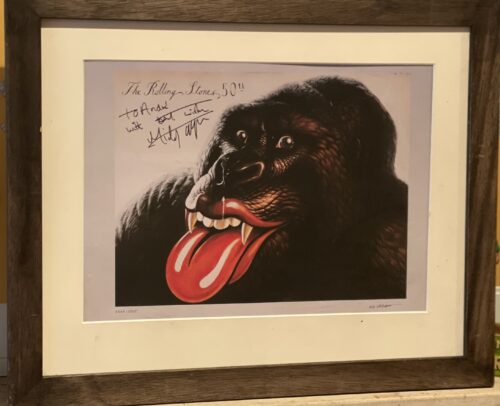
-
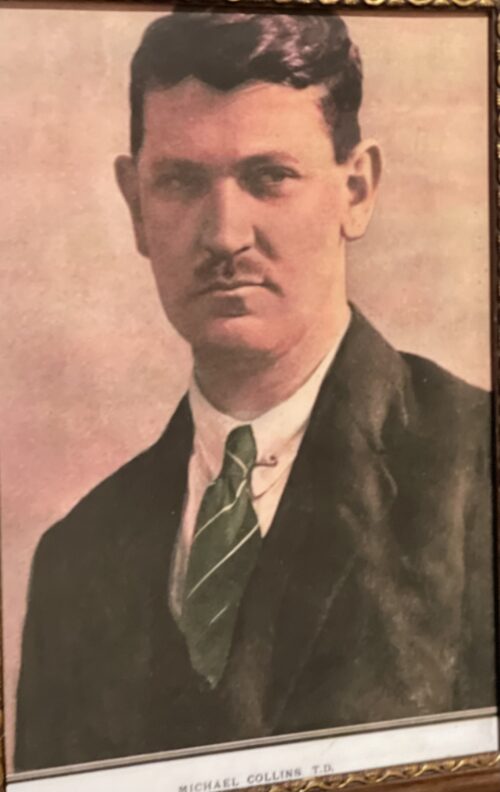
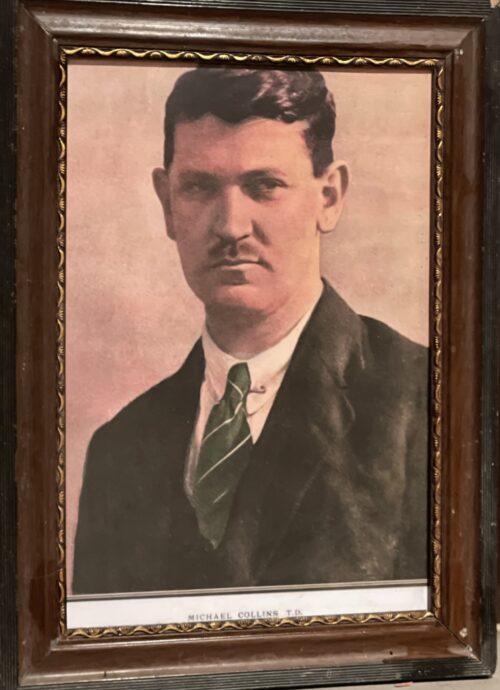
 40cm x 37cm Michael Collins (16 October 1890 – 22 August 1922) was an Irish revolutionary, soldier and politician who was a leading figure in the early-20th century struggle for Irish independence.During the War of Independence he was Director of Intelligence of the Irish Republican Army (IRA) and a government minister of the self-declared Irish Republic. He was then Chairman of the Provisional Government of the Irish Free State from January 1922 and commander-in-chief of the National Army from July until his death in an ambush in August 1922, during the Civil War. Collins was born in Woodfield, County Cork, the youngest of eight children. He moved to London in 1906 to become a clerk in the Post Office Savings Bank at Blythe House. He was a member of the London GAA, through which he became associated with the Irish Republican Brotherhood and the Gaelic League. He returned to Ireland in January 1916 and fought in the Easter Rising. He was taken prisoner and held in the Frongoch internment camp as a prisoner of war, but he was released in December 1916. Collins subsequently rose through the ranks of the Irish Volunteers and Sinn Féin. He was elected as a Teachta Dála for South Cork in December 1918. Sinn Féin's elected members formed an Irish parliament, the First Dáil, in January 1919 and declared the independence of the Irish Republic. Collins was appointed Minister for Finance. In the ensuing War of Independence, he was Director of Organisation and Adjutant General for the Irish Volunteers, and Director of Intelligence of the IRA. He gained fame as a guerrilla warfare strategist, planning many successful attacks on British forces together with 'the Squad', such as the "Bloody Sunday" assassinations of key British intelligence agents in November 1920. After the July 1921 ceasefire, Collins was one of five plenipotentiaries sent by the Dáil cabinet at the request of Éamon de Valera, to negotiate peace terms in London. The resulting Anglo-Irish Treaty, signed in December 1921, would establish the Irish Free State but depended on an oath of allegiance to the Crown. This was the clause in the treaty de Valera and other republican leaders found hardest to accept. Collins viewed the treaty as offering "the freedom to achieve freedom", and helped persuade a majority of the Dáil to ratify the treaty. A provisional government was formed under his chairmanship in early 1922. During this time he secretly provided support for an IRA offensive in Northern Ireland. It was soon disrupted by the Irish Civil War, in which Collins was commander-in-chief of the National Army. He was shot and killed in an ambush by anti-Treaty forces on 22 August 1922
40cm x 37cm Michael Collins (16 October 1890 – 22 August 1922) was an Irish revolutionary, soldier and politician who was a leading figure in the early-20th century struggle for Irish independence.During the War of Independence he was Director of Intelligence of the Irish Republican Army (IRA) and a government minister of the self-declared Irish Republic. He was then Chairman of the Provisional Government of the Irish Free State from January 1922 and commander-in-chief of the National Army from July until his death in an ambush in August 1922, during the Civil War. Collins was born in Woodfield, County Cork, the youngest of eight children. He moved to London in 1906 to become a clerk in the Post Office Savings Bank at Blythe House. He was a member of the London GAA, through which he became associated with the Irish Republican Brotherhood and the Gaelic League. He returned to Ireland in January 1916 and fought in the Easter Rising. He was taken prisoner and held in the Frongoch internment camp as a prisoner of war, but he was released in December 1916. Collins subsequently rose through the ranks of the Irish Volunteers and Sinn Féin. He was elected as a Teachta Dála for South Cork in December 1918. Sinn Féin's elected members formed an Irish parliament, the First Dáil, in January 1919 and declared the independence of the Irish Republic. Collins was appointed Minister for Finance. In the ensuing War of Independence, he was Director of Organisation and Adjutant General for the Irish Volunteers, and Director of Intelligence of the IRA. He gained fame as a guerrilla warfare strategist, planning many successful attacks on British forces together with 'the Squad', such as the "Bloody Sunday" assassinations of key British intelligence agents in November 1920. After the July 1921 ceasefire, Collins was one of five plenipotentiaries sent by the Dáil cabinet at the request of Éamon de Valera, to negotiate peace terms in London. The resulting Anglo-Irish Treaty, signed in December 1921, would establish the Irish Free State but depended on an oath of allegiance to the Crown. This was the clause in the treaty de Valera and other republican leaders found hardest to accept. Collins viewed the treaty as offering "the freedom to achieve freedom", and helped persuade a majority of the Dáil to ratify the treaty. A provisional government was formed under his chairmanship in early 1922. During this time he secretly provided support for an IRA offensive in Northern Ireland. It was soon disrupted by the Irish Civil War, in which Collins was commander-in-chief of the National Army. He was shot and killed in an ambush by anti-Treaty forces on 22 August 1922 -

 43cm x 38cm Dublin The Easter Rising (Irish: Éirí Amach na Cásca), also known as the Easter Rebellion, was an armed insurrection in Ireland during Easter Week in April 1916. The Rising was launched by Irish republicans against British rule in Ireland with the aim of establishing an independent Irish Republic while the United Kingdom was fighting the First World War. It was the most significant uprising in Ireland since the rebellion of 1798 and the first armed conflict of the Irish revolutionary period. Sixteen of the Rising's leaders were executed from May 1916. The nature of the executions, and subsequent political developments, ultimately contributed to an increase in popular support for Irish independence. Organised by a seven-man Military Council of the Irish Republican Brotherhood, the Rising began on Easter Monday, 24 April 1916 and lasted for six days.Members of the Irish Volunteers, led by schoolmaster and Irish language activist Patrick Pearse, joined by the smaller Irish Citizen Army of James Connolly and 200 women of Cumann na mBan, seized strategically important buildings in Dublin and proclaimed the Irish Republic. The British Army brought in thousands of reinforcements as well as artillery and a gunboat. There was street fighting on the routes into the city centre, where the rebels slowed the British advance and inflicted many casualties. Elsewhere in Dublin, the fighting mainly consisted of sniping and long-range