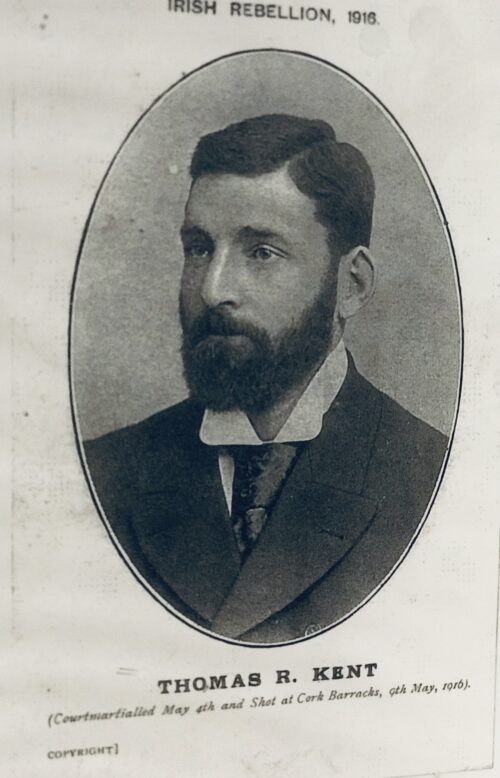
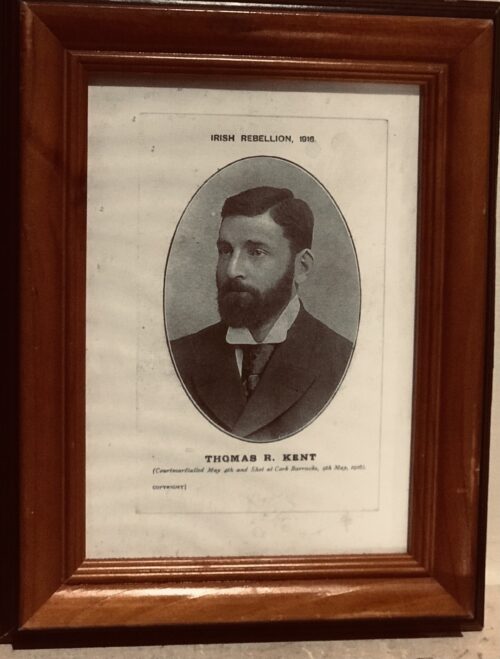
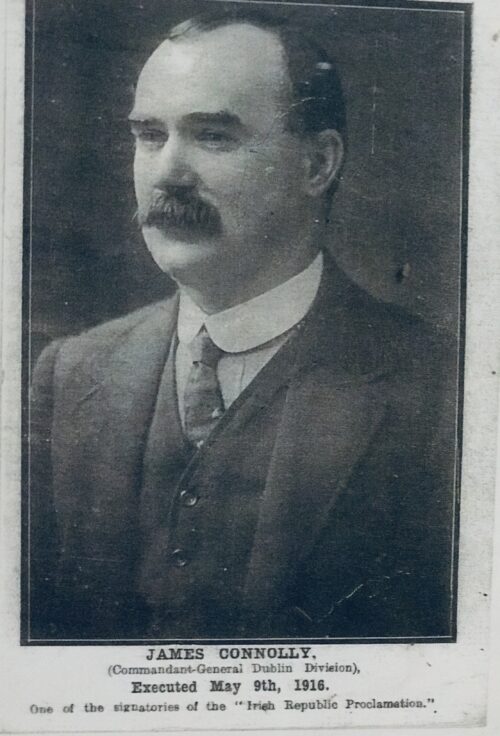
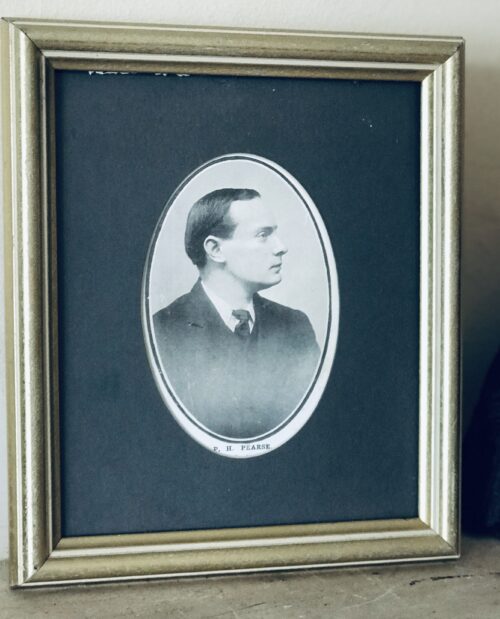
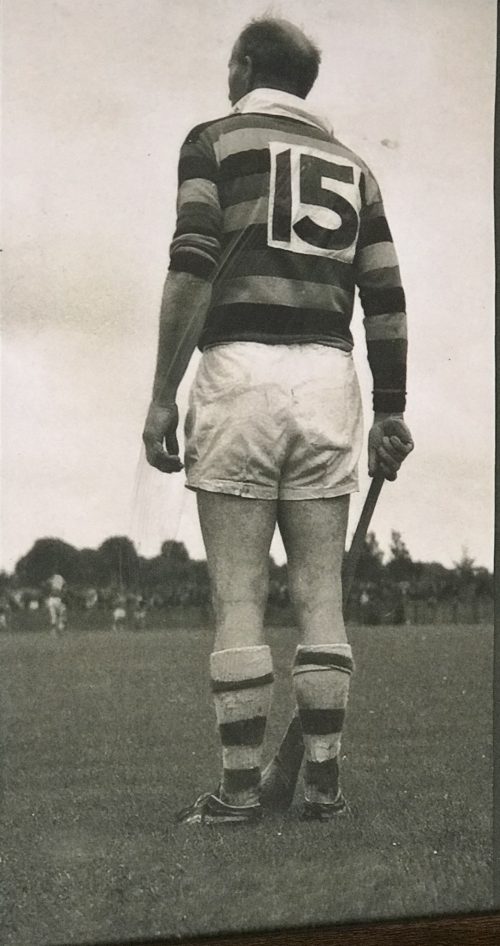
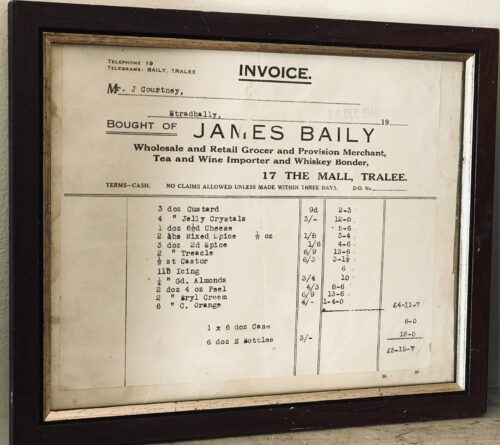
