posed a threat to the troops and that their shooting had been unjustified. British Prime Minister David Cameron responded to the report by issuing a landmark apology for the shooting:
There is no point in trying to soften or equivocate what is in this report. It is clear from the tribunal’s authoritative conclusions that the events of Bloody Sunday were in no way justified….What happened should never, ever have happened….Some members of our armed forces acted wrongly. The government is ultimately responsible for the conduct of the armed forces and for that, on behalf of the government, indeed, on behalf of our country, I am deeply sorry.
In all, more than 480 people were killed as a result of the conflict in Northern Ireland in 1972, which proved to be the deadliest single year in the Troubles. That total included more than 100 fatalities for the British army, as the IRA escalated its onslaught. On July 21, “Bloody Friday,” nine people were killed and scores were injured when some two dozen bombs were detonated by the Provos in Belfast. Earlier, in March, frustrated with the Northern Ireland government’s failure to calm the situation, the British government suspended the Northern Ireland Parliament and reinstituted direct rule by Westminster.
Beginning in the mid-1970s, the IRA shifted the emphasis of its “Long War” from direct engagements with British troops to smaller-scale secretive operations, including the bombing of cities in Britain—a change of tactics the British military described as a shift from “insurgency” to “terrorism.” Similarly, the loyalist groups began setting off bombs in Ireland. Meanwhile, paramilitary violence at mid-decade (1974–76) resulted in the civilian deaths of some 370 Catholics and 88 Protestants.
Northern Ireland: peace movement Protesters against ongoing violence in Northern Ireland gathering on Shankill Road, Belfast, Northern Ireland, August 1976.Peace PeopleThe Sunningdale Agreement, hunger strikes, Bobby Sands, and the Brighton bombing
A glimmer of hope was offered by the Sunningdale Agreement , named for the English city in which it was negotiated in 1973. That agreement led to the creation of a new Northern Ireland Assembly, with proportional representation for all parties, and to the establishment of a Council of Ireland, which was to provide a role for Ireland in the affairs of Northern Ireland. Frustrated by the diminution of their political power and furious at the participation of the republic, loyalists scuttled the power-sharing plan with a general strike that brought the province to a halt in May 1974 and eventually forced a return to direct rule, which remained in place for some 25 years.
For the remainder of the decade, violence ebbed and flowed, cease-fires lingered and lapsed, and tit-for-tat bombings and assassinations continued, including the high-profile killing at sea in August 1979 of Lord Mountbatten, a relative of both Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip. In 1976 the opening of the specially designed Maze prison brought with it a shift in the treatment of IRA inmates from that of prisoners of war to that of common criminals. Seeking a return to their Special Category Status, the prisoners struck back, first staging the “blanket protest,” in which they refused to put on prison uniforms and instead wore only blankets, and then, in 1978, the “dirty protest,” in which inmates smeared the walls of their cells with excrement. The government of recently elected Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher refused to buckle, even in the face of hunger strikes in 1980–81 that led to the deaths of 10 prisoners, including Bobby Sands, who had won a seat in the British Parliament while incarcerated and fasting.
Sands’s election helped convince Sinn Féin, then operating as the political wing of the IRA, that the struggle for unification should be pursued at the ballot box as well as with the Armalite rifle. In June 1983 Sinn Féin leader Gerry Adams won a seat in Parliament representing West Belfast, though he refused to take it to avoid taking the compulsory oath of loyalty to the British queen.
The Anglo-Irish Agreement and Downing Street Declaration
In October 1984 an IRA bomb attack on the Conservative Party Conference in Brighton, England, took five lives and threatened that of Thatcher. Though she remained steadfast in the face of this attack, it was the “Iron Lady” who in November 1985 joined Irish Taoiseach Garret FitzGerald in signing the Anglo-Irish Agreement, under which both countries guaranteed that any change in the status of Northern Ireland would come about only with the consent of the majority of the people of Northern Ireland. The accordalso established the Intergovernmental Conference, which gave Ireland a consultative role in the political and security affairs of Northern Ireland for the first time. Finally, the agreement stipulated that power would be devolved back upon the government of Northern Ireland only if unionists and nationalists participated in power sharing.
Anglo-Irish Agreement (1985) Irish Taoiseach (Prime Minister) Garret FitzGerald and British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher signing the Anglo-Irish Agreement, November 15, 1985.Peter Kemp/APThe loyalists’ vehement opposition to the agreement included the resignation of all 15 unionist members of the House of Commons and a ramping up of violence. In the meantime, IRA bombings in London made headlines, and the reach of the British security forces extended to the killing of three Provos in Gibraltar. Behind the scenes, however, negotiations were underway. In 1993 British Prime Minister John Major and Irish Taoiseach Albert Reynolds issued the so-called Downing Street Declaration , which established a framework for all-party peace talks. A cease-fire declared by the Provos in 1994 and joined by the principal loyalist paramilitary groups fell apart in 1996 because Sinn Féin, which had replaced the more moderate Social Democratic and Labour Party (SDLP) as the leading nationalist party, had been excluded from peace talks because of the IRA’s continuing bombing campaign. Nevertheless, the unionists were at the table, prepared to consider a solution that included the participation of the republic of Ireland. After the IRA resumed its cease-fire in 1997, Sinn Féin was welcomed back to the talks, which now included the British and Irish governments, the SDLP, the Alliance Party of Northern Ireland, the UUP, and the Ulster Democratic Party, among others, though not the Paisley-led DUP, which was protesting the inclusion of Sinn Féin.
The Good Friday Agreement, the Omagh bombing, peace, and power sharing
Those talks, mediated by former U.S. senator George Mitchell, led to the Good Friday Agreement (Belfast Agreement), reached April 10, 1998. That landmark accordprovided for the creation of a power-sharing Northern Ireland Assembly, established an institutional arrangement for cross-border cooperation between the governments of Ireland and Northern Ireland on a range of issues, and lay the groundwork for continued consultation between the British and Irish governments. On May 22 Ireland and Northern Ireland held a joint referendum on the agreement, which was approved by 94 percent of those who voted in the republic and 71 percent of those voting in Northern Ireland, where Catholic approval of the accord (96 percent) was much higher than Protestant assent (52 per cent). Nonetheless, it was an IRA splinter group, the Real Irish Republican Army, which most dramatically violated the spirit of the agreement, with a bombing in Omagh in August that took 29 lives.
Elections for the new Assembly were held in June, but the IRA’s failure to decommission delayed the formation of the power-sharing Northern Ireland Executive until December 1999, when the IRA promised to fulfill its obligation to disarm. That month the republic of Ireland modified its constitution, removing its territorial claims to the whole of the island, and the United Kingdom yielded direct rule of Northern Ireland. Ostensibly the Troubles had come to end, but, though Northern Ireland began its most tranquil era in a generation, the peace was fragile. Sectarian antagonism persisted, the process of decommissioning was slow on both sides, and the rolling out of the new institutions was fitful, resulting in suspensions of devolution and the reimposition of direct rule.
In July 2005, however, the IRA announced that it had ordered all its units to “dump arms,” would henceforth pursue its goals only through peaceful means, and would work with international inspectors “to verifiably put its arms beyond use.” At a press conference in September, a spokesman for the Independent International Commission on Decommissioning stated, “We are satisfied that the arms decommissioned represent the totality of the IRA’s arsenal.” Decommissioning by unionist paramilitaries and other republican groups followed..
-

 25cm x 30cm Glasgow
25cm x 30cm GlasgowThe Troubles, also called Northern Ireland conflict, violent sectarian conflict from about 1968 to 1998 in Northern Irelandbetween the overwhelmingly Protestantunionists (loyalists), who desired the province to remain part of the United Kingdom, and the overwhelmingly Roman Catholic nationalists (republicans), who wanted Northern Ireland to become part of the republic of Ireland. The other major players in the conflict were the British army, Royal Ulster Constabulary (RUC), and Ulster Defence Regiment (UDR; from 1992 called the Royal Irish Regiment), and their avowed purpose was to play a peacekeeping role, most prominently between the nationalist Irish Republican Army(IRA), which viewed the conflict as a guerrilla war for national independence, and the unionist paramilitary forces, which characterized the IRA’s aggression as terrorism. Marked by street fighting, sensational bombings, sniper attacks, roadblocks, and internment without trial, the confrontation had the characteristics of a civil war, notwithstanding its textbook categorization as a “low-intensity conflict.” Some 3,600 people were killed and more than 30,000 more were wounded before a peaceful solution, which involved the governments of both the United Kingdom and Ireland, was effectively reached in 1998, leading to a power-sharing arrangement in the Northern Ireland Assembly at Stormont.
