-

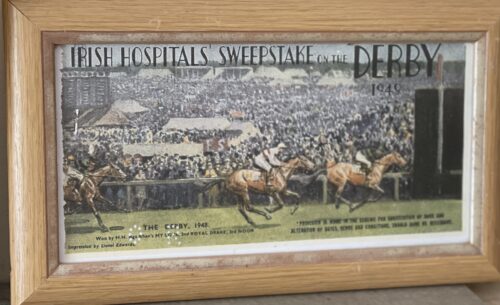 Vintage ticket for the Irish Hospital Sweepstakes 1949 Epsom Derby Dublin 35cm x 20cm The Irish Hospital Sweepstake was a lottery established in the Irish Free State in 1930 as the Irish Free State Hospitals' Sweepstake to finance hospitals. It is generally referred to as the Irish Sweepstake, frequently abbreviated to Irish Sweeps or Irish Sweep. The Public Charitable Hospitals (Temporary Provisions) Act, 1930 was the act that established the lottery; as this act expired in 1934, in accordance with its terms, the Public Hospitals Acts were the legislative basis for the scheme thereafter. The main organisers were Richard Duggan, Captain Spencer Freeman and Joe McGrath. Duggan was a well known Dublin bookmaker who had organised a number of sweepstakes in the decade prior to setting up the Hospitals' Sweepstake. Captain Freeman was a Welsh-born engineer and former captain in the British Army. After the Constitution of Ireland was enacted in 1937, the name Irish Hospitals' Sweepstake was adopted. The sweepstake was established because there was a need for investment in hospitals and medical services and the public finances were unable to meet this expense at the time. As the people of Ireland were unable to raise sufficient funds, because of the low population, a significant amount of the funds were raised in the United Kingdom and United States, often among the emigrant Irish. Potentially winning tickets were drawn from rotating drums, usually by nurses in uniform. Each such ticket was assigned to a horse expected to run in one of several horse races, including the Cambridgeshire Handicap, Derby and Grand National. Tickets that drew the favourite horses thus stood a higher likelihood of winning and a series of winning horses had to be chosen on the accumulator system, allowing for enormous prizes. The original sweepstake draws were held at The Mansion House, Dublin on 19 May 1939 under the supervision of the Chief Commissioner of Police, and were moved to the more permanent fixture at the Royal Dublin Society (RDS) in Ballsbridge later in 1940. The Adelaide Hospital in Dublin was the only hospital at the time not to accept money from the Hospitals Trust, as the governors disapproved of sweepstakes. From the 1960s onwards, revenues declined. The offices were moved to Lotamore House in Cork. Although giving the appearance of a public charitable lottery, with nurses featured prominently in the advertising and drawings, the Sweepstake was in fact a private for-profit lottery company, and the owners were paid substantial dividends from the profits. Fortune Magazine described it as "a private company run for profit and its handful of stockholders have used their earnings from the sweepstakes to build a group of industrial enterprises that loom quite large in the modest Irish economy. Waterford Glass, Irish Glass Bottle Company and many other new Irish companies were financed by money from this enterprise and up to 5,000 people were given jobs."[3] By his death in 1966, Joe McGrath had interests in the racing industry, and held the Renault dealership for Ireland besides large financial and property assets. He was known throughout Ireland for his tough business attitude but also by his generous spirit.At that time, Ireland was still one of the poorer countries in Europe; he believed in investment in Ireland. His home, Cabinteely House, was donated to the state in 1986. The house and the surrounding park are now in the ownership of Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown County Council who have invested in restoring and maintaining the house and grounds as a public park. In 1986, the Irish government created a new public lottery, and the company failed to secure the new contract to manage it. The final sweepstake was held in January 1986 and the company was unsuccessful for a licence bid for the Irish National Lottery, which was won by An Post later that year. The company went into voluntary liquidation in March 1987. The majority of workers did not have a pension scheme but the sweepstake had fed many families during lean times and was regarded as a safe job.The Public Hospitals (Amendment) Act, 1990 was enacted for the orderly winding up of the scheme which had by then almost £500,000 in unclaimed prizes and accrued interest. A collection of advertising material relating to the Irish Hospitals' Sweepstakes is among the Special Collections of National Irish Visual Arts Library. At the time of the Sweepstake's inception, lotteries were generally illegal in the United Kingdom, the United States and Canada. In the absence of other readily available lotteries, the Irish Sweeps became popular. Even though tickets were illegal outside Ireland, millions were sold in the US and Great Britain. How many of these tickets failed to make it back for the drawing is unknown. The United States Customs Service alone confiscated and destroyed several million counterfoils from shipments being returned to Ireland. In the UK, the sweepstakes caused some strain in Anglo-Irish relations, and the Betting and Lotteries Act 1934 was passed by the parliament of the UK to prevent export and import of lottery related materials. The United States Congress had outlawed the use of the US Postal Service for lottery purposes in 1890. A thriving black market sprang up for tickets in both jurisdictions. From the 1950s onwards, as the American, British and Canadian governments relaxed their attitudes towards this form of gambling, and went into the lottery business themselves, the Irish Sweeps, never legal in the United States,declined in popularity. Origins: Co Galway Dimensions :39cm x 31cmThe original sweepstake draws were held at The Mansion House, Dublin on 19 May 1939 under the supervision of the Chief Commissioner of Police, and were moved to the more permanent fixture at the Royal Dublin Society (RDS) in Ballsbridge later in 1940. The Adelaide Hospital in Dublin was the only hospital at the time not to accept money from the Hospitals Trust, as the governors disapproved of sweepstakes. From the 1960s onwards, revenues declined. The offices were moved to Lotamore House in Cork. Although giving the appearance of a public charitable lottery, with nurses featured prominently in the advertising and drawings, the Sweepstake was in fact a private for-profit lottery company, and the owners were paid substantial dividends from the profits. Fortune Magazine described it as "a private company run for profit and its handful of stockholders have used their earnings from the sweepstakes to build a group of industrial enterprises that loom quite large in the modest Irish economy. Waterford Glass, Irish Glass Bottle Company and many other new Irish companies were financed by money from this enterprise and up to 5,000 people were given jobs."By his death in 1966, Joe McGrath had interests in the racing industry, and held the Renault dealership for Ireland besides large financial and property assets. He was known throughout Ireland for his tough business attitude but also by his generous spirit. At that time, Ireland was still one of the poorer countries in Europe; he believed in investment in Ireland. His home, Cabinteely House, was donated to the state in 1986. The house and the surrounding park are now in the ownership of Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown County Council who have invested in restoring and maintaining the house and grounds as a public park. In 1986, the Irish government created a new public lottery, and the company failed to secure the new contract to manage it. The final sweepstake was held in January 1986 and the company was unsuccessful for a licence bid for the Irish National Lottery, which was won by An Post later that year. The company went into voluntary liquidation in March 1987. The majority of workers did not have a pension scheme but the sweepstake had fed many families during lean times and was regarded as a safe job.The Public Hospitals (Amendment) Act, 1990 was enacted for the orderly winding up of the scheme,which had by then almost £500,000 in unclaimed prizes and accrued interest. A collection of advertising material relating to the Irish Hospitals' Sweepstakes is among the Special Collections of National Irish Visual Arts Library.