gun battles. The main rebel positions were gradually surrounded and bombarded with artillery. There were isolated actions in other parts of Ireland; Volunteer leader Eoin MacNeill had issued a countermand in a bid to halt the Rising, which greatly reduced the number of rebels who mobilised. With much greater numbers and heavier weapons, the British Army suppressed the Rising. Pearse agreed to an unconditional surrender on Saturday 29 April, although sporadic fighting continued briefly. After the surrender, the country remained under martial law. About 3,500 people were taken prisoner by the British and 1,800 of them were sent to internment camps or prisons in Britain. Most of the leaders of the Rising were executed following courts-martial. The Rising brought physical force republicanism back to the forefront of Irish politics, which for nearly fifty years had been dominated by constitutional nationalism. Opposition to the British reaction to the Rising contributed to changes in public opinion and the move toward independence, as shown in the December 1918 election in Ireland which was won by the Sinn Féin party, which convened the First Dáil and declared independence. Of the 485 people killed, 260 were civilians, 143 were British military and police personnel, and 82 were Irish rebels, including 16 rebels executed for their roles in the Rising. More than 2,600 people were wounded. Many of the civilians were killed or wounded by British artillery fire or were mistaken for rebels. Others were caught in the crossfire during firefights between the British and the rebels. The shelling and resulting fires left parts of central Dublin in ruins.
43cm x 38cm Dublin The Easter Rising (Irish: Éirí Amach na Cásca), also known as the Easter Rebellion, was an armed insurrection in Ireland during Easter Week in April 1916. The Rising was launched by Irish republicans against British rule in Ireland with the aim of establishing an independent Irish Republic while the United Kingdom was fighting the First World War. It was the most significant uprising in Ireland since the rebellion of 1798 and the first armed conflict of the Irish revolutionary period. Sixteen of the Rising's leaders were executed from May 1916. The nature of the executions, and subsequent political developments, ultimately contributed to an increase in popular support for Irish independence. Organised by a seven-man Military Council of the Irish Republican Brotherhood, the Rising began on Easter Monday, 24 April 1916 and lasted for six days.Members of the Irish Volunteers, led by schoolmaster and Irish language activist Patrick Pearse, joined by the smaller Irish Citizen Army of James Connolly and 200 women of Cumann na mBan, seized strategically important buildings in Dublin and proclaimed the Irish Republic. The British Army brought in thousands of reinforcements as well as artillery and a gunboat. There was street fighting on the routes into the city centre, where the rebels slowed the British advance and inflicted many casualties. Elsewhere in Dublin, the fighting mainly consisted of sniping and long-range gun battles. The main rebel positions were gradually surrounded and bombarded with artillery. There were isolated actions in other parts of Ireland; Volunteer leader Eoin MacNeill had issued a countermand in a bid to halt the Rising, which greatly reduced the number of rebels who mobilised. With much greater numbers and heavier weapons, the British Army suppressed the Rising. Pearse agreed to an unconditional surrender on Saturday 29 April, although sporadic fighting continued briefly. After the surrender, the country remained under martial law. About 3,500 people were taken prisoner by the British and 1,800 of them were sent to internment camps or prisons in Britain. Most of the leaders of the Rising were executed following courts-martial. The Rising brought physical force republicanism back to the forefront of Irish politics, which for nearly fifty years had been dominated by constitutional nationalism. Opposition to the British reaction to the Rising contributed to changes in public opinion and the move toward independence, as shown in the December 1918 election in Ireland which was won by the Sinn Féin party, which convened the First Dáil and declared independence. Of the 485 people killed, 260 were civilians, 143 were British military and police personnel, and 82 were Irish rebels, including 16 rebels executed for their roles in the Rising. More than 2,600 people were wounded. Many of the civilians were killed or wounded by British artillery fire or were mistaken for rebels. Others were caught in the crossfire during firefights between the British and the rebels. The shelling and resulting fires left parts of central Dublin in ruins. -

 58cm x 42cm Quaint vintage poster of a jaunting car carrying a group around Phoenix Park- the giant Wellington monument can be seen in the background. The Wellington Monument or sometimes the Wellington Testimonial,is an obelisk located in the Phoenix Park, Dublin, Ireland. The testimonial is situated at the southeast end of the Park, overlooking Kilmainham and the River Liffey. The structure is 62 metres (203 ft) tall, making it the largest obelisk in Europe
58cm x 42cm Quaint vintage poster of a jaunting car carrying a group around Phoenix Park- the giant Wellington monument can be seen in the background. The Wellington Monument or sometimes the Wellington Testimonial,is an obelisk located in the Phoenix Park, Dublin, Ireland. The testimonial is situated at the southeast end of the Park, overlooking Kilmainham and the River Liffey. The structure is 62 metres (203 ft) tall, making it the largest obelisk in EuropeHistory
The Wellington Testimonial was built to commemorate the victories of Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington. Wellington, the British politician and general, also known as the 'Iron Duke', was born in Ireland. Originally planned to be located in Merrion Square, it was built in the Phoenix Park after opposition from the square's residents. The obelisk was designed by the architect Sir Robert Smirke and the foundation stone was laid in 1817. In 1820, the project ran out of construction funds and the structure remained unfinished until 18 June 1861 when it was opened to the public. There were also plans for a statue of Wellington on horseback, but a shortage of funds ruled that out.Features
There are four bronze plaques cast from cannons captured at Waterloo – three of which have pictorial representations of his career while the fourth has an inscription. The plaques depict 'Civil and Religious Liberty' by John Hogan, 'Waterloo' by Thomas Farrell and the 'Indian Wars' by Joseph Robinson Kirk. The inscription reads:- Asia and Europe, saved by thee, proclaim
- Invincible in war thy deathless name,
- Now round thy brow the civic oak we twine
- That every earthly glory may be thine.
