-

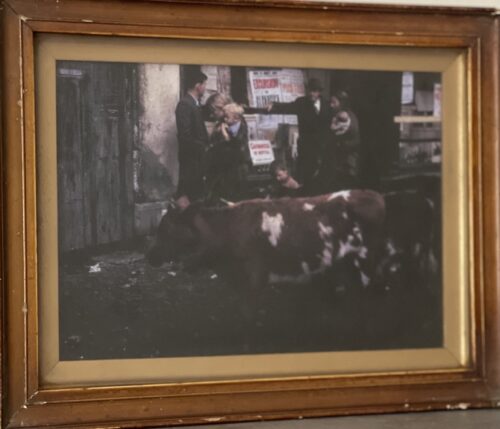
 50cm x 65cm Artane Dublin Classic Smithwicks Ale Advertising Showcard-(1960s era)-Brewed in Ireland.Please contact us directly at irishpubemporium@gmail.com for pricing and shipment quotation. The old Smithwicks brewery is on the site of a Franciscan abbey, where monks had brewed ale since the 14th century, and ruins of the original abbey still remain on its grounds. The old brewery has since been renovated and now hosts "The Smithwick's Experience Kilkenny" visitor attraction and centre.At the time of its closure, it was Ireland's oldest operating brewery. John Smithwick was an orphan who had settled in Kilkenny. Shortly after his arrival, Smithwick went into the brewing business with Richard Cole on a piece of land that Cole had leased from the Duke of Ormond in 1705. Five years later, John Smithwick became the owner of the land. The brewery stayed small, servicing a loyal local following while John Smithwick diversified. Following John Smithwick's death, the brewery temporarily fell out of family hands. John Smithwick's great grandson, Edmond bought the brewery land back freehold and worked to reshape its future. Edmond concentrated on discovering new markets and successfully building export trade. Drinkers in England, Scotland and Wales developed a taste for Smithwick's brews and output increased fivefold. As a result of substantial contributions made to St Mary's Cathedral, Edmond became great friends with Irish liberal Daniel O'Connell, who later became godfather to one of his sons. Edmond Smithwick became well known and respected by the people of Kilkenny who elected him town mayor four times. In 1800, export sales began to fall and the brewing industry encountered difficulty. To combat this, the Smithwick family increased production in their maltings, began selling mineral water and delivered butter with the ale from the back of their drays.By 1900, output was at an all-time low and the then owner James Smithwick was advised by auditors to shut the doors of the brewery. Instead, James reduced the range of beers they produced and set out to find new markets. He secured military contracts and soon after saw output increase again. James' son, Walter, took control in 1930 and steered the brewery to success through the hardships of both World War II and increasingly challenging weather conditions.By January 1950, Smithwick's was exporting ale to Boston.Smithwick's was purchased from Walter Smithwick in 1965 by Guinness and is now, along with Guinness, part of Diageo. Together, Guinness & Co. and Smithwick's developed and launched Smithwick's Draught Ale in 1966. By 1979, half a million barrels were sold each year.In 1980, Smithwick's began exporting to France. In 1993, Smithwick's Draught became Canada's leading imported ale.By 2010, Smithwick's continued to be brewed in Dundalk and Kilkenny with tankers sent to Dublin to be kegged for the on trade market. Cans and bottles were packaged by IBC in Belfast.Production in the Kilkenny brewery finished on 31 December 2013 and Smithwicks brands are now produced in the Diageo St.James' Gate brewery in Dublin.The original Kilkenny site was sold to Kilkenny County Council, with a small portion of the site dedicated to the opening of a visitor's centre, the "Smithwick's Experience Kilkenny".
50cm x 65cm Artane Dublin Classic Smithwicks Ale Advertising Showcard-(1960s era)-Brewed in Ireland.Please contact us directly at irishpubemporium@gmail.com for pricing and shipment quotation. The old Smithwicks brewery is on the site of a Franciscan abbey, where monks had brewed ale since the 14th century, and ruins of the original abbey still remain on its grounds. The old brewery has since been renovated and now hosts "The Smithwick's Experience Kilkenny" visitor attraction and centre.At the time of its closure, it was Ireland's oldest operating brewery. John Smithwick was an orphan who had settled in Kilkenny. Shortly after his arrival, Smithwick went into the brewing business with Richard Cole on a piece of land that Cole had leased from the Duke of Ormond in 1705. Five years later, John Smithwick became the owner of the land. The brewery stayed small, servicing a loyal local following while John Smithwick diversified. Following John Smithwick's death, the brewery temporarily fell out of family hands. John Smithwick's great grandson, Edmond bought the brewery land back freehold and worked to reshape its future. Edmond concentrated on discovering new markets and successfully building export trade. Drinkers in England, Scotland and Wales developed a taste for Smithwick's brews and output increased fivefold. As a result of substantial contributions made to St Mary's Cathedral, Edmond became great friends with Irish liberal Daniel O'Connell, who later became godfather to one of his sons. Edmond Smithwick became well known and respected by the people