Vintage ticket for the Irish Hospital Sweepstakes 1949 Epsom Derby Dublin 35cm x 20cm The Irish Hospital Sweepstake was a lottery established in the Irish Free State in 1930 as the Irish Free State Hospitals' Sweepstake to finance hospitals. It is generally referred to as the Irish Sweepstake, frequently abbreviated to Irish Sweeps or Irish Sweep. The Public Charitable Hospitals (Temporary Provisions) Act, 1930 was the act that established the lottery; as this act expired in 1934, in accordance with its terms, the Public Hospitals Acts were the legislative basis for the scheme thereafter. The main organisers were Richard Duggan, Captain Spencer Freeman and Joe McGrath. Duggan was a well known Dublin bookmaker who had organised a number of sweepstakes in the decade prior to setting up the Hospitals' Sweepstake. Captain Freeman was a Welsh-born engineer and former captain in the British Army. After the Constitution of Ireland was enacted in 1937, the name Irish Hospitals' Sweepstake was adopted. The sweepstake was established because there was a need for investment in hospitals and medical services and the public finances were unable to meet this expense at the time. As the people of Ireland were unable to raise sufficient funds, because of the low population, a significant amount of the funds were raised in the United Kingdom and United States, often among the emigrant Irish. Potentially winning tickets were drawn from rotating drums, usually by nurses in uniform. Each such ticket was assigned to a horse expected to run in one of several horse races, including the Cambridgeshire Handicap, Derby and Grand National. Tickets that drew the favourite horses thus stood a higher likelihood of winning and a series of winning horses had to be chosen on the accumulator system, allowing for enormous prizes. The original sweepstake draws were held at The Mansion House, Dublin on 19 May 1939 under the supervision of the Chief Commissioner of Police, and were moved to the more permanent fixture at the Royal Dublin Society (RDS) in Ballsbridge later in 1940. The Adelaide Hospital in Dublin was the only hospital at the time not to accept money from the Hospitals Trust, as the governors disapproved of sweepstakes. From the 1960s onwards, revenues declined. The offices were moved to Lotamore House in Cork. Although giving the appearance of a public charitable lottery, with nurses featured prominently in the advertising and drawings, the Sweepstake was in fact a private for-profit lottery company, and the owners were paid substantial dividends from the profits. Fortune Magazine described it as "a private company run for profit and its handful of stockholders have used their earnings from the sweepstakes to build a group of industrial enterprises that loom quite large in the modest Irish economy. Waterford Glass, Irish Glass Bottle Company and many other new Irish companies were financed by money from this enterprise and up to 5,000 people were given jobs."[3] By his death in 1966, Joe McGrath had interests in the racing industry, and held the Renault dealership for Ireland besides large financial and property assets. He was known throughout Ireland for his tough business attitude but also by his generous spirit.At that time, Ireland was still one of the poorer countries in Europe; he believed in investment in Ireland. His home, Cabinteely House, was donated to the state in 1986. The house and the surrounding park are now in the ownership of Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown County Council who have invested in restoring and maintaining the house and grounds as a public park. In 1986, the Irish government created a new public lottery, and the company failed to secure the new contract to manage it. The final sweepstake was held in January 1986 and the company was unsuccessful for a licence bid for the Irish National Lottery, which was won by An Post later that year. The company went into voluntary liquidation in March 1987. The majority of workers did not have a pension scheme but the sweepstake had fed many families during lean times and was regarded as a safe job.The Public Hospitals (Amendment) Act, 1990 was enacted for the orderly winding up of the scheme which had by then almost £500,000 in unclaimed prizes and accrued interest. A collection of advertising material relating to the Irish Hospitals' Sweepstakes is among the Special Collections of National Irish Visual Arts Library. At the time of the Sweepstake's inception, lotteries were generally illegal in the United Kingdom, the United States and Canada. In the absence of other readily available lotteries, the Irish Sweeps became popular. Even though tickets were illegal outside Ireland, millions were sold in the US and Great Britain. How many of these tickets failed to make it back for the drawing is unknown. The United States Customs Service alone confiscated and destroyed several million counterfoils from shipments being returned to Ireland. In the UK, the sweepstakes caused some strain in Anglo-Irish relations, and the Betting and Lotteries Act 1934 was passed by the parliament of the UK to prevent export and import of lottery related materials. The United States Congress had outlawed the use of the US Postal Service for lottery purposes in 1890. A thriving black market sprang up for tickets in both jurisdictions. From the 1950s onwards, as the American, British and Canadian governments relaxed their attitudes towards this form of gambling, and went into the lottery business themselves, the Irish Sweeps, never legal in the United States,declined in popularity. Origins: Co Galway Dimensions :39cm x 31cmThe original sweepstake draws were held at The Mansion House, Dublin on 19 May 1939 under the supervision of the Chief Commissioner of Police, and were moved to the more permanent fixture at the Royal Dublin Society (RDS) in Ballsbridge later in 1940. The Adelaide Hospital in Dublin was the only hospital at the time not to accept money from the Hospitals Trust, as the governors disapproved of sweepstakes. From the 1960s onwards, revenues declined. The offices were moved to Lotamore House in Cork. Although giving the appearance of a public charitable lottery, with nurses featured prominently in the advertising and drawings, the Sweepstake was in fact a private for-profit lottery company, and the owners were paid substantial dividends from the profits. Fortune Magazine described it as "a private company run for profit and its handful of stockholders have used their earnings from the sweepstakes to build a group of industrial enterprises that loom quite large in the modest Irish economy. Waterford Glass, Irish Glass Bottle Company and many other new Irish companies were financed by money from this enterprise and up to 5,000 people were given jobs."By his death in 1966, Joe McGrath had interests in the racing industry, and held the Renault dealership for Ireland besides large financial and property assets. He was known throughout Ireland for his tough business attitude but also by his generous spirit. At that time, Ireland was still one of the poorer countries in Europe; he believed in investment in Ireland. His home, Cabinteely House, was donated to the state in 1986. The house and the surrounding park are now in the ownership of Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown County Council who have invested in restoring and maintaining the house and grounds as a public park. In 1986, the Irish government created a new public lottery, and the company failed to secure the new contract to manage it. The final sweepstake was held in January 1986 and the company was unsuccessful for a licence bid for the Irish National Lottery, which was won by An Post later that year. The company went into voluntary liquidation in March 1987. The majority of workers did not have a pension scheme but the sweepstake had fed many families during lean times and was regarded as a safe job.The Public Hospitals (Amendment) Act, 1990 was enacted for the orderly winding up of the scheme,which had by then almost £500,000 in unclaimed prizes and accrued interest. A collection of advertising material relating to the Irish Hospitals' Sweepstakes is among the Special Collections of National Irish Visual Arts Library. -

 25cm x 35cm LimerickAnd given that The Bohemian is situated on Doyle’s Corner it seems an apt subject. Doyle’s Corner has an interesting history of which this particular pub is a part of. Back around the turn of the century, the intersection of The North Circular and The Phibsborough Road was known as Dunphy’s Corner. Now, this is where it starts to get a bit confusing because the word Doyle is about to be bandied about as much as it might do in a series or two of Father Ted. The name Dunphy’s Corner was derived from another public house which sits directly across the road from The Bohemian – now named Doyle’s Corner, formerly named Doyle’s. The pub that provided this named was owned by a man named Thomas Dunphy who presided over it from the mid-1800s up to around the 1890s. The name Dunphy’s Corner must have been widely used by Dubliners because it’s well represented in song, literature and lore. It gets a mention in Peadar Kearney’s anti-enlistment Ballad about the recruiting sergeant William Bailey (Lankum do a great version), who is said to have stood on the corner in the process of his enlisting. And Peadar might have been working on a subliminal as well as a perceptible level here because ‘going round Dunphy’s Corner‘, as it would have been put, was seemingly an idiom used to describe those who had gone to the great beyond, given its nodal point on the route taken by hearses on their way to Glasnevin. Those familiar with the first half of Ulysses, might remember that Poor Dignam went the very same way along that route in the earlier stages of the book. So in the mid-1890s or so along came John Doyle. And John Doyle fancied he might usurp Dunphy and in setting about doing this, he acquired both number 160 and number 66 Phibsborough Road and placed within each of them a public house which bore his name. It was a trick the evidently worked because, as I’m sure you will know, the corner is still referred to as Doyle’s. Seemingly someone by the name of Murphy – proprietor of the nearby Botanic House – took ownership of The Bohemian in the 1970s and figured he could usurp Doyle by erecting signs which read ‘Murphy’s Corner’. But the inhabitants of Phibsborough and Dubliners alike never took to it. So it remains – Doyle’s Corner.
25cm x 35cm LimerickAnd given that The Bohemian is situated on Doyle’s Corner it seems an apt subject. Doyle’s Corner has an interesting history of which this particular pub is a part of. Back around the turn of the century, the intersection of The North Circular and The Phibsborough Road was known as Dunphy’s Corner. Now, this is where it starts to get a bit confusing because the word Doyle is about to be bandied about as much as it might do in a series or two of Father Ted. The name Dunphy’s Corner was derived from another public house which sits directly across the road from The Bohemian – now named Doyle’s Corner, formerly named Doyle’s. The pub that provided this named was owned by a man named Thomas Dunphy who presided over it from the mid-1800s up to around the 1890s. The name Dunphy’s Corner must have been widely used by Dubliners because it’s well represented in song, literature and lore. It gets a mention in Peadar Kearney’s anti-enlistment Ballad about the recruiting sergeant William Bailey (Lankum do a great version), who is said to have stood on the corner in the process of his enlisting. And Peadar might have been working on a subliminal as well as a perceptible level here because ‘going round Dunphy’s Corner‘, as it would have been put, was seemingly an idiom used to describe those who had gone to the great beyond, given its nodal point on the route taken by hearses on their way to Glasnevin. Those familiar with the first half of Ulysses, might remember that Poor Dignam went the very same way along that route in the earlier stages of the book. So in the mid-1890s or so along came John Doyle. And John Doyle fancied he might usurp Dunphy and in setting about doing this, he acquired both number 160 and number 66 Phibsborough Road and placed within each of them a public house which bore his name. It was a trick the evidently worked because, as I’m sure you will know, the corner is still referred to as Doyle’s. Seemingly someone by the name of Murphy – proprietor of the nearby Botanic House – took ownership of The Bohemian in the 1970s and figured he could usurp Doyle by erecting signs which read ‘Murphy’s Corner’. But the inhabitants of Phibsborough and Dubliners alike never took to it. So it remains – Doyle’s Corner.Next to a statue or the freedom of the city, perhaps the most select honour you can earn in Dublin is to have a street corner named after you in perpetuity. It’s a very rare distinction, available mainly – it seems – to publicans, whose premises command an important junction for a substantial period. It’s also entirely in the public’s gift, not officialdom’s. And the vast majority of city corners are never so named. I can think of fewer than 10 that have been, including Doyle’s, Hanlon’s, Hart’s, Kelly’s, and Leonard’s. Some of those names have long outlived the original businesses, although that said, “perpetuity” may be overstating their lease, as the case of Doyle’s illustrates.