Cultural references
The monument is referenced throughout James Joyce's Finnegans Wake. The first page of the novel alludes to a giant whose head is at "Howth Castle and Environs" and whose toes are at "a knock out in the park (p. 3)"; John Bishop extends the analogy, interpreting this centrally located obelisk as the prone giant's male member. A few pages later, the monument is the site of the fictional "Willingdone Museyroom" (p. 8). -
Out of stock

 Ferrars History of Limerick was first published in 1787.There are very few copies still in existence and these 5 prints were generously taken from 16 original engravings in the first edition .They depict the Siege of Limerick in 1691,St Marys Cathedral,De Burgos Castle in Castleconnell,The Exchange building and the first page of the book. 35cm x 40cm LimerickThe History of Limerick by James Ferrar published in 1787 is a history of Limerick city from ancient times until the late 18th century. Limerick was an important medieval stronghold, became an important port and trading centre, was subject to a series of sieges in the 17th century and finally experienced a brief golden age of prosperity during the Georgian period of the late 18th century. Limerick or Luimneach was an ancient settlement long before the Vikings captured it and established their own town there in the 9th century. They used it as a base for trade and also to launch raids up the River Shannon against monastic sites like Clonmacnoise and other wealthy Christian centres. However in the 11th century the last Viking king of Limerick was defeated by King Brian Boru. In 1174, the Norman conquerors who had already seized Dublin , Leinster and Munster captured the city of Limerick . It was given its city charter by King Richard I in 1197 and a castle fortress was built by King John about 1200. The medieval city featured a walled town known as Englishtown on the north side of the River Shannon. Irishtown was inhabited by the Irish and Vikings was on the south side of the river. Both were eventually walled and linked by bridges over the Shannon . Limerick would retain formidable defenses until the 17th century when it experienced four separate sieges during the period of the English Civil War and the Williamite Wars. Catholic rebels forced the English garrison to surrender in 1642 and a Parliamentarian Army in turn forced a Catholic and Royalist garrison to surrender in 1651. It was twice besieged in 1690 and 1691 by the forces of William III of Orange who forced Jacobins fighting on the sides of the Catholic James II to surrender and go into exile. From the late 17th to the 19th centuries an Anglo-Irish Protestant elite controlled Ireland . In Limerick in the late 1700s Limerick merchants prospered and Edmund Pery, 1st Viscount Pery had much of the south side of the city redesigned with a grid of Georgian brick terraces and neo-classical stone buildings. The Georgian area still survives in the 21st century and Prey Square is named in Edmund Prey's honour. Unfortunately the Irish economy declined in the early 19th century as the Irish Parliament was switched from College Green, Dublin to the House of Commons in London and Ireland remained a near feudal agricultural society as Britain rapidly industrialised. Like Dublin , Limerick 's best days were behind it as slums flourished and in the 1840s the city population swelled as the poor fled from the land after the failure of the potato crop.
Ferrars History of Limerick was first published in 1787.There are very few copies still in existence and these 5 prints were generously taken from 16 original engravings in the first edition .They depict the Siege of Limerick in 1691,St Marys Cathedral,De Burgos Castle in Castleconnell,The Exchange building and the first page of the book. 35cm x 40cm LimerickThe History of Limerick by James Ferrar published in 1787 is a history of Limerick city from ancient times until the late 18th century. Limerick was an important medieval stronghold, became an important port and trading centre, was subject to a series of sieges in the 17th century and finally experienced a brief golden age of prosperity during the Georgian period of the late 18th century. Limerick or Luimneach was an ancient settlement long before the Vikings captured it and established their own town there in the 9th century. They used it as a base for trade and also to launch raids up the River Shannon against monastic sites like Clonmacnoise and other wealthy Christian centres. However in the 11th century the last Viking king of Limerick was defeated by King Brian Boru. In 1174, the Norman conquerors who had already seized Dublin , Leinster and Munster captured the city of Limerick . It was given its city charter by King Richard I in 1197 and a castle fortress was built by King John about 1200. The medieval city featured a walled town known as Englishtown on the north side of the River Shannon. Irishtown was inhabited by the Irish and Vikings was on the south side of the river. Both were eventually walled and linked by bridges over the Shannon . Limerick would retain formidable defenses until the 17th century when it experienced four separate sieges during the period of the English Civil War and the Williamite Wars. Catholic rebels forced the English garrison to surrender in 1642 and a Parliamentarian Army in turn forced a Catholic and Royalist garrison to surrender in 1651. It was twice besieged in 1690 and 1691 by the forces of William III of Orange who forced Jacobins fighting on the sides of the Catholic James II to surrender and go into exile. From the late 17th to the 19th centuries an Anglo-Irish Protestant elite controlled Ireland . In Limerick in the late 1700s Limerick merchants prospered and Edmund Pery, 1st Viscount Pery had much of the south side of the city redesigned with a grid of Georgian brick terraces and neo-classical stone buildings. The Georgian area still survives in the 21st century and Prey Square is named in Edmund Prey's honour. Unfortunately the Irish economy declined in the early 19th century as the Irish Parliament was switched from College Green, Dublin to the House of Commons in London and Ireland remained a near feudal agricultural society as Britain rapidly industrialised. Like Dublin , Limerick 's best days were behind it as slums flourished and in the 1840s the city population swelled as the poor fled from the land after the failure of the potato crop. -

 St Marys Cathedral from Ferrars History of Limerick, first published in 1787.There are very few copies still in existence and these 5 prints were generously taken from 16 original engravings in the first edition 35cm x 40cm Limerick Limerick Cathedral (Saint Mary's) is dedicated to the Blessed Virgin Mary and was founded in 1168 and is the oldest building in Limerick which is in use. It has the only complete set of misericords left in Ireland. In 1111, the Synod of Ráth Breasail decided that "Saint Mary's church" would become the cathedral church of the Diocese of Limerick. According to tradition, Domnall Mór Ua Briain, the last King of Munster, founded the present cathedral on the site of his palace on King's Island in 1168.[3] The palace had been built on the site of the Viking meeting place, or "Thingmote" – the Vikings' most westerly European stronghold.[1] This had been the centre of government in the early medieval Viking city. Parts of the palace may be incorporated into the present structure of the cathedral, most prominently the great west door, which is claimed to have been the original main entrance to the royal palace.The west door is now only used on ceremonial occasions. The bishops of Limerick have for centuries knocked on this door and entered by it as part of their installation ceremony. According to tradition, during the many sieges of Limerick the defenders of the city used the stones around the west door to sharpen their swords and arrows, and the marks they made in the stonework can be seen there today. The tower of Saint Mary's Cathedral was added in the 14th century. It rises to 120 feet (36.58 meters), containing a peal of 8 bells, of which 6 were cast by John Taylor & Co, Loughborough, and 2 cast in Whitechapel, London. The tower also contains a stationary service bell, which can be rung from the ground floor.