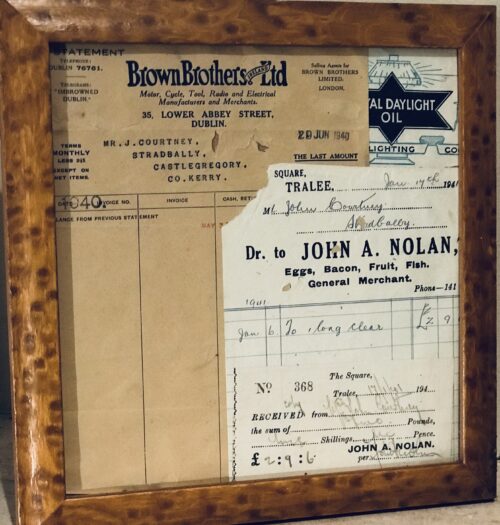
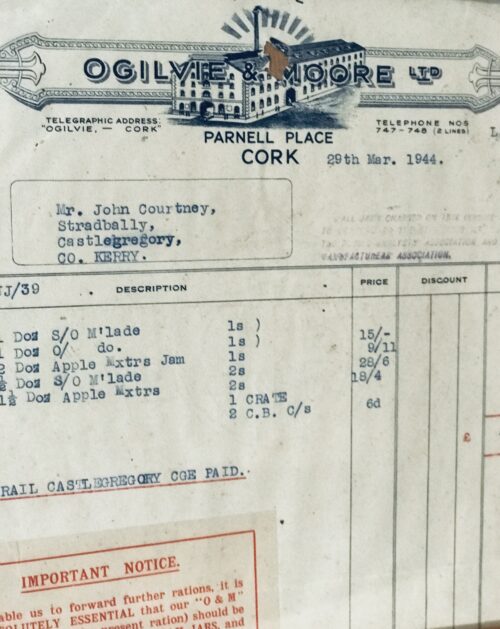
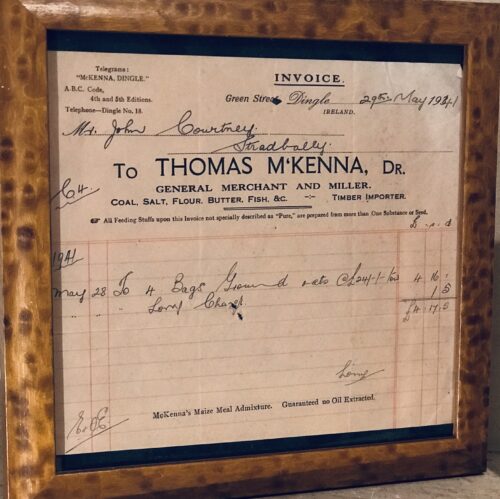
A very interesting Royal Munster Fusiliers Poster with the history and battle honours of the storied regiment.