Deep origins
The story of the Troubles is inextricably entwined with the history of Ireland as whole and, as such, can be seen as stemming from the first British incursion on the island, the Anglo-Norman invasion of the late 12th century, which left a wave of settlers whose descendants became known as the “Old English.” Thereafter, for nearly eight centuries, England and then Great Britain as a whole would dominate affairs in Ireland. Colonizing British landlords widely displaced Irish landholders. The most successful of these “plantations” began taking hold in the early 17th century in Ulster, the northernmost of Ireland’s four traditional provinces, previously a centre of rebellion, where the planters included English and Scottish tenants as well as British landlords. Because of the plantation of Ulster, as Irish history unfolded—with the struggle for the emancipation of the island’s Catholic majority under the supremacy of the Protestant ascendancy, along with the Irish nationalist pursuit of Home Rule and then independence after the island’s formal union with Great Britain in 1801—Ulster developed as a region where the Protestant settlers outnumbered the indigenousIrish. Unlike earlier English settlers, most of the 17th-century English and Scottish settlers and their descendants did not assimilate with the Irish. Instead, they held on tightly to British identity and remained steadfastly loyal to the British crown.
The formation of Northern Ireland, Catholic grievances, and the leadership of Terence O’Neill
Of the nine modern counties that constituted Ulster in the early 20th century, four—Antrim, Down, Armagh, and Londonderry (Derry)—had significant Protestant loyalist majorities; two—Fermanagh and Tyrone—had small Catholic nationalist majorities; and three—Donegal, Cavan, and Monaghan—had significant Catholic nationalist majorities. In 1920, during the Irish War of Independence (1919–21), the British Parliament, responding largely to the wishes of Ulster loyalists, enacted the Government of Ireland Act , which divided the island into two self-governing areas with devolved Home Rule-like powers. What would come to be known as Northern Ireland was formed by Ulster’s four majority loyalist counties along with Fermanagh and Tyrone. Donegal, Cavan, and Monaghan were combined with the island’s remaining 23 counties to form southern Ireland. The Anglo-Irish Treaty that ended the War of Independence then created the Irish Free State in the south, giving it dominion status within the British Empire. It also allowed Northern Ireland the option of remaining outside of the Free State, which it unsurprisingly chose to do.
Thus, in 1922 Northern Ireland began functioning as a self-governing region of the United Kingdom. Two-thirds of its population (about one million people) was Protestant and about one-third (roughly 500,000 people) was Catholic. Well before partition, Northern Ireland, particularly Belfast, had attracted economic migrants from elsewhere in Ireland seeking employment in its flourishing linen-making and shipbuilding industries. The best jobs had gone to Protestants, but the humming local economy still provided work for Catholics. Over and above the long-standing dominance of Northern Ireland politics that resulted for the Ulster Unionist Party (UUP) by virtue of the Protestants’ sheer numerical advantage, loyalist control of local politics was ensured by the gerrymandering of electoral districts that concentrated and minimized Catholic representation. Moreover, by restricting the franchise to ratepayers (the taxpaying heads of households) and their spouses, representation was further limited for Catholic households, which tended to be larger (and more likely to include unemployed adult children) than their Protestant counterparts. Those who paid rates for more than one residence (more likely to be Protestants) were granted an additional vote for each ward in which they held property (up to six votes). Catholics argued that they were discriminated against when it came to the allocation of public housing, appointments to public service jobs, and government investment in neighbourhoods. They were also more likely to be the subjects of police harassment by the almost exclusively Protestant RUC and Ulster Special Constabulary (B Specials).
The divide between Catholics and Protestants in Northern Ireland had little to do with theological differences but instead was grounded in culture and politics. Neither Irish history nor the Irish language was taught in schools in Northern Ireland, it was illegal to fly the flag of the Irish republic, and from 1956 to 1974 Sinn Féin, the party of Irish republicanism, also was banned in Northern Ireland. Catholics by and large identified as Irish and sought the incorporation of Northern Ireland into the Irish state. The great bulk of Protestants saw themselves as British and feared that they would lose their culture and privilege if Northern Ireland were subsumed by the republic. They expressed their partisan solidarity through involvement with Protestant unionist fraternal organizations such as the Orange Order, which found its inspiration in the victory of King William III (William of Orange) at the Battle of the Boyne in 1690 over his deposed Catholic predecessor, James II, whose siege of the Protestant community of Londonderry had earlier been broken by William. Despite these tensions, for 40 or so years after partition the status of unionist-dominated Northern Ireland was relatively stable.
IRA graffiti “IRA” spray-painted on a container, Derry (Londonderry), Northern Ireland.© Attila Jandi/Dreamstime.comRecognizing that any attempt to reinvigorate Northern Ireland’s declining industrial economy in the early 1960s would also need to address the province’s percolatingpolitical and social tensions, the newly elected prime minister of Northern Ireland, Terence O’Neill, not only reached out to the nationalist community but also, in early 1965, exchanged visits with Irish Taoiseach (Prime Minister) Seán Lemass—a radical step, given that the republic’s constitution included an assertion of sovereignty over the whole island. Nevertheless, O’Neill’s efforts were seen as inadequate by nationalists and as too conciliatory by loyalists, including the Rev. Ian Paisley, who became one of the most vehement and influential representatives of unionist reaction.
Civil rights activism, the Battle of Bogside, and the arrival of the British army
Contrary to the policies of UUP governments that disadvantaged Catholics, the Education Act that the Northern Ireland Parliament passed into law in 1947 increased educational opportunities for all citizens of the province. As a result, the generation of well-educated Catholics who came of age in the 1960s had new expectations for more equitable treatment. At a time when political activism was on the rise in Europe—from the events of May 1968 in France to the Prague Spring—and when the American civil rights movement was making great strides, Catholic activists in Northern Ireland such as John Humeand Bernadette Devlin came together to form civil rightsgroups such as the Northern Ireland Civil Rights Association (NICRA).
Although more than one violently disrupted political march has been pointed to as the starting point of the Troubles, it can be argued that the catalyzing event occurred on October 5, 1968, in Derry, where a march had been organized by the NICRA to protest discrimination and gerrymandering. The march was banned when unionists announced that they would be staging a counterdemonstration, but the NICRA decided to carry out their protest anyway. Rioting then erupted after the RUC violently suppressed the marchers with batons and a water cannon.
Similarly inflammatory were the events surrounding a march held by loyalists in Londonderry on August 12, 1969. Two days of rioting that became known as the Battle of Bogside (after the Catholic area in which the confrontation occurred) stemmed from the escalating clash between nationalists and the RUC, which was acting as a buffer between loyalist marchers and Catholic residents of the area. Rioting in support of the nationalists then erupted in Belfast and elsewhere, and the British army was dispatched to restore calm. Thereafter, violent confrontation only escalated, and the Troubles (a name that neither characterized the nature of the conflict nor assigned blame for it to one side or the other) had clearly begun.
The emergence of the Provisional IRA and the loyalist paramilitaries
Initially, the nationalists welcomed the British army as protectors and as a balance for the Protestant-leaning RUC. In time, however, the army would be viewed by nationalists as another version of the enemy, especially after its aggressive efforts to disarm republican paramilitaries. In the process, the Irish Republican Army (IRA) became the defender of the nationalist cause. From its base in Ireland(which had formally left the Commonwealth in 1949), the IRA had mounted an ineffectual guerrilla effort in support of Northern Ireland’s nationalists from 1956 to 1962, but, as the 1960s progressed, the IRA became less concerned with affairs in the north than with advancing a Marxist political agenda. As a result, a splinter group, the Provisional Irish Republican Army (Provos), which was prepared to use force to bring about unification, emerged as the champion of Northern Ireland’s nationalists. (The Official IRA would conduct operations in support of the republicans in Northern Ireland until undertaking a cease-fire in 1972, after which it effectively ceded the title of the IRA in the north to the Provos.) Believing that their fight was a continuation of the Irish War of Independence, the Provos adopted the tactics of guerrilla warfare, financed partly by members of the Irish diaspora in the United States and later supplied with arms and munitions by the government of Libyan strongman Muammar al-Qaddafi. Unionists also took up arms, swelling the numbers of loyalist paramilitary organizations, most notably the Ulster Volunteer Force (UVF) and Ulster Defence Association UDA).
British soldier in Northern Ireland Local people walking past a British soldier on guard in Northern Ireland, August 1969.Peter Kemp—AP/Shutterstock.comInternment, “peace walls,” and “Bloody Sunday”
In an attempt to address nationalist grievances, electoral boundaries were redrawn more fairly, efforts were made to rectify discrimination in housing and public employment, and the B Specials were decommissioned. At the same time, the government of Northern Ireland responded to the growing unrest by introducing increasingly stringent security measures, including internment (detention without trial). The overwhelming majority of those arrested, however, were nationalists.
As the 1970s progressed, rioting became more common in Belfast and Derry, bombings of public places (by both loyalists and republicans) increased, and both sides of the conflict perpetrated violent, deadly atrocities. Barbed wire laid by British soldiers to separate the sectarian communitiesevolved into brick and steel “peace walls,” some of which stood 45 feet (14 metres) high, segregating loyalist and republican enclaves, most famously the Falls Road Catholic community and the Shankill Protestant community of Belfast.
On January 30, 1972, the conflict reached a new level of intensity when British paratroopers fired on Catholic civil rights demonstrators in Londonderry, killing 13 and injuring 14 others (one of whom later died). The incident, which became known as “Bloody Sunday,” contributed to a spike in Provos recruitment and would remain controversial for decades, hinging on the question of which side fired first. In 2010 the Saville Report , the final pronouncement of a British government inquiry into the event, concluded that none of the victims had posed a threat to the troops and that their shooting had been unjustified. British Prime Minister David Cameron responded to the report by issuing a landmark apology for the shooting:
There is no point in trying to soften or equivocate what is in this report. It is clear from the tribunal’s authoritative conclusions that the events of Bloody Sunday were in no way justified….What happened should never, ever have happened….Some members of our armed forces acted wrongly. The government is ultimately responsible for the conduct of the armed forces and for that, on behalf of the government, indeed, on behalf of our country, I am deeply sorry.
