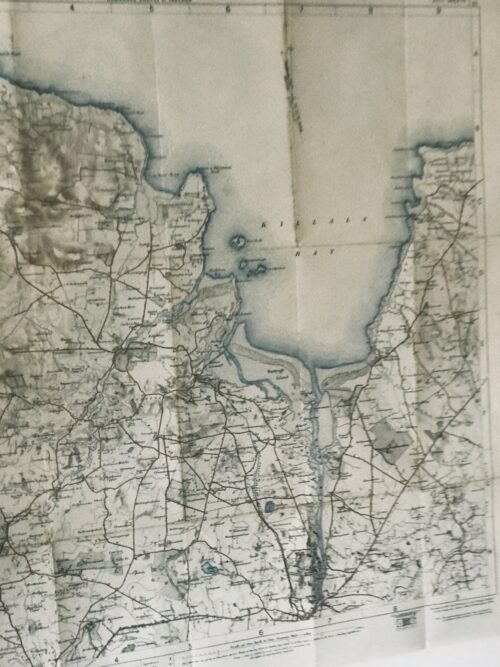
Original ordnance survey map from 19 of Killala Bay Co Mayo in superb frame.
Westport Co Mayo 65cm x 65cm
Killala is a quiet seaside resort but the harbour warehouses show that it was once a busy port. This remote little town enjoys a place of disproportionate importance in the history of Ireland, as it was here that the French first halted when they invaded in 1798.
The 1798 French invasion of Ireland
On August 6, 1798, General Humbert’s “Army of Ireland” set sail from La Rochelle destined for Killala, Co. Mayo …
La Rochelle’s harbour.
On July 19, 1798, the French Directory authorises the sending of three expeditions to Ireland and gives command of the first one to General Humbert.
On August 6, 1798, General Humbert’s Army of Ireland sailed from La Rochelle in three frigates La Concorde, La Franchise, La Médée, carrying 1,025 French troops, 3 light field cannons, 3,000 muskets, and 400 sabres.
There were also a number of Irish among Humbert’s command. These included Bartholomew Teeling and Fr. Henry O Kane.
This tiny force, together with its Irish allies, was to conduct an extraordinary campaign that shook the British Empire.
During 16 days they sailed taking a circuitous route to avoid detection by the British navy.
The mission of this little French expeditionary force was to provide military assistance to the Irish rebels of the “Rising of ’98” – sometimes referred to as “Bliadhan na bhFrancach” or
“The Year of the French” – in their attempt to free Ireland from English domination.
The fleet had originally planned to land in Co. Donegal, but due to storm and no doubt influenced by the presence of Fr. O Kane who was a native of Killala the fleet sailed into Killala Bay.

Kilcumminn head, Co. Mayo
On the 22nd of August, 1798, the three frigates landed at Kilcummin flying the English colours.
Edwin and Arthur Stock, sons of the Protestant Bishop of Killala, who had sailed out to meet them, greeted them. The two were captured, the English flag taken down and the French flag hoisted.
One of the first to disembark was Fr. O Kane who spoke to the locals in Irish which was the native tongue of most of the Irish at that time.
Word soon filtered to native Irish throughout Mayo and Sligo.

Kilcumminn strand,landing-place of the French
Bishop Stock also heard of the arrival and he sent messages to the local gentry among them the Jacksons, the Knoxs, Binghams, Palmers and Kirkwoods. Into the relative quiescence of northwest Ireland, the French expeditionary force fell like a thunderbolt.
By about 7pm the landing was complete.

General Humbert
Young Général Jean-Joseph-Amable Humbert (the landing occurred on his 31st birthday), a canny veteran of irregular warfare against the insurgents of the Vendée, was well aware of the odds against him in a conventional military showdown, but also of the multiplying effects of surprise and speed.
He was also keenly aware of the importance of early victory for exciting the morale of the Irish insurgents and dismaying the ill-trained loyalist militia.
The first military confrontation occurred on the afternoon of 22 August, when Colonel Jean Sarrazin led a group of French Grenadiers south to the nearby village of Killala.

Killala, viewed from the north.
The garrison of 200 men included a handful of regulars of the 17th Foot (Leicestershire Regiment), but was mostly composed of the Yeomanry, an ill-trained part-time paramilitary
constabulary.
With a portion of Sarrazin’s force circling around the British left flank and the remainder pressing a frontal attack with the bayonet, the unnerved Loyalists fired one ragged volley and then fled in terror towards Ballina.
Three Frenchmen were slightly wounded, bishop Stock’s palace was taken over as Humbert’s H.Q. and several of the yeomen were taken prisoner.

