-
 Fire damaged but still robustly intact cast iron Capel St street sign .This pieced of Dublin history was acquired in the UK where the story goes a former British soldier brought it home as a souvenir after extracting it from the post 1916 Easter rising burning rubble.Whether this anecdote is true or not, we feel this is a unique and once off item not to be missed ! For further information on pricing and shipping costs please contact us directly at irishpubemporium@gmail.com 60cm x 14cm 5kg It is sometimes claimed that the street takes its name from the chapel of St Mary's Abbey; other Capel Streets may be named after chapels, but this one is named after Arthur Capell, 1st Earl of Essex, Lord Lieutenant of Ireland 1672–1677. Built by Sir Humphrey Jervis in the late 17th century, he also built Essex Bridge (today Grattan Bridge), and the street was known for its mansions and a royal mint. In the 18th century, it became a commercial hub, with two-bay buildings replacing the "Dutch Billy" houses.The Capel Street Theatre also stood there in the 18th century. The Torch Theatre operated on Capel Street in 1935–41. The street declined in the 20th century, before a revival around the 1980s. Today it is known for its variety of restaurants, shops, cafés and pubs; as Panti, the owner of Pantibar put it, "You can buy a lightbulb, sexual lubricant, Brazilian rice, get a pint and go to a trad session." Louis Copeland's tailor is another notable business.
Fire damaged but still robustly intact cast iron Capel St street sign .This pieced of Dublin history was acquired in the UK where the story goes a former British soldier brought it home as a souvenir after extracting it from the post 1916 Easter rising burning rubble.Whether this anecdote is true or not, we feel this is a unique and once off item not to be missed ! For further information on pricing and shipping costs please contact us directly at irishpubemporium@gmail.com 60cm x 14cm 5kg It is sometimes claimed that the street takes its name from the chapel of St Mary's Abbey; other Capel Streets may be named after chapels, but this one is named after Arthur Capell, 1st Earl of Essex, Lord Lieutenant of Ireland 1672–1677. Built by Sir Humphrey Jervis in the late 17th century, he also built Essex Bridge (today Grattan Bridge), and the street was known for its mansions and a royal mint. In the 18th century, it became a commercial hub, with two-bay buildings replacing the "Dutch Billy" houses.The Capel Street Theatre also stood there in the 18th century. The Torch Theatre operated on Capel Street in 1935–41. The street declined in the 20th century, before a revival around the 1980s. Today it is known for its variety of restaurants, shops, cafés and pubs; as Panti, the owner of Pantibar put it, "You can buy a lightbulb, sexual lubricant, Brazilian rice, get a pint and go to a trad session." Louis Copeland's tailor is another notable business. -
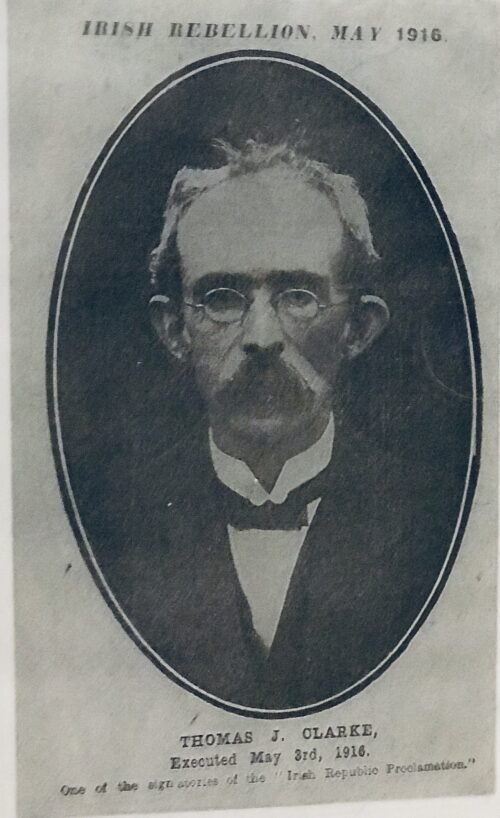
 Beautiful and poignant collection of four of the 1916 Easter Rising Rebel Leaders who were executed by the British Crown Forces at Kilmainham Jail a few weeks later.Featured here are Padraig Pearse,Thomas Clarke,James Connolly and The O'Rahilly(not executed but who was killed in action at the GPO). Thomas James Clarke ( 11 March 1858 – 3 May 1916) was an Irish republican and a leader of the Irish Republican Brotherhood from Dungannon, County Tyrone. Clarke was arguably the person most responsible for the 1916 Easter Rising. A proponent of armed struggle against British rule in Ireland for most of his life, Clarke spent 15 years in English prisons prior to his role in the Easter Rising, and was executed by firing squad after it was defeated.
Beautiful and poignant collection of four of the 1916 Easter Rising Rebel Leaders who were executed by the British Crown Forces at Kilmainham Jail a few weeks later.Featured here are Padraig Pearse,Thomas Clarke,James Connolly and The O'Rahilly(not executed but who was killed in action at the GPO). Thomas James Clarke ( 11 March 1858 – 3 May 1916) was an Irish republican and a leader of the Irish Republican Brotherhood from Dungannon, County Tyrone. Clarke was arguably the person most responsible for the 1916 Easter Rising. A proponent of armed struggle against British rule in Ireland for most of his life, Clarke spent 15 years in English prisons prior to his role in the Easter Rising, and was executed by firing squad after it was defeated.Early life
Clarke was born at Hurst Castle, Milford-on-Sea, Hampshire, England, opposite the Isle of Wight, to Irish parents,Mary Palmer and James Clarke, who was a sergeant in the British Army. In 1865, after spending some years in South Africa, Sgt. Clarke was transferred to Dungannon, County Tyrone, Ireland, and it was there that Tom grew up.Irish Republican Brotherhood
In 1878, at the age of 20, he joined the Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB) following the visit to Dungannon by John Daly, and by 1880 he was centre (head) of the local IRB circle. In August that year, after a member of the Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC) had shot and killed a man during riots between the Orange Order and the Ancient Order of Hibernians in Dungannon, Clarke and other IRB members attacked some RIC men in Irish Street. They were driven back, however, and Clarke, fearing arrest, fled to the United States. In 1883, Clarke was sent to London, under the alias of "Henry Wilson",[5] to take part in the Fenian dynamite campaign advocated by Jeremiah O'Donovan Rossa, one of the IRB leaders exiled in the United States. British authorities were already following those involved, aided by informants, and Clarke was arrested in possession of dynamite, along with three others. He was tried and sentenced to penal servitude for life on 28 May 1883 at London's Old Bailey.He subsequently served 15 years in Pentonville and other British prisons. In 1896, he was one of only five remaining Fenian prisoners in British jails and a series of public meetings in Ireland called for their release. At one meeting, John Redmond MP, leader of the ParnelliteIrish National League, said of him: "Wilson is a man of whom no words of praise could be too high. I have learned in my many visits to Portland for five years to love, honour and respect Henry Wilson. I have seen day after day how his brave spirit was keeping him alive ... I have seen year after year the fading away of his physical strength". Following his release in 1898 he moved to Brooklyn in the United States where he married Kathleen Daly, 21 years his junior, whose uncle, John Daly, he had met in prison. Clarke worked for the Clan na Gael under John Devoy. In 1906 the couple moved to a 30-acre (120,000 m2) farm in Manorville, New York, and bought another 30 acres (120,000 m2) there in 1907, shortly before returning to Ireland later that same year. In Ireland, Clarke opened a tobacconist shop in Dublin and immersed himself in the IRB which was undergoing a substantial rejuvenation under the guidance of younger men such as Bulmer Hobson and Denis McCullough. Clarke had a very close kinship with Hobson, who along with Seán MacDermott, became his protegé. Clarke supported the striking members of the Irish Transport and General Workers' Union during the 1913 Dublin Lockout and refused to sell copies of the Irish Independent, a newspaper owned by union-busting industrialist and press baron William Martin Murphy, at his tobacco shop.Irish Volunteers
When the Irish Volunteers were formed in 1913, Clarke took a keen interest, but took no part in the organisation, knowing that as a felon and well-known Irish nationalist he would lend discredit to the Volunteers. Nevertheless, with MacDermott, Hobson, and other IRB members such as Eamonn Ceannt taking important roles in the Volunteers, it was clear that the IRB would have substantial, if not total, control, (particularly after the co-option of Paidraig Pearse, already a leading member of the Volunteers, into the IRB at the end of 1913). This proved largely to be the case until leader of the Irish Parliamentary Party, John Redmond, demanded the Provisional Committee accept 25 additional members of the Party's choosing, giving IPP loyalists a majority stake. Though most of the hard-liners stood against this, Redmond's decree was accepted, partially due to the support given by Hobson. Clarke never forgave him for what he considered a treasonous act.Planning the uprising
Following Clarke's falling out with Hobson, MacDermott and Clarke became almost inseparable. The two of them, as secretary and treasurer, respectively, de facto ran the IRB, although it was still under the nominal head of other men: James Deakin, and later McCullough. In 1915 Clarke and MacDermott established the Military Committee of the IRB to plan what later became the Easter Rising. The members were Pearse, Ceannt and Joseph Plunkett, with Clarke and MacDermott adding themselves shortly thereafter. When the old Fenian Jeremiah O'Donovan Rossa died in 1915 Clarke used his funeral (and Pearse's graveside oration) to mobilise the Volunteers and heighten expectation of imminent action. When an agreement was reached with leading Marxist James Connolly and his Irish Citizen Army in January 1916, Connolly was added to the committee, with Thomas MacDonagh added at the last minute in April. These seven men were the signatories of the Proclamation of the Republic, with Clarke as the first signatory. It has been said that Clarke indeed would have been the declared President and Commander-in-chief, but he refused any military rank and such honours; these were given to Pearse, who was more well-known and respected on a national level. Kathleen Clarke later claimed that her husband, and not Pearse, was first president of the Irish Republic.Easter Rising
Clarke was located at headquarters in the General Post Office (GPO) during the events of Easter Week, where rebel forces were largely composed of Irish Citizen Army members under the command of Connolly. Though he held no formal military rank, Clarke was recognised by the garrison as one of the commanders, and was active throughout the week. Late in the week, the GPO had to be evacuated due to fire. The leaders gathered in a house in Moore Street, from where Pearse ordered the surrender on 29 April. Clarke wrote on the wall of the house, "We had to evacuate the GPO. The boys put up a grand fight, and that fight will save the soul of Ireland."He was arrested after the surrender. He and the other commanders were taken to the Rotundawhere he was stripped of his clothing in front of the other prisoners. He was later held in Kilmainham Gaol. He was court-martialled and executed by firing squad, along with Pearse and MacDonagh on 3 May 1916. Before his execution, he asked his wife Kathleen to convey a message to the Irish people: "My comrades and I believe we have struck the first successful blow for freedom, and so sure as we are going out this morning so sure will freedom come as a direct result of our action...In this belief, we die happy."Works[edit]
- Glimpses of an Irish Felon's Prison Life (1922: The National Publications Committee, Cork)
Legacy[edit]
After her husband's execution, Kathleen Clarke was elected a TD in the First and Second Dála, notably speaking against the Anglo-Irish Treaty.- Thomas Clarke Tower in Ballymun was named after him. The top floor was used as a short stay hotel before its demolition in April 2008.
- Dundalk railway station was given the name Clarke on 10 April 1966 in commemoration of Clarke's role in the 1916 Rising.
- The Tom Clarke Bridge is a tolled bridge across the River Liffey in Dublin. The bridge, officially named after Clarke, is popularly referred to as the East-Link Bridge.
- He also featured on postage stamps in 1966.
- Dungannon Thomas Clarkes, a successful GAA Club and Gaelic football team in Clarke's hometown in County Tyrone are also named after him.
- Dungannon has a 1916 Society named in his honour, Cumann Thomáis ui Chléirigh www.tomclarkesociety.com
- Clarke Square in Collins Barracks
-
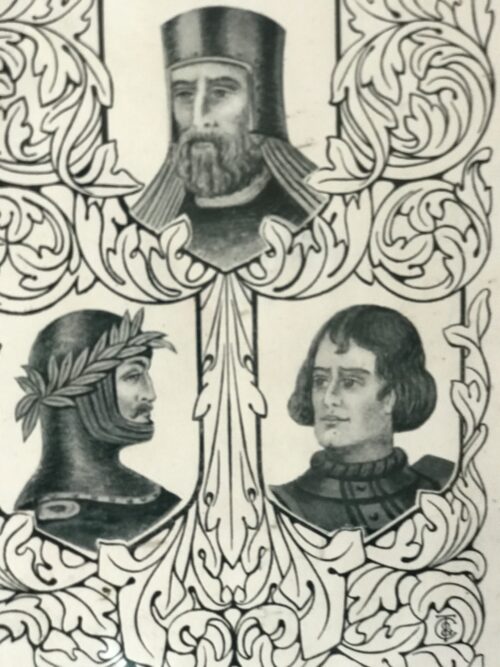

 27cm x 22cm Richard de Clare, 2nd Earl of Pembroke (of the first creation), Lord of Leinster, Justiciar of Ireland (1130 – 20 April 1176), also known as Richard FitzGilbert, was an Anglo-Norman nobleman notable for his leading role in the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland. Like his father, Richard fitz Gilbert has since become commonly known by his nickname Strongbow , which may be a mistranscription or mistranslation of "Striguil."His son Gilbert de Striguil (or de Strigoil) died unmarried before 1189 and the earldom passed via Richard's daughter Isabel to her spouse William Marshall. Edward Bruce, a Scotsman, was the last High King of Ireland and reigned between 1315 and 1318. He died on this day, October 14, in 1318. Over seven hundred years ago, the last High King of Ireland was crowned. The man chosen was a Scotsman - Edward Bruce, died on this day, October 13, in 1318. The English colonists in Ireland vehemently opposed him.Edward, the brother of the King of Scotland, Robert the Bruce, led a three-year military campaign, known as the Bruce Invasion, against the Anglo-Norman lordship of Ireland.Thomas FitzGerald
27cm x 22cm Richard de Clare, 2nd Earl of Pembroke (of the first creation), Lord of Leinster, Justiciar of Ireland (1130 – 20 April 1176), also known as Richard FitzGilbert, was an Anglo-Norman nobleman notable for his leading role in the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland. Like his father, Richard fitz Gilbert has since become commonly known by his nickname Strongbow , which may be a mistranscription or mistranslation of "Striguil."His son Gilbert de Striguil (or de Strigoil) died unmarried before 1189 and the earldom passed via Richard's daughter Isabel to her spouse William Marshall. Edward Bruce, a Scotsman, was the last High King of Ireland and reigned between 1315 and 1318. He died on this day, October 14, in 1318. Over seven hundred years ago, the last High King of Ireland was crowned. The man chosen was a Scotsman - Edward Bruce, died on this day, October 13, in 1318. The English colonists in Ireland vehemently opposed him.Edward, the brother of the King of Scotland, Robert the Bruce, led a three-year military campaign, known as the Bruce Invasion, against the Anglo-Norman lordship of Ireland.Thomas FitzGeraldThe Earl of Kildare 
Reign 1534–1537 Predecessor Gerald FitzGerald Successor Title forfeited Born 1513 Died 3 February 1537 (aged 24) Tyburn, London, Kingdom of England Noble family FitzGerald dynasty Father Gerald FitzGerald Mother Elizabeth Zouche Religion Roman Catholicism Thomas FitzGerald, 10th Earl of Kildare (1513 – 3 February, 1537), also known as Silken Thomas (Irish: Tomás an tSíoda), was a leading figure in 16th-century Irish history. Thomas Fitzgerald was born in London in 1513, the son of Gerald FitzGerald, 9th Earl of Kildare and his first wife Elizabeth Zouche, who was a distant cousin of Henry VII. In February 1534, his father was summoned to London and appointed the 21-year-old Thomas (by then Lord Offaly) deputy governor of Ireland in his absence. In June 1534 Thomas heard rumours that his father had been executed in the Tower of London and that the English government intended the same fate for himself and his uncles. 16th-century woodcut of Silken Thomas's attack on Dublin Castle
16th-century woodcut of Silken Thomas's attack on Dublin CastleKildare rebellion (1534–1535)
He summoned the Council to St. Mary's Abbey, Dublin, and on 11 June, accompanied by 140 armoured gallowglasses with silk fringes on their helmets (from which he got his nickname), rode to the abbey and publicly renounced his allegiance to his cousin King Henry VIII, Lord of Ireland. The Chancellor, Archbishop John Alen, attempted to persuade him not to commit himself to such a rash proceeding; but the young lord's harper, understanding only Irish, and seeing signs of wavering in FitzGerald's bearing, commenced to recite a poem in praise of the deeds of his ancestors, telling him at the same time that he lingered there over long. Roused by this he threw down the sword of state and rushed from the hall, followed by his adherents. The council sent an order for his immediate arrest to the Lord Mayor of Dublin, who, however, had not sufficient force at his disposal. The Earl of Desmond and many of his father's oldest and best friends reasoned with him; but he was not to be turned from his purpose. As Vice-Deputy, Kildare had under his control most of the Pale fortresses, and large government stores. Dublin Castle alone held out for the King of England. Lord Offaly called the lords of the Pale to the siege of the Castle; those who refused to swear fidelity to him he sent as prisoners to his Maynooth Castle. Goods and chattels belonging to the King's subjects he declared forfeited, and he announced his intention of exiling or putting to death all born in England. He sent messengers to his cousin and friend Lord Butler, son of the Earl of Ormond, offering to divide the kingdom with him if he would join his cause, but Butler refused. Several children of the citizens of Dublin in different parts of the Pale were seized as hostages for the good behavior of the city. In July, he attacked Dublin Castle, but his army was routed. He was, rightly or wrongly, judged to be responsible for the execution at Artane of Archbishop Alen, who had tried to mediate; this lost him support from the clergy. According to a long-established tradition, the killers, John Teeling and Nicholas Wafer, misunderstood his order, given in Irish, to "take this fellow away" as an order to kill Alen. By this time his father had taken ill and died in London, and he had technically succeeded as 10th earl, but the Crown never confirmed his title. He retreated to his stronghold at Maynooth Castle, but in March 1535 this was taken by an English force under Sir William Skeffington by bribing a guard, while Thomas was absent gathering reinforcements to relieve it. The surrendered garrison was put to death, which became known as the "Maynooth Pardon". Thomas had wrongly assumed that his cause would attract overwhelming support, in particular from Catholics opposed to Henry VIII's English Reformation. But Henry's new policy also outlawed Lutheranism, and so Henry was not finally excommunicated until 1538. In July, Lord Leonard Grey arrived from England as Lord Deputy of Ireland; Fitzgerald, seeing his army melting away and his allies submitting one by one, asked pardon for his offences. He was still a formidable opponent, and Grey, wishing to avoid a prolonged conflict, guaranteed his personal safety and persuaded him to submit unconditionally to the King's mercy. According to the Irish Tree Council, legend has it that Silken Thomas played a lute under the boughs of the now oldest planted tree in Ireland, the Silken thomas Yew Tree, the night before he surrendered to King Henry VIII. in the 1500s.In October 1535 he was sent as a prisoner to the Tower. Despite Grey's guarantee, he was executed with his five unclesat Tyburn on 3 February 1537. According to G. G. Nichols, the five uncles were "...draune from the Tower in to Tyborne, and there alle hongyd and hedded and quartered, save the Lord Thomas for he was but hongyd and hedded and his body buried at the Crost Freeres in the qwere..." The Attainder of the Earl of Kildare Act 1536 was passed to permit his execution and the confiscation of his property. The 1536 Act remained law until it was repealed by the Statute Law Revision (Pre-1922) Act 2005. Silken Thomas's revolt caused Henry to pay more attention to Irish matters, and was a factor in the creation of the Kingdom of Ireland in 1541. In particular the powers of the lords deputy were curbed, and policies such as surrender and regrant were introduced. To provide for greater security the Royal Irish Army was established as a standing army. Dress of gallowglasses c. 1521. Many fought on Fitzgerald's side.
