-

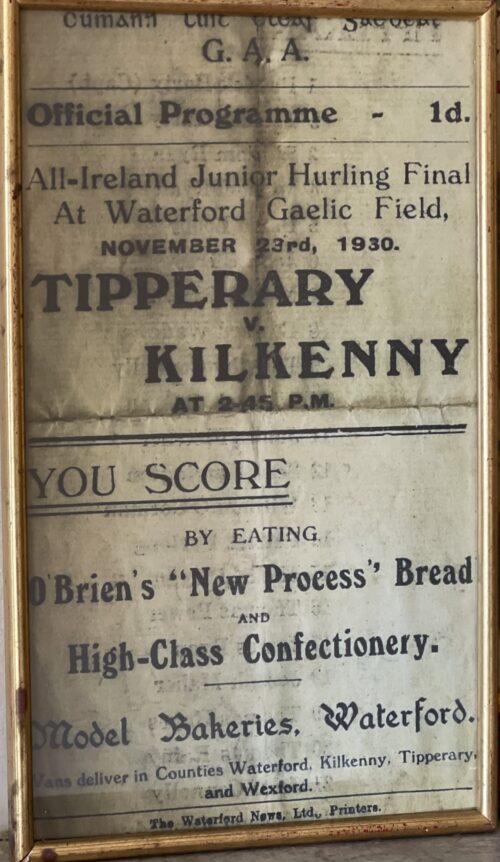 40cm x 23cm Thurles Co Tipperary The All-Ireland Junior Hurling Championship was a hurling competition organized by the Gaelic Athletic Association in Ireland. The competition was originally contested by the second teams of the strong counties, and the first teams of the weaker counties. In the years from 1961 to 1973 and from 1997 until now, the strong counties have competed for the All-Ireland Intermediate Hurling Championship instead. The competition was then restricted to the weaker counties. The competition was discontinued after 2004 as these counties now compete for the Nicky Rackard Cup instead. From 1974 to 1982, the original format of the competition was abandoned, and the competition was incorporated in Division 3 of the National Hurling League. The original format, including the strong hurling counties was re-introduced in 1983. 1930 – TIPPERARY: Paddy Harty (Captain), Tom Harty, Willie Ryan, Tim Connolly, Mick McGann, Martin Browne, Ned Wade, Tom Ryan, Jack Dwyer, Mick Ryan, Dan Looby, Pat Furlong, Bill O’Gorman, Joe Fletcher, Sean Harrington.
40cm x 23cm Thurles Co Tipperary The All-Ireland Junior Hurling Championship was a hurling competition organized by the Gaelic Athletic Association in Ireland. The competition was originally contested by the second teams of the strong counties, and the first teams of the weaker counties. In the years from 1961 to 1973 and from 1997 until now, the strong counties have competed for the All-Ireland Intermediate Hurling Championship instead. The competition was then restricted to the weaker counties. The competition was discontinued after 2004 as these counties now compete for the Nicky Rackard Cup instead. From 1974 to 1982, the original format of the competition was abandoned, and the competition was incorporated in Division 3 of the National Hurling League. The original format, including the strong hurling counties was re-introduced in 1983. 1930 – TIPPERARY: Paddy Harty (Captain), Tom Harty, Willie Ryan, Tim Connolly, Mick McGann, Martin Browne, Ned Wade, Tom Ryan, Jack Dwyer, Mick Ryan, Dan Looby, Pat Furlong, Bill O’Gorman, Joe Fletcher, Sean Harrington. -

 Daniel Breen (11 August 1894 – 27 December 1969) was a volunteer in the Irish Republican Armyduring the Irish War of Independence and the Irish Civil War. In later years he was a Fianna Fáil politician.
Daniel Breen (11 August 1894 – 27 December 1969) was a volunteer in the Irish Republican Armyduring the Irish War of Independence and the Irish Civil War. In later years he was a Fianna Fáil politician.Background
Dan Breen was born in Grange, Donohill parish, County Tipperary. His father died when Breen was six, leaving the family very poor. He was educated locally, before becoming a plasterer and later a linesman on the Great Southern Railways.Irish Revolutionary Period
War of Independence
Breen was sworn into the Irish Republican Brotherhood in 1912 and the Irish Volunteers in 1914. On 21 January 1919, the day the First Dáil met in Dublin, Breen—who described himself as "a soldier first and foremost"—took part in the Soloheadbeg Ambush.The ambush party of eight men, nominally led by Séumas Robinson, attacked two Royal Irish Constabulary men who were escorting explosives to a quarry. The two policemen, James McDonnell and Patrick O’Connell, were fatally shot during the incident. The ambush is considered to be the first incident of the Irish War of Independence. Breen later recalled:"...we took the action deliberately, having thought over the matter and talked it over between us. [Seán] Treacyhad stated to me that the only way of starting a war was to kill someone, and we wanted to start a war, so we intended to kill some of the police whom we looked upon as the foremost and most important branch of the enemy forces ... The only regret that we had following the ambush was that there were only two policemen in it, instead of the six we had expected..."
During the conflict, the British put a £1,000 price on Breen's head, which was later raised to £10,000.He quickly established himself as a leader within the Irish Republican Army (IRA). He was known for his courage. On 13 May 1919, he helped rescue his comrade Seán Hogan at gunpoint from a heavily guarded train at Knocklong station in County Limerick. Breen, who was wounded, remembered how the battalion was "vehemently denounced as a cold-blooded assassins" and roundly condemned by the Catholic Church. After the fight, Seán Treacy, Séumas Robinson and Breen met Michael Collins in Dublin, where they were told to escape from the area. They agreed they would "fight it out, of course". Breen and Treacy shot their way out through a British military cordon in the northern suburb of Drumcondra (Fernside). They escaped, only for Treacy to be killed the next day. Breen was shot at least four times, twice in the lung. The British reaction was to make Tipperary a 'Special Military Area', with curfews and travel permits. Volunteer GHQ authorised enterprising attacks on barracks. Richard Mulcahy noted that British policy had "pushed rather turbulent spirits such as Breen and Treacy into the Dublin area". The inculcation of the principles of guerrilla warfare was to become an essential part of all training. They joined Collins' Squad of assassins, later known as the Dublin Guard, when Tipperary became "too hot for them". and Dublin was the centre of the war. Breen was present in December 1919 at the ambush in Ashtown beside Phoenix Park in Dublin where Martin Savage was killed while trying to assassinate the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland, Viscount French. The IRA men hid behind hedges and a dungheap as the convoy of vehicles came past. They had been instructed to ignore the first car, but this contained their target, Lord French. Their roadblock failed as a policeman removed the horse and cart intended to stop the car. Breen rejected the Anglo-Irish Treaty, which made him, like many others, angry and embittered:I would never have handled a gun or fired a shot… to obtain this Treaty… writing on the second anniversary of Martin Savage's death, do you suppose that he sacrificed his life in attempting to kill one British Governor-General to make room for another British Governor-General?
Regarding the continued existence of Northern Ireland from 1922, and an inevitable further war to conquer it to create a united Ireland, Breen commented:- "To me, a united Ireland of two million people would be preferable to an Ireland of four and a half million divided into three or four factions".
