-
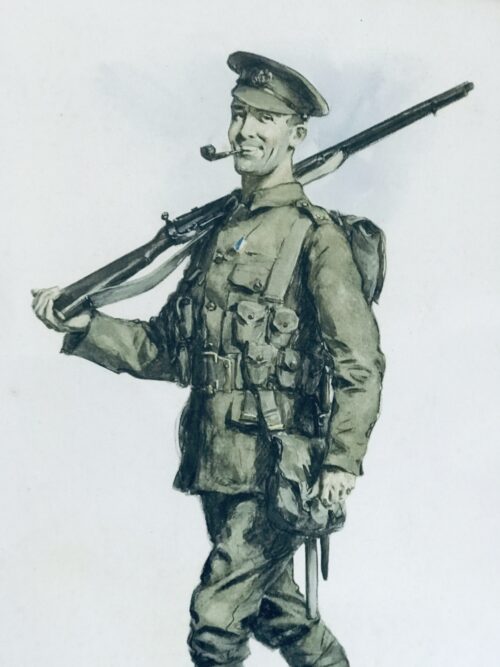

 Very charming and interesting print of a smiling Irish soldier with a pipe in his mouth on his way to the front during WW1.Over 200,000 Irishmen served with the British Armed Forces in WW1 with more than 50,000 fatalities .The song Its a long long way to Tipperary became the song of the War with even the Germans singing a translated version in their own trenches after Count John McCormack recorded the definitive version in 1914.This print hung in a pub in Tipperary owned by an old woman whose father and two uncles were all killed during the carnage of the First World War. Cahir Co Tipperary 52cm x 42cm
Very charming and interesting print of a smiling Irish soldier with a pipe in his mouth on his way to the front during WW1.Over 200,000 Irishmen served with the British Armed Forces in WW1 with more than 50,000 fatalities .The song Its a long long way to Tipperary became the song of the War with even the Germans singing a translated version in their own trenches after Count John McCormack recorded the definitive version in 1914.This print hung in a pub in Tipperary owned by an old woman whose father and two uncles were all killed during the carnage of the First World War. Cahir Co Tipperary 52cm x 42cm -
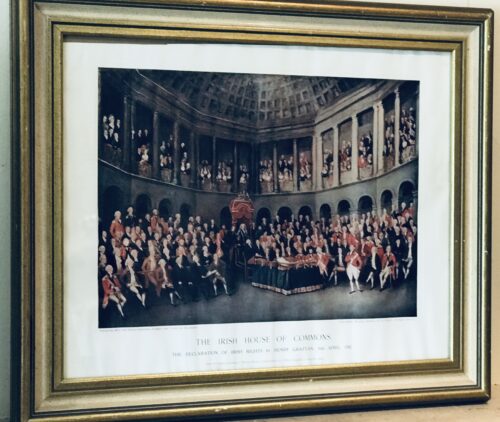
 50cm x 60cm Dublin This rare and historical print depicts Grattans Irish House of Parliament before it fell under the Act of Union in 1800,whereupon Ireland would be governed from London for the next 120 years.This parliament was loyal to the King and was essentially an assembly of the leading members of the landed gentry of the country,loyal to the Anglican Church of Ireland who owned most of the land.The politicians of the national party now fought for the Irish parliament, not with the intention of liberating the Catholic majority, but to set the Irish parliament free from constitutional bondage to the British Privy Council. By virtue of Poynings' Law, a statute of King Henry VII of England, all proposed Irish legislation had to be submitted to the Privy Council for its approval under the Great Seal of England before being passed by the Irish parliament. A bill so approved might be accepted or rejected, but not amended. More recent British Acts had further emphasised the complete dependence of the Irish parliament, and the appellate jurisdiction of the Irish House of Lords had also been annulled. Moreover, the British Houses claimed and exercised the power to legislate directly for Ireland without even the nominal concurrence of the parliament in Dublin. This was the constitution which William Molyneux and Swift had denounced, which Flood had attacked, and which Grattan was to destroy, becoming leaders of the Patriot movement.Calls for the legislative independence of Ireland at the Irish Volunteer Convention at Dungannon greatly influenced the decision of the government in 1782 to make concessions. It was through ranks of Volunteers drawn up outside the parliament house in Dublin that Grattan passed on 16 April 1782, amidst unparalleled popular enthusiasm, to move a declaration of the independence of the Irish parliament. "I found Ireland on her knees," Grattan exclaimed, "I watched over her with a paternal solicitude; I have traced her progress from injuries to arms, and from arms to liberty. Spirit of Swift, spirit of Molyneux, your genius has prevailed! Ireland is now a nation!" After a month of negotiation the claims of Ireland were conceded. The gratitude of his countrymen to Grattan was shown by a parliamentary grant of £100,000, which had to be reduced by half before he would accept it.Grattan then asked for the British House of Commons to reconfirm the London government's decision, and on 22 January 1783 the final Act was passed by parliament in London.However by 1800 under the Act of Union Grattans Parliament would cease to exist. From the perspective of Great Britain, the union was desirable because of the uncertainty that followed the Irish Rebellion of 1798 and the French Revolution of 1789; if Ireland adopted Catholic Emancipation, willingly or not, a Roman Catholic parliament could break away from Britain and ally with the French, while the same measure within a united kingdom would exclude that possibility. Also the Irish and British parliaments, when creating a regency during King George III's "madness", gave the Prince Regent different powers. These considerations led Great Britain to decide to attempt merger of the two kingdoms and their parliaments.The final passage of the Act in the Irish Parliament was achieved with substantial majorities, in part according to contemporary documents through bribery, namely the awarding of peerages and honours to critics to get their votes.Whereas the first attempt had been defeated in the Irish House of Commons by 109 votes against to 104 for, the second vote in 1800 produced a result of 158 to 115. Yet in the heart of every Irishman,whatever his politics or religion ,there is a tender spot for Grattans Parliament and the genius, wit and oratory of its members will live long and be cherished with pride by their countrymen.The present Bank of Ireland at College Green,directly adjacent to Trinity College Dublin,was the site of the old Parliament building ,built in1729 and the worlds first purpose built bi-cameral Parliament House .Architects were Pearce and James Gandon .
50cm x 60cm Dublin This rare and historical print depicts Grattans Irish House of Parliament before it fell under the Act of Union in 1800,whereupon Ireland would be governed from London for the next 120 years.This parliament was loyal to the King and was essentially an assembly of the leading members of the landed gentry of the country,loyal to the Anglican Church of Ireland who owned most of the land.The politicians of the national party now fought for the Irish parliament, not with the intention of liberating the Catholic majority, but to set the Irish parliament free from constitutional bondage to the British Privy Council. By virtue of Poynings' Law, a statute of King Henry VII of England, all proposed Irish legislation had to be submitted to the Privy Council for its approval under the Great Seal of England before being passed by the Irish parliament. A bill so approved might be accepted or rejected, but not amended. More recent British Acts had further emphasised the complete dependence of the Irish parliament, and the appellate jurisdiction of the Irish House of Lords had also been annulled. Moreover, the British Houses claimed and exercised the power to legislate directly for Ireland without even the nominal concurrence of the parliament in Dublin. This was the constitution which William Molyneux and Swift had denounced, which Flood had attacked, and which Grattan was to destroy, becoming leaders of the Patriot movement.Calls for the legislative independence of Ireland at the Irish Volunteer Convention at Dungannon greatly influenced the decision of the government in 1782 to make concessions. It was through ranks of Volunteers drawn up outside the parliament house in Dublin that Grattan passed on 16 April 1782, amidst unparalleled popular enthusiasm, to move a declaration of the independence of the Irish parliament. "I found Ireland on her knees," Grattan exclaimed, "I watched over her with a paternal solicitude; I have traced her progress from injuries to arms, and from arms to liberty. Spirit of Swift, spirit of Molyneux, your genius has prevailed! Ireland is now a nation!" After a month of negotiation the claims of Ireland were conceded. The gratitude of his countrymen to Grattan was shown by a parliamentary grant of £100,000, which had to be reduced by half before he would accept it.Grattan then asked for the British House of Commons to reconfirm the London government's decision, and on 22 January 1783 the final Act was passed by parliament in London.However by 1800 under the Act of Union Grattans Parliament would cease to exist. From the perspective of Great Britain, the union was desirable because of the uncertainty that followed the Irish Rebellion of 1798 and the French Revolution of 1789; if Ireland adopted Catholic Emancipation, willingly or not, a Roman Catholic parliament could break away from Britain and ally with the French, while the same measure within a united kingdom would exclude that possibility. Also the Irish and British parliaments, when creating a regency during King George III's "madness", gave the Prince Regent different powers. These considerations led Great Britain to decide to attempt merger of the two kingdoms and their parliaments.The final passage of the Act in the Irish Parliament was achieved with substantial majorities, in part according to contemporary documents through bribery, namely the awarding of peerages and honours to critics to get their votes.Whereas the first attempt had been defeated in the Irish House of Commons by 109 votes against to 104 for, the second vote in 1800 produced a result of 158 to 115. Yet in the heart of every Irishman,whatever his politics or religion ,there is a tender spot for Grattans Parliament and the genius, wit and oratory of its members will live long and be cherished with pride by their countrymen.The present Bank of Ireland at College Green,directly adjacent to Trinity College Dublin,was the site of the old Parliament building ,built in1729 and the worlds first purpose built bi-cameral Parliament House .Architects were Pearce and James Gandon . The Irish House of Commons by Francis Wheatley (1780) shows Grattan (standing on right in red jacket) addressing the House.