Dress of gallowglasses c. 1521. Many fought on Fitzgerald's side. -
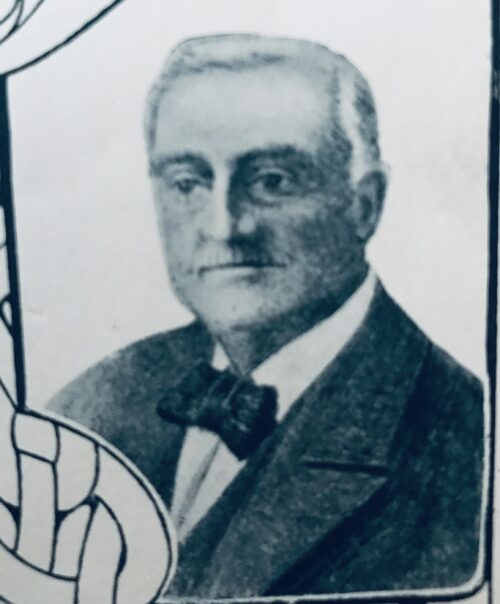
 27cm x 22cm Charles Stewart Parnell (1846-1891) will be remembered as one of the most iconic and indeed controversial politicians in Irish history.MP and Leader of the Irish Parliamentary or Home Rule Party from1882 to 1891 until revelations of his adulterous love affair with Kitty O'Shea forced his resignation.He died shortly afterwards from pneumonia in the arms of his newly divorced and remarried wife Katherine.His death was considered to be a direct result of the stresses he endured because of the Victorian era scandal and his subsequent funeral at Glasnevin Cemetery in Dublin was attended by more than 200000 people.His notability was such that his gravestone of unhewn Wicklow granite, erected in 1940,reads only Parnell. This faithful portrayal of Parnell,well over 130 years old, by the artist JG Wills dates to 1884 and is a beautiful homage to the "uncrowned king of Ireland". Daniel O'Connell (18th August 1775 – 15 May 1847), often referred to as The Liberator or The Emancipator,was an Irish political leader in the first half of the 19th century. He campaigned for Catholic emancipation—including the right for Catholics to sit in the Westminster Parliament, denied for over 100 years—and repeal of the Acts of Union which combined Great Britain and Ireland. Throughout his career in Irish politics, O'Connell was able to gain a large following among the Irish masses in support of him and his Catholic Association. O'Connell's main strategy was one of political reformism, working within the parliamentary structures of the British state in Ireland and forming an alliance of convenience with the Whigs. More radical elements broke with O'Connell to found the Young Ireland movement. O'Connell was born at Carhan near Cahersiveen, County Kerry, to the O'Connells of Derrynane, a once-wealthy Roman Catholic family that had been dispossessed of its lands. His parents were Morgan O'Connell and Catherine O'Mullane. Among his uncles was Daniel Charles, Count O'Connell, an officer in the Irish Brigades of the French Army. A famous aunt was Eibhlín Dubh Ní Chonaill, while Sir James O'Connell, 1st Baronet, was his younger brother. Under the patronage of his wealthy bachelor uncle Maurice "Hunting Cap" O'Connell. O'Connell was first sent with his brother Maurice to Reddington Academy at Long Island, near Queenstown (Cobh) They both studied at Douai in France from 1790 and O'Connell was admitted as a barrister to Lincoln's Inn in 1794, transferring to Dublin's King's Inns two years later. In his early years, he became acquainted with the pro-democracy radicals of the time and committed himself to bringing equal rights and religious tolerance to his own country.While in Dublin studying for the law, O'Connell was under his Uncle Maurice's instructions not to become involved in any militia activity. When Wolfe Tone's French invasion fleet entered Bantry Bay in December 1796, O'Connell found himself in a quandary. Politics was the cause of his unsettlement. Dennis Gwynn in his Daniel O'Connell: The Irish Liberator suggests that the unsettlement was because he was enrolled as a volunteer in defence of Government, yet the Government was intensifying its persecution of the Catholic people—of which he was one.He desired to enter Parliament, yet every allowance that the Catholics had been led to anticipate, two years previously, was now flatly vetoed. As a law student, O'Connell was aware of his own talents, but the higher ranks of the Bar were closed to him. He read the Jockey Club as a picture of the governing class in England and was persuaded by it that, "vice reigns triumphant in the English court at this day. The spirit of liberty shrinks to protect property from the attacks of French innovators. The corrupt higher orders tremble for their vicious enjoyments." O'Connell's studies at the time had concentrated upon the legal and political history of Ireland, and the debates of the Historical Society concerned the records of governments, and from this he was to conclude, according to one of his biographers, "in Ireland the whole policy of the Government was to repress the people and to maintain the ascendancy of a privileged and corrupt minority". On 3 January 1797, in an atmosphere of alarm over the French invasion fleet in Bantry Bay, he wrote to his uncle saying that he was the last of his colleagues to join a volunteer corps and "being young, active, healthy and single" he could offer no plausible excuse.Later that month, for the sake of expediency, he joined the Lawyers' Artillery Corps. On 19 May 1798, O'Connell was called to the Irish Bar and became a barrister. Four days later, the United Irishmen staged their rebellion which was put down by the British with great bloodshed. O'Connell did not support the rebellion; he believed that the Irish would have to assert themselves politically rather than by force. He went on the Munster circuit, and for over a decade, he went into a fairly quiet period of private law practice in the South of Ireland.He was reputed to have the largest income of any Irish barrister but, due to natural extravagance and a growing family, was usually in debt; his brother remarked caustically that Daniel was in debt all his life from the age of seventeen. Although he was ultimately to inherit Derrynane from his uncle Maurice, the old man lived to be almost 100 and in the event Daniel's inheritance did not cover his debts. He also condemned Robert Emmet's Rebellion of 1803. Of Emmet, a Protestant, he wrote: "A man who could coolly prepare so much bloodshed, so many murders—and such horrors of every kind has ceased to be an object of compassion." Despite his opposition to the use of violence, he was willing to defend those accused of political crimes, particularly if he suspected that they had been falsely accused, as in the Doneraile conspiracy trials of 1829, his last notable court appearance. He was noted for his fearlessness in court: if he thought poorly of a judge (as was very often the case) he had no hesitation in making this clear. Most famous perhaps was his retort to Baron McClelland, who had said that as a barrister he would never have taken the course O'Connell had adopted: O'Connell said that McClelland had never been his model as a barrister, neither would he take directions from him as a judge. He did not lack the ambition to become a judge himself: in particular he was attracted by the position of Master of the Rolls in Ireland, yet although he was offered it more than once, finally refused. O'Connell returned to politics in the 1810s. In 1811, he established the Catholic Board, which campaigned for Catholic emancipation, that is, the opportunity for Irish Catholics to become members of parliament. In 1823, he set up the Catholic Association which embraced other aims to better Irish Catholics, such as: electoral reform, reform of the Church of Ireland, tenants' rights, and economic development. The Association was funded by membership dues of one penny per month, a minimal amount designed to attract Catholic peasants. The subscription was highly successful, and the Association raised a large sum of money in its first year. The money was used to campaign for Catholic emancipation, specifically funding pro-emancipation members of parliament (MPs) standing for the British House of Commons.O'Connell's home at Derrynane Co KerryMembers of the Association were liable to prosecution under an eighteenth-century statute, and the Crown moved to suppress the Association by a series of prosecutions, with mixed success. O'Connell was often briefed for the defence, and showed extraordinary vigour in pleading the rights of Catholics to argue for emancipation. He clashed repeatedly with William Saurin, the Attorney General for Ireland and most influential figure in the Dublin administration, and political differences between the two men were fuelled by a bitter personal antipathy. In 1815 a serious event in his life occurred. Dublin Corporation was considered a stronghold of the Protestant Ascendancy and O'Connell, in an 1815 speech, referred to it as a "beggarly corporation".Its members and leaders were outraged and because O'Connell would not apologise, one of their number, the noted duellist John D'Esterre, challenged him. The duel had filled Dublin Castle (from where the British Government administered Ireland) with tense excitement at the prospect that O'Connell would be killed. They regarded O'Connell as "worse than a public nuisance", and would have welcomed any prospect of seeing him removed at this time. O'Connell met D'Esterre and mortally wounded him (he was shot in the hip, the bullet then lodging in his stomach), in a duel at Oughterard, County Kildare. His conscience was bitterly sore by the fact that, not only had he killed a man, but he had left his family almost destitute. O'Connell offered to "share his income" with D'Esterre's widow, but she declined; however, she consented to accept an allowance for her daughter, which O'Connell regularly paid for more than thirty years until his death. The memory of the duel haunted him for the remainder of his life, and he refused ever to fight another, being prepared to risk accusations of cowardice rather than kill again. As part of his campaign for Catholic emancipation, O'Connell created the Catholic Association in 1823; this organisation acted as a pressure group against the British government so as to achieve emancipation. The Catholic Rent, which was established in 1824 by O'Connell and the Catholic Church raised funds from which O'Connell was able to help finance the Catholic Association in its push for emancipation. Official opinion was gradually swinging towards emancipation, as shown by the summary dismissal of William Saurin, the Attorney General and a leading opponent of religious toleration, whom O'Connell called "our mortal foe". O'Connell stood in a by-election to the British House of Commons in 1828 for County Clare against William Vesey Fitzgerald, who had just joined the British Cabinet as President of the Board of Trade. By law at the time, Cabinet office was deemed to be "an office of profit" under the Crown, requiring the promoted man to obtain the endorsement of his constituents by standing for re-election. After O'Connell won election, he was unable to take his seat as members of parliament had to take the Oath of Supremacy, which was incompatible with Catholicism. The Prime Minister, the Duke of Wellington, and the Home Secretary, Sir Robert Peel, even though they opposed Catholic participation in Parliament, saw that denying O'Connell his seat would cause outrage and could lead to another rebellion or uprising in Ireland, which was about 85% Catholic. Peel and Wellington managed to convince King George IV that Catholic emancipation and the right of Catholics and Presbyterians and members of all Christian faiths other than the established Church of Ireland to sit in Parliament needed to be established; with the help of the Whigs, it became law in 1829. However, the Emancipation Act was not made retroactive, meaning that O'Connell had either to seek re-election or to attempt to take the oath of supremacy. When O'Connell attempted on 15 May to take his seat without taking the oath of supremacy, Solicitor-General Nicholas Conyngham Tindal moved that his seat be declared vacant and another election ordered; O'Connell was elected unopposed on 30 July 1829. He took his seat when Parliament resumed in February 1830, by which time Henry Charles Howard, 13th Duke of Norfolk and Earl of Surrey, had already become the first Roman Catholic to have taken advantage of the Emancipation Act and sit in Parliament. "Wellington is the King of England", King George IV once complained, "O'Connell is King of Ireland, and I am only the dean of Windsor." The regal jest expressed the general admiration for O'Connell at the height of his career. The Catholic emancipation campaign led by O'Connell served as the precedent and model for the emancipation of British Jews, the subsequent Jews Relief Act 1858 allowing Jewish MPs to omit the words in the Oath of Allegiance "and I make this Declaration upon the true Faith of a Christian". Ironically, considering O'Connell's dedication to peaceful methods of political agitation, his greatest political achievement ushered in a period of violence in Ireland. There was an obligation for those working the land to support the established Church (i.e., the United Church of England and Ireland) by payments known as tithes. The fact that the vast majority of those working the land in Ireland were Catholic or Presbyterian tenant farmers, supporting what was a minority religion within that island (but not the United Kingdom as a whole), had been causing tension for some time. In December 1830, he and several others were tried for holding a meeting as an association or assemblage in violation of the orders of the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland, but the statute expired in course of judgment and the prosecution was terminated by the judiciary. An initially peaceful campaign of non-payment turned violent in 1831 when the newly founded Irish Constabulary were used to seize property in lieu of payment resulting in the Tithe War of 1831–1836. Although opposed to the use of force, O'Connell successfully defended participants in the Battle of Carrickshock and all the defendants were acquitted. Nonetheless O'Connell rejected William Sharman Crawford's call for the complete abolition of tithes in 1838, as he felt he could not embarrass the Whigs (the Lichfield House Compact secured an alliance between Whigs, radicals and Irish MPs in 1835). In 1841, Daniel O'Connell became the first Roman Catholic Lord Mayor of Dublin since the reign of James II, who had been the last Roman Catholic monarch of England, Ireland and Scotland.
27cm x 22cm Charles Stewart Parnell (1846-1891) will be remembered as one of the most iconic and indeed controversial politicians in Irish history.MP and Leader of the Irish Parliamentary or Home Rule Party from1882 to 1891 until revelations of his adulterous love affair with Kitty O'Shea forced his resignation.He died shortly afterwards from pneumonia in the arms of his newly divorced and remarried wife Katherine.His death was considered to be a direct result of the stresses he endured because of the Victorian era scandal and his subsequent funeral at Glasnevin Cemetery in Dublin was attended by more than 200000 people.His notability was such that his gravestone of unhewn Wicklow granite, erected in 1940,reads only Parnell. This faithful portrayal of Parnell,well over 130 years old, by the artist JG Wills dates to 1884 and is a beautiful homage to the "uncrowned king of Ireland". Daniel O'Connell (18th August 1775 – 15 May 1847), often referred to as The Liberator or The Emancipator,was an Irish political leader in the first half of the 19th century. He campaigned for Catholic emancipation—including the right for Catholics to sit in the Westminster Parliament, denied for over 100 years—and repeal of the Acts of Union which combined Great Britain and Ireland. Throughout his career in Irish politics, O'Connell was able to gain a large following among the Irish masses in support of him and his Catholic Association. O'Connell's main strategy was one of political reformism, working within the parliamentary structures of the British state in Ireland and forming an alliance of convenience with the Whigs. More radical elements broke with O'Connell to found the Young Ireland movement. O'Connell was born at Carhan near Cahersiveen, County Kerry, to the O'Connells of Derrynane, a once-wealthy Roman Catholic family that had been dispossessed of its lands. His parents were Morgan O'Connell and Catherine O'Mullane. Among his uncles was Daniel Charles, Count O'Connell, an officer in the Irish Brigades of the French Army. A famous aunt was Eibhlín Dubh Ní Chonaill, while Sir James O'Connell, 1st Baronet, was his younger brother. Under the patronage of his wealthy bachelor uncle Maurice "Hunting Cap" O'Connell. O'Connell was first sent with his brother Maurice to Reddington Academy at Long Island, near Queenstown (Cobh) They both studied at Douai in France from 1790 and O'Connell was admitted as a barrister to Lincoln's Inn in 1794, transferring to Dublin's King's Inns two years later. In his early years, he became acquainted with the pro-democracy radicals of the time and committed himself to bringing equal rights and religious tolerance to his own country.While in Dublin studying for the law, O'Connell was under his Uncle Maurice's instructions not to become involved in any militia activity. When Wolfe Tone's French invasion fleet entered Bantry Bay in December 1796, O'Connell found himself in a quandary. Politics was the cause of his unsettlement. Dennis Gwynn in his Daniel O'Connell: The Irish Liberator suggests that the unsettlement was because he was enrolled as a volunteer in defence of Government, yet the Government was intensifying its persecution of the Catholic people—of which he was one.He desired to enter Parliament, yet every allowance that the Catholics had been led to anticipate, two years previously, was now flatly vetoed. As a law student, O'Connell was aware of his own talents, but the higher ranks of the Bar were closed to him. He read the Jockey Club as a picture of the governing class in England and was persuaded by it that, "vice reigns triumphant in the English court at this day. The spirit of liberty shrinks to protect property from the attacks of French innovators. The corrupt higher orders tremble for their vicious enjoyments." O'Connell's studies at the time had concentrated upon the legal and political history of Ireland, and the debates of the Historical Society concerned the records of governments, and from this he was to conclude, according to one of his biographers, "in Ireland the whole policy of the Government was to repress the people and to maintain the ascendancy of a privileged and corrupt minority". On 3 January 1797, in an atmosphere of alarm over the French invasion fleet in Bantry Bay, he wrote to his uncle saying that he was the last of his colleagues to join a volunteer corps and "being young, active, healthy and single" he could offer no plausible excuse.Later that month, for the sake of expediency, he joined the Lawyers' Artillery Corps. On 19 May 1798, O'Connell was called to the Irish Bar and became a barrister. Four days later, the United Irishmen staged their rebellion which was put down by the British with great bloodshed. O'Connell did not support the rebellion; he believed that the Irish would have to assert themselves politically rather than by force. He went on the Munster circuit, and for over a decade, he went into a fairly quiet period of private law practice in the South of Ireland.He was reputed to have the largest income of any Irish barrister but, due to natural extravagance and a growing family, was usually in debt; his brother remarked caustically that Daniel was in debt all his life from the age of seventeen. Although he was ultimately to inherit Derrynane from his uncle Maurice, the old man lived to be almost 100 and in the event Daniel's inheritance did not cover his debts. He also condemned Robert Emmet's Rebellion of 1803. Of Emmet, a Protestant, he wrote: "A man who could coolly prepare so much bloodshed, so many murders—and such horrors of every kind has ceased to be an object of compassion." Despite his opposition to the use of violence, he was willing to defend those accused of political crimes, particularly if he suspected that they had been falsely accused, as in the Doneraile conspiracy trials of 1829, his last notable court appearance. He was noted for his fearlessness in court: if he thought poorly of a judge (as was very often the case) he had no hesitation in making this clear. Most famous perhaps was his retort to Baron McClelland, who had said that as a barrister he would never have taken the course O'Connell had adopted: O'Connell said that McClelland had never been his model as a barrister, neither would he take directions from him as a judge. He did not lack the ambition to become a judge himself: in particular he was attracted by the position of Master of the Rolls in Ireland, yet although he was offered it more than once, finally refused. O'Connell returned to politics in the 1810s. In 1811, he established the Catholic Board, which campaigned for Catholic emancipation, that is, the opportunity for Irish Catholics to become members of parliament. In 1823, he set up the Catholic Association which embraced other aims to better Irish Catholics, such as: electoral reform, reform of the Church of Ireland, tenants' rights, and economic development. The Association was funded by membership dues of one penny per month, a minimal amount designed to attract Catholic peasants. The subscription was highly successful, and the Association raised a large sum of money in its first year. The money was used to campaign for Catholic emancipation, specifically funding pro-emancipation members of parliament (MPs) standing for the British House of Commons.O'Connell's home at Derrynane Co KerryMembers of the Association were liable to prosecution under an eighteenth-century statute, and the Crown moved to suppress the Association by a series of prosecutions, with mixed success. O'Connell was often briefed for the defence, and showed extraordinary vigour in pleading the rights of Catholics to argue for emancipation. He clashed repeatedly with William Saurin, the Attorney General for Ireland and most influential figure in the Dublin administration, and political differences between the two men were fuelled by a bitter personal antipathy. In 1815 a serious event in his life occurred. Dublin Corporation was considered a stronghold of the Protestant Ascendancy and O'Connell, in an 1815 speech, referred to it as a "beggarly corporation".Its members and leaders were outraged and because O'Connell would not apologise, one of their number, the noted duellist John D'Esterre, challenged him. The duel had filled Dublin Castle (from where the British Government administered Ireland) with tense excitement at the prospect that O'Connell would be killed. They regarded O'Connell as "worse than a public nuisance", and would have welcomed any prospect of seeing him removed at this time. O'Connell met D'Esterre and mortally wounded him (he was shot in the hip, the bullet then lodging in his stomach), in a duel at Oughterard, County Kildare. His conscience was bitterly sore by the fact that, not only had he killed a man, but he had left his family almost destitute. O'Connell offered to "share his income" with D'Esterre's widow, but she declined; however, she consented to accept an allowance for her daughter, which O'Connell regularly paid for more than thirty years until his death. The memory of the duel haunted him for the remainder of his life, and he refused ever to fight another, being prepared to risk accusations of cowardice rather than kill again. As part of his campaign for Catholic emancipation, O'Connell created the Catholic Association in 1823; this organisation acted as a pressure group against the British government so as to achieve emancipation. The Catholic Rent, which was established in 1824 by O'Connell and the Catholic Church raised funds from which O'Connell was able to help finance the Catholic Association in its push for emancipation. Official opinion was gradually swinging towards emancipation, as shown by the summary dismissal of William Saurin, the Attorney General and a leading opponent of religious toleration, whom O'Connell called "our mortal foe". O'Connell stood in a by-election to the British House of Commons in 1828 for County Clare against William Vesey Fitzgerald, who had just joined the British Cabinet as President of the Board of Trade. By law at the time, Cabinet office was deemed to be "an office of profit" under the Crown, requiring the promoted man to obtain the endorsement of his constituents by standing for re-election. After O'Connell won election, he was unable to take his seat as members of parliament had to take the Oath of Supremacy, which was incompatible with Catholicism. The Prime Minister, the Duke of Wellington, and the Home Secretary, Sir Robert Peel, even though they opposed Catholic participation in Parliament, saw that denying O'Connell his seat would cause outrage and could lead to another rebellion or uprising in Ireland, which was about 85% Catholic. Peel and Wellington managed to convince King George IV that Catholic emancipation and the right of Catholics and Presbyterians and members of all Christian faiths other than the established Church of Ireland to sit in Parliament needed to be established; with the help of the Whigs, it became law in 1829. However, the Emancipation Act was not made retroactive, meaning that O'Connell had either to seek re-election or to attempt to take the oath of supremacy. When O'Connell attempted on 15 May to take his seat without taking the oath of supremacy, Solicitor-General Nicholas Conyngham Tindal moved that his seat be declared vacant and another election ordered; O'Connell was elected unopposed on 30 July 1829. He took his seat when Parliament resumed in February 1830, by which time Henry Charles Howard, 13th Duke of Norfolk and Earl of Surrey, had already become the first Roman Catholic to have taken advantage of the Emancipation Act and sit in Parliament. "Wellington is the King of England", King George IV once complained, "O'Connell is King of Ireland, and I am only the dean of Windsor." The regal jest expressed the general admiration for O'Connell at the height of his career. The Catholic emancipation campaign led by O'Connell served as the precedent and model for the emancipation of British Jews, the subsequent Jews Relief Act 1858 allowing Jewish MPs to omit the words in the Oath of Allegiance "and I make this Declaration upon the true Faith of a Christian". Ironically, considering O'Connell's dedication to peaceful methods of political agitation, his greatest political achievement ushered in a period of violence in Ireland. There was an obligation for those working the land to support the established Church (i.e., the United Church of England and Ireland) by payments known as tithes. The fact that the vast majority of those working the land in Ireland were Catholic or Presbyterian tenant farmers, supporting what was a minority religion within that island (but not the United Kingdom as a whole), had been causing tension for some time. In December 1830, he and several others were tried for holding a meeting as an association or assemblage in violation of the orders of the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland, but the statute expired in course of judgment and the prosecution was terminated by the judiciary. An initially peaceful campaign of non-payment turned violent in 1831 when the newly founded Irish Constabulary were used to seize property in lieu of payment resulting in the Tithe War of 1831–1836. Although opposed to the use of force, O'Connell successfully defended participants in the Battle of Carrickshock and all the defendants were acquitted. Nonetheless O'Connell rejected William Sharman Crawford's call for the complete abolition of tithes in 1838, as he felt he could not embarrass the Whigs (the Lichfield House Compact secured an alliance between Whigs, radicals and Irish MPs in 1835). In 1841, Daniel O'Connell became the first Roman Catholic Lord Mayor of Dublin since the reign of James II, who had been the last Roman Catholic monarch of England, Ireland and Scotland. Statue of Daniel O'Connell outside St Patrick's Cathedral, MelbourneOnce Catholic emancipation was achieved, O'Connell campaigned for repeal of the Act of Union, which in 1801 had merged the Parliaments of the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland to form the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. To campaign for repeal, O'Connell set up the Repeal Association. He argued for the re-creation of an independent Kingdom of Ireland to govern itself, with Queen Victoria as the Queen of Ireland. To push for this, he held a series of "Monster Meetings" throughout much of Ireland outside the Protestant and Unionist-dominated province of Ulster. They were so called because each was attended by around 100,000 people. These rallies concerned the British Government and the Prime Minister, Sir Robert Peel, banned one such proposed monster meeting at Clontarf, County Dublin, just outside Dublin city in 1843. This move was made after the biggest monster meeting was held at Tara. Tara held great significance to the Irish population as it was the historic seat of the High Kings of Ireland. Clontarf was symbolic because of its association with the Battle of Clontarf in 1014, when the Irish King Brian Boru defeated his rival Maelmordha, although Brian himself died during the battle. Despite appeals from his supporters, O'Connell refused to defy the authorities and he called off the meeting, as he was unwilling to risk bloodshed and had no others. He was arrested, charged with conspiracy and sentenced to a year's imprisonment and a fine of £2,000, although he was released after three months by the House of Lords, which quashed the conviction and severely criticised the unfairness of the trial. Having deprived himself of his most potent weapon, the monster meeting, O'Connell with his health failing had no plan and dissension broke out in the Repeal Association.
Statue of Daniel O'Connell outside St Patrick's Cathedral, MelbourneOnce Catholic emancipation was achieved, O'Connell campaigned for repeal of the Act of Union, which in 1801 had merged the Parliaments of the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland to form the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. To campaign for repeal, O'Connell set up the Repeal Association. He argued for the re-creation of an independent Kingdom of Ireland to govern itself, with Queen Victoria as the Queen of Ireland. To push for this, he held a series of "Monster Meetings" throughout much of Ireland outside the Protestant and Unionist-dominated province of Ulster. They were so called because each was attended by around 100,000 people. These rallies concerned the British Government and the Prime Minister, Sir Robert Peel, banned one such proposed monster meeting at Clontarf, County Dublin, just outside Dublin city in 1843. This move was made after the biggest monster meeting was held at Tara. Tara held great significance to the Irish population as it was the historic seat of the High Kings of Ireland. Clontarf was symbolic because of its association with the Battle of Clontarf in 1014, when the Irish King Brian Boru defeated his rival Maelmordha, although Brian himself died during the battle. Despite appeals from his supporters, O'Connell refused to defy the authorities and he called off the meeting, as he was unwilling to risk bloodshed and had no others. He was arrested, charged with conspiracy and sentenced to a year's imprisonment and a fine of £2,000, although he was released after three months by the House of Lords, which quashed the conviction and severely criticised the unfairness of the trial. Having deprived himself of his most potent weapon, the monster meeting, O'Connell with his health failing had no plan and dissension broke out in the Repeal Association. The Monster Meeting at Clifden in 1843 by Joseph Patrick Haverty. O'Connell is depicted in the center addressing the gathered masses.
The Monster Meeting at Clifden in 1843 by Joseph Patrick Haverty. O'Connell is depicted in the center addressing the gathered masses.