In all, more than 480 people were killed as a result of the conflict in Northern Ireland in 1972, which proved to be the deadliest single year in the Troubles. That total included more than 100 fatalities for the British army, as the IRA escalated its onslaught. On July 21, “Bloody Friday,” nine people were killed and scores were injured when some two dozen bombs were detonated by the Provos in Belfast. Earlier, in March, frustrated with the Northern Ireland government’s failure to calm the situation, the British government suspended the Northern Ireland Parliament and reinstituted direct rule by Westminster.
Beginning in the mid-1970s, the IRA shifted the emphasis of its “Long War” from direct engagements with British troops to smaller-scale secretive operations, including the bombing of cities in Britain—a change of tactics the British military described as a shift from “insurgency” to “terrorism.” Similarly, the loyalist groups began setting off bombs in Ireland. Meanwhile, paramilitary violence at mid-decade (1974–76) resulted in the civilian deaths of some 370 Catholics and 88 Protestants.
Northern Ireland: peace movement Protesters against ongoing violence in Northern Ireland gathering on Shankill Road, Belfast, Northern Ireland, August 1976.Peace PeopleThe Sunningdale Agreement, hunger strikes, Bobby Sands, and the Brighton bombing
A glimmer of hope was offered by the Sunningdale Agreement , named for the English city in which it was negotiated in 1973. That agreement led to the creation of a new Northern Ireland Assembly, with proportional representation for all parties, and to the establishment of a Council of Ireland, which was to provide a role for Ireland in the affairs of Northern Ireland. Frustrated by the diminution of their political power and furious at the participation of the republic, loyalists scuttled the power-sharing plan with a general strike that brought the province to a halt in May 1974 and eventually forced a return to direct rule, which remained in place for some 25 years.
For the remainder of the decade, violence ebbed and flowed, cease-fires lingered and lapsed, and tit-for-tat bombings and assassinations continued, including the high-profile killing at sea in August 1979 of Lord Mountbatten, a relative of both Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip. In 1976 the opening of the specially designed Maze prison brought with it a shift in the treatment of IRA inmates from that of prisoners of war to that of common criminals. Seeking a return to their Special Category Status, the prisoners struck back, first staging the “blanket protest,” in which they refused to put on prison uniforms and instead wore only blankets, and then, in 1978, the “dirty protest,” in which inmates smeared the walls of their cells with excrement. The government of recently elected Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher refused to buckle, even in the face of hunger strikes in 1980–81 that led to the deaths of 10 prisoners, including Bobby Sands, who had won a seat in the British Parliament while incarcerated and fasting.
Sands’s election helped convince Sinn Féin, then operating as the political wing of the IRA, that the struggle for unification should be pursued at the ballot box as well as with the Armalite rifle. In June 1983 Sinn Féin leader Gerry Adams won a seat in Parliament representing West Belfast, though he refused to take it to avoid taking the compulsory oath of loyalty to the British queen.
The Anglo-Irish Agreement and Downing Street Declaration
In October 1984 an IRA bomb attack on the Conservative Party Conference in Brighton, England, took five lives and threatened that of Thatcher. Though she remained steadfast in the face of this attack, it was the “Iron Lady” who in November 1985 joined Irish Taoiseach Garret FitzGerald in signing the Anglo-Irish Agreement, under which both countries guaranteed that any change in the status of Northern Ireland would come about only with the consent of the majority of the people of Northern Ireland. The accordalso established the Intergovernmental Conference, which gave Ireland a consultative role in the political and security affairs of Northern Ireland for the first time. Finally, the agreement stipulated that power would be devolved back upon the government of Northern Ireland only if unionists and nationalists participated in power sharing.
Anglo-Irish Agreement (1985) Irish Taoiseach (Prime Minister) Garret FitzGerald and British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher signing the Anglo-Irish Agreement, November 15, 1985.Peter Kemp/APThe loyalists’ vehement opposition to the agreement included the resignation of all 15 unionist members of the House of Commons and a ramping up of violence. In the meantime, IRA bombings in London made headlines, and the reach of the British security forces extended to the killing of three Provos in Gibraltar. Behind the scenes, however, negotiations were underway. In 1993 British Prime Minister John Major and Irish Taoiseach Albert Reynolds issued the so-called Downing Street Declaration , which established a framework for all-party peace talks. A cease-fire declared by the Provos in 1994 and joined by the principal loyalist paramilitary groups fell apart in 1996 because Sinn Féin, which had replaced the more moderate Social Democratic and Labour Party (SDLP) as the leading nationalist party, had been excluded from peace talks because of the IRA’s continuing bombing campaign. Nevertheless, the unionists were at the table, prepared to consider a solution that included the participation of the republic of Ireland. After the IRA resumed its cease-fire in 1997, Sinn Féin was welcomed back to the talks, which now included the British and Irish governments, the SDLP, the Alliance Party of Northern Ireland, the UUP, and the Ulster Democratic Party, among others, though not the Paisley-led DUP, which was protesting the inclusion of Sinn Féin.
The Good Friday Agreement, the Omagh bombing, peace, and power sharing
Those talks, mediated by former U.S. senator George Mitchell, led to the Good Friday Agreement (Belfast Agreement), reached April 10, 1998. That landmark accordprovided for the creation of a power-sharing Northern Ireland Assembly, established an institutional arrangement for cross-border cooperation between the governments of Ireland and Northern Ireland on a range of issues, and lay the groundwork for continued consultation between the British and Irish governments. On May 22 Ireland and Northern Ireland held a joint referendum on the agreement, which was approved by 94 percent of those who voted in the republic and 71 percent of those voting in Northern Ireland, where Catholic approval of the accord (96 percent) was much higher than Protestant assent (52 per cent). Nonetheless, it was an IRA splinter group, the Real Irish Republican Army, which most dramatically violated the spirit of the agreement, with a bombing in Omagh in August that took 29 lives.
Elections for the new Assembly were held in June, but the IRA’s failure to decommission delayed the formation of the power-sharing Northern Ireland Executive until December 1999, when the IRA promised to fulfill its obligation to disarm. That month the republic of Ireland modified its constitution, removing its territorial claims to the whole of the island, and the United Kingdom yielded direct rule of Northern Ireland. Ostensibly the Troubles had come to end, but, though Northern Ireland began its most tranquil era in a generation, the peace was fragile. Sectarian antagonism persisted, the process of decommissioning was slow on both sides, and the rolling out of the new institutions was fitful, resulting in suspensions of devolution and the reimposition of direct rule.
In July 2005, however, the IRA announced that it had ordered all its units to “dump arms,” would henceforth pursue its goals only through peaceful means, and would work with international inspectors “to verifiably put its arms beyond use.” At a press conference in September, a spokesman for the Independent International Commission on Decommissioning stated, “We are satisfied that the arms decommissioned represent the totality of the IRA’s arsenal.” Decommissioning by unionist paramilitaries and other republican groups followed..
-

 25cm x 30cm Glasgow
25cm x 30cm GlasgowThe Troubles, also called Northern Ireland conflict, violent sectarian conflict from about 1968 to 1998 in Northern Irelandbetween the overwhelmingly Protestantunionists (loyalists), who desired the province to remain part of the United Kingdom, and the overwhelmingly Roman Catholic nationalists (republicans), who wanted Northern Ireland to become part of the republic of Ireland. The other major players in the conflict were the British army, Royal Ulster Constabulary (RUC), and Ulster Defence Regiment (UDR; from 1992 called the Royal Irish Regiment), and their avowed purpose was to play a peacekeeping role, most prominently between the nationalist Irish Republican Army(IRA), which viewed the conflict as a guerrilla war for national independence, and the unionist paramilitary forces, which characterized the IRA’s aggression as terrorism. Marked by street fighting, sensational bombings, sniper attacks, roadblocks, and internment without trial, the confrontation had the characteristics of a civil war, notwithstanding its textbook categorization as a “low-intensity conflict.” Some 3,600 people were killed and more than 30,000 more were wounded before a peaceful solution, which involved the governments of both the United Kingdom and Ireland, was effectively reached in 1998, leading to a power-sharing arrangement in the Northern Ireland Assembly at Stormont.
Deep origins
The story of the Troubles is inextricably entwined with the history of Ireland as whole and, as such, can be seen as stemming from the first British incursion on the island, the Anglo-Norman invasion of the late 12th century, which left a wave of settlers whose descendants became known as the “Old English.” Thereafter, for nearly eight centuries, England and then Great Britain as a whole would dominate affairs in Ireland. Colonizing British landlords widely displaced Irish landholders. The most successful of these “plantations” began taking hold in the early 17th century in Ulster, the northernmost of Ireland’s four traditional provinces, previously a centre of rebellion, where the planters included English and Scottish tenants as well as British landlords. Because of the plantation of Ulster, as Irish history unfolded—with the struggle for the emancipation of the island’s Catholic majority under the supremacy of the Protestant ascendancy, along with the Irish nationalist pursuit of Home Rule and then independence after the island’s formal union with Great Britain in 1801—Ulster developed as a region where the Protestant settlers outnumbered the indigenousIrish. Unlike earlier English settlers, most of the 17th-century English and Scottish settlers and their descendants did not assimilate with the Irish. Instead, they held on tightly to British identity and remained steadfastly loyal to the British crown.