Origins:Glin Co Limerick. Dimensions : 23cm x 32cm Glazed
The
Royal Munster Fusiliers was a
line infantry regiment of the
British Army from 1881 to 1922. It traced its origins to the
East India Company's Bengal European Regiment raised in 1652, which later became the
101st Regiment of Foot (Royal Bengal Fusiliers). The Royal Munster Fusiliers were formed in 1881 by the merger of the 101st Regiment of Foot and the
104th Regiment of Foot (Bengal Fusiliers). One of eight
Irish regiments raised largely in Ireland, it had its
home depot in
Tralee and served as the county regiment for
Cork,
Clare,
Limerick and
Kerry.
At its formation the regiment comprised two
regular and two
militia battalions.
The Royal Munster Fusiliers served in
India before the regiment fought in the
Second Boer War. Prior to the
First World War, the regiment's three militia battalions were converted into
reserve battalions, and a further six battalions were added to the regiment's establishment during the war. The regiment fought with distinction throughout the Great War and won three
Victoria Crosses by the conflict's conclusion in 1918.
Following establishment of the independent
Irish Free State in 1922, the five regiments that had their traditional recruiting grounds in the counties of the new state were disbanded and the Royal Munster Fusiliers ceased to be as a regiment on 31 July 1922.
History
Origins
Before the regiment was reformed as part of a reorganization of the British Army in 1881, the Royal Munster Fusilier's historic background went back as far as 1652 with the formation of the
Bengal European Regiment by the
Honourable East India Company.
This regiment would eventually become the
101st Regiment of Foot (Royal Bengal Fusiliers), or the
1st Bengal European Fusiliers. The East India Company formed the
104th Regiment of Foot (Bengal Fusiliers), or
2nd Bengal European Fusiliers, from this regiment in 1765. Both regiments, which were composed exclusively of white soldiers, not Indian
sepoys, played pivotal roles in the British conquest of India throughout the 18th and 19th centuries.
As well as the Royal Munster Fusilier's origins as part of the East India Company, the regiment's reserve battalions also traced their lineage to the
Militia of
Munster (namely the South Cork Light Infantry Militia, the Kerry Militia and the Royal Limerick County Militia, which became the 3rd, 4th and 5th Battalions, respectively).
While both the
fusilier regiments had originated and served as "European" regiments of the East India Company, they were transferred to the British Army in 1861 when the British Crown took control of the company's private army after the
Indian Mutiny of 1857.
Formation
The second half of the 19th Century saw the beginning of widespread reforms in the British Army which would eventually result in the formation of the Royal Munster Fusiliers. The first of these reforms saw the localisation of recruiting districts in Britain and Ireland between 1873 and 1874 under the
Cardwell Reforms. Five of the historic East India Company's European infantry battalions were given Irish territorial titles under the
Childers Reforms of 1881. The former Bengal Fusilier regiments were merged into a single regiment to become the 1st Battalion, Royal Munster Fusiliers and the 2nd Battalion, Royal Munster Fusiliers, while the 3rd, 4th and 5th Royal Munster Fusilier battalions were the
militia units.
The Reforms linked regiments to recruiting areas – which in case of the Royal Munster Fusiliers were the counties of
Clare,
Cork,
Kerry, and
Limerick. Militarily, the whole of Ireland was administered as a separate command with Command Headquarters at Parkgate (
Phoenix Park) Dublin, directly under the
War Office in London.
The regimental depot was located at
Ballymullen Barracks,
Tralee,
Co. Kerry.
Second Boer War

The 1st Battalion, Royal Munster Fusiliers in South Africa during the
Second Boer War, 1901.
Following the outbreak of the
Second Boer War in South Africa in October 1899, a number of regiments from areas containing large centres of population formed additional regular battalions. The Royal Munster Fusiliers were announced to be among those regiments set to form 3rd and 4th regular battalions in February 1900,
but they do not appear to have done so.
The 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers embarked for South Africa in 1899, and would serve there throughout the entire Second Boer War. Initially, the battalion took part in
Lord Robert's advance into the
Orange Free State. Following this, the battalion was attached to the
20th Brigade and fought at the
Battle of Belmont. With the beginning of the war's guerrilla warfare phase, the battalion took part in numerous pacification campaigns against the
Boers in
Pretoria and
Western Transvaal.