Irish Civil War
Breen was elected to Dáil Éireann at the 1923 general election as a Republican anti-Treaty Teachta Dála (TD) for the Tipperary constituency.Following the Anglo-Irish Treaty, Breen joined the Anti-Treaty IRA in the Civil War, fighting against those of his former comrades in arms who supported the Treaty. He was arrested by the National Army of the Irish Free State and interned at Limerick Prison. He spent two months there before going on hunger strike for six days, followed by a thirst strike of six days. Breen was released after he signed a document pleading to desist from attacking the Free State. Breen wrote a best-selling account of his guerrilla days, My Fight for Irish Freedom, in 1924, later republished by Rena Dardis and Anvil Press.Politics
Fianna Fáil TD
Breen represented Tipperary from the Fourth Dáil in 1923 as a Republican with Éamon de Valera and Frank Aiken.He was the first anti-Treaty TD to take his seat, in 1927. Standing as an Independent Republican he was defeated in the June 1927 general election. Thereafter Breen travelled to the United States, where he opened a speakeasy. He returned to Ireland in 1932 following the death of his mother,and regained his seat as a member of Fianna Fáil in the Dáil at that year's general election. He represented his Tipperary constituency without a break until his retirement at the 1965 election.Political views
Breen supported the Republican side during the Spanish Civil War. During World War II, he was said to hold largely pro-Axis views, with admiration for Erwin Rommel.When the fascist political party Ailtirí na hAiséirghe failed to win any seats in the 1944 Irish general election, he remarked that he was sorry that the party had not done better, as he had studied their programme and found a lot to commend. In 1946, Breen became secretary of the Save the German Children Society. He attended the funeral of Nazi spy Hermann Gortz on 27 May 1947.Irish-American John S. Monagan visited Breen in 1948, and was surprised to see two pictures of Adolf Hitler, a medallion of Napoleon and a Telefunken radio. Breen told him "the revolution didn't work out," and "to get the government they have now, I wouldn't have lost a night's sleep." He also said that he fought for freedom, but not for democracy.In 1943, Breen sent his "congratulations to the Führer. May he live long to lead Europe on the road to peace, security and happiness". After the end of World War II in Europe, the German Legation in Dublin was taken over by diplomats from the USA in May 1945, and ".. they found a recent letter from Breen asking the German minister to forward his birthday wishes to the Führer, just days before Hitler committed suicide." Breen was co-chairman of the anti-Vietnam War organisation "Irish Voice on Vietnam".Personal life
Breen was married on 12 June 1921, during the War of Independence, to Brigid Malone, a Dublin Cumann na mBan woman and sister of Lieutenant Michael Malone who was killed in action at the Battle of Mount Street Bridge during the 1916 Rising. They had met in Dublin when she helped to nurse him while he was recovering from a bullet wound. Seán Hogan was best man, and the bride's sister Aine Malone was the bridesmaid. Photographs of the wedding celebrations taken by 5th Battalion intelligence officer Séan Sharkey are published in The Tipperary Third Brigade a photographic record. Breen was, at the time, one of the most wanted men in Ireland, and South Tipperary was under martial law, yet a large celebration was held. The wedding took place at Purcell's, "Glenagat House", New Inn, County Tipperary. Many of the key members of the Third Tipperary Brigade attended, including flying column leaders Dinny Lacey and Hogan. Breen was the brother in-law of Commandant Theobald Wolfe Tone FitzGerald, the painter of the Irish Republic Flag that flew over the GPO during the Easter Rising in 1916. The Breens had two children, Donal and Granya. Breen was an atheist.Death
Breen died in Dublin in 1969, aged 75, and was buried in Donohill, near his birthplace. His funeral was the largest seen in west Tipperary since that of his close friend and comrade-in-arms, Seán Treacy, at Kilfeacle in October 1920. An estimated attendance of 10,000 mourners assembled in the tiny hamlet, giving ample testimony to the esteem in which he was held. Breen was the subject of a 2007 biography, Dan Breen and the IRA by Joe Ambrose.In popular culture
Breen is mentioned in the Irish folk ballad "The Galtee Mountain Boy", along with Seán Moylan, Dinny Lacey, and Seán Hogan. The song, written by Patsy Halloran, recalls some of the travels of a "Flying column" from Tipperary as they fought during the Irish War of Independence, and later against the pro-Treaty side during the Irish Civil War. The trophy for the Tipperary Senior Hurling Championship is named after him. -
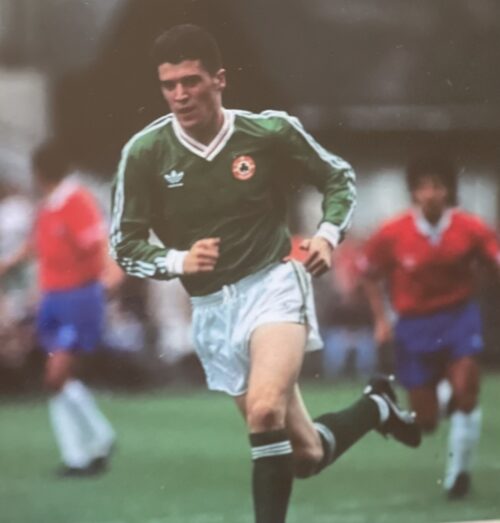
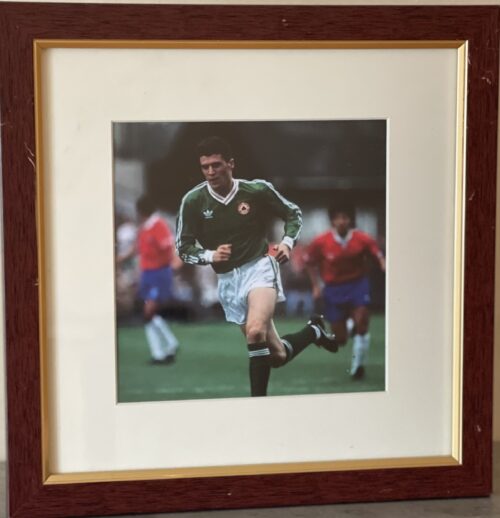
 I 30cm x 30cm Limerick Roy Maurice Keane (born 10 August 1971) is an Irish football manager and former professional player. He is the joint most successful Irish footballer of all time, having won 19 major trophies in his club career, 17 of which came during his time at English club Manchester United. He served as the assistant manager of the Republic of Ireland national teamfrom 2013 until 2018. Regarded as one of the best midfielders of his generation, he was named by Pelé in the FIFA 100 list of the world's greatest living players in 2004.Noted for his hardened and brash demeanour, he was ranked at No. 11 on The Times' list of the 50 "hardest" footballers in history in 2007. Keane was inducted into the Premier League Hall of Fame in 2021. In his 18-year playing career, Keane played for Cobh Ramblers, Nottingham Forest, and Manchester United, before ending his career at Celtic. He was a dominating box-to-box midfielder, noted for his aggressive and highly competitive style of play, an attitude that helped him excel as captain of Manchester United from 1997 until his departure in 2005. Keane helped United achieve a sustained period of success during his 12 years at the club. He then signed for Celtic, where he won a domestic double before he retired as a player in 2006. Keane played at the international level for the Republic of Ireland over 14 years, most of which he spent as captain. At the 1994 FIFA World Cup, he played in every Republic of Ireland game. He was sent home from the 2002 FIFA World Cup after a dispute with national coach Mick McCarthy over the team's training facilities. Keane was appointed manager of Sunderland shortly after his retirement as a player and took the club from 23rd position in the Football League Championship, in late August, to win the division title and gain promotion to the Premier League. He resigned in December 2008,and from April 2009 to January 2011, he was manager of Championship club Ipswich Town. In November 2013, he was appointed assistant manager of the Republic of Ireland national team by manager Martin O'Neill. Keane has also worked as a studio analyst for British channels ITV's and Sky Sportsfootball coverage.
I 30cm x 30cm Limerick Roy Maurice Keane (born 10 August 1971) is an Irish football manager and former professional player. He is the joint most successful Irish footballer of all time, having won 19 major trophies in his club career, 17 of which came during his time at English club Manchester United. He served as the assistant manager of the Republic of Ireland national teamfrom 2013 until 2018. Regarded as one of the best midfielders of his generation, he was named by Pelé in the FIFA 100 list of the world's greatest living players in 2004.Noted for his hardened and brash demeanour, he was ranked at No. 11 on The Times' list of the 50 "hardest" footballers in history in 2007. Keane was inducted into the Premier League Hall of Fame in 2021. In his 18-year playing career, Keane played for Cobh Ramblers, Nottingham Forest, and Manchester United, before ending his career at Celtic. He was a dominating box-to-box midfielder, noted for his aggressive and highly competitive style of play, an attitude that helped him excel as captain of Manchester United from 1997 until his departure in 2005. Keane helped United achieve a sustained period of success during his 12 years at the club. He then signed for Celtic, where he won a domestic double before he retired as a player in 2006. Keane played at the international level for the Republic of Ireland over 14 years, most of which he spent as captain. At the 1994 FIFA World Cup, he played in every Republic of Ireland game. He was sent home from the 2002 FIFA World Cup after a dispute with national coach Mick McCarthy over the team's training facilities. Keane was appointed manager of Sunderland shortly after his retirement as a player and took the club from 23rd position in the Football League Championship, in late August, to win the division title and gain promotion to the Premier League. He resigned in December 2008,and from April 2009 to January 2011, he was manager of Championship club Ipswich Town. In November 2013, he was appointed assistant manager of the Republic of Ireland national team by manager Martin O'Neill. Keane has also worked as a studio analyst for British channels ITV's and Sky Sportsfootball coverage. -
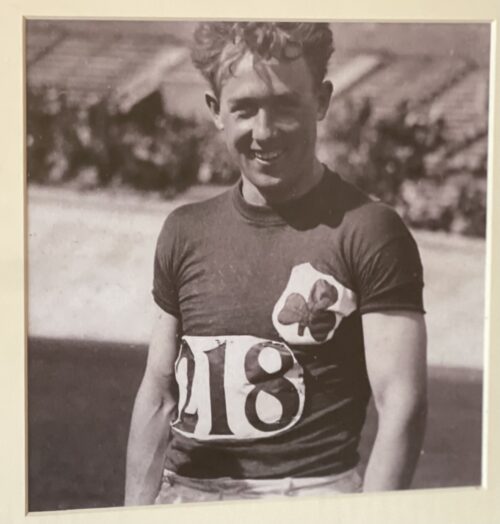
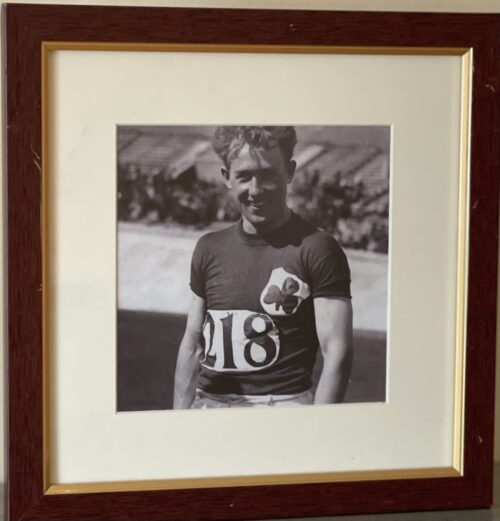
 30cm x 30cm Patrick "Pat" O'Callaghan (28 January 1906 – 1 December 1991) was an Irish athlete and Olympic gold medallist. He was the first athlete from Ireland to win an Olympic medal under the Irish flag rather than the British. In sport he then became regarded as one of Ireland's greatest-ever athletes.
