33cm x 57cm
In the winter of 1893, prospectors
Patrick (Paddy) Hannan,
Tom Flanagan, and Dan Shea were travelling to Mount Youle, when one of their horses cast a shoe. During the halt in their journey, the men noticed signs of gold in the area around the foot of what is now the Mount Charlotte gold mine, located on a small hill north of the current city, and decided to stay and investigate. On 17 June 1893, Hannan filed a Reward Claim, leading to hundreds of men swarming to the area in search of gold, and Kalgoorlie, originally called Hannan's Find, was born.

Hannan Street in September 1930; the Exchange Hotel is at the centre, with the Palace Hotel on the right.
The population of the town was 2,018 (1,516 males and 502 females) in 1898.
The mining of gold, along with other metals such as
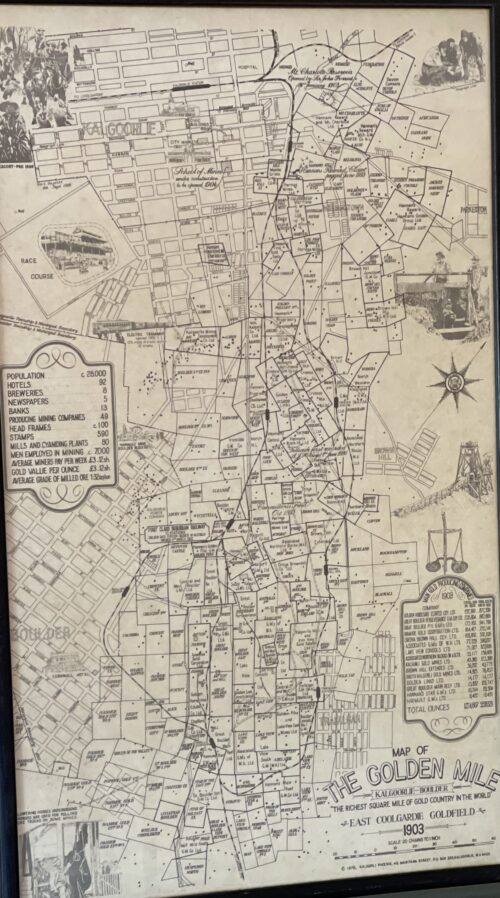
nickel, has been a major industry in Kalgoorlie ever since, and today employs about one-quarter of Kalgoorlie's workforce and generates a significant proportion of its income. The concentrated area of large gold mines surrounding the original Hannan's find is often referred to as the Golden Mile, and was sometimes referred to as the world's richest square mile of earth.
In 1901, the population of Kalgoorlie was 4,793 (3,087 males and 1,706 females) which increased to 6,790 (3,904 males and 2,886 females) by 1903.
The
3 ft 6 in (
1,067 mm) narrow-gauge
Government Eastern Goldfields Railway line reached
Kalgoorlie station in 1896, and the main named railway service from Perth was the overnight sleeper train
The Westland, which ran until the 1970s. In 1917, a
4 ft 8+1⁄2 in(
1,435 mm)
standard gauge railway line was completed, connecting Kalgoorlie to
Port Augusta,
South Australia, across 2,000 kilometres (1,243 mi) of desert, and consequently the rest of the eastern states. The
standardisation of the railway connecting Perth (which changed route from the narrow-gauge route) in 1968 completed the
Sydney–Perth railway, making rail travel from Perth to
Sydney possible; the
Indian Pacific rail service commenced soon after. During the 1890s, the Goldfields area boomed as a whole, with an area population exceeding 200,000, composed mainly of prospectors. The area gained a reputation for being a "wild west", notorious for its bandits and prostitutes. This rapid increase in population and claims of neglect by the state government in Perth led to the proposition of the new state of
Auralia, but with the sudden diaspora after the Gold Rush, these plans fell through.
Places, famous or infamous, for which Kalgoorlie is noted include its
water pipeline, designed by
C. Y. O'Connor and bringing in fresh water from
Mundaring Weir near Perth, its
Hay Street brothels, its
two-up school, the goldfields railway loopline, the Kalgoorlie Town Hall, the Paddy Hannan statue/drinking fountain, the
Super Pit, and Mount Charlotte lookout. Its main street is
Hannan Street, named after the town's founder. One of the infamous brothels also serves as a museum and is a major national attraction.
Paddy Hannan was the son of John Hannan and Bridget Lynch, and was baptised on 26 April 1840 in the town of
Quin, County Clare, Ireland. His baptismal record shows that his godparents (sponsors) were Margaret Lynch and John O'Brien. Many of the people in his family emigrated to Australia from 1852 onwards, and close ties were maintained. Two of Hannan's nieces would welcome Hannan into their house for the last years of his life.
Hannan emigrated to Australia when he was 22, arriving in Melbourne on 23 December 1862 aboard the
Henry Fernie from Liverpool. He is recorded in the passenger list as Pat Hannan, a labourer.
Prospecting success