The formation of Northern Ireland, Catholic grievances, and the leadership of Terence O’Neill
Of the nine modern counties that constituted Ulster in the early 20th century, four—Antrim, Down, Armagh, and Londonderry (Derry)—had significant Protestant loyalist majorities; two—Fermanagh and Tyrone—had small Catholic nationalist majorities; and three—Donegal, Cavan, and Monaghan—had significant Catholic nationalist majorities. In 1920, during the Irish War of Independence (1919–21), the British Parliament, responding largely to the wishes of Ulster loyalists, enacted the Government of Ireland Act , which divided the island into two self-governing areas with devolved Home Rule-like powers. What would come to be known as Northern Ireland was formed by Ulster’s four majority loyalist counties along with Fermanagh and Tyrone. Donegal, Cavan, and Monaghan were combined with the island’s remaining 23 counties to form southern Ireland. The Anglo-Irish Treaty that ended the War of Independence then created the Irish Free State in the south, giving it dominion status within the British Empire. It also allowed Northern Ireland the option of remaining outside of the Free State, which it unsurprisingly chose to do.
Thus, in 1922 Northern Ireland began functioning as a self-governing region of the United Kingdom. Two-thirds of its population (about one million people) was Protestant and about one-third (roughly 500,000 people) was Catholic. Well before partition, Northern Ireland, particularly Belfast, had attracted economic migrants from elsewhere in Ireland seeking employment in its flourishing linen-making and shipbuilding industries. The best jobs had gone to Protestants, but the humming local economy still provided work for Catholics. Over and above the long-standing dominance of Northern Ireland politics that resulted for the Ulster Unionist Party (UUP) by virtue of the Protestants’ sheer numerical advantage, loyalist control of local politics was ensured by the gerrymandering of electoral districts that concentrated and minimized Catholic representation. Moreover, by restricting the franchise to ratepayers (the taxpaying heads of households) and their spouses, representation was further limited for Catholic households, which tended to be larger (and more likely to include unemployed adult children) than their Protestant counterparts. Those who paid rates for more than one residence (more likely to be Protestants) were granted an additional vote for each ward in which they held property (up to six votes). Catholics argued that they were discriminated against when it came to the allocation of public housing, appointments to public service jobs, and government investment in neighbourhoods. They were also more likely to be the subjects of police harassment by the almost exclusively Protestant RUC and Ulster Special Constabulary (B Specials).
The divide between Catholics and Protestants in Northern Ireland had little to do with theological differences but instead was grounded in culture and politics. Neither Irish history nor the Irish language was taught in schools in Northern Ireland, it was illegal to fly the flag of the Irish republic, and from 1956 to 1974 Sinn Féin, the party of Irish republicanism, also was banned in Northern Ireland. Catholics by and large identified as Irish and sought the incorporation of Northern Ireland into the Irish state. The great bulk of Protestants saw themselves as British and feared that they would lose their culture and privilege if Northern Ireland were subsumed by the republic. They expressed their partisan solidarity through involvement with Protestant unionist fraternal organizations such as the Orange Order, which found its inspiration in the victory of King William III (William of Orange) at the Battle of the Boyne in 1690 over his deposed Catholic predecessor, James II, whose siege of the Protestant community of Londonderry had earlier been broken by William. Despite these tensions, for 40 or so years after partition the status of unionist-dominated Northern Ireland was relatively stable.
IRA graffiti “IRA” spray-painted on a container, Derry (Londonderry), Northern Ireland.© Attila Jandi/Dreamstime.comRecognizing that any attempt to reinvigorate Northern Ireland’s declining industrial economy in the early 1960s would also need to address the province’s percolatingpolitical and social tensions, the newly elected prime minister of Northern Ireland, Terence O’Neill, not only reached out to the nationalist community but also, in early 1965, exchanged visits with Irish Taoiseach (Prime Minister) Seán Lemass—a radical step, given that the republic’s constitution included an assertion of sovereignty over the whole island. Nevertheless, O’Neill’s efforts were seen as inadequate by nationalists and as too conciliatory by loyalists, including the Rev. Ian Paisley, who became one of the most vehement and influential representatives of unionist reaction.
Civil rights activism, the Battle of Bogside, and the arrival of the British army
Contrary to the policies of UUP governments that disadvantaged Catholics, the Education Act that the Northern Ireland Parliament passed into law in 1947 increased educational opportunities for all citizens of the province. As a result, the generation of well-educated Catholics who came of age in the 1960s had new expectations for more equitable treatment. At a time when political activism was on the rise in Europe—from the events of May 1968 in France to the Prague Spring—and when the American civil rights movement was making great strides, Catholic activists in Northern Ireland such as John Humeand Bernadette Devlin came together to form civil rightsgroups such as the Northern Ireland Civil Rights Association (NICRA).
Although more than one violently disrupted political march has been pointed to as the starting point of the Troubles, it can be argued that the catalyzing event occurred on October 5, 1968, in Derry, where a march had been organized by the NICRA to protest discrimination and gerrymandering. The march was banned when unionists announced that they would be staging a counterdemonstration, but the NICRA decided to carry out their protest anyway. Rioting then erupted after the RUC violently suppressed the marchers with batons and a water cannon.
Similarly inflammatory were the events surrounding a march held by loyalists in Londonderry on August 12, 1969. Two days of rioting that became known as the Battle of Bogside (after the Catholic area in which the confrontation occurred) stemmed from the escalating clash between nationalists and the RUC, which was acting as a buffer between loyalist marchers and Catholic residents of the area. Rioting in support of the nationalists then erupted in Belfast and elsewhere, and the British army was dispatched to restore calm. Thereafter, violent confrontation only escalated, and the Troubles (a name that neither characterized the nature of the conflict nor assigned blame for it to one side or the other) had clearly begun.
The emergence of the Provisional IRA and the loyalist paramilitaries
Initially, the nationalists welcomed the British army as protectors and as a balance for the Protestant-leaning RUC. In time, however, the army would be viewed by nationalists as another version of the enemy, especially after its aggressive efforts to disarm republican paramilitaries. In the process, the Irish Republican Army (IRA) became the defender of the nationalist cause. From its base in Ireland(which had formally left the Commonwealth in 1949), the IRA had mounted an ineffectual guerrilla effort in support of Northern Ireland’s nationalists from 1956 to 1962, but, as the 1960s progressed, the IRA became less concerned with affairs in the north than with advancing a Marxist political agenda. As a result, a splinter group, the Provisional Irish Republican Army (Provos), which was prepared to use force to bring about unification, emerged as the champion of Northern Ireland’s nationalists. (The Official IRA would conduct operations in support of the republicans in Northern Ireland until undertaking a cease-fire in 1972, after which it effectively ceded the title of the IRA in the north to the Provos.) Believing that their fight was a continuation of the Irish War of Independence, the Provos adopted the tactics of guerrilla warfare, financed partly by members of the Irish diaspora in the United States and later supplied with arms and munitions by the government of Libyan strongman Muammar al-Qaddafi. Unionists also took up arms, swelling the numbers of loyalist paramilitary organizations, most notably the Ulster Volunteer Force (UVF) and Ulster Defence Association UDA).
British soldier in Northern Ireland Local people walking past a British soldier on guard in Northern Ireland, August 1969.Peter Kemp—AP/Shutterstock.comInternment, “peace walls,” and “Bloody Sunday”
In an attempt to address nationalist grievances, electoral boundaries were redrawn more fairly, efforts were made to rectify discrimination in housing and public employment, and the B Specials were decommissioned. At the same time, the government of Northern Ireland responded to the growing unrest by introducing increasingly stringent security measures, including internment (detention without trial). The overwhelming majority of those arrested, however, were nationalists.
As the 1970s progressed, rioting became more common in Belfast and Derry, bombings of public places (by both loyalists and republicans) increased, and both sides of the conflict perpetrated violent, deadly atrocities. Barbed wire laid by British soldiers to separate the sectarian communitiesevolved into brick and steel “peace walls,” some of which stood 45 feet (14 metres) high, segregating loyalist and republican enclaves, most famously the Falls Road Catholic community and the Shankill Protestant community of Belfast.
On January 30, 1972, the conflict reached a new level of intensity when British paratroopers fired on Catholic civil rights demonstrators in Londonderry, killing 13 and injuring 14 others (one of whom later died). The incident, which became known as “Bloody Sunday,” contributed to a spike in Provos recruitment and would remain controversial for decades, hinging on the question of which side fired first. In 2010 the Saville Report , the final pronouncement of a British government inquiry into the event, concluded that none of the victims had posed a threat to the troops and that their shooting had been unjustified. British Prime Minister David Cameron responded to the report by issuing a landmark apology for the shooting:
There is no point in trying to soften or equivocate what is in this report. It is clear from the tribunal’s authoritative conclusions that the events of Bloody Sunday were in no way justified….What happened should never, ever have happened….Some members of our armed forces acted wrongly. The government is ultimately responsible for the conduct of the armed forces and for that, on behalf of the government, indeed, on behalf of our country, I am deeply sorry.