Anyone who was at the annual Bloomsday re-enactment in Glasnevin last Sunday will have been reminded that Doyle’s Corner, in nearby Phibsboro, used to be “Dunphy’s”. As such, it was mentioned in Ulysses for its prominent role in city funerals, including the fictional Paddy Dignam’s, as the last right-angle turn towards the cemetery.
Hence, as Leopold Bloom’s interior voice records: “Dunphy’s corner. Mourning coaches drawn up drowning their grief. A pause by the wayside. Tiptop position for a pub. Expect we’ll pull up here on the way back to drink his health. Pass around the consolation. Elixir of life.”
It also inspires a joke by one of the other passengers in the carriage: “First round Dunphy’s, Mr Dedalus said, nodding. Gordon Bennett Cup.”
His reference to the famous motor race may have been a nod to the haste with which some corteges used to move in those years, under pressure from the cemetery’s restrictive opening hours. In a series of newspaper essays, The Streets of Dublin 1910-11, the then Alderman Thomas Kelly complained he had never seen in any other Irish city “the galloping which, more especially on Sunday’s, disgraces Dublin funerals”.
That same alderman – a future Sinn Féin TD – was the Kelly for whom Kelly’s Corner is named, an honour all the more unusual because he owned a shop rather than a pub. But for apparent immortality in those years, his corner would have had to bow to Dunphy’s, which enjoyed a whole different level of fame. As he also writes, “Rounding Dunphy’s Corner” had become a popular Dublin euphemism for life’s last journey.
Even in 1904, however, Dunphy’s pub had already made way for one called Doyle’s, and the corner name gradually followed. There must have been a period when it was known as both, because the news archives for 1906 have a story about a collapse of scaffolding at “Doyle’s Corner”, during rebuilding of the premises there. Among five people injured, incidentally, was “a man named Coleman, from Exchange Street”, who had also survived the sewer gas tragedy in a manhole on Burgh Quay the year previous (to which there remains today a monument). Talk about luck.
No doubt even the indestructible Coleman rounded Dunphy’s Corner eventually. In any case, by the 1920s, the Phibsboro Junction was firmly established as Doyle’s Corner, and is still known as that, its latter-day notoriety secured by regular mentions on AA Roadwatch. Nobody calls it Dunphy’s Corner anymore.
Mind you, the same location proves that mere changes of ownership do not in themselves confer naming privileges. For a time in the middle of the last century, I gather, there was also a Murphy’s pub on the site, the owner of which erected a sign proclaiming “Murphy’s Corner”. The public did not take the hint.
-

 25cm x 35cm Limerick The 1906 Irish Rugby XV that played South Africa in Belfast in the first ever test match between the two nationsThe Irish Rugby Football Union (IRFU) (Irish: Cumann Rugbaí na hÉireann) is the body managing rugby union in the island of Ireland (both Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland). The IRFU has its head office at 10/12 Lansdowne Roadand home ground at Aviva Stadium, where adult men's Irish rugby union international matches are played. In addition, the Union also owns the Ravenhill Stadium in Belfast, Thomond Park in Limerick and a number of grounds in provincial areas that have been rented to clubs. Initially, there were two unions: the Irish Football Union, which had jurisdiction over clubs in Leinster, Munster and parts of Ulster and was founded in December 1874, and the Northern Football Union of Ireland, which controlled the Belfast area and was founded in January 1875.The IRFU was formed in 1879 as an amalgamation of these two organisations and branches of the new IRFU were formed in Leinster, Munster and Ulster. The Connacht Branch was formed in 1900. The IRFU was a founding member of the International Rugby Football Board, now known as World Rugby, in 1886 with Scotland and Wales. (England refused to join until 1890.) Following the political partition of Ireland into separate national states, the Republic of Ireland (originally the Irish Free State then Éire) and Northern Ireland (a political division of the United Kingdom), the then Committee of the Irish Rugby Football Union decided that it would continue to administer its affairs on the basis of the full 32 Irish counties and the traditional four provinces of Ireland: Leinster (12 counties), Ulster (9 counties), Munster (6 counties), and Connacht (5 counties). This led to the unusual, but not unique, situation among international rugby union teams, where the Irish representative teams are drawn from players from two separate political, national territories: Ireland (an independent, sovereign state) and Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom). To maintain the unity of Irish rugby union and the linkages between North and South, the IRFU purchased a new ground in 1923 in the Ravenhill district of Belfast at a cost of £2,300.The last full International at Ravenhill involving Ireland for more than a half-century took place in 1953–54 against Scotland who were victorious by 2 tries (6 points) to nil. Australia played Romania in the 1999 World Cup at the ground. The next full International played at Ravenhill was the Rugby World Cup warm-up match against Italy in August 2007 due to the temporary closure of Lansdowne Road for reconstruction. The four provincial branches of the IRFU first ran cup competitions during the 1880s. Although these tournaments still take place every year, their significance has been diminished by the advent of an All-Ireland league of 48 Senior Clubs in 1990. The four provincial teams have played an Interprovincial Championship since the 1920s and continue to be the focal point for players aspiring to the international level. These are Munster, Leinster, Ulster and Connacht. All four provinces play at the senior level as members of the United Rugby Championship.24 November
25cm x 35cm Limerick The 1906 Irish Rugby XV that played South Africa in Belfast in the first ever test match between the two nationsThe Irish Rugby Football Union (IRFU) (Irish: Cumann Rugbaí na hÉireann) is the body managing rugby union in the island of Ireland (both Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland). The IRFU has its head office at 10/12 Lansdowne Roadand home ground at Aviva Stadium, where adult men's Irish rugby union international matches are played. In addition, the Union also owns the Ravenhill Stadium in Belfast, Thomond Park in Limerick and a number of grounds in provincial areas that have been rented to clubs. Initially, there were two unions: the Irish Football Union, which had jurisdiction over clubs in Leinster, Munster and parts of Ulster and was founded in December 1874, and the Northern Football Union of Ireland, which controlled the Belfast area and was founded in January 1875.The IRFU was formed in 1879 as an amalgamation of these two organisations and branches of the new IRFU were formed in Leinster, Munster and Ulster. The Connacht Branch was formed in 1900. The IRFU was a founding member of the International Rugby Football Board, now known as World Rugby, in 1886 with Scotland and Wales. (England refused to join until 1890.) Following the political partition of Ireland into separate national states, the Republic of Ireland (originally the Irish Free State then Éire) and Northern Ireland (a political division of the United Kingdom), the then Committee of the Irish Rugby Football Union decided that it would continue to administer its affairs on the basis of the full 32 Irish counties and the traditional four provinces of Ireland: Leinster (12 counties), Ulster (9 counties), Munster (6 counties), and Connacht (5 counties). This led to the unusual, but not unique, situation among international rugby union teams, where the Irish representative teams are drawn from players from two separate political, national territories: Ireland (an independent, sovereign state) and Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom). To maintain the unity of Irish rugby union and the linkages between North and South, the IRFU purchased a new ground in 1923 in the Ravenhill district of Belfast at a cost of £2,300.The last full International at Ravenhill involving Ireland for more than a half-century took place in 1953–54 against Scotland who were victorious by 2 tries (6 points) to nil. Australia played Romania in the 1999 World Cup at the ground. The next full International played at Ravenhill was the Rugby World Cup warm-up match against Italy in August 2007 due to the temporary closure of Lansdowne Road for reconstruction. The four provincial branches of the IRFU first ran cup competitions during the 1880s. Although these tournaments still take place every year, their significance has been diminished by the advent of an All-Ireland league of 48 Senior Clubs in 1990. The four provincial teams have played an Interprovincial Championship since the 1920s and continue to be the focal point for players aspiring to the international level. These are Munster, Leinster, Ulster and Connacht. All four provinces play at the senior level as members of the United Rugby Championship.24 NovemberIreland 
12–15  South Africa
South AfricaTry: Sugars (2), Maclear Pen: Parke Report Try: Loubser (2), Krige, Stegmann Pen: Joubert Balmoral Showgrounds, Belfast Attendance: 15,000 Referee: JD Tulloch (Scotland) -

 25cm x 35cm Limerick The 1921 Five Nations Championship was the seventh series of the rugby union Five Nations Championship following the inclusion of France into the Home Nations Championship. Including the previous Home Nations Championships, this was the thirty-fourth series of the annual northern hemisphere rugby union championship. Ten matches were played between 15 January and 9 April. It was contested by England, France, Ireland, Scotland and Wales.