The Irish House of Commons by Francis Wheatley (1780) shows Grattan (standing on right in red jacket) addressing the House. -
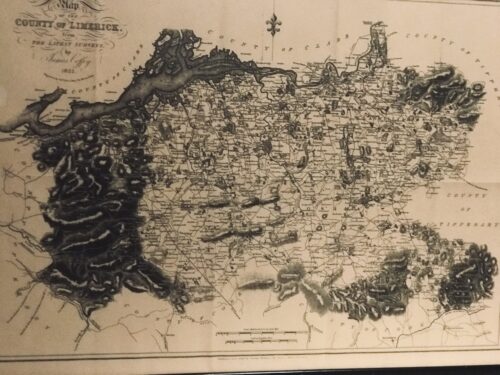
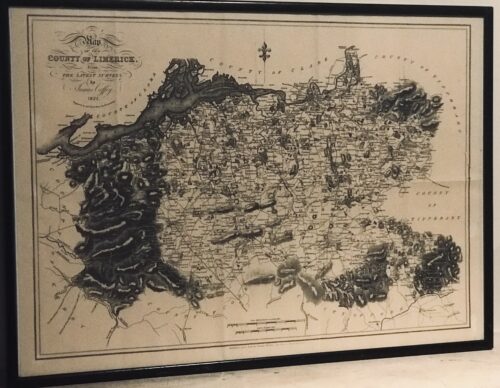 Very interesting map of Co Limerick from the 1825 surveys by the well known cartographer James Coffey.From the Latest Surveys. By James Coffey. 1825. Engraved by Sidney Hall, Bury Street, Bloomsbury. Published and sold by George McKern, 106, George Street, Limerick. Scale in Irish and English Miles. Framed and glazed. Bruree Co Limerick 45cm x 60cm
Very interesting map of Co Limerick from the 1825 surveys by the well known cartographer James Coffey.From the Latest Surveys. By James Coffey. 1825. Engraved by Sidney Hall, Bury Street, Bloomsbury. Published and sold by George McKern, 106, George Street, Limerick. Scale in Irish and English Miles. Framed and glazed. Bruree Co Limerick 45cm x 60cm -
 Exquisitely presented Limerick Soviet of 1919 Historical Display. Origins: Limerick City Dimensions: 72cm x 44cm Glazed The Limerick Soviet was a self-declared Irish soviet that existed from 15 to 27 April 1919 in County Limerick, Ireland. At the beginning of the Irish War of Independence, a general strike was organised by the Limerick Trades and Labour Council, as a protest against the British Army's declaration of a "Special Military Area" under the Defence of the Realm Act, which covered most of Limerick city and a part of the county. The soviet ran the city for the period, printed its own money and organised the supply of food. The Limerick Soviet was one of a number of Irish soviets declared between 1919 and 1923. From January 1919 the Irish War of Independence developed as a guerrilla conflict between the Irish Republican Army (IRA) (backed by Sinn Féin's Dáil Éireann), and the British government. On 6 April 1919 the IRA tried to liberate Robert Byrne, who was under arrest by the Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC) police in a hospital, being treated for the effects of a hunger strike. In the rescue attempt Constable Martin O'Brien was fatally wounded and another policeman was seriously injured. Byrne was also wounded and died later on the same day. In response, on 9 April British Army Brigadier Griffin declared the city to be a Special Military Area, with RIC permits required for all wanting to enter and leave the city as of Monday 14 April.British Army troops and armoured vehicles were deployed in the city. On Friday 11 April a meeting of the United Trades and Labour Council, to which Byrne had been a delegate, took place. At that meeting Irish Transport and General Workers' Union (ITGWU) representative Sean Dowling proposed that the trade unions take over Town Hall and have meetings there, but the proposal was not voted on. On Saturday 12 April the ITGWU workers in the Cleeve's factory in Lansdowne voted to go on strike. On Sunday 13 April, after a twelve-hour discussion and lobbying of the delegates by workers, a general strike was called by the city's United Trades and Labour Council. Responsibility for the direction of the strike was devolved to a committee that described itself as a soviet as of 14 April.The committee had the example of the Dublin general strike of 1913 and "soviet" (meaning a self-governing committee) had become a popular term after 1917 from the soviets that had led to the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic. A transatlantic air race was being organised from Bawnmore in County Limerick at the same time, but was cancelled. The assembled journalists from England and America took up the story of an Irish soviet and interviewed the organisers. The Trades Council chairman John Cronin was described as the "father of the baby Soviet." Ruth Russell of the Chicago Tribune remarked on the religiosity of the strike committee, observed "the bells of the nearby St. Munchin's Church tolled the Angelus and all the red-badged guards rose and blessed themselves." The Sinn Féin Mayor of Limerick, Phons O'Mara told Russell there is no prospect of socialism, as "There can't be, the people here are Catholics." The general strike was extended to a boycott of the troops. A special strike committee was set up to print their own money, control food prices and publish newspapers. The businesses of the city accepted the strike currency. Outside Limerick there was some sympathy in Dublin, but not in the main Irish industrial area around Belfast. The National Union of Railwaymen did not help. The strike committee organised food and fuel supplies, printed its own money based on the British shilling, and published its own newspaper called 'The Worker's Bulletin'Cinemas opened with the sign “Working under authority of the strike committee” posted. Local newspapers were allowed to publish once a week as long as they had the caption "Published by Permission of the Strike Committee". On 21 April 'The Worker's Bulletin' remarked that "A new and perfect system of organisation has been worked out by a clever and gifted mind, and ere long we shall show the world what Irish workers are capable of doing when left to their own resources." On Easter Monday 1919, the newspaper stated "The strike is a worker's strike and is no more Sinn Féin than any other strike." Liam Cahill argues "The soviet attitude to private property was essentially pragmatic. So long as shopkeepers were willing to act under the soviet's dictates, there was no practical reason to commandeer their premises."While the strike was described by some as a revolution, Cahill adds that: "In the end the soviet was basically an emotional and spontaneous protest on essentially nationalist and humanitarian grounds, rather than anything based on socialist or even trade union aims." After two weeks the Sinn Féin Lord Mayor of Limerick, Phons O'Mara, and the Catholic bishop Denis Hallinan called for the strike to end, and the Strike Committee issued a proclamation on 27 April 1919 stating that the strike was over. Origins : Limerick Dimensions : 72cm x 44cm 4kg
Exquisitely presented Limerick Soviet of 1919 Historical Display. Origins: Limerick City Dimensions: 72cm x 44cm Glazed The Limerick Soviet was a self-declared Irish soviet that existed from 15 to 27 April 1919 in County Limerick, Ireland. At the beginning of the Irish War of Independence, a general strike was organised by the Limerick Trades and Labour Council, as a protest against the British Army's declaration of a "Special Military Area" under the Defence of the Realm Act, which covered most of Limerick city and a part of the county. The soviet ran the city for the period, printed its own money and organised the supply of food. The Limerick Soviet was one of a number of Irish soviets declared between 1919 and 1923. From January 1919 the Irish War of Independence developed as a guerrilla conflict between the Irish Republican Army (IRA) (backed by Sinn Féin's Dáil Éireann), and the British government. On 6 April 1919 the IRA tried to liberate Robert Byrne, who was under arrest by the Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC) police in a hospital, being treated for the effects of a hunger strike. In the rescue attempt Constable Martin O'Brien was fatally wounded and another policeman was seriously injured. Byrne was also wounded and died later on the same day. In response, on 9 April British Army Brigadier Griffin declared the city to be a Special Military Area, with RIC permits required for all wanting to enter and leave the city as of Monday 14 April.British Army troops and armoured vehicles were deployed in the city. On Friday 11 April a meeting of the United Trades and Labour Council, to which Byrne had been a delegate, took place. At that meeting Irish Transport and General Workers' Union (ITGWU) representative Sean Dowling proposed that the trade unions take over Town Hall and have meetings there, but the proposal was not voted on. On Saturday 12 April the ITGWU workers in the Cleeve's factory in Lansdowne voted to go on strike. On Sunday 13 April, after a twelve-hour discussion and lobbying of the delegates by workers, a general strike was called by the city's United Trades and Labour Council. Responsibility for the direction of the strike was devolved to a committee that described itself as a soviet as of 14 April.The committee had the example of the Dublin general strike of 1913 and "soviet" (meaning a self-governing committee) had become a popular term after 1917 from the soviets that had led to the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic. A transatlantic air race was being organised from Bawnmore in County Limerick at the same time, but was cancelled. The assembled journalists from England and America took up the story of an Irish soviet and interviewed the organisers. The Trades Council chairman John Cronin was described as the "father of the baby Soviet." Ruth Russell of the Chicago Tribune remarked on the religiosity of the strike committee, observed "the bells of the nearby St. Munchin's Church tolled the Angelus and all the red-badged guards rose and blessed themselves." The Sinn Féin Mayor of Limerick, Phons O'Mara told Russell there is no prospect of socialism, as "There can't be, the people here are Catholics." The general strike was extended to a boycott of the troops. A special strike committee was set up to print their own money, control food prices and publish newspapers. The businesses of the city accepted the strike currency. Outside Limerick there was some sympathy in Dublin, but not in the main Irish industrial area around Belfast. The National Union of Railwaymen did not help. The strike committee organised food and fuel supplies, printed its own money based on the British shilling, and published its own newspaper called 'The Worker's Bulletin'Cinemas opened with the sign “Working under authority of the strike committee” posted. Local newspapers were allowed to publish once a week as long as they had the caption "Published by Permission of the Strike Committee". On 21 April 'The Worker's Bulletin' remarked that "A new and perfect system of organisation has been worked out by a clever and gifted mind, and ere long we shall show the world what Irish workers are capable of doing when left to their own resources." On Easter Monday 1919, the newspaper stated "The strike is a worker's strike and is no more Sinn Féin than any other strike." Liam Cahill argues "The soviet attitude to private property was essentially pragmatic. So long as shopkeepers were willing to act under the soviet's dictates, there was no practical reason to commandeer their premises."While the strike was described by some as a revolution, Cahill adds that: "In the end the soviet was basically an emotional and spontaneous protest on essentially nationalist and humanitarian grounds, rather than anything based on socialist or even trade union aims." After two weeks the Sinn Féin Lord Mayor of Limerick, Phons O'Mara, and the Catholic bishop Denis Hallinan called for the strike to end, and the Strike Committee issued a proclamation on 27 April 1919 stating that the strike was over. Origins : Limerick Dimensions : 72cm x 44cm 4kg -