Hannan's Western Australian miner's right, 1893
In 1893 in Western Australia, Hannan and his partners were the first to find gold near Mount Charlotte, less than 40 kilometres from the existing
Coolgardie Goldfields. Hannan,
Flanagan and
Shea were following a large number of prospectors who set out for a rumoured new prospect at Mount Youle.
One version of the story of the find has it that on the night of 14 June 1893, Hannan found gold in a gully. Not wanting to cause a rush, he concealed the find. During the night the trio moved one of their horses into the scrub. The following morning Hannan informed the main party they were going to stay behind to find their lost horse. After the main group moved off east, the three men started to pick up the gold and peg out their lease.
Amongst the various counter-claims to emerge over the years, one lively version of the story was told in 1909 by Fred Dugan (another prospector, who was present at the time) relating how Thomas Flanagan found the first nuggets, and covered his find with brushwood to conceal it until the following day.
By law, those finding "payable" gold were required to report the fact to the warden's office within seven days, so Hannan set off for Coolgardie to register their find, doing so on 17 June 1893.
It has been suggested that Hannan, rather than Flanagan or Shea, was chosen to officially register the claim because only he could read and write, but there is evidence that Flanagan was literate, since, in 1864, he had clearly signed the official death certificate of his brother John Flanagan, and had written his own place of residence at the time - White Hills (in Bendigo, Victoria, Australia).
The other possible reasons for Hannan going alone to the office at Coolgardie are set out by Martyn Webb,
who relates that:
The fact that Flanagan and Shea were able to secure another 100 ounces while Hannan was away registering their claim at Coolgardie might help to explain why Hannan was chosen ... simply because they were better at specking than he was – it needs good eyesight. On the other hand, since the journey was arduous and had to be done as quickly as possible, Hannan might have been chosen because, as Uren and others suggest, he was the youngest and the fittest of the three. … The most likely reason … was that he was the undisputed leader of the party.
— Webb, p. 103
Hannan registered the claim in Flanagan's name as well as his own. Within hours a stampede began. It was estimated that about 400 men were prospecting in the area within three days, and over 1,000 within a week.
Final years

Hannan's grave in Melbourne Central Cemetery, Section Y
In 1904, at the age of sixty-four, Hannan was granted an annual pension of £150 by the
Government of Western Australia.
Having searched for gold throughout his adult life, he did not cease his prospecting activities until after 1910, his seventieth year. At that time he went to live with two of his nieces in Fallon Street, Brunswick, Victoria (close to the city of Melbourne).
He died there in 1925 and was buried in Melbourne Central Cemetery, in the Catholic section, near the North Gate.
In 1993 his grave was restored by the citizens of Kalgoorlie, led by Tess Thomson, as a part of the celebration of the 100-year anniversary of the original find by Hannan, Flanagan and Shea.
Legacy

1929 statue of Paddy Hannan in Kalgoorlie, Western Australia
In memory of a man who is regarded as the founder of Kalgoorlie, the main street and a suburb in Kalgoorlie both bear Hannan's name, and in 1929 a statue of him by the sculptor John MacLeod
was erected there.
The city boasts several commemorative plaques to the three Irishmen, Hannan, Flanagan and Shea. A popular Irish pub at the
Burswood Entertainment Complex was also named after Hannan.
In Ireland there is a plaque dedicated to his memory opposite
Quin Abbey, Quin, County Clare,
and there is a bust with an explanatory dedication on display inside the DeValera Library in Ennis, County Clare.



















 62cm x 45cm
An absolute once off piece of Irish Memorabilia .We at the Irish Pub Emporium were so lucky to acquire from a private collector .These superb castiron road signs were commissioned by the Irish Free State in the late 1940s post and were initially the responsibility of the newly formed Irish Tourism Organisation -Fógra Failte (later to become Bord Failte and then Failte Ireland).
"The former '
62cm x 45cm
An absolute once off piece of Irish Memorabilia .We at the Irish Pub Emporium were so lucky to acquire from a private collector .These superb castiron road signs were commissioned by the Irish Free State in the late 1940s post and were initially the responsibility of the newly formed Irish Tourism Organisation -Fógra Failte (later to become Bord Failte and then Failte Ireland).
"The former '




















