-

 Ennis Co Clare 50cm x 60cm De Valera was a near demagogue type politician who dominated Irish Political life from 1917 to 1973,whether as Prime Minister or President or as leader of the Opposition.Known as the Long Fella,Irish people either loved or hated him-there was simply no ambivalent feelings about this most polarising of politicians.This fine portrait of De Valera catches him perfectly and would make a superb addition to any Irish Pub ,both at home or abroad with a Fianna Fail or Republican bias or anyone from Clare,a county where he was always at his most popular. Eamon de Valera, first registered as George de Valero; changed some time before 1901 to Edward de Valera;14 October 1882 – 29 August 1975) was a prominent statesman and political leader in 20th-century Ireland. His political career spanned over half a century, from 1917 to 1973; he served several terms as head of government and head of state. He also led the introduction of the Constitution of Ireland. Prior to de Valera's political career, he was a Commandant at Boland's Mill during the 1916 Easter Rising, an Irish revolution that would eventually contribute to Irish independence. He was arrested, sentenced to death but released for a variety of reasons, including the public response to the British execution of Rising leaders. He returned to Ireland after being jailed in England and became one of the leading political figures of the War of Independence. After the signing of the Anglo-Irish Treaty, de Valera served as the political leader of Anti-Treaty Sinn Fein until 1926, when he, along with many supporters, left the party to set up Fianna Fáil, a new political party which abandoned the policy of abstentionism from Dáil Éireann. From there, de Valera would go on to be at the forefront of Irish politics until the turn of the 1960s. He took over as President of the Executive Councilfrom W. T. Cosgrave and later Taoiseach, with the passing of Bunreacht Na hEireann (Irish constitution) in 1937. He would serve as Taoiseach on 3 occasions; from 1937 to 1948, from 1951 to 1954 and finally from 1957 to 1959. He remains the longest serving Taoiseach by total days served in the post. He resigned in 1959 upon his election as President of Ireland. By then, he had been Leader of Fianna Fáil for 33 years, and he, along with older founding members, began to take a less prominent role relative to newer ministers such as Jack Lynch, Charles Haughey and Neil Blaney. He would serve as President from 1959 to 1973, two full terms in office. De Valera's political beliefs evolved from militant Irish republicanism to strong social, cultural and economic conservatism.He has been characterised by a stern, unbending, devious demeanor. His roles in the Civil War have also portrayed him as a divisive figure in Irish history. Biographer Tim Pat Coogan sees his time in power as being characterised by economic and cultural stagnation, while Diarmaid Ferriter argues that the stereotype of de Valera as an austere, cold and even backward figure was largely manufactured in the 1960s and is misguided.
Ennis Co Clare 50cm x 60cm De Valera was a near demagogue type politician who dominated Irish Political life from 1917 to 1973,whether as Prime Minister or President or as leader of the Opposition.Known as the Long Fella,Irish people either loved or hated him-there was simply no ambivalent feelings about this most polarising of politicians.This fine portrait of De Valera catches him perfectly and would make a superb addition to any Irish Pub ,both at home or abroad with a Fianna Fail or Republican bias or anyone from Clare,a county where he was always at his most popular. Eamon de Valera, first registered as George de Valero; changed some time before 1901 to Edward de Valera;14 October 1882 – 29 August 1975) was a prominent statesman and political leader in 20th-century Ireland. His political career spanned over half a century, from 1917 to 1973; he served several terms as head of government and head of state. He also led the introduction of the Constitution of Ireland. Prior to de Valera's political career, he was a Commandant at Boland's Mill during the 1916 Easter Rising, an Irish revolution that would eventually