Daniel O'Connell is honoured on the first commemorative stamps of Ireland, issued in 1929. O'Connell died of softening of the brain (cerebral softening) in 1847 in Genoa, Italy, while on a pilgrimage to Rome at the age of 71; his term in prison had seriously weakened him, and the appallingly cold weather he had to endure on his journey was probably the final blow. According to his dying wish, his heart was buried in Rome (at Sant'Agata dei Goti, then the chapel of the Irish College), and the remainder of his body in Glasnevin Cemetery in Dublin, beneath a round tower. His sons are buried in his crypt. On 6 August 1875, Charles Herbert Mackintosh won the gold and silver medals offered by the St. Patrick's Society during the O'Connell centenary at Major's Hill Park in Ottawa, Ontario for a prize poem entitled The Irish Liberator. O'Connell's philosophy and career have inspired leaders all over the world, including Mahatma Gandhi (1869–1948) and Martin Luther King (1929–1968). He was told by William Makepeace Thackeray (1811–1863) "you have done more for your nation than any man since Washington ever did". William Gladstone (1809–1898) described him as "the greatest popular leader the world has ever seen". Honoré de Balzac (1799–1850) wrote that "Napoleon and O'Connell were the only great men the 19th century had ever seen." Jean-Henri Merle d'Aubigné (1794–1872) wrote that "the only man like Luther, in the power he wielded was O'Connell". William Grenville (1759–1834) wrote that "history will speak of him as one of the most remarkable men that ever lived". O'Connell met, befriended, and became a great inspiration to Frederick Douglass (1818–1895) a former American slave who became a highly influential leader of the abolitionist movement, social reformer, orator, writer and statesman. O'Connell's attacks on slavery were made with his usual vigour, and often gave great offence, especially in the United States: he called George Washington a hypocrite, and was challenged to a duel by Andrew Stevenson, the American minister, whom he was reported to have called a slave breeder. Notwithstanding his pronounced opposition to slavery, however, O'Connell, in the words of Lee M. Jenkins in her 1999 Irish Review article "Beyond the Pale: Frederick Douglass in Cork", "accepted money for his Repeal cause from Southern slaveholders". The founder of the Irish Labour Party and executed Easter Rising leader James Connolly, devoted a chapter in his 1910 book "Labour in Irish History" entitled "A chapter of horrors: Daniel O'Connell and the working class" in which he criticised O'Connell's parliamentary record, accusing him of siding consistently with the interests of the propertied classes of the United Kingdom. And Patrick Pearse, Connolly's fellow leader of the Easter Rising, wrote: "The leaders in Ireland have nearly always left the people at the critical moment. ... O'Connell recoiled before the cannon at Clontarf" though adding "I do not blame these men; you or I might have done the same. It is a terrible responsibility to be cast on a man, that of bidding the cannon speak and the grapeshot pour". In O'Connell's lifetime, the aims of his Repeal Association—an independent Kingdom of Ireland governing itself but keeping the British monarch as its Head of State—proved too radical for the British government of the time to accept, and brought upon O'Connell persecution and suppression. O'Connell is known in Ireland as "The Liberator" or "The Great Emancipator" for his success in achieving Catholic Emancipation. O'Connell admired Latin American liberator Simón Bolívar, and one of his sons, Morgan O'Connell, was a volunteer officer in Bolívar's army in 1820, aged 15. The principal street in the centre of Dublin, previously called Sackville Street, was renamed O'Connell Street in his honour in the early 20th century after the Irish Free Statecame into being.His statue (made by the sculptor John Henry Foley, who also designed the sculptures of the Albert Memorial in London) stands at one end of the street, with a statue of Charles Stewart Parnell at the other end. The main street of Limerick is also named after O'Connell, also with a statue at the end (in the centre of the Crescent). O'Connell Streets also exist in Ennis, Sligo, Athlone, Kilkee, Clonmel. Dungarvan and Waterford. The Daniel O'Connell Bridge was built over the Ophir River, Central Otago, New Zealand in 1880. There is a statue honouring O'Connell outside St Patrick's Cathedral in Melbourne, Australia.There is a museum commemorating him in Derrynane House, near the village of Derrynane, County Kerry, which was once owned by his family.He was a member of the Literary Association of the Friends of Poland as well.Mausoleum of Daniel O'Connell in Glasnevin CemeteryIn 1802 O'Connell married his third cousin, Mary O'Connell. It was a love marriage, and to persist in it was an act of considerable courage, since Daniel's uncle Maurice was outraged (as Mary had no fortune) and for a time threatened to disinherit them. They had four daughters (three surviving), Ellen(1805–1883), Catherine (1808), Elizabeth (1810), and Rickarda (1815) and four sons. The sons—Maurice (1803), Morgan (1804), John (1810), and Daniel(1816)—all sat in Parliament. The marriage was happy and Mary's death in 1837 was a blow from which her husband never fully recovered. He was a devoted father; O'Faoláin suggests that despite his wide acquaintance he had few close friends and therefore the family circle meant a great deal to him. O'Connell assisted his younger son, Daniel junior, to acquire the Phoenix Brewery in James's Street, Dublin in 1831. The brewery produced a brand known as "O'Connell's Ale" and enjoyed some popularity. By 1832, O'Connell was forced to state that he would not be a political patron of the brewing trade or his son's company, until he was no longer a member of parliament, particularly because O'Connell and Arthur Guinness were political enemies. Guinness was the "moderate" liberal candidate, O'Connell was the "radical" liberal candidate. The rivalry caused dozens of Irish firms to boycott Guinness during the 1841 Repeal election. It was at this time that Guinness was accused of supporting the "Orange system", and its beer was known as "Protestant porter". When the O'Connell family left brewing, the rights to "O'Connell Dublin Ale" was sold to John D'Arcy. The brewing business proved to be unsuccessful though, and after a few years was taken over by the manager, John Brennan, while Daniel junior embraced a political career. Brennan changed the name back to the Phoenix Brewery but continued to brew and sell O'Connell's Ale. When the Phoenix Brewery was effectively closed after being absorbed into the Guinness complex in 1909, the brewing of O'Connell's Ale was carried out by John D'Arcy and Son Ltd at the Anchor Brewery in Usher Street. In 1926, D'Arcy's ceased trading and the firm of Watkins, Jameson and Pim carried on the brewing until they too succumbed to the pressures of trying to compete with Guinness. Daniel junior was the committee chairman of the licensed trade association of the period and gave considerable and valuable support to Daniel O'Connell in his public life. Some time later a quarrel arose and O'Connell turned his back on the association and became a strong advocate of temperance. During the period of Fr. Mathew's total abstinence crusades many temperance rallies were held, the most notable being a huge rally held on St. Patrick's Day in 1841. Daniel O'Connell was a guest of honour at another such rally held at the Rotunda Hospital. 1834 portrait of Daniel O'Connell by George HayterMichael Doheny, in his The Felon's Track, says that the very character of emancipation has assumed an "exaggerated and false guise" and that it is an error to call it emancipation. He went on, that it was neither the first nor the last nor even the most important in the concessions, which are entitled to the name of emancipation, and that no one remembered the men whose exertions "wrung from the reluctant spirit of a far darker time the right of living, of worship, of enjoying property, and exercising the franchise".Doheny's opinion was, that the penalties of the "Penal Laws" had been long abolished, and that barbarous code had been compressed into cold and stolid exclusiveness and yet Mr. O'Connell monopolised its entire renown. The view put forward by John Mitchel, also one of the leading members of the Young Ireland movement, in his "Jail Journal" was that there were two distinct movements in Ireland during this period, which were rousing the people, one was the Catholic Relief Agitation (led by O'Connell), which was both open and legal, the other was the secret societies known as the Ribbon and White—boy movements. The first proposed the admission of professional and genteel Catholics to Parliament and to the honours of the professions, all under British law—the other, originating in an utter horror and defiance of British law, contemplated nothing less than a social, and ultimately, a political revolution. According to Mitchel, for fear of the latter, Great Britain with a "very ill grace yielded to the first". Mitchel agrees that Sir Robert Peel and the Duke of Wellington said they brought in this measure, to avert civil war; but says that "no British statesman ever officially tells the truth, or assigns to any act its real motive." Their real motive was, according to Mitchel, to buy into the British interests, the landed and educated Catholics, these "Respectable Catholics" would then be contented, and "become West Britons" from that day.
1834 portrait of Daniel O'Connell by George HayterMichael Doheny, in his The Felon's Track, says that the very character of emancipation has assumed an "exaggerated and false guise" and that it is an error to call it emancipation. He went on, that it was neither the first nor the last nor even the most important in the concessions, which are entitled to the name of emancipation, and that no one remembered the men whose exertions "wrung from the reluctant spirit of a far darker time the right of living, of worship, of enjoying property, and exercising the franchise".Doheny's opinion was, that the penalties of the "Penal Laws" had been long abolished, and that barbarous code had been compressed into cold and stolid exclusiveness and yet Mr. O'Connell monopolised its entire renown. The view put forward by John Mitchel, also one of the leading members of the Young Ireland movement, in his "Jail Journal" was that there were two distinct movements in Ireland during this period, which were rousing the people, one was the Catholic Relief Agitation (led by O'Connell), which was both open and legal, the other was the secret societies known as the Ribbon and White—boy movements. The first proposed the admission of professional and genteel Catholics to Parliament and to the honours of the professions, all under British law—the other, originating in an utter horror and defiance of British law, contemplated nothing less than a social, and ultimately, a political revolution. According to Mitchel, for fear of the latter, Great Britain with a "very ill grace yielded to the first". Mitchel agrees that Sir Robert Peel and the Duke of Wellington said they brought in this measure, to avert civil war; but says that "no British statesman ever officially tells the truth, or assigns to any act its real motive." Their real motive was, according to Mitchel, to buy into the British interests, the landed and educated Catholics, these "Respectable Catholics" would then be contented, and "become West Britons" from that day. O'Connell is on the left edge in this painting which is of the 1840 World Anti-Slavery Convention.A critic of violent insurrection in Ireland, O'Connell once said that "the altar of liberty totters when it is cemented only with blood", and yet as late as 1841, O'Connell had whipped his MPs into line to keep the (First) Opium War going in China. The Tories at the time had proposed a motion of censure over the war, and O'Connell had to call upon his MPs to support the Whig Government. As a result of this intervention, the Government was saved. Politically, he focused on parliamentary and populist methods to force change and made regular declarations of his loyalty to the British Crown. He often warned the British establishment that if they did not reform the governance of Ireland, Irishmen would start to listen to the "counsels of violent men". Successive British governments continued to ignore this advice, long after his death, although he succeeded in extracting by the sheer force of will and the power of the Catholic peasants and clergy much of what he wanted, i.e., eliminating disabilities on Roman Catholics; ensuring that lawfully elected Roman Catholics could serve their constituencies in the British Parliament (until the Irish Parliament was restored); and amending the Oath of Allegiance so as to remove clauses offensive to Roman Catholics who could then take the Oath in good conscience. Although a native speaker of the Irish language, O'Connell encouraged Irish people to learn English to better themselves.Although he is best known for the campaign for Catholic emancipation; he also supported similar efforts for Irish Jews. At his insistence, in 1846, the British law "De Judaismo", which prescribed a special dress for Jews, was repealed. O'Connell said: "Ireland has claims on your ancient race, it is the only country that I know of unsullied by any one act of persecution of the Jews".In April 1835, misled by inaccurate press reports, O'Connell thought Disraeli had slandered him and launched an outspoken attack upon him: Disraeli sought satisfaction by challenging O'Connell's son Morgan to a duel, Daniel having sworn never to duel again after previously killing a man. Morgan declined, replying that he was not responsible for his father's words.
O'Connell is on the left edge in this painting which is of the 1840 World Anti-Slavery Convention.A critic of violent insurrection in Ireland, O'Connell once said that "the altar of liberty totters when it is cemented only with blood", and yet as late as 1841, O'Connell had whipped his MPs into line to keep the (First) Opium War going in China. The Tories at the time had proposed a motion of censure over the war, and O'Connell had to call upon his MPs to support the Whig Government. As a result of this intervention, the Government was saved. Politically, he focused on parliamentary and populist methods to force change and made regular declarations of his loyalty to the British Crown. He often warned the British establishment that if they did not reform the governance of Ireland, Irishmen would start to listen to the "counsels of violent men". Successive British governments continued to ignore this advice, long after his death, although he succeeded in extracting by the sheer force of will and the power of the Catholic peasants and clergy much of what he wanted, i.e., eliminating disabilities on Roman Catholics; ensuring that lawfully elected Roman Catholics could serve their constituencies in the British Parliament (until the Irish Parliament was restored); and amending the Oath of Allegiance so as to remove clauses offensive to Roman Catholics who could then take the Oath in good conscience. Although a native speaker of the Irish language, O'Connell encouraged Irish people to learn English to better themselves.Although he is best known for the campaign for Catholic emancipation; he also supported similar efforts for Irish Jews. At his insistence, in 1846, the British law "De Judaismo", which prescribed a special dress for Jews, was repealed. O'Connell said: "Ireland has claims on your ancient race, it is the only country that I know of unsullied by any one act of persecution of the Jews".In April 1835, misled by inaccurate press reports, O'Connell thought Disraeli had slandered him and launched an outspoken attack upon him: Disraeli sought satisfaction by challenging O'Connell's son Morgan to a duel, Daniel having sworn never to duel again after previously killing a man. Morgan declined, replying that he was not responsible for his father's words. "Daniel O'Connell: The Champion of Liberty" poster published in Pennsylvania, 1847
"Daniel O'Connell: The Champion of Liberty" poster published in Pennsylvania, 1847 O'Connell's grave in Glasnevin Cemetery, Dublin. In accordance with his final words – "My body to Ireland, my heart to Rome, and my soul to heaven" – his embalmed heart was interred in a silver casket and sent to Rome, though it is now lost.
O'Connell's grave in Glasnevin Cemetery, Dublin. In accordance with his final words – "My body to Ireland, my heart to Rome, and my soul to heaven" – his embalmed heart was interred in a silver casket and sent to Rome, though it is now lost.- "The altar of liberty totters when it is cemented only with blood." (Written in his Journal, December 1796, and one of O'Connell's most well-known quotes. Quoted by O'Ferrall, F., Daniel O'Connell, Dublin, 1981, p. 12)
- "Gentlemen, you may soon have the alternative to live as slaves or die as free men." (speaking in Mallow, County Cork)
- "Good God, what a brute man becomes when ignorant and oppressed. Oh Liberty! What horrors are committed in thy name! May every virtuous revolutionist remember the horrors of Wexford!" (Written in his journal, 2 January 1799, referring to the recent 1798 Rebellion. Quoted from Vol I, p. 205, of O'Neill Daunt, W. J., Personal Recollections of the Late Daniel O'Connell, M.P., 2 Vols, London, 1848.)
- "My days—the blossom of my youth and the flower of my manhood—have been darkened by the dreariness of servitude. In this my native land—in the land of my sires—I am degraded without fault as an alien and an outcast." (July 1812, aged 37, reflecting on the failure to secure equal rights or Catholic Emancipation for Catholics in Ireland. Quoted from Vol I, p. 185, of O'Connell, J. (ed.) The Life and Speeches of Daniel O'Connell, 2 Vols, Dublin, 1846)
- "How cruel the Penal Laws are which exclude me from a fair trial with men whom I look upon as so much my inferiors ...'. (O'Connell's Correspondence, Letter No 700, Vol II)
- "I want to make all Europe and America know it—I want to make England feel her weakness if she refuses to give the justice we [the Irish] require—the restoration of our domestic parliament ..." (Speech given at a 'monster' meeting held at Drogheda, June 1843)
- "There is an utter ignorance of, and indifference to, our sufferings and privations ... What care they for us, provided we be submissive, pay the taxes, furnish recruits for the Army and Navy and bless the masters who either despise or oppress or combine both? The apathy that exists respecting Ireland is worse than the national antipathy they bear us." (Letter to T. M. Ray, 1839, on English attitudes to Ireland (O'Connell, Correspondence, Vol VI, Letter No. 2588))
- "No person knows better than you do that the domination of England is the sole and blighting curse of this country. It is the incubus that sits on our energies, stops the pulsation of the nation's heart and leaves to Ireland not gay vitality but horrid the convulsions of a troubled dream." (Letter to Bishop Doyle, 1831 (O'Connell Correspondence, Vol IV, Letter No. 1860))
- "The principle of my political life ... is, that all ameliorations and improvements in political institutions can be obtained by persevering in a perfectly peaceable and legal course, and cannot be obtained by forcible means, or if they could be got by forcible means, such means create more evils than they cure, and leave the country worse than they found it.' (Writing in The Nationnewspaper, 18 November 1843)
- "No man was ever a good soldier but the man who goes into the battle determined to conquer, or not to come back from the battle field (cheers). No other principle makes a good soldier." (O'Connell recalling the spirited conduct of the Irish soldiers in Wellington's army, at the Monster meeting held at Mullaghmast.)
- "The poor old Duke [of Wellington]! What shall I say of him? To be sure he was born in Ireland, but being born in a stable does not make a man a horse." (Shaw's Authenticated Report of the Irish State Trials (1844), p. 93)
- "Every religion is good—every religion is true to him who in his good caution and conscience believes it." (As defence counsel in R. v Magee (1813), pleading for religious tolerance.)
- "Ireland is too poor for a poor law." (In response to the Poor Relief Act of 1839 that set up the workhouses.
-
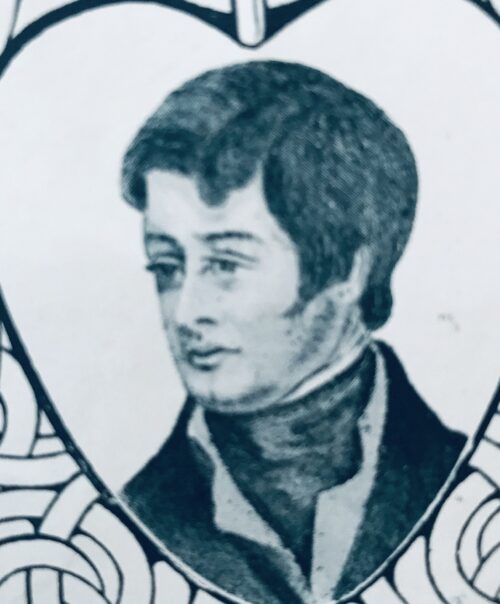

 27cm x 22cm Robert Emmet (4 March 1778 – 20 September 1803) was an Irish Republican, and Irish nationalist patriot, orator and rebel leader. After leading an abortive rebellion against British rule in 1803 he was captured then tried and executed for high treason against the British king George III of Great Britain and Ireland. Emmet came from a wealthy Anglo-Irish Protestant ascendancy Church of Ireland family who sympathized with Irish Catholics and Protestant Dissenters, particularly in Ulster, such as the Presbyterians and their lack of representation in Parliament. The Emmet family also sympathized with the rebel colonists, or "patriots", in the American Revolution. While Emmet's efforts to rebel against British rule failed, his actions and speech after his conviction inspired his compatriots.
27cm x 22cm Robert Emmet (4 March 1778 – 20 September 1803) was an Irish Republican, and Irish nationalist patriot, orator and rebel leader. After leading an abortive rebellion against British rule in 1803 he was captured then tried and executed for high treason against the British king George III of Great Britain and Ireland. Emmet came from a wealthy Anglo-Irish Protestant ascendancy Church of Ireland family who sympathized with Irish Catholics and Protestant Dissenters, particularly in Ulster, such as the Presbyterians and their lack of representation in Parliament. The Emmet family also sympathized with the rebel colonists, or "patriots", in the American Revolution. While Emmet's efforts to rebel against British rule failed, his actions and speech after his conviction inspired his compatriots.Early life
Emmet was born at 109 St. Stephen's Green, in Dublin on 4 March 1778. He was the youngest son of Dr Robert Emmet (1729–1802), a court physician, and his wife, Elizabeth Mason (1739–1803). The Emmets were financially comfortable, members of the Protestant Ascendancywith a house at St Stephen's Green and a country residence near Milltown. One of his elder brothers was an Irish Republican and Nationalist Thomas Addis Emmet, a close friend of Theobald Wolfe Tone, who was a frequent visitor to the house when Robert was a child. Emmet attended Oswald's school, in Dopping's-court, off Golden-lane.Emmet entered Trinity College Dublin in October 1793, at the age of fifteen. In December 1797 he joined the College Historical Society, a debating society.Career as a revolutionary
While Emmet was at college, his brother Thomas and some of his friends became involved in political activism. Robert became secretary of a secret United Irish Committee in college, and was expelled in April 1798 as a result. That same year he fled to France to avoid the many British arrests of nationalists that were taking place in Ireland. While in France, Emmet supposedly garnered the support of Napoleon, who had promised to lend support when the upcoming revolution started.However this pledged support existed in Emmet's imagination, as Napoleon was fully involved from early 1798 in organising the French invasion of Egypt. Napoleon was in Toulon from 9 May 1798, before the Irish Rebellion of 1798 had begun, yet there is no record of Emmet travelling to Toulon to see him. After the 1798 rising, Emmet was involved in reorganising the defeated United Irish Society. In April 1799 a warrant was issued for his arrest. He escaped and soon after travelled to the continent in the hope of securing French military aid, but his efforts were unsuccessful. The French Consulate dictatorship was however focused on new peace treaties, that resulted in the Treaty of Lunéville in 1801 and the Treaty of Amiens (March 1802). Emmet returned to Ireland in October 1802. In March the following year, he began preparations for another uprising. In the meantime, the French Consulate was holding on to Holland, Switzerland and Piedmont, in a manner contrary to the Treaty of Amiens, and so the treaty was ended by the British government in May 1803.1803 rebellion
After his return to Ireland, Emmet began to prepare a new rebellion, with fellow revolutionaries Thomas Russell and James Hope. He began to manufacture weapons and explosives at a number of premises in Dublin and developed a folding pike fitted with a hinge that allowed it to be concealed under a cloak. Unlike in 1798, the revolutionaries concealed their preparations, but a premature explosion at one of Emmet's arms depots killed a man. Emmet was forced to advance the date of the rising before the authorities' suspicions were aroused. Emmet was unable to secure the help of Michael Dwyer's Wicklow rebels. Many rebels from Kildare turned back due to the scarcity of firearms they had been promised, but the rising went ahead in Dublin on the evening of 23 July 1803. About 10,000 copies were printed of a proclamation in the name of the "Provisional Government", which influenced the 1916 Proclamation; most were destroyed by the authorities. Emmet wore a uniform of a green coat with white facings, white breeches, top-boots, and a cocked hat with feathers.[5] Failing to seize Dublin Castle, which was lightly defended, the rising of some 200 men amounted to a large-scale disturbance in the Thomas Street area. Emmet saw a dragoon being pulled from his horse and piked to death, the sight of which prompted him to call off the rising to avoid further bloodshed. But, he had lost all control of his followers. In one incident, the Lord Chief Justice of Ireland, Lord Kilwarden, was dragged from his carriage and stabbed by pikes. Found still alive, he was taken to a watch-house where he died shortly thereafter. He had been reviled as chief prosecutor of William Orr in 1797, but he was also the judge who granted habeas corpus to Wolfe Tone in 1798. Kilwarden's nephew, the Rev. Mr. Wolfe, was also murdered. Sporadic clashes continued into the night until finally quelled by British military forces.Capture and trial
Emmet fled into hiding, moving from Rathfarnham to Harold's Cross so that he could be near his sweetheart, Sarah Curran. He likely could have escaped to France, had he not insisted upon returning with Anne Devlin in order to take leave of Sarah Curran, to whom he was engaged. She was daughter of John Philpot Curran.Emmet was captured on 25 August and taken to the Castle, then removed to Kilmainham. Vigorous but ineffectual efforts were made to procure his escape. He was tried for treason on 19 September; the Crown repaired the weaknesses in its case by secretly buying the assistance of Emmet's defense attorney, Leonard McNally, for £200 and a pension.But McNally's assistant Peter Burrowes could not be bought and he pleaded the case as best he could. On 19 September, Emmet was found guilty of high treason. Before sentencing Emmet delivered a speech, the Speech from the Dock. It is especially remembered for its closing sentences and secured his posthumous fame among executed Irish republicans. It was printed in 1835 in Manchester for the bookseller TP Carlile.Let no man write my epitaph; for as no man who knows my motives dare now vindicate them, let not prejudice or ignorance, asperse them. Let them and me rest in obscurity and peace, and my tomb remain un-inscribed, and my memory in oblivion, until other times and other men can do justice to my character. When my country takes her place among the nations of the earth, then and not till then, let my epitaph be written. I have done.