25cm x 35cm Limerick The 1921 Five Nations Championship was the seventh series of the rugby union Five Nations Championship following the inclusion of France into the Home Nations Championship. Including the previous Home Nations Championships, this was the thirty-fourth series of the annual northern hemisphere rugby union championship. Ten matches were played between 15 January and 9 April. It was contested by England, France, Ireland, Scotland and Wales.Table
Position Nation Games Points Table points Played Won Drawn Lost For Against Difference 1  England
England4 4 0 0 61 9 +52 8 2  France
France4 2 0 2 33 32 +1 4 2  Wales
Wales4 2 0 2 29 36 −7 4 4  Scotland
Scotland4 1 0 3 22 38 −16 2 4  Ireland
Ireland4 1 0 3 19 49 −30 2 Results[edit]
The Irish Rugby Football Union (IRFU) (Irish: Cumann Rugbaí na hÉireann) is the body managing rugby union in the island of Ireland (both Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland). The IRFU has its head office at 10/12 Lansdowne Roadand home ground at Aviva Stadium, where adult men's Irish rugby union international matches are played. In addition, the Union also owns the Ravenhill Stadium in Belfast, Thomond Park in Limerick and a number of grounds in provincial areas that have been rented to clubs. Initially, there were two unions: the Irish Football Union, which had jurisdiction over clubs in Leinster, Munster and parts of Ulster and was founded in December 1874, and the Northern Football Union of Ireland, which controlled the Belfast area and was founded in January 1875.The IRFU was formed in 1879 as an amalgamation of these two organisations and branches of the new IRFU were formed in Leinster, Munster and Ulster. The Connacht Branch was formed in 1900. The IRFU was a founding member of the International Rugby Football Board, now known as World Rugby, in 1886 with Scotland and Wales. (England refused to join until 1890.) Following the political partition of Ireland into separate national states, the Republic of Ireland (originally the Irish Free State then Éire) and Northern Ireland (a political division of the United Kingdom), the then Committee of the Irish Rugby Football Union decided that it would continue to administer its affairs on the basis of the full 32 Irish counties and the traditional four provinces of Ireland: Leinster (12 counties), Ulster (9 counties), Munster (6 counties), and Connacht (5 counties). This led to the unusual, but not unique, situation among international rugby union teams, where the Irish representative teams are drawn from players from two separate political, national territories: Ireland (an independent, sovereign state) and Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom). To maintain the unity of Irish rugby union and the linkages between North and South, the IRFU purchased a new ground in 1923 in the Ravenhill district of Belfast at a cost of £2,300.The last full International at Ravenhill involving Ireland for more than a half-century took place in 1953–54 against Scotland who were victorious by 2 tries (6 points) to nil. Australia played Romania in the 1999 World Cup at the ground. The next full International played at Ravenhill was the Rugby World Cup warm-up match against Italy in August 2007 due to the temporary closure of Lansdowne Road for reconstruction. The four provincial branches of the IRFU first ran cup competitions during the 1880s. Although these tournaments still take place every year, their significance has been diminished by the advent of an All-Ireland league of 48 Senior Clubs in 1990. The four provincial teams have played an Interprovincial Championship since the 1920s and continue to be the focal point for players aspiring to the international level. These are Munster, Leinster, Ulster and Connacht. All four provinces play at the senior level as members of the United Rugby Championship. -

 25cm x 35cm. Limerick Patrick John "Kangaroo Kicker" O'Dea (17 March 1872 – 5 April 1962) was an Irish-Australian rules and American footballplayer and coach. An Australian by birth, O'Dea played Australian rules football for the Melbourne Football Club in the Victorian Football Association (VFA). In 1898 and 1899, O'Dea played American football at the University of Wisconsin–Madison in the United States, where he excelled in the kicking game. He then served as the head football coach at the University of Notre Dame from 1900 to 1901 and at the University of Missouri in 1902, compiling a career college footballrecord of 19–7–2. O'Dea was inducted into the College Football Hall of Fame as a player in 1962.
25cm x 35cm. Limerick Patrick John "Kangaroo Kicker" O'Dea (17 March 1872 – 5 April 1962) was an Irish-Australian rules and American footballplayer and coach. An Australian by birth, O'Dea played Australian rules football for the Melbourne Football Club in the Victorian Football Association (VFA). In 1898 and 1899, O'Dea played American football at the University of Wisconsin–Madison in the United States, where he excelled in the kicking game. He then served as the head football coach at the University of Notre Dame from 1900 to 1901 and at the University of Missouri in 1902, compiling a career college footballrecord of 19–7–2. O'Dea was inducted into the College Football Hall of Fame as a player in 1962.Early life
O'Dea was born in Kilmore, Victoria, Australia to an Irish-born father and a Victorian-born mother. He was the third child of seven children. As a child he attended Christian Brothers College and Xavier College. As a 16-year-old he received a bronze medallion from the Royal Humane Society of Australasia for rescuing a woman at Mordialloc beach.Playing career
O'Dea played American football at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, where he was their star fullback from 1896–1899 and captained the 1898 and 1899 teams. In those days fullbacks punted and often did the placekicking. In the 1898 edition of the Northwestern game, which was played in a blizzard, he drop kicked a 62-yard field goal, and had a 116-yard punt. This earned him the nickname "Kangaroo Kicker". Wisconsin then headed into a Thanksgiving Day showdown with 1898 Western champions Michigan with only the narrow loss to Yale marring their record. New songs were composed for the occasion including “Oh, Pat O’Dea” to the popular tune “Margery”. The chorus ran: "Oh Pat O’Dea, oh Pat O’Dea, We love you more and more. Oh Pat O’Dea, oh Pat O’Dea, You’re the boy that we adore; Your leg is ever sure and true, And always kicks a goal or two. The team and rooters worship you. Oh Pat O’Dea." The final verse concluded: "To this brave lad forever we shall proudly sing. He is the boy we love. And in the games we play The cry “O’Dea, ”We’ll yell to every foe, because their game will show There is no other lad to see like Pat O’Dea. The East and West will surely have to see That we can’t lose in Patrick’s shoes, For he’s the only boy in all this land so free. The famous punter, Pat O’Dea." In the 1899 game, he returned a kickoff 90 yards for a touchdown, and had four field goals. He was selected as an All-American team member in 1899.Coaching career
Notre Dame
From 1900 to 1901, O'Dea coached at the University of Notre Dame, and compiled a 14–4–2 record.Missouri
O'Dea was the tenth head football coach for the University of Missouri–Columbia Tigers located in Columbia, Missouri and he held that position for the 1902 season. His career coaching record at Missouri was 5 wins, 3 losses, and 0 ties. This ranks him 22nd at Missouri in total wins and tenth at Missouri in winning percentage.Later life
After coaching, he disappeared from public view in 1917, having decided that he didn't like being treated as a celebrity, and it was assumed by Wisconsin fans that O'Dea had died fighting in World War I. In 1934, he was discovered living under an assumed name in California and came back to Wisconsin to a hero's welcome. He later appeared on Bob Hope's All-American football team announcement shows. He was inducted into the College Football Hall of Fame on 3 April 1962. He died the next day at the University of California, San Francisco Medical Center. Pat O'Dea died on 4 April 1962 at the age of 90 after an illness. While he was in hospital he received a get-well message from President John Kennedy. O'Dea's obituary in the New York Times commented on his kicking achievements including a 110-yard punt, though against Minnesota in 1897 and not Yale in 1899, and his 62-yard goal against Northwestern in 1898. -

 25cm x 35cm Limerick Commemorative stamp issued in 1974 to mark the centenary of the founding of the Irish Rugby Football Union (IRFU). he Irish Rugby Football Union (IRFU) (Irish: Cumann Rugbaí na hÉireann) is the body managing rugby union in the island of Ireland (both Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland). The IRFU has its head office at 10/12 Lansdowne Roadand home ground at Aviva Stadium, where adult men's Irish rugby union international matches are played. In addition, the Union also owns the Ravenhill Stadium in Belfast, Thomond Park in Limerick and a number of grounds in provincial areas that have been rented to clubs. Initially, there were two unions: the Irish Football Union, which had jurisdiction over clubs in Leinster, Munster and parts of Ulster and was founded in December 1874, and the Northern Football Union of Ireland, which controlled the Belfast area and was founded in January 1875.The IRFU was formed in 1879 as an amalgamation of these two organisations and branches of the new IRFU were formed in Leinster, Munster and Ulster. The Connacht Branch was formed in 1900. The IRFU was a founding member of the International Rugby Football Board, now known as World Rugby, in 1886 with Scotland and Wales. (England refused to join until 1890.) Following the political partition of Ireland into separate national states, the Republic of Ireland (originally the Irish Free State then Éire) and Northern Ireland (a political division of the United Kingdom), the then Committee of the Irish Rugby Football Union decided that it would continue to administer its affairs on the basis of the full 32 Irish counties and the traditional four provinces of Ireland: Leinster (12 counties), Ulster (9 counties), Munster (6 counties), and Connacht (5 counties). This led to the unusual, but not unique, situation among international rugby union teams, where the Irish representative teams are drawn from players from two separate political, national territories: Ireland (an independent, sovereign state) and Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom). To maintain the unity of Irish rugby union and the linkages between North and South, the IRFU purchased a new ground in 1923 in the Ravenhill district of Belfast at a cost of £2,300.The last full International at Ravenhill involving Ireland for more than a half-century took place in 1953–54 against Scotland who were victorious by 2 tries (6 points) to nil. Australia played Romania in the 1999 World Cup at the ground. The next full International played at Ravenhill was the Rugby World Cup warm-up match against Italy in August 2007 due to the temporary closure of Lansdowne Road for reconstruction. The four provincial branches of the IRFU first ran cup competitions during the 1880s. Although these tournaments still take place every year, their significance has been diminished by the advent of an All-Ireland league of 48 Senior Clubs in 1990. The four provincial teams have played an Interprovincial Championship since the 1920s and continue to be the focal point for players aspiring to the international level. These are Munster, Leinster, Ulster and Connacht. All four provinces play at the senior level as members of the United Rugby Championship.