St Marys Cathedral from Ferrars History of Limerick, first published in 1787.There are very few copies still in existence and these 5 prints were generously taken from 16 original engravings in the first edition 35cm x 40cm Limerick Limerick Cathedral (Saint Mary's) is dedicated to the Blessed Virgin Mary and was founded in 1168 and is the oldest building in Limerick which is in use. It has the only complete set of misericords left in Ireland. In 1111, the Synod of Ráth Breasail decided that "Saint Mary's church" would become the cathedral church of the Diocese of Limerick. According to tradition, Domnall Mór Ua Briain, the last King of Munster, founded the present cathedral on the site of his palace on King's Island in 1168.[3] The palace had been built on the site of the Viking meeting place, or "Thingmote" – the Vikings' most westerly European stronghold.[1] This had been the centre of government in the early medieval Viking city. Parts of the palace may be incorporated into the present structure of the cathedral, most prominently the great west door, which is claimed to have been the original main entrance to the royal palace.The west door is now only used on ceremonial occasions. The bishops of Limerick have for centuries knocked on this door and entered by it as part of their installation ceremony. According to tradition, during the many sieges of Limerick the defenders of the city used the stones around the west door to sharpen their swords and arrows, and the marks they made in the stonework can be seen there today. The tower of Saint Mary's Cathedral was added in the 14th century. It rises to 120 feet (36.58 meters), containing a peal of 8 bells, of which 6 were cast by John Taylor & Co, Loughborough, and 2 cast in Whitechapel, London. The tower also contains a stationary service bell, which can be rung from the ground floor.Notable burials
-
Bishop Charles Graves The cathedral graveyard contains many graves and tombs of notable people. The physician Samuel Crumpe is buried in the graveyard near the great west door. Prince Milo of Montenegro, Frances Condell (first woman Mayor of Limerick) and Bishop Charles Graves are also interred in the grounds. The last High King of Munster, Domnall was purportedly buried in the cathedral, with the remnants of his stone coffin still visible in the Cathedral chancel. Bishop Cornelius O'Dea is buried alongside several other Bishops of Limerick in what is believed to be an Episcopal vault underneath the chancel itself. Also notable are the Sexton, Barrington, Boyd and Vanderkiste tombs along the south entrance pathway.
From the Irish Reformation to the 19th century
There are five chandeliers which hang from the ceiling. These are only lit on special occasions. The larger three of the five were made in Dublin and presented in 1759 by the Limerick Corporation. The belfry holds a peal of eight bells, six of which were presented by William Yorke, mayor of Limerick, in 1673. An active team of bell ringers travels the country to compete with other campanologists.Saint Mary's received its organ in 1624, when Bishop Bernard Adams donated one. It has been rebuilt over the centuries and was most recently renovated in 1968 and 2005. In 1620 the English-born judge Luke Gernon, a resident of Limerick, wrote a flattering description of the cathedral: "not large, but lightsome, and by the providence of the Bishop fairly beautified within, and as gloriously served with singing and organs". During the Irish Confederacy wars, the cathedral was briefly transferred to Roman Catholic hands. The bishop of Limerick, Richard Arthur, was buried in the cathedral in 1646. In 1651, after Oliver Cromwell's forces captured Limerick, the cathedral was used as a stable by the parliamentary army. This misuse was short lived, but was a similar fate to that suffered by some of the other great cathedrals during the Cromwellian campaign in Ireland. The troops also removed the cathedral's original 13 ft Pre-Reformation high altar from the cathedral. The altar was only reinstated in the 1960s. It is the largest such altar in Ireland and the UK, carved from a single limestone block. The altar is used for communion services at major festivals and remains in its historic location in what is now the chapel of the Virgin Mary or Lady Chapel. In 1691, the cathedral suffered considerable damage, particularly on the east end, during the Williamite Siege of Limerick.After the Treaty of Limerick, William granted £1,000 towards repairs. There are cannonball from 1691 in the Glentworth Chapel/Saint George's Chapel inside.From the 19th century to the 20th century
In 1968, the Irish Government commissioned two postage stamps to commemorate the cathedral's 800 year anniversary. A picture of one of the stamps is displayed on this page. In 1991, there was a large £2.5 million restoration programme which was completed in 1996 with the excavation and re-laying of the floors as well as the installation of underfloor central heating. Restoration continues today to a lesser degree.From the 20th century to the 21st century
Today the cathedral is still used for its original purpose as a place of worship and prayer for everybody. It is also the 3rd biggest tourist attraction in Limerick. It is open to the public every day from 9:00 am to 4:45 pm. For Tourists there is a €5 admission charge upon entry. This money is essential for the upkeep of the building, and without it, the cathedral simply could not function. Following the retirement of the Very Rev'd Maurice Sirr on 24 June 2012, Bishop Trevor Williams announced the appointment of the Reverend Sandra Ann Pragnell as Dean of Limerick and Rector of Limerick City Parish. She was the first female dean of the cathedral and rector of Limerick City Parish, and retired in January 2017. It was announced on 27 August 2017, that the Reverend Canon Niall James Sloane was to become the 63rd Dean of Limerick and the new rector of Limerick City Parish; with his installation and institution taking place on 21 October 2017 in the cathedral. The cathedral grounds holds United Nations Memorial Plaque with the names of all the Irish men who died while serving in the United Nations