of Kilkenny who elected him town mayor four times. In 1800, export sales began to fall and the brewing industry encountered difficulty. To combat this, the Smithwick family increased production in their maltings, began selling mineral water and delivered butter with the ale from the back of their drays.By 1900, output was at an all-time low and the then owner James Smithwick was advised by auditors to shut the doors of the brewery. Instead, James reduced the range of beers they produced and set out to find new markets. He secured military contracts and soon after saw output increase again. James' son, Walter, took control in 1930 and steered the brewery to success through the hardships of both World War II and increasingly challenging weather conditions.By January 1950, Smithwick's was exporting ale to Boston.Smithwick's was purchased from Walter Smithwick in 1965 by Guinness and is now, along with Guinness, part of Diageo. Together, Guinness & Co. and Smithwick's developed and launched Smithwick's Draught Ale in 1966. By 1979, half a million barrels were sold each year.In 1980, Smithwick's began exporting to France. In 1993, Smithwick's Draught became Canada's leading imported ale.By 2010, Smithwick's continued to be brewed in Dundalk and Kilkenny with tankers sent to Dublin to be kegged for the on trade market. Cans and bottles were packaged by IBC in Belfast.Production in the Kilkenny brewery finished on 31 December 2013 and Smithwicks brands are now produced in the Diageo St.James' Gate brewery in Dublin.The original Kilkenny site was sold to Kilkenny County Council, with a small portion of the site dedicated to the opening of a visitor's centre, the "Smithwick's Experience Kilkenny". -
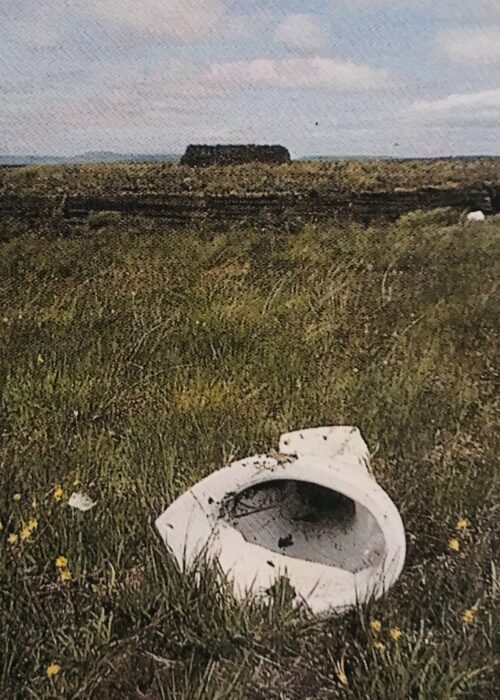

 We were very fortunate to acquire this very famous poster-The Bogs of Ireland.A collage of some very interesting toilets recorded for eternity by the renowned photographer John Morris.This poster is now completely out of print and is difficult to acquire.Makes a wonderful addition to anyone's favourite sanctuary and place of solitude! Each poster is individually numbered. Dimensions : 65cm x 45cm
We were very fortunate to acquire this very famous poster-The Bogs of Ireland.A collage of some very interesting toilets recorded for eternity by the renowned photographer John Morris.This poster is now completely out of print and is difficult to acquire.Makes a wonderful addition to anyone's favourite sanctuary and place of solitude! Each poster is individually numbered. Dimensions : 65cm x 45cm -

 Guinness advertising has become an institution, virtually since Arthur Guinness set up the brewery in 1779.Today Guinness advertising is not just a subject for fond remembrance of past campaigns - nowadays its a subject for the specialist collector.Every item, from original artwork to old Guinness labels -has a price and a buyer. 30cm x 25cm Bruff Co Limerick All Guinness advertising has done is create a focal point for peoples interest in and affection for,Guinness itself- that curious looking drink with a curious sounding name. Indeed its tempting to talk about Guinness advertising as if it were a generic term,describing a particular type or style of advertising.This is not the case-in its form, content and approach ,Guinness advertising has been as varied as the communications media it has enployed. When the brewery giant first began advertising in 1928,there had been very little study done in the field of market research and the critical analysis of what became to be called the "persuasion industry' had yet to take place.In launching its first campaign, however,Guinness decreed that its advertisements 'should at all times be done extremely well and in good taste -S.H Benson Ltd.,the venerable advertising agency charged with carrying out that edict,began with a refreshing directness- an appetising pint of what is affectionately called the 'black stuff' and the simple slogan:'GUINNESS is good for you.' Guinness has since always been among the leaders in the development of the craft of advertising and from the outset, they have been particularly conscious of their public responsibilities as an advertiser.Its fair to say no other alcoholic beverage has acquired the universal goodwill possessed by Guinness.Stanley Penn,one of Bensons copyrighters once remarked ' Guinness always enjoyed their advertising.They liked their advertising to be liked'.and so Bensons gave the already household Guinness name character and personality ,they made its friend more than a mere acquaintance. After a few years ,some money and a lot of imagination later,Bensons began mixing their Guinness with a dash or two of levity and humour.It was the beginning of many years of fun and frolics-starting with John Gilroys' charming menagerie of Guinness guzzling animals and the most outrageous puns and parodies- right up to the present day.