In all, more than 480 people were killed as a result of the conflict in Northern Ireland in 1972, which proved to be the deadliest single year in the Troubles. That total included more than 100 fatalities for the British army, as the IRA escalated its onslaught. On July 21, “Bloody Friday,” nine people were killed and scores were injured when some two dozen bombs were detonated by the Provos in Belfast. Earlier, in March, frustrated with the Northern Ireland government’s failure to calm the situation, the British government suspended the Northern Ireland Parliament and reinstituted direct rule by Westminster.
Beginning in the mid-1970s, the IRA shifted the emphasis of its “Long War” from direct engagements with British troops to smaller-scale secretive operations, including the bombing of cities in Britain—a change of tactics the British military described as a shift from “insurgency” to “terrorism.” Similarly, the loyalist groups began setting off bombs in Ireland. Meanwhile, paramilitary violence at mid-decade (1974–76) resulted in the civilian deaths of some 370 Catholics and 88 Protestants.
Northern Ireland: peace movement Protesters against ongoing violence in Northern Ireland gathering on Shankill Road, Belfast, Northern Ireland, August 1976.Peace PeopleThe Sunningdale Agreement, hunger strikes, Bobby Sands, and the Brighton bombing
A glimmer of hope was offered by the Sunningdale Agreement , named for the English city in which it was negotiated in 1973. That agreement led to the creation of a new Northern Ireland Assembly, with proportional representation for all parties, and to the establishment of a Council of Ireland, which was to provide a role for Ireland in the affairs of Northern Ireland. Frustrated by the diminution of their political power and furious at the participation of the republic, loyalists scuttled the power-sharing plan with a general strike that brought the province to a halt in May 1974 and eventually forced a return to direct rule, which remained in place for some 25 years.
For the remainder of the decade, violence ebbed and flowed, cease-fires lingered and lapsed, and tit-for-tat bombings and assassinations continued, including the high-profile killing at sea in August 1979 of Lord Mountbatten, a relative of both Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip. In 1976 the opening of the specially designed Maze prison brought with it a shift in the treatment of IRA inmates from that of prisoners of war to that of common criminals. Seeking a return to their Special Category Status, the prisoners struck back, first staging the “blanket protest,” in which they refused to put on prison uniforms and instead wore only blankets, and then, in 1978, the “dirty protest,” in which inmates smeared the walls of their cells with excrement. The government of recently elected Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher refused to buckle, even in the face of hunger strikes in 1980–81 that led to the deaths of 10 prisoners, including Bobby Sands, who had won a seat in the British Parliament while incarcerated and fasting.
Sands’s election helped convince Sinn Féin, then operating as the political wing of the IRA, that the struggle for unification should be pursued at the ballot box as well as with the Armalite rifle. In June 1983 Sinn Féin leader Gerry Adams won a seat in Parliament representing West Belfast, though he refused to take it to avoid taking the compulsory oath of loyalty to the British queen.
The Anglo-Irish Agreement and Downing Street Declaration
In October 1984 an IRA bomb attack on the Conservative Party Conference in Brighton, England, took five lives and threatened that of Thatcher. Though she remained steadfast in the face of this attack, it was the “Iron Lady” who in November 1985 joined Irish Taoiseach Garret FitzGerald in signing the Anglo-Irish Agreement, under which both countries guaranteed that any change in the status of Northern Ireland would come about only with the consent of the majority of the people of Northern Ireland. The accordalso established the Intergovernmental Conference, which gave Ireland a consultative role in the political and security affairs of Northern Ireland for the first time. Finally, the agreement stipulated that power would be devolved back upon the government of Northern Ireland only if unionists and nationalists participated in power sharing.
Anglo-Irish Agreement (1985) Irish Taoiseach (Prime Minister) Garret FitzGerald and British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher signing the Anglo-Irish Agreement, November 15, 1985.Peter Kemp/APThe loyalists’ vehement opposition to the agreement included the resignation of all 15 unionist members of the House of Commons and a ramping up of violence. In the meantime, IRA bombings in London made headlines, and the reach of the British security forces extended to the killing of three Provos in Gibraltar. Behind the scenes, however, negotiations were underway. In 1993 British Prime Minister John Major and Irish Taoiseach Albert Reynolds issued the so-called Downing Street Declaration , which established a framework for all-party peace talks. A cease-fire declared by the Provos in 1994 and joined by the principal loyalist paramilitary groups fell apart in 1996 because Sinn Féin, which had replaced the more moderate Social Democratic and Labour Party (SDLP) as the leading nationalist party, had been excluded from peace talks because of the IRA’s continuing bombing campaign. Nevertheless, the unionists were at the table, prepared to consider a solution that included the participation of the republic of Ireland. After the IRA resumed its cease-fire in 1997, Sinn Féin was welcomed back to the talks, which now included the British and Irish governments, the SDLP, the Alliance Party of Northern Ireland, the UUP, and the Ulster Democratic Party, among others, though not the Paisley-led DUP, which was protesting the inclusion of Sinn Féin.
The Good Friday Agreement, the Omagh bombing, peace, and power sharing
Those talks, mediated by former U.S. senator George Mitchell, led to the Good Friday Agreement (Belfast Agreement), reached April 10, 1998. That landmark accordprovided for the creation of a power-sharing Northern Ireland Assembly, established an institutional arrangement for cross-border cooperation between the governments of Ireland and Northern Ireland on a range of issues, and lay the groundwork for continued consultation between the British and Irish governments. On May 22 Ireland and Northern Ireland held a joint referendum on the agreement, which was approved by 94 percent of those who voted in the republic and 71 percent of those voting in Northern Ireland, where Catholic approval of the accord (96 percent) was much higher than Protestant assent (52 per cent). Nonetheless, it was an IRA splinter group, the Real Irish Republican Army, which most dramatically violated the spirit of the agreement, with a bombing in Omagh in August that took 29 lives.
Elections for the new Assembly were held in June, but the IRA’s failure to decommission delayed the formation of the power-sharing Northern Ireland Executive until December 1999, when the IRA promised to fulfill its obligation to disarm. That month the republic of Ireland modified its constitution, removing its territorial claims to the whole of the island, and the United Kingdom yielded direct rule of Northern Ireland. Ostensibly the Troubles had come to end, but, though Northern Ireland began its most tranquil era in a generation, the peace was fragile. Sectarian antagonism persisted, the process of decommissioning was slow on both sides, and the rolling out of the new institutions was fitful, resulting in suspensions of devolution and the reimposition of direct rule.
In July 2005, however, the IRA announced that it had ordered all its units to “dump arms,” would henceforth pursue its goals only through peaceful means, and would work with international inspectors “to verifiably put its arms beyond use.” At a press conference in September, a spokesman for the Independent International Commission on Decommissioning stated, “We are satisfied that the arms decommissioned represent the totality of the IRA’s arsenal.” Decommissioning by unionist paramilitaries and other republican groups followed..
-

 35cm x 25cm Limerick William Butler Yeats (13 June 1865 – 28 January 1939) was an Irish poet, dramatist, prose writer and one of the foremost figures of 20th-century literature. A pillar of the Irish literary establishment, he helped to found the Abbey Theatre, and in his later years served two terms as a Senator of the Irish Free State. He was a driving force behind the Irish Literary Revival along with Lady Gregory, Edward Martyn and others. Yeats was born in Sandymount, Ireland, and educated there and in London. He was a Protestant and member of the Anglo-Irish community. He spent childhood holidays in County Sligo and studied poetry from an early age, when he became fascinated by Irish legends and the occult. These topics feature in the first phase of his work, which lasted roughly until the turn of the 20th century. His earliest volume of verse was published in 1889, and its slow-paced and lyrical poems display debts to Edmund Spenser, Percy Bysshe Shelley, and the poets of the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood. From 1900, his poetry grew more physical and realistic. He largely renounced the transcendental beliefs of his youth, though he remained preoccupied with physical and spiritual masks, as well as with cyclical theories of life. In 1923, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature.