30cm x 30cm Patrick "Pat" O'Callaghan (28 January 1906 – 1 December 1991) was an Irish athlete and Olympic gold medallist. He was the first athlete from Ireland to win an Olympic medal under the Irish flag rather than the British. In sport he then became regarded as one of Ireland's greatest-ever athletes.Early and private life
Pat O'Callaghan was born in the townland of Knockaneroe, near Kanturk, County Cork, on 28 January 1906, the second of three sons born to Paddy O'Callaghan, a farmer, and Jane Healy. He began his education at the age of two at Derrygalun national school. O'Callaghan progressed to secondary school in Kanturk and at the age of fifteen he won a scholarship to the Patrician Academy in Mallow. During his year in the Patrician Academy he cycled the 32-mile round trip from Derrygalun every day and he never missed a class. O'Callaghan subsequently studied medicine at the Royal College of Surgeons in Dublin. Following his graduation in 1926 he joined the Royal Air Force Medical Service. He returned to Ireland in 1928 and set up his own medical practice in Clonmel, County Tipperary where he worked until his retirement in 1984.O'Callaghan was also a renowned field sports practitioner, greyhound trainer and storyteller.Sporting career
Early sporting life
O’Callaghan was born into a family that had a huge interest in a variety of different sports. His uncle, Tim Vaughan, was a national sprint champion and played Gaelic football with Cork in 1893. O’Callaghan's eldest brother, Seán, also enjoyed football as well as winning a national 440 yards hurdles title, while his other brother, Con, was also regarded as a gifted runner, jumper and thrower. O’Callaghan's early sporting passions included hunting, poaching and Gaelic football. He was regarded as an excellent midfielder on the Banteer football team, while he also lined out with the Banteer hurling team. At university in Dublin O’Callaghan broadened his sporting experiences by joining the local senior rugby club. This was at a time when the Gaelic Athletic Association ‘ban’ forbade players of Gaelic games from playing "foreign sports". It was also in Dublin that O’Callaghan first developed an interest in hammer-throwing. In 1926, he returned to his native Duhallow where he set up a training regime in hammer-throwing. Here he fashioned his own hammer by boring a one-inch hole through a 16 lb shot and filling it with the ball-bearing core of a bicycle pedal. He also set up a throwing circle in a nearby field where he trained. In 1927, O’Callaghan returned to Dublin where he won that year's hammer championship with a throw of 142’ 3”. In 1928, he retained his national title with a throw of 162’ 6”, a win which allowed him to represent the Ireland at the forthcoming Olympic Games in Amsterdam. On the same day, O’Callaghan's brother, Con, won the shot put and the decathlon and also qualified for the Olympic Games. Between winning his national title and competing in the Olympic Games O’Callaghan improved his throwing distance by recording a distance of 166’ 11” at the Royal Ulster ConstabularySports in Belfast.1928 Olympic Games
In the summer of 1928, the three O’Callaghan brothers paid their own fares when travelling to the Olympic Games in Amsterdam. Pat O’Callaghan finished in sixth place in the preliminary round and started the final with a throw of 155’ 9”. This put him in third place behind Ossian Skiöld of Sweden, but ahead of Malcolm Nokes, the favourite from Great Britain. For his second throw, O’Callaghan used the Swede's own hammer and recorded a throw of 168’ 7”. This was 4’ more than Skoeld's throw and resulted in a first gold medal for O’Callaghan and for Ireland. The podium presentation was particularly emotional as it was the first time at an Olympic Games that the Irish tricolour was raised and Amhrán na bhFiann was played.Success in Ireland
After returning from the Olympic Games, O’Callaghan cemented his reputation as a great athlete with additional successes between 1929 and 1932. In the national championships of 1930 he won the hammer, shot-putt, 56 lbs without follow, 56 lbs over-the-bar, discus and high jump. In the summer of 1930, O’Callaghan took part in a two-day invitation event in Stockholm where Oissian Skoeld was expected to gain revenge on the Irishman for the defeat in Amsterdam. On the first day of the competition, Skoeld broke his own European record with his very first throw. O’Callaghan followed immediately and overtook him with his own first throw and breaking the new record. On the second day of the event both O’Callaghan and Skoeld were neck-and-neck, when the former, with his last throw, set a new European record of 178’ 8” to win.1932 Summer Olympics
By the time the 1932 Summer Olympics came around O’Callaghan was regularly throwing the hammer over 170 feet. The Irish team were much better organised on that occasion and the whole journey to Los Angeles was funded by a church-gate collection. Shortly before departing on the 6,000-mile boat and train journey across the Atlantic O’Callaghan collected a fifth hammer title at the national championships. On arrival in Los Angeles O’Callaghan's preparations of the defence of his title came unstuck. The surface of the hammer circle had always been of grass or clay and throwers wore field shoes with steel spikes set into the heel and sole for grip. In Los Angeles, however, a cinder surface was to be provided. The Olympic Committee of Ireland had failed to notify O’Callaghan of this change. Consequently, he came to the arena with three pairs of spiked shoes for a grass or clay surface and time did not permit a change of shoe. He wore his shortest spikes, but found that they caught in the hard gritty slab and impeded his crucial third turn. In spite of being severely impeded, he managed to qualify for the final stage of the competition with his third throw of 171’ 3”. While the final of the 400m hurdles was delayed, O’Callaghan hunted down a hacksaw and a file in the groundskeeper's shack and he cut off the spikes. O’Callaghan's second throw reached a distance of 176’ 11”, a result which allowed him to retain his Olympic title. It was Ireland's second gold medal of the day as Bob Tisdall had earlier won a gold medal in the 400m hurdles.Retirement
Due to the celebrations after the Olympic Games O’Callaghan didn't take part in the national athletic championships in Ireland in 1933. In spite of that he still worked hard on his training and he experimented with a fourth turn to set a new European record at 178’ 9”. By this stage O’Callaghan was rated as the top thrower in the world by the leading international sports journalists. In the early 1930s controversy raged between the British AAA and the National Athletic and Cycling Association of Ireland (NACAI). The British AAA claimed jurisdiction in Northern Ireland while the NACAI claimed jurisdiction over the entire island of Ireland regardless of political division. The controversy came to a head in the lead-up to the 1936 Summer Olympics when the IAAF finally disqualified the NACAI. O’Callaghan remained loyal to the NACAI, a decision which effectively brought an end to his international athletic career. No Irish team travelled to the 1936 Olympic Games, however O’Callaghan travelled to Berlin as a private spectator. After Berlin, O’Callaghan's international career was over. He declined to join the new Irish Amateur Athletics Union (IAAU) or subsequent IOC recognised Amateur Athletics Union of Eire (AAUE) and continued to compete under NACAI rules. At Fermoy in 1937 he threw 195’ 4” – more than seven feet ahead of the world record set by his old friend Paddy 'Chicken' Ryan in 1913. This record, however, was not ratified by the AAUE or the IAAF. In retirement O’Callaghan remained interested in athletics. He travelled to every Olympic Games up until 1988 and enjoyed fishing and poaching in Clonmel. He died on 1 December 1991.Legacy
O'Callaghan was the flag bearer for Ireland at the 1932 Olympics. In 1960, he became the first person to receive the Texaco Hall of Fame Award. He was made a Freeman of Clonmel in 1984, and was honorary president of Commercials Gaelic Football Club. The Dr. Pat O'Callaghan Sports Complex at Cashel Rd, Clonmel which is the home of Clonmel Town Football Club is named after him, and in January 2007 his statue was raised in Banteer, County Cork. -

 60cm x 50cm Limerick
60cm x 50cm Limerick
Paddy is a brand of blended Irish whiskey produced by Irish Distillers, at the Midleton distillery in County Cork, on behalf of Sazerac, a privately held American company. Irish distillers owned the brand until its sale to Sazerac in 2016. As of 2016, Paddy is the fourth largest selling Irish whiskey in the WorldHistory The Cork Distilleries Company was founded in 1867 to merge four existing distilleries in Cork city (the North Mall, the Green, Watercourse Road, and Daly's) under the control of one group.A fifth distillery, the Midleton distillery, joined the group soon after in 1868. In 1882, the company hired a young Corkman called Paddy Flaherty as a salesman. Flaherty travelled the pubs of Cork marketing the company's unwieldy named "Cork Distilleries Company Old Irish Whiskey".His sales techniques (which including free rounds of drinks for customers) were so good, that when publicans ran low on stock they would write the distillery to reorder cases of "Paddy Flaherty's whiskey". In 1912, with his name having become synonymous with the whiskey, the distillery officially renamed the whiskey Paddy Irish Whiskey in his honour. In 1920s and 1930s in Ireland, whiskey was sold in casks from the distillery to wholesalers, who would in turn sell it on to publicans.To prevent fluctuations in quality due to middlemen diluting their casks, Cork Distilleries Company decided to bottle their own whiskey known as Paddy, becoming one of the first to do so. In 1988, following an unsolicited takeover offer by Grand Metropolitan, Irish Distillers approached Pernod Ricard and subsequently became a subsidiary of the French drinks conglomerate, following a friendly takeover bid. In 2016, Pernod Ricard sold the Paddy brand to Sazerac, a privately held American firm for an undisclosed fee. Pernod Ricard stated that the sale was in order "simplify" their portfolio, and allow for more targeted investment in their other Irish whiskey brands, such as Jameson and Powers. At the time of the sale, Paddy was the fourth largest selling Irish whiskey brand in the world, with sales of 200,000 9-litre cases per annum, across 28 countries worldwide. Paddy whiskey is distilled three times and matured in oak casks for up to seven years.Compared with other Irish whiskeys, Paddy has a comparatively low pot still content and a high malt content in its blend. Jim Murray, author of the Whiskey bible, has rated Paddy as "one of the softest of all Ireland's whiskeys".