 Superb vintage WW1 recruitment poster imploring the young men of Ireland to join the British Army.The poster depicts a lone piper with the famous mascot of the Royal Irish Regiment ,an Irish Wolfhound. 47cm x 38cm Nenagh Co TipperaryThe British Army was a volunteer force when war broke out in 1914, and within weeks thousands of Irishmen had signed up to serve 'King and Country'. Ireland had a strong military tradition in the British armed forces, dating back to at least the early 1500s, and when war was declared on August 4, 1914, there were some 20,000 Irishmen already serving from a total army strength of some 247,000. In addition, there were another 30,000 in the first-line reserve, from a total of 145,000. But more were quickly needed. Secretary for War Lord Kitchener told the British cabinet that it would be a three-year conflict requiring at least one million men, meaning a recruitment drive was immediately undertaken. Posters quickly appeared across the country, focused on attracting men from all background Some appealed to a sense of duty and honour, but appeared to be aimed at British-born nationals rather than Irishmen.
Superb vintage WW1 recruitment poster imploring the young men of Ireland to join the British Army.The poster depicts a lone piper with the famous mascot of the Royal Irish Regiment ,an Irish Wolfhound. 47cm x 38cm Nenagh Co TipperaryThe British Army was a volunteer force when war broke out in 1914, and within weeks thousands of Irishmen had signed up to serve 'King and Country'. Ireland had a strong military tradition in the British armed forces, dating back to at least the early 1500s, and when war was declared on August 4, 1914, there were some 20,000 Irishmen already serving from a total army strength of some 247,000. In addition, there were another 30,000 in the first-line reserve, from a total of 145,000. But more were quickly needed. Secretary for War Lord Kitchener told the British cabinet that it would be a three-year conflict requiring at least one million men, meaning a recruitment drive was immediately undertaken. Posters quickly appeared across the country, focused on attracting men from all background Some appealed to a sense of duty and honour, but appeared to be aimed at British-born nationals rather than Irishmen. -

 Limited Edition no 17/200 of the Republican Bulletin as issued by the Anti Treaty Side during the Irish Civil War.These pamphlets were distributed to the general public and sold at 1p per edition. 32cm x 54cm Limerick The Irish Civil War (28 June 1922 – 24 May 1923) was a conflict that followed the Irish War of Independence and accompanied the establishment of the Irish Free State, an entity independent from the United Kingdom but within the British Empire. The civil war was waged between two opposing groups, the pro-treaty Provisional Government and the anti-treaty Irish Republican Army (IRA), over the Anglo-Irish Treaty. The forces of the Provisional Government (which became the Free State in December 1922) supported the Treaty, while the anti-treaty opposition saw it as a betrayal of the Irish Republic (which had been proclaimed during the Easter Rising). Many of those who fought on both sides in the conflict had been members of the IRA during the War of Independence. The Civil War was won by the pro-treaty Free State forces, who benefited from substantial quantities of weapons provided by the British Government. The conflict may have claimed more lives than the War of Independence that preceded it, and left Irish society divided and embittered for generations. Today, two of the main political parties in the Republic of Ireland, Fine Gael and Fianna Fáil, are direct descendants of the opposing sides of the war.
Limited Edition no 17/200 of the Republican Bulletin as issued by the Anti Treaty Side during the Irish Civil War.These pamphlets were distributed to the general public and sold at 1p per edition. 32cm x 54cm Limerick The Irish Civil War (28 June 1922 – 24 May 1923) was a conflict that followed the Irish War of Independence and accompanied the establishment of the Irish Free State, an entity independent from the United Kingdom but within the British Empire. The civil war was waged between two opposing groups, the pro-treaty Provisional Government and the anti-treaty Irish Republican Army (IRA), over the Anglo-Irish Treaty. The forces of the Provisional Government (which became the Free State in December 1922) supported the Treaty, while the anti-treaty opposition saw it as a betrayal of the Irish Republic (which had been proclaimed during the Easter Rising). Many of those who fought on both sides in the conflict had been members of the IRA during the War of Independence. The Civil War was won by the pro-treaty Free State forces, who benefited from substantial quantities of weapons provided by the British Government. The conflict may have claimed more lives than the War of Independence that preceded it, and left Irish society divided and embittered for generations. Today, two of the main political parties in the Republic of Ireland, Fine Gael and Fianna Fáil, are direct descendants of the opposing sides of the war. -
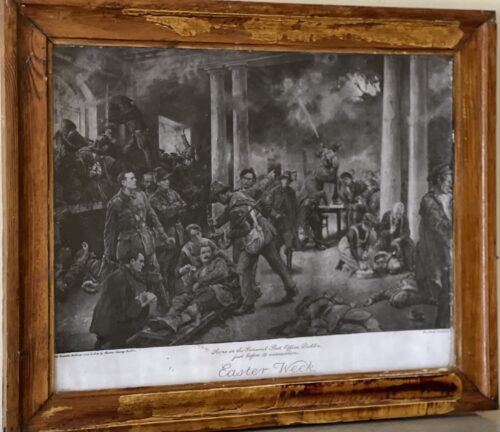
 40cm x 50cm Dublin The Easter Rising (Irish: Éirí Amach na Cásca), also known as the Easter Rebellion, was an armed insurrection in Ireland during Easter Week in April 1916. The Rising was launched by Irish republicans against British rule in Ireland with the aim of establishing an independent Irish Republic while the United Kingdom was fighting the First World War. It was the most significant uprising in Ireland since the rebellion of 1798 and the first armed conflict of the Irish revolutionary period. Sixteen of the Rising's leaders were executed from May 1916. The nature of the executions, and subsequent political developments, ultimately contributed to an increase in popular support for Irish independence. Organised by a seven-man Military Council of the Irish Republican Brotherhood, the Rising began on Easter Monday, 24 April 1916 and lasted for six days. Members of the Irish Volunteers, led by schoolmaster and Irish language activist Patrick Pearse, joined by the smaller Irish Citizen Army of James Connolly and 200 women of Cumann na mBan, seized strategically important buildings in Dublin and proclaimed the Irish Republic. The British Army brought in thousands of reinforcements as well as artillery and a gunboat. There was street fighting on the routes into the city centre, where the rebels slowed the British advance and inflicted many casualties. Elsewhere in Dublin, the fighting mainly consisted of sniping and long-range gun battles. The main rebel positions were gradually surrounded and bombarded with artillery. There were isolated actions in other parts of Ireland; Volunteer leader Eoin MacNeill had issued a countermand in a bid to halt the Rising, which greatly reduced the number of rebels who mobilised. With much greater numbers and heavier weapons, the British Army suppressed the Rising. Pearse agreed to an unconditional surrender on Saturday 29 April, although sporadic fighting continued briefly. After the surrender, the country remained under martial law. About 3,500 people were taken prisoner by the British and 1,800 of them were sent to internment camps or prisons in Britain. Most of the leaders of the Rising were executed following courts-martial. The Rising brought physical force republicanism back to the forefront of Irish politics, which for nearly fifty years had been dominated by constitutional nationalism. Opposition to the British reaction to the Rising contributed to changes in public opinion and the move toward independence, as shown in the December 1918 election in Ireland which was won by the Sinn Féin party, which convened the First Dáil and declared independence. Of the 485 people killed, 260 were civilians, 143 were British military and police personnel, and 82 were Irish rebels, including 16 rebels executed for their roles in the Rising. More than 2,600 people were wounded. Many of the civilians were killed or wounded by British artillery fire or were mistaken for rebels. Others were caught in the crossfire during firefights between the British and the rebels. The shelling and resulting fires left parts of central Dublin in ruins.