35cm x 25cm Limerick William Butler Yeats (13 June 1865 – 28 January 1939) was an Irish poet, dramatist, prose writer and one of the foremost figures of 20th-century literature. A pillar of the Irish literary establishment, he helped to found the Abbey Theatre, and in his later years served two terms as a Senator of the Irish Free State. He was a driving force behind the Irish Literary Revival along with Lady Gregory, Edward Martyn and others. Yeats was born in Sandymount, Ireland, and educated there and in London. He was a Protestant and member of the Anglo-Irish community. He spent childhood holidays in County Sligo and studied poetry from an early age, when he became fascinated by Irish legends and the occult. These topics feature in the first phase of his work, which lasted roughly until the turn of the 20th century. His earliest volume of verse was published in 1889, and its slow-paced and lyrical poems display debts to Edmund Spenser, Percy Bysshe Shelley, and the poets of the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood. From 1900, his poetry grew more physical and realistic. He largely renounced the transcendental beliefs of his youth, though he remained preoccupied with physical and spiritual masks, as well as with cyclical theories of life. In 1923, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature. -

 25cm x 35cm Limerick Major Michael John O'Leary VC (29 September 1890 – 2 August 1961) was an Irish recipient of the Victoria Cross, the most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth forces. O'Leary achieved his award for single-handedly charging and destroying two German barricades defended by machine gun positions near the French village of Cuinchy, in a localised operation on the Western Front during the First World War. At the time of his action, O'Leary was a nine-year veteran of the British armed forces and by the time he retired from the British Army in 1921, he had reached the rank of lieutenant. He served in the army again during the Second World War, although his later service was blighted by periods of ill-health. At his final retirement from the military in 1945, O'Leary was an Army major in command of a prisoner of war camp. Between the wars, O'Leary spent many years employed as a police officer in Canada and is sometimes considered to be a Canadian recipient of the Victoria Cross. Following the Second World War he worked as a building contractor in London, where he died in 1961.Early life O'Leary was born in 1890, one of four children of Daniel and Margaret O'Leary, who owned a farm at Inchigeela, near Macroom in County Cork, Ireland. Daniel O'Leary was a fervent Irish nationalist and keen sportsman who participated in competitive weightlifting and football. Aged 16 and unwilling to continue to work on his parent's land, Michael O'Leary joined the Royal Navy, serving at the shore establishment HMS Vivid at Devonport for several years until rheumatism in his knees forced his departure from the service. Within a few months however, O'Leary had again tired of the farm and joined the Irish Guards regiment of the British Army. O'Leary served three years with the Irish Guards, leaving in August 1913 to join the Royal North-West Mounted Police (RNWMP) in Saskatchewan, Canada. Operating from Regina, Constable O'Leary was soon commended for his bravery in capturing two criminals following a two-hour gunbattle, for which service he was presented with a gold ring. At the outbreak of the First World War in Europe during August 1914, O'Leary was given permission to leave the RNWMP and return to Britain in order to rejoin the army as an active reservist. On 22 October, O'Leary was mobilized and on 23 November he joined his regiment in France, then fighting with the British Expeditionary Force, entrenched in Flanders. First World War service During December 1914, O'Leary saw heavy fighting with the Irish Guards and was Mentioned in Despatches and subsequently promoted to lance corporal on 5 January 1915. Three weeks later, on 30 January, the Irish Guards were ordered to prepare for an attack on German positions near Cuinchy on the La Bassée Canal, a response to a successful German operation in the area five days before. The Germans attacked first however, and on the morning of 1 February seized a stretch of canal embankment on the western end of the 2nd Brigade line from a company of Coldstream Guards. This section, known as the Hollow, was tactically important as it defended a culvert that passed underneath a railway embankment. 4 Company of Irish Guards, originally in reserve, were tasked with joining the Coldstream Guards in retaking the position at 04:00, but the attack was met with heavy machine gun fire and most of the assault party, including all of the Irish Guards officers, were killed or wounded To replace these officers, Second Lieutenant Innes of 1 Company was ordered forward to gather the survivors and withdraw, forming up at a barricade on the edge of the Hollow. Innes regrouped the survivors and, following a heavy bombardment from supporting artillery and with his own company providing covering fire, assisted the Coldstream Guards in a second attack at 10:15.Weighed down with entrenching equipment, the attacking Coldstream Guardsmen faltered and began to suffer heavy casualties. Innes too came under heavy fire from a German barricade to their front equipped with a machine gun. O'Leary had been serving as Innes's orderly, and had joined him in the operations earlier in the morning and again in the second attack. Charging past the rest of the assault party, O'Leary closed with the first German barricade at the top of the railway embankment and fired five shots, killing the gun's crew. Continuing forward, O'Leary confronted a second barricade, also armed with a machine gun 60 yards (55 m) further on and again mounted the railway embankment, to avoid the marshy ground on either side. The Germans spotted his approach, but could not bring their gun to bear on him before he opened fire, killing three soldiers and capturing two others after he ran out of ammunition.Reportedly, O'Leary had made his advance on the second barricade "intent upon killing another German to whom he had taken a dislike". Having disabled both guns and enabled the recapture of the British position, O'Leary then returned to his unit with his prisoners, apparently "as cool as if he had been for a walk in the park." For his actions, O'Leary received a battlefield promotion to sergeant on 4 February and was recommended for the Victoria Cross, which was gazetted on 16 February: No. 3556 Lance-Corporal Michael O'Leary, 1st Battalion, Irish Guards For conspicuous bravery at Cuinchy on the 1st February, 1915. When forming one of the storming party which advanced against the enemy's barricades he rushed to the front and himself killed five Germans who were holding the first barricade, after which he attacked a second barricade, about 60 yards further on, which he captured, after killing three of the enemy and making prisoners of two more. Lance-Corporal O'Leary thus practically captured the enemy's position by himself and prevented the attacking party from being fired upon. The London Gazette, 16 February 1915 Returning to Britain to receive his medal from King George V at Buckingham Palace on 22 June 1915, O'Leary was given a grand reception attended by thousands of Londoners in Hyde Park on 10 July. He was also the subject of much patriotic writing, including a poem in the Daily Mail and the short play O'Flaherty V.C. by George Bernard Shaw.Tributes came from numerous prominent figures of the day, including Sir Arthur Conan Doyle who said that "No writer in fiction would dare to fasten such an achievement on any of his characters, but the Irish have always had a reputation of being wonderful fighters, and Lance-Corporal Michael O’Leary is clearly one of them." and Thomas Scanlan who said: "I heard early this week of the great achievements of the Irish Guards. All Ireland is proud of O’Leary. He fully deserves the high honour that has been conferred upon him. Ireland is grateful to him."His reception was repeated in Macroom when he visited Ireland, with crowds turning out to applaud him. Daniel O'Leary was interviewed in a local newspaper regarding his son's exploit but was reportedly unimpressed, commenting: "I am surprised he didn't do more. I often laid out twenty men myself with a stick coming from Macroom Fair, and it is a bad trial of Mick that he could kill only eight, and he having a rifle and bayonet." O'Leary was further rewarded for his service, being advanced to a commissioned rank as a second lieutenant with the Connaught Rangers,and he was also presented with a Russian decoration, the Cross of St. George (third class).Despite his popularity with the crowds in London and Macroom, he was jeered by Ulster Volunteers at a recruitment drive in Ballaghaderrin during the autumn of 1915. This treatment caused such a scandal that it was raised in the Houses of Parliament in December. In 1916, O'Leary travelled to Salonika with the 5th battalion of the Connaught Rangers to serve in the Balkans campaign, remaining in theatre until the end of the war, following which he was stationed in Dover with the 2nd battalion until demobilised in 1921.During his service in the Balkans, O'Leary contracted malaria, which was to have severe negative effects on his health for the rest of his life. O'Leary was in the same regiment as the British actor Stanley Holloway and they served together in France. After the war ended, they remained close friends and Holloway often stayed in The May Fair Hotel where O'Leary worked as a concierge. Later life Leaving his wife Greta and their two children in Britain, O'Leary returned to Canada in March 1921 with the purported intention of rejoining the RNWMP, newly renamed the Royal Canadian Mounted Police. For unknown reasons, this plan came to nothing and after some months giving lectures on his war service and working in a publishing house, O'Leary joined the Ontario Provincial Police, charged with enforcing the prohibition laws. In 1924, with his family recently arrived from England, O'Leary left the Ontario police force and became a police sergeant with the Michigan Central Railway in Bridgeburg, Ontario, receiving £33 a month. In 1925, O'Leary was the subject of several scandals, being arrested for smuggling illegal immigrants and later for irregularities in his investigations. Although he was acquitted both times, he spent a week in prison following the second arrest and lost his job with the railway. Several months later, the municipal authorities in Hamilton, Ontario loaned him £70 to pay for him and his family to return to Ireland. Although his family sailed on the SS Leticia, O'Leary remained in Ontario, working with the attorney general's office. With his health in serious decline, the British Legion arranged for O'Leary to return to Britain and work in their poppy factory. By 1932, O'Leary was living in Southborne Avenue in Colindale, had regained his health and found employment as a commissionaire at The May Fair Hotel in London, at which he was involved in charitable events for wounded servicemen. With the mobilisation of the British Army in 1939, O'Leary returned to military service as a captain in the Middlesex Regiment. O'Leary was sent to France as part of the British Expeditionary Force but had returned to Britain before the Battle of France due to a recurrence of his malaria. No longer fit for full active service, O'Leary was transferred to the Pioneer Corps and took command of a prisoner of war camp in Southern England. In 1945, he was discharged from the military as unfit for duty on medical grounds as a major and found work as a building contractor, in which career he remained until his retirement in 1954. Two of O'Leary's sons had also served in the military during the war, with both receiving the Distinguished Flying Cross for their actions. As a Victoria Cross recipient, O'Leary joined the VE day parade in 1946, but at the 1956 Centenary VC review his place was taken by an imposter travelling in a bath chair. With his health again declining, O'Leary moved to Limesdale Gardens in Edgware shortly before his death in 1961 at the Whittington Hospital in Islington. O'Leary was buried at Mill Hill Cemetery following a funeral service at the Roman Catholic Annunciation Church in Burnt Oak which was attended by an honour guard from the Irish Guards and six of his children. His medals were later presented to the Irish Guards, and are on display at the Regimental Headquarters. He is also remembered in his birthplace, the macroom-online website listing him as a prominent citizen and states that "while many might consider he was fighting with the wrong army, in the wrong war, he was nevertheless a very brave, resourceful and capable soldier who deserved the honours bestowed upon him."