The 3rd (
Militia) Battalion, Royal Munster Fusiliers, formerly the South Cork Light Infantry, was embodied in early December 1899, and 435 officers and men embarked the
SS Sumatra for
South Africa on 23 February 1900.
The 2nd Battalion, Royal Munster Fusiliers, arrived in South Africa from India in December 1901 and served during the closing stages of the campaign, garrisoning
blockhouses in the northeast of the
Orange River Colony.
Following the end of the war in 1902 the 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers were sent to India. More than 520 officers and men left
Cape Town on the SS
Lake Manitoba in September 1902, arriving at
Bombay the following month and were then stationed at
Multan in
Punjab.
They would later take part in actions against the tribes of the
North-West Frontier in 1908. The 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers left South Africa soon after their sister battalion, and 450 officers and men returned to
Cork Harbour on the SS
Orient in early November 1902.
First World War
Prior to
the First World War, the Royal Munster Fusiliers were an established strength of two regular service and three reserve
battalions.
With the outbreak of war in August 1914, the need for further divisions resulted in the creation of a
New Army made up of volunteers who would serve for the duration of the war. This rapid expansion of the British Army would significantly increase the size of the Royal Munster Fusiliers who between their regular, reserve and volunteer battalions would have a combined strength of
11 raised battalions throughout the war.
At the outbreak of war the 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers was acting as a regular
garrison in
Rangoon, Burma, having being based in the
Far East since they had left
Fermoy in 1899 to fight in the Second Boer War.
The 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers were based at
Aldershot, England as part of the 1st Army Brigade of the
1st Infantry Division at the outbreak of war.
At the outbreak of war the Royal Munster Fusiliers three reserve battalions were all mobilised on 4 August 1914 and the regimental colours were sent to Tralee for safekeeping there until after the
Armistice
Regular Army
1914: Arrival in France and the Great Retreat

Men of the 2nd Battalion, Royal Munster Fusiliers in
Aldershot just prior to the outbreak of the First World War, 1914.
At the outbreak of war, the 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers was under strength, and reservists were called up from the regimental depots at
Tralee and
Fermoyamid much local cheering, to join the battalion at Aldershot which brought the battalion up to a strength of 27 officers and 971 other ranks before its departure to France on 13 August 1914.
As part of the
British Expeditionary Force, the 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers took part in the
Battle of Mons and on 27 August were given the arduous task of forming the rearguard to cover the retreat of the 1st Division in the face of the German advance, with instructions to retreat only if ordered. The Munster's made an epic stand in a renowned rearguard action during the
defence of Etreux, losing 9 officers and 87 other ranks killed while holding out,
with most of the rest of the battalion being surrounded and taken prisoner after running out of ammunition. The Munster's had stemmed the Germans, who were five or six times their strength, for over a day, allowing their division to escape. The loss on an entire battalion so early in the war was a disaster for the regiment. When the scattered battalion reassembled on 29 August it was down to a mere 5 officers and 196 other ranks. The remnants of the 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers were withdrawn to be recuperated before returning to battle, seeing action most notably at
Langemarck, Belgium on 22 October. By 5 November, recruits from home brought its strength up to over 800 men.
The battalion next saw action near
Zillebeke, Belgium on 12 November and helped to defend against the last great German effort in the
First Battle of Ypres. From 15 November, as snows began, they drove off further attacks, with
trench warfare now becoming dominant. In early December they aided in the evacuation of the
Ypres Benedictine Convent, whose occupants subsequently established
Kylemore Abbey in
Connemara, Ireland.
The battalion was moved south to the
Festubert sector in France, after a 36-hour march were ordered on 22 December to fill a gap by taking two lines of trenches.
There were 200 casualties in the first 10 minutes of heavy fire. Withdrawing in total exhaustion on the next day, many wounded drowned in water-filled shell holes. Throughout Christmas and New Year they were fully occupied maintaining the trenches. On 25 January, the Kaiser's birthday the Germans tried unsuccessfully to break through with terrific shellfire. There then followed three months of rebuilding and training the battalion when it numbered 28 officers and 700 other ranks in May. Only four of the officers were pre-war.
1915: Gallipoli and the Second Battle of Ypres
The 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers, who had been stationed in Burma, arrived back at
Avonmouth, UK in January 1915, and were entrained for
Coventrywhere it was assigned to the 86th Brigade of the
29th Division (United Kingdom). In March it sailed for the
Dardanelles, Turkey, when it numbered 28 officers and 1,002 other ranks.