Ireland forever – l’Irlande pour toujours
A French soldier then climbed to the top of the palace and removed the British flag, which was replaced by a green and gold flag bearing the inscription ‘Erin Go Bragh’ (Ireland forever).

General Humbert statue in Killala.
LIBERTY, EQUALITY, FRATERNITY, UNION
“After several unsuccessful attempts behold at last Frenchmen arrived amongst you . . .
“Brave Irishmen, our cause is common. Like you we hold as indefeasible the right of all nations to liberty. Like you we are persuaded that the peace of the world shall ever be troubled as long as the British ministry is suffered to make with impunity a traffic of the industry and blood of the people . . .
“Union, Liberty, the Irish Republic! Such is our shout. Let us march. Our hearts are devoted to you; our glory is in your happiness.”
From General Humbert’s Proclamation
of 22nd August, 1798.
(This last sentence of Humbert’s Proclamation became our pub’s motto!)

Mémorial de Ballina
This initial humbling of their oppressors had the desired effect on the local population, bringing forward thousands of eager, though ignorant and ill-disciplined Irish volunteers who were hastily equipped and formed into companies.
Muskets were issued to some, but as in the uprisings elsewhere in Ireland that year, most of the insurgents were armed with crude pikes, scythes, and hay-forks.
On the 24th of August, having captured Killala, Humbert sent two groups under
Sarrazin (provisionally promoted to Général de Brigade by Humbert on 23 August) and
Adjudant-General Fontaine to capture Ballina.
That night a fight took place between Sarrazin’s troops and the British at Rosserk. The English eventually retreated in confusion.
The next morning the French/Irish troops captured Ballina under cover of darkness. The Irish peasants lit bundles of straw to show them their way. This approach road to Ballina has since been known as Bothair na Sop. They took Ballina without much resistance.
The English for the most part fled towards Foxford where they would have their forces waiting for the French advance on Castlebar.

Humbert – Windy Gap Pass
The British commander in County Mayo, General Hutchinson, expected Humbert to continue south along the only decent road out of Ballina toward Castlebar, the commercial and strategic center of the region.
Where the road crosses the River Moy at Foxford, Hutchinson placed a strong blocking force with ample artillery.
Clashes of French and British patrols along the Ballina-Foxford road appeared to confirm British expectations.
Humbert, closely questioning the locals, learned that there was an alternative route to Castlebar, a barely-practicable goat-trail that ran west of Lough Conn, over the Windy Gap pass, and then south to the town. He resolved to take this route.

“Tour D’Humbert” signposts in Lahardane
To further the deception, the Franco-Irish forces marched out of Ballina along the Foxford road at sunset on August 26 with ostentatious noise and shouted boasts of expected victory at Foxford, then doubled back in silence and darkness to the west of Loch Conn.
At midnight, Humbert’s army was in Lahardane.
The local priest, Father Andrew Conroy, was fluent in French from his time at seminary in Nantes.
He gave precious directions to the French officers and marshalled the people to provide food and assistance to the troops. In the aftermath of the campaign, Father Conroy was arrested, tried, and executed by the vengeful British.

Sion Hill (now built-up)
After a rigorous night-march of 40 km (25 miles), Humbert’s 800 French, 600 Irish, and 1 laboriously manhandled gun reached Castlebar on 27 August.
A yeoman farmer who had been tending to his cattle had spotted the French/Irish advance party.
He immediately fled to Castlebar to warn the British commander of the eminent arrival of the French/Irish forces.
The English forces took up position at Sion Hill just outside the town. Humbert approached and took account of the English position.

Batlle of Castlebar known as “Races of Castlebar”.
Following a number of attacks in which they were hit by British cannon, Humbert decided to regroup and divided his troops, splitting them to the left and right so as to attack the English flanks.
The Irish drove a herd of cattle ahead of them causing confusion in the English rank.
The French/Irish made an effective bayonet charge through the centre.