Peacekeepers.The History of Limerick by James Ferrar published in 1787 is a history of Limerick city from ancient times until the late 18th century. Limerick was an important medieval stronghold, became an important port and trading centre, was subject to a series of sieges in the 17th century and finally experienced a brief golden age of prosperity during the Georgian period of the late 18th century. Limerick or Luimneach was an ancient settlement long before the Vikings captured it and established their own town there in the 9th century. They used it as a base for trade and also to launch raids up the River Shannon against monastic sites like Clonmacnoise and other wealthy Christian centres. However in the 11th century the last Viking king of Limerick was defeated by King Brian Boru. In 1174, the Norman conquerors who had already seized Dublin , Leinster and Munster captured the city of Limerick . It was given its city charter by King Richard I in 1197 and a castle fortress was built by King John about 1200. The medieval city featured a walled town known as Englishtown on the north side of the River Shannon. Irishtown was inhabited by the Irish and Vikings was on the south side of the river. Both were eventually walled and linked by bridges over the Shannon . Limerick would retain formidable defenses until the 17th century when it experienced four separate sieges during the period of the English Civil War and the Williamite Wars. Catholic rebels forced the English garrison to surrender in 1642 and a Parliamentarian Army in turn forced a Catholic and Royalist garrison to surrender in 1651. It was twice besieged in 1690 and 1691 by the forces of William III of Orange who forced Jacobins fighting on the sides of the Catholic James II to surrender and go into exile. From the late 17th to the 19th centuries an Anglo-Irish Protestant elite controlled Ireland . In Limerick in the late 1700s Limerick merchants prospered and Edmund Pery, 1st Viscount Pery had much of the south side of the city redesigned with a grid of Georgian brick terraces and neo-classical stone buildings. The Georgian area still survives in the 21st century and Prey Square is named in Edmund Prey's honour. Unfortunately the Irish economy declined in the early 19th century as the Irish Parliament was switched from College Green, Dublin to the House of Commons in London and Ireland remained a near feudal agricultural society as Britain rapidly industrialised. Like Dublin , Limerick 's best days were behind it as slums flourished and in the 1840s the city population swelled as the poor fled from the land after the failure of the potato crop. -
-
Out of stock
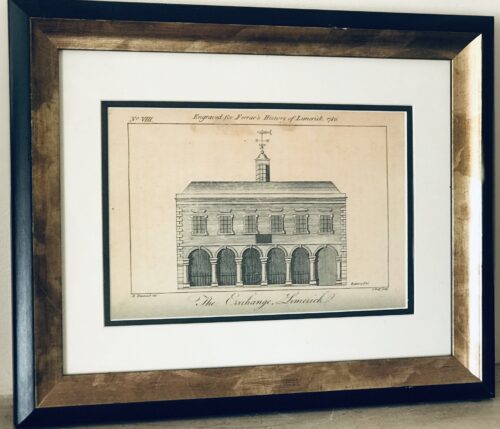
 Superb print of The Exchange Limerick from Ferrars History of Limerick,first published in 1787.There are very few copies still in existence and these 5 prints were generously taken from 16 original engravings in the first edition . 35cm x 40cm Limerickrcaded six-bay single-storey limestone exterior wall forming the remains of the former Exchange, originally built in 1673, rebuilt in 1702 and again in between 1777-78. Forms part of the wall which surrounds Saint Mary's Cathedral graveyard and faces onto Nicholas Street. Historically in use as an evening national school. Now much obscured by vegetative growth. The blind arcade of seven arches is formed by half-engaged Tuscan columns standing on limestone base, breaking to centre arch and end bay to west. Profiled archivolts unseen. Entablature to parapet obscured. Roughly squared and coursed rubble limestone infill between arches. At either end is an ashlar limestone pier engaged with end columns, giving strength of composition to the broad intercolumniation. Plaque to Cathedral wall reads: This Exchange Was Rebuilt At Expense Of The Corporation Of Limerick The First Year Of The Reign Of Queen Anne Anno Dom 1702 William Davis Esquire Mayor Rawley Colroys Robert Wilkinson Sheriffs'.
Superb print of The Exchange Limerick from Ferrars History of Limerick,first published in 1787.There are very few copies still in existence and these 5 prints were generously taken from 16 original engravings in the first edition . 35cm x 40cm Limerickrcaded six-bay single-storey limestone exterior wall forming the remains of the former Exchange, originally built in 1673, rebuilt in 1702 and again in between 1777-78. Forms part of the wall which surrounds Saint Mary's Cathedral graveyard and faces onto Nicholas Street. Historically in use as an evening national school. Now much obscured by vegetative growth. The blind arcade of seven arches is formed by half-engaged Tuscan columns standing on limestone base, breaking to centre arch and end bay to west. Profiled archivolts unseen. Entablature to parapet obscured. Roughly squared and coursed rubble limestone infill between arches. At either end is an ashlar limestone pier engaged with end columns, giving strength of composition to the broad intercolumniation. Plaque to Cathedral wall reads: This Exchange Was Rebuilt At Expense Of The Corporation Of Limerick The First Year Of The Reign Of Queen Anne Anno Dom 1702 William Davis Esquire Mayor Rawley Colroys Robert Wilkinson Sheriffs'.Appraisal
What remains of this impressive architectural composition is an important and enriching palimpsest to the site and complex of Saint Mary's Cathedral. The secular use of which shows the economic importance of the building given its proximity to the cathedral. Henry Denmead was responsible for the reworking in 1777-78. James Pain was paid £432.17s 5d for repairs and alterations in April 1815, while George Richard Pain carried out further repairs in June 1819 to the cost of £182.1s 2½ d. On the 1872 Ordnance Survey the building was in use as a national school, and the floor plan represented was of a single unified space opening onto Nicholas Street and three small secondary rooms to the rear. A passage or corridor to the west appears to have given access to the Church grounds, and the building to the rear looked onto a walled graveyard. A lane, now gone, called Grid Iron Lane, ran along the east side elevation of the structure, returning at right angles to meet Bridge Street.