Turkey had joined the
Central Powers's side in November 1914, the object of the landing on the Dardanelles peninsula was to open the
Dardanelles Strait in the
Battle of Gallipoli to enable
Allied relief convoys reach Russia. Aboard the
SS River Clyde, a converted collier with a capacity for over 2,000 men, they arrived on 25 April together with the 1st Battalion
The Royal Dublin Fusiliers and some companies of the
Royal Hampshires.
The SS River Clyde ran gently ashore, its exit bows facing the beach, for what was to be the troubled British
landing at Cape Helles. Small boats first carried companies of
Dubliners to the beach, however four hidden Turkish machine gun posts opened fire and decimated them. Lighters to the shore were roped together and two companies of Munsters poured out on to the bow's gangway but were also hit by machine gun fire, with one survivor saying they were 'literally slaughtered like rats in a trap'.
Many of the Munsters jumped from the gangway in the face of the withering fire and some drowned under their heavy equipment. Those men who continued down the gangway were mown down until all the boats and lighters were filled with dead and wounded. The ship's commanding officer, Captain
Edward Unwin, on being informed that they were not succeeding, replied "in British military tradition, offensives once begun are never called off". Unwin was awarded the
Victoria Cross for his actions that day.
At daybreak the next day, just three companies of Munsters, two companies of Hampshires and one company of Dubliners had made it to the shelter of some dunes. On 26 April they took fort
Sedd-el-Bahr overlooking the bay, charging and taking the village behind and held off several Turkish counterattacks. It was in this attack that the heroic actions of
William Cosgrove won the regiment's first
Victoria Cross. The 28 April saw a renewed attack in the
Battle for Krithia village, but the survivors of the landing were withdrawn by 29 April due to heavy losses and amalgamated with the surviving Dublin Fusiliers, to form the "Dubsters" battalion of 8 officers and 770 men.

The Last General Absolution of the Munsters at Rue du Bois administered
by their chaplain
Father Francis Gleeson
The Turks launched a renewed attack on the night of 1 May, with one Royal Munster Fusilier saying "they crept up in the dark into our trenches bayoneting our men before we knew it had begun. Bayoneting on both sides was terrible. At dawn the Turks were mowed down, and heaps of bodies and streams of blood remaining everywhere."
The battalion was reduced to 4 officers and 430 men, with the Turks attempting further attacks the following days only to be driven off once again, but the combined force of Munster and Dublin Fusiliers were down to 372 men by 11 April. Both the Munsters and Dubliners received new drafts on 29 May and became separate units again. By 4 June, the 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers numbered 40 officers and 500 other ranks, but many the new recruits were young and inexperienced. The Munsters withheld a further Turkish attack on 17 June, killing over 300 Turks. The arrival of further new drafts replenished the battalion to 23 officers and other 588 ranks. The Munsters took part in the Division's assault on 28 June which secured five trench lines. This provoked a general attack by the Turkish side along the Cape Helles front on 5 July, but the Turks were repulsed after suffering heavy losses.
The 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers participated in limited actions into the middle of July. A month's rest was promised on 15 July, but by 22 July the battalion were back in action, their strength around 500 of whom only 3 officers and 314 men remained from those who first landed on 25 April. The climax of the Gallipoli came with the Suvla attack on 21 August in the
Battle of Scimitar Hill, the Turks inflicted severe casualties. The unsuccessful attack cost the Munsters 3 officers and 79 men that day alone.
There was little further action other than holding front lines from September through to November, when the weather worsened. Late in November, gales swept over the peninsula, hundreds were drowned in the flooded trenches or from exposure and frostbite. Faced with defeat, the British decided to withdraw from the peninsula and the 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers was evacuated as it arrived, on the
River Clyde, sailing on 2 January 1916 for
Alexandria. From there it sailed with the rest of the 29th Division and arrived in France on 22 March. 3 years of warfare still remained for the battalion on the
Western Front, but the battalion had already suffered 45% of its total losses for the entire war at Gallipoli, and numbered just 24 officers and 287 men when disembarking in France.
While their sister battalion had been fighting on the shores of Gallipoli, the 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers had continued to serve on the Western Front and faced their first major action of 1915 in the
Second Battle of Ypres, during which they fought at the
Battle of Neuve Chapelle. The day before the attack was to be launched on 9 May, the battalion received
Absolution from their chaplain,
Father Francis Gleeson,an event which would become depicted in the famous "Rue du Bois" painting by
Fortunino Matania.