An earlier and more credible version of the speech was published in 1818, taken from the notes of his counsel Peter Burrowes, in a biography on Sarah Curran's father John, emphasising that Emmet's epitaph should be written on the future vindication of his character, and not specifically when Ireland took its place as a nation. It closed:I am here ready to die. I am not allowed to vindicate my character; no man shall dare to vindicate my character; and when I am prevented from vindicating myself, let no man dare to calumniate me. Let my character and my motives repose in obscurity and peace, till other times and other men can do them justice. Then shall my character be vindicated; then may my epitaph be written.
The modern historian Patrick Geoghehan wrote in 2003: "At last count there are over seventy different versions of the text, but most of these are later reworkings and have little claim to acceptance." Chief Justice Lord Norbury sentenced Emmet to be hanged, drawn and quartered, as was customary for conviction of treason. The following day, 20 September, Emmet was executed in Thomas Street in front of St. Catherine's. He was hanged and then beheaded once dead. As family members and friends of Robert had also been arrested, including some who had nothing to do with the rebellion, no one came forward to claim his remains out of fear of arrest. Robert Emmet is described as slight in person; his features were regular, his forehead high, his eyes bright and full of expression, his nose sharp, thin, and straight, the lower part of his face slightly pock-marked, his complexion sallow.[5]Burial
Emmet's remains were first delivered to Newgate Prison and then back to Kilmainham Gaol, where the jailer was under instructions that if no one claimed them they were to be buried in a nearby hospital's burial grounds called 'Bully's Acre' in Kilmainham. A later search there found no remains. It is claimed that Emmet's remains were secretly removed from Bully's Acre and reinterred in St Michan's, a Dublin church with strong United Irish associations, though it was never confirmed.Speculation has continued regarding the whereabouts of Emmet's remains. It was suspected that they were buried secretly in the vault of a Dublin Anglican church. When the vault was inspected in the 1950s a headless corpse was found, suspected of being Emmet's, but could not be identified. Widely accepted is the theory that Emmet's remains were transferred to St Peter's Church in Aungier St. under cover of the burial of Robert's sister, Mary Anne Holmes, in 1804. In the 1980s the church was de-consecrated and all the coffins were removed from the vaults. The church has since been demolished.Legacy
Emmet became a heroic figure in Irish history. His speech from the dock is widely quoted and remembered, especially among Irish nationalists. As he and his family also supported the American Revolutionary War, he is remembered there as well.Emmet's housekeeper, Anne Devlin, is also remembered in Irish history for enduring torture without providing information to the authorities. Robert Emmet's older brother, Thomas Addis Emmet emigrated to the United States shortly after Robert's execution. He eventually served as the New York State Attorney General. His descendants include the prominent American portrait painters Lydia Field Emmet, Rosina Emmet Sherwood, Ellen Emmet Rand, and Jane Emmet de Glehn, who were Robert Emmet's great-grand-nieces. Another descendant is American playwright Robert Emmet Sherwood. Golf course architect Devereux Emmet, electrical engineer William Le Roy Emmet, United States Army colonel Robert Temple Emmet, and attorney and sportsman C. Temple Emmet were among his great-grand-nephews. Robert Emmet was honoured on two Irish postage stamps issued in 1953, commemorating the 150th anniversary of his death
Robert Emmet was honoured on two Irish postage stamps issued in 1953, commemorating the 150th anniversary of his deathRepresentation in popular culture
Robert Emmet wrote a letter from his cell in Kilmainham Gaol, Dublin on 8 September 1803. He addressed it to "Miss Sarah Curran, the Priory, Rathfarnham" and handed it to a prison warden, George Dunn, whom he trusted to deliver it. Dunn betrayed him and gave the letter to the government authorities. Due to Emmet's attempt to hide near Curran, which cost him his life, and his parting letter to her, Emmet became known as a legendary romantic character, appealing to the Victorian Era's appetite for Romanticism. His story was the subject of stage melodramas during the 19th century, most notably Dion Boucicault's inaccurate 1884 play Robert Emmet. He mistakenly portrayed Emmet and Curran as Roman Catholics (they were both Protestants), her father John Philpot Curran being portrayed as a Unionist, and Emmet being killed onstage by firing squad. Robert's friend from Trinity College, Thomas Moore, championed his cause by writing popular ballads about him and Sarah Curran, such as- Oh breathe not his name! let it sleep in the shade,
- Where cold and unhonoured his relics are laid!
- No trump tells thy virtues—the grave where they rest
- With thy dust shall remain unpolluted by fame,
- Till thy foes, by the world and by fortune caressed,
- Shall pass like a mist from the light of thy name.
Honours
Places named after Emmet in the United States include Emmetsburg, Iowa; Emmet, Nebraska;Emmet County, Iowa; Emmett, Michigan and Emmet County, Michigan.[20] The Robert Emmet Elementary School in Chicago, Illinois was named for him. Two time All Ireland Club Camogie Champions Robert Emmet's GAC Slaughtneil is named after him. Emmet Park in Savannah, Georgia was named after Emmet after urging from the large Irish born population in the city. Statues were erected in his honour:- A life size bronze statue of Robert Emmet by Jerome Connor stands in St Stephen's Green, Dublin, the parkland beside which Emmet was born.
- A bronze statue of Emmet by Jerome Connor stands in Washington, DC on Embassy Row (Massachusetts Avenue NW and S Street NW). A public commemoration of Emmet's execution and legacy is held annually on the fourth Sunday in September by the Irish American Unity Conference.
- A copy of this statue was installed on the Music Concourse in front of the California Academy of Sciences in San Francisco's Golden Gate Park.
-
Bronze statue of Robert Emmet, 1916, by Jerome Connor, from the collection of the Smithsonian American Art Museum. It is installed in Washington, DC's Embassy Row.
-
Statue of Robert Emmet in St Stephens Green, Dublin
-
Reproduction of Robert Emmet statue in San Francisco's Golden Gate Park
- A statue of Robert Emmet is in the courthouse square in Emmetsburg, Iowa.
Early life
Wolfe Tone was born on 20 June 1763. His family were descended from a French Protestant family who fled to England from Gascony in the 16th century to escape religious persecution. A branch of the family settled in Dublin in the 17th century. Theobald's father, Peter Tone, was a coach-maker who had a farm near Sallins, County Kildare and belonged to the Church of Ireland. His mother came from a Catholic merchant family who converted to Protestantism after Theobald was born. His maternal grandfather was captain of a vessel in the West India trade. He was baptised as Theobald Wolfe Tone in honour of his godfather, Theobald Wolfe of Blackhall, County Kildare, a first cousin of Arthur Wolfe, 1st Viscount Kilwarden. However, it was widely believed that Tone was the son of Theobald Wolfe, which, if true, made him a half-brother of the poet Charles Wolfe. After his death, he was widely referred to as Wolfe Tone. In 1783, Tone found work as a tutor to Anthony and Robert, younger half-brothers of Richard Martin MP of Galway, a prominent supporter of Catholic emancipation, at Dangan, the Martin family home.Tone fell in love with Martin's wife, but later wrote that it came to nothing. During this period he briefly considered a career in the theatre as an actor. He studied law at Trinity College Dublin, where he became an active member in the College Historical Society debating club and was elected its auditor in 1785. He graduated BA in February 1786.He qualified as a barrister in King's Inns at the age of 26 after keeping the requisite terms as a student member of the Middle Temple in London. As a student, he eloped with Martha Witherington, daughter of William and Catherine Witherington (née Fanning) of Dublin.She would go on to change her name to Matilda, at Tone's request. When they married, Tone was 22, and Matilda was about 16. In 1796, while he was in France and she in Hamburg he wrote in his journal: "She is the delight of my eyes, the joy of my heart, the only object for which I wish to live. I doat upon her to distraction." Disappointed at finding no support for a plan that he had submitted to William Pitt the Younger, to found a military colony in Hawaii, Tone initially planned to enlist as a soldier in the East India Company, but applied too late in the year, when no more ships would be sent out until the following spring.Politician
In September 1791, Tone published An Argument on behalf of the Catholics of Ireland, signed "A Northern Whig". It displayed the growing breach between Whig patriots like Henry Flood and Henry Grattan, who sought Catholic emancipation and parliamentary reform without severing the tie to England. Tone expressed contempt for the constitution Grattan obtained from the British government in 1782. Himself an Anglican, Tone urged co-operation between the religions in Ireland as the only means of obtaining redress of Irish grievances. The British government had just passed the Roman Catholic Relief Act 1791, but the Dublin parliament was in no hurry to do so. In October 1791 Tone converted these ideas into practical policy by founding, in conjunction with Thomas Russell (1767–1803), Napper Tandy and others, the Society of the United Irishmen. Until 1794, this society aimed at no more than the formation of a political union between Catholics and Protestants, with a view to obtaining a liberal measure of parliamentary reform. In 1792 he was appointed an assistant secretary of the Catholic Committee. The Catholics involved were not united regarding the steps they were to take, and in December 1791, sixty-eight members withdrew, led by Lord Kenmare, with the support of the higher clergy. When the British government questioned the legality of the Catholic Convention called in December 1792, Tone drew up for the committee a statement of the case on which a favourable opinion of counsel was obtained. A petition was made to King George III early in 1793, and that year the re-enfranchisement of Catholics was enacted – if they owned property as "forty-shilling freeholders". They could again be called as barristers and serve as army officers. They could not, however, enter parliament or be made state officials above grand jurors. The Convention voted to Tone a sum of £1,500 with a gold medal and voted to dissolve. In this new climate of goodwill the Maynooth College Act 1795 was passed. Sectarian animosity threatened to undermine the United Irishmen movement: two secret societies in Ulster fought against each other: the agrarian Protestant Peep o' Day Boys and their Catholic opponents the Defenders. Tone's aim was to unite both into a revolutionary army of Irish "men of no property". Tone himself admitted that with him hatred of England had always been "rather an instinct than a principle," though until his views should become more generally accepted in Ireland he was prepared to work for reform as distinguished from revolution. But he desired to root out the popular respect for the names of Charlemont and Grattan, and to transfer to more violent leaders the conduct of the national movement. Wolfe Tone's principles were drawn from the French Convention, and he was a disciple of Georges Danton and Thomas Paine.Revolutionary in exile
In 1794 the Society of United Irishmen became a sworn association, using oaths that aimed at the overthrow of the Kingdom of Ireland. Given that France and Britain had been at war since early 1793, administering or making such oaths turned a reformist republican society that had wanted to extend the franchise within the existing system into a republican revolutionary one. Affiliating more closely with the new French Republic also associated Tone with its evolving policy of "Dechristianization", which was strongly opposed by the Catholic Church in Ireland. Although he was seen as a Catholic champion in the early 1790s, most of his wealthier Catholic supporters fell away in 1794. Also in 1794, the United Irishmen, persuaded that no party in the Dublin parliament (where being an MP was limited to Anglicans) seemed likely to accept their scheme of universal manhood suffrage and equal electoral districts, began to recast their hopes on a French invasion. An Irish clergyman living in England, the Reverend William Jackson, who had taken in revolutionary opinions during his long stay in France, came to Ireland to ascertain to what extent the Irish people were ready to support a French invasion. Tone drew up a memorandum for Jackson on the state of Ireland, which he described as ripe for revolution. An attorney named Cockayne, to whom Jackson had imprudently disclosed his mission, betrayed the memorandum to the government.In April 1794 Jackson was arrested on a charge of treason and dramatically committed suicide during his trial. Several of the leading United Irishmen, including Archibald Hamilton Rowan, fled the country; the papers of the United Irishmen were seized by the Dublin administration, and for a time the organisation was broken up. Tone, who had not attended meetings of the society since May 1793, remained in Ireland until after the trial of Jackson and was advised to leave Ireland in April 1795. Having friends among the government party, including members of the Beresford family, he succeeded in making terms with the government and emigrated to the United States, where he arrived in May 1795.Before leaving, he and his family travelled to Belfast, and it was at the summit of Cavehill that Tone made the Cavehill Compact with fellow Irish radicals, including Russell and McCracken, promising "never to desist in our efforts until we had subverted the authority of England over our country, and asserted our independence." The United Irishmen reformed in 1796. The Society began seriously to look to France to support a rising with troops. Living in Philadelphia, Tone wrote a few months later to Thomas Russell expressing unqualified dislike of the American people, whom he imagined to be no more truly democratic in sentiment and no less attached to authority than the British; he described George Washington as a "high-flying aristocrat", and he found the aristocracy of money and achievement in America still less to his liking than the European aristocracy of birth.Tone also lived briefly in West Chester and in Downingtown, Pennsylvania. Finding himself at Philadelphia in the company of Reynolds, Rowan, and Tandy, Tone went to Paris to persuade the French government to send an expedition to invade Ireland. In February 1796 he arrived in Paris and had interviews with De La Croix and Carnot, who were impressed by his energy, sincerity, and ability. A commission was given him as adjutant-general in the French army, which he hoped might protect him from the penalty of treason in the event of capture by the British; though he himself claimed the authorship of a proclamation said to have been issued by the United Irishmen, enjoining that all Irishmen taken with arms in their hands in the British service should be instantly shot; and he supported a project for landing La Legion Noire in England, who were to burn Bristol. A sympathizer wrote of him, in French, saying: Statue of Tone, Bantry, County Cork
Statue of Tone, Bantry, County CorkWolf Tone was sent to France to claim the support of the Directory, under the express condition that the French should come to Ireland as allies, and should act under direction of the new government, as Rochambeau had done in America. With this view, Tone had frequently conferences at Paris with Hoche; and the Directory finally determined to send from Brest a fleet of forty-five sail, with an army of fifteen thousand men, under the charge of this able general, December 15, 1796. England was saved by a violent tempest.
Hoche's Expedition and the 1798 Rebellion
The French Directory planned a military landing in Ireland in support of the coming revolution foretold by Tone. The Directory possessed information from Lord Edward FitzGerald and Arthur O'Connor confirming Tone, and prepared to despatch an expedition under Louis Lazare Hoche. On 15 December 1796, the expedition, consisting of forty-three sail and carrying about 14,450 men with a large supply of war material for distribution in Ireland, sailed from Brest.Tone accompanied it as "Adjutant-general Smith" and had the greatest contempt for the seamanship of the French sailors, who were unable to land due to severe gales.They waited for days off Bantry Bay, waiting for the winds to ease, but eventually returned to France. Tone served for some months in the French army under Hoche, who had become the French Republic's minister of war after his victory against the Austrians at the Battle of Neuwied on the Rhine in April 1797. In June 1797 Tone took part in preparations for a military expedition to Ireland from the Batavian Republic, a puppet state created during the Batavian Revolution in the Low Countries in January 1795. However, the Batavian fleet under Dutch Vice-Admiral Jan de Winter was delayed in the harbour of Texel island that summer by unfavourable easterly winds and from mid-August by a British North-Sea fleet blockade. It eventually put to sea in the first week of October only to be immediately crushed by Admiral Adam Duncan in the Battle of Camperdown on October 11, 1797. Tone then returned to Paris. General Hoche, once tasked with an Irish expeditionary force, died of tuberculosis on 19 September 1797 at Wetzlar after returning to his command on France's Rhine frontier. In Ireland the membership of the United Irish had reached 300,000, about 6% of the population, but a vicious counter-insurgency campaign in 1797 weakened the organisation and forced the leadership to launch a rising without French aid. More importantly, in a largely devoutly Catholic country, the Roman Catholic hierarchy was completely opposed to the United Irish, as they were allied to the French who had just invaded Rome and set up the anti-clerical "Roman Republic" in early 1798. Napoleon Bonaparte, with whom Tone had several interviews at this time, was less disposed than Hoche had been to undertake in earnest an Irish expedition; and when the Rising broke out in Ireland in 1798 he had started for Egypt. When Tone urged the Directory to send effective assistance to the Irish rebels, all that could be promised was a number of raids to descend simultaneously around the Irish coast. One of these under General Humbert succeeded in landing a force near Killala, County Mayo, and gained some success in Connacht (particularly at Castlebar) before it was subdued by General Lake and Charles Cornwallis. Wolfe Tone's brother Matthew was captured, tried by court-martial, and hanged; a second raid, accompanied by In End of the Irish Invasion ; — or – the Destruction of the French Armada(1797), James Gillray caricatured the failure of Hoche's expedition.
In End of the Irish Invasion ; — or – the Destruction of the French Armada(1797), James Gillray caricatured the failure of Hoche's expedition. -

 27cm x 22cmOur parish patron saint, St. Columbkille, is not well known outside of Ireland and Scotland, yet he is one of the three great saints of Ireland and was the first missionary to Scotland. Born in 521 in Donegal, Ireland, to a family connected to kings and princes, Columb was a gifted man with incredible talents. He wrote poetry and music, established churches and monasteries, preached the gospel, and painted manuscripts. Columb’s family sent him off to study under the future St. Finnian at Clonard Abbey, where he surrendered his princely claims, became a monk, and was ordained. He spent the next 15 years preaching and teaching in Ireland. As was the custom in those days, he combined study and prayer with manual labor. By the time he was 25, he had founded 27 Irish monasteries, including those at Derry, Durrow, and Kells, as well as some 40 churches. His work for the Church gained him the addition of “kille” to his name. Columb means “dove” in Gaelic and kille is “church”, so he came to be known as the “church’s dove”. Columb lived, with every ounce of his energy, the commission of Jesus to “go and make disciples.” There is a famous tale about Columbkille that stands as one of the first copyright cases on record: Columbkille was so anxious to have a copy of Finnian’s Psalter that he shut himself up at night in the church that contained it and secretly transcribed it by hand. He was discovered by a monk who watched him through the keyhole and reported it to his superior. Bibles and prayer books were so scarce in those days that Abbot Finnian claimed the copy, refusing to allow it to leave the monastery. Columbkille refused to surrender it until he was obliged to do so, under protest, on Finnian's appeal to King Diarmaid, who said, "To every cow its calf," meaning to every book its copy. While historically a bit unclear, an unfortunate period followed, during which, owing to Columbkille's protection of a refugee and his impassioned denunciation of an injustice by King Diarmaid, war broke out between the clans of Ireland, and Columbkille became an exile of his own accord. Filled with remorse on account of those who had been slain in battle and condemned by many of his own friends, he experienced a change of heart and an irresistible call to preach to those who had not heard the gospel. In 563, at the age of 42, he left Ireland with 12 companions and landed on an island now known as Iona. Here on this desolate rock, only three miles long and two miles wide, he began his work. Iona became a center of Christian learning, the heart of Celtic Christianity, and a potent factor in the conversion of the Picts, Scots, and Northern English. Monks from the monasteries established by Columbkille would later travel to mainland Europe and Christianize the Frank and Germanic tribes. There are many miracles and incredible events recorded in the biography of St. Columbkille. His memory remains a potent force in Celtic lands, and his poetry and songs are still sung: “Alone with none but Thee, my God, I journey on my way; what need I fear when Thou art near, O King of night and day?"St. Patrick, (flourished 5th century, Britain and Ireland; feast day March 17), patron saint and national apostle of Ireland, credited with bringing Christianity to Ireland and probably responsible in part for the Christianization of the Picts and Anglo-Saxons. He is known only from two short works, the Confessio, a spiritual autobiography, and his Letter to Coroticus, a denunciation of British mistreatment of Irish Christians.