Castlebar Memorial
The English retreated down Staball Hill. Another attack occurred at Main St. Bridge. The English defended the bridge for some time using forces from the Longford and Kilkenny militias and Fraser Fencibles (a Scottish regiment).
There was confused fighting in the town as knots of the more stalwart British, notably the Fraser Fencibles and Roden’s Dragoons, attempted to make a stand.
The bulk of the redcoat forces, abandoning all guns, standards, and baggage, ran in headlong flight down the road to Tuam, 54 km (34 miles) to the southeast; some apparently did not stop until reaching Athlone, a further 68 km (42 miles) away.
General Lake’s army being dissolved.
The event has since become mockingly known among the Irish as
“The Castlebar Races.”
In all the attack only lasted six hours from 6a.m. to 12 noon and has been
described by Thomas Pakenham in The Year of Liberty as one of the most ignominious defeats in British military history.
Following this brilliant victory, Humbert spent the next few days resting and reorganizing his army, absorbing many hundreds of new Irish volunteers including some 250 deserters from the Longford and Kilkenny Militias.
The “Republic of Connaught” was proclaimed and a makeshift revolutionary government installed.
Army of Ireland – Liberty, Equality
Head quarters at Castlebar, 14th Fructidor, sixth Year of the French Republic, One and Indivisible.
General Humbert, Commander in Chief of the Army of Ireland, desirous of organizing with the least possible delay, an administrative power for the Province of Connaught, decrees as follows:
1. The Government of the Province of Connaught shall reside at Castlebar till further orders.
2. The Government shall be composed of twelve members, who shall be named by the General-in-chief of the French Army.
3. Citizen
JOHN MOORE is named President of the Government of the Province of Connaught, he is specially entrusted with the nomination and reunion of the members of the Government.
4. The Government shall occupy itself immediately in organizing the Military power of the Province of Connaught, and with providing subsistence for the French and Irish Armies.
5. There shall be organized eight regiments of infantry, each of twelve hundred men, and four regiments of cavalry, each of six hundred men.
6. The Government shall declare rebels and traitors to the country all those who having received clothing and arms, shall not join the army within four and twenty hours.
7. Every individual from sixteen years of age to forty, inclusive, is REQUIRED in the name of the Irish Republic, to betake himself instantly to the French Camp, to march in a mass against the common enemy.
The General Commanding-in-Chief
HUMBERT.

Lord Cornwallis
It was obvious that after the fiasco of Castlebar, the Crown forces in Ireland would marshal every possible resource to crush Humbert.
Lord Cornwallis (the same who had surrendered to Washington at Yorktown), now the Viceroy and Commander-in-Chief in Ireland, moved west from Dublin to take personal command of the campaign.
By the 2nd of September, Cornwallis had 7,800 men, including two reliable Scottish regiments (the Sutherland and Rehy Fencibles) concentrated at Tuam, organized into four brigades under Generals Hunter, Campbell, Hutchinson, and Moore (later the hero of Corunna), and a further 2,800 at Boyle.
Cornwallis advanced from Tuam on the 4th of September, but on arriving at Castlebar on the 5th found only a small Franco-Irish rearguard.
Aware of the impossibility of defeating the well-equipped and far more numerous Crown forces, and with no sign of reinforcements from France, Humbert had marched off to the east on 4 September, under cover of darkness, taking his army, now totalling 3,000 men, towards Sligo, covering 58 miles in 36 hours. The long march had begun.
Some Irish troops under French officers remained to protect Killala and receive the expected reinforcements.

Collooney, Co. Sligo
On the morning of the 5th of September, an English army from Sligo under Col Vereker attacks the Franco-Irish army at Collooney with its left protected by the Ballysadare River and its right anchored on a steep, wooded hill. Humbert again outmanoeuvres them.
In what may be one of the greatest feats of individual bravery in the long history of the Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars,
Colonel Bartholomew Teeling, a United Irishman holding a French commission, galloped forward alone to the British line, pistolled the enemy gunner at point-blank range, and rode back unscathed under a hail of musket-fire.
Inspired by his example, the Irish and French surged forward and routed the Loyalists.
The English retreated with heavy losses as far as Ballyshannon, County Donegal.