The British bombardment began at 5 a.m. and the Munsters then pressed forward with extraordinary bravery, with German fire sweeping no-mans-land. Some of the Munsters audaciously charging ahead through the German lines, briefly waving a green flag on its breastwork, then moved beyond until cut off by the British artillery bombardment that followed, which killed many men sheltering in shell craters. By 11 a.m. the 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers was withdrawn with only 3 officers and 200 men remaining, having lost 19 officers and 370 men killed, wounded or captured. The Munsters was one of only two British battalions to reach the German lines but they had suffered the regiment's highest loss of any one day of the war, with 11 officers and 140 men killed in action. It was an unsuccessful day for the British forces overall, with casualties exceeding 11,000, the devastating losses exposing the British forces weakness in artillery.
The summer was relatively quiet for the 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers after the battalion moved to the
Loos sector in June, with casualties in July and August occurring from shelling. With other forces being withdrawn to reinforce the
Gallipoli Campaign, no reinforcements or recruits arrived during the summer, keeping the battalion weak as the
Loos offensive began on 25 September 1915. The Munsters were held in reserve at first but they were soon tasked with holding the line and suffered over 200 casualties, leaving the battalion with around 350 soldiers all ranks, which further reduced to 250 by the time the battle died down on 13 October.
John Redmond M.P., the Irish leader, visited the battalion a month later on 15 November and promised to fill the depleted 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers with Irish recruits.
There followed three months of bitter winter weather in appalling trench conditions. New recruits began arriving over the winter, but in the relative inactivity, 65 men were hit by harassing random fire while 40 men went down with frostbite and trench fever in the
Arctic weather before the winter had ended.
1916: The Battle of the Somme
The 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers entered the front lines in France for the first time on 23 April 1916 at the
Somme sector, where they slowly built up strength to 26 officers and 476 men. On 29 May, the battalion was assigned to the
48th Brigade of the
16th (Irish) Division at
Béthune and they were reinforced by members from the disbanded 9th Royal Munster Fusiliers, bringing the Battalion up to full strength. The Munsters remained in the area of the
Loos salient into August with only intermittent casualties.
When the 16th Irish Division was ordered south of the Somme battlefield, the 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers entered the line facing the strategic town of Ginchy on 5 September, having suffered over 200 casualties by gas-shelling on the way. The Munsters took part in the ensuing attack and triumphant
capture of Ginchy by the 16th Division but at a high cost for the battalion which was reduced to 5 officers and 305 other ranks.
A London newspaper headlined
How the Irish took Ginchy – Splendid daring of the Irish troops
In May, the 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers received many of the personnel from the disbanded 9th Royal Munster Fusiliers, bringing it up to strength for the summer campaign. The battalions' first noteworthy operation was the carefully planned
Liévin raid on 25 June. It was during this action that Lieutenant
Arthur Batten-Pooll would win the regiment's second Victoria Cross, although losses were heavy for the battalion with 5 officers and 60 other ranks killed or wounded.
The 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers were transferred with its division down to the Somme sector in July for the opening of the
Battle of the Somme, entering the lines on 14 July and capturing its objectives two days later. The battalion repulsed the German counterattack on 18 July, with an officer and 26 men killed, 127 wounded and 50 gassed. The Munsters were in reserve until 20 August, when they entered the lines once again for steady fighting but ran into heavy off-target and ineffective British artillery bombardment, killing 4 officers and 29 other ranks. A continual toll of casualties made September a costly month for the battalion. After a month's break in October, the 2 Royal Munster Fusiliers returned to the Somme for maintenance duties, then went into the mud filled front-line trenches from 27 November onwards, with a steady stream of casualties from frostbite and raids continuing to the end of December. Throughout the Somme campaign the 2RMF retained its local and Irish character.
Following the end of their involvement in the Battle of the Somme, 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers was moved northwards to
Ypres in Belgium and also absorbed the remnants of the 8th Royal Munster Fusiliers on 23 November to bring it up to a strength of 48 officers and 1,069 men by 1 December. The Munsters spent Christmas 1916 in the trenches, but as the New Year arrived, an official report relates "as if by mutual consent both sides ceased fire a minute or two before the close of the old year. On the stroke of midnight the pipers tuned up and gave us
The Old Year out and the New Year in,
A Nation Once Again ,
God Save Ireland, and a few more songs of the old country, N.C.O.s and men joining lustily in the choruses".
1917: The Battle of Messines and Passchendaele

Old Royal Munster Fusiliers insignia
The Kaiser knows each Munster, by the Shamrock on his cap,
and the famous Bengal Tiger, ever ready for a scrap.
With all his big battalions, Prussian guards and grenadiers,
he feared to face the bayonets of the Munster Fusiliers.