40cm x 50cm Dublin The Easter Rising (Irish: Éirí Amach na Cásca), also known as the Easter Rebellion, was an armed insurrection in Ireland during Easter Week in April 1916. The Rising was launched by Irish republicans against British rule in Ireland with the aim of establishing an independent Irish Republic while the United Kingdom was fighting the First World War. It was the most significant uprising in Ireland since the rebellion of 1798 and the first armed conflict of the Irish revolutionary period. Sixteen of the Rising's leaders were executed from May 1916. The nature of the executions, and subsequent political developments, ultimately contributed to an increase in popular support for Irish independence. Organised by a seven-man Military Council of the Irish Republican Brotherhood, the Rising began on Easter Monday, 24 April 1916 and lasted for six days. Members of the Irish Volunteers, led by schoolmaster and Irish language activist Patrick Pearse, joined by the smaller Irish Citizen Army of James Connolly and 200 women of Cumann na mBan, seized strategically important buildings in Dublin and proclaimed the Irish Republic. The British Army brought in thousands of reinforcements as well as artillery and a gunboat. There was street fighting on the routes into the city centre, where the rebels slowed the British advance and inflicted many casualties. Elsewhere in Dublin, the fighting mainly consisted of sniping and long-range gun battles. The main rebel positions were gradually surrounded and bombarded with artillery. There were isolated actions in other parts of Ireland; Volunteer leader Eoin MacNeill had issued a countermand in a bid to halt the Rising, which greatly reduced the number of rebels who mobilised. With much greater numbers and heavier weapons, the British Army suppressed the Rising. Pearse agreed to an unconditional surrender on Saturday 29 April, although sporadic fighting continued briefly. After the surrender, the country remained under martial law. About 3,500 people were taken prisoner by the British and 1,800 of them were sent to internment camps or prisons in Britain. Most of the leaders of the Rising were executed following courts-martial. The Rising brought physical force republicanism back to the forefront of Irish politics, which for nearly fifty years had been dominated by constitutional nationalism. Opposition to the British reaction to the Rising contributed to changes in public opinion and the move toward independence, as shown in the December 1918 election in Ireland which was won by the Sinn Féin party, which convened the First Dáil and declared independence. Of the 485 people killed, 260 were civilians, 143 were British military and police personnel, and 82 were Irish rebels, including 16 rebels executed for their roles in the Rising. More than 2,600 people were wounded. Many of the civilians were killed or wounded by British artillery fire or were mistaken for rebels. Others were caught in the crossfire during firefights between the British and the rebels. The shelling and resulting fires left parts of central Dublin in ruins. -
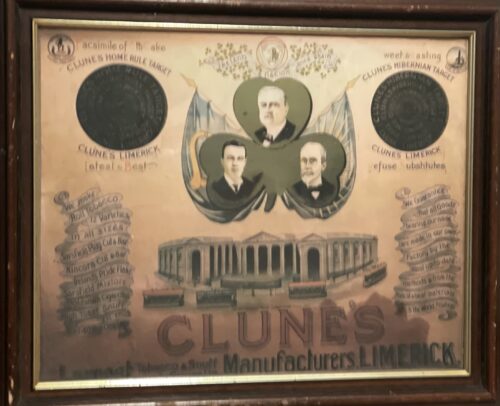
 51cm x 63cm In 1929, Limerick city was the home to two large of tobacco factories Spillane’s and Clune’s who imported tobacco from the United States, Egypt and Turkey as well as locally grown tobacco to produce their famed products. Spillane’s Tobacco Factory on Sarsfield Street was started by John Spillane in 1829 and was known as ‘The House of Garryowen’. A hundred years later they were employing a hundred people. The famous Garryowen plug formed 80 per cent of the factories output while they had other products including Popular and Treaty bar plugs, Hazel Nut plug, Special Flake, Handy Cut Flake, snuffs, Cashel, High Toast, White Top and Craven A cigarettes. To meet a special demand from the North of Ireland the factory produced a type of plug known as Long Square. Spillane’s closed in 1958 with the loss of 150 jobs after the building was purchased by Murray Ltd, of Dublin the year previous. Their building is where the old Dunnes Stores building stands today. William Spillane who was the Mayor of Limerick in 1885 built the Spillane Tower which today is better known as the ‘Snuff Box’ on the banks of the Shannon river at Corkanree. The other large factory was Clune’s Tobacco Factory on Denmark Street. It opened in the late 1872 and had about 60 employees in 1929. The firm specialised in Big Bar Plug, every two ounces of which is stamped Thomond. They also excelled in the Far-Famed Limerick Twist. They were also known for Kincora Plug, Sarsfield Plug, Home Rule, Hibernian, Target, Ireland’s Pride and Two Flake. A popular item associated with tobacco factories are the cigarette cards. Cigarette cards were originally produced as a small piece of card which was designed to protect the individual cigarettes from being squashed as the original packaging was paper and not the card boxes that we know today. We must not forget M.Cahill’s of Wickham Street which housed a snuff factory in 1870 in the basement of the building and operated for over sixty years. The business was founded by Michael Cahill (c.1846-1918) who was also the director of the Limerick Race Company. Cahill’s became Ireland’s longest running tobacco store and is still in operation offering a selection of cigar, teas and “gentleman’s gifts” including Swiss army knives, hipflasks and pipes. Sharon Slater
51cm x 63cm In 1929, Limerick city was the home to two large of tobacco factories Spillane’s and Clune’s who imported tobacco from the United States, Egypt and Turkey as well as locally grown tobacco to produce their famed products. Spillane’s Tobacco Factory on Sarsfield Street was started by John Spillane in 1829 and was known as ‘The House of Garryowen’. A hundred years later they were employing a hundred people. The famous Garryowen plug formed 80 per cent of the factories output while they had other products including Popular and Treaty bar plugs, Hazel Nut plug, Special Flake, Handy Cut Flake, snuffs, Cashel, High Toast, White Top and Craven A cigarettes. To meet a special demand from the North of Ireland the factory produced a type of plug known as Long Square. Spillane’s closed in 1958 with the loss of 150 jobs after the building was purchased by Murray Ltd, of Dublin the year previous. Their building is where the old Dunnes Stores building stands today. William Spillane who was the Mayor of Limerick in 1885 built the Spillane Tower which today is better known as the ‘Snuff Box’ on the banks of the Shannon river at Corkanree. The other large factory was Clune’s Tobacco Factory on Denmark Street. It opened in the late 1872 and had about 60 employees in 1929. The firm specialised in Big Bar Plug, every two ounces of which is stamped Thomond. They also excelled in the Far-Famed Limerick Twist. They were also known for Kincora Plug, Sarsfield Plug, Home Rule, Hibernian, Target, Ireland’s Pride and Two Flake. A popular item associated with tobacco factories are the cigarette cards. Cigarette cards were originally produced as a small piece of card which was designed to protect the individual cigarettes from being squashed as the original packaging was paper and not the card boxes that we know today. We must not forget M.Cahill’s of Wickham Street which housed a snuff factory in 1870 in the basement of the building and operated for over sixty years. The business was founded by Michael Cahill (c.1846-1918) who was also the director of the Limerick Race Company. Cahill’s became Ireland’s longest running tobacco store and is still in operation offering a selection of cigar, teas and “gentleman’s gifts” including Swiss army knives, hipflasks and pipes. Sharon Slater -
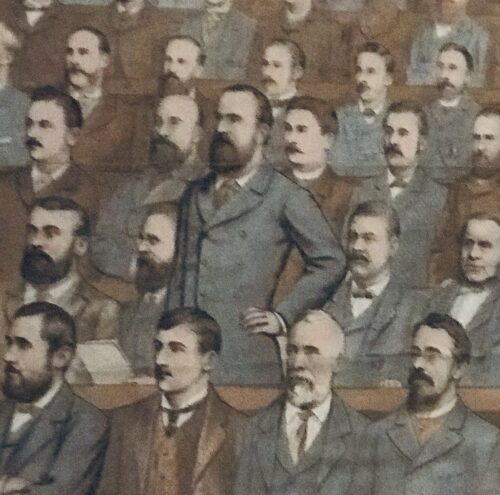

 Extremely rare,interesting print of the Irish Benches of the Irish Parliamentary Party in the House of Commons in 1885,with all members identified by name and number. Gort Co Galway 45 cm x 60cm The Irish Parliamentary Party or more commonly called the Irish Party or the Home Rule Party) was formed in 1874 by Isaac Butt, the leader of the Nationalist Party, replacing the Home Rule League, as official parliamentary party for Irish nationalist Members of Parliament (MPs) elected to the House of Commons at Westminster within the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland up until 1918. Its central objectives were legislative independence for Ireland and land reform. Its constitutional movement was instrumental in laying the groundwork for Irish self-government through three Irish Home Rule bills.Instrumental to the party's rise and fall was the iconic statesman,Charles Stewart Parnell.