Introduced 1879, renamed as Paddy in 1912 -

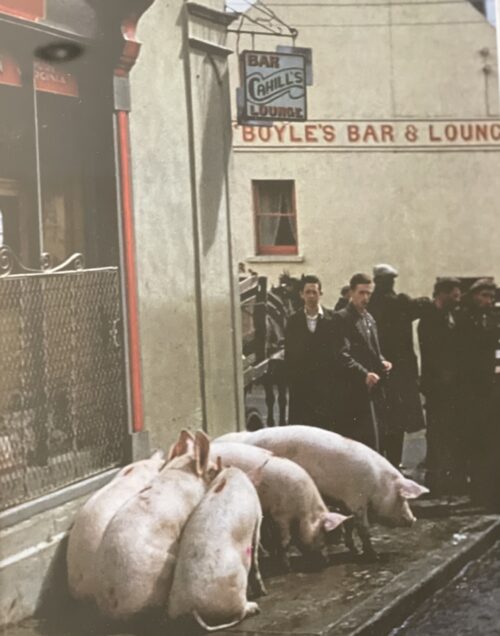
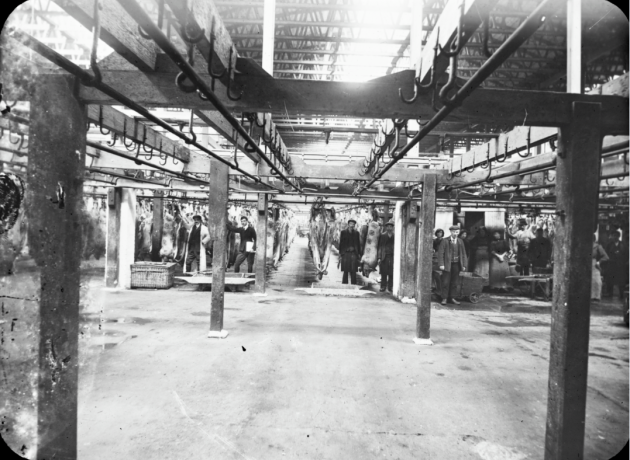
 40cm x 34cm LimerickMuch of the last century, and indeed for well over half of the present one, Limerick's importance was directly attributed to her three well-known bacon factories, namely, J. Matterson & Sons, Roches Street, established in 1816 by Mr. John Russell, a Cumberland man in con-junction with Mr. Matterson, using the method of curing then current in Berwick-on-Tweed. W.J. Shaw & Sons, founded in the year 1831 at Mulgrave Street by William John Shaw, a descendant of a County Down family, and O'Mara's bacon factory, Roches Street, which had its origin in Mungret Street some few years before 1839, when James O'Mara from Toomevara started curing bacon in the basement of his house there. Apparently, this basement business flourished, for in 1839 he moved to Roches Street to the premises it last occupied .About the middle of the last century, for some reason now difficult to fathom, Limerick bacon and especially Limerick hams, became well-known for their excellent flavour throughout the English-speaking world. It is on record that Glasgow curers in an effort to produce hams equal in excellence to those of Limerick, imported Limerick workmen who were supposed to know all about the way in which the meat was turned out at home. Apparently, they did not bring secrets with them for their efforts were unsuccessful. There were also much larger bacon factories in parts of the British Isles; for instance, Belfast is reputed to have exported four times the number of hams produced in Limerick, and places like Glasgow and Liverpool had several factories producing very large quantities of bacon as well. None of them, however, quite matched' those produced in the three local factories for flavour and quality.O’MARA’S, MATTERSON’S, SHAW’S and Denny’s were the names that made Limerick famous for its bacon produce for 180 years – earning it the nickname ‘Pigstown’. The reputation of Limerick ham, the food culture that arose from a plentiful supply of cheap products, the story of the pork butchers, the pig buyers, the sounds of the city with factory horns signalling the call to work – all of these still resonate in Limerick in the memories of its citizens and former workers. A definitive account of this industry that operated at the centre of the city, supplied by the farms of rural county Limerick for over 180 years will be documented in a new book called Pigtown – A History of Limerick’s Bacon Industry. Ruth Guiry was commissioned to undertake the research under the guidance of Dr Maura Cronin from Mary Immaculate College and one of the 27 people she interviewed to understand the role the bacon factories had in Limerick was Joe Hayes. Joe Hayes started working in a bacon factory in 1962, aged 16 years old. He worked with his dad, and later on with his two sons until the factory closed in 1986. “When the factory closed, a group of us got our own little unit, we rented it, and produced our own sausages, puddings and things.” It was a huge part of Limerick’s social scene: four generations of Joe’s family worked in bacon factories, with uncles, sisters, brothers, sons and cousins all working in the factory at one time or another: “If one factory was caic, you wouldn’t have a problem getting a job in the other one. And he doesn’t mince his word when talking about the work they did. “They brought the pigs in, we killed the pigs, and prepared the bacon: that’s the way it was in the bacon factories.” When asked about if there were ever animal cruelty protests, he laughs at the idea.
40cm x 34cm LimerickMuch of the last century, and indeed for well over half of the present one, Limerick's importance was directly attributed to her three well-known bacon factories, namely, J. Matterson & Sons, Roches Street, established in 1816 by Mr. John Russell, a Cumberland man in con-junction with Mr. Matterson, using the method of curing then current in Berwick-on-Tweed. W.J. Shaw & Sons, founded in the year 1831 at Mulgrave Street by William John Shaw, a descendant of a County Down family, and O'Mara's bacon factory, Roches Street, which had its origin in Mungret Street some few years before 1839, when James O'Mara from Toomevara started curing bacon in the basement of his house there. Apparently, this basement business flourished, for in 1839 he moved to Roches Street to the premises it last occupied .About the middle of the last century, for some reason now difficult to fathom, Limerick bacon and especially Limerick hams, became well-known for their excellent flavour throughout the English-speaking world. It is on record that Glasgow curers in an effort to produce hams equal in excellence to those of Limerick, imported Limerick workmen who were supposed to know all about the way in which the meat was turned out at home. Apparently, they did not bring secrets with them for their efforts were unsuccessful. There were also much larger bacon factories in parts of the British Isles; for instance, Belfast is reputed to have exported four times the number of hams produced in Limerick, and places like Glasgow and Liverpool had several factories producing very large quantities of bacon as well. None of them, however, quite matched' those produced in the three local factories for flavour and quality.O’MARA’S, MATTERSON’S, SHAW’S and Denny’s were the names that made Limerick famous for its bacon produce for 180 years – earning it the nickname ‘Pigstown’. The reputation of Limerick ham, the food culture that arose from a plentiful supply of cheap products, the story of the pork butchers, the pig buyers, the sounds of the city with factory horns signalling the call to work – all of these still resonate in Limerick in the memories of its citizens and former workers. A definitive account of this industry that operated at the centre of the city, supplied by the farms of rural county Limerick for over 180 years will be documented in a new book called Pigtown – A History of Limerick’s Bacon Industry. Ruth Guiry was commissioned to undertake the research under the guidance of Dr Maura Cronin from Mary Immaculate College and one of the 27 people she interviewed to understand the role the bacon factories had in Limerick was Joe Hayes. Joe Hayes started working in a bacon factory in 1962, aged 16 years old. He worked with his dad, and later on with his two sons until the factory closed in 1986. “When the factory closed, a group of us got our own little unit, we rented it, and produced our own sausages, puddings and things.” It was a huge part of Limerick’s social scene: four generations of Joe’s family worked in bacon factories, with uncles, sisters, brothers, sons and cousins all working in the factory at one time or another: “If one factory was caic, you wouldn’t have a problem getting a job in the other one. And he doesn’t mince his word when talking about the work they did. “They brought the pigs in, we killed the pigs, and prepared the bacon: that’s the way it was in the bacon factories.” When asked about if there were ever animal cruelty protests, he laughs at the idea.