Guinness advertising has become an institution, virtually since Arthur Guinness set up the brewery in 1779.Today Guinness advertising is not just a subject for fond remembrance of past campaigns - nowadays its a subject for the specialist collector.Every item, from original artwork to old Guinness labels -has a price and a buyer. 30cm x 25cm Bruff Co Limerick All Guinness advertising has done is create a focal point for peoples interest in and affection for,Guinness itself- that curious looking drink with a curious sounding name. Indeed its tempting to talk about Guinness advertising as if it were a generic term,describing a particular type or style of advertising.This is not the case-in its form, content and approach ,Guinness advertising has been as varied as the communications media it has enployed. When the brewery giant first began advertising in 1928,there had been very little study done in the field of market research and the critical analysis of what became to be called the "persuasion industry' had yet to take place.In launching its first campaign, however,Guinness decreed that its advertisements 'should at all times be done extremely well and in good taste -S.H Benson Ltd.,the venerable advertising agency charged with carrying out that edict,began with a refreshing directness- an appetising pint of what is affectionately called the 'black stuff' and the simple slogan:'GUINNESS is good for you.' Guinness has since always been among the leaders in the development of the craft of advertising and from the outset, they have been particularly conscious of their public responsibilities as an advertiser.Its fair to say no other alcoholic beverage has acquired the universal goodwill possessed by Guinness.Stanley Penn,one of Bensons copyrighters once remarked ' Guinness always enjoyed their advertising.They liked their advertising to be liked'.and so Bensons gave the already household Guinness name character and personality ,they made its friend more than a mere acquaintance. After a few years ,some money and a lot of imagination later,Bensons began mixing their Guinness with a dash or two of levity and humour.It was the beginning of many years of fun and frolics-starting with John Gilroys' charming menagerie of Guinness guzzling animals and the most outrageous puns and parodies- right up to the present day. -
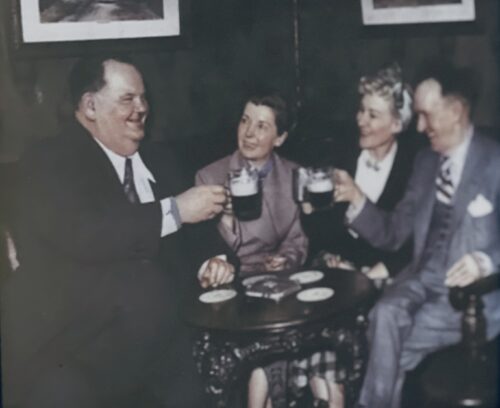
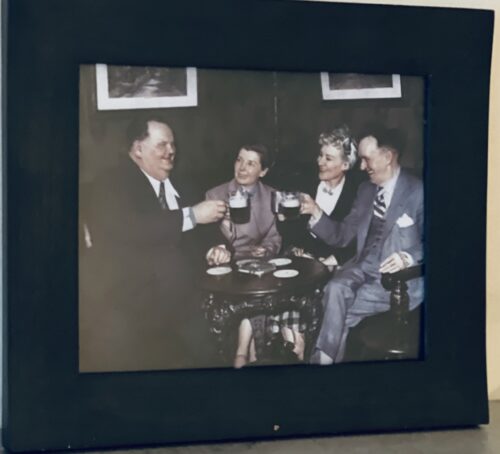
 32cm x 27cm
32cm x 27cmTHE famous comedy team of Stan Laurel and Oliver Hardy were scheduled to disembark from the liner ‘America’ which called at Cobh today from New York. No elaborate reception was planned, and the shipping officials carried out the usual arrangements for the arrival of important passengers.
The famous pair wanted no fuss, and of course, the liner company officals were anxious to carry out to the letter the wishes of their first-class passengers.
Mr Sean O’Brien, Irish manager of US Lines, said his officials were there to greet them and satisfy their slightest wish.
But often on the occasion when the planning is most careful, something goes wrong. And in this case it did. For neither the comedians, nor their wives, nor the company officials, nor the police nor the many other people associated with the life of a trans- Atlantic port of call, reckoned with the children, to whom the funny faces and the queer screen antics of the cuckoo comedians is better known than the president of the US.
The entire children’s population of Cobh must have played truant from school for they blocked all traffic, and despite the presence of several vastly amused policemen, they clung onto Laurel and Hardy.
They begged for autographs, ruffled their ties and generally gave them a whole-hearted reception.
Non-plussed, but only for a moment, the comedians entered into the fun of the affair, and nobody could accuse them of being stinted in giving autographs.
Twenty-three stone Hardy (22st 12lbs to be exact) commented: “We were absolutely overwhelmed. There scarcely ever was a film scene like it. They are grand children, and Stan and I are grateful to them.”
There was no great advance publicity, but all of Cobh and outlying districts seemed to know that Laurel and Hardy had arrived. Family parties went out in small boats and cheered as the tender bearing the passengers from the liner drew into the quayside.
The party were taken by Mr O’Brien to hear the carillon bells of Cobh Cathedral and the comedians told an Echo reporter that hearing the ‘Cuckoo Song’ played on the bells was one of the greatest thrills of their lives.
Later, the party went to kiss the Blarney Stone. All performed the traditional rite of kissing except Hardy, who commented: “Nobody would hold me. I am too big.”
Ald P McGrath, Lord Mayor of Cork, accompanied by Mr AA Healy, TC, received them at the City Hall and was photographed with them. Asked to nominate their favourite film the bluff Oliver replied: “Fra Diavolo.”
They have been partners for thirty years. Subsequently the comedians and their wives left for Dublin where they are to fulfil a theatrical engagement.
Amongst the others who met them in Cobh was Mrs D Murphy, on behalf of Mr George Heffernan, Tourist Agent, Cork.
Another passenger to disembark from the vessel was the Hon Kit Clardy, Republican Senator from Michigan. He intends to spend a short holiday in this country. In all, 117 disembarked at Cobh.
Embarking passengers included a party of 40 pilgrims from Cork to Lourdes and Liseux. The spiritual director to the party is Rev Maurice Walsh, SMA, and the pilgrimage arrangements were in the hands of Miss B Arnold, of Mr Heffernan’s agency.
