14 men executed in Kilmainham Gaol
A 15th man, Thomas Kent, has also been executed in Cork
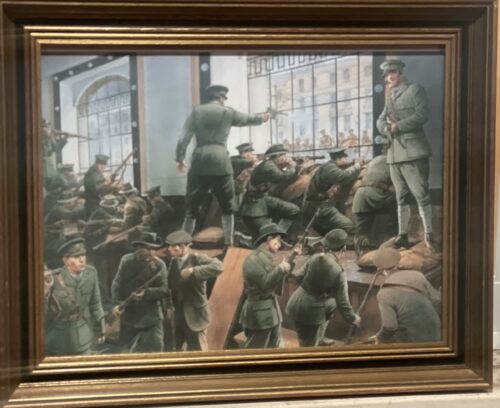
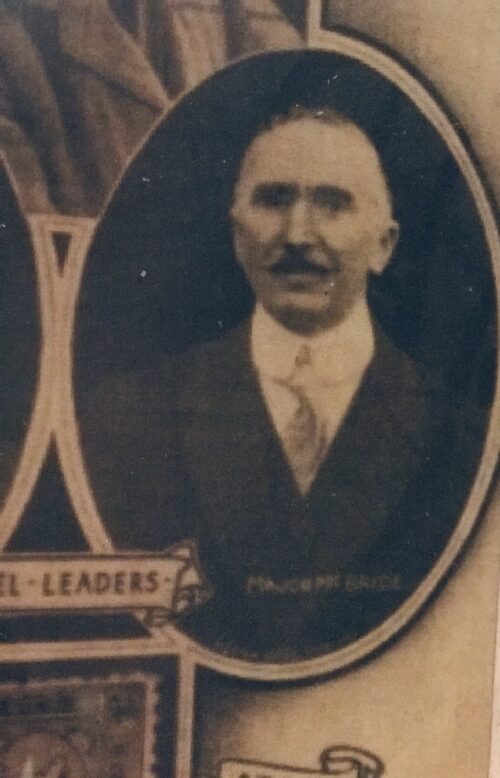
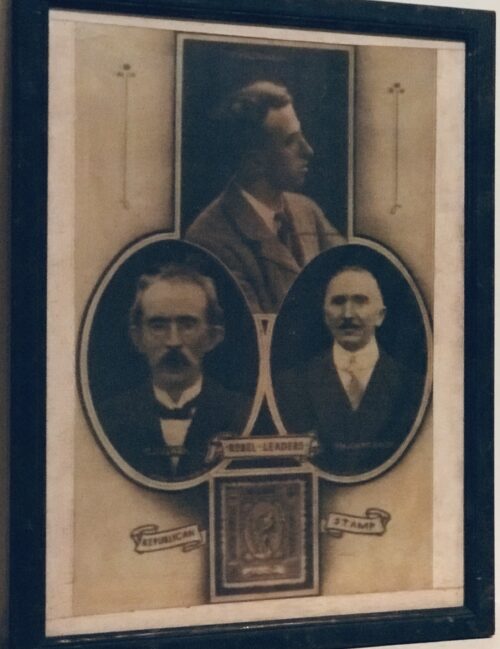
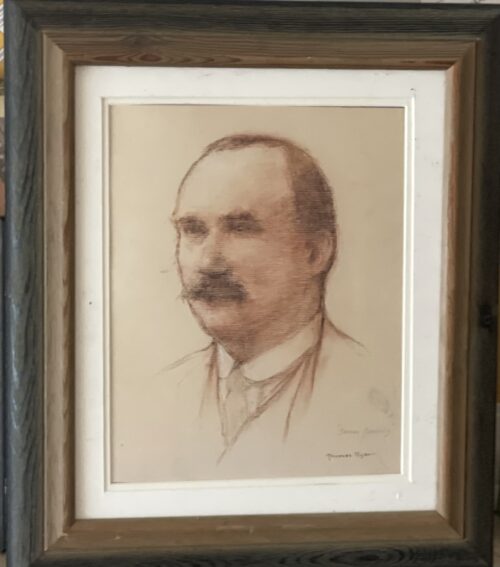
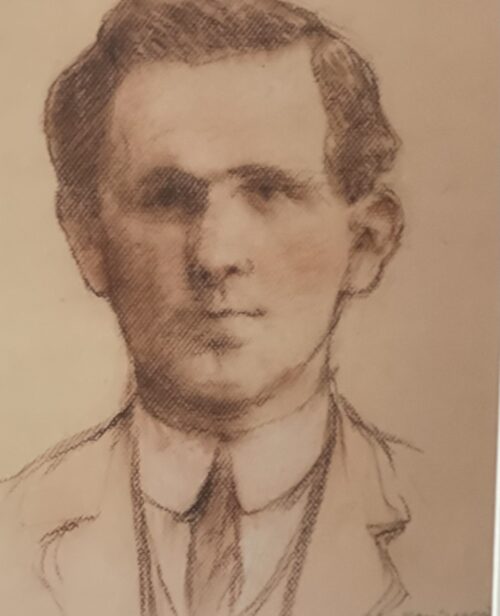
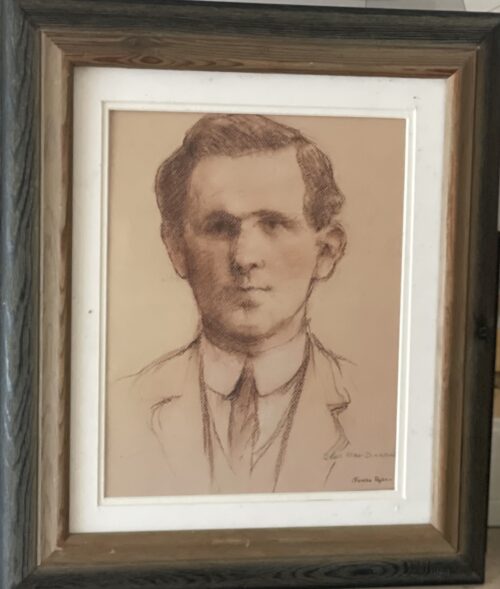
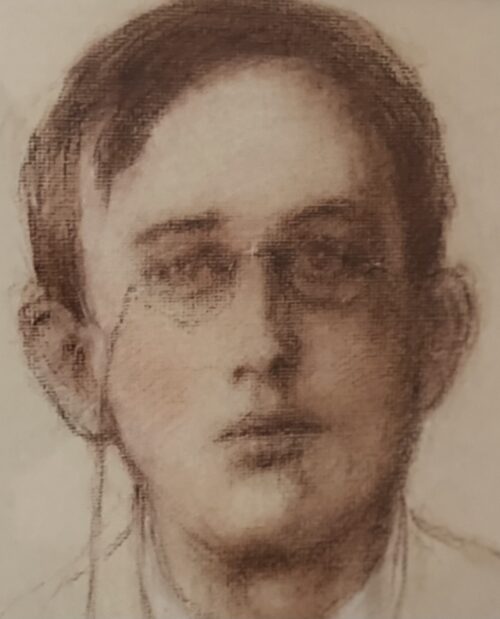
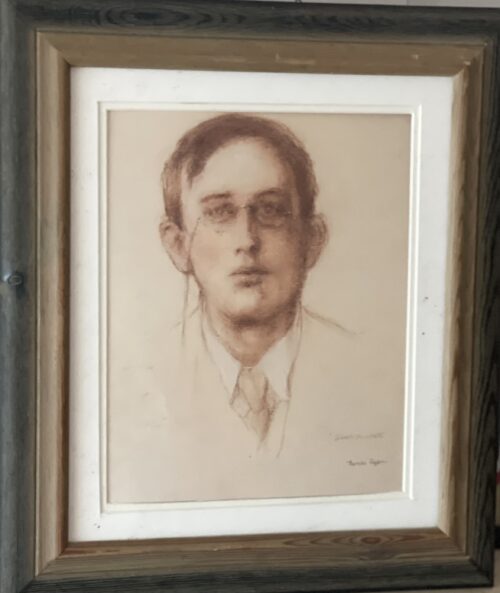
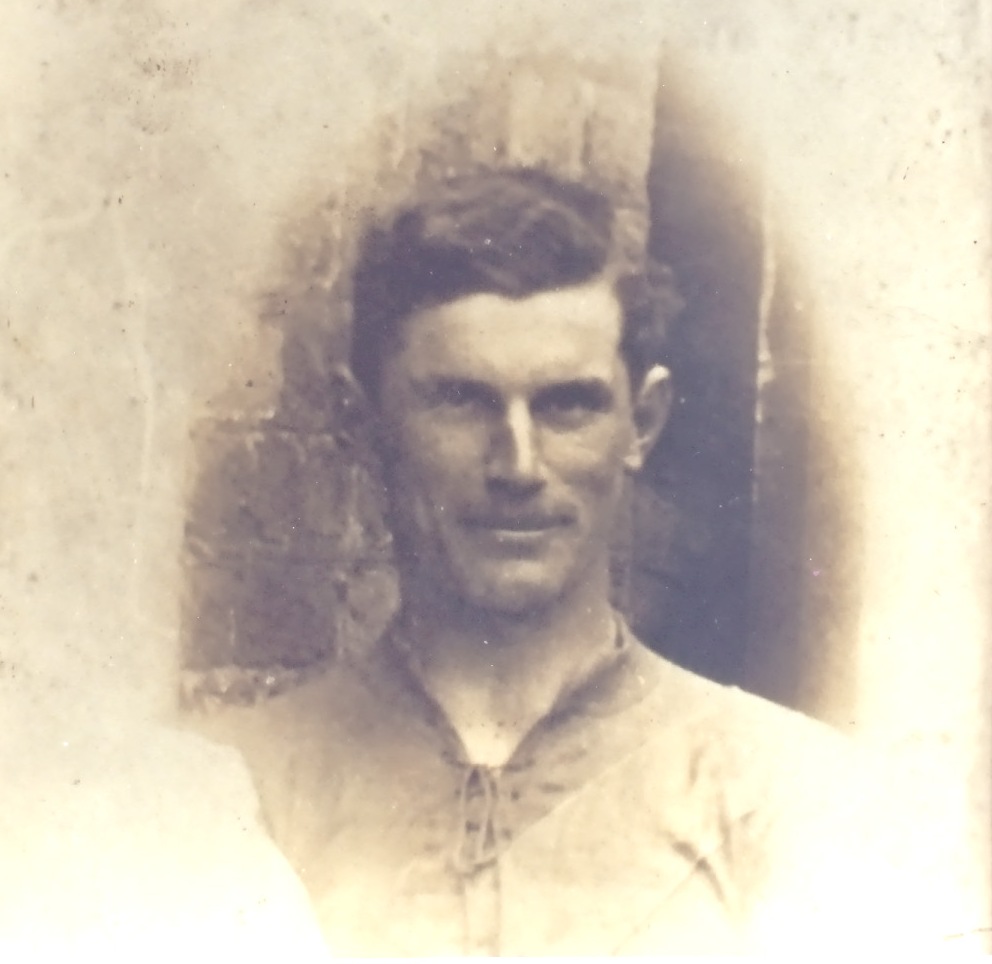
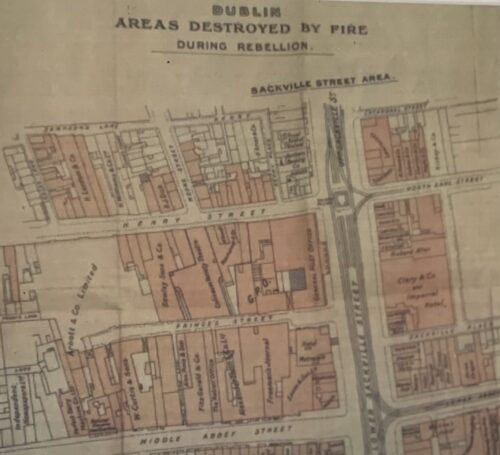
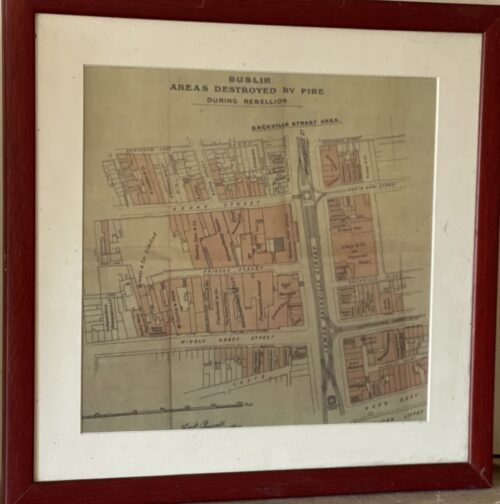
Dublin, 13 May 1916 - 14 men have been executed in Kilmainham Gaol for their involvement in the recent Dublin rebellion. The executions were carried out by firing squad at dawn. The men had earlier been tried in secrecy at Richmond Barracks in Dublin at a series of field general courts-martial where they were permitted no defence counsel. The executions began on the morning of 3 May with Patrick Pearse, Thomas Clarke and Thomas MacDonagh being shot by firing squad at the Stonebreaker’s Yard