27cm x 22cmOur parish patron saint, St. Columbkille, is not well known outside of Ireland and Scotland, yet he is one of the three great saints of Ireland and was the first missionary to Scotland. Born in 521 in Donegal, Ireland, to a family connected to kings and princes, Columb was a gifted man with incredible talents. He wrote poetry and music, established churches and monasteries, preached the gospel, and painted manuscripts. Columb’s family sent him off to study under the future St. Finnian at Clonard Abbey, where he surrendered his princely claims, became a monk, and was ordained. He spent the next 15 years preaching and teaching in Ireland. As was the custom in those days, he combined study and prayer with manual labor. By the time he was 25, he had founded 27 Irish monasteries, including those at Derry, Durrow, and Kells, as well as some 40 churches. His work for the Church gained him the addition of “kille” to his name. Columb means “dove” in Gaelic and kille is “church”, so he came to be known as the “church’s dove”. Columb lived, with every ounce of his energy, the commission of Jesus to “go and make disciples.” There is a famous tale about Columbkille that stands as one of the first copyright cases on record: Columbkille was so anxious to have a copy of Finnian’s Psalter that he shut himself up at night in the church that contained it and secretly transcribed it by hand. He was discovered by a monk who watched him through the keyhole and reported it to his superior. Bibles and prayer books were so scarce in those days that Abbot Finnian claimed the copy, refusing to allow it to leave the monastery. Columbkille refused to surrender it until he was obliged to do so, under protest, on Finnian's appeal to King Diarmaid, who said, "To every cow its calf," meaning to every book its copy. While historically a bit unclear, an unfortunate period followed, during which, owing to Columbkille's protection of a refugee and his impassioned denunciation of an injustice by King Diarmaid, war broke out between the clans of Ireland, and Columbkille became an exile of his own accord. Filled with remorse on account of those who had been slain in battle and condemned by many of his own friends, he experienced a change of heart and an irresistible call to preach to those who had not heard the gospel. In 563, at the age of 42, he left Ireland with 12 companions and landed on an island now known as Iona. Here on this desolate rock, only three miles long and two miles wide, he began his work. Iona became a center of Christian learning, the heart of Celtic Christianity, and a potent factor in the conversion of the Picts, Scots, and Northern English. Monks from the monasteries established by Columbkille would later travel to mainland Europe and Christianize the Frank and Germanic tribes. There are many miracles and incredible events recorded in the biography of St. Columbkille. His memory remains a potent force in Celtic lands, and his poetry and songs are still sung: “Alone with none but Thee, my God, I journey on my way; what need I fear when Thou art near, O King of night and day?"St. Patrick, (flourished 5th century, Britain and Ireland; feast day March 17), patron saint and national apostle of Ireland, credited with bringing Christianity to Ireland and probably responsible in part for the Christianization of the Picts and Anglo-Saxons. He is known only from two short works, the Confessio, a spiritual autobiography, and his Letter to Coroticus, a denunciation of British mistreatment of Irish Christians.Patrick was born in Britain of a Romanized family. At age 16 he was torn by Irish raiders from the villa of his father, Calpurnius, a deacon and minor local official, and carried into slavery in Ireland. He spent six bleak years there as a herdsman, during which he turned with fervour to his faith. Upon dreaming that the ship in which he was to escape was ready, he fled his master and found passage to Britain. There he came near to starvation and suffered a second brief captivity before he was reunited with his family. Thereafter, he may have paid a short visit to the Continent.The best known passage in the Confessio tells of a dream, after his return to Britain, in which one Victoricus delivered him a letter headed “The Voice of the Irish.” As he read it, he seemed to hear a certain company of Irish beseeching him to walk once more among them. “Deeply moved,” he says, “I could read no more.” Nevertheless, because of the shortcomings of his education, he was reluctant for a long time to respond to the call. Even on the eve of reembarkation for Ireland he was beset by doubts of his fitness for the task. Once in the field, however, his hesitations vanished. Utterly confident in the Lord, he journeyed far and wide, baptizing and confirming with untiring zeal. In diplomatic fashion he brought gifts to a kinglet here and a lawgiver there but accepted none from any. On at least one occasion, he was cast into chains. On another, he addressed with lyrical pathos a last farewell to his converts who had been slain or kidnapped by the soldiers of Coroticus. The phenomenal success of Patrick’s mission is not, however, the full measure of his personality. Since his writings have come to be better understood, it is increasingly recognized that, despite their occasional incoherence, they mirror a truth and a simplicity of the rarest quality. Not since St. Augustine of Hippohad any religious diarist bared his inmost soul as Patrick did in his writings. As D.A. Binchy, the most austerely critical of Patrician (i.e., of Patrick) scholars, put it, “The moral and spiritual greatness of the man shines through every stumbling sentence of his ‘rustic’ Latin.” It is not possible to say with any assurance when Patrick was born. There are, however, a number of pointers to his missionary career having lain within the second half of the 5th century. In the Coroticus letter, his mention of the Franks as still “heathen” indicates that the letter must have been written between 451, the date generally accepted as that of the Franks’ irruption into Gaul as far as the Somme River, and 496, when they were baptized en masse. Patrick, who speaks of himself as having evangelized heathen Ireland, is not to be confused with Palladius, sent by Pope Celestine I in 431 as “first bishop to the Irish believers in Christ.”Before the end of the 7th century, Patrick had become a legendary figure, and the legends have continued to grow. One of these would have it that he drove the snakes of Ireland into the sea to their destruction. Patrick himself wrote that he raised people from the dead, and a 12th-century hagiography places this number at 33 men, some of whom are said to have been deceased for many years. He also reportedly prayed for the provision of food for hungry sailors traveling by land through a desolate area, and a herd of swine miraculously appeared.Another legend, probably the most popular, is that of the shamrock, which has him explain the concept of the Holy Trinity, three persons in one God, to an unbeliever by showing him the three-leaved plant with one stalk. Traditionally, Irishmen have worn shamrocks, the national flower of Ireland, in their lapels on St. Patrick’s Day, March 17. t Brendan was born in Annagh, Co. Kerry in 484. Very little is known about his life when he was young, but reports told how brightly lit angels hovered over the house when he was born. He was ordained a priest by Bishop Erc in 512. St. Brendan set up a lot of monasteries in Ireland. One was set up at Ardfert, at the foot of Mount Brandan in Co. Kerry. However, the most famous one was at Clonfert in Co. Galway. That monastery was set up in 560 – that’s almost 1,500 years ago! Today there is a big cathedral at Clonfert where he is buried.St Brendan the Navigator Courtesy of An PostOf all the Irish saints, St. Brendan was the most adventurous. He loved travelling on the sea and was very skilled with the coracle (small boat). On some of his earlier ventures, he visited Britain, many of the islands off the coast of Scotland and possibly even Iceland.Yet, St. Brendan’s longest adventure at sea was still to come. A manuscript was written in the 9thcentury that tells the story of his famous voyage in search of Hy Brasail, or the Island of the Blessed. This manuscript is called Navigatio Sancti Brendani Abbatis. That is Latin for ‘Voyage of St. Brendan the Abbot’. This voyage lasted for seven years. He probably travelled to Iceland, Greenland and maybe even America. The manuscript is full of the adventures of St. Brendan’s journey. One story tells how St. Brendan landed on an island that was actually a great big sea-monster. Another story tells how he narrowly escaped a sea-cat as big as a horse!In the 1970s, an explorer called Tim Severin read The Voyage of St. Brendan the Abbot. He decided to follow St. Brendan’s journey and to travel in the same type of boat St. Brendan had – a coracle. He proved that St Brendan may have been the first European to set foot in America. St Brendan died in 578 at Annaghdown. His feast day is celebrated on 16thMay, and he is known as the patron saint of seafarers and travellers. -
-
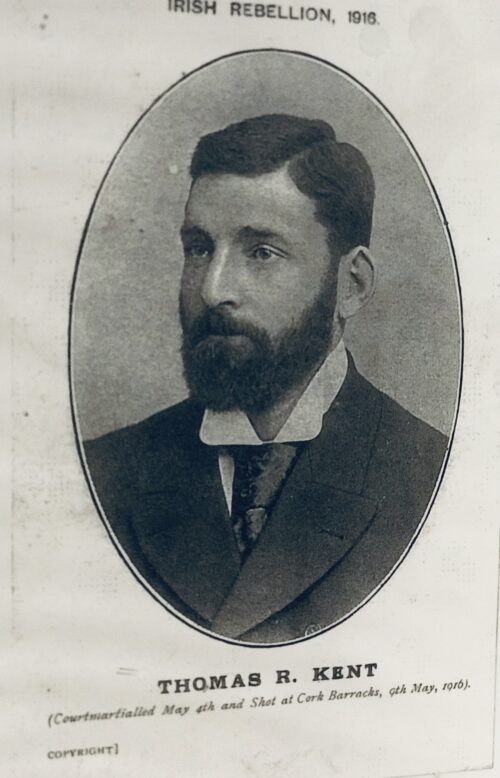
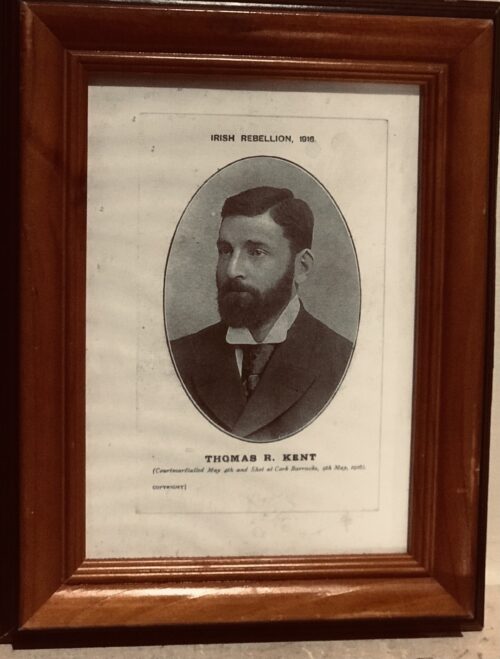
 Beautiful and poignant collection of four of the 1916 Easter Rising Rebel Leaders who were executed by the British Crown Forces at Kilmainham Jail a few weeks later.Featured here are Padraig Pearse,Thomas Clarke,James Connolly,Thomas Kent Thomas Kent (Irish: Tomás Ceannt; 29 August 1865 – 9 May 1916) was an Irish nationalist who was court-martialled and executed following a gunfight with the Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC) on 9 May 1916, in the immediate aftermath of the Easter Rising.
Beautiful and poignant collection of four of the 1916 Easter Rising Rebel Leaders who were executed by the British Crown Forces at Kilmainham Jail a few weeks later.Featured here are Padraig Pearse,Thomas Clarke,James Connolly,Thomas Kent Thomas Kent (Irish: Tomás Ceannt; 29 August 1865 – 9 May 1916) was an Irish nationalist who was court-martialled and executed following a gunfight with the Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC) on 9 May 1916, in the immediate aftermath of the Easter Rising.Easter Rising
Kent was part of a prominent nationalist family who lived at Bawnard House, Castlelyons, County Cork. They were prepared to take part in the Easter Rising, but when the mobilisation order was countermanded, they stayed at home. The rising nevertheless went ahead in Dublin, and the RIC was sent to arrest well-known sympathizers throughout the country, including known members of the Irish Republican Brotherhood, Sinn Féin, and the Irish Volunteers. When the Kent residence was raided they were met with resistance from Thomas and his brothers Richard, David and William. A gunfight lasted for four hours, in which an RIC officer, Head Constable William Rowe, was killed and David Kent was seriously wounded. Eventually the Kents were forced to surrender, although Richard made a last minute dash for freedom and was fatally wounded.Trial and execution
Thomas and William Kent were tried by court martial on the charge of armed rebellion. William was acquitted, but Thomas was sentenced to death. David Kent was brought to Dublin where he was charged with the same offence, found guilty and sentenced to death, but the sentence was commuted and he was sentenced to five years penal servitude. Thomas Kent was executed by firing squad in Cork on 9 May 1916, the only person outside of Dublin to be shot for his role in the events surrounding Easter Week (Roger Casement was hanged for treason in London). Kent was buried in the grounds of Cork Prison, formerly the Military Detention Barracks at the rear Collins Barracks, Cork (formerly Victoria Barracks). The former army married quarters to the rear of Collins Barracks are named in his honour.State funeral
Taoiseach Enda Kenny offered a state funeral to the Kent family early in 2015, which they accepted. Kent's remains were exhumed from Cork prison in June 2015 after being buried for 99 years. The analysis of Kent's remains, which had been found in a shallow, quicklime-filled grave, involved the State Pathologist's Office, the National Forensic Coordination Office at the Garda Technical Bureau, Forensic Science Ireland, and scientists from University College Dublin, and the scientific team was led by Dr. Jens Carlsson from the University of California-Davis. The State funeral was held on 18 September 2015 at St Nicholas' Church in Castlelyons. Kent lay in state at Collins Barracks in Cork the day before. The requiem mass was attended by President Michael D. Higgins, with Enda Kenny delivering the graveside oration.Memorials
The main railway station in Cork, Kent Station was named after Thomas Kent in 1966. The bridge over the River Blackwater in Fermoy, Co. Cork, where Thomas Kent was detained following his arrest, was named after him and his brothers in 2016. Bust of Kent at Cork Kent railway station by sculptor James MacCarthy.
Bust of Kent at Cork Kent railway station by sculptor James MacCarthy. -
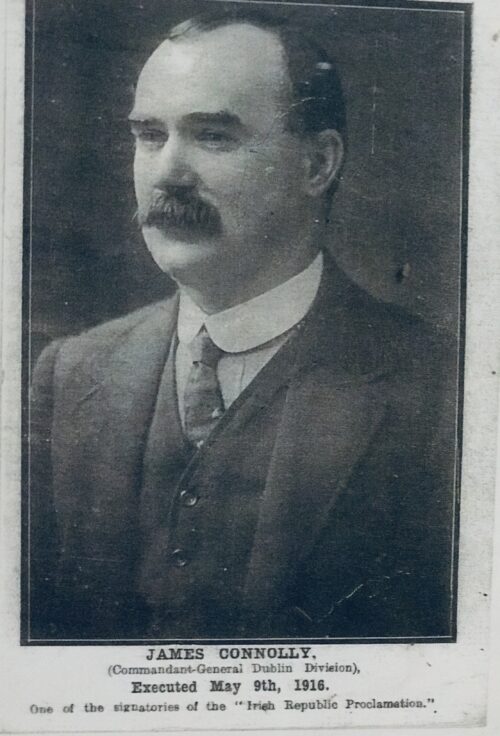

 Beautiful and poignant collection of four of the 1916 Easter Rising Rebel Leaders who were executed by the British Crown Forces at Kilmainham Jail a few weeks later.Featured here are Padraig Pearse,Thomas Clarke,James Connolly,Thomas Kent. James Connolly (5 June 1868 – 12 May 1916) was an Irish republican and socialist leader. Connolly was born in the Cowgate area of Edinburgh, Scotland, to Irish parents. He left school for working life at the age of 11. He also took a role in Scottish and American politics. He was a member of the Industrial Workers of the World and founder of the Irish Socialist Republican Party. With James Larkin, he was centrally involved in the Dublin lock-out of 1913, as a result of which the two men formed the Irish Citizen Army (ICA) that year. He opposed British rule in Ireland, and was one of the leaders of the Easter Rising of 1916. He was executed by firing squad following the Rising.
Beautiful and poignant collection of four of the 1916 Easter Rising Rebel Leaders who were executed by the British Crown Forces at Kilmainham Jail a few weeks later.Featured here are Padraig Pearse,Thomas Clarke,James Connolly,Thomas Kent. James Connolly (5 June 1868 – 12 May 1916) was an Irish republican and socialist leader. Connolly was born in the Cowgate area of Edinburgh, Scotland, to Irish parents. He left school for working life at the age of 11. He also took a role in Scottish and American politics. He was a member of the Industrial Workers of the World and founder of the Irish Socialist Republican Party. With James Larkin, he was centrally involved in the Dublin lock-out of 1913, as a result of which the two men formed the Irish Citizen Army (ICA) that year. He opposed British rule in Ireland, and was one of the leaders of the Easter Rising of 1916. He was executed by firing squad following the Rising.Early life
Connolly was born in an Edinburgh slum in 1868, the third son of Irish parents John Connolly and Mary McGinn.His parents had moved to Scotland from County Monaghan, Ireland, and settled in the Cowgate, a ghetto where thousands of Irish people lived. He spoke with a Scottish accent throughout his life. He was born in St Patrick's Roman Catholic parish, in the Cowgate district of Edinburgh known as "Little Ireland". His father and grandfathers were labourers.He had an education up to the age of about ten in the local Catholic primary school. He left and worked in labouring jobs. Owing to the economic difficulties he was having, like his eldest brother John, he joined the British Army. He enlisted at age 14, falsifying his age and giving his name as Reid, as his brother John had done. He served in Ireland with the 2nd Battalion of the Royal Scots Regiment for nearly seven years, during a turbulent period in rural areas known as the Land War.He would later become involved in the land issue. He developed a deep hatred for the British Army that lasted his entire life.When he heard that his regiment was being transferred to India, he deserted. Connolly had another reason for not wanting to go to India; a young woman by the name of Lillie Reynolds. Lillie moved to Scotland with James after he left the army and they married in April 1890.They settled in Edinburgh. There, Connolly began to get involved in the Scottish Socialist Federation,[17] but with a young family to support, he needed a way to provide for them. He briefly established a cobbler's shop in 1895, but this failed after a few monthsas his shoe-mending skills were insufficient.He was strongly active with the socialist movement at the time, and prioritized this over his cobbling.Socialist involvement
In the 1880s, Connolly became influenced by Friedrich Engels and Karl Marx and would later advocate a type of socialism that was based in Marxist theory.[21] Connolly described himself as a socialist, while acknowledging the influence of Marx. He became secretary of the Scottish Socialist Federation. At the time his brother John was secretary; after John spoke at a rally in favour of the eight-hour day, however, he was fired from his job with the Edinburgh Corporation, so while he looked for work, James took over as secretary. During this time, Connolly became involved with the Independent Labour Party which Keir Hardie had formed in 1893. At some time during this period, he took up the study of, and advocated the use of, the neutral international language, Esperanto. His interest in Esperanto is implicit in his 1898 article "The Language Movement", which primarily attempts to promote socialism to the nationalist revolutionaries involved in the Gaelic Revival. By 1892 he was involved in the Scottish Socialist Federation, acting as its secretary from 1895. Two months after the birth of his third daughter, word came to Connolly that the Dublin Socialist Club was looking for a full-time secretary, a job that offered a salary of a pound a week. Connolly and his family moved to Dublin,where he took up the position. At his instigation, the club quickly evolved into the Irish Socialist Republican Party (ISRP).The ISRP is regarded by many Irish historians as a party of pivotal importance in the early history of Irish socialism and republicanism. While active as a socialist in Great Britain, Connolly was the founding editor of The Socialist newspaper and was among the founders of the Socialist Labour Partywhich split from the Social Democratic Federation in 1903. Connolly joined Maud Gonne and Arthur Griffith in the Dublin protests against the Boer War. A combination of frustration with the progress of the ISRP and economic necessity caused him to emigrate to the United States in September 1903, with no plans as to what he would do there.While in America he was a member of the Socialist Labor Party of America (1906), the Socialist Party of America (1909) and the Industrial Workers of the World, and founded the Irish Socialist Federation in New York, 1907. He famously had a chapter of his 1910 book Labour in Irish History entitled "A chapter of horrors: Daniel O’Connell and the working class." critical of the achiever of Catholic Emancipation 60 years earlier. On Connolly's return to Ireland in 1910 he was right-hand man to James Larkin in the Irish Transport and General Workers Union. He stood twice for the Wood Quay ward of Dublin Corporation but was unsuccessful. His name, and those of his family, appears in the 1911 Census of Ireland - his occupation is listed as "National Organiser Socialist Party".In 1913, in response to the Lockout, he, along with an ex-British officer, Jack White, founded the Irish Citizen Army (ICA), an armed and well-trained body of labour men whose aim was to defend workers and strikers, particularly from the frequent brutality of the Dublin Metropolitan Police. Though they only numbered about 250 at most, their goal soon became the establishment of an independent and socialist Irish nation. He also founded the Irish Labour Party as the political wing of the Irish Trades Union Congress in 1912 and was a member of its National Executive. Around this time he met Winifred Carney in Belfast, who became his secretary and would later accompany him during the Easter Rising. Like Vladimir Lenin, Connolly opposed the First World War explicitly from a socialist perspective. Rejecting the Redmondite position, he declared "I know of no foreign enemy of this country except the British Government."After Ireland is free, says the patriot who won't touch Socialism, we will protect all classes, and if you won't pay your rent you will be evicted same as now. But the evicting party, under command of the sheriff, will wear green uniforms and the Harp without the Crown, and the warrant turning you out on the roadside will be stamped with the arms of the Irish Republic.James Connolly, in Workers' Republic, 1899Easter Rising
Connolly and the ICA made plans for an armed uprising during the war, independently of the Irish Volunteers. In early 1916, believing the Volunteers were dithering, he attempted to goad them into action by threatening to send the ICA against the British Empire alone, if necessary. This alarmed the members of the Irish Republican Brotherhood, who had already infiltrated the Volunteers and had plans for an insurrection that very year. In order to talk Connolly out of any such rash action, the IRB leaders, including Tom Clarke and Patrick Pearse, met with Connolly to see if an agreement could be reached. During the meeting, the IRB and the ICA agreed to act together at Easter of that year. During the Easter Rising, beginning on 24 April 1916, Connolly was Commandant of the Dublin Brigade. As the Dublin Brigade had the most substantial role in the rising, he was de factocommander-in-chief. Connolly's leadership in the Easter rising was considered formidable. Michael Collins said of Connolly that he "would have followed him through hell." Following the surrender, he said to other prisoners: "Don't worry. Those of us that signed the proclamation will be shot. But the rest of you will be set free."Death
Connolly was not actually held in gaol, but in a room (now called the "Connolly Room") at the State Apartments in Dublin Castle, which had been converted to a first-aid station for troops recovering from the war. Connolly was sentenced to death by firing squad for his part in the rising. On 12 May 1916 he was taken by military ambulance to Royal Hospital Kilmainham, across the road from Kilmainham Gaol, and from there taken to the gaol, where he was to be executed. While Connolly was still in hospital in Dublin Castle, during a visit from his wife and daughter, he said: "The Socialists will not understand why I am here; they forget I am an Irishman." Connolly had been so badly injured from the fighting (a doctor had already said he had no more than a day or two to live, but the execution order was still given) that he was unable to stand before the firing squad; he was carried to a prison courtyard on a stretcher. His absolution and last rites were administered by a Capuchin, Father Aloysius Travers. Asked to pray for the soldiers about to shoot him, he said: "I will say a prayer for all men who do their duty according to their lights."Instead of being marched to the same spot where the others had been executed, at the far end of the execution yard, he was tied to a chair and then shot. His body (along with those of the other leaders) was put in a mass grave without a coffin. The executions of the rebel leaders deeply angered the majority of the Irish population, most of whom had shown no support during the rebellion. It was Connolly's execution that caused the most controversy.Historians have pointed to the manner of execution of Connolly and similar rebels, along with their actions, as being factors that caused public awareness of their desires and goals and gathered support for the movements that they had died fighting for. The executions were not well received, even throughout Britain, and drew unwanted attention from the United States, which the British Government was seeking to bring into the war in Europe. H. H. Asquith, the Prime Minister, ordered that no more executions were to take place; an exception being that of Roger Casement, who was charged with high treasonand had not yet been tried. Location of Connolly's execution at Kilmainham Gaolin Dublin
Location of Connolly's execution at Kilmainham Gaolin DublinFamily
James Connolly and his wife Lillie had seven children. Nora became an influential writer and campaigner within the Irish-republican movement as an adult. Roddy continued his father's politics. In later years, both became members of the Oireachtas (Irish parliament). Moira became a doctor and married Richard Beech. One of Connolly's daughters Mona died in 1904 aged 13, when she burned herself while she did the washing for an aunt. Three months after James Connolly's execution his wife was received into the Catholic Church, at Church St. on 15 August.Legacy
Connolly's legacy in Ireland is mainly due to his contribution to the republican cause; his legacy as a socialist has been claimed by a variety of left-wing and left-republican groups, and he is also associated with the Labour Party which he founded. Connolly was among the few European members of the Second International who opposed, outright, World War I. This put him at odds with most of the socialist leaders of Europe. He was influenced by and heavily involved with the radical Industrial Workers of the World labour union, and envisaged socialism as Industrial Union control of production. Also he envisioned the IWW forming their own political party that would bring together the feuding socialist groups such as the Socialist Labor Party of America and the Socialist Party of America.Likewise, he envisaged independent Ireland as a socialist republic. His connection and views on Revolutionary Unionism and Syndicalism have raised debate on if his image for a workers republic would be one of State or Grassroots socialism.For a time he was involved with De Leonism and the Second International until he later broke with both. In Scotland, Connolly's thinking influenced socialists such as John Maclean, who would, like him, combine his leftist thinking with nationalist ideas when he formed the Scottish Workers Republican Party. The Connolly Association, a British organisation campaigning for Irish unity and independence, is named after Connolly. In 1928, Follonsby miners' lodge in the Durham coalfield unfurled a newly designed banner that included a portrait of Connolly on it. The banner was burned in 1938, replaced but then painted over in 1940. A reproduction of the 1938 Connolly banner was commissioned in 2011 by the Follonsby Miners’ Lodge Banner Association and it is regularly paraded at various events in County Durham ('Old King Coal' at Beamish Open Air museum, 'The Seven men of Jarrow' commemoration every June, the Durham Miners' Gala every second Saturday in July, the Tommy Hepburn annual memorial every October), in the wider UK and Ireland. There is a statue of James Connolly in Dublin, outside Liberty Hall, the offices of the SIPTU trade union. Another statue of Connolly stands in Union Park, Chicago near the offices of the UE union. There is a bust of Connolly in Troy, New York, in the park behind the statue of Uncle Sam. In March 2016 a statue of Connolly was unveiled by Department of Culture, Arts and Leisure minister Carál Ní Chuilín, and Connolly's great grandson, James Connolly Heron, on Falls Road in Belfast. In a 1972 interview on The Dick Cavett Show, John Lennon stated that James Connolly was an inspiration for his song, "Woman Is the Nigger of the World". Lennon quoted Connolly's 'the female is the slave of the slave' in explaining the feminist inspiration for the song. Connolly Station, one of the two main railway stations in Dublin, and Connolly Hospital, Blanchardstown, are named in his honour. In a 2002, BBC television production, 100 Greatest Britons where the British public were asked to register their vote, Connolly was voted in 64th place. In 1968, Irish group The Wolfe Tones released a single named "James Connolly", which reached number 15 in the Irish charts. The band Black 47 wrote and performed a song about Connolly that appears on their album Fire of Freedom. Irish singer-songwriter Niall Connolly has a song "May 12th, 1916 - A Song for James Connolly" on his album Dream Your Way Out of This One(2017). -
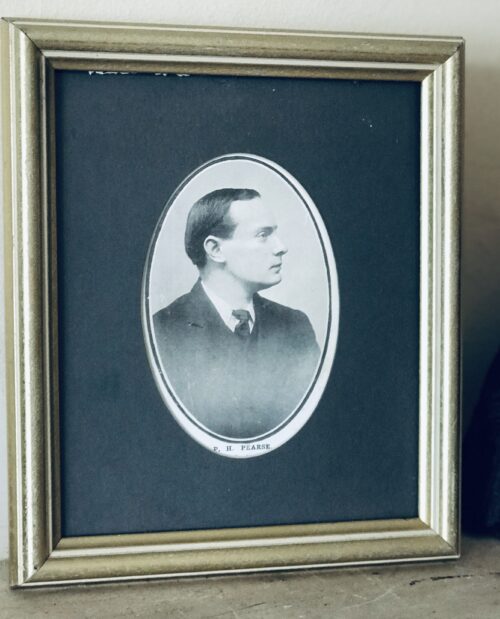
 Beautiful and poignant collection of four of the 1916 Easter Rising Rebel Leaders who were executed by the British Crown Forces at Kilmainham Jail a few weeks later.Featured here are Padraig Pearse,Thomas Clarke,James Connolly,Thomas Kent. Patrick Pearse, in full Patrick Henry Pearse, Patrick also spelled in Irish Pádraic, (born November 10, 1879, Dublin, Ireland—died May 3, 1916, Dublin), Irish nationalist leader, poet, and educator. He was the first president of the provisional government of the Irish republic proclaimed in Dublin on April 24, 1916, and was commander in chief of the Irish forces in the anti-British Easter Rising that began on the same day.The son of an English sculptor and his Irish wife, Pearse became a director of the Gaelic League (founded 1893 for the preservation of the Irish language) and edited (1903–09) its weekly newspaper, An Claidheamh Soluis (“The Sword of Light”). To further promote the Irish language as a weapon against British domination, he published tales from old Irish manuscripts and a collection (1914) of his own poems in the modern Irish idiom. He founded St. Enda’s College (1908), near Dublin, as a bilingual institution with its teaching based on Irish traditions and culture. On the formation of the Irish Volunteers (November 1913) as a counterforce against the Ulster Volunteers (militant supporters of the Anglo-Irish union), Pearse became a member of their provisional committee, and he contributed poems and articles to their newspaper, The Irish Volunteer. In July 1914 he was made a member of the supreme council of the Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB). After the Irish Volunteers split (September 1914), he became a leader of the more extreme nationalist section, which opposed any support for Great Britain in World War I. He came to believe that the blood of martyrs would be required to liberate Ireland, and on that theme he delivered a famous oration in August 1915 at the burial of Jeremiah O’Donovan, known as O’Donovan Rossa, a veteran of Sinn Féin.Pearse’s Collected Works appeared in 1917–22 (3 vol.) and again in 1924 (5 vol.), and his Political Writings and Speeches appeared in 1952.