-
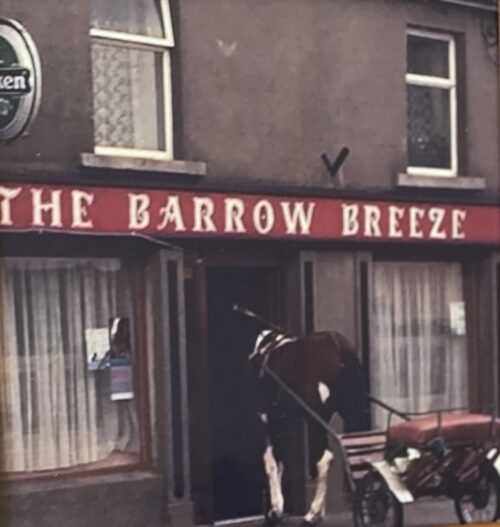
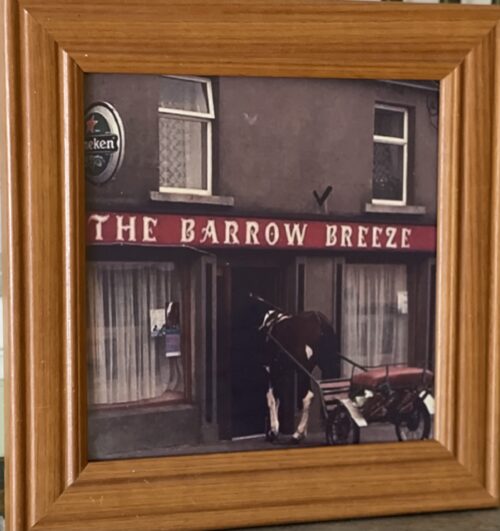
 27cm x 27cm The Barrow Breeze is a pub in the capital of the Irish Sporthorse business-Goresbridge Co Kilkenny. Goresbridge (Irish: An Droichead Nua, meaning 'The New Bridge') is a small village located in the east of County Kilkenny, in the province of Leinster, Ireland. Goresbridge is named after a 1756 bridge, built by Colonel Ralph Gore, which provides a crossing of the River Barrow between County Kilkenny and County Carlow in the South-East region. Located 2.75 miles (4.43 km) from Gowran on the R702 (Kilkenny−Enniscorthy) regional road, and approximately 20 kilometres (12 mi) east of Kilkenny. Part of the civil parish is Grangesilvia which is in the barony of Gowran. King Charles II granted Arthur Gore the townland of Barrowmount. The "Battle of Goresbridge" occurred there in June 1798. The 2011 census the population of the census town was 361. The local authority is Kilkenny County Council. Goresbridge gives its name to a district electoral division Goresbridge was located in historic Gaelic kingdom of Ossory (Osraige). Following the Williamite–Jacobite War King Charles II gave grants of land which had been forfeited by the Roman Catholic owners. Arthur Gore obtained a grant of land, the townland of Barrowmount in parish of Grangesilvia, from Charles II,and by the end of the 17th century the Gore family were well established. "Goresbridge" was named for the family and the New Bridge built in 1756 by Colonel Ralph Gore. On the 1846 OSI map of Ireland the village is referred to it as Newbridge.
27cm x 27cm The Barrow Breeze is a pub in the capital of the Irish Sporthorse business-Goresbridge Co Kilkenny. Goresbridge (Irish: An Droichead Nua, meaning 'The New Bridge') is a small village located in the east of County Kilkenny, in the province of Leinster, Ireland. Goresbridge is named after a 1756 bridge, built by Colonel Ralph Gore, which provides a crossing of the River Barrow between County Kilkenny and County Carlow in the South-East region. Located 2.75 miles (4.43 km) from Gowran on the R702 (Kilkenny−Enniscorthy) regional road, and approximately 20 kilometres (12 mi) east of Kilkenny. Part of the civil parish is Grangesilvia which is in the barony of Gowran. King Charles II granted Arthur Gore the townland of Barrowmount. The "Battle of Goresbridge" occurred there in June 1798. The 2011 census the population of the census town was 361. The local authority is Kilkenny County Council. Goresbridge gives its name to a district electoral division Goresbridge was located in historic Gaelic kingdom of Ossory (Osraige). Following the Williamite–Jacobite War King Charles II gave grants of land which had been forfeited by the Roman Catholic owners. Arthur Gore obtained a grant of land, the townland of Barrowmount in parish of Grangesilvia, from Charles II,and by the end of the 17th century the Gore family were well established. "Goresbridge" was named for the family and the New Bridge built in 1756 by Colonel Ralph Gore. On the 1846 OSI map of Ireland the village is referred to it as Newbridge.Gore's Bridge
Gore's Bridge has nine-arch's granite bridge crossing of the River Barrow between County Kilkenny and County Carlow. Built in 1756 by Colonel Ralph Gore the Earl of Ross. This mid eighteenth-century elegantly-composed landmark was built using unrefined Carlow granite.It represents an important element of civil engineering and transport heritage and formed a vital link between the two counties.Battle of Goresbridge
The Battle of Goresbridge occurred during the Irish Rebellion on 23 June 1798 at Gore's Bridge.During the Wexford Rebellion, and just days Battle of Vinegar Hill, Wexford insurgents attempted to use the Gore's Bridge. The locally stationed Wexford Militia were defeated, they lost their cavalry, twenty eight soldiers were captured, and the rest fled to Kilkenny.There is a carved granite memorial adjacent to the bridge.Transport
Goresbridge railway station opened on 26 October 1870, closed for passenger traffic on 26 January 1931 and for goods traffic on 27 January 1947, finally closing altogether on 1 April 1963. Kilbride Coaches services Goresbridge from Graiguenamanagh or Kilkenny twice a day, except Sundays -
 55cm x 45cm Luke Kelly (17 November 1940 – 30 January 1984) was an Irish singer, folk musician and actor from Dublin, Ireland. Born into a working-class household in Dublin city, Kelly moved to England in his late teens and by his early 20s had become involved in a folk music revival. Returning to Dublin in the 1960s, he is noted as a founding member of the band The Dubliners in 1962. Becoming known for his distinctive singing style, and sometimes political messages, the Irish Postand other commentators have regarded Kelly as one of Ireland's greatest folk singers. Early life Luke Kelly was born into a working-class family in Lattimore Cottages at 1 Sheriff Street.His maternal grandmother, who was a MacDonald from Scotland, lived with the family until her death in 1953. His father who was Irish- also named Luke- was shot and severely wounded as a child by British soldiers from the King's Own Scottish Borderers during the 1914 Bachelor's Walk massacre.His father worked all his life in Jacob's biscuit factory and enjoyed playing football. The elder Luke was a keen singer: Luke junior's brother Paddy later recalled that "he had this talent... to sing negro spirituals by people like Paul Robeson, we used to sit around and join in — that was our entertainment". After Dublin Corporation demolished Lattimore Cottages in 1942, the Kellys became the first family to move into the St. Laurence O’Toole flats, where Luke spent the bulk of his childhood, although the family were forced to move by a fire in 1953 and settled in the Whitehall area. Both Luke and Paddy played club Gaelic football and soccer as children. Kelly left school at thirteen and after a number of years of odd-jobbing, he went to England in 1958.[6] Working at steel fixing with his brother Paddy on a building site in Wolverhampton, he was apparently sacked after asking for higher pay. He worked a number of odd jobs, including a period as a vacuum cleaner salesman.Describing himself as a beatnik, he travelled Northern England in search of work, summarising his life in this period as "cleaning lavatories, cleaning windows, cleaning railways, but very rarely cleaning my face".