The History of Limerick by James Ferrar published in 1787 is a history of Limerick city from ancient times until the late 18th century. Limerick was an important medieval stronghold, became an important port and trading centre, was subject to a series of sieges in the 17th century and finally experienced a brief golden age of prosperity during the Georgian period of the late 18th century. Limerick or Luimneach was an ancient settlement long before the Vikings captured it and established their own town there in the 9th century. They used it as a base for trade and also to launch raids up the River Shannon against monastic sites like Clonmacnoise and other wealthy Christian centres. However in the 11th century the last Viking king of Limerick was defeated by King Brian Boru. In 1174, the Norman conquerors who had already seized Dublin , Leinster and Munster captured the city of Limerick . It was given its city charter by King Richard I in 1197 and a castle fortress was built by King John about 1200. The medieval city featured a walled town known as Englishtown on the north side of the River Shannon. Irishtown was inhabited by the Irish and Vikings was on the south side of the river. Both were eventually walled and linked by bridges over the Shannon . Limerick would retain formidable defenses until the 17th century when it experienced four separate sieges during the period of the English Civil War and the Williamite Wars. Catholic rebels forced the English garrison to surrender in 1642 and a Parliamentarian Army in turn forced a Catholic and Royalist garrison to surrender in 1651. It was twice besieged in 1690 and 1691 by the forces of William III of Orange who forced Jacobins fighting on the sides of the Catholic James II to surrender and go into exile. From the late 17th to the 19th centuries an Anglo-Irish Protestant elite controlled Ireland . In Limerick in the late 1700s Limerick merchants prospered and Edmund Pery, 1st Viscount Pery had much of the south side of the city redesigned with a grid of Georgian brick terraces and neo-classical stone buildings. The Georgian area still survives in the 21st century and Prey Square is named in Edmund Prey's honour. Unfortunately the Irish economy declined in the early 19th century as the Irish Parliament was switched from College Green, Dublin to the House of Commons in London and Ireland remained a near feudal agricultural society as Britain rapidly industrialised. Like Dublin , Limerick 's best days were behind it as slums flourished and in the 1840s the city population swelled as the poor fled from the land after the failure of the potato crop. -
Out of stock
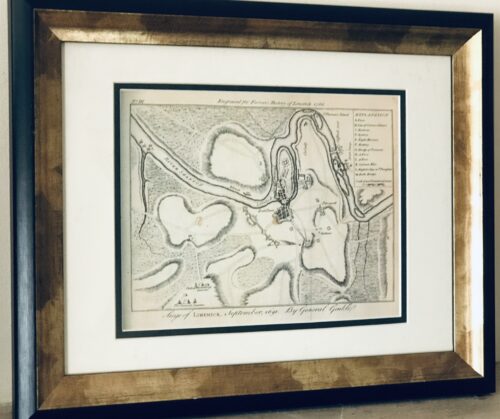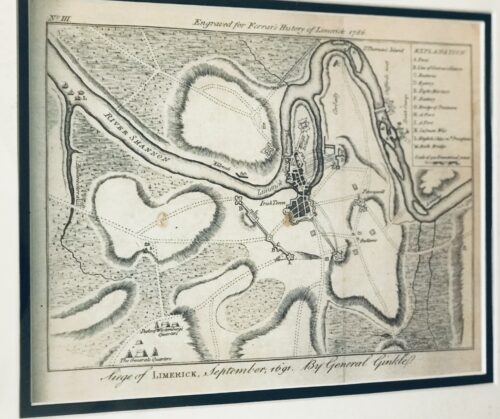
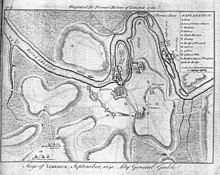
 The Siege of Limerick 1691 from the definitive Ferrars History of Limerick was first published in 1787 There are very few copies still in existence and these 5 prints were generously taken from 16 original engravings in the first edition . 35cm x 40cm Limerick The Siege of Limerick in western Ireland was a second siege of the town during the Williamite War in Ireland (1689–1691). The city, held by Jacobite forces was able to beat off a Williamite assault in 1690. However, after a second siege in August–October 1691, it surrendered on favourable terms. By the time of the second siege, the military situation had turned against the Jacobites; their main force had been badly defeated at the Battle of Aughrim in July, with over 4,000 killed, including their commander, the Marquis de St Ruth, and thousands more either taken prisoner or deserted. The town of Galway capitulated in July 1691; its Jacobite garrison was accorded 'all the honours of war,' which allowed them to retain their weapons and receive a free pass to Limerick. However, although its defences had been considerably strengthened since 1690, morale was now much lower after a series of defeats and retreats. By now, siege warfare was an exact art, the rules of which were so well understood wagering on their outcome and duration had become a popular craze; the then enormous sum of £200,000 was alleged to have been bet on the siege. The Williamite general Godert de Ginkell surrounded the city and bombarded it, tearing a breach in the walls of English town. A surprise Williamite attack drove the Irish defenders from the earthworks defending Thomond bridge, sending its Irish defenders reeling back towards Limerick. The French defenders of the main gate of the city refused to open it for the fleeing Irish and about 800 of them were cut down or drowned in the river Shannon.
The Siege of Limerick 1691 from the definitive Ferrars History of Limerick was first published in 1787 There are very few copies still in existence and these 5 prints were generously taken from 16 original engravings in the first edition . 35cm x 40cm Limerick The Siege of Limerick in western Ireland was a second siege of the town during the Williamite War in Ireland (1689–1691). The city, held by Jacobite forces was able to beat off a Williamite assault in 1690. However, after a second siege in August–October 1691, it surrendered on favourable terms. By the time of the second siege, the military situation had turned against the Jacobites; their main force had been badly defeated at the Battle of Aughrim in July, with over 4,000 killed, including their commander, the Marquis de St Ruth, and thousands more either taken prisoner or deserted. The town of Galway capitulated in July 1691; its Jacobite garrison was accorded 'all the honours of war,' which allowed them to retain their weapons and receive a free pass to Limerick. However, although its defences had been considerably strengthened since 1690, morale was now much lower after a series of defeats and retreats. By now, siege warfare was an exact art, the rules of which were so well understood wagering on their outcome and duration had become a popular craze; the then enormous sum of £200,000 was alleged to have been bet on the siege. The Williamite general Godert de Ginkell surrounded the city and bombarded it, tearing a breach in the walls of English town. A surprise Williamite attack drove the Irish defenders from the earthworks defending Thomond bridge, sending its Irish defenders reeling back towards Limerick. The French defenders of the main gate of the city refused to open it for the fleeing Irish and about 800 of them were cut down or drowned in the river Shannon.Capitulation and treaty
After this point, Patrick Sarsfield ousted the Chevalier de Tessé and the Marquis d'Usson, the French commanders in Limerick, and began negotiations to surrender. He and Ginkel concluded a treaty that promised to respect the civilian population of Limerick, tolerate the Catholic religion in Ireland, guarantee against the confiscation of Catholic-owned land and allow Sarsfield and the fully-armed Jacobite army to withdraw to France. Limerick capitulated under those favourable terms in October 1691. Sarsfield left Ireland with 10,000 soldiers and 4,000 women and children to enter the French service, a journey that has become known as the Flight of the Wild Geese. The terms of the Treaty of Limerick were not honoured by the 1697 Protestant-dominated Irish Parliament, and Catholics were subjected to the continuous oppression of the Penal Laws, which discriminated against them until the early 19th centuryThe History of Limerick by James Ferrar published in 1787 is a history of Limerick city from ancient times until the late 18th century. Limerick was an important medieval stronghold, became an important port and trading centre, was subject to a series of sieges in the 17th century and finally experienced a brief golden age of prosperity during the Georgian period of the late 18th century. Limerick or Luimneach was an ancient settlement long before the Vikings captured it and established their own town there in the 9th century. They used it as a base for trade and also to launch raids up the River Shannon against monastic sites like Clonmacnoise and other wealthy Christian centres. However in the 11th century the last Viking king of Limerick was defeated by King Brian Boru. In 1174, the Norman conquerors who had already seized Dublin , Leinster and Munster captured the city of Limerick . It was given its city charter by King Richard I in 1197 and a castle fortress was built by King John about 1200. The medieval city featured a walled town known as Englishtown on the north side of the River Shannon. Irishtown was inhabited by the Irish and Vikings was on the south side of the river. Both were eventually walled and linked by bridges over the Shannon . Limerick would retain formidable defenses until the 17th century when it experienced four separate sieges during the period of the English Civil War and the Williamite Wars. Catholic rebels forced the English garrison to surrender in 1642 and a Parliamentarian Army in turn forced a Catholic and Royalist garrison to surrender in 1651. It was twice besieged in 1690 and 1691 by the forces of William III of Orange who forced Jacobins fighting on the sides of the Catholic James II to surrender and go into exile. From the late 17th to the 19th centuries an Anglo-Irish Protestant elite controlled Ireland . In Limerick in the late 1700s Limerick merchants prospered and Edmund Pery, 1st Viscount Pery had much of the south side of the city redesigned with a grid of Georgian brick terraces and neo-classical stone buildings. The Georgian area still survives in the 21st century and Prey Square is named in Edmund Prey's honour. Unfortunately the Irish economy declined in the early 19th century as the Irish Parliament was switched from College Green, Dublin to the House of Commons in London and Ireland remained a near feudal agricultural society as Britain rapidly industrialised. Like Dublin , Limerick 's best days were behind it as slums flourished and in the 1840s the city population swelled as the poor fled from the land after the failure of the potato crop.