They started at 8am and finished at 5.30 working a 40 hour week when the factory closed in 1986, but despite their work, the people who worked in factories often couldn’t afford to buy the expensive cuts of meat. After the expensive cuts were prepared, the offal, the spare ribs, the pigs’ heads would go to the poorer people. “The blood was used to make the pudding, the packet, the tripe was made off the belly. Everything was used off the pig, and it fed Limerick city.” It was a way of life down in Limerick, so when the factories closed, thousands of people working in a bacon factories were out of jobs, and thousands of families were affected. But it wasn’t the competition from big supermarkets that did it – it was free trade. The Danes, the French, the Dutch all started exporting their products here, and Limerick factories didn’t have the money to export to compete. “Michael O’Mara’s funeral was this week – he was the last of the bacon factory managers.” says Joe. “After the Limerick factory closed, he tried doing different bits and pieces, but nothing worked out for him, so he worked in a factory for a couple of years before retiring.” Joe Hayes himself is retired now, and when he buys his meat he gets it in a supermarket. “Meat is meat,” he says.”But if I see the tricolour flag, I’ll still buy it even if it’s dearer.” Pigtown - A History of Limerick’s Bacon Industry by Ruth Guiry is co-edited by Dr Maura Cronin and Jacqui Hayes.People still eat sausages and bacon – where do they think they come from? -
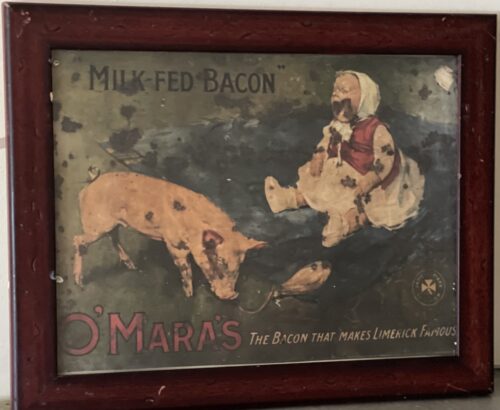
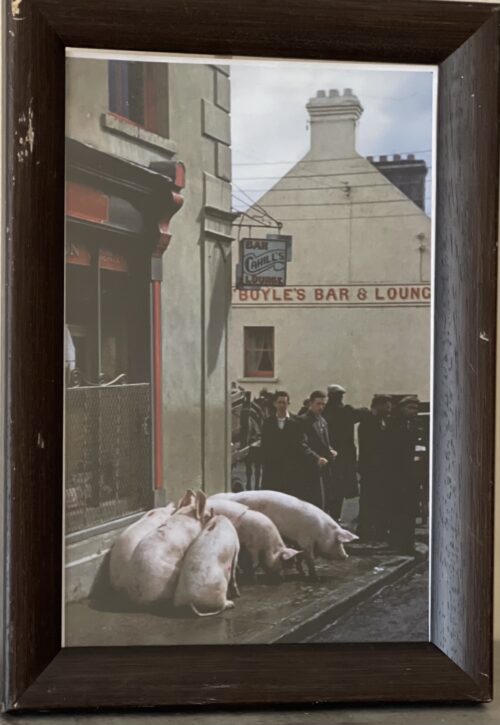
 47cm x 37cm LimerickMuch of the last century, and indeed for well over half of the present one, Limerick's importance was directly attributed to her three well-known bacon factories, namely, J. Matterson & Sons, Roches Street, established in 1816 by Mr. John Russell, a Cumberland man in con-junction with Mr. Matterson, using the method of curing then current in Berwick-on-Tweed. W.J. Shaw & Sons, founded in the year 1831 at Mulgrave Street by William John Shaw, a descendant of a County Down family, and O'Mara's bacon factory, Roches Street, which had its origin in Mungret Street some few years before 1839, when James O'Mara from Toomevara started curing bacon in the basement of his house there. Apparently, this basement business flourished, for in 1839 he moved to Roches Street to the premises it last occupied .About the middle of the last century, for some reason now difficult to fathom, Limerick bacon and especially Limerick hams, became well-known for their excellent flavour throughout the English-speaking world. It is on record that Glasgow curers in an effort to produce hams equal in excellence to those of Limerick, imported Limerick workmen who were supposed to know all about the way in which the meat was turned out at home. Apparently, they did not bring secrets with them for their efforts were unsuccessful. There were also much larger bacon factories in parts of the British Isles; for instance, Belfast is reputed to have exported four times the number of hams produced in Limerick, and places like Glasgow and Liverpool had several factories producing very large quantities of bacon as well. None of them, however, quite matched' those produced in the three local factories for flavour and quality.O’MARA’S, MATTERSON’S, SHAW’S and Denny’s were the names that made Limerick famous for its bacon produce for 180 years – earning it the nickname ‘Pigstown’. The reputation of Limerick ham, the food culture that arose from a plentiful supply of cheap products, the story of the pork butchers, the pig buyers, the sounds of the city with factory horns signalling the call to work – all of these still resonate in Limerick in the memories of its citizens and former workers. A definitive account of this industry that operated at the centre of the city, supplied by the farms of rural county Limerick for over 180 years will be documented in a new book called Pigtown – A History of Limerick’s Bacon Industry. Ruth Guiry was commissioned to undertake the research under the guidance of Dr Maura Cronin from Mary Immaculate College and one of the 27 people she interviewed to understand the role the bacon factories had in Limerick was Joe Hayes. Joe Hayes started working in a bacon factory in 1962, aged 16 years old. He worked with his dad, and later on with his two sons until the factory closed in 1986. “When the factory closed, a group of us got our own little unit, we rented it, and produced our own sausages, puddings and things.” It was a huge part of Limerick’s social scene: four generations of Joe’s family worked in bacon factories, with uncles, sisters, brothers, sons and cousins all working in the factory at one time or another: “If one factory was caic, you wouldn’t have a problem getting a job in the other one. And he doesn’t mince his word when talking about the work they did. “They brought the pigs in, we killed the pigs, and prepared the bacon: that’s the way it was in the bacon factories.” When asked about if there were ever animal cruelty protests, he laughs at the idea.
47cm x 37cm LimerickMuch of the last century, and indeed for well over half of the present one, Limerick's importance was directly attributed to her three well-known bacon factories, namely, J. Matterson & Sons, Roches Street, established in 1816 by Mr. John Russell, a Cumberland man in con-junction with Mr. Matterson, using the method of curing then current in Berwick-on-Tweed. W.J. Shaw & Sons, founded in the year 1831 at Mulgrave Street by William John Shaw, a descendant of a County Down family, and O'Mara's bacon factory, Roches Street, which had its origin in Mungret Street some few years before 1839, when James O'Mara from Toomevara started curing bacon in the basement of his house there. Apparently, this basement business flourished, for in 1839 he moved to Roches Street to the premises it last occupied .About the middle of the last century, for some reason now difficult to fathom, Limerick bacon and especially Limerick hams, became well-known for their excellent flavour throughout the English-speaking world. It is on record that Glasgow curers in an effort to produce hams equal in excellence to those of Limerick, imported Limerick workmen who were supposed to know all about the way in which the meat was turned out at home. Apparently, they did not bring secrets with them for their efforts were unsuccessful. There were also much larger bacon factories in parts of the British Isles; for instance, Belfast is reputed to have exported four times the number of hams produced in Limerick, and places like Glasgow and Liverpool had several factories producing very large quantities of bacon as well. None of them, however, quite matched' those produced in the three local factories for flavour and quality.O’MARA’S, MATTERSON’S, SHAW’S and Denny’s were the names that made Limerick famous for its bacon produce for 180 years – earning it the nickname ‘Pigstown’. The reputation of Limerick ham, the food culture that arose from a plentiful supply of cheap products, the story of the pork butchers, the pig buyers, the sounds of the city with factory horns signalling the call to work – all of these still resonate in Limerick in the memories of its citizens and former workers. A definitive account of this industry that operated at the centre of the city, supplied by the farms of rural county Limerick for over 180 years will be documented in a new book called Pigtown – A History of Limerick’s Bacon Industry. Ruth Guiry was commissioned to undertake the research under the guidance of Dr Maura Cronin from Mary Immaculate College and one of the 27 people she interviewed to understand the role the bacon factories had in Limerick was Joe Hayes. Joe Hayes started working in a bacon factory in 1962, aged 16 years old. He worked with his dad, and later on with his two sons until the factory closed in 1986. “When the factory closed, a group of us got our own little unit, we rented it, and produced our own sausages, puddings and things.” It was a huge part of Limerick’s social scene: four generations of Joe’s family worked in bacon factories, with uncles, sisters, brothers, sons and cousins all working in the factory at one time or another: “If one factory was caic, you wouldn’t have a problem getting a job in the other one. And he doesn’t mince his word when talking about the work they did. “They brought the pigs in, we killed the pigs, and prepared the bacon: that’s the way it was in the bacon factories.” When asked about if there were ever animal cruelty protests, he laughs at the idea.