Beautiful and poignant collection of four of the 1916 Easter Rising Rebel Leaders who were executed by the British Crown Forces at Kilmainham Jail a few weeks later.Featured here are Padraig Pearse,Thomas Clarke,James Connolly,Thomas Kent. Patrick Pearse, in full Patrick Henry Pearse, Patrick also spelled in Irish Pádraic, (born November 10, 1879, Dublin, Ireland—died May 3, 1916, Dublin), Irish nationalist leader, poet, and educator. He was the first president of the provisional government of the Irish republic proclaimed in Dublin on April 24, 1916, and was commander in chief of the Irish forces in the anti-British Easter Rising that began on the same day.The son of an English sculptor and his Irish wife, Pearse became a director of the Gaelic League (founded 1893 for the preservation of the Irish language) and edited (1903–09) its weekly newspaper, An Claidheamh Soluis (“The Sword of Light”). To further promote the Irish language as a weapon against British domination, he published tales from old Irish manuscripts and a collection (1914) of his own poems in the modern Irish idiom. He founded St. Enda’s College (1908), near Dublin, as a bilingual institution with its teaching based on Irish traditions and culture. On the formation of the Irish Volunteers (November 1913) as a counterforce against the Ulster Volunteers (militant supporters of the Anglo-Irish union), Pearse became a member of their provisional committee, and he contributed poems and articles to their newspaper, The Irish Volunteer. In July 1914 he was made a member of the supreme council of the Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB). After the Irish Volunteers split (September 1914), he became a leader of the more extreme nationalist section, which opposed any support for Great Britain in World War I. He came to believe that the blood of martyrs would be required to liberate Ireland, and on that theme he delivered a famous oration in August 1915 at the burial of Jeremiah O’Donovan, known as O’Donovan Rossa, a veteran of Sinn Féin.Pearse’s Collected Works appeared in 1917–22 (3 vol.) and again in 1924 (5 vol.), and his Political Writings and Speeches appeared in 1952. -
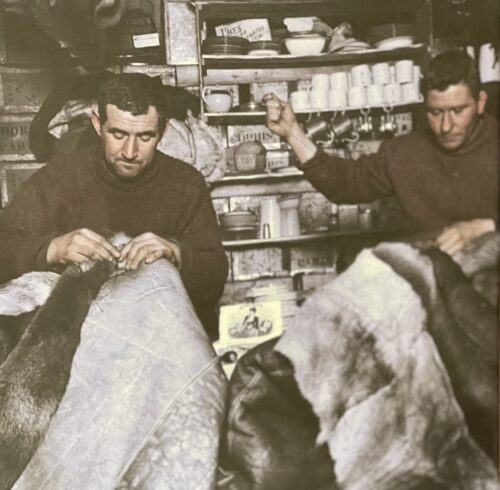

 27cm x 27cm Castlegregory Co Kerry Fine framed print of the legendary Irish Antarctic explorer and hero,Tom Crean mending blankets with his colleague on Shackleton's final Expedition Thomas Crean (c. 16 February 1877 – 27 July 1938) was an Irish seaman and Antarctic explorer who was awarded the Albert Medal for Lifesaving. Crean was a member of three major expeditions to Antarctica during the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration, including Robert Falcon Scott's 1911–1913 Terra Nova Expedition. This saw the race to reach the South Pole lost to Roald Amundsen and ended in the deaths of Scott and his party. During the expedition, Crean's 35-statute-mile (56 km) solo walk across the Ross Ice Shelf to save the life of Edward Evans led to him receiving the Albert Medal. Crean left the family farm near Annascaul, in County Kerry, to enlist in the Royal Navy at age 16. In 1901, while serving on Ringarooma in New Zealand, he volunteered to join Scott's 1901–1904 Discovery Expedition to Antarctica, thus beginning his exploring career. After his experience on the Terra Nova, Crean's third and final Antarctic venture was as second officer on Ernest Shackleton's Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition. After the ship Endurance became beset in the pack ice and sank, Crean and the ship's company spent 492 days drifting on the ice before undertaking a journey in the ship's lifeboats to Elephant Island. He was a member of the crew which made a small-boat journey of 800 nautical miles (1,500 km) from Elephant Island to South Georgia Island to seek aid for the stranded party. After retiring from the navy on health grounds in 1920, Crean ran his pub the South Pole Inn in County Kerry with his wife and daughters. He died in 1938. Crean was born around 16 February 1877 in the farming area of Gurtuchrane near the village of Annascaul on Corca Dhuibhne in County Kerry, Ireland, to Patrick and Catherine (née Courtney) Crean. One of 11 siblings with 7 brothers and 3 sisters. He attended the local Catholic school (at nearby Brackluin), leaving at the age of 12 to help on the family farm. Many sources, including Smith, give Crean's date of birth as 20 July 1877,but more recent scholarship demonstrates this is unlikely given parish records. At the age of 16, he enlisted in the Royal Navy at the naval station in nearby Minard Inlet, possibly after an argument with his father.His enlistment as a boy second class is recorded in Royal Navy records on 10 July 1893. Crean's initial naval apprenticeship was aboard the training ship Impregnable at Devonport. In November 1894, he was transferred to Devastation. In December 1894, Crean was posted to HMS Wild Swan a screw sloop as the ship headed to South America to join the Pacific Station. In 1895, Crean was serving in the Americas aboard Royal Arthur, the flagship assigned to the Pacific squadron’s base at Esquimalt in Canada. He was by this time, rated an ordinary seaman. Less than a year later, while serving a second term of service aboard Wild Swan he was rated an able seaman.He later joined the Navy's torpedo school ship, Defiance. By 1899, Crean had advanced to the rate of petty officer, second class and was serving in Vivid.In 1900, Crean was ledgered to the cruiser HMS Ringarooma, which was part of the Royal Navy's Australian Squadron based in Sydney. On 18 December 1901, he was demoted from petty officer to able seaman for an unspecified misdemeanour.In December 1901, the Ringarooma was ordered to assist Robert Falcon Scott's ship Discovery when it was docked at Lyttelton Harbour awaiting to departure to Antarctica. When an able seaman of Scott's ship deserted after striking a petty officer, a replacement was required; Crean volunteered, and was accepted.
27cm x 27cm Castlegregory Co Kerry Fine framed print of the legendary Irish Antarctic explorer and hero,Tom Crean mending blankets with his colleague on Shackleton's final Expedition Thomas Crean (c. 16 February 1877 – 27 July 1938) was an Irish seaman and Antarctic explorer who was awarded the Albert Medal for Lifesaving. Crean was a member of three major expeditions to Antarctica during the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration, including Robert Falcon Scott's 1911–1913 Terra Nova Expedition. This saw the race to reach the South Pole lost to Roald Amundsen and ended in the deaths of Scott and his party. During the expedition, Crean's 35-statute-mile (56 km) solo walk across the Ross Ice Shelf to save the life of Edward Evans led to him receiving the Albert Medal. Crean left the family farm near Annascaul, in County Kerry, to enlist in the Royal Navy at age 16. In 1901, while serving on Ringarooma in New Zealand, he volunteered to join Scott's 1901–1904 Discovery Expedition to Antarctica, thus beginning his exploring career. After his experience on the Terra Nova, Crean's third and final Antarctic venture was as second officer on Ernest Shackleton's Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition. After the ship Endurance became beset in the pack ice and sank, Crean and the ship's company spent 492 days drifting on the ice before undertaking a journey in the ship's lifeboats to Elephant Island. He was a member of the crew which made a small-boat journey of 800 nautical miles (1,500 km) from Elephant Island to South Georgia Island to seek aid for the stranded party. After retiring from the navy on health grounds in 1920, Crean ran his pub the South Pole Inn in County Kerry with his wife and daughters. He died in 1938. Crean was born around 16 February 1877 in the farming area of Gurtuchrane near the village of Annascaul on Corca Dhuibhne in County Kerry, Ireland, to Patrick and Catherine (née Courtney) Crean. One of 11 siblings with 7 brothers and 3 sisters. He attended the local Catholic school (at nearby Brackluin), leaving at the age of 12 to help on the family farm. Many sources, including Smith, give Crean's date of birth as 20 July 1877,but more recent scholarship demonstrates this is unlikely given parish records. At the age of 16, he enlisted in the Royal Navy at the naval station in nearby Minard Inlet, possibly after an argument with his father.His enlistment as a boy second class is recorded in Royal Navy records on 10 July 1893. Crean's initial naval apprenticeship was aboard the training ship Impregnable at Devonport. In November 1894, he was transferred to Devastation. In December 1894, Crean was posted to HMS Wild Swan a screw sloop as the ship headed to South America to join the Pacific Station. In 1895, Crean was serving in the Americas aboard Royal Arthur, the flagship assigned to the Pacific squadron’s base at Esquimalt in Canada. He was by this time, rated an ordinary seaman. Less than a year later, while serving a second term of service aboard Wild Swan he was rated an able seaman.He later joined the Navy's torpedo school ship, Defiance. By 1899, Crean had advanced to the rate of petty officer, second class and was serving in Vivid.In 1900, Crean was ledgered to the cruiser HMS Ringarooma, which was part of the Royal Navy's Australian Squadron based in Sydney. On 18 December 1901, he was demoted from petty officer to able seaman for an unspecified misdemeanour.In December 1901, the Ringarooma was ordered to assist Robert Falcon Scott's ship Discovery when it was docked at Lyttelton Harbour awaiting to departure to Antarctica. When an able seaman of Scott's ship deserted after striking a petty officer, a replacement was required; Crean volunteered, and was accepted.Discovery Expedition, 1901–1904
Discovery sailed to the Antarctic on 21 December 1901, and seven weeks later, on 8 February 1902, arrived in McMurdo Sound, where she anchored at a spot which was later designated "Hut Point".Here the men established the base from which they would launch scientific and exploratory sledging journeys. Crean proved to be one of the most efficient man-haulers in the party; over the expedition as a whole, only seven of the 48-member party logged more time in harness than Crean's 149 days.]Crean had a good sense of humour and was well liked by his companions. Scott's second-in-command, Albert Armitage, wrote in his book Two Years in the Antarctic that "Crean was an Irishman with a fund of wit and an even temper which nothing disturbed." Crean accompanied Lieutenant Michael Barne on three sledging trips across the Ross Ice Shelf, then known as the "Great Ice Barrier". These included the 12-man party led by Barne which set out on 30 October 1902 to lay depots in support of the main southern journey undertaken by Scott, Shackleton and Edward Wilson. On 11 November the Barne party passed the previous furthest south mark,set by Carsten Borchgrevink in 1900 at 78°50'S, a record which they held briefly until the southern party itself passed it on its way to an eventual 82°17'S. During the Antarctic winter of 1902 Discovery became locked in the ice. Efforts to free her during the summer of 1902–03 failed, and although some of the expedition's members (including Ernest Shackleton) left in a relief ship, Crean and the majority of the party remained in the Antarctic until the ship was finally freed in February 1904. After returning to regular naval duty, Crean was promoted to petty officer, first class, on Scott's recommendation.Between expeditions, 1904–1910
Crean came back to regular duty at the naval base at Chatham, Kent, serving first in Pembroke in 1904 and later transferring to the torpedo school on Vernon. Crean had caught Captain Scott's attention with his attitude and work ethic on the Discovery Expedition, and in 1906 Scott requested that Crean join him on Victorious.Over the next few years, Crean followed Scott successively to Albemarle, Essex and Bulwark.By 1907, Scott was planning his second expedition to the Antarctic. Meanwhile, Ernest Shackleton's Nimrod Expedition, 1907–09, despite reaching a new furthest south record of 88°23'S, had failed to reach the South Pole. Scott was with Crean when the news of Shackleton's near miss became public; it is recorded that Scott observed to Crean: "I think we'd better have a shot next."Terra Nova Expedition, 1910–1913
Scott held Crean in high regard, so he was among the first people recruited for the Terra Nova Expedition, which set out for the Antarctic in June 1910, and one of the few men in the party with previous polar experience. After the expedition's arrival in McMurdo Sound in January 1911, Crean was as part of the 13-man team who established "One Ton Depot",130 statute miles (210 km) from Hut Point.so named because of the large amount of food and equipment cached there on the projected route to the South Pole. Returning from the depot to base camp at Cape Evans, Crean, accompanied by Apsley Cherry-Garrard and Henry "Birdie" Bowers, experienced near-disaster when camping on unstable sea ice. During the night the ice broke up, leaving the men adrift on an ice floe and separated from their sledges. Crean probably saved the group's lives, by leaping from floe to floe until he reached the Barrier edge and was able to summon help.Crean departed with Scott in November 1911, for the attempt at the South Pole. This journey had three stages: 400 statute miles (640 km) across the Barrier, 120 statute miles (190 km) up the heavily crevassed Beardmore Glacier to an altitude of 10,000 feet (3,000 m) above sea level, and then another 350 statute miles (560 km) to the Pole.At regular intervals, supporting parties returned to base; Crean was in the final group of eight men that marched on to the polar plateau and reached 87°32'S, 168 statute miles (270 km) from the pole. Here, on 4 January 1912, Scott selected his final polar party: Crean, William Lashly and Edward Evans were ordered to return to base, while Scott, Edgar Evans, Edward Wilson, Bowers and Lawrence Oates continued to the pole. Crean's biographer Michael Smith suggests that Crean would have been a better choice for the polar party than Edgar Evans, who was weakened by a recent hand injury (of which Scott was unaware). Crean, considered one of the toughest men in the expedition, had led a pony across the Barrier and had thus been saved much of the hard labour of man-hauling.Scott's critical biographer Roland Huntford records that the surgeon Edward L Atkinson, who had accompanied the southern party to the top of the Beardmore, had recommended either Lashly or Crean for the polar party rather than Edgar Evans.Scott in his diary recorded that Crean wept with disappointment at the prospect of having to turn back, so close to the goal. Soon after heading north on the 700-statute-mile (1,100 km) journey back to base camp, Crean's party lost the trail back to the Beardmore Glacier, and were faced with a long detour around a large icefall.With food supplies short, and needing to reach their next supply depot, the group made the decision to slide on their sledge, uncontrolled, down the icefall. The three men slid 2,000 feet (600 m),dodging crevasses up to 200 feet (61 m) wide, and ending their descent by overturning on an ice ridge. Evans later wrote: "How we ever escaped entirely uninjured is beyond me to explain". The gamble at the icefall succeeded, and the men reached their depot two days later.However, they had great difficulty navigating down the glacier. Lashly wrote: "I cannot describe the maze we got into and the hairbreadth escapes we have had to pass through."In his attempts to find the way down, Evans removed his goggles and subsequently suffered agonies of snow blindness that made him into a passenger. When the party was finally free of the glacier and on the level surface of the Barrier, Evans began to display the first symptoms of scurvy. By early February he was in great pain, his joints were swollen and discoloured, and he was passing blood. Through the efforts of Crean and Lashly the group struggled towards One Ton Depot, which they reached on 11 February. At this point Evans collapsed; Crean thought he had died and, according to Evans's account, "his hot tears fell on my face". With over 100 statute miles (160 km) still to travel before the relative safety of Hut Point, Crean and Lashly began hauling Evans on the sledge, "eking out his life with the last few drops of brandy that they still had with them".On 18 February they arrived at Corner Camp, still 35 statute miles (56 km) from Hut Point, with only one or two days' food rations left and still four or five days' man-hauling to do. They then decided that Crean should go on alone, to fetch help. With only a little chocolate and three biscuits to sustain him, without a tent or survival equipment,Crean walked the distance to Hut Point in 18 hours, arriving in a state of collapse to find Atkinson there, with the dog driver Dmtri Gerov. Crean reached safety just ahead of a fierce blizzard, which probably would have killed him, and which delayed the rescue party by a day and a half.Atkinson led a successful rescue, and Lashly and Evans were both brought to base camp alive. Crean modestly played down the significance of his feat of endurance. In a rare written account, he wrote in a letter: "So it fell to my lot to do the 30 miles for help, and only a couple of biscuits and a stick of chocolate to do it. Well, sir, I was very weak when I reached the hut." Scott's party failed to return. The winter of 1912 at Cape Evans was a sombre one, with the knowledge that the polar party had undoubtedly perished. Frank Debenhamwrote that "in the winter it was once again Crean who was the mainstay for cheerfulness in the now depleted mess deck part of the hut." In November 1912, Crean was one of the 11-man search party that found the remains of the polar party. On 12 November they spotted a cairn of snow, which proved to be a tent against which the drift had piled up. It contained the bodies of Scott, Wilson, and Bowers.Crean later wrote, referring to Scott in understated fashion, that he had "lost a good friend". On 12 February 1913 Crean and the remaining crew of the Terra Nova arrived in Lyttelton, New Zealand, and in June the ship returned to Cardiff.At Buckingham Palace the surviving members of the expedition were awarded Polar Medals by King George and Prince Louis of Battenberg, the First Sea Lord.Crean and Lashly were both awarded the Albert Medal, 2nd Class for saving Evans's life, these were presented by the King at Buckingham Palace on 26 July 1913. Crean was promoted to the rank of chief petty officer, retroactive to 9 September 1910. Petty officers Edgar Evans and Crean mending sleeping bags (May 1911)
Petty officers Edgar Evans and Crean mending sleeping bags (May 1911)Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition (Endurance Expedition), 1914–1917
In October 1913, a close friend of Captain Scott, Joseph Foster Stackhouse, announced plans for a British Antarctic Expedition with a mission to explore the uncharted coastlines between King Edward VII Land and Graham Land. The expedition was due to depart England in August 1914 aboard RRS Discovery, the ship of Crean’s first mission to Antarctica. In February 1914, Stackhouse confirmed that Crean was to join the expedition as Boatswain, however, in April 1914, Stackhouse’s plans were postponed. This left Shackleton free to recruit Crean to his expedition which was also scheduled to depart in August 1914. Shackleton knew Crean well from the Discovery Expedition, and also knew of his exploits on Scott's last expedition. Like Scott, Shackleton trusted Crean:he was worth, in Shackleton's own word, "trumps".Crean joined Shackleton's Imperial Transantarctic Expedition on 25 May 1914, as second officer, with a varied range of duties. In the absence of a Canadian dog-handling expert who was hired but never appeared, Crean took charge of one of the dog-handling teams,and was later involved in the care and nurture of the pups born to one of his dogs, Sally, early in the expedition. On 19 January 1915 the expedition's ship, the Endurance, was beset in the Weddell Sea pack ice. In the early efforts to free her, Crean narrowly escaped being crushed by a sudden movement in the ice. The ship drifted in the ice for months, eventually sinking on 21 November. Shackleton informed the men that they would drag the food, gear, and three lifeboats across the pack ice, to Snow Hill or Robertson Island, 200 statute miles (320 km) away. Because of uneven ice conditions, pressure ridges, and the danger of ice breakup which could separate the men, they soon abandoned this plan: the men pitched camp and decided to wait. They hoped that the clockwise drift of the pack would carry them 400 statute miles (640 km) to Paulet Island where they knew there was a hut with emergency supplies. But the pack ice held firm as it carried the men well past Paulet Island, and did not break up until 9 April. The crew then had to sail and row the three ill-equipped lifeboats through the pack ice to Elephant Island, a trip which lasted five days. Crean and Hubert Hudson, the navigating officer of the Endurance, piloted their lifeboat with Crean effectively in charge as Hudson appeared to have suffered a breakdown. Upon reaching Elephant Island, Crean was one of the "four fittest men" detailed by Shackleton to find a safe camping-ground.Shackleton decided that, rather than waiting for a rescue ship that would probably never arrive, one of the lifeboats should be strengthened so that a crew could sail it to South Georgia and arrange a rescue. After the party was settled on a penguin rookeryabove the high-water mark, a group of men led by ship's carpenter Harry McNish began modifying one of the lifeboats—the James Caird—in preparation for this journey, which Shackleton would lead. Frank Wild, who would be in command of the party remaining on Elephant Island, wanted the dependable Crean to stay with him;Shackleton initially agreed, but changed his mind after Crean begged to be included in the boat's crew of six. The 800-nautical-mile (1,500 km) boat journey to South Georgia, described by polar historian Caroline Alexander as one of the most extraordinary feats of seamanship and navigation in recorded history, took 17 days through gales and snow squalls, in seas which the navigator, Frank Worsley, described as a "mountainous westerly swell".After setting off on 24 April 1916 with just the barest navigational equipment, they reached South Georgia on 10 May 1916. Shackleton, in his later account of the journey, recalled Crean's tuneless singing at the tiller: "He always sang when he was steering, and nobody ever discovered what the song was ... but somehow it was cheerful". The party made its South Georgia landfall on the uninhabited southern coast, having decided that the risk of aiming directly for the whaling stations on the north side was too great; if they missed the island to the north they would be swept out into the Atlantic Ocean.The original plan was to work the James Caird around the coast, but the boat's rudder had broken off after their initial landing, and some of the party were, in Shackleton's view, unfit for further travel. The three fittest men—Shackleton, Crean, and Worsley—were decided to trek 30 statute miles (48 km) across the island's glaciated surface, in a hazardous 36-hour journey to the nearest manned whaling station. This trek was the first recorded crossing of the mountainous island, completed without tents, sleeping bags, or map—their only mountaineering equipment was a carpenter's adze, a length of alpine rope, and screws from the James Caird hammered through their boots to serve as crampons.They arrived at the whaling station at Stromness, tired and dirty, hair long and matted, faces blackened by months of cooking by blubber stoves—"the world's dirtiest men", according to Worsley.They quickly organized a boat to pick up the three on the other side of South Georgia, but thereafter it took Shackleton three months and four attempts by ship to rescue the other 22 men still on Elephant Island.Later life
After returning to Britain in November 1916, Crean resumed naval duties. On 15 December 1916 he was promoted to the rank of warrant officer (as a boatswain), in recognition of his service on the Endurance, and was awarded his third Polar Medal. A month later, in April, he was granted a licence for the sale and consumption of alcohol from his dwelling house, a premises he had purchased in 1916. The business was left in the care of family while he served out his time in the Royal Navy. On 5 September 1917, Crean married Ellen Herlihy of Annascaul. In early 1920, Shackleton was organising another Antarctic expedition, later to be known as the Shackleton-Rowett Expedition. He invited Crean to join him, along with other officers from the Endurance. By this time, however, Crean's second daughter had arrived, and he had plans to open a business following his naval career. He turned down Shackleton's invitation.On his last naval assignment, with HMS Hecla, Crean suffered a bad fall which caused lasting effects to his vision. As a result, he was retired on medical grounds on 24 March 1920. He and Ellen opened a small public house in Annascaul, which he called the South Pole Inn.The couple had three daughters, Mary, Kate, and Eileen, although Kate died when she was four years old. Throughout his life, Crean remained an extremely modest man. When he returned to Kerry, he put all of his medals away and never again spoke about his experiences in the Antarctic. There is no reliable evidence of Crean giving any interviews to the press.Smith speculates that this may have been because Kerry was a hotbed of Irish nationalism and later Irish republicanism, and, along with County Cork, an epicentre of violence.The Crean family were once subject to a Black and Tan raid during the Irish War of Independence. Their inn was ransacked until the raiders happened across Crean's framed photo in Royal Navy dress uniform and medals. They then left his inn.On 13 April 1920, Tom Crean was present among crowds gathered in Tralee to protest against the treatment of republican prisoners who had gone on a hunger strike in Mountjoy jail. Crean's older brother was Cornelius Crean, a sergeant in the Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC).Cornelius was based in County Cork, where he served with the RIC during the War of Independence.Sgt. Crean was killed during an IRA ambush near Upton on 25 April 1920.In 1938, Crean became ill with a burst appendix. He was taken to the nearest hospital in Tralee, but as no surgeon was available, he was transferred to the Bon Secours Hospital in Cork, where his appendix was removed. Because the operation had been delayed, an infection developed, and after a week in the hospital he died on 27 July 1938. He was buried in his family's tomb at the cemetery in Ballynacourty, Corkaguiney, County Kerry. Statue of Crean in Annascaul
Statue of Crean in AnnascaulLegacy
- Mount Crean 8,630 feet (2,630 m) in Victoria Land, Antarctica and Mount Crean 2,300 feet (700 m) in Greenland
- Crean Glacier on South Georgia.