25cm x 35cm Limerick Commemorative stamp issued in 1974 to mark the centenary of the founding of the Irish Rugby Football Union (IRFU). he Irish Rugby Football Union (IRFU) (Irish: Cumann Rugbaí na hÉireann) is the body managing rugby union in the island of Ireland (both Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland). The IRFU has its head office at 10/12 Lansdowne Roadand home ground at Aviva Stadium, where adult men's Irish rugby union international matches are played. In addition, the Union also owns the Ravenhill Stadium in Belfast, Thomond Park in Limerick and a number of grounds in provincial areas that have been rented to clubs. Initially, there were two unions: the Irish Football Union, which had jurisdiction over clubs in Leinster, Munster and parts of Ulster and was founded in December 1874, and the Northern Football Union of Ireland, which controlled the Belfast area and was founded in January 1875.The IRFU was formed in 1879 as an amalgamation of these two organisations and branches of the new IRFU were formed in Leinster, Munster and Ulster. The Connacht Branch was formed in 1900. The IRFU was a founding member of the International Rugby Football Board, now known as World Rugby, in 1886 with Scotland and Wales. (England refused to join until 1890.) Following the political partition of Ireland into separate national states, the Republic of Ireland (originally the Irish Free State then Éire) and Northern Ireland (a political division of the United Kingdom), the then Committee of the Irish Rugby Football Union decided that it would continue to administer its affairs on the basis of the full 32 Irish counties and the traditional four provinces of Ireland: Leinster (12 counties), Ulster (9 counties), Munster (6 counties), and Connacht (5 counties). This led to the unusual, but not unique, situation among international rugby union teams, where the Irish representative teams are drawn from players from two separate political, national territories: Ireland (an independent, sovereign state) and Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom). To maintain the unity of Irish rugby union and the linkages between North and South, the IRFU purchased a new ground in 1923 in the Ravenhill district of Belfast at a cost of £2,300.The last full International at Ravenhill involving Ireland for more than a half-century took place in 1953–54 against Scotland who were victorious by 2 tries (6 points) to nil. Australia played Romania in the 1999 World Cup at the ground. The next full International played at Ravenhill was the Rugby World Cup warm-up match against Italy in August 2007 due to the temporary closure of Lansdowne Road for reconstruction. The four provincial branches of the IRFU first ran cup competitions during the 1880s. Although these tournaments still take place every year, their significance has been diminished by the advent of an All-Ireland league of 48 Senior Clubs in 1990. The four provincial teams have played an Interprovincial Championship since the 1920s and continue to be the focal point for players aspiring to the international level. These are Munster, Leinster, Ulster and Connacht. All four provinces play at the senior level as members of the United Rugby Championship. -
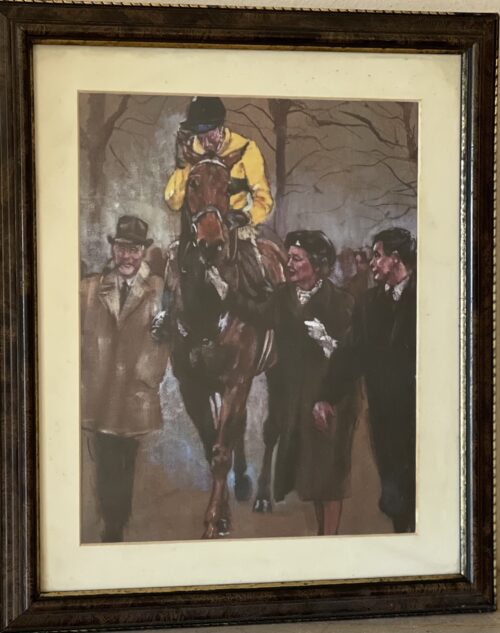
 45cm x 35cm Naas Co Kildare Arkle (19 April 1957 – 31 May 1970) was an Irish Thoroughbred racehorse. A bay gelding by Archive out of Bright Cherry, he was the grandson of the unbeaten (in 14 races) flat racehorse and prepotent sire Nearco. Arkle was born at Ballymacoll Stud, County Meath, by Mrs Mary Alison Baker of Malahow House, near Naul, County Dublin. He was named after the mountain Arkle in Sutherland, Scotland that bordered the Duchess of Westminster’s Sutherland estate. Owned by Anne Grosvenor, Duchess of Westminster, he was trained by Tom Dreaper at Greenogue, Kilsallaghan in County Meath, Ireland, and ridden during his steeplechasing career by Pat Taaffe. At 212, his Timeform rating is the highest ever awarded to a steeplechaser. Only Flyingbolt, also trained by Dreaper, had a rating anywhere near his at 210. Next on their ratings are Sprinter Sacre on 192 and then Kauto Star and Mill House on 191. Despite his career being cut short by injury, Arkle won three Cheltenham Gold Cups, the Blue Riband of steeplechasing, and a host of other top prizes. On 19th April, 2014 a magnificent 1.1 scale bronze statue was unveiled in Ashbourne, County Meath in commemoration of Arkle. In the 1964 Cheltenham Gold Cup, Arkle beat Mill House (who had won the race the previous year) by five lengths to claim his first Gold Cup at odds of 7/4. It was the last time he did not start as the favourite for a race. Only two other horses entered the Gold Cup that year. The racing authorities in Ireland took the unprecedented step in the Irish Grand National of devising two weight systems — one to be used when Arkle was running and one when he was not. Arkle won the 1964 race by only one length, but he carried two and half stones more than his rivals. The following year's Gold Cup saw Arkle beat Mill House by twenty lengths at odds of 3/10. In the 1966 renewal, he was the shortest-priced favourite in history to win the Gold Cup, starting at odds of 1/10. He won the race by thirty lengths despite a mistake early in the race where he ploughed through a fence. However, it did not stop his momentum, nor did he ever look like falling. Arkle had a strange quirk in that he crossed his forelegs when jumping a fence. He went through the season 1965/66 unbeaten in five races. Arkle won 27 of his 35 starts and won at distances from 1m 6f up to 3m 5f. Legendary Racing commentator Peter O'Sullevan has called Arkle a freak of nature — something unlikely to be seen again. Besides winning three consecutive Cheltenham Gold Cups (1964, 1965, 1966) and the 1965 King George VI Chase, Arkle triumphed in a number of other important handicap chases, including the 1964 Irish Grand National (under 12-0), the 1964 and 1965 Hennessy Gold Cups (both times under 12-7), the 1965 Gallagher Gold Cup (conceding 16 lb to Mill House while breaking the course record by 17 seconds), and the 1965 Whitbread Gold Cup(under 12-7). In the 1966 Hennessy, he failed by only half a length to give Stalbridge Colonist 35 lb. The scale of the task Arkle faced is shown by the winner coming second and third in the two following Cheltenham Gold Cups, while in third place was the future 1969 Gold Cup winner, What A Myth. In December 1966, Arkle raced in the King George VI Chase at Kempton Park but struck the guard rail with a hoof when jumping the open ditch, which resulted in a fractured pedal bone; despite this injury, he completed the race and finished second. He was in plaster for four months and, though he made a good enough recovery to go back into training, he never ran again. He was retired and ridden as a hack by his owner and then succumbed to what has been variously described as advanced arthritis or possibly brucellosis and was put down at the early age of 13. Arkle became a national legend in Ireland. His strength was jokingly claimed to come from drinking 2 pints of Guinness a day. At one point, the slogan Arkle for President was written on a wall in Dublin. The horse was often referred to simply as "Himself", and he supposedly received items of fan mail addressed to 'Himself, Ireland'. The Irish government-owned Irish National Stud, at Tully, Kildare, Co. Kildare, Ireland, has the skeleton of Arkle on display in its museum. A statue in his memory was erected in Ashbourne Co. Meath in April 2014.