They started at 8am and finished at 5.30 working a 40 hour week when the factory closed in 1986, but despite their work, the people who worked in factories often couldn’t afford to buy the expensive cuts of meat. After the expensive cuts were prepared, the offal, the spare ribs, the pigs’ heads would go to the poorer people. “The blood was used to make the pudding, the packet, the tripe was made off the belly. Everything was used off the pig, and it fed Limerick city.” It was a way of life down in Limerick, so when the factories closed, thousands of people working in a bacon factories were out of jobs, and thousands of families were affected. But it wasn’t the competition from big supermarkets that did it – it was free trade. The Danes, the French, the Dutch all started exporting their products here, and Limerick factories didn’t have the money to export to compete. “Michael O’Mara’s funeral was this week – he was the last of the bacon factory managers.” says Joe. “After the Limerick factory closed, he tried doing different bits and pieces, but nothing worked out for him, so he worked in a factory for a couple of years before retiring.” Joe Hayes himself is retired now, and when he buys his meat he gets it in a supermarket. “Meat is meat,” he says.”But if I see the tricolour flag, I’ll still buy it even if it’s dearer.” Pigtown - A History of Limerick’s Bacon Industry by Ruth Guiry is co-edited by Dr Maura Cronin and Jacqui Hayes.People still eat sausages and bacon – where do they think they come from? -

 47cm x 37cm Limerick The building itself it is a terraced eight-bay four-storey late-Victorian commercial building, It was built across 1895 and 1896 for J McCarthy and Sons, Wholesale Tea and Wine Merchants. Named the Clancarty (family of Carty) Buildings, the building was designed by architect and built by John Delaney. The Cork Examiner on 10 August 1896 (p.9) describes the impressive building: “No person passing through George’s street, can fail to see and admire the beautiful structure, which has just been completed. The facade is 54 feet long and 48 feet high, divided into four storeys, with round headed windows in the classic style, and extends more than the whole length of George’s Street, as between Cook street and Marlboro Street. The ground floor is divided by handsome wrought pilasters and consoles, each console decorated with floral swags, with a richly-moulded dental cornice immediately over the facia. This basement is perfectly fire proof, the walls being built of brick and cement, whilst the ceiling and floor over are composed of a solid block of concrete. The first, second and third floors immediately overhead are altogether occupied by the firm as warerooms to meet the requirements of their immense business as tea and wine merchants and whiskey shippers, the growth of which necessitates this great extension of their premises”.
47cm x 37cm Limerick The building itself it is a terraced eight-bay four-storey late-Victorian commercial building, It was built across 1895 and 1896 for J McCarthy and Sons, Wholesale Tea and Wine Merchants. Named the Clancarty (family of Carty) Buildings, the building was designed by architect and built by John Delaney. The Cork Examiner on 10 August 1896 (p.9) describes the impressive building: “No person passing through George’s street, can fail to see and admire the beautiful structure, which has just been completed. The facade is 54 feet long and 48 feet high, divided into four storeys, with round headed windows in the classic style, and extends more than the whole length of George’s Street, as between Cook street and Marlboro Street. The ground floor is divided by handsome wrought pilasters and consoles, each console decorated with floral swags, with a richly-moulded dental cornice immediately over the facia. This basement is perfectly fire proof, the walls being built of brick and cement, whilst the ceiling and floor over are composed of a solid block of concrete. The first, second and third floors immediately overhead are altogether occupied by the firm as warerooms to meet the requirements of their immense business as tea and wine merchants and whiskey shippers, the growth of which necessitates this great extension of their premises”.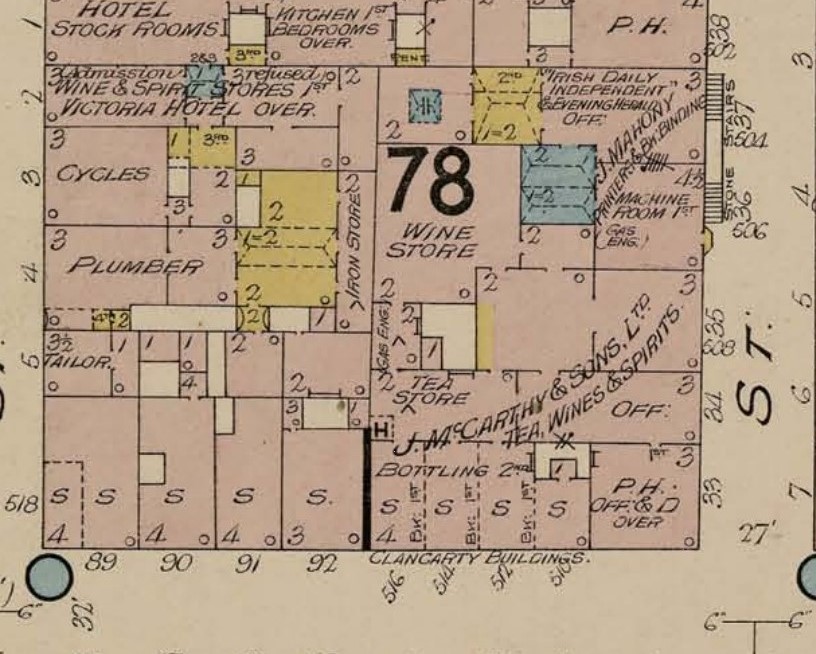
J McCarthy and Sons, Wholesale Tea and Wine Merchants as shown in Goads Insurance Map of Cork, 1906 (source: Kieran McCarthy) 
Description of Clancarty Buildings, Cork Examiner, 10 August 1896, p.9 (source: Cork City Library) -

 47cm x 37cm Limerick The building itself it is a terraced eight-bay four-storey late-Victorian commercial building, It was built across 1895 and 1896 for J McCarthy and Sons, Wholesale Tea and Wine Merchants. Named the Clancarty (family of Carty) Buildings, the building was designed by architect and built by John Delaney. The Cork Examiner on 10 August 1896 (p.9) describes the impressive building: “No person passing through George’s street, can fail to see and admire the beautiful structure, which has just been completed. The facade is 54 feet long and 48 feet high, divided into four storeys, with round headed windows in the classic style, and extends more than the whole length of George’s Street, as between Cook street and Marlboro Street. The ground floor is divided by handsome wrought pilasters and consoles, each console decorated with floral swags, with a richly-moulded dental cornice immediately over the facia. This basement is perfectly fire proof, the walls being built of brick and cement, whilst the ceiling and floor over are composed of a solid block of concrete. The first, second and third floors immediately overhead are altogether occupied by the firm as warerooms to meet the requirements of their immense business as tea and wine merchants and whiskey shippers, the growth of which necessitates this great extension of their premises”.
47cm x 37cm Limerick The building itself it is a terraced eight-bay four-storey late-Victorian commercial building, It was built across 1895 and 1896 for J McCarthy and Sons, Wholesale Tea and Wine Merchants. Named the Clancarty (family of Carty) Buildings, the building was designed by architect and built by John Delaney. The Cork Examiner on 10 August 1896 (p.9) describes the impressive building: “No person passing through George’s street, can fail to see and admire the beautiful structure, which has just been completed. The facade is 54 feet long and 48 feet high, divided into four storeys, with round headed windows in the classic style, and extends more than the whole length of George’s Street, as between Cook street and Marlboro Street. The ground floor is divided by handsome wrought pilasters and consoles, each console decorated with floral swags, with a richly-moulded dental cornice immediately over the facia. This basement is perfectly fire proof, the walls being built of brick and cement, whilst the ceiling and floor over are composed of a solid block of concrete. The first, second and third floors immediately overhead are altogether occupied by the firm as warerooms to meet the requirements of their immense business as tea and wine merchants and whiskey shippers, the growth of which necessitates this great extension of their premises”.