25cm x 35cm Limerick Major Michael John O'Leary VC (29 September 1890 – 2 August 1961) was an Irish recipient of the Victoria Cross, the most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth forces. O'Leary achieved his award for single-handedly charging and destroying two German barricades defended by machine gun positions near the French village of Cuinchy, in a localised operation on the Western Front during the First World War. At the time of his action, O'Leary was a nine-year veteran of the British armed forces and by the time he retired from the British Army in 1921, he had reached the rank of lieutenant. He served in the army again during the Second World War, although his later service was blighted by periods of ill-health. At his final retirement from the military in 1945, O'Leary was an Army major in command of a prisoner of war camp. Between the wars, O'Leary spent many years employed as a police officer in Canada and is sometimes considered to be a Canadian recipient of the Victoria Cross. Following the Second World War he worked as a building contractor in London, where he died in 1961.Early life O'Leary was born in 1890, one of four children of Daniel and Margaret O'Leary, who owned a farm at Inchigeela, near Macroom in County Cork, Ireland. Daniel O'Leary was a fervent Irish nationalist and keen sportsman who participated in competitive weightlifting and football. Aged 16 and unwilling to continue to work on his parent's land, Michael O'Leary joined the Royal Navy, serving at the shore establishment HMS Vivid at Devonport for several years until rheumatism in his knees forced his departure from the service. Within a few months however, O'Leary had again tired of the farm and joined the Irish Guards regiment of the British Army. O'Leary served three years with the Irish Guards, leaving in August 1913 to join the Royal North-West Mounted Police (RNWMP) in Saskatchewan, Canada. Operating from Regina, Constable O'Leary was soon commended for his bravery in capturing two criminals following a two-hour gunbattle, for which service he was presented with a gold ring. At the outbreak of the First World War in Europe during August 1914, O'Leary was given permission to leave the RNWMP and return to Britain in order to rejoin the army as an active reservist. On 22 October, O'Leary was mobilized and on 23 November he joined his regiment in France, then fighting with the British Expeditionary Force, entrenched in Flanders. First World War service During December 1914, O'Leary saw heavy fighting with the Irish Guards and was Mentioned in Despatches and subsequently promoted to lance corporal on 5 January 1915. Three weeks later, on 30 January, the Irish Guards were ordered to prepare for an attack on German positions near Cuinchy on the La Bassée Canal, a response to a successful German operation in the area five days before. The Germans attacked first however, and on the morning of 1 February seized a stretch of canal embankment on the western end of the 2nd Brigade line from a company of Coldstream Guards. This section, known as the Hollow, was tactically important as it defended a culvert that passed underneath a railway embankment. 4 Company of Irish Guards, originally in reserve, were tasked with joining the Coldstream Guards in retaking the position at 04:00, but the attack was met with heavy machine gun fire and most of the assault party, including all of the Irish Guards officers, were killed or wounded To replace these officers, Second Lieutenant Innes of 1 Company was ordered forward to gather the survivors and withdraw, forming up at a barricade on the edge of the Hollow. Innes regrouped the survivors and, following a heavy bombardment from supporting artillery and with his own company providing covering fire, assisted the Coldstream Guards in a second attack at 10:15.Weighed down with entrenching equipment, the attacking Coldstream Guardsmen faltered and began to suffer heavy casualties. Innes too came under heavy fire from a German barricade to their front equipped with a machine gun. O'Leary had been serving as Innes's orderly, and had joined him in the operations earlier in the morning and again in the second attack. Charging past the rest of the assault party, O'Leary closed with the first German barricade at the top of the railway embankment and fired five shots, killing the gun's crew. Continuing forward, O'Leary confronted a second barricade, also armed with a machine gun 60 yards (55 m) further on and again mounted the railway embankment, to avoid the marshy ground on either side. The Germans spotted his approach, but could not bring their gun to bear on him before he opened fire, killing three soldiers and capturing two others after he ran out of ammunition.Reportedly, O'Leary had made his advance on the second barricade "intent upon killing another German to whom he had taken a dislike". Having disabled both guns and enabled the recapture of the British position, O'Leary then returned to his unit with his prisoners, apparently "as cool as if he had been for a walk in the park." For his actions, O'Leary received a battlefield promotion to sergeant on 4 February and was recommended for the Victoria Cross, which was gazetted on 16 February: No. 3556 Lance-Corporal Michael O'Leary, 1st Battalion, Irish Guards For conspicuous bravery at Cuinchy on the 1st February, 1915. When forming one of the storming party which advanced against the enemy's barricades he rushed to the front and himself killed five Germans who were holding the first barricade, after which he attacked a second barricade, about 60 yards further on, which he captured, after killing three of the enemy and making prisoners of two more. Lance-Corporal O'Leary thus practically captured the enemy's position by himself and prevented the attacking party from being fired upon. The London Gazette, 16 February 1915 Returning to Britain to receive his medal from King George V at Buckingham Palace on 22 June 1915, O'Leary was given a grand reception attended by thousands of Londoners in Hyde Park on 10 July. He was also the subject of much patriotic writing, including a poem in the Daily Mail and the short play O'Flaherty V.C. by George Bernard Shaw.Tributes came from numerous prominent figures of the day, including Sir Arthur Conan Doyle who said that "No writer in fiction would dare to fasten such an achievement on any of his characters, but the Irish have always had a reputation of being wonderful fighters, and Lance-Corporal Michael O’Leary is clearly one of them." and Thomas Scanlan who said: "I heard early this week of the great achievements of the Irish Guards. All Ireland is proud of O’Leary. He fully deserves the high honour that has been conferred upon him. Ireland is grateful to him."His reception was repeated in Macroom when he visited Ireland, with crowds turning out to applaud him. Daniel O'Leary was interviewed in a local newspaper regarding his son's exploit but was reportedly unimpressed, commenting: "I am surprised he didn't do more. I often laid out twenty men myself with a stick coming from Macroom Fair, and it is a bad trial of Mick that he could kill only eight, and he having a rifle and bayonet." O'Leary was further rewarded for his service, being advanced to a commissioned rank as a second lieutenant with the Connaught Rangers,and he was also presented with a Russian decoration, the Cross of St. George (third class).Despite his popularity with the crowds in London and Macroom, he was jeered by Ulster Volunteers at a recruitment drive in Ballaghaderrin during the autumn of 1915. This treatment caused such a scandal that it was raised in the Houses of Parliament in December. In 1916, O'Leary travelled to Salonika with the 5th battalion of the Connaught Rangers to serve in the Balkans campaign, remaining in theatre until the end of the war, following which he was stationed in Dover with the 2nd battalion until demobilised in 1921.During his service in the Balkans, O'Leary contracted malaria, which was to have severe negative effects on his health for the rest of his life. O'Leary was in the same regiment as the British actor Stanley Holloway and they served together in France. After the war ended, they remained close friends and Holloway often stayed in The May Fair Hotel where O'Leary worked as a concierge. Later life Leaving his wife Greta and their two children in Britain, O'Leary returned to Canada in March 1921 with the purported intention of rejoining the RNWMP, newly renamed the Royal Canadian Mounted Police. For unknown reasons, this plan came to nothing and after some months giving lectures on his war service and working in a publishing house, O'Leary joined the Ontario Provincial Police, charged with enforcing the prohibition laws. In 1924, with his family recently arrived from England, O'Leary left the Ontario police force and became a police sergeant with the Michigan Central Railway in Bridgeburg, Ontario, receiving £33 a month. In 1925, O'Leary was the subject of several scandals, being arrested for smuggling illegal immigrants and later for irregularities in his investigations. Although he was acquitted both times, he spent a week in prison following the second arrest and lost his job with the railway. Several months later, the municipal authorities in Hamilton, Ontario loaned him £70 to pay for him and his family to return to Ireland. Although his family sailed on the SS Leticia, O'Leary remained in Ontario, working with the attorney general's office. With his health in serious decline, the British Legion arranged for O'Leary to return to Britain and work in their poppy factory. By 1932, O'Leary was living in Southborne Avenue in Colindale, had regained his health and found employment as a commissionaire at The May Fair Hotel in London, at which he was involved in charitable events for wounded servicemen. With the mobilisation of the British Army in 1939, O'Leary returned to military service as a captain in the Middlesex Regiment. O'Leary was sent to France as part of the British Expeditionary Force but had returned to Britain before the Battle of France due to a recurrence of his malaria. No longer fit for full active service, O'Leary was transferred to the Pioneer Corps and took command of a prisoner of war camp in Southern England. In 1945, he was discharged from the military as unfit for duty on medical grounds as a major and found work as a building contractor, in which career he remained until his retirement in 1954. Two of O'Leary's sons had also served in the military during the war, with both receiving the Distinguished Flying Cross for their actions. As a Victoria Cross recipient, O'Leary joined the VE day parade in 1946, but at the 1956 Centenary VC review his place was taken by an imposter travelling in a bath chair. With his health again declining, O'Leary moved to Limesdale Gardens in Edgware shortly before his death in 1961 at the Whittington Hospital in Islington. O'Leary was buried at Mill Hill Cemetery following a funeral service at the Roman Catholic Annunciation Church in Burnt Oak which was attended by an honour guard from the Irish Guards and six of his children. His medals were later presented to the Irish Guards, and are on display at the Regimental Headquarters. He is also remembered in his birthplace, the macroom-online website listing him as a prominent citizen and states that "while many might consider he was fighting with the wrong army, in the wrong war, he was nevertheless a very brave, resourceful and capable soldier who deserved the honours bestowed upon him." -

 35cm x 25cm Limerick Earl William Gill (14 October 1932 – 4 May 2014) was an Irish trumpet-player and bandleader who, with the Hoedowners, achieved fourteen Top 20 hits in the Irish charts between 1966 and 1973. As "Tim Pat", he also had a solo hit in 1971 with a novelty song, "Poor Poor Farmer".