- Crean Lake on South Georgia.
- An eight-part 1985 television series, The Last Place on Earth, told the story of Scott's expedition to the South Pole. Hugh Grant and Max von Sydow starred with Irish actor Daragh O'Malley, who portrayed Tom Crean.
- A one-man play, Tom Crean – Antarctic Explorer, has been widely performed since 2001 by author Aidan Dooley, including a special showing at the South Pole Inn, Annascaul, in October 2001. Present were Crean's daughters, Eileen and Mary, both in their 80s. Apparently he never told them stories of his exploits; according to Eileen: "He put his medals and his sword in a box ... and that was that. He was a very humble man".
- In July 2003, a bronze statue of Crean was unveiled across from his pub in Annascaul. It depicts him leaning against a crate whilst holding a pair of hiking poles in one hand and two of his beloved sled dog pups in the other.
- Until its closure in 2017, the Dingle Brewing Company produced 'Tom Crean Lager', named in his honour. In 2016, Crean's granddaughter, Aileen Crean O’Brien, launched 'Expedition Ale' in partnership with Torc Breweries
- In February 2021 it was announced that a new research vessel being commissioned by the Irish government’s Department of Agriculture, Food and the Marinewould be named 'RV Tom Crean', in Crean’s honour.
-
 38cm x 32cm Castlegregory Co Kerry Fine framed portrait of the legendary Irish Antarctic explorer and hero,Tom Crean. Thomas Crean (c. 16 February 1877 – 27 July 1938) was an Irish seaman and Antarctic explorer who was awarded the Albert Medal for Lifesaving. Crean was a member of three major expeditions to Antarctica during the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration, including Robert Falcon Scott's 1911–1913 Terra Nova Expedition. This saw the race to reach the South Pole lost to Roald Amundsen and ended in the deaths of Scott and his party. During the expedition, Crean's 35-statute-mile (56 km) solo walk across the Ross Ice Shelf to save the life of Edward Evans led to him receiving the Albert Medal. Crean left the family farm near Annascaul, in County Kerry, to enlist in the Royal Navy at age 16. In 1901, while serving on Ringarooma in New Zealand, he volunteered to join Scott's 1901–1904 Discovery Expedition to Antarctica, thus beginning his exploring career. After his experience on the Terra Nova, Crean's third and final Antarctic venture was as second officer on Ernest Shackleton's Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition. After the ship Endurance became beset in the pack ice and sank, Crean and the ship's company spent 492 days drifting on the ice before undertaking a journey in the ship's lifeboats to Elephant Island. He was a member of the crew which made a small-boat journey of 800 nautical miles (1,500 km) from Elephant Island to South Georgia Island to seek aid for the stranded party. After retiring from the navy on health grounds in 1920, Crean ran his pub the South Pole Inn in County Kerry with his wife and daughters. He died in 1938. Crean was born around 16 February 1877 in the farming area of Gurtuchrane near the village of Annascaul on Corca Dhuibhne in County Kerry, Ireland, to Patrick and Catherine (née Courtney) Crean. One of 11 siblings with 7 brothers and 3 sisters. He attended the local Catholic school (at nearby Brackluin), leaving at the age of 12 to help on the family farm. Many sources, including Smith, give Crean's date of birth as 20 July 1877,but more recent scholarship demonstrates this is unlikely given parish records. At the age of 16, he enlisted in the Royal Navy at the naval station in nearby Minard Inlet, possibly after an argument with his father.His enlistment as a boy second class is recorded in Royal Navy records on 10 July 1893. Crean's initial naval apprenticeship was aboard the training ship Impregnable at Devonport. In November 1894, he was transferred to Devastation. In December 1894, Crean was posted to HMS Wild Swan a screw sloop as the ship headed to South America to join the Pacific Station. In 1895, Crean was serving in the Americas aboard Royal Arthur, the flagship assigned to the Pacific squadron’s base at Esquimalt in Canada. He was by this time, rated an ordinary seaman. Less than a year later, while serving a second term of service aboard Wild Swan he was rated an able seaman.He later joined the Navy's torpedo school ship, Defiance. By 1899, Crean had advanced to the rate of petty officer, second class and was serving in Vivid.In 1900, Crean was ledgered to the cruiser HMS Ringarooma, which was part of the Royal Navy's Australian Squadron based in Sydney. On 18 December 1901, he was demoted from petty officer to able seaman for an unspecified misdemeanour.In December 1901, the Ringarooma was ordered to assist Robert Falcon Scott's ship Discovery when it was docked at Lyttelton Harbour awaiting to departure to Antarctica. When an able seaman of Scott's ship deserted after striking a petty officer, a replacement was required; Crean volunteered, and was accepted.
38cm x 32cm Castlegregory Co Kerry Fine framed portrait of the legendary Irish Antarctic explorer and hero,Tom Crean. Thomas Crean (c. 16 February 1877 – 27 July 1938) was an Irish seaman and Antarctic explorer who was awarded the Albert Medal for Lifesaving. Crean was a member of three major expeditions to Antarctica during the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration, including Robert Falcon Scott's 1911–1913 Terra Nova Expedition. This saw the race to reach the South Pole lost to Roald Amundsen and ended in the deaths of Scott and his party. During the expedition, Crean's 35-statute-mile (56 km) solo walk across the Ross Ice Shelf to save the life of Edward Evans led to him receiving the Albert Medal. Crean left the family farm near Annascaul, in County Kerry, to enlist in the Royal Navy at age 16. In 1901, while serving on Ringarooma in New Zealand, he volunteered to join Scott's 1901–1904 Discovery Expedition to Antarctica, thus beginning his exploring career. After his experience on the Terra Nova, Crean's third and final Antarctic venture was as second officer on Ernest Shackleton's Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition. After the ship Endurance became beset in the pack ice and sank, Crean and the ship's company spent 492 days drifting on the ice before undertaking a journey in the ship's lifeboats to Elephant Island. He was a member of the crew which made a small-boat journey of 800 nautical miles (1,500 km) from Elephant Island to South Georgia Island to seek aid for the stranded party. After retiring from the navy on health grounds in 1920, Crean ran his pub the South Pole Inn in County Kerry with his wife and daughters. He died in 1938. Crean was born around 16 February 1877 in the farming area of Gurtuchrane near the village of Annascaul on Corca Dhuibhne in County Kerry, Ireland, to Patrick and Catherine (née Courtney) Crean. One of 11 siblings with 7 brothers and 3 sisters. He attended the local Catholic school (at nearby Brackluin), leaving at the age of 12 to help on the family farm. Many sources, including Smith, give Crean's date of birth as 20 July 1877,but more recent scholarship demonstrates this is unlikely given parish records. At the age of 16, he enlisted in the Royal Navy at the naval station in nearby Minard Inlet, possibly after an argument with his father.His enlistment as a boy second class is recorded in Royal Navy records on 10 July 1893. Crean's initial naval apprenticeship was aboard the training ship Impregnable at Devonport. In November 1894, he was transferred to Devastation. In December 1894, Crean was posted to HMS Wild Swan a screw sloop as the ship headed to South America to join the Pacific Station. In 1895, Crean was serving in the Americas aboard Royal Arthur, the flagship assigned to the Pacific squadron’s base at Esquimalt in Canada. He was by this time, rated an ordinary seaman. Less than a year later, while serving a second term of service aboard Wild Swan he was rated an able seaman.He later joined the Navy's torpedo school ship, Defiance. By 1899, Crean had advanced to the rate of petty officer, second class and was serving in Vivid.In 1900, Crean was ledgered to the cruiser HMS Ringarooma, which was part of the Royal Navy's Australian Squadron based in Sydney. On 18 December 1901, he was demoted from petty officer to able seaman for an unspecified misdemeanour.In December 1901, the Ringarooma was ordered to assist Robert Falcon Scott's ship Discovery when it was docked at Lyttelton Harbour awaiting to departure to Antarctica. When an able seaman of Scott's ship deserted after striking a petty officer, a replacement was required; Crean volunteered, and was accepted.Discovery Expedition, 1901–1904
Discovery sailed to the Antarctic on 21 December 1901, and seven weeks later, on 8 February 1902, arrived in McMurdo Sound, where she anchored at a spot which was later designated "Hut Point".Here the men established the base from which they would launch scientific and exploratory sledging journeys. Crean proved to be one of the most efficient man-haulers in the party; over the expedition as a whole, only seven of the 48-member party logged more time in harness than Crean's 149 days.]Crean had a good sense of humour and was well liked by his companions. Scott's second-in-command, Albert Armitage, wrote in his book Two Years in the Antarctic that "Crean was an Irishman with a fund of wit and an even temper which nothing disturbed." Crean accompanied Lieutenant Michael Barne on three sledging trips across the Ross Ice Shelf, then known as the "Great Ice Barrier". These included the 12-man party led by Barne which set out on 30 October 1902 to lay depots in support of the main southern journey undertaken by Scott, Shackleton and Edward Wilson. On 11 November the Barne party passed the previous furthest south mark,set by Carsten Borchgrevink in 1900 at 78°50'S, a record which they held briefly until the southern party itself passed it on its way to an eventual 82°17'S. During the Antarctic winter of 1902 Discovery became locked in the ice. Efforts to free her during the summer of 1902–03 failed, and although some of the expedition's members (including Ernest Shackleton) left in a relief ship, Crean and the majority of the party remained in the Antarctic until the ship was finally freed in February 1904. After returning to regular naval duty, Crean was promoted to petty officer, first class, on Scott's recommendation.Between expeditions, 1904–1910
Crean came back to regular duty at the naval base at Chatham, Kent, serving first in Pembroke in 1904 and later transferring to the torpedo school on Vernon. Crean had caught Captain Scott's attention with his attitude and work ethic on the Discovery Expedition, and in 1906 Scott requested that Crean join him on Victorious.Over the next few years, Crean followed Scott successively to Albemarle, Essex and Bulwark.By 1907, Scott was planning his second expedition to the Antarctic. Meanwhile, Ernest Shackleton's Nimrod Expedition, 1907–09, despite reaching a new furthest south record of 88°23'S, had failed to reach the South Pole. Scott was with Crean when the news of Shackleton's near miss became public; it is recorded that Scott observed to Crean: "I think we'd better have a shot next."Terra Nova Expedition, 1910–1913
Scott held Crean in high regard, so he was among the first people recruited for the Terra Nova Expedition, which set out for the Antarctic in June 1910, and one of the few men in the party with previous polar experience. After the expedition's arrival in McMurdo Sound in January 1911, Crean was as part of the 13-man team who established "One Ton Depot",130 statute miles (210 km) from Hut Point.so named because of the large amount of food and equipment cached there on the projected route to the South Pole. Returning from the depot to base camp at Cape Evans, Crean, accompanied by Apsley Cherry-Garrard and Henry "Birdie" Bowers, experienced near-disaster when camping on unstable sea ice. During the night the ice broke up, leaving the men adrift on an ice floe and separated from their sledges. Crean probably saved the group's lives, by leaping from floe to floe until he reached the Barrier edge and was able to summon help.Crean departed with Scott in November 1911, for the attempt at the South Pole. This journey had three stages: 400 statute miles (640 km) across the Barrier, 120 statute miles (190 km) up the heavily crevassed Beardmore Glacier to an altitude of 10,000 feet (3,000 m) above sea level, and then another 350 statute miles (560 km) to the Pole.At regular intervals, supporting parties returned to base; Crean was in the final group of eight men that marched on to the polar plateau and reached 87°32'S, 168 statute miles (270 km) from the pole. Here, on 4 January 1912, Scott selected his final polar party: Crean, William Lashly and Edward Evans were ordered to return to base, while Scott, Edgar Evans, Edward Wilson, Bowers and Lawrence Oates continued to the pole. Crean's biographer Michael Smith suggests that Crean would have been a better choice for the polar party than Edgar Evans, who was weakened by a recent hand injury (of which Scott was unaware). Crean, considered one of the toughest men in the expedition, had led a pony across the Barrier and had thus been saved much of the hard labour of man-hauling.Scott's critical biographer Roland Huntford records that the surgeon Edward L Atkinson, who had accompanied the southern party to the top of the Beardmore, had recommended either Lashly or Crean for the polar party rather than Edgar Evans.Scott in his diary recorded that Crean wept with disappointment at the prospect of having to turn back, so close to the goal. Soon after heading north on the 700-statute-mile (1,100 km) journey back to base camp, Crean's party lost the trail back to the Beardmore Glacier, and were faced with a long detour around a large icefall.With food supplies short, and needing to reach their next supply depot, the group made the decision to slide on their sledge, uncontrolled, down the icefall. The three men slid 2,000 feet (600 m),dodging crevasses up to 200 feet (61 m) wide, and ending their descent by overturning on an ice ridge. Evans later wrote: "How we ever escaped entirely uninjured is beyond me to explain". The gamble at the icefall succeeded, and the men reached their depot two days later.However, they had great difficulty navigating down the glacier. Lashly wrote: "I cannot describe the maze we got into and the hairbreadth escapes we have had to pass through."In his attempts to find the way down, Evans removed his goggles and subsequently suffered agonies of snow blindness that made him into a passenger. When the party was finally free of the glacier and on the level surface of the Barrier, Evans began to display the first symptoms of scurvy. By early February he was in great pain, his joints were swollen and discoloured, and he was passing blood. Through the efforts of Crean and Lashly the group struggled towards One Ton Depot, which they reached on 11 February. At this point Evans collapsed; Crean thought he had died and, according to Evans's account, "his hot tears fell on my face". With over 100 statute miles (160 km) still to travel before the relative safety of Hut Point, Crean and Lashly began hauling Evans on the sledge, "eking out his life with the last few drops of brandy that they still had with them".On 18 February they arrived at Corner Camp, still 35 statute miles (56 km) from Hut Point, with only one or two days' food rations left and still four or five days' man-hauling to do. They then decided that Crean should go on alone, to fetch help. With only a little chocolate and three biscuits to sustain him, without a tent or survival equipment,Crean walked the distance to Hut Point in 18 hours, arriving in a state of collapse to find Atkinson there, with the dog driver Dmtri Gerov. Crean reached safety just ahead of a fierce blizzard, which probably would have killed him, and which delayed the rescue party by a day and a half.Atkinson led a successful rescue, and Lashly and Evans were both brought to base camp alive. Crean modestly played down the significance of his feat of endurance. In a rare written account, he wrote in a letter: "So it fell to my lot to do the 30 miles for help, and only a couple of biscuits and a stick of chocolate to do it. Well, sir, I was very weak when I reached the hut." Scott's party failed to return. The winter of 1912 at Cape Evans was a sombre one, with the knowledge that the polar party had undoubtedly perished. Frank Debenhamwrote that "in the winter it was once again Crean who was the mainstay for cheerfulness in the now depleted mess deck part of the hut." In November 1912, Crean was one of the 11-man search party that found the remains of the polar party. On 12 November they spotted a cairn of snow, which proved to be a tent against which the drift had piled up. It contained the bodies of Scott, Wilson, and Bowers.Crean later wrote, referring to Scott in understated fashion, that he had "lost a good friend". On 12 February 1913 Crean and the remaining crew of the Terra Nova arrived in Lyttelton, New Zealand, and in June the ship returned to Cardiff.At Buckingham Palace the surviving members of the expedition were awarded Polar Medals by King George and Prince Louis of Battenberg, the First Sea Lord.Crean and Lashly were both awarded the Albert Medal, 2nd Class for saving Evans's life, these were presented by the King at Buckingham Palace on 26 July 1913. Crean was promoted to the rank of chief petty officer, retroactive to 9 September 1910. Petty officers Edgar Evans and Crean mending sleeping bags (May 1911)
Petty officers Edgar Evans and Crean mending sleeping bags (May 1911)Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition (Endurance Expedition), 1914–1917
In October 1913, a close friend of Captain Scott, Joseph Foster Stackhouse, announced plans for a British Antarctic Expedition with a mission to explore the uncharted coastlines between King Edward VII Land and Graham Land. The expedition was due to depart England in August 1914 aboard RRS Discovery, the ship of Crean’s first mission to Antarctica. In February 1914, Stackhouse confirmed that Crean was to join the expedition as Boatswain, however, in April 1914, Stackhouse’s plans were postponed. This left Shackleton free to recruit Crean to his expedition which was also scheduled to depart in August 1914. Shackleton knew Crean well from the Discovery Expedition, and also knew of his exploits on Scott's last expedition. Like Scott, Shackleton trusted Crean:he was worth, in Shackleton's own word, "trumps".Crean joined Shackleton's Imperial Transantarctic Expedition on 25 May 1914, as second officer, with a varied range of duties. In the absence of a Canadian dog-handling expert who was hired but never appeared, Crean took charge of one of the dog-handling teams,and was later involved in the care and nurture of the pups born to one of his dogs, Sally, early in the expedition. On 19 January 1915 the expedition's ship, the Endurance, was beset in the Weddell Sea pack ice. In the early efforts to free her, Crean narrowly escaped being crushed by a sudden movement in the ice. The ship drifted in the ice for months, eventually sinking on 21 November. Shackleton informed the men that they would drag the food, gear, and three lifeboats across the pack ice, to Snow Hill or Robertson Island, 200 statute miles (320 km) away. Because of uneven ice conditions, pressure ridges, and the danger of ice breakup which could separate the men, they soon abandoned this plan: the men pitched camp and decided to wait. They hoped that the clockwise drift of the pack would carry them 400 statute miles (640 km) to Paulet Island where they knew there was a hut with emergency supplies. But the pack ice held firm as it carried the men well past Paulet Island, and did not break up until 9 April. The crew then had to sail and row the three ill-equipped lifeboats through the pack ice to Elephant Island, a trip which lasted five days. Crean and Hubert Hudson, the navigating officer of the Endurance, piloted their lifeboat with Crean effectively in charge as Hudson appeared to have suffered a breakdown. Upon reaching Elephant Island, Crean was one of the "four fittest men" detailed by Shackleton to find a safe camping-ground.Shackleton decided that, rather than waiting for a rescue ship that would probably never arrive, one of the lifeboats should be strengthened so that a crew could sail it to South Georgia and arrange a rescue. After the party was settled on a penguin rookeryabove the high-water mark, a group of men led by ship's carpenter Harry McNish began modifying one of the lifeboats—the James Caird—in preparation for this journey, which Shackleton would lead. Frank Wild, who would be in command of the party remaining on Elephant Island, wanted the dependable Crean to stay with him;Shackleton initially agreed, but changed his mind after Crean begged to be included in the boat's crew of six. The 800-nautical-mile (1,500 km) boat journey to South Georgia, described by polar historian Caroline Alexander as one of the most extraordinary feats of seamanship and navigation in recorded history, took 17 days through gales and snow squalls, in seas which the navigator, Frank Worsley, described as a "mountainous westerly swell".After setting off on 24 April 1916 with just the barest navigational equipment, they reached South Georgia on 10 May 1916. Shackleton, in his later account of the journey, recalled Crean's tuneless singing at the tiller: "He always sang when he was steering, and nobody ever discovered what the song was ... but somehow it was cheerful". The party made its South Georgia landfall on the uninhabited southern coast, having decided that the risk of aiming directly for the whaling stations on the north side was too great; if they missed the island to the north they would be swept out into the Atlantic Ocean.The original plan was to work the James Caird around the coast, but the boat's rudder had broken off after their initial landing, and some of the party were, in Shackleton's view, unfit for further travel. The three fittest men—Shackleton, Crean, and Worsley—were decided to trek 30 statute miles (48 km) across the island's glaciated surface, in a hazardous 36-hour journey to the nearest manned whaling station. This trek was the first recorded crossing of the mountainous island, completed without tents, sleeping bags, or map—their only mountaineering equipment was a carpenter's adze, a length of alpine rope, and screws from the James Caird hammered through their boots to serve as crampons.They arrived at the whaling station at Stromness, tired and dirty, hair long and matted, faces blackened by months of cooking by blubber stoves—"the world's dirtiest men", according to Worsley.They quickly organized a boat to pick up the three on the other side of South Georgia, but thereafter it took Shackleton three months and four attempts by ship to rescue the other 22 men still on Elephant Island.Later life
After returning to Britain in November 1916, Crean resumed naval duties. On 15 December 1916 he was promoted to the rank of warrant officer (as a boatswain), in recognition of his service on the Endurance, and was awarded his third Polar Medal. A month later, in April, he was granted a licence for the sale and consumption of alcohol from his dwelling house, a premises he had purchased in 1916. The business was left in the care of family while he served out his time in the Royal Navy. On 5 September 1917, Crean married Ellen Herlihy of Annascaul. In early 1920, Shackleton was organising another Antarctic expedition, later to be known as the Shackleton-Rowett Expedition. He invited Crean to join him, along with other officers from the Endurance. By this time, however, Crean's second daughter had arrived, and he had plans to open a business following his naval career. He turned down Shackleton's invitation.On his last naval assignment, with HMS Hecla, Crean suffered a bad fall which caused lasting effects to his vision. As a result, he was retired on medical grounds on 24 March 1920. He and Ellen opened a small public house in Annascaul, which he called the South Pole Inn.The couple had three daughters, Mary, Kate, and Eileen, although Kate died when she was four years old. Throughout his life, Crean remained an extremely modest man. When he returned to Kerry, he put all of his medals away and never again spoke about his experiences in the Antarctic. There is no reliable evidence of Crean giving any interviews to the press.Smith speculates that this may have been because Kerry was a hotbed of Irish nationalism and later Irish republicanism, and, along with County Cork, an epicentre of violence.The Crean family were once subject to a Black and Tan raid during the Irish War of Independence. Their inn was ransacked until the raiders happened across Crean's framed photo in Royal Navy dress uniform and medals. They then left his inn.On 13 April 1920, Tom Crean was present among crowds gathered in Tralee to protest against the treatment of republican prisoners who had gone on a hunger strike in Mountjoy jail. Crean's older brother was Cornelius Crean, a sergeant in the Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC).Cornelius was based in County Cork, where he served with the RIC during the War of Independence.Sgt. Crean was killed during an IRA ambush near Upton on 25 April 1920.In 1938, Crean became ill with a burst appendix. He was taken to the nearest hospital in Tralee, but as no surgeon was available, he was transferred to the Bon Secours Hospital in Cork, where his appendix was removed. Because the operation had been delayed, an infection developed, and after a week in the hospital he died on 27 July 1938. He was buried in his family's tomb at the cemetery in Ballynacourty, Corkaguiney, County Kerry. Statue of Crean in Annascaul
Statue of Crean in AnnascaulLegacy
- Mount Crean 8,630 feet (2,630 m) in Victoria Land, Antarctica and Mount Crean 2,300 feet (700 m) in Greenland
- Crean Glacier on South Georgia.