in Kilmainham Gaol. The following morning Joseph Plunkett, Edward Daly, Michael O'Hanrahan and Willie Pearse were shot, followed by John MacBride on the morning after. Éamonn Ceannt, Michael Mallin, Seán Heuston and Con Colbert were shot on 8 May, followed by Seán Mac Diarmadaand James Connolly on 12 May. There are reports that Connolly was already grievously ill and was unable to stand in front on the firing squad that shot him. Among the men who have been shot are all seven signatories of the Proclamation of the Irish Republic that was posted on walls around Dublin during the rebellion and was read aloud outside the GPO on Sackville Street by Patrick Pearse on Easter Monday. A further execution in Co. Cork took place on 9 May where Thomas Kent was shot after his arrest 7 days earlier. Mr Kent had been heavily linked with land agitation in Cork, but it is not clear that he had any involvement in the Rising in Dublin.
Cartoon from Issues and Events commenting on the freedom of Ireland. (Image: Villanova University)
Other rebels Also executed were leaders of various garrisons of volunteers who took over key buildings around Dublin. The decisions to single out Willie Pearse and John MacBride for execution appear unrelated to any rank they held, however. Other rebel leaders – including Eamon de Valera and Constance Markievicz – remain in custody and it is not clear what their fate will be. In London, Roger Casement awaits trial for treason and is being held in the Tower of London, following his arrest in Co. Kerry on Good Friday. It appears that Casement was attempting to facilitate a shipment of arms from Germany for use in the rebellion. Meanwhile, the arrests of hundreds of people associated, or deemed by the authorities to be associated with the Rising, continues. Those arrested are being interned, with some being sent across the Irish Sea to England and Wales. [Editor's note: This is an article from Century Ireland, a fortnightly online newspaper, written from the perspective of a journalist 100 years ago, based on news reports of the time.]