55cm x 45cm Luke Kelly (17 November 1940 – 30 January 1984) was an Irish singer, folk musician and actor from Dublin, Ireland. Born into a working-class household in Dublin city, Kelly moved to England in his late teens and by his early 20s had become involved in a folk music revival. Returning to Dublin in the 1960s, he is noted as a founding member of the band The Dubliners in 1962. Becoming known for his distinctive singing style, and sometimes political messages, the Irish Postand other commentators have regarded Kelly as one of Ireland's greatest folk singers. Early life Luke Kelly was born into a working-class family in Lattimore Cottages at 1 Sheriff Street.His maternal grandmother, who was a MacDonald from Scotland, lived with the family until her death in 1953. His father who was Irish- also named Luke- was shot and severely wounded as a child by British soldiers from the King's Own Scottish Borderers during the 1914 Bachelor's Walk massacre.His father worked all his life in Jacob's biscuit factory and enjoyed playing football. The elder Luke was a keen singer: Luke junior's brother Paddy later recalled that "he had this talent... to sing negro spirituals by people like Paul Robeson, we used to sit around and join in — that was our entertainment". After Dublin Corporation demolished Lattimore Cottages in 1942, the Kellys became the first family to move into the St. Laurence O’Toole flats, where Luke spent the bulk of his childhood, although the family were forced to move by a fire in 1953 and settled in the Whitehall area. Both Luke and Paddy played club Gaelic football and soccer as children. Kelly left school at thirteen and after a number of years of odd-jobbing, he went to England in 1958.[6] Working at steel fixing with his brother Paddy on a building site in Wolverhampton, he was apparently sacked after asking for higher pay. He worked a number of odd jobs, including a period as a vacuum cleaner salesman.Describing himself as a beatnik, he travelled Northern England in search of work, summarising his life in this period as "cleaning lavatories, cleaning windows, cleaning railways, but very rarely cleaning my face".Musical beginnings
Kelly had been interested in music during his teenage years: he regularly attended céilithe with his sister Mona and listened to American vocalists including: Fats Domino, Al Jolson, Frank Sinatra and Perry Como. He also had an interest in theatre and musicals, being involved with the staging of plays by Dublin's Marian Arts Society. The first folk club he came across was in the Bridge Hotel, Newcastle upon Tyne in early 1960.Having already acquired the use of a banjo, he started memorising songs. In Leeds he brought his banjo to sessions in McReady's pub. The folk revival was under way in England: at the centre of it was Ewan MacColl who scripted a radio programme called Ballads and Blues. A revival in the skiffle genre also injected a certain energy into folk singing at the time. Kelly started busking. On a trip home he went to a fleadh cheoil in Milltown Malbay on the advice of Johnny Moynihan. He listened to recordings of Woody Guthrie and Pete Seeger. He also developed his political convictions which, as Ronnie Drew pointed out after his death, he stuck to throughout his life. As Drew also pointed out, he "learned to sing with perfect diction". Kelly befriended Sean Mulready in Birmingham and lived in his home for a period.Mulready was a teacher who was forced from his job in Dublin because of his communist beliefs. Mulready had strong music links; a sister, Kathleen Moynihan was a founder member of Comhaltas Ceoltóirí Éireann, and he was related by marriage to Festy Conlon, the County Galway whistle player. Mulready's brother-in-law, Ned Stapleton, taught Kelly "The Rocky Road to Dublin".During this period he studied literature and politics under the tutelage of Mulready, his wife Mollie, and Marxist classicist George Derwent Thomson: Kelly later stated that his interest in music grew parallel to his interest in politics. Kelly bought his first banjo, which had five strings and a long neck, and played it in the style of Pete Seeger and Tommy Makem. At the same time, Kelly began a habit of reading, and also began playing golf on one of Birmingham's municipal courses. He got involved in the Jug O'Punch folk club run by Ian Campbell. He befriended Dominic Behan and they performed in folk clubs and Irish pubs from London to Glasgow. In London pubs, like "The Favourite", he would hear street singer Margaret Barry and musicians in exile like Roger Sherlock, Seamus Ennis, Bobby Casey and Mairtín Byrnes. Luke Kelly was by now active in the Connolly Association, a left-wing grouping strongest among the emigres in England, and he also joined the Young Communist League: he toured Irish pubs playing his set and selling the Connolly Association's newspaper The Irish Democrat. By 1962 George Derwent Thomson had offered him the opportunity to further his educational and political development by attending university in Prague. However, Kelly turned down the offer in favour of pursuing his career in folk music. He was also to start frequenting Ewan MacColl and Peggy Seeger's Singer Club in London.The Dubliners