— Verse from a song published during the Great War
Following a period of rest in January 1917, the 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers were returned the front trenches again in February at
Barleux, with the thawing weather resulting in extremely muddy conditions in the trenches. In March, the first major event was the German withdrawal from the old Somme battlefield to the newly constructed
Hindenburg Line. The battalion followed across the Somme, but was held up into May removing mines and booby-traps and repairing communications. The Munsters then moved to near
Nieuwpoort in
Flanders for an intended amphibious landing, with an impressive strength of 43 officers and 1,070 men, which was aborted following a surprise German attack on 10 July. The Munsters were then moved with their division to
Dunkirk for another amphibious attempt near
Zeebrugge to link with a land offensive through
Passchendaele, but this was also cancelled when the land offensive did not gain enough footing.
For the men of the 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers, rotating routine trench duties continued up to the middle of March with light casualties (2 officers and 20 men killed). The battalion rehearsed special training during April and May for the assault on the strategic
Messines Ridge. The Flanders offensive began at 3.10am on 7 June 1917 with the detonation of nineteen huge mines previously burrowed under the German lines. This was followed by the advance of the 16th Irish Division opposite the village of Wytschaete, to the right the
36th (Ulster) Division opposite the village of Messines, the largest ever concentration of Irish soldiers on a battlefield.
The 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers took all its objectives on schedule despite the loss of nearly all of its supporting tanks. The subsequent battle was a complete success militarily for the British, with the two Irish divisions showing great fortitude, advancing over two miles in a few days with minimal losses, which was exceptional by Western Front standards. The battalion was then relieved, and returned to the Ypres salient front section in August. Continuous rain turned the battlefront into a sea of mud causing a multitude of casualties and failure to take specific positions, reducing the battalion to 37 officers and 701 men. The Munsters were moved with its Division back south into France where it built up to 1,089 all ranks.
The 16th (Irish) Division, and with it the 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers, took up positions north of the main attack during the first
Battle of Cambrai which opened on 21 November with the use of over 450 British tanks. The Munsters advanced with such speed that only one enemy machine gun post was manned in time to open fire, which was taken with one loss. Considering the success of capturing a difficult objective without tank support and taking 170 prisoners, losses were light, and followed previously unsuccessful attempts by other units during the summer. The 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers final front tour of 1917 ended on 2 December when the Division was moved south to take over a French section.
By 6 November 1917, the 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers now numbered 20 officers and 630 other ranks when it arrived at "Irish Farm" in the Ypres salient. The ground was a quagmire full of water-logged shell-holes following four months of battle. It was to be the last British effort of the
Passchendaele campaign. The Munsters were to be one of two battalions leading the 1st Division's attack at 6 a.m. on 10 November. Weighed down with equipment, they waded waist deep through mud and water, initially taking all objectives within 45 minutes. Seeing the progress by the
Canadians on the right, the men of the Munsters pressed on. However, the
South Wales Borders advance had left a gap the Germans made use of to cut off most of the 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers who then had to fight their way back to the British lines. A roll call took three hours later saw only 7 officers and 240 other ranks present with 12 officers and 393 other ranks having become casualties. The battalion was moved out to
Brieulles for reforming for the rest of the year.
1918: The German Spring Offensive and Final Victory

Two officers of the 2nd Battalion, Royal Munster Fusiliers man a machine gun on the
Western Front.
From January through to March, the 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers was involved in various engagements in snow, frost and mud. By St. Patrick's Day 1918, it became clear that the Germans were gaining the initiative and their forecast "Big Move" was awaited.
By the end of January 1918 the 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers numbered 44 officers and 823 other ranks, and was then transferred to the 48th Brigade of the
16th (Irish) Division on 3 February near
Peronnewhere it entered the lines a week later. The division was now under the command of General
Hubert Gough.
The British front was at its lengthiest when the German
Spring Offensive opened with a devastating bombardment early on 21 March 1918, after which a fierce attack by fresh troops was launched. The 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers suffered badly from the shelling but held the Germans up all night, before they broke through and overwhelmed the Munsters who dashed to retreat, with some making it to a high ridge trench where they were driven out and retired to
Epehy by dark, fog having allowed the Germans to infiltrate easily. The next day the battalion was withdrawn to
Tincourt where the depleted 16th (Irish) Division was concentrated, with the 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers now numbering only 290 other ranks, from 629 the day before. On 22 March, the battalion crossed back over the
Somme at
Péronne.
By 25 March, the battalion had lost 27 officers and 550 men, as the rest tried to reform, holding off several attacks and near encirclements. The Munsters formed a 400-man column and attempted a night retreat, half reaching friendly positions next morning at
Hamel.
The 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers was fortunate to be in reserve as the Germans opened the offensive with a gas-bombardment. By the next day, the battalion was heavily engaged, the enemy using a new zigzag attack strategy. The battalion retaliated but was forced to withdraw and were quickly down to 7 officers and 450 men. There was then a general withdrawal across the Somme at
Peronne, by which time the battalion was reduced to just 290 men.