-
Out of stock

 35cm x 40cm Limerick City The definitive Ferrars History of Limerick was first published in 1787 There are very few copies still in existence and these 5 prints were generously taken from 16 original engravings in the first edition . Castleconnell, picturesquely situated on a rock overlooking the Shannon, about six miles north of Limerick, became the principal castle of the Bourkes in West Clanwilliam. This was the ancient seat of the O'Conaings, and took their name Caislean-ui-Chonaine. It subsequently fell into the possession of the O'Briens of Thomond. King John made a grant of Castleconnell, with five knights' fees, to William de Burgh, who erected a strong castle there. Walter De Burgh, about the end of the thirteenth century, considerably enlarged and strengthened this castle, which was the chief stronghold of his descendants at the end of the sixteenth century.The History of Limerick by James Ferrar published in 1787 is a history of Limerick city from ancient times until the late 18th century. Limerick was an important medieval stronghold, became an important port and trading centre, was subject to a series of sieges in the 17th century and finally experienced a brief golden age of prosperity during the Georgian period of the late 18th century. Limerick or Luimneach was an ancient settlement long before the Vikings captured it and established their own town there in the 9th century. They used it as a base for trade and also to launch raids up the River Shannon against monastic sites like Clonmacnoise and other wealthy Christian centres. However in the 11th century the last Viking king of Limerick was defeated by King Brian Boru. In 1174, the Norman conquerors who had already seized Dublin , Leinster and Munster captured the city of Limerick . It was given its city charter by King Richard I in 1197 and a castle fortress was built by King John about 1200. The medieval city featured a walled town known as Englishtown on the north side of the River Shannon. Irishtown was inhabited by the Irish and Vikings was on the south side of the river. Both were eventually walled and linked by bridges over the Shannon . Limerick would retain formidable defenses until the 17th century when it experienced four separate sieges during the period of the English Civil War and the Williamite Wars. Catholic rebels forced the English garrison to surrender in 1642 and a Parliamentarian Army in turn forced a Catholic and Royalist garrison to surrender in 1651. It was twice besieged in 1690 and 1691 by the forces of William III of Orange who forced Jacobins fighting on the sides of the Catholic James II to surrender and go into exile. From the late 17th to the 19th centuries an Anglo-Irish Protestant elite controlled Ireland . In Limerick in the late 1700s Limerick merchants prospered and Edmund Pery, 1st Viscount Pery had much of the south side of the city redesigned with a grid of Georgian brick terraces and neo-classical stone buildings. The Georgian area still survives in the 21st century and Prey Square is named in Edmund Prey's honour. Unfortunately the Irish economy declined in the early 19th century as the Irish Parliament was switched from College Green, Dublin to the House of Commons in London and Ireland remained a near feudal agricultural society as Britain rapidly industrialised. Like Dublin , Limerick 's best days were behind it as slums flourished and in the 1840s the city population swelled as the poor fled from the land after the failure of the potato crop.
35cm x 40cm Limerick City The definitive Ferrars History of Limerick was first published in 1787 There are very few copies still in existence and these 5 prints were generously taken from 16 original engravings in the first edition . Castleconnell, picturesquely situated on a rock overlooking the Shannon, about six miles north of Limerick, became the principal castle of the Bourkes in West Clanwilliam. This was the ancient seat of the O'Conaings, and took their name Caislean-ui-Chonaine. It subsequently fell into the possession of the O'Briens of Thomond. King John made a grant of Castleconnell, with five knights' fees, to William de Burgh, who erected a strong castle there. Walter De Burgh, about the end of the thirteenth century, considerably enlarged and strengthened this castle, which was the chief stronghold of his descendants at the end of the sixteenth century.The History of Limerick by James Ferrar published in 1787 is a history of Limerick city from ancient times until the late 18th century. Limerick was an important medieval stronghold, became an important port and trading centre, was subject to a series of sieges in the 17th century and finally experienced a brief golden age of prosperity during the Georgian period of the late 18th century. Limerick or Luimneach was an ancient settlement long before the Vikings captured it and established their own town there in the 9th century. They used it as a base for trade and also to launch raids up the River Shannon against monastic sites like Clonmacnoise and other wealthy Christian centres. However in the 11th century the last Viking king of Limerick was defeated by King Brian Boru. In 1174, the Norman conquerors who had already seized Dublin , Leinster and Munster captured the city of Limerick . It was given its city charter by King Richard I in 1197 and a castle fortress was built by King John about 1200. The medieval city featured a walled town known as Englishtown on the north side of the River Shannon. Irishtown was inhabited by the Irish and Vikings was on the south side of the river. Both were eventually walled and linked by bridges over the Shannon . Limerick would retain formidable defenses until the 17th century when