contribute to Irish independence. He was arrested, sentenced to death but released for a variety of reasons, including the public response to the British execution of Rising leaders. He returned to Ireland after being jailed in England and became one of the leading political figures of the War of Independence. After the signing of the Anglo-Irish Treaty, de Valera served as the political leader of Anti-Treaty Sinn Fein until 1926, when he, along with many supporters, left the party to set up Fianna Fáil, a new political party which abandoned the policy of abstentionism from Dáil Éireann. From there, de Valera would go on to be at the forefront of Irish politics until the turn of the 1960s. He took over as President of the Executive Councilfrom W. T. Cosgrave and later Taoiseach, with the passing of Bunreacht Na hEireann (Irish constitution) in 1937. He would serve as Taoiseach on 3 occasions; from 1937 to 1948, from 1951 to 1954 and finally from 1957 to 1959. He remains the longest serving Taoiseach by total days served in the post. He resigned in 1959 upon his election as President of Ireland. By then, he had been Leader of Fianna Fáil for 33 years, and he, along with older founding members, began to take a less prominent role relative to newer ministers such as Jack Lynch, Charles Haughey and Neil Blaney. He would serve as President from 1959 to 1973, two full terms in office. De Valera's political beliefs evolved from militant Irish republicanism to strong social, cultural and economic conservatism.He has been characterised by a stern, unbending, devious demeanor. His roles in the Civil War have also portrayed him as a divisive figure in Irish history. Biographer Tim Pat Coogan sees his time in power as being characterised by economic and cultural stagnation, while Diarmaid Ferriter argues that the stereotype of de Valera as an austere, cold and even backward figure was largely manufactured in the 1960s and is misguided. -
Out of stock
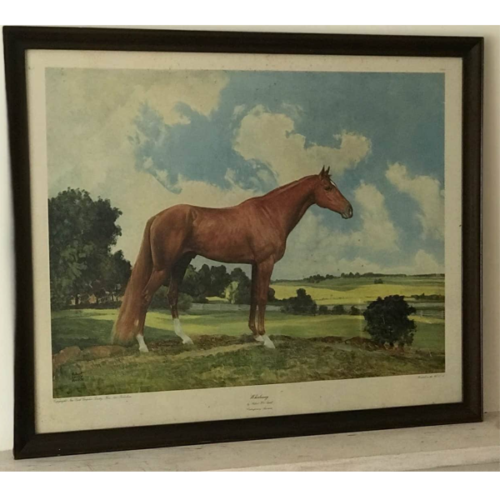 Whirlaway was an outstanding US racehorse and winner of the 1941 American Triple Crown.Origins :Co Limerick Dimensions :65 x 80.5cm. 9kg Unglazed
Whirlaway was an outstanding US racehorse and winner of the 1941 American Triple Crown.Origins :Co Limerick Dimensions :65 x 80.5cm. 9kg Unglazed
He was voted the American Champion Two-Year-Old Colt in 1940 by Turf & Sports Digest magazine. The rival Daily Racing Form award was won by Our Boots. Jimmy Jones, son of the colt's trainer, recalled that "Whirlaway was a creature of habit. You had to create habits for him. So we created the habits we wanted him to do." Whirlaway was regarded as having a "quirky" personality.The champion colt had a habit of "bearing out," drifting toward the middle of the racetrack, during the latter part of his races and losing as a result. In preparations for the Kentucky Derby, this had been such a problem that trainer Ben A. Jones fitted the colt with a full-cup blinker over his right eye. In Whirlaway's final workout before the Derby, Jones cut a small hole in the blinker so that the horse had a tiny field of vision. Jones positioned himself ten feet off the inner rail and told jockey Eddie Arcaro to ride the horse through that space. Whirlaway was able to see his trainer, Arcaro was able to keep him on a straight path, and Whirlaway won the Kentucky Derby by tying the current (as of 2018) record margin of 8 lengths.Whirlaway 
Sire Blenheim Grandsire Blandford Dam Dustwhirl Damsire Sweep Sex Stallion Foaled 1938 Country United States Colour Chestnut Breeder Calumet Farm Owner Calumet Farm Trainer Ben A. Jones Record 60: 32-15-9 Earnings $561,161 Major wins Breeders' Futurity Stakes (1940) Hopeful Stakes (1940) Saratoga Special Stakes (1940) Walden Stakes (1940) A. J. Joyner Handicap (1941) Travers Stakes (1941) Lawrence Realization Stakes (1941) Saranac Handicap (1941) Dwyer Stakes (1941) American Derby (1941) Massachusetts Handicap (1942) Narragansett Special (1942) Clark Handicap (1942) Jockey Club Gold Cup (1942) Louisiana Handicap (1942) Washington Handicap (1942) Trenton Handicap (1942) American Classic Race wins: Kentucky Derby (1941) Preakness Stakes (1941) Belmont Stakes (1941) Awards 5th U.S. Triple