The German offensive had decimated the 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers to a shadow of its previous strength. The
16th (Irish) Division was reduced to cadre, having suffered the heaviest losses of any British division during the March retreat. The 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers was transferred to the
57th (2nd W.Lancs) Division which had not seen action since its arrival in February 1917.
The 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers was largely destroyed by the German offensive, losing 36 officers and 796 other ranks since 21 March. The battalion moved northwards to amalgamate with the equally hard hit 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers at
Inghem on 14 April, with the resulting unit numbering 28 officers and 896 other ranks. The 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers was then reduced to a training cadre of 11 officers, who left the 16th (Irish) Division to provide instruction for newly arrived
American Expeditionary Force.
In May, the 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers entered the lines again at
Gommecourt, a quiet sector during the summer. On 27 August, the battalion again entered the line for an attack near
Croisilles, taking enemy support trenches on the
Hindenburg Line in half an hour with minimal losses. This was followed by the assault of 2 September when
Martin Doyle won the battalion's third Victoria Cross on the
Drocourt–
Queant Line south of the river
Scarpe, with the battalion suffering 350 casualties. The battalion was then relieved and received replacements and trained in preparation for the assault on the
Cambrai to
St. Quentin line. With a 3,000-yard advance on 27 September,
Graincourt was captured by the Munsters. The Germans counter-attacked, recapturing many positions. The battalion remained under shellfire even behind the lines and was reduced to 7 officers and 261 men by 3 October.
The battalion supported the final attack of the
Battle of Cambrai on 8 October, which was found to be evacuated the following day as the Germans were in disorganised retreat. The 57th Division was then sent north to
Armentières, with the Munsters entering the line on 17 October, with no resistance.
Lille was captured the following day and the battalion provided a guard of honour for the French President's visit to the city on 21 October. The 1st Royal Munster Fusiliers was billeted in Lille until the
Armistice of 11 November 1918.
The 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers began reconstruction on 7 June 1918 when most of the 6th Royal Munster Fusiliers who had returned from
Palestine were transferred to the 2nd Royal Munster Fusiliers. The battalion made its last transfer to the 150th Brigade of the
50th Division at
Arras for the beginning of the
Hundred Days Offensive. On 1 October, the battalion was transported to
Épehy, which had been the scene of its Spring Offensive experiences back in March, and it was again ordered into the lines on 4 October, to capture
Le Catelet. The Munsters largely gaining their objective, however, they had to retire after encountering heavy counterattacks and failures elsewhere on the line, losing many 6st Royal Munster Fusiliers pre-war veterans who had survived Gallipoli. The 50th Division's advance was resumed on 10 October, and the battalion was reduced to 13 officers and 411 men by 16 October.
The
Battle of Épehy began on 18 October to drive the Germans behind the river, with the Munsters going in next day in fog surprising the Germans and taking many prisoner as well the objectives. The Munsters overran their objectives and were caught in another Division's barrage, with heavy losses experienced. They were then withdrawn and reorganised for what to be their final operation of the war, successfully taking a large area around
Haute Noyelles on 4 November, the number of prisoners taken indicative of the low state of German morale. After a counter-bombardment on 7 November the battalion was withdrawn for the remaining days up until the
Armistice.
New Army
With the outbreak of
World War I in August 1914 the immediate need for a considerable expansion of the British Army resulted in the formation of the
New Army under
Lord Kitchener. The war target was seventy divisions in all, the New Army to have thirty volunteer divisions separate and under Army Order 324, as additional from the Regular Army, with a planned period of service of at least three years. On 7 August a general
United Kingdom-wide call for 100,000 volunteers aged 19–30 was issued. The battalions were to be distinguished by the word 'Service' after their number.
The first new battalions were raised as units of Kitchener's new
K1 Army Group, which led to the formation of the 6th and 7th (Service) Battalions, Royal Munster Fusiliers which were a part of the
30th Brigade of the
10th (Irish) Division, under the command of General
Bryan Mahon. The 8th and 9th (Service) Battalions, Royal Munster Fusiliers followed as units of the
16th (Irish) Division's 47th and 48th Brigades, part of Kitchener's second new
K2 Army Group. The 16th Division was placed under the command of
Major General William Hickie.
In the course of the war heavy losses suffered by the two Regular Royal Munster Fusilier Battalions caused the new service battalions to be disbanded and absorbed in turn by the regular battalions, the last on 2 June 1918 when the 8th (Service) Battalion, Royal Munster Fusiliers was amalgamated with the 1st Battalion, Royal Munster Fusiliers.