In 1961 there was a folk music revival or "ballad boom", as it was later termed, in waiting in Ireland.The Abbey Tavern sessions in Howth were the forerunner to sessions in the Hollybrook, Clontarf, the International Bar and the Grafton Cinema. Luke Kelly returned to Dublin in 1962. O'Donoghue's Pub was already established as a session house and soon Kelly was singing with, among others, Ronnie Drew and Barney McKenna. Other early people playing at O'Donoghues included The Fureys, father and sons, John Keenan and Sean Og McKenna, Johnny Moynihan, Andy Irvine, Seamus Ennis, Willy Clancy and Mairtin Byrnes. A concert John Molloy organised in the Hibernian Hotel led to his "Ballad Tour of Ireland" with the Ronnie Drew Ballad Group (billed in one town as the Ronnie Drew Ballet Group). This tour led to the Abbey Tavern and the Royal Marine Hotel and then to jam-packed sessions in the Embankment, Tallaght. Ciarán Bourke joined the group, followed later by John Sheahan. They renamed themselves The Dubliners at Kelly's suggestion, as he was reading James Joyce's book of short stories, entitled Dubliners, at the time.Kelly was the leading vocalist for the group's eponymous debut album in 1964, which included his rendition of "The Rocky Road to Dublin". Barney McKenna later noted that Kelly was the only singer he'd heard sing it to the rhythm it was played on the fiddle. In 1964 Luke Kelly left the group for nearly two years and was replaced by Bobby Lynch and John Sheahan. Kelly went with Deirdre O'Connell, founder of the Focus Theatre, whom he was to marry the following year, back to London and became involved in Ewan MacColl's "gathering". The Critics, as it was called, was formed to explore folk traditions and help young singers. During this period he retained his political commitments, becoming increasingly active in the Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament. Kelly also met and befriended Michael O'Riordan, the General Secretary of the Irish Workers' Party, and the two developed a "personal-political friendship". Kelly endorsed O'Riordan for election, and held a rally in his name during campaigning in 1965.In 1965, he sang 'The Rocky Road to Dublin' with Liam Clancy on his first, self-titled solo album. Bobby Lynch left The Dubliners, John Sheahan and Kelly rejoined. They recorded an album in the Gate Theatre, Dublin, played the Cambridge Folk Festival and recorded Irish Night Out, a live album with, among others, exiles Margaret Barry, Michael Gorman and Jimmy Powers. They also played a concert in the National Stadium in Dublin with Pete Seeger as special guest. They were on the road to success: Top Twenty hits with "Seven Drunken Nights" and "The Black Velvet Band", The Ed Sullivan Show in 1968 and a tour of New Zealand and Australia. The ballad boom in Ireland was becoming increasingly commercialised with bar and pub owners building ever larger venues for pay-in performances. Ewan MacColl and Peggy Seeger on a visit to Dublin expressed concern to Kelly about his drinking.[citation needed] Christy Moore and Kelly became acquainted in the 1960s.During his Planxty days, Moore got to know Kelly well. In 1972 The Dubliners themselves performed in Richard's Cork Leg, based on the "incomplete works" of Brendan Behan. In 1973, Kelly took to the stage performing as King Herod in Jesus Christ Superstar. The arrival of a new manager for The Dubliners, Derry composer Phil Coulter, resulted in a collaboration that produced three of Kelly's most notable performances: “The Town I Loved So Well”, "Hand me Down my Bible", and “Scorn Not His Simplicity”, a song about Phil's son who had Down Syndrome.Kelly had such respect for the latter song that he only performed it once for a television recording and rarely, if ever, sang it at the Dubliners' often boisterous events. His interpretations of “On Raglan Road” and "Scorn Not His Simplicity" became significant points of reference in Irish folk music.His version of "Raglan Road" came about when the poem's author, Patrick Kavanagh, heard him singing in a Dublin pub, and approached Kelly to say that he should sing the poem (which is set to the tune of “The Dawning of the Day”). Kelly remained a politically engaged musician, becoming a supporter of the movement against South African apartheid and performing at benefit concerts for the Irish Traveller community,and many of the songs he recorded dealt with social issues, the arms race and the Cold War, trade unionism and Irish republicanism, ("The Springhill Disaster", "Joe Hill", "The Button Pusher", "Alabama 1958" and "God Save Ireland" all being examples of his concerns).Personal life
Luke Kelly married Deirdre O'Connell in 1965, but they separated in the early 1970s.Kelly spent the last eight years of his life living with his partner Madeleine Seiler, who is from Germany.Final years
Kelly's health deteriorated in the 1970s. Kelly himself spoke about his problems with alcohol. On 30 June 1980 during a concert in the Cork Opera House he collapsed on the stage. He had already suffered for some time from migraines and forgetfulness - including forgetting what country he was in whilst visiting Iceland - which had been ascribed to his intense schedule, alcohol consumption, and "party lifestyle". A brain tumour was diagnosed.Although Kelly toured with the Dubliners after enduring an operation, his health deteriorated further. He forgot lyrics and had to take longer breaks in concerts as he felt weak. In addition following his emergency surgery after his collapse in Cork, he became more withdrawn, preferring the company of Madeleine at home to performing.On his European tour he managed to perform with the band for most of the show in Carre for their Live in Carre album. However, in autumn 1983 he had to leave the stage in Traun, Austria and again in Mannheim, Germany. Shortly after this, he had to cancel the tour of southern Germany, and after a short stay in hospital in Heidelberg he was flown back to Dublin. After another operation he spent Christmas with his family but was taken into hospital again in the New Year, where he died on 30 January 1984.Kelly's funeral in Whitehall attracted thousands of mourners from across Ireland.His gravestone in Glasnevin Cemetery, Dublin, bears the inscription: Luke Kelly – Dubliner. Sean Cannon took Kelly's place in The Dubliners. He had been performing with the Dubliners since 1982,due to the deterioration of Kelly's health.Legacy