- Crean Lake on South Georgia.
- An eight-part 1985 television series, The Last Place on Earth, told the story of Scott's expedition to the South Pole. Hugh Grant and Max von Sydow starred with Irish actor Daragh O'Malley, who portrayed Tom Crean.
- A one-man play, Tom Crean – Antarctic Explorer, has been widely performed since 2001 by author Aidan Dooley, including a special showing at the South Pole Inn, Annascaul, in October 2001. Present were Crean's daughters, Eileen and Mary, both in their 80s. Apparently he never told them stories of his exploits; according to Eileen: "He put his medals and his sword in a box ... and that was that. He was a very humble man".
- In July 2003, a bronze statue of Crean was unveiled across from his pub in Annascaul. It depicts him leaning against a crate whilst holding a pair of hiking poles in one hand and two of his beloved sled dog pups in the other.
- Until its closure in 2017, the Dingle Brewing Company produced 'Tom Crean Lager', named in his honour. In 2016, Crean's granddaughter, Aileen Crean O’Brien, launched 'Expedition Ale' in partnership with Torc Breweries
- In February 2021 it was announced that a new research vessel being commissioned by the Irish government’s Department of Agriculture, Food and the Marinewould be named 'RV Tom Crean', in Crean’s honour.
-

 25cm x 35cm Limerick Major Michael John O'Leary VC (29 September 1890 – 2 August 1961) was an Irish recipient of the Victoria Cross, the most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth forces. O'Leary achieved his award for single-handedly charging and destroying two German barricades defended by machine gun positions near the French village of Cuinchy, in a localised operation on the Western Front during the First World War. At the time of his action, O'Leary was a nine-year veteran of the British armed forces and by the time he retired from the British Army in 1921, he had reached the rank of lieutenant. He served in the army again during the Second World War, although his later service was blighted by periods of ill-health. At his final retirement from the military in 1945, O'Leary was an Army major in command of a prisoner of war camp. Between the wars, O'Leary spent many years employed as a police officer in Canada and is sometimes considered to be a Canadian recipient of the Victoria Cross. Following the Second World War he worked as a building contractor in London, where he died in 1961.Early life O'Leary was born in 1890, one of four children of Daniel and Margaret O'Leary, who owned a farm at Inchigeela, near Macroom in County Cork, Ireland. Daniel O'Leary was a fervent Irish nationalist and keen sportsman who participated in competitive weightlifting and football. Aged 16 and unwilling to continue to work on his parent's land, Michael O'Leary joined the Royal Navy, serving at the shore establishment HMS Vivid at Devonport for several years until rheumatism in his knees forced his departure from the service. Within a few months however, O'Leary had again tired of the farm and joined the Irish Guards regiment of the British Army. O'Leary served three years with the Irish Guards, leaving in August 1913 to join the Royal North-West Mounted Police (RNWMP) in Saskatchewan, Canada. Operating from Regina, Constable O'Leary was soon commended for his bravery in capturing two criminals following a two-hour gunbattle, for which service he was presented with a gold ring. At the outbreak of the First World War in Europe during August 1914, O'Leary was given permission to leave the RNWMP and return to Britain in order to rejoin the army as an active reservist. On 22 October, O'Leary was mobilized and on 23 November he joined his regiment in France, then fighting with the British Expeditionary Force, entrenched in Flanders. First World War service During December 1914, O'Leary saw heavy fighting with the Irish Guards and was Mentioned in Despatches and subsequently promoted to lance corporal on 5 January 1915. Three weeks later, on 30 January, the Irish Guards were ordered to prepare for an attack on German positions near Cuinchy on the La Bassée Canal, a response to a successful German operation in the area five days before. The Germans attacked first however, and on the morning of 1 February seized a stretch of canal embankment on the western end of the 2nd Brigade line from a company of Coldstream Guards. This section, known as the Hollow, was tactically important as it defended a culvert that passed underneath a railway embankment. 4 Company of Irish Guards, originally in reserve, were tasked with joining the Coldstream Guards in retaking the position at 04:00, but the attack was met with heavy machine gun fire and most of the assault party, including all of the Irish Guards officers, were killed or wounded To replace these officers, Second Lieutenant Innes of 1 Company was ordered forward to gather the survivors and withdraw, forming up at a barricade on the edge of the Hollow. Innes regrouped the survivors and, following a heavy bombardment from supporting artillery and with his own company providing covering fire, assisted the Coldstream Guards in a second attack at 10:15.Weighed down with entrenching equipment, the attacking Coldstream Guardsmen faltered and began to suffer heavy casualties. Innes too came under heavy fire from a German barricade to their front equipped with a machine gun. O'Leary had been serving as Innes's orderly, and had joined him in the operations earlier in the morning and again in the second attack. Charging past the rest of the assault party, O'Leary closed with the first German barricade at the top of the railway embankment and fired five shots, killing the gun's crew. Continuing forward, O'Leary confronted a second barricade, also armed with a machine gun 60 yards (55 m) further on and again mounted the railway embankment, to avoid the marshy ground on either side. The Germans spotted his approach, but could not bring their gun to bear on him before he opened fire, killing three soldiers and capturing two others after he ran out of ammunition.Reportedly, O'Leary had made his advance on the second barricade "intent upon killing another German to whom he had taken a dislike". Having disabled both guns and enabled the recapture of the British position, O'Leary then returned to his unit with his prisoners, apparently "as cool as if he had been for a walk in the park." For his actions, O'Leary received a battlefield promotion to sergeant on 4 February and was recommended for the Victoria Cross, which was gazetted on 16 February: No. 3556 Lance-Corporal Michael O'Leary, 1st Battalion, Irish Guards For conspicuous bravery at Cuinchy on the 1st February, 1915. When forming one of the storming party which advanced against the enemy's barricades he rushed to the front and himself killed five Germans who were holding the first barricade, after which he attacked a second barricade, about 60 yards further on, which he captured, after killing three of the enemy and making prisoners of two more. Lance-Corporal O'Leary thus practically captured the enemy's position by himself and prevented the attacking party from being fired upon. The London Gazette, 16 February 1915 Returning to Britain to receive his medal from King George V at Buckingham Palace on 22 June 1915, O'Leary was given a grand reception attended by thousands of Londoners in Hyde Park on 10 July. He was also the subject of much patriotic writing, including a poem in the Daily Mail and the short play O'Flaherty V.C. by George Bernard Shaw.Tributes came from numerous prominent figures of the day, including Sir Arthur Conan Doyle who said that "No writer in fiction would dare to fasten such an achievement on any of his characters, but the Irish have always had a reputation of being wonderful fighters, and Lance-Corporal Michael O’Leary is clearly one of them." and Thomas Scanlan who said: "I heard early this week of the great achievements of the Irish Guards. All Ireland is proud of O’Leary. He fully deserves the high honour that has been conferred upon him. Ireland is grateful to him."His reception was repeated in Macroom when he visited Ireland, with crowds turning out to applaud him. Daniel O'Leary was interviewed in a local newspaper regarding his son's exploit but was reportedly unimpressed, commenting: "I am surprised he didn't do more. I often laid out twenty men myself with a stick coming from Macroom Fair, and it is a bad trial of Mick that he could kill only eight, and he having a rifle and bayonet." O'Leary was further rewarded for his service, being advanced to a commissioned rank as a second lieutenant with the Connaught Rangers,and he was also presented with a Russian decoration, the Cross of St. George (third class).Despite his popularity with the crowds in London and Macroom, he was jeered by Ulster Volunteers at a recruitment drive in Ballaghaderrin during the autumn of 1915. This treatment caused such a scandal that it was raised in the Houses of Parliament in December. In 1916, O'Leary travelled to Salonika with the 5th battalion of the Connaught Rangers to serve in the Balkans campaign, remaining in theatre until the end of the war, following which he was stationed in Dover with the 2nd battalion until demobilised in 1921.During his service in the Balkans, O'Leary contracted malaria, which was to have severe negative effects on his health for the rest of his life. O'Leary was in the same regiment as the British actor Stanley Holloway and they served together in France. After the war ended, they remained close friends and Holloway often stayed in The May Fair Hotel where O'Leary worked as a concierge. Later life Leaving his wife Greta and their two children in Britain, O'Leary returned to Canada in March 1921 with the purported intention of rejoining the RNWMP, newly renamed the Royal Canadian Mounted Police. For unknown reasons, this plan came to nothing and after some months giving lectures on his war service and working in a publishing house, O'Leary joined the Ontario Provincial Police, charged with enforcing the prohibition laws. In 1924, with his family recently arrived from England, O'Leary left the Ontario police force and became a police sergeant with the Michigan Central Railway in Bridgeburg, Ontario, receiving £33 a month. In 1925, O'Leary was the subject of several scandals, being arrested for smuggling illegal immigrants and later for irregularities in his investigations. Although he was acquitted both times, he spent a week in prison following the second arrest and lost his job with the railway. Several months later, the municipal authorities in Hamilton, Ontario loaned him £70 to pay for him and his family to return to Ireland. Although his family sailed on the SS Leticia, O'Leary remained in Ontario, working with the attorney general's office. With his health in serious decline, the British Legion arranged for O'Leary to return to Britain and work in their poppy factory. By 1932, O'Leary was living in Southborne Avenue in Colindale, had regained his health and found employment as a commissionaire at The May Fair Hotel in London, at which he was involved in charitable events for wounded servicemen. With the mobilisation of the British Army in 1939, O'Leary returned to military service as a captain in the Middlesex Regiment. O'Leary was sent to France as part of the British Expeditionary Force but had returned to Britain before the Battle of France due to a recurrence of his malaria. No longer fit for full active service, O'Leary was transferred to the Pioneer Corps and took command of a prisoner of war camp in Southern England. In 1945, he was discharged from the military as unfit for duty on medical grounds as a major and found work as a building contractor, in which career he remained until his retirement in 1954. Two of O'Leary's sons had also served in the military during the war, with both receiving the Distinguished Flying Cross for their actions. As a Victoria Cross recipient, O'Leary joined the VE day parade in 1946, but at the 1956 Centenary VC review his place was taken by an imposter travelling in a bath chair. With his health again declining, O'Leary moved to Limesdale Gardens in Edgware shortly before his death in 1961 at the Whittington Hospital in Islington. O'Leary was buried at Mill Hill Cemetery following a funeral service at the Roman Catholic Annunciation Church in Burnt Oak which was attended by an honour guard from the Irish Guards and six of his children. His medals were later presented to the Irish Guards, and are on display at the Regimental Headquarters. He is also remembered in his birthplace, the macroom-online website listing him as a prominent citizen and states that "while many might consider he was fighting with the wrong army, in the wrong war, he was nevertheless a very brave, resourceful and capable soldier who deserved the honours bestowed upon him."
25cm x 35cm Limerick Major Michael John O'Leary VC (29 September 1890 – 2 August 1961) was an Irish recipient of the Victoria Cross, the most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth forces. O'Leary achieved his award for single-handedly charging and destroying two German barricades defended by machine gun positions near the French village of Cuinchy, in a localised operation on the Western Front during the First World War. At the time of his action, O'Leary was a nine-year veteran of the British armed forces and by the time he retired from the British Army in 1921, he had reached the rank of lieutenant. He served in the army again during the Second World War, although his later service was blighted by periods of ill-health. At his final retirement from the military in 1945, O'Leary was an Army major in command of a prisoner of war camp. Between the wars, O'Leary spent many years employed as a police officer in Canada and is sometimes considered to be a Canadian recipient of the Victoria Cross. Following the Second World War he worked as a building contractor in London, where he died in 1961.Early life O'Leary was born in 1890, one of four children of Daniel and Margaret O'Leary, who owned a farm at Inchigeela, near Macroom in County Cork, Ireland. Daniel O'Leary was a fervent Irish nationalist and keen sportsman who participated in competitive weightlifting and football. Aged 16 and unwilling to continue to work on his parent's land, Michael O'Leary joined the Royal Navy, serving at the shore establishment HMS Vivid at Devonport for several years until rheumatism in his knees forced his departure from the service. Within a few months however, O'Leary had again tired of the farm and joined the Irish Guards regiment of the British Army. O'Leary served three years with the Irish Guards, leaving in August 1913 to join the Royal North-West Mounted Police (RNWMP) in Saskatchewan, Canada. Operating from Regina, Constable O'Leary was soon commended for his bravery in capturing two criminals following a two-hour gunbattle, for which service he was presented with a gold ring. At the outbreak of the First World War in Europe during August 1914, O'Leary was given permission to leave the RNWMP and return to Britain in order to rejoin the army as an active reservist. On 22 October, O'Leary was mobilized and on 23 November he joined his regiment in France, then fighting with the British Expeditionary Force, entrenched in Flanders. First World War service During December 1914, O'Leary saw heavy fighting with the Irish Guards and was Mentioned in Despatches and subsequently promoted to lance corporal on 5 January 1915. Three weeks later, on 30 January, the Irish Guards were ordered to prepare for an attack on German positions near Cuinchy on the La Bassée Canal, a response to a successful German operation in the area five days before. The Germans attacked first however, and on the morning of 1 February seized a stretch of canal embankment on the western end of the 2nd Brigade line from a company of Coldstream Guards. This section, known as the Hollow, was tactically important as it defended a culvert that passed underneath a railway embankment. 4 Company of Irish Guards, originally in reserve, were tasked with joining the Coldstream Guards in retaking the position at 04:00, but the attack was met with heavy machine gun fire and most of the assault party, including all of the Irish Guards officers, were killed or wounded To replace these officers, Second Lieutenant Innes of 1 Company was ordered forward to gather the survivors and withdraw, forming up at a barricade on the edge of the Hollow. Innes regrouped the survivors and, following a heavy bombardment from supporting artillery and with his own company providing covering fire, assisted the Coldstream Guards in a second attack at 10:15.Weighed down with entrenching equipment, the attacking Coldstream Guardsmen faltered and began to suffer heavy casualties. Innes too came under heavy fire from a German barricade to their front equipped with a machine gun. O'Leary had been serving as Innes's orderly, and had joined him in the operations earlier in the morning and again in the second attack. Charging past the rest of the assault party, O'Leary closed with the first German barricade at the top of the railway embankment and fired five shots, killing the gun's crew. Continuing forward, O'Leary confronted a second barricade, also armed with a machine gun 60 yards (55 m) further on and again mounted the railway embankment, to avoid the marshy ground on either side. The Germans spotted his approach, but could not bring their gun to bear on him before he opened fire, killing three soldiers and capturing two others after he ran out of ammunition.Reportedly, O'Leary had made his advance on the second barricade "intent upon killing another German to whom he had taken a dislike". Having disabled both guns and enabled the recapture of the British position, O'Leary then returned to his unit with his prisoners, apparently "as cool as if he had been for a walk in the park." For his actions, O'Leary received a battlefield promotion to sergeant on 4 February and was recommended for the Victoria Cross, which was gazetted on 16 February: No. 3556 Lance-Corporal Michael O'Leary, 1st Battalion, Irish Guards For conspicuous bravery at Cuinchy on the 1st February, 1915. When forming one of the storming party which advanced against the enemy's barricades he rushed to the front and himself killed five Germans who were holding the first barricade, after which he attacked a second barricade, about 60 yards further on, which he captured, after killing three of the enemy and making prisoners of two more. Lance-Corporal O'Leary thus practically captured the enemy's position by himself and prevented the attacking party from being fired upon. The London Gazette, 16 February 1915 Returning to Britain to receive his medal from King George V at Buckingham Palace on 22 June 1915, O'Leary was given a grand reception attended by thousands of Londoners in Hyde Park on 10 July. He was also the subject of much patriotic writing, including a poem in the Daily Mail and the short play O'Flaherty V.C. by George Bernard Shaw.Tributes came from numerous prominent figures of the day, including Sir Arthur Conan Doyle who said that "No writer in fiction would dare to fasten such an achievement on any of his characters, but the Irish have always had a reputation of being wonderful fighters, and Lance-Corporal Michael O’Leary is clearly one of them." and Thomas Scanlan who said: "I heard early this week of the great achievements of the Irish Guards. All Ireland is proud of O’Leary. He fully deserves the high honour that has been conferred upon him. Ireland is grateful to him."His reception was repeated in Macroom when he visited Ireland, with crowds turning out to applaud him. Daniel O'Leary was interviewed in a local newspaper regarding his son's exploit but was reportedly unimpressed, commenting: "I am surprised he didn't do more. I often laid out twenty men myself with a stick coming from Macroom Fair, and it is a bad trial of Mick that he could kill only eight, and he having a rifle and bayonet." O'Leary was further rewarded for his service, being advanced to a commissioned rank as a second lieutenant with the Connaught Rangers,and he was also presented with a Russian decoration, the Cross of St. George (third class).Despite his popularity with the crowds in London and Macroom, he was jeered by Ulster Volunteers at a recruitment drive in Ballaghaderrin during the autumn of 1915. This treatment caused such a scandal that it was raised in the Houses of Parliament in December. In 1916, O'Leary travelled to Salonika with the 5th battalion of the Connaught Rangers to serve in the Balkans campaign, remaining in theatre until the end of the war, following which he was stationed in Dover with the 2nd battalion until demobilised in 1921.During his service in the Balkans, O'Leary contracted malaria, which was to have severe negative effects on his health for the rest of his life. O'Leary was in the same regiment as the British actor Stanley Holloway and they served together in France. After the war ended, they remained close friends and Holloway often stayed in The May Fair Hotel where O'Leary worked as a concierge. Later life Leaving his wife Greta and their two children in Britain, O'Leary returned to Canada in March 1921 with the purported intention of rejoining the RNWMP, newly renamed the Royal Canadian Mounted Police. For unknown reasons, this plan came to nothing and after some months giving lectures on his war service and working in a publishing house, O'Leary joined the Ontario Provincial Police, charged with enforcing the prohibition laws. In 1924, with his family recently arrived from England, O'Leary left the Ontario police force and became a police sergeant with the Michigan Central Railway in Bridgeburg, Ontario, receiving £33 a month. In 1925, O'Leary was the subject of several scandals, being arrested for smuggling illegal immigrants and later for irregularities in his investigations. Although he was acquitted both times, he spent a week in prison following the second arrest and lost his job with the railway. Several months later, the municipal authorities in Hamilton, Ontario loaned him £70 to pay for him and his family to return to Ireland. Although his family sailed on the SS Leticia, O'Leary remained in Ontario, working with the attorney general's office. With his health in serious decline, the British Legion arranged for O'Leary to return to Britain and work in their poppy factory. By 1932, O'Leary was living in Southborne Avenue in Colindale, had regained his health and found employment as a commissionaire at The May Fair Hotel in London, at which he was involved in charitable events for wounded servicemen. With the mobilisation of the British Army in 1939, O'Leary returned to military service as a captain in the Middlesex Regiment. O'Leary was sent to France as part of the British Expeditionary Force but had returned to Britain before the Battle of France due to a recurrence of his malaria. No longer fit for full active service, O'Leary was transferred to the Pioneer Corps and took command of a prisoner of war camp in Southern England. In 1945, he was discharged from the military as unfit for duty on medical grounds as a major and found work as a building contractor, in which career he remained until his retirement in 1954. Two of O'Leary's sons had also served in the military during the war, with both receiving the Distinguished Flying Cross for their actions. As a Victoria Cross recipient, O'Leary joined the VE day parade in 1946, but at the 1956 Centenary VC review his place was taken by an imposter travelling in a bath chair. With his health again declining, O'Leary moved to Limesdale Gardens in Edgware shortly before his death in 1961 at the Whittington Hospital in Islington. O'Leary was buried at Mill Hill Cemetery following a funeral service at the Roman Catholic Annunciation Church in Burnt Oak which was attended by an honour guard from the Irish Guards and six of his children. His medals were later presented to the Irish Guards, and are on display at the Regimental Headquarters. He is also remembered in his birthplace, the macroom-online website listing him as a prominent citizen and states that "while many might consider he was fighting with the wrong army, in the wrong war, he was nevertheless a very brave, resourceful and capable soldier who deserved the honours bestowed upon him."






