Extremely rare,interesting print of the Irish Benches of the Irish Parliamentary Party in the House of Commons in 1885,with all members identified by name and number. Gort Co Galway 45 cm x 60cm The Irish Parliamentary Party or more commonly called the Irish Party or the Home Rule Party) was formed in 1874 by Isaac Butt, the leader of the Nationalist Party, replacing the Home Rule League, as official parliamentary party for Irish nationalist Members of Parliament (MPs) elected to the House of Commons at Westminster within the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland up until 1918. Its central objectives were legislative independence for Ireland and land reform. Its constitutional movement was instrumental in laying the groundwork for Irish self-government through three Irish Home Rule bills.Instrumental to the party's rise and fall was the iconic statesman,Charles Stewart Parnell. -
Out of stock
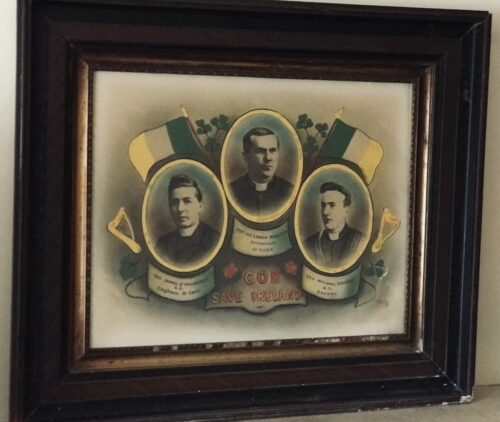
 62cm x 72cm Scarriff Co Clare This extremely rare print commemorates three Catholic priests killed during the bloody War of Independence between the IRA and British Crown Forces : Fr James O’Callaghan Clogheen,Canon Magnier Dunmanway and Fr Michael Griffin Galway .Indeed the 100 year anniversaries of three callous murders are all due in the next few months. Fr O Callaghan was shot in cold blood in Cork city by a group of drunken Black and Tans.Canon Magnier,an elderly priest in poor health, was shot along with a young parishioner outside the village of Dunmanway in Co Cork and Fr Griffin was taken from his home and assassinated in Galway .An estimated 20,000 people attended his funeral. This poignant and extremely rare print,dating from that period pays homage to these holy men who were all cruelly murdered in cold blood whilst unarmed by tyrannical British Military forces.The notorious murder of a young West of Ireland priest who was lured from his home before being shot in the head and buried in a bog by British forces is to be commemorated with a series of events in Galway City next year. The disappearance and murder of Fr Michael Griffin (28) sent shock waves across Ireland in November 1920, prompting a front-page news story in the New York Times, a cable expressing outrage from the Bishop of Chicago, and tough questions about British atrocities in Ireland in the British Parliament. It was one of the most notorious killings of the War of Independence when reprisals were commonplace, and the hated Black and Tans – recruited from Britain to put the rebellious Irish in their place – roamed the land. The body of the popular young curate was discovered in an unmarked grave in bogland a few miles west of Galway City six days after his disappearance and, from the outset, locals in Galway blamed the Black and Tans for the shocking crime. An estimated crowd of 12,000 people gathered outside St Joseph’s Church in Galway City for his Requiem Mass, which was concelebrated by the Archbishop of Tuam, the bishops of Galway and Clonfert, and almost 150 priests from across the West of Ireland. A native of East Galway, Fr Griffin was suspected of having republican sympathies by British forces at the time, who were angered by the disappearance of a local primary school principal, Patrick Joyce, a week before the young priest went missing. Joyce was accused of feeding information to the crown forces by members of the Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB), who had intercepted five of his letters at the mail sorting office in Galway. Collusion with the despised British crown forces was seen as treason at the time and Joyce was shot in the head by republicans after they presented him with evidence at a secret trial in an isolated house outside the city. November 1920 was a particularly violent time in Galway. A pregnant young woman had been shot by the Black and Tans outside her family home in rural Ardrahan, two Galway city men had been shot dead, and republican prisoners were on hunger strike in Galway gaol. Men from the area had been interned without trial, there was a curfew across the city, and British forces were highly suspicious of young priests like Fr Griffin, who were believed to have republican sympathies. Members of the St Joseph’s Parish Council formed a new committee this week to organize a series of events in Fr Griffin’s memory in Galway in November of next year. Although the city will be in “party mode” when Galway becomes the European Capital of Culture in 2020, committee chairman Cllr John Connolly believes people need to remember their history and the sacrifices made in Galway to secure Irish freedom.“A lot of people don’t realise how tough life was in Galway during the War of Independence. Between the beginning of September and the end of November 1920, you had the death of Seamus Quirke, Sean Mulvoy, and Michael Walsh, who was a member of the Urban District Council,” Connolly told IrishCentral this week. “They were all known republicans and republican sympathisers. You also had the death of Patrick Joyce, who was the principal of Bearna National School, who was of a different political persuasion. He was considered an informer, who was informing the British forces in Galway of the activities of the Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB).” The British believed Fr Griffin had given the last rites to Walsh and Quirke, two well-known republicans in Galway. They also believed he may have heard the last confession of Patrick Joyce and that he knew who had abducted him. Controversy surrounded Joyce’s case for decades, as his body was only found in a field to the west of Galway in the 1990s. His direct family – who emigrated to Australia – always maintained his innocence of collusion allegations. “The Black and Tans really went on the rampage in Galway when Joyce disappeared, throwing grenades into houses, killing livestock belonging to people, and burning the premises of the Galway Express newspaper,” recalled Connolly this week. “Fr Griffin went missing on November 14 and his body was found on the 20th. Locals believed that people in the area knew where the body was, but they were afraid of uncovering it in case of reprisals from British forces, who were searching for Patrick Joyce at that stage,” said Cllr Connolly. It is known that three men called to Fr Griffin’s house at Montpellier Terrace late on a Sunday night and that he agreed to accompany them. A neighbor heard him speak to the men, who were Irish, at the front door and he was never seen again. Historians believe the British shot him at their nearby base at Lenaboy Castle, Taylor’s Hill, that same night and then dumped him in an unmarked grave. Locals found the body on the following Saturday evening but were so afraid of the British that they waited until 7 am on Sunday morning before bringing his body to St Joseph’s Church in the city. Fr Griffin was found with a bullet in his head, indicating he had been shot at close range. “He was brought in on a horse and cart. They had to disguise the cart with large milk churns, in case the British forces stopped them. The British were still looking for Patrick Joyce and they were upset that he had been kidnapped. They saw his disappearance as a direct threat to their own intelligence operation,” explained Connolly. “The idea that a clergyman would be treated like this was a new low I think for the British forces in the city and, indeed in the country, that they had taken this action against a priest.” Fr Griffin from Gurteen, Co Galway, had a great love for the Irish language and was popular for his dealings with the old, the young, and the poor. He was moved by the injustice he witnessed around him every day due to the British occupation. As soon as he was reported missing, locals in Galway blamed the British crown forces. After his disappearance, Bishop O’Dea and the priests of Galway issued a statement to condemn his abduction from his home. “We cannot but hold the British Government responsible for this outrage upon the Catholic priesthood of Ireland,” they said. “He has been secretly forced from his house in the dead of night by undisciplined men. Without warrant, or charge, or proof of wrongdoing he has been deprived of his liberty and, for all we know, his life. Unhappily, the only uncommon feature in this case is that he is a priest; the crime in this respect being almost unique; in as much as every civilised country in the world recognises priests as men of peace, and treats them as such.” Connolly and Fr Martin Downey, Parish Priest of St Joseph’s, have formed a new committee to organize a series of events to remember the popular young priest next November. “Really and truly, Fr Griffin got no trial. It’s fitting that his centenary should be commemorated because it was a bleak time in Galway. That a highly respected member of the community was taken out and killed like this, we do need to remind ourselves that Galway was a dark place at the time and the sacrifice of those who lost their lives should not be forgotten,” said Connolly.