it experienced four separate sieges during the period of the English Civil War and the Williamite Wars. Catholic rebels forced the English garrison to surrender in 1642 and a Parliamentarian Army in turn forced a Catholic and Royalist garrison to surrender in 1651. It was twice besieged in 1690 and 1691 by the forces of William III of Orange who forced Jacobins fighting on the sides of the Catholic James II to surrender and go into exile. From the late 17th to the 19th centuries an Anglo-Irish Protestant elite controlled Ireland . In Limerick in the late 1700s Limerick merchants prospered and Edmund Pery, 1st Viscount Pery had much of the south side of the city redesigned with a grid of Georgian brick terraces and neo-classical stone buildings. The Georgian area still survives in the 21st century and Prey Square is named in Edmund Prey's honour. Unfortunately the Irish economy declined in the early 19th century as the Irish Parliament was switched from College Green, Dublin to the House of Commons in London and Ireland remained a near feudal agricultural society as Britain rapidly industrialised. Like Dublin , Limerick 's best days were behind it as slums flourished and in the 1840s the city population swelled as the poor fled from the land after the failure of the potato crop. -
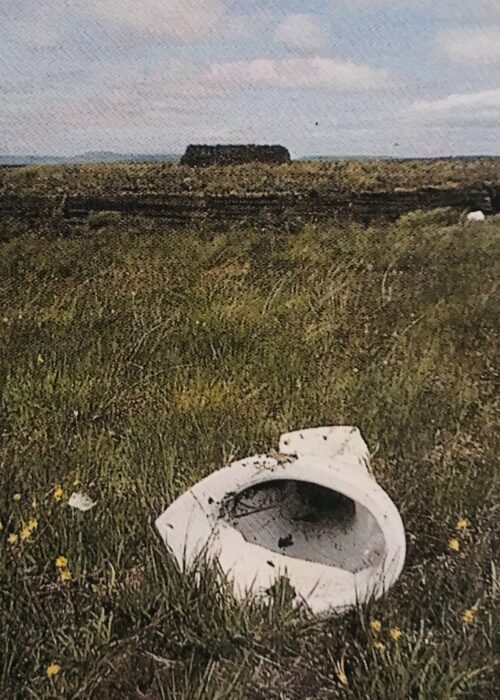
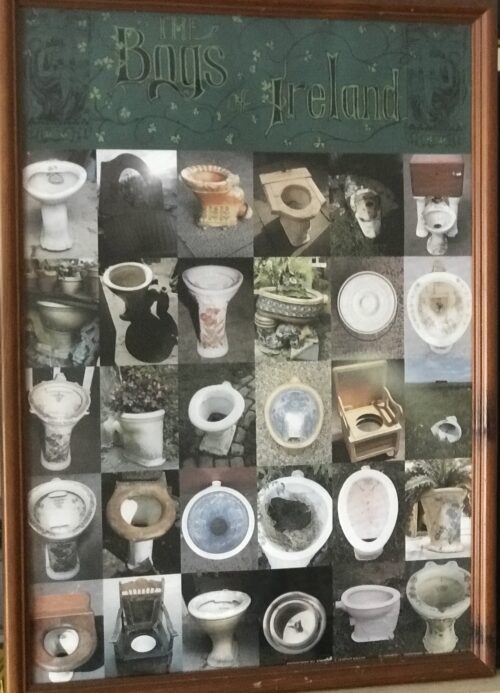
 Well framed Bogs of Ireland Print. We were very fortunate to acquire this very famous poster-The Bogs of Ireland.A collage of some very interesting toilets recorded for eternity by the renowned photographer John Morris.This poster is now completely out of print and is difficult to acquire.Makes a wonderful addition to anyone's favourite sanctuary and place of solitude! Dimensions : 65cm x 45cm
Well framed Bogs of Ireland Print. We were very fortunate to acquire this very famous poster-The Bogs of Ireland.A collage of some very interesting toilets recorded for eternity by the renowned photographer John Morris.This poster is now completely out of print and is difficult to acquire.Makes a wonderful addition to anyone's favourite sanctuary and place of solitude! Dimensions : 65cm x 45cm -

 24cm x 40cm The original company was founded in Belfast by Archibald Kirker and William Greer in 1885. From their bonded warehouse on Academy St. in the heart of Belfast they sourced and blended the best of Irish Whiskey. The Shamrock Irish Whiskey was one such blend.They went on to found the Connswater distillery and became one of ireland’s largest exporters.
24cm x 40cm The original company was founded in Belfast by Archibald Kirker and William Greer in 1885. From their bonded warehouse on Academy St. in the heart of Belfast they sourced and blended the best of Irish Whiskey. The Shamrock Irish Whiskey was one such blend.They went on to found the Connswater distillery and became one of ireland’s largest exporters. -

 57cm x 48cm The Dewar's whisky brand was created by John Dewar, Sr. in 1846.Under the control of his two sons, John A. Dewar Jr. and Thomas "Tommy" Dewar, the brand expanded to become a global market leader by 1896 and began to win several awards, including a gold medal in the 1904 St. Louis World's Fair. Tommy became famous as the author of a travel journal, Ramble Round the Globe, which documented his travels while publicizing the Dewar name. Dewar's eventually expanded their product by constructing the Aberfeldy Distillery in 1896.The company joined Distillers Company in 1925. Distillers was acquired by Guinness in 1986, and Guinness merged with Grand Metropolitan to form Diageo in 1997. Diageo sold Dewar's to Bacardi the next year. Dewar's rose to prominence in the United States when Andrew Carnegie requested a small keg of Dewar's Scotch whisky be sent to the White House for President James Garfield's inauguration. Carnegie also sent the same gift to President Benjamin Harrisonon his inauguration eight years later. In 1987, numerous cases of still perfect Dewar's Scotch were recovered by underwater archaeologist E. Lee Spence from the shipwreck of the SS Regina, which sank in Lake Huron in 1913.
57cm x 48cm The Dewar's whisky brand was created by John Dewar, Sr. in 1846.Under the control of his two sons, John A. Dewar Jr. and Thomas "Tommy" Dewar, the brand expanded to become a global market leader by 1896 and began to win several awards, including a gold medal in the 1904 St. Louis World's Fair. Tommy became famous as the author of a travel journal, Ramble Round the Globe, which documented his travels while publicizing the Dewar name. Dewar's eventually expanded their product by constructing the Aberfeldy Distillery in 1896.The company joined Distillers Company in 1925. Distillers was acquired by Guinness in 1986, and Guinness merged with Grand Metropolitan to form Diageo in 1997. Diageo sold Dewar's to Bacardi the next year. Dewar's rose to prominence in the United States when Andrew Carnegie requested a small keg of Dewar's Scotch whisky be sent to the White House for President James Garfield's inauguration. Carnegie also sent the same gift to President Benjamin Harrisonon his inauguration eight years later. In 1987, numerous cases of still perfect Dewar's Scotch were recovered by underwater archaeologist E. Lee Spence from the shipwreck of the SS Regina, which sank in Lake Huron in 1913. John Dewar & Sons 1926 client correspondence with watermark on document
John Dewar & Sons 1926 client correspondence with watermark on documentNotable processes
Dewar's pioneered the process of "marrying" the whisky in oak casks to allow the blend to age as one within the casks. After the blend is created, the whisky is returned to an oak cask and aged even further to obtain a smooth, robust finish.