J McCarthy and Sons, Wholesale Tea and Wine Merchants as shown in Goads Insurance Map of Cork, 1906 (source: Kieran McCarthy) 
Description of Clancarty Buildings, Cork Examiner, 10 August 1896, p.9 (source: Cork City Library) -

 24cm x 40cm The Green Distillery was an Irish whiskey distillery which was established in Cork City, Ireland in 1796. In 1867, the distillery was purchased by the Cork Distilleries Company (CDC), in an amalgamation of five Cork distilleries.Production of whiskey at the distillery likely ceased soon afters its acquisition by the CDC.However, the distillery is known to have remained in use a bonded store by the Cork Distilleries Company for several years thereafter.In the mid-twentieth century, the distillery resumed operations as a gin distillery for a period of time, however, it has since been almost completely demolished. The distillery was notable for its use of an early continuous distillation apparatus, invented by the distillery's then co-owner, Joseph Shee. The distillery began life on 12 May 1796, when two distillers, Robert Allan and Denis Corcoran purchased a dwelling house and maltings on North York Street (now Thomas Davis Street) from Bartholomew Foley, a draper. The malthouse had formerly been owned by Thomas Wood, a maltster, in 1780. In 1802, the Allan and Corcoran are recorded as working a 762 gallon still. In the years that followed, the distillery seems to have changed hands several times. Around 1812, the business was being run by two brothers, Thomas and Joseph Shee, Benjamin Hodges, and some others.Thomas Shee acted as the distiller working a 201 gallon still, while Joseph acted a marketing agent based in London.Hodges and the others may have been silent partners who provided capital but nothing else, as their connection with the distillery soon disappeared. Output was recorded at 100,000 gallons in 1828.In June 1830, the Shees entered financial difficulties, and ownership passed to Joseph Shee. Joseph continued operations using capital provided by James Kiernan under a mortgage, while Thomas Shee remained on as a distiller.In 1833, excise records show that the distillery paid a duty charge of £26,716, which equated to about 160,000 gallons proof.By 1835, Kiernan took outright control of the distillery. When Kiernan died in December 1844, his will specified that the distillery should be put up for sale. It was purchased on 27 July 1845 by George Waters, who was previously a co-owner of Daly's Distillery on John Street, until the dissolution of the partnership following the death of one of the partners. Waters ran the distillery until his retirement around 1867, after which the distillery was purchased by the Cork Distilleries Company (CDC), in an amalgamation of five Cork distilleries. Under CDC, distilling ceased at the distillery in the 1880s, with production transferred to their nearby North Mall distillery. Subsequently, the Green Distillery was used as a bonded store for some time.However, in the mid-twentieth century, new equipment was installed in the Green Distillery, with production of gin occurring there for a period of time. According to Irish Distillers, who absorbed the Cork Distilleries Company in the 1960s, a warehouse on the site was used to store whiskey in bond until the 1980s.Since then, the distillery has been almost completely demolished, with only a small archway remaining. However, one of original pot stills is still in use, currently employed as an experimental still at the nearby New Midleton Distillery.
24cm x 40cm The Green Distillery was an Irish whiskey distillery which was established in Cork City, Ireland in 1796. In 1867, the distillery was purchased by the Cork Distilleries Company (CDC), in an amalgamation of five Cork distilleries.Production of whiskey at the distillery likely ceased soon afters its acquisition by the CDC.However, the distillery is known to have remained in use a bonded store by the Cork Distilleries Company for several years thereafter.In the mid-twentieth century, the distillery resumed operations as a gin distillery for a period of time, however, it has since been almost completely demolished. The distillery was notable for its use of an early continuous distillation apparatus, invented by the distillery's then co-owner, Joseph Shee. The distillery began life on 12 May 1796, when two distillers, Robert Allan and Denis Corcoran purchased a dwelling house and maltings on North York Street (now Thomas Davis Street) from Bartholomew Foley, a draper. The malthouse had formerly been owned by Thomas Wood, a maltster, in 1780. In 1802, the Allan and Corcoran are recorded as working a 762 gallon still. In the years that followed, the distillery seems to have changed hands several times. Around 1812, the business was being run by two brothers, Thomas and Joseph Shee, Benjamin Hodges, and some others.Thomas Shee acted as the distiller working a 201 gallon still, while Joseph acted a marketing agent based in London.Hodges and the others may have been silent partners who provided capital but nothing else, as their connection with the distillery soon disappeared. Output was recorded at 100,000 gallons in 1828.In June 1830, the Shees entered financial difficulties, and ownership passed to Joseph Shee. Joseph continued operations using capital provided by James Kiernan under a mortgage, while Thomas Shee remained on as a distiller.In 1833, excise records show that the distillery paid a duty charge of £26,716, which equated to about 160,000 gallons proof.By 1835, Kiernan took outright control of the distillery. When Kiernan died in December 1844, his will specified that the distillery should be put up for sale. It was purchased on 27 July 1845 by George Waters, who was previously a co-owner of Daly's Distillery on John Street, until the dissolution of the partnership following the death of one of the partners. Waters ran the distillery until his retirement around 1867, after which the distillery was purchased by the Cork Distilleries Company (CDC), in an amalgamation of five Cork distilleries. Under CDC, distilling ceased at the distillery in the 1880s, with production transferred to their nearby North Mall distillery. Subsequently, the Green Distillery was used as a bonded store for some time.However, in the mid-twentieth century, new equipment was installed in the Green Distillery, with production of gin occurring there for a period of time. According to Irish Distillers, who absorbed the Cork Distilleries Company in the 1960s, a warehouse on the site was used to store whiskey in bond until the 1980s.Since then, the distillery has been almost completely demolished, with only a small archway remaining. However, one of original pot stills is still in use, currently employed as an experimental still at the nearby New Midleton Distillery.Notability
The distillery was home to an early continuous distillation apparatus, was which installed and used at the distillery for almost twenty years. The apparatus, which the distiller's co-owner, Joseph Shee, patented in 1834, was similar to Jean‐Édouard Adam's 1801 design, and consisted of a four pot stills connected in series. Though thought to have been effective, the apparatus was not widely adopted. In particular, as a more efficient apparatus, the Coffey Still was patented by another Irish distiller, Aeneas Coffey, in 1830.Daly's Distillery was an Irish whiskey distillery which operated in Cork City, Ireland from around 1820 to 1869. In 1867, the distillery was purchased by the Cork Distilleries Company (CDC), in an amalgamation of five cork distilleries. Two years later, in 1869, as the smallest CDC distillery, Daly's Distillery ceased operations. In the years that followed its closure, some of the buildings became part of Shaw's Flour Mill, and Murphy's Brewery, with others continuing to be used as warehouses by Cork Distilleries Company for several years (though information is difficult to come by, their continued existence is mentioned in Alfred Barnard's 1887 account of the distilleries of the United Kingdom).History
In 1798, the firm of James Daly & Co. was established as a rectifying distillery and wine merchants at a premises on Blarney St., Cork. In 1820, this was relocated to 32 John Street.As some sources state that the John distillery was established in 1807, and it is known that a William Lyons ran a distillery on John Street in the early 1800s, it is possible that Daly purchased an existing distillery on John Street. In 1822, James Daly's nephew John Murray joined the partnership. In 1828, the distillery is reported to have an output of 87,874 gallons of spirit.However, in 1833, output of only 39,000 gallons per annum was reported, which was low compared with some of the Irish distillers of the era; for instance, at that time Murphy's Distillery in nearby Midleton, had an output of over 400,000 gallons per annum. On James Daly's death, in 1850, the partnership, which at that point had consisted of James Daly, Maurice Murray (John Murray's son) and George Waters, was dissolved, with Maurice Murray taking sole ownership of the distillery, which continued to trade as James Daly & Co. After leaving the partnership, George Waters went on to purchase and run the nearby Green distillery. In 1853, Murray rebuilt and significantly extended the distillery, expanding onto neighbouring streets. By the late 1860s, the distillery had grown to occupy 3 acres, consisting of a brewhouse, distillery and maltings on John Street; granaries on Leitrim Street; and eight bonded warehouses scattered across John Street, Leitrim Street and Watercourse Road.According to accounts from the time, whiskey from the distillery, some of which was aged for seven years or more, was mainly exported "to the colonies".In particular, it was said that in Australia the whiskey sold at a premium to other whiskeys. A well respected member of the Irish distilling industry at the time, the distillery's owner Maurice Murray, conducted significant correspondence with William Ewart Gladstone, the then British Chancellor of the Exchequer, on behalf of the Irish distillers, with regard to the duties placed on Irish whiskey. In 1867, Daly's Distillery, was absorbed into Cork Distilleries Company (CDC), in an amalgamation of five Cork distilleries. As the smallest of the five distilleries, Daly's closed soon after the amalgamation, in 1869. Following its closure, Maurice Murray is known to have continued to work for the CDC at the North Mall Distillery, along with his son Daly Murray. The main distillery buildings later became part of Shaw's Flour Mill, while other buildings were incorporated into the nearby Murphy's Brewery, which was run by relatives of James Murphy of the Midleton Distillery, who was the driving force behind the establishment of the Cork Distilleries Company. One of the distillery buildings, now named "the Mill", is still visible on 32 Lower John Street, Cork. -