62cm x 72cm Scarriff Co Clare This extremely rare print commemorates three Catholic priests killed during the bloody War of Independence between the IRA and British Crown Forces : Fr James O’Callaghan Clogheen,Canon Magnier Dunmanway and Fr Michael Griffin Galway .Indeed the 100 year anniversaries of three callous murders are all due in the next few months. Fr O Callaghan was shot in cold blood in Cork city by a group of drunken Black and Tans.Canon Magnier,an elderly priest in poor health, was shot along with a young parishioner outside the village of Dunmanway in Co Cork and Fr Griffin was taken from his home and assassinated in Galway .An estimated 20,000 people attended his funeral. This poignant and extremely rare print,dating from that period pays homage to these holy men who were all cruelly murdered in cold blood whilst unarmed by tyrannical British Military forces.The notorious murder of a young West of Ireland priest who was lured from his home before being shot in the head and buried in a bog by British forces is to be commemorated with a series of events in Galway City next year. The disappearance and murder of Fr Michael Griffin (28) sent shock waves across Ireland in November 1920, prompting a front-page news story in the New York Times, a cable expressing outrage from the Bishop of Chicago, and tough questions about British atrocities in Ireland in the British Parliament. It was one of the most notorious killings of the War of Independence when reprisals were commonplace, and the hated Black and Tans – recruited from Britain to put the rebellious Irish in their place – roamed the land. The body of the popular young curate was discovered in an unmarked grave in bogland a few miles west of Galway City six days after his disappearance and, from the outset, locals in Galway blamed the Black and Tans for the shocking crime. An estimated crowd of 12,000 people gathered outside St Joseph’s Church in Galway City for his Requiem Mass, which was concelebrated by the Archbishop of Tuam, the bishops of Galway and Clonfert, and almost 150 priests from across the West of Ireland. A native of East Galway, Fr Griffin was suspected of having republican sympathies by British forces at the time, who were angered by the disappearance of a local primary school principal, Patrick Joyce, a week before the young priest went missing. Joyce was accused of feeding information to the crown forces by members of the Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB), who had intercepted five of his letters at the mail sorting office in Galway. Collusion with the despised British crown forces was seen as treason at the time and Joyce was shot in the head by republicans after they presented him with evidence at a secret trial in an isolated house outside the city. November 1920 was a particularly violent time in Galway. A pregnant young woman had been shot by the Black and Tans outside her family home in rural Ardrahan, two Galway city men had been shot dead, and republican prisoners were on hunger strike in Galway gaol. Men from the area had been interned without trial, there was a curfew across the city, and British forces were highly suspicious of young priests like Fr Griffin, who were believed to have republican sympathies. Members of the St Joseph’s Parish Council formed a new committee this week to organize a series of events in Fr Griffin’s memory in Galway in November of next year. Although the city will be in “party mode” when Galway becomes the European Capital of Culture in 2020, committee chairman Cllr John Connolly believes people need to remember their history and the sacrifices made in Galway to secure Irish freedom.“A lot of people don’t realise how tough life was in Galway during the War of Independence. Between the beginning of September and the end of November 1920, you had the death of Seamus Quirke, Sean Mulvoy, and Michael Walsh, who was a member of the Urban District Council,” Connolly told IrishCentral this week. “They were all known republicans and republican sympathisers. You also had the death of Patrick Joyce, who was the principal of Bearna National School, who was of a different political persuasion. He was considered an informer, who was informing the British forces in Galway of the activities of the Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB).” The British believed Fr Griffin had given the last rites to Walsh and Quirke, two well-known republicans in Galway. They also believed he may have heard the last confession of Patrick Joyce and that he knew who had abducted him. Controversy surrounded Joyce’s case for decades, as his body was only found in a field to the west of Galway in the 1990s. His direct family – who emigrated to Australia – always maintained his innocence of collusion allegations. “The Black and Tans really went on the rampage in Galway when Joyce disappeared, throwing grenades into houses, killing livestock belonging to people, and burning the premises of the Galway Express newspaper,” recalled Connolly this week. “Fr Griffin went missing on November 14 and his body was found on the 20th. Locals believed that people in the area knew where the body was, but they were afraid of uncovering it in case of reprisals from British forces, who were searching for Patrick Joyce at that stage,” said Cllr Connolly. It is known that three men called to Fr Griffin’s house at Montpellier Terrace late on a Sunday night and that he agreed to accompany them. A neighbor heard him speak to the men, who were Irish, at the front door and he was never seen again. Historians believe the British shot him at their nearby base at Lenaboy Castle, Taylor’s Hill, that same night and then dumped him in an unmarked grave. Locals found the body on the following Saturday evening but were so afraid of the British that they waited until 7 am on Sunday morning before bringing his body to St Joseph’s Church in the city. Fr Griffin was found with a bullet in his head, indicating he had been shot at close range. “He was brought in on a horse and cart. They had to disguise the cart with large milk churns, in case the British forces stopped them. The British were still looking for Patrick Joyce and they were upset that he had been kidnapped. They saw his disappearance as a direct threat to their own intelligence operation,” explained Connolly. “The idea that a clergyman would be treated like this was a new low I think for the British forces in the city and, indeed in the country, that they had taken this action against a priest.” Fr Griffin from Gurteen, Co Galway, had a great love for the Irish language and was popular for his dealings with the old, the young, and the poor. He was moved by the injustice he witnessed around him every day due to the British occupation. As soon as he was reported missing, locals in Galway blamed the British crown forces. After his disappearance, Bishop O’Dea and the priests of Galway issued a statement to condemn his abduction from his home. “We cannot but hold the British Government responsible for this outrage upon the Catholic priesthood of Ireland,” they said. “He has been secretly forced from his house in the dead of night by undisciplined men. Without warrant, or charge, or proof of wrongdoing he has been deprived of his liberty and, for all we know, his life. Unhappily, the only uncommon feature in this case is that he is a priest; the crime in this respect being almost unique; in as much as every civilised country in the world recognises priests as men of peace, and treats them as such.” Connolly and Fr Martin Downey, Parish Priest of St Joseph’s, have formed a new committee to organize a series of events to remember the popular young priest next November. “Really and truly, Fr Griffin got no trial. It’s fitting that his centenary should be commemorated because it was a bleak time in Galway. That a highly respected member of the community was taken out and killed like this, we do need to remind ourselves that Galway was a dark place at the time and the sacrifice of those who lost their lives should not be forgotten,” said Connolly.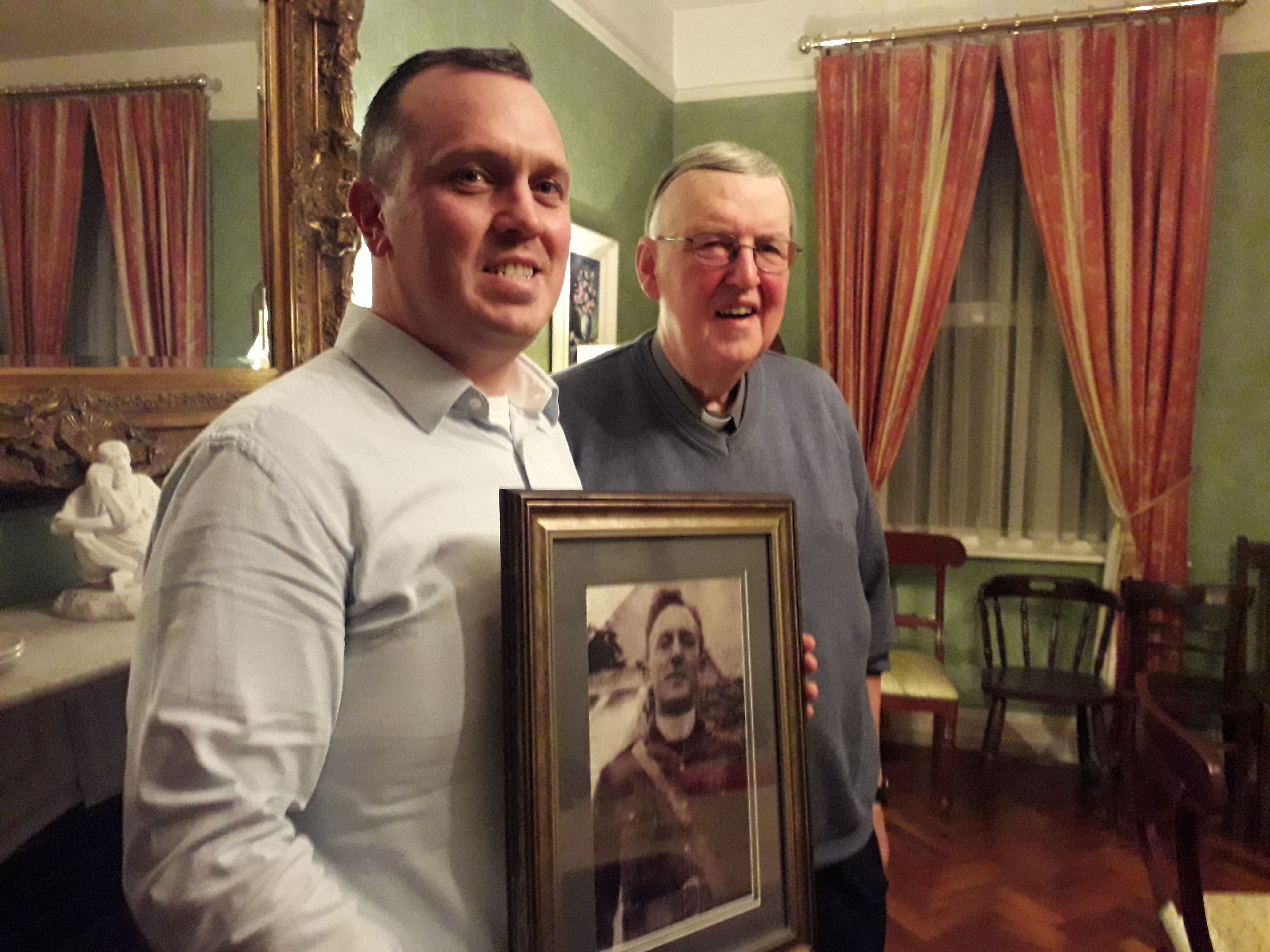 2
2John Connolly and Fr Martin Downey, with a photo of Fr Griffin, courtesy of Ciaran Tierney Digital Storyteller.