35cm x 25cm Limerick Earl William Gill (14 October 1932 – 4 May 2014) was an Irish trumpet-player and bandleader who, with the Hoedowners, achieved fourteen Top 20 hits in the Irish charts between 1966 and 1973. As "Tim Pat", he also had a solo hit in 1971 with a novelty song, "Poor Poor Farmer".Early life and career
Earl Gill was raised in Dublin's East Wall district by his parents, William and Mary (née Hunter).His father was a pianist at the Queen's Theatre while his mother played the cello.As a boy Gill studied piano at the Royal Irish Academy of Music.] However, at the age of twelve he was involved in an accident which led to the loss of the two middle fingers of his left hand. From then on he concentrated on the trumpet and was soon proficient enough to perform in public while still in his teens. During the early 1950s, Gill played with several of Dublin's leading bands in venues such as the Olympia Theatre and the Gresham Hotel. In 1954, he formed his own band and within two years they were established as the resident dance band at the Shelbourne Hotel.Among the musicians who played in the Earl Gill Band during the 1950s was saxophonist Sonny Knowles who later found fame in Ireland as a cabaret singer. In 1959, Gill and his band were hired to back singer Ruby Murray on her tour of North America.Showband years
In 1965, Gill and his colleagues were signed up as the house band on a new Telefís Éireann country music show called Hoedown. Fronted by their new lead singer, Sean Dunphy, the band changed their name to the Hoedowners.A year later their single "Wonderful world of my dreams" reached number five in the Irish charts.The band achieved a further thirteen Top 20 hits between 1966 and 1973, becoming one of Ireland's most successful showbands. While most of their recordings highlighted Dunphy's singing voice, Earl Gill's trumpet took the lead on the instrumental single, "Sunset" (an arrangement of Offenbach's “Barcarolle”), released in 1967. "Sunset" failed to make the top twenty but Gill had greater success with his next solo recording, which he also produced. Wearing a false beard, shabby clothes and Wellington boots, he adopted the persona of "Tim Pat", a down-at-heel farmer who appeared on The Late Late Show to perform his new single, "The Poor Poor Farmer". The marketing ploy worked and the record rose to number three in the Irish Charts in February 1971.Later years
Following the disbandment of The Hoedowners in 1973, Gill continued to play a prominent role on the Irish music scene. He was one of a number of Irish jazz musicians, including Louis Stewart and Noel Kelehan, who performed together on an ad hoc basis at events such as the Cork Jazz Festival. Gill managed a number of pop groups, including folk rock act, Spud.He also produced recordings by The Dubliners. In the late-1970s and 1980s he was the musical director of several significant shows, including the Cavan International Song Contest, and Noel Pearson's production of Gilbert & Sullivan's H.M.S. Pinafore. In 1990, Gill released his first solo album, Enchantment, on which he played a selection of traditional Irish melodies and popular show tunes.He continued to perform live throughout Ireland until his retirement in 2012.Personal life
Earl Gill died in hospital aged eighty-one and is buried in Shanganagh Cemetery. He was married to Deirdre Kenny who predeceased him. They had three children: Derek, Earl junior, and Susan. In March 1995 Gill married his second wife, Mavis Ascott, and they had a son named Robin. -

 35cm x 25cm Limerick"Danny Boy" is a ballad, written by English songwriter Frederic Weatherly in 1913, and set to the traditional Irish melody of "Londonderry Air".
35cm x 25cm Limerick"Danny Boy" is a ballad, written by English songwriter Frederic Weatherly in 1913, and set to the traditional Irish melody of "Londonderry Air".
In 1910, in Bath, Somerset, the English lawyer and lyricist Frederic Weatherly initially wrote the words to "Danny Boy" to a tune other than "Londonderry Air". After his Irish-born sister-in-law Margaret Enright Weatherly (known as Jess) in the United States sent him a copy of "Londonderry Air" in 1913 (an alternative version of the story has her singing the air to him in 1912 with different lyrics), Weatherly modified the lyrics of "Danny Boy" to fit the rhyme and meter of "Londonderry Air". Weatherly gave the song to the vocalist Elsie Griffin, who made it one of the most popular songs of the new century. In 1915, Ernestine Schumann-Heink produced the first recording of "Danny Boy". Jane Ross of Limavady is credited with collecting the melody of "Londonderry Air" in the mid-19th century from a musician she encountered."Danny Boy"  Danny Boy
Danny BoySong Published 1913 Genre Folk Songwriter(s) Frederic Weatherly (lyrics) in 1910 Recording Performed by Celtic Aire of the United States Air Force BandLyrics
The 1913 lyrics by Frederick E. Weatherly:Oh, Danny boy, the pipes, the pipes are calling From glen to glen, and down the mountain side. The summer's gone, and all the roses falling, It's you, It's you must go and I must bide. But come ye back when summer's in the meadow, Or when the valley's hushed and white with snow, It's I'll be there in sunshine or in shadow,— Oh, Danny boy, Oh Danny boy, I love you so! But when ye come, and all the flowers are dying, If I am dead, as dead I well may be, Ye'll come and find the place where I am lying, And kneel and say an Avé there for me. And I shall hear, though soft you tread above me, And all my grave will warmer, sweeter be, For you will bend and tell me that you love me, And I shall sleep in peace until you come to me!Meaning
There are various conjectures about the meaning of "Danny Boy".Some interpret the song to be a message from a parent to a son going off to war or participating in the Irish uprising (as suggested by the reference to "pipes calling glen to glen") or emigrating as part of the Irish diaspora. The 1918 version of the sheet music with Weatherly's printed signature included alternative lyrics ("Eily Dear"), with the instructions that "when sung by a man, the words in italic should be used; the song then becomes "Eily Dear", so that "Danny Boy" is only to be sung by a lady". Nonetheless, it is unclear whether this was Weatherly's intent.Usage
- Percy Grainger's Irish Tune from County Derry adapts the Danny Boy/Londonderry Air melody for wind ensemble in 1918.
- The song is popular for funerals; but the National Catholic Reporter wrote in 2001 that it "cannot be played during Mass."
Select recordings
"Danny Boy" has been recorded multiple times by a variety of performers. Several versions are listed below in chronological order.- 1940 Judy Garland Little Nellie Kelly soundtrack. Garland also sang it live at her concerts in Ireland and Scotland and most famously at her New York Palace Theatre debut in 1951.
- 1940 Glenn Miller and His Orchestra released a single that climbed to #17 in "Pop Memories 1890-1954" (not Billboard's charts);Arranged by Glenn Miller and pianist Chummy MacGregor.
- 1941 Bing Crosby Merry Christmas. "Danny Boy" was paired with "I'll Be Home for Christmas" on its original single. Recorded July 5, 1941.
- 1941 Deanna Durbin in the film It Started with Eve
- 1950 Al Hibbler released a single that rose to #9 on the R&B chart[12]
- 1959 Conway Twitty's version charted at #10 on the Billboard Hot 100, #18 on Top R&B.(banned by the BBC)
- 1961 Andy Williams used the song's title for his album Danny Boy and Other Songs I Love to Sing. The single hit #15 on the U.S. adult contemporary and #64 on the Hot 100 charts.
- 1964 Patti LaBelle and the Bluebelles released a single that peaked at #76 on the Hot 100.
- 1965 Jackie Wilson's version rose to #94 on the Hot 100 and #25 on the R&B charts.
- 1967 Ray Price's single hit #60 on the Hot 100 and #9 on the Country charts.
- 1992 Eric Clapton recorded an instrumental version released as a bonus track for Change the World [6]
- 1992 John McDermott released the song as an independent single.
- 1998 Sinéad O'Connor sang the song over Davy Spillane's uilleann pipes on Spillane's album The Sea of Dreams. Actor-filmmaker Gabriel Byrne said this version is his favourite.
- 2002 Johnny Cash recorded the song on his album American IV: The Man Comes Around, working with producer Rick Rubin in what would come to be the last album released during his lifetime. Cash had previously recorded the