45cm x 35cm Naas Co Kildare Arkle (19 April 1957 – 31 May 1970) was an Irish Thoroughbred racehorse. A bay gelding by Archive out of Bright Cherry, he was the grandson of the unbeaten (in 14 races) flat racehorse and prepotent sire Nearco. Arkle was born at Ballymacoll Stud, County Meath, by Mrs Mary Alison Baker of Malahow House, near Naul, County Dublin. He was named after the mountain Arkle in Sutherland, Scotland that bordered the Duchess of Westminster’s Sutherland estate. Owned by Anne Grosvenor, Duchess of Westminster, he was trained by Tom Dreaper at Greenogue, Kilsallaghan in County Meath, Ireland, and ridden during his steeplechasing career by Pat Taaffe. At 212, his Timeform rating is the highest ever awarded to a steeplechaser. Only Flyingbolt, also trained by Dreaper, had a rating anywhere near his at 210. Next on their ratings are Sprinter Sacre on 192 and then Kauto Star and Mill House on 191. Despite his career being cut short by injury, Arkle won three Cheltenham Gold Cups, the Blue Riband of steeplechasing, and a host of other top prizes. On 19th April, 2014 a magnificent 1.1 scale bronze statue was unveiled in Ashbourne, County Meath in commemoration of Arkle. In the 1964 Cheltenham Gold Cup, Arkle beat Mill House (who had won the race the previous year) by five lengths to claim his first Gold Cup at odds of 7/4. It was the last time he did not start as the favourite for a race. Only two other horses entered the Gold Cup that year. The racing authorities in Ireland took the unprecedented step in the Irish Grand National of devising two weight systems — one to be used when Arkle was running and one when he was not. Arkle won the 1964 race by only one length, but he carried two and half stones more than his rivals. The following year's Gold Cup saw Arkle beat Mill House by twenty lengths at odds of 3/10. In the 1966 renewal, he was the shortest-priced favourite in history to win the Gold Cup, starting at odds of 1/10. He won the race by thirty lengths despite a mistake early in the race where he ploughed through a fence. However, it did not stop his momentum, nor did he ever look like falling. Arkle had a strange quirk in that he crossed his forelegs when jumping a fence. He went through the season 1965/66 unbeaten in five races. Arkle won 27 of his 35 starts and won at distances from 1m 6f up to 3m 5f. Legendary Racing commentator Peter O'Sullevan has called Arkle a freak of nature — something unlikely to be seen again. Besides winning three consecutive Cheltenham Gold Cups (1964, 1965, 1966) and the 1965 King George VI Chase, Arkle triumphed in a number of other important handicap chases, including the 1964 Irish Grand National (under 12-0), the 1964 and 1965 Hennessy Gold Cups (both times under 12-7), the 1965 Gallagher Gold Cup (conceding 16 lb to Mill House while breaking the course record by 17 seconds), and the 1965 Whitbread Gold Cup(under 12-7). In the 1966 Hennessy, he failed by only half a length to give Stalbridge Colonist 35 lb. The scale of the task Arkle faced is shown by the winner coming second and third in the two following Cheltenham Gold Cups, while in third place was the future 1969 Gold Cup winner, What A Myth. In December 1966, Arkle raced in the King George VI Chase at Kempton Park but struck the guard rail with a hoof when jumping the open ditch, which resulted in a fractured pedal bone; despite this injury, he completed the race and finished second. He was in plaster for four months and, though he made a good enough recovery to go back into training, he never ran again. He was retired and ridden as a hack by his owner and then succumbed to what has been variously described as advanced arthritis or possibly brucellosis and was put down at the early age of 13. Arkle became a national legend in Ireland. His strength was jokingly claimed to come from drinking 2 pints of Guinness a day. At one point, the slogan Arkle for President was written on a wall in Dublin. The horse was often referred to simply as "Himself", and he supposedly received items of fan mail addressed to 'Himself, Ireland'. The Irish government-owned Irish National Stud, at Tully, Kildare, Co. Kildare, Ireland, has the skeleton of Arkle on display in its museum. A statue in his memory was erected in Ashbourne Co. Meath in April 2014. -
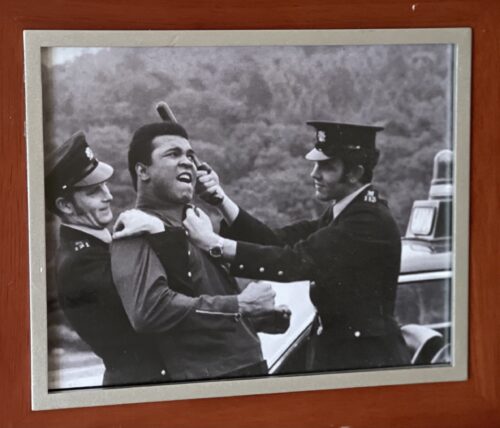
 29cm x 36cm. Dublin Famous picture during The Greatest's visit to Ireland of Muhammad Ali play fighting with two members of An Garda Siochana.Some memory for those officers to tell their grandchildren about ! July 19, 1972, Muhammad Ali fought Al 'Blue' Lewis at Croke Park in Dublin, causing quite a stir in Ireland.Decades later, an Irish documentary recounting the epic fight not only won awards but also won the approval of Ali's daughter Jamilah Ali. "When Ali Came to Ireland" is an Irish documentary that details Muhammad Ali's trip to Dublin for a fight against Al 'Blue' Lewis at Croke Park. In 2013 the film was screened at the Chicago film festival, where Jamilah Ali was in attendance. TheJournal.ie reported that following the screening, Jamilah said "I've seen so much footage of my father over the years but the amazing thing about watching this film was that I had seen none of the footage of him in Ireland... I loved the film from the beginning to the end." The film highlights a moment in Ali's career where he was set to stage a world comeback. He had been recently released from prison after refusing to join the Vietnam War as a conscientious objector. His opponent Al Lewis had also just been released on parole after serving time in Detroit for a murder charge, and he intended to use his boxing career as "a path to a new life." The movie that won an IFTA in 2013 documents the spectacle in Croke Park, Ali's presence in Ireland and how the public reacted to his being there. It also demonstrates how Ali came to be in Dublin for a fight in the first place, highlighting the involvement of "former Kerry strongman"Michael "Butty" Sugrue. Sugrue's story also proved to be revelatory to his family- in a quote from Ross Whittaker, co-director of the film, he speaks about how Sugrue's grandchildren had never had the chance to meet him. "We were amazed when we screened the film in London to find that Butty Sugrue's granddaughters had never heard their grandfather speak. He had died before they were born and they'd never seen footage of him in which he had spoken." After their 1972 meeting, however, Sugrue and Ali's fortunes took two divergent paths. Ali returned to the ring in America to further glories and fanfare before his retirement, while Sugrue lost a small fortune on the Dublin fight and after dying in London was laid to rest in an unmarked grave in his hometown of Killorglin, Co Kerry. The Louisville Lip was also incredibly proud of his County Clare roots. Today we recall the man's star quality and his Irish ancestry. The death of boxing legend Muhammad Ali at 74 in June 2016, from Parkinson’s, would have brought back many glorious memories of the greatest athlete of our times. At the height of his career, Ali was the most graceful, talented, and brilliant heavyweight boxer who ever stepped inside the ropes. I remember seeing him enter the room at the American Ireland Fund dinner in 2011 and grown men, including the Irish leader Enda Kenny, were simply awestruck that they were in the presence of the greatest living legend. Ali was more than a boxer, of course, he was a fighter who refused to become cannon fodder in the Vietnam War, the greatest mistaken war America entered until the invasion of Iraq. He was also a poet, a showman, a lover of many women, a devout Muslim, and simply a legend. Ali's stance to end the Vietnam War when he refused to be drafted cost us the best years of his sporting life. He came back still a brilliant boxer, but the man who could float like a butterfly could never quite recover that greatness. Still, the fights with Joe Frazier, the rope-a-dope that saw him defeat George Foreman in Zaire in the "Rumble in the Jungle" will forever enshrine his name in history.