Reprisal Killing of Cork PriestIn the aftermath of the devestating attack on a police patrol at Blackpool in Cork City on May 14, 1921, in which three RIC members lost their life, large forces of military and police flooded the area and much of the Blackpool area was ransacked. Several arrests were made and throughout the city, rumours circulated of major military operations involving widespread savage reprisals. Just before 4am, on the following morning, the Sundays Well home of Alderman Liam De Roiste was raided by a group of masked men, all members of the Royal Irish Constabulary. He himself was not at home, but Father Seamus O'Callaghan, a curate based at Clogheen on the outskirts of the city, happened to be in the house at the time. Having been awakened by the hammering at the door, Fr O'Callaghan went to the window and informed the men outside that De Roiste was not at home. The front door was then broken in and at least one of the police ran up the stairs and fired a number of shots at the priest, who fell mortally wounded. The assailaints then made their escape. Fr O'Callaghan died a number of hours later. A native of Newcestown, West Cork, he was widely admired by the people of Cork having, as a young man, closely identified himself with the Nationalist cause. His funeral was attended by many thousands, despite widespread intimidation of the mourners by crown forces. He is buried in the grounds of the Church of the Most Precious Blood, Clogheen. -
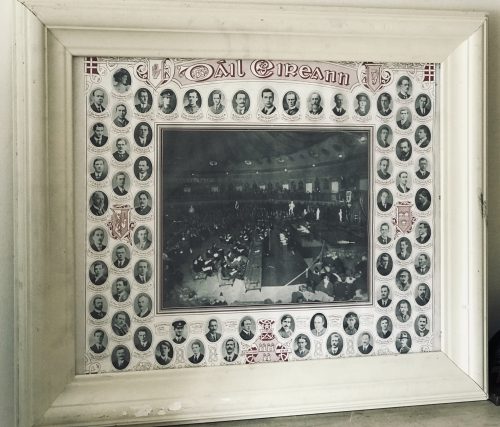 Unique print depicting the very first Dáil Eireann which took place at the Mansion House in Dublin on the 21st January 1919.53cm x 65cm. Loughrea Co Galway
Unique print depicting the very first Dáil Eireann which took place at the Mansion House in Dublin on the 21st January 1919.53cm x 65cm. Loughrea Co Galway
The First Dáil (Irish: An Chéad Dáil) was Dáil Éireann as it convened from 1919 to 1921. It was the first meeting of the unicameral parliament of the revolutionary Irish Republic. In the December 1918 election to the Parliament of the United Kingdom, the Irish republican party Sinn Féin won a landslide victory in Ireland. In line with their manifesto, its MPs refused to take their seats, and on 21 January 1919 they founded a separate parliament in Dublin called Dáil Éireann ("Assembly of Ireland"). They declared Irish independence, ratifying the Proclamation of the Irish Republicthat had been issued in the 1916 Easter Rising, and adopted a provisional constitution. Its first meeting happened on the same day as one of the first engagements of what became the Irish War of Independence. Although the Dáil had not authorised any armed action, it became a "symbol of popular resistance and a source of legitimacy for fighting men in the guerrilla war that developed". The Dáil was outlawed by the British government in September 1919, and thereafter it met in secret. The First Dáil met 21 times and its main business was establishing the Irish Republic.It created the beginnings of an independent Irish government and state apparatus. Following the May 1921 elections, the First Dáil was succeeded by the Second Dáil of 1921–1922First Dáil ← New assembly 2nd Dáil → 
Overview Legislative body Dáil Éireann Jurisdiction Irish Republic Meeting place Mansion House, Dublin Term 21 January 1919 – 10 May 1921 Election 1918 general election Government Government of the 1st Dáil Members 73 Ceann Comhairle Cathal Brugha (1919) George Noble Plunkett(1919) Seán T. O'Kelly (1919–21) President of Dáil Éireann Cathal Brugha (1919) President of the Irish Republic Éamon de Valera (1919–21) Sessions 1st 21 January 1919 – 10 May 1921 Background
In 1918 Ireland was a part of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and was represented in the British House of Commons by 105 MPs. From 1882, most Irish MPs were members of the Irish Parliamentary Party (IPP) who strove in several Home Rule Bills to achieve self-government for Ireland within the United Kingdom by constitutional means. This approach put the Government of Ireland Act 1914 on the statute book but its implementation was postponed with the outbreak of the World War I. In the meantime the more radical Sinn Féin party grew in strength. Sinn Féin's founder, Arthur Griffith, believed Irish nationalists should emulate the Hungarian nationalists who had gained partial independence from Austria. In 1867, led by Ferenc Deák, Hungarian representatives had boycotted the Imperial parliament in Vienna and unilaterally established their own legislature in Budapest. The Austrian government had eventually become reconciled to this new state of affairs. Members of Sinn Féin also, however, supported gaining independence by means of an armed uprising if necessary. In April 1916, during the First World War, Irish republicans launched an uprising against British rule in Ireland, called the Easter Rising. They proclaimed an Irish Republic. After a week of heavy fighting, mostly in Dublin, the rising was put down by British forces. About 3,500 people were taken prisoner by the British, many of whom had played no part in the Rising. Most of the Rising's leaders were executed. The rising, the British response, and the British attempt to introduce conscription in Ireland, led to greater public support for Sinn Féin and Irish independence. The party was also helped by the 1918 Representation of the People Act which increased the Irish electorate from around 700,000 to about two million. In the 1918 general election, Sinn Féin won 73 out of the 105 Irish seats in the House of Commons. Elections were held almost entirely under the 'first-past-the-post voting' system. In 25 constituencies, Sinn Féin won the seats unopposed. Unionists (including Ulster Unionist Labour Association) won 26 seats, all but three of which were in the six counties that today form Northern Ireland, and the IPP won only six (down from 84), all but one in Ulster. The Labour Party did not stand in the election, allowing the electorate to decide between home rule or a republic by having a clear choice between the two nationalist parties. The IPP won a smaller share of seats than votes due to the first-past-the-post system. Sinn Féin's manifesto had pledged to establish an Irish Republic by founding "a constituent assembly comprising persons chosen by Irish constituencies" which could then "speak and act in the name of the Irish people". Once elected the Sinn Féin MPs chose to follow through with their manifesto.First meeting
Sinn Féin had held several meetings in early January to plan the first sitting of the Dáil. On 8 January, it publicly announced its intention to convene the assembly. On the night of 11 January, the Dublin Metropolitan Police raided Sinn Féin headquarters and seized drafts of the documents that would be issued at the assembly. As a result, the British administration was fully aware what was being planned. The first meeting of Dáil Éireann began at 3:30 pm on 21 January in the Round Room of the Mansion House, the residence of the Lord Mayor of Dublin. It lasted about two hours. The packed audience in the Round Room rose in acclaim for the members of the Dáil as they walked into the room, and many waved Irish tricolour flags. A tricolour was also displayed above the lectern. Among the audience were the Lord Mayor Laurence O'Neill and Maud Gonne. Scores of Irish and international journalists were reporting on the proceedings. Outside, Dawson Street was thronged with onlookers. Irish Volunteers controlled the crowds, and police were also present. Precautions had been taken in case the assembly was raided by the British authorities. A reception for British soldiers of the Royal Dublin Fusiliers, who had been prisoners of war in Germany, had ended shortly beforehand. Twenty-seven Sinn Féin MPs attended. Invitations had been sent to all elected MPs in Ireland, but the Unionists and Irish Parliamentary Party MPs declined to attend. The IPP's Thomas Harbison, MP for North East Tyrone, acknowledged the invitation but wrote he should "decline for obvious reasons". He expressed sympathy with the call for Ireland to have a hearing at the Paris Peace Conference. Sir Robert Henry Woods was the only unionist who declined rather than ignored his invitation.Sixty-nine Sinn Féin MPs had been elected (four of whom represented more than one constituency), but thirty-four were in prison, and eight others could not attend for various reasons. Those in prison were described as being "imprisoned by the foreigners" (fé ghlas ag Gallaibh).Michael Collins and Harry Boland were marked in the roll as i láthair (present), but the record was later amended to show that they were as láthair (absent). At the time, they were in England planning the escape of Éamon de Valera from Lincoln Prison, and did not wish to draw attention to their absence. Being a first and highly symbolic meeting, the proceedings of the Dáil were held wholly in the Irish language, although translations of the documents were also read out in English and French. George Noble Plunkett opened the session and nominated Cathal Brugha as acting Ceann Comhairle (chairman or speaker), which was accepted. Both actions "immediately associated the Dáil with the 1916 Rising, during which Brugha had been seriously wounded, and after which Plunkett’s son had been executed as a signatory to the famed Proclamation".Brugha then called upon Father Michael O'Flanagan to say a prayer.Declarations and constitution