Luke Kelly's legacy and contributions to Irish music and culture have been described as "iconic" and have been captured in a number of documentaries and anthologies. The influence of his Scottish grandmother was influential in Kelly's help in preserving important traditional Scottish songs such as "Mormond Braes", the Canadian folk song "Peggy Gordon", "Robert Burns", "Parcel of Rogues", "Tibbie Dunbar", Hamish Henderson's "Freedom Come-All-Ye", and Thurso Berwick's "Scottish Breakaway". The Ballybough Bridge in the north inner city of Dublin was renamed the Luke Kelly Bridge, and in November 2004 Dublin City Council voted unanimously to erect a bronze statue of Luke Kelly. However, the Dublin Docklands Authority subsequently stated that it could no longer afford to fund the statue. In 2010, councillor Christy Burke of Dublin City Council appealed to members of the music community including Bono, Phil Coulter and Enya to help build it. Paddy Reilly recorded a tribute to Kelly entitled "The Dublin Minstrel". It featured on his Gold And Silver Years, Celtic Collections and the Essential Paddy Reilly CD's. The Dubliners recorded the song on their Live at Vicar Street DVD/CD. The song was composed by Declan O'Donoghue, the Racing Correspondent of The Irish Sun. At Christmas 2005 writer-director Michael Feeney Callan's documentary, Luke Kelly: The Performer, was released and outsold U2's latest DVD during the festive season and into 2006, acquiring platinum sales status. The documentary told Kelly's story through the words of the Dubliners, Donovan, Ralph McTell and others and featured full versions of rarely seen performances such as the early sixties' Ed Sullivan Show. A later documentary, Luke Kelly: Prince of the City, was also well received. Two statues of Kelly were unveiled in Dublin in January 2019, to mark the 35th anniversary of his death.One, a life-size seated bronze by John Coll, is on South King Street. The second sculpture, a marble portrait head by Vera Klute, is on Sheriff Street. The Klute sculpture was vandalised on several occasions in 2019 and 2020, in each case being restored by graffiti-removal specialists. Sculpture of Luke Kelly on Sheriff Street by Vera Klute. Unveiled in 2019
Sculpture of Luke Kelly on Sheriff Street by Vera Klute. Unveiled in 2019 -

 Superb poster depicting the myriad of Irish literary greats throughout the ages -to name but a few,Thomas Moore,JM Synge,WB Yeats,Joyce,Oscar Wilde,Patrick Kavanagh,G.B Shaw etc 84cm x 54cm Irish Literature comprises writings in the Irish, Latin, and English (including Ulster Scots) languages on the island of Ireland. The earliest recorded Irish writing dates from the seventh century and was produced by monks writing in both Latin and Early Irish. In addition to scriptural writing, the monks of Ireland recorded both poetry and mythological tales. There is a large surviving body of Irish mythological writing, including tales such as The Táin and Mad King Sweeny. The English language was introduced to Ireland in the thirteenth century, following the Norman invasion of Ireland. The Irish language, however, remained the dominant language of Irish literature down to the nineteenth century, despite a slow decline which began in the seventeenth century with the expansion of English power. The latter part of the nineteenth century saw a rapid replacement of Irish by English in the greater part of the country. At the end of the century, however, cultural nationalism displayed a new energy, marked by the Gaelic Revival(which encouraged a modern literature in Irish) and more generally by the Irish Literary Revival. The Anglo-Irish literary tradition found its first great exponents in Richard Head and Jonathan Swift followed by Laurence Sterne, Oliver Goldsmith and Richard Brinsley Sheridan. At the end of 19th century and throughout the 20th century, the Irish literature get an unprecedented sequence of worldwide successful works, especially those by Oscar Wilde, Bram Stoker, James Joyce, W. B. Yeats, Samuel Beckett, C.S. Lewis and George Bernard Shaw, prominent writers who left Ireland to make a life in other European countries such as England, France and Switzerland. The descendants of Scottish settlers in Ulster formed the Ulster-Scots writing tradition, having an especially strong tradition of rhyming poetry. Though English was the dominant Irish literary language in the twentieth century, much work of high quality appeared in Irish Gaelic. A pioneering modernist writer in Irish was Pádraic Ó Conaire, and traditional life was given vigorous expression in a series of autobiographies by native Irish speakers from the west coast, exemplified by the work of Tomás Ó Criomhthain and Peig Sayers. The outstanding modernist prose writer in Irish was Máirtín Ó Cadhain, and prominent poets included Máirtín Ó Direáin, Seán Ó Ríordáin and Máire Mhac an tSaoi. Prominent bilingual writers included Brendan Behan (who wrote poetry and a play in Irish) and