29cm x 36cm. Dublin Famous picture during The Greatest's visit to Ireland of Muhammad Ali play fighting with two members of An Garda Siochana.Some memory for those officers to tell their grandchildren about ! July 19, 1972, Muhammad Ali fought Al 'Blue' Lewis at Croke Park in Dublin, causing quite a stir in Ireland.Decades later, an Irish documentary recounting the epic fight not only won awards but also won the approval of Ali's daughter Jamilah Ali. "When Ali Came to Ireland" is an Irish documentary that details Muhammad Ali's trip to Dublin for a fight against Al 'Blue' Lewis at Croke Park. In 2013 the film was screened at the Chicago film festival, where Jamilah Ali was in attendance. TheJournal.ie reported that following the screening, Jamilah said "I've seen so much footage of my father over the years but the amazing thing about watching this film was that I had seen none of the footage of him in Ireland... I loved the film from the beginning to the end." The film highlights a moment in Ali's career where he was set to stage a world comeback. He had been recently released from prison after refusing to join the Vietnam War as a conscientious objector. His opponent Al Lewis had also just been released on parole after serving time in Detroit for a murder charge, and he intended to use his boxing career as "a path to a new life." The movie that won an IFTA in 2013 documents the spectacle in Croke Park, Ali's presence in Ireland and how the public reacted to his being there. It also demonstrates how Ali came to be in Dublin for a fight in the first place, highlighting the involvement of "former Kerry strongman"Michael "Butty" Sugrue. Sugrue's story also proved to be revelatory to his family- in a quote from Ross Whittaker, co-director of the film, he speaks about how Sugrue's grandchildren had never had the chance to meet him. "We were amazed when we screened the film in London to find that Butty Sugrue's granddaughters had never heard their grandfather speak. He had died before they were born and they'd never seen footage of him in which he had spoken." After their 1972 meeting, however, Sugrue and Ali's fortunes took two divergent paths. Ali returned to the ring in America to further glories and fanfare before his retirement, while Sugrue lost a small fortune on the Dublin fight and after dying in London was laid to rest in an unmarked grave in his hometown of Killorglin, Co Kerry. The Louisville Lip was also incredibly proud of his County Clare roots. Today we recall the man's star quality and his Irish ancestry. The death of boxing legend Muhammad Ali at 74 in June 2016, from Parkinson’s, would have brought back many glorious memories of the greatest athlete of our times. At the height of his career, Ali was the most graceful, talented, and brilliant heavyweight boxer who ever stepped inside the ropes. I remember seeing him enter the room at the American Ireland Fund dinner in 2011 and grown men, including the Irish leader Enda Kenny, were simply awestruck that they were in the presence of the greatest living legend. Ali was more than a boxer, of course, he was a fighter who refused to become cannon fodder in the Vietnam War, the greatest mistaken war America entered until the invasion of Iraq. He was also a poet, a showman, a lover of many women, a devout Muslim, and simply a legend. Ali's stance to end the Vietnam War when he refused to be drafted cost us the best years of his sporting life. He came back still a brilliant boxer, but the man who could float like a butterfly could never quite recover that greatness. Still, the fights with Joe Frazier, the rope-a-dope that saw him defeat George Foreman in Zaire in the "Rumble in the Jungle" will forever enshrine his name in history.Muhammad Ali's Irish roots explained
The astonishing fact that he had Irish roots, being descended from Abe Grady, an Irishman from Ennis, County Clare, only became known later in life. He returned to Ireland where he had fought and defeated Al “Blue” Lewis in Croke Park in 1972 almost seven years ago in 2009 to help raise money for his non–profit Muhammad Ali Center, a cultural and educational center in Louisville, Kentucky, and other hospices. He was also there to become the first Freeman of the town. The boxing great is no stranger to Irish shores and previously made a famous trip to Ireland in 1972 when he sat down with Cathal O’Shannon of RTE for a fascinating television interview. What’s more, genealogist Antoinette O'Brien discovered that one of Ali’s great-grandfathers emigrated to the United States from County Clare, meaning that the three-time heavyweight world champion joins the likes of President Obama and Professor Henry Louis Gates Jr. as prominent African-Americans with Irish heritage. In the 1860s, Abe Grady left Ennis in County Clare to start a new life in America. He would make his home in Kentucky and marry a free African-American woman. The couple started a family, and one of their daughters was Odessa Lee Grady. Odessa met and married Cassius Clay, Sr. and on January 17, 1942, Cassius junior was born. Cassius Clay changed his name to Muhammad Ali when he became a Muslim in 1964. Ali, an Olympic gold medalist at the 1960 games in Rome, has been suffering from Parkinson's for some years but was committed to raising funds for his center During his visit to Clare, he was mobbed by tens of thousands of locals who turned out to meet him and show him the area where his great-grandfather came from.Tracing Muhammad Ali's roots back to County Clare
Historian Dick Eastman had traced Ali’s roots back to Abe Grady the Clare emigrant to Kentucky and the freed slave he married. Eastman wrote: “An 1855 land survey of Ennis, a town in County Clare, Ireland, contains a reference to John Grady, who was renting a house in Turnpike Road in the center of the town. His rent payment was fifteen shillings a month. A few years later, his son Abe Grady immigrated to the United States. He settled in Kentucky." Also, around the year 1855, a man and a woman who were both freed slaves, originally from Liberia, purchased land in or around Duck Lick Creek, Logan, Kentucky. The two married, raised a family and farmed the land. These free blacks went by the name, Morehead, the name of white slave owners of the area. Odessa Grady Clay, Cassius Clay's mother, was the great-granddaughter of the freed slave Tom Morehead and of John Grady of Ennis, whose son Abe had emigrated from Ireland to the United States. She named her son Cassius in honor of a famous Kentucky abolitionist of that time. When he changed his name to Muhammad Ali in 1964, the famous boxer remarked, "Why should I keep my white slavemaster name visible and my black ancestors invisible, unknown, unhonored?" Ali was not only the greatest sporting figure, but he was also the best-known person in the world at his height, revered from Africa to Asia and all over the world. To the end, he was a battler, shown rare courage fighting Parkinson’s Disease, and surviving far longer than most sufferers from the disease. -

 Framed photo of the gallant 2007 Limerick Hurlers who reached the All Ireland final where they were beaten by an all time great Kilkenny Team. 53cm x 68cm Limerick In 2007, Limerick shook up the hurling landscape by reaching their first All Ireland final since 1996 in an attempt to win their first Liam McCarthy Cup since all the way back in 1973. However, the wait would go on… until it was ended gloriously in 2018.The final in Croke Park turned out to be an anti-climax for Treaty supporters as they fell to the all conquering Kilkenny on a scoreline of 2-19 to 1-15.
Framed photo of the gallant 2007 Limerick Hurlers who reached the All Ireland final where they were beaten by an all time great Kilkenny Team. 53cm x 68cm Limerick In 2007, Limerick shook up the hurling landscape by reaching their first All Ireland final since 1996 in an attempt to win their first Liam McCarthy Cup since all the way back in 1973. However, the wait would go on… until it was ended gloriously in 2018.The final in Croke Park turned out to be an anti-climax for Treaty supporters as they fell to the all conquering Kilkenny on a scoreline of 2-19 to 1-15. However, the Limerick players of 2007 will go down as heroes on Shannonside, regardless of a sub-standard performance on the first Sunday of September.
After an epic Munster championship, which saw Richie Bennis’s side go to two replays with Tipperary, eventually coming out on top after extra-time in the third game before succumbing to a Dan Shanahan inspired Waterford in the final, Limerick went on to gather a momentum that would see them all the way to a clash with Brian Cody’s charges with the All Ireland title on the line.
However, the Limerick players of 2007 will go down as heroes on Shannonside, regardless of a sub-standard performance on the first Sunday of September.
After an epic Munster championship, which saw Richie Bennis’s side go to two replays with Tipperary, eventually coming out on top after extra-time in the third game before succumbing to a Dan Shanahan inspired Waterford in the final, Limerick went on to gather a momentum that would see them all the way to a clash with Brian Cody’s charges with the All Ireland title on the line.
 Henry Shefflin was the Cats captain that year and notched 1-2 for himself on the big day, while Eddie Brennan top-scored with a tally of 1-5.
Henry Shefflin was the Cats captain that year and notched 1-2 for himself on the big day, while Eddie Brennan top-scored with a tally of 1-5.
-

 Boher Co Limerick 35cm x 48cm The 1994 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship Final was the 107th All-Ireland Final and the culmination of the 1994 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship. The match was held at Croke Park, Dublin, on 4 September 1994, between Offaly and Limerick. The Munster champions lost to their Leinster opponents on a score line of 3-16 to 2-13. The match is known as 'the five-minute final' due to the sensational comeback by Offaly who scored 2-5 to win the game in the last five minutes. With five minutes of normal time remaining, Limerick were leading by 2-13 to 1-11 and looked to be heading to their first title in 21 years when Offaly were awarded a free 20 metres from the goal. Limerick goalkeeper Joe Quaid later admitted that he was to blame for the resultant goal in that he didn't organise his defence well enough to stop a low-struck free from Johnny Dooley.[3] Quaid was erroneously blamed for Offaly's second goal after what was described as a quick and errant puck-out leading to Pat O'Connor putting Offaly a point ahead with a low shot to the net. Quaid later described the puck-out: "I didn’t rush back to the goals. I went back and picked up the ball, walked behind the goals like I normally would. Hegarty was out in the middle of the field on his own. I dropped the ball into his hand 70 yards out from goal. He caught the ball and in contact the ball squirted out of his hands." Because the television coverage was still showing a replay of the first goal, very few people got to see the build up to the second and when live transmission was resumed, the sliotar was still dropping towards Pat O'Connor leading people to assume that Quaid rushed his puck-out.Limerick went on to lose the game by 3-16 to 2-13.
Boher Co Limerick 35cm x 48cm The 1994 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship Final was the 107th All-Ireland Final and the culmination of the 1994 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship. The match was held at Croke Park, Dublin, on 4 September 1994, between Offaly and Limerick. The Munster champions lost to their Leinster opponents on a score line of 3-16 to 2-13. The match is known as 'the five-minute final' due to the sensational comeback by Offaly who scored 2-5 to win the game in the last five minutes. With five minutes of normal time remaining, Limerick were leading by 2-13 to 1-11 and looked to be heading to their first title in 21 years when Offaly were awarded a free 20 metres from the goal. Limerick goalkeeper Joe Quaid later admitted that he was to blame for the resultant goal in that he didn't organise his defence well enough to stop a low-struck free from Johnny Dooley.[3] Quaid was erroneously blamed for Offaly's second goal after what was described as a quick and errant puck-out leading to Pat O'Connor putting Offaly a point ahead with a low shot to the net. Quaid later described the puck-out: "I didn’t rush back to the goals. I went back and picked up the ball, walked behind the goals like I normally would. Hegarty was out in the middle of the field on his own. I dropped the ball into his hand 70 yards out from goal. He caught the ball and in contact the ball squirted out of his hands." Because the television coverage was still showing a replay of the first goal, very few people got to see the build up to the second and when live transmission was resumed, the sliotar was still dropping towards Pat O'Connor leading people to assume that Quaid rushed his puck-out.Limerick went on to lose the game by 3-16 to 2-13. -

 Framed Fight poster of Collins v Eubank at Millstreet 1995. 90cm x 68cm Co Cork Stephen Collins (born 21 July 1964) is an Irish former professional boxer who competed from 1986 to 1997. Known as the Celtic Warrior, Collins is the most successful Irish boxer in recent professional boxing history, having held the WBOmiddleweight and super-middleweight titles simultaneously and never losing a fight as champion. Collins' first nineteen professional fights all took place in the United States. In 1988 he won the Irish middleweight title, and the regional American USBA middleweight title the following year, defending the latter successfully in Atlantic City and Las Vegas. In his first two world championship challenges, both for the WBA middleweight title, Collins lost a unanimous decision to Mike McCallum in 1990 and a majority decision to Reggie Johnson in 1992. He also challenged unsuccessfully for the European middleweight title later in 1992, losing a split decision to Sumbu Kalambay in Italy. It was not until Collins reached his early 30s that he fulfilled his potential, becoming WBO middleweight champion in his third world title attempt with a fifth-round TKO victory over Chris Pyatt in 1994, before then moving up in weight to defeat the undefeated Chris Eubank and claim the WBO super-middleweight title in 1995. More success followed, as Collins successfully defended his title by winning the rematch against Eubank later in the year. Collins successfully defended his title another six times before pulling out of a proposed fight in October 1997 against rising Welsh star, Joe Calzaghe, and retiring from the sport, with Collins frustrated by his inability to get a fight against the pound for pound number one boxer of the time, Roy Jones Jr., who was then fighting in the light-heavyweight division. Having competed against some of the best boxers on both sides of the Atlantic during his career, Collins tends to be linked more to an era in the UK during which there was a notable rivalry between British boxers Chris Eubank and Nigel Benn, both of whom Collins fought and defeated twice.