A number of short documents were then read out and adopted. These were the:- Dáil Constitution
- Declaration of Independence
- Message to the Free Nations of the World – calling for international recognition of Irish independence
- Democratic Programme – a declaration of social and economic policy
Reactions
The first meeting of the Dáil and its declaration of independence was headline news in Ireland and abroad. However, the press censorship that began during the First World War was continued by the British administration in Ireland after the war. The Press Censor forbade all Irish newspapers from publishing the Dáil's declarations. That evening, a British unionist view of events was printed in a newspaper. It said that the British Lord Lieutenant of Ireland, "Lord French, is today the master of Ireland. He alone [...] will decide upon the type of government the country is to have, and it is he rather than any member of the House of Commons, who will be the judge of political and industrial reforms". Lord French's observer at the meeting, George Moore, was impressed by its orderliness and told French that the Dáil represented "the general feeling in the country".The Irish Times, then the voice of the Unionist status quo, called the events both farcical and dangerous. Irish republicans, and many nationalist newspapers, saw the meeting as momentous and the beginning of "a new epoch".According to one observer: "It is difficult to convey the intensity of feeling which pervaded the Round Room, the feeling that great things were happening, even greater things impending, and that in looking around the room he saw a glimpse of the Ireland of the future". One American journalist was more accurate than most when he forecast that "The British government apparently intends to ignore the Sinn Fein republic until it undertakes to enforce laws that are in conflict with those established by the British; then the trouble is likely to begin".Irish War of Independence
Members of the Irish Volunteers, a republican paramilitary organization, "believed that the election of the Dáil and its declaration of independence had given them the right to pursue the republic in the manner they saw fit". It began to refer to itself as the Irish Republican Army (IRA).The First Dáil was "a visible symbol of popular resistance and a source of legitimacy for fighting men in the guerrilla war that developed". On the same day as the Dáil's first meeting, two officers of the Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC) were killed in an ambush in County Tipperary by members of the Irish Volunteers. The Volunteers seized the explosives the officers had been guarding. This action had not been authorised by the Irish Volunteer leadership nor by the Dáil. Although the Dáil and the Irish Volunteers had some overlapping membership, they were separate and neither controlled the other. After the founding of the Dáil, steps were taken to make the Volunteers the army of the new self-declared republic. On 31 January 1919 the Volunteers' official journal, An tÓglách ("The Volunteer"), stated that Ireland and England were at war, and that the founding of Dáil Éireann and its declaration of independence justified the Irish Volunteers in treating "the armed forces of the enemy – whether soldiers or policemen – exactly as a national army would treat the members of an invading army". In August 1920, the Dáil adopted a motion that the Irish Volunteers, "as a standing army", would swear allegiance to it and to the Republic. The Soloheadbeg ambush "and others like it that occurred during 1919 were not […] intended to be the first shots in a general war of independence, though that is what they turned out to be".It is thus seen as one of the first actions of the Irish War of Independence. The Dáil did not debate whether it would "accept a state of war" with, or declare war on, the United Kingdom until 11 March 1921. It was agreed unanimously to give President De Valera the power to accept or declare war at the most opportune time, but he never did so. In September 1919 the Dáil was declared illegal by the British authorities and thereafter met only intermittently and at various locations. The Dáil also set about attempting to secure de factoauthority for the Irish Republic throughout the country. This included the establishment of a parallel judicial system known as the Dáil Courts. The First Dáil held its last meeting on 10 May 1921. After elections on 24 May the Dáil was succeeded by the Second Dáil which sat for the first time on 16 August 1921.Prominent members
 Members of the First Dáil, 10 April 1919. 1st row (left to right): L. Ginnell, M. Collins, C. Brugha, A. Griffith, É. de Valera, Count Plunkett, E. MacNeill, W. T. Cosgrave and E. Blythe. 2nd row (l to r): P. J. Moloney, T. MacSwiney, R. Mulcahy, J. O'Doherty, S. O'Mahony, J. Dolan, J. McGuinness, P. O'Keefe, M. Staines, J. McGrath, B. Cusack, L. de Róiste, M. Colivet and M. O'Flanagan ((VP of Sinn Féin). 3rd row (l to r): P. Ward, A. McCabe, D. FitzGerald, J. Sweeny, R. Hayes, C. Collins, P. Ó Máille, J. O'Mara, B. O'Higgins, S. Burke and K. O'Higgins. 4th row (l to r): J. McDonagh and S. MacEntee. 5th row (l to r): P. Béaslaí, R. Barton and P. Galligan. 6th row (l to r): P. Shanahan and S. Etchingham.
Members of the First Dáil, 10 April 1919. 1st row (left to right): L. Ginnell, M. Collins, C. Brugha, A. Griffith, É. de Valera, Count Plunkett, E. MacNeill, W. T. Cosgrave and E. Blythe. 2nd row (l to r): P. J. Moloney, T. MacSwiney, R. Mulcahy, J. O'Doherty, S. O'Mahony, J. Dolan, J. McGuinness, P. O'Keefe, M. Staines, J. McGrath, B. Cusack, L. de Róiste, M. Colivet and M. O'Flanagan ((VP of Sinn Féin). 3rd row (l to r): P. Ward, A. McCabe, D. FitzGerald, J. Sweeny, R. Hayes, C. Collins, P. Ó Máille, J. O'Mara, B. O'Higgins, S. Burke and K. O'Higgins. 4th row (l to r): J. McDonagh and S. MacEntee. 5th row (l to r): P. Béaslaí, R. Barton and P. Galligan. 6th row (l to r): P. Shanahan and S. Etchingham.Legacy
The First Dáil and the general election of 1918 came to occupy a central place in Irish republicanism and nationalism. Today the name Dáil Éireann is used for the lower house of the modern Oireachtas (parliament) of the Republic of Ireland. Successive Dála (plural for Dáil) continue to be numbered from the "First Dáil" convened in 1919. The current Dáil, elected in 2020, is accordingly the "33rd Dáil". The 1918 general election was the last time the whole island of Ireland voted as a unit until elections to the European Parliament over sixty years later. The landslide victory for Sinn Féin was seen by Irish republicans as an overwhelming endorsement of the principle of a united independent Ireland.Until recently republican paramilitary groups, such as the Provisional IRA, often claimed that their campaigns derived legitimacy from this 1918 mandate, and some still do. The First Dáil "created the beginnings of an independent Irish governmental and bureaucratic machine", and was a means by which "a formal constitution for the new state was created".It also "provided the personnel and the authority to conclude the articles of agreement with Britain and bring the war to an end". The Irish state has commemorated the founding of the First Dáil several times, as "the anniversary of when a constitutionally elected majority of MPs declared the right of the Irish people to have their own democratic state". Seán MacEntee, who died on 10 January 1984 at the age of 94, was the last surviving member of the First Dáil.