Ballinamuck pikeman
Cornwallis has now divided his army in two, one half under General Lake to pursue the enemy and the other half, under his own personal command, to protect the line of the river Shannon.
The French and Irish “must not cross”.
Meanwhile, the United Irishmen of Longford and Westmeath have assembled.
They capture Wilson’s Hospital near Mullingar but fail to take the town of Granard.
Humbert, on hearing of the midlands rising decides to link up with the insurgents there.
He is now near Manorhamilton but changes and goes straight for Granard. He abandons some of the heavier guns so as to make more speed.
So far he has eluded the cordon closing in around him. With some luck he hopes to slip past the net, reach Granard and then strike for Dublin which is virtually unprotected as most of the garrison have been moved to Connacht.
The Franco-Irish army reaches Drumkeerin in the evening of September 6. An envoy from Lord Cornwallis offers terms for surrender but they are rejected.
On September 7, shortly before noon Humbert’s army crosses the Shannon at Ballintra Bridge just south of Loch Allen, but they fail in an attempt to demolish the bridge behind them.
His army shows signs of fatigue and skirmishes with the English advance guard become more frequent. The race for Granard quickens.
The Franco-Irish army reaches Cloone, in South Leitrim, while Cornwallis, with 15,000 men is at Mohill, five miles away. Humbert gets news that he is surrounded and outnumbered but decides to push on even if the best he can now do is to make a token resistance before surrender.
On September 8, 1798, near the small village of Ballinamuck, County Longford, Humbert drew up his 859 French troops in line of battle.
There could be little doubt of the outcome.
Behind Humbert was Cornwallis blocking Humbert’s way to Dublin. In front was Lake’s 6000 men.
The battle which lasted but half an hour commenced with Colonel Crawford’s dragoons cutting through the Irish rebels.
When the British grand assault poured up the hill from three sides, in overwhelming numbers, Humbert gave the order to surrender.

Humbert surrenders in Ballinamuck
The French officers followed their general’s signal and ordered their men to lay down their muskets. A second body of British cavalry had reined in seeing the signs of surrender, but Colonel Teeling, an Irish officer in the French army, had not signaled surrender so British infantry advanced on them. Crawford attacked a large contingent of Irishmen with his dragoons, their sabres sparing only those with officers insignia, hanging to be their fate.
Later testimonies reveal that on arresting Humbert, General Lake could not conceal his astonishment:
“Where is your army?”
Lake demanded
“This is it all”
Humbert replied, indicating his soldiers.
“And what were you planning to do with this lot?”
Lake asked.
“We were going to Dublin to break the irons of a nation that suffers under your yoke”
Humbert said.
“That is an idea that could only be born in a Frenchman’s brains!”
Lake declared.

Humbert surrenders in Ballinamuck
Humbert and the French prisoners were conducted to Dublin and treated with all the consideration that could be given to gallant prisoners after an honorable defeat.
Not so the Irish. Accounts vary, but it appears that many of the Irish were cut down where they stood, or driven into the bog south of the hill where they were hunted down and slaughtered.
Captured Irish officers, even those bearing legitimate commissions in the French army, were seized and hanged as traitors. Such was Bartholomew Teeling, Matthew Tone and Gunner James Magee’s fate.
“After having obtained the greatest successes and made the arms of the French Republic triumph during my stay in Ireland, I have at length been obliged to submit to a superior force of 30,000 troops.”
General Humbert’s Report to the French Directory after Ballinamuck.
‘A SHORT BUT VERY FATIGUING CAMPAIGN’
English historians have always treated General Humbert’s expedition to Ireland with ridicule, but Brian O hUiginn was fond of quoting Plowden the military correspondent of the London Times who held a different view. This expert wrote some years ago:
“In these operations described by Cornwallis to the Duke of Portland as a short but very fatiguing campaign, a raiding party of 1000 French landed in Ireland without opposition, after sixteen days of navigation, unobserved by the British Navy; defeated and drove back the British troops opposing them on four separate occasions; routed a force of second line troops of at least double its strength; captured eleven British guns; held the field for seventeen days; entirely occupied the attention of all the available troops of a garrison of Ireland 150,000 strong; penetrated almost to the centre of the island, and compelled the Lord Lieutenant to send an urgent requisition to London for ‘as great a reinforcement as possible.’ “
This was a fine tribute to General Humbert and his troops.

- In Humbert’s footsteps 2013 – Killala & Castlebar

- In Humbert’s footsteps 2013 – Killala & Castlebar

- In Humbert’s footsteps 2013 – Killala & Castlebar

- In Humbert’s footsteps 2013 – Killala & Castlebar
The Charentais of the expedition.
Many Charentais took part in the expedition. Among them:
Daniel Savary, who was born in Salles sur Mer (17), was in command of the naval division charged with transporting the expedition from La Rochelle to Killala.
François Babin, born in Péré (17), became Commander of the Castlebar battalion.
Jean Jobit, born in Chateauneuf en Charente (16), was a Commander on the Castlebar battlefield in Castlebar.
Jean-Paul Leugerat, born in Barbezières (16), died during the battle of Castlebar.