Framed Fight poster of Collins v Eubank at Millstreet 1995. 90cm x 68cm Co Cork Stephen Collins (born 21 July 1964) is an Irish former professional boxer who competed from 1986 to 1997. Known as the Celtic Warrior, Collins is the most successful Irish boxer in recent professional boxing history, having held the WBOmiddleweight and super-middleweight titles simultaneously and never losing a fight as champion. Collins' first nineteen professional fights all took place in the United States. In 1988 he won the Irish middleweight title, and the regional American USBA middleweight title the following year, defending the latter successfully in Atlantic City and Las Vegas. In his first two world championship challenges, both for the WBA middleweight title, Collins lost a unanimous decision to Mike McCallum in 1990 and a majority decision to Reggie Johnson in 1992. He also challenged unsuccessfully for the European middleweight title later in 1992, losing a split decision to Sumbu Kalambay in Italy. It was not until Collins reached his early 30s that he fulfilled his potential, becoming WBO middleweight champion in his third world title attempt with a fifth-round TKO victory over Chris Pyatt in 1994, before then moving up in weight to defeat the undefeated Chris Eubank and claim the WBO super-middleweight title in 1995. More success followed, as Collins successfully defended his title by winning the rematch against Eubank later in the year. Collins successfully defended his title another six times before pulling out of a proposed fight in October 1997 against rising Welsh star, Joe Calzaghe, and retiring from the sport, with Collins frustrated by his inability to get a fight against the pound for pound number one boxer of the time, Roy Jones Jr., who was then fighting in the light-heavyweight division. Having competed against some of the best boxers on both sides of the Atlantic during his career, Collins tends to be linked more to an era in the UK during which there was a notable rivalry between British boxers Chris Eubank and Nigel Benn, both of whom Collins fought and defeated twice.Early years in Boston
Steve Collins won 26 Irish titles as an amateur before turning professional in Massachusetts, US in October 1986. Collins worked out of the Petronelli Brothers gym in Brockton, Massachusetts alongside Marvin Hagler. His debut fight was against Julio Mercado on the undercard of a bill that featured Irish Americans; his future trainer Freddie Roach and the future Fight of the Year winner Micky Ward. Collins beat Mercado by way of knockout in the third round. In Boston, Massachusetts in 1988, he defeated former Olympian and British Super Middleweight champion Sam Storey to win the Irish middleweight title, then defeated world No. 5, Kevin Watts to win the USBA middleweight title. After reaching 16–0, Collins stepped in as a substitute in a WBA middleweight title fight after Michael Watson was injured in training, and fought 12 rounds against Mike McCallum in Boston in 1990. Collins was supported by a large crowd of Irish Americans as he battled the champion McCallum, with the fight being close early on before McCallum started to tire as Collins gained momentum in the later stages to bring a close finish at the end of 12 exciting rounds. McCallum got the win by unanimous decision. In 1992, Collins lost a majority decision to Reggie Johnson in a closely contested slugfest for the vacant WBA middleweight title (which had been stripped from McCallum because he signed to fight IBF champion James Toney). Collins then lost by split decision to Sumbu Kalambay for the European title in Italy, before beating Gerhard Botes of South Africa to win the WBA Penta-Continental middleweight title in 1993.WBO middleweight champion
Collins then moved to Belfast under the management of Barney Eastwood before basing himself in England where he joined Barry Hearn's Matchroom Boxing. Alongside him was Paul "Silky" Jones, his sparring partner and good friend who later went on to become WBO light-middleweight title holder. Collins was trained by Freddie King in the Romford training camp. In May 1994, Collins finally won a world title by defeating Chris Pyatt by stoppage in five rounds to become the WBO middleweight champion. Early in 1995, Collins relinquished this title without a defence as he was having difficulty making the 160lbs middleweight limit. In March 1995, Chris Eubank (41-0-2) had been scheduled to have a third WBO super-middleweight title fight against Ray Close. Eubank and Close had two fights over the previous two years (their first fight a draw, and their second fight a narrow split decision win for Eubank), but Close was forced to withdraw from their scheduled third fight after failing an MRI brain scan. Collins then stepped into Close's place, moving up to super-middleweight to take on Eubank.WBO super-middleweight champion
Collins defeated the then unbeaten long-reigning champion Chris Eubank in Millstreet, County Cork, Ireland, in March 1995, by unanimous decision (115–111, 116–114, 114–113), to win the WBO super-middleweight title. Collins had enlisted the help of a guru, and they led the press to believe that Collins would be hypnotised for the fight, which noticeably unsettled Eubank. True to form, Collins sat in his corner and did not move, listening to headphones during Eubank's ring entrance. Collins knocked Eubank down in the eighth round, and was well ahead on the scorecards at the end of Round 9, but Eubank finished the fight strongly as he tried to save his unbeaten record and knocked Collins down in the tenth round, coming close to a stoppage. Eubank was unable to finish the job, and Collins held on for victory. In their September 1995 rematch in Cork, Collins performed brilliantly, changing his usual fighting style by adopting wild, brawling tactics throughout which Eubank really struggled to deal with. Despite most TV pundits and commentators giving Collins a wide points victory with scorecards in the region of 117–111 and 118–110, the three judges saw the fight very differently with Collins only winning by a close split decision, 115–113, 115–113 and 114–115. Collins successfully defended his WBO super-middleweight title seven times, including two fights against Nigel Benn in 1996. In the summer of 1997, Collins reportedly stated in the press that he had no motivation left, as he had spent the best part of his career chasing Roy Jones Jr. for a fight that had been promised to him many times. Collins is reported to have stated in Boxing World that he had spent so long chasing Roy Jones Jr. that money was no longer important; that he would "fight him in a phone box in front of two men and a dog". but the bout never materialised. A WBO super-middleweight title fight against Joe Calzaghe was agreed for October 1997, but Collins got injured 10 days before the scheduled fight, got stripped of his title by the WBO, with Collins then making a statement saying that fighting Calzaghe would do nothing to satisfy the desire he had for fighting Jones. Collins then added he wanted to retire on a high note with a good pay day, "Joe is a good up-and-coming kid, but he wouldn't fill a parish church". As Collins couldn't get the fight with Jones, Collins decided to retire. In 1999, Collins announced his decision to come out of retirement to fight Roy Jones Jr. Controversy surrounded the proposed fight, as WBC and WBA light heavyweight champion Jones decided to fight the IBF light heavyweight champion and old Collins foe Reggie Johnson (which Jones won by a shutout 120–106 on all three judges' scorecards), and it was revealed that Collins would have to fight Calzaghe before a showdown with Jones. Collins had accepted this and started to prepare to fight Calzaghe. In training, Collins collapsed during a sparring session with Howard Eastman. Although tests and a brain scan could not find any problems, Collins decided that it was a warning to make him stop boxing, and he retired for a second time. Collins retired in 1997, with a record of 39 fights, 36 wins (21 knockouts) and 3 losses. Collins has not entirely faded from the spotlight since his retirement. In 1998 he appeared in the film Lock, Stock and Two Smoking Barrels as a boxing gym bouncer. In 1999 he made a cameo appearance in "Sweetest Thing", a music video by U2. On 15 January 2013, at the age of 48, Collins announced plans to fight Roy Jones Jr.He went on to appear in a number of exhibition bouts in preparation for the proposed Jones fight. In 2017 Collins joined the Army Reserve's 253 Provost Company of the 4th Regiment Royal Military Police in London where he had been living for the previous 20 years. He gained promotion to Lance Corporal and qualified as an army boxing coach. His brother Roddy Collins is a former professional footballer and manager. His brother Paschal was a professional boxer and now a leading professional boxing coach plus manager. His eldest son Stevie Jnr is a retired rugby player and a retired professional boxer who now coaches and manages boxers His youngest son Luke is an active amateur boxer and qualified amateur boxing coach