Flann O'Brien. Two novels by O'Brien, At Swim Two Birdsand The Third Policeman, are considered early examples of postmodern fiction, but he also wrote a satirical novel in Irish called An Béal Bocht(translated as The Poor Mouth). Liam O'Flaherty, who gained fame as a writer in English, also published a book of short stories in Irish (Dúil). Most attention has been given to Irish writers who wrote in English and who were at the forefront of the modernist movement, notably James Joyce, whose novel Ulysses is considered one of the most influential of the century. The playwright Samuel Beckett, in addition to a large amount of prose fiction, wrote a number of important plays, including Waiting for Godot. Several Irish writers have excelled at short story writing, in particular Frank O'Connor and William Trevor. In the late twentieth century Irish poets, especially those from Northern Ireland, came to prominence with Derek Mahon, John Montague, Seamus Heaney and Paul Muldoon. Other notable Irish writers from the twentieth century include, poet Patrick Kavanagh, dramatists Tom Murphy and Brian Friel and novelists Edna O'Brien and John McGahern. Well-known Irish writers in English in the twenty-first century include Colum McCann, Anne Enright, Roddy Doyle, Sebastian Barry, Colm Toibín and John Banville, all of whom have all won major awards. Younger writers include Paul Murray, Kevin Barry, Emma Donoghue, Donal Ryan and dramatist Martin McDonagh. Writing in Irish has also continued to flourish. Origins : Dublin Dimensions : 90cm x 60cm 8kg
Superb poster depicting the myriad of Irish literary greats throughout the ages -to name but a few,Thomas Moore,JM Synge,WB Yeats,Joyce,Oscar Wilde,Patrick Kavanagh,G.B Shaw etc 84cm x 54cm Irish Literature comprises writings in the Irish, Latin, and English (including Ulster Scots) languages on the island of Ireland. The earliest recorded Irish writing dates from the seventh century and was produced by monks writing in both Latin and Early Irish. In addition to scriptural writing, the monks of Ireland recorded both poetry and mythological tales. There is a large surviving body of Irish mythological writing, including tales such as The Táin and Mad King Sweeny. The English language was introduced to Ireland in the thirteenth century, following the Norman invasion of Ireland. The Irish language, however, remained the dominant language of Irish literature down to the nineteenth century, despite a slow decline which began in the seventeenth century with the expansion of English power. The latter part of the nineteenth century saw a rapid replacement of Irish by English in the greater part of the country. At the end of the century, however, cultural nationalism displayed a new energy, marked by the Gaelic Revival(which encouraged a modern literature in Irish) and more generally by the Irish Literary Revival. The Anglo-Irish literary tradition found its first great exponents in Richard Head and Jonathan Swift followed by Laurence Sterne, Oliver Goldsmith and Richard Brinsley Sheridan. At the end of 19th century and throughout the 20th century, the Irish literature get an unprecedented sequence of worldwide successful works, especially those by Oscar Wilde, Bram Stoker, James Joyce, W. B. Yeats, Samuel Beckett, C.S. Lewis and George Bernard Shaw, prominent writers who left Ireland to make a life in other European countries such as England, France and Switzerland. The descendants of Scottish settlers in Ulster formed the Ulster-Scots writing tradition, having an especially strong tradition of rhyming poetry. Though English was the dominant Irish literary language in the twentieth century, much work of high quality appeared in Irish Gaelic. A pioneering modernist writer in Irish was Pádraic Ó Conaire, and traditional life was given vigorous expression in a series of autobiographies by native Irish speakers from the west coast, exemplified by the work of Tomás Ó Criomhthain and Peig Sayers. The outstanding modernist prose writer in Irish was Máirtín Ó Cadhain, and prominent poets included Máirtín Ó Direáin, Seán Ó Ríordáin and Máire Mhac an tSaoi. Prominent bilingual writers included Brendan Behan (who wrote poetry and a play in Irish) and Flann O'Brien. Two novels by O'Brien, At Swim Two Birdsand The Third Policeman, are considered early examples of postmodern fiction, but he also wrote a satirical novel in Irish called An Béal Bocht(translated as The Poor Mouth). Liam O'Flaherty, who gained fame as a writer in English, also published a book of short stories in Irish (Dúil). Most attention has been given to Irish writers who wrote in English and who were at the forefront of the modernist movement, notably James Joyce, whose novel Ulysses is considered one of the most influential of the century. The playwright Samuel Beckett, in addition to a large amount of prose fiction, wrote a number of important plays, including Waiting for Godot. Several Irish writers have excelled at short story writing, in particular Frank O'Connor and William Trevor. In the late twentieth century Irish poets, especially those from Northern Ireland, came to prominence with Derek Mahon, John Montague, Seamus Heaney and Paul Muldoon. Other notable Irish writers from the twentieth century include, poet Patrick Kavanagh, dramatists Tom Murphy and Brian Friel and novelists Edna O'Brien and John McGahern. Well-known Irish writers in English in the twenty-first century include Colum McCann, Anne Enright, Roddy Doyle, Sebastian Barry, Colm Toibín and John Banville, all of whom have all won major awards. Younger writers include Paul Murray, Kevin Barry, Emma Donoghue, Donal Ryan and dramatist Martin McDonagh. Writing in Irish has also continued to flourish. Origins : Dublin Dimensions : 90cm x 60cm 8kg