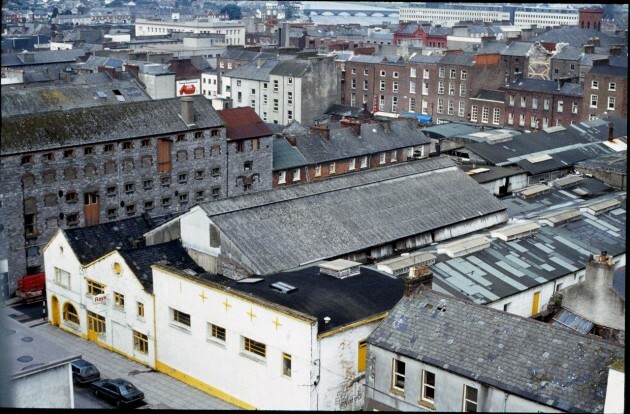
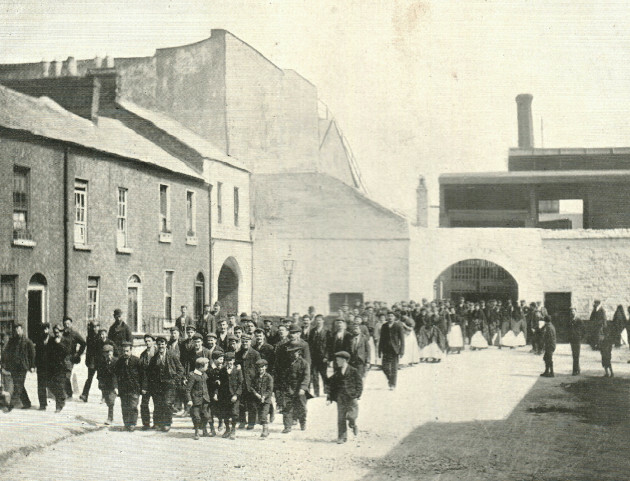
 47cm x 37cm LimerickFor much of the last century, and indeed for well over half of the present one, Limerick's importance was directly attributed to her three well-known bacon factories, namely, J. Matterson & Sons, Roches Street, established in 1816 by Mr. John Russell, a Cumberland man in conjunction with Mr. Matterson, using the method of curing then current in Berwick-on-Tweed. W.J. Shaw & Sons, founded in the year 1831 at Mulgrave Street by William John Shaw, a descendant of a County Down family, and O'Mara's bacon factory, Roches Street, which had its origin in Mungret Street some few years before 1839, when James O'Mara from Toomevara started curing bacon in the basement of his house there. Apparently, this basement business flourished, for in 1839 he moved to Roches Street to the premises it occupies today.About the middle of the last century, for some reason now difficult to fathom, Limerick bacon and especially Limerick hams, became well known for their excellent flavour throughout the English-speaking world. It is on record that Glasgow curers in an effort to produce hams equal in excellence to those of Limerick, imported Limerick workmen who were supposed to know all about the way in which the meat was turned out at home. Apparently, they did not bring secrets with them for their efforts were unsuccessful, There were also much larger bacon factories in parts of the British Isles; for instance, Belfast is reputed to have exported four times the number of hams produced in Limerick, and places like Glasgow and Liverpool had several factories producing very large quantities of bacon as well. None of them, however, quite matched' those produced in the three local factories for flavour and taste. O’MARA’S, MATTERSON’S, SHAW’S and Denny’s were the names that made Limerick famous for its bacon produce for 180 years – earning it the nickname ‘Pigstown’. The reputation of Limerick ham, the food culture that arose from a plentiful supply of cheap products, the story of the pork butchers, the pig buyers, the sounds of the city with factory horns signalling the call to work – all of these still resonate in Limerick in the memories of its citizens and former workers. A definitive account of this industry that operated at the centre of the city, supplied by the farms of rural county Limerick for over 180 years will be documented in a new book called Pigtown – A History of Limerick’s Bacon Industry. Ruth Guiry was commissioned to undertake the research under the guidance of Dr Maura Cronin from Mary Immaculate College and one of the 27 people she interviewed to understand the role the bacon factories had in Limerick was Joe Hayes. Joe Hayes started working in a bacon factory in 1962, aged 16 years old. He worked with his dad, and later on with his two sons until the factory closed in 1986. “When the factory closed, a group of us got our own little unit, we rented it, and produced our own sausages, puddings and things.” It was a huge part of Limerick’s social scene: four generations of Joe’s family worked in bacon factories, with uncles, sisters, brothers, sons and cousins all working in the factory at one time or another: “If one factory was caic, you wouldn’t have a problem getting a job in the other one. And he doesn’t mince his word when talking about the work they did. “They brought the pigs in, we killed the pigs, and prepared the bacon: that’s the way it was in the bacon factories.” When asked about if there were ever animal cruelty protests, he laughs at the idea.
47cm x 37cm LimerickFor much of the last century, and indeed for well over half of the present one, Limerick's importance was directly attributed to her three well-known bacon factories, namely, J. Matterson & Sons, Roches Street, established in 1816 by Mr. John Russell, a Cumberland man in conjunction with Mr. Matterson, using the method of curing then current in Berwick-on-Tweed. W.J. Shaw & Sons, founded in the year 1831 at Mulgrave Street by William John Shaw, a descendant of a County Down family, and O'Mara's bacon factory, Roches Street, which had its origin in Mungret Street some few years before 1839, when James O'Mara from Toomevara started curing bacon in the basement of his house there. Apparently, this basement business flourished, for in 1839 he moved to Roches Street to the premises it occupies today.About the middle of the last century, for some reason now difficult to fathom, Limerick bacon and especially Limerick hams, became well known for their excellent flavour throughout the English-speaking world. It is on record that Glasgow curers in an effort to produce hams equal in excellence to those of Limerick, imported Limerick workmen who were supposed to know all about the way in which the meat was turned out at home. Apparently, they did not bring secrets with them for their efforts were unsuccessful, There were also much larger bacon factories in parts of the British Isles; for instance, Belfast is reputed to have exported four times the number of hams produced in Limerick, and places like Glasgow and Liverpool had several factories producing very large quantities of bacon as well. None of them, however, quite matched' those produced in the three local factories for flavour and taste. O’MARA’S, MATTERSON’S, SHAW’S and Denny’s were the names that made Limerick famous for its bacon produce for 180 years – earning it the nickname ‘Pigstown’. The reputation of Limerick ham, the food culture that arose from a plentiful supply of cheap products, the story of the pork butchers, the pig buyers, the sounds of the city with factory horns signalling the call to work – all of these still resonate in Limerick in the memories of its citizens and former workers. A definitive account of this industry that operated at the centre of the city, supplied by the farms of rural county Limerick for over 180 years will be documented in a new book called Pigtown – A History of Limerick’s Bacon Industry. Ruth Guiry was commissioned to undertake the research under the guidance of Dr Maura Cronin from Mary Immaculate College and one of the 27 people she interviewed to understand the role the bacon factories had in Limerick was Joe Hayes. Joe Hayes started working in a bacon factory in 1962, aged 16 years old. He worked with his dad, and later on with his two sons until the factory closed in 1986. “When the factory closed, a group of us got our own little unit, we rented it, and produced our own sausages, puddings and things.” It was a huge part of Limerick’s social scene: four generations of Joe’s family worked in bacon factories, with uncles, sisters, brothers, sons and cousins all working in the factory at one time or another: “If one factory was caic, you wouldn’t have a problem getting a job in the other one. And he doesn’t mince his word when talking about the work they did. “They brought the pigs in, we killed the pigs, and prepared the bacon: that’s the way it was in the bacon factories.” When asked about if there were ever animal cruelty protests, he laughs at the idea.
They started at 8am and finished at 5.30 working a 40 hour week when the factory closed in 1986, but despite their work, the people who worked in factories often couldn’t afford to buy the expensive cuts of meat. After the expensive cuts were prepared, the offal, the spare ribs, the pigs’ heads would go to the poorer people. “The blood was used to make the pudding, the packet, the tripe was made off the belly. Everything was used off the pig, and it fed Limerick city.” It was a way of life down in Limerick, so when the factories closed, thousands of people working in a bacon factories were out of jobs, and thousands of families were affected. But it wasn’t the competition from big supermarkets that did it – it was free trade. The Danes, the French, the Dutch all started exporting their products here, and Limerick factories didn’t have the money to export to compete. “Michael O’Mara’s funeral was this week – he was the last of the bacon factory managers.” says Joe. “After the Limerick factory closed, he tried doing different bits and pieces, but nothing worked out for him, so he worked in a factory for a couple of years before retiring.” Joe Hayes himself is retired now, and when he buys his meat he gets it in a supermarket. “Meat is meat,” he says.”But if I see the tricolour flag, I’ll still buy it even if it’s dearer.” Pigtown - A History of Limerick’s Bacon Industry by Ruth Guiry is co-edited by Dr Maura Cronin and Jacqui Hayes.People still eat sausages and bacon – where do they think they come from?