Crown Champion (1941) TSD American Champion Two-Year-Old Colt(1940) U.S. Champion 3-Yr-Old Colt (1941) United States Horse of the Year (1941 & 1942) U.S. Champion Older Male Horse (1942) Whirlaway (April 2, 1938 – April 6, 1953) was an American champion thoroughbred racehorse. The chestnut horse was sired by English Derby winner Blenheim, out of the broodmare Dustwhirl. Whirlaway was bred at Calumet Farm in Lexington, Kentucky. Trained by Ben A. Jones and ridden by Eddie Arcaro, Whirlaway won the U.S. Triple Crown in 1941. Whirlaway was widely known as "Mr. Longtail" because his tail was especially long and thick and it would blow far out behind him during races, flowing dramatically in the wind. Racing record
Trained by Ben A. Jones and ridden by Arcaro, Whirlaway won the U.S. Triple Crown in 1941. He also won the Lawrence Realization Stakes and the Travers Stakes that year; Whirlaway is the only horse ever to win both the Triple Crown and the Travers, sometimes referred to as a "superfecta".He was voted the Horse of the Year in 1941, beating Alsab by 96 votes to 91 in a poll conducted by the Turf and Sport Digest magazine.A year later, Whirlaway repeated his win in the poll, beating Alsab with 76 votes to his rival's 45. Arcaro was the sole rider for Whirlaway in all of his 3-year-old victories, but dismounted for most of the 1942 season, when he served a long suspension for racing infractions. Jockey George Woolf took the reins for the majority of the 1942 season. In a major upset on July 4, 1942 at Empire City Race Track, Whirlaway ran second to Tola Rose who easily won by four lengths in track record time. On July 15, Whirlaway broke the Suffolk Downs track record for a mile and one-eighth with a time of 1:48 1/5 in winning the Massachusetts Handicap. Whirlaway and Alsab continued their 1941 rivalry through 1942. On September 19, 1942, Alsab defeated the Triple Crown champion in a match race at Narragansett Park in Pawtucket, Rhode Island. Although Whirlaway closed strongly through the stretch, Alsab lasted by a nose as both horses flew home through the stretch run. Whirlaway was named Horse of the Year for 1942 after defeating Alsab in a subsequent race and having 12 wins for the year to Alsab's 9. Woolf, who had previously won the Pimlico Special in 1938 on Seabiscuit and in 1940 on Challedon, rode the 1941 Triple Crown winner at a leisurely pace during the 1942 Pimlico Special in a walkover victory. No opponent had been found to challenge Whirlaway for the race. On December 12, more than twenty thousand people turned out to watch Whirlaway win the inaugural Louisiana Handicap at the Fair Grounds Race Course. The newly formed Thoroughbred Racing Association staged this event as a war-relief effort. Whirlaway entered stud at Calumet Farm in the spring of 1944 at age six. Among his best offspring were Scattered (winner of the Coaching Club American Oaks); Whirl Some (Selima Stakes), Dart By (All American Handicap) and Whirling Bat[10] (winner of the 1951 Louisiana Derby). In August 1950, Calumet Farm leased Whirlaway to French breeder Marcel Boussac, who stood the horse at his breeding farm, Haras de Fresnay-le-Buffard. Boussac purchased Whirlaway from Calumet in September 1952.[11] The stallion died at Boussac's French stud in 1953.[12][13] Whirlaway was elected to the National Museum of Racing and Hall of Fame in 1959. In The Blood-Horse magazine's ranking of the top 100 U.S. thoroughbred champions of the 20th century, he was No. 26. Whir -
Out of stock
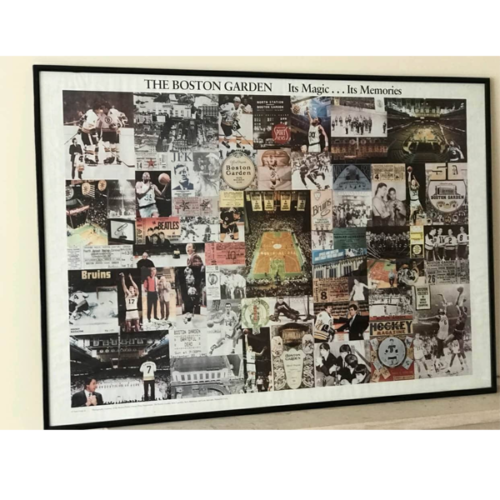 Irish pubs don't just decorate their space with Irish memorabilia.Such is our affinity with the US in particular, that often you see American sports and other pieces of memorabilia on display.And over time we have added such nuggets to our extensive collection.This framed collage of memories from the Boston Garden originated from a pub in Kerry,the owners of which had plenty of family connections in Boston,some of whom actually worked at the Garden.Hence this lovely piece getting sent across the Atlantic. This wonderful poster depicts many of the great events that took place in the Garden over the years.
Irish pubs don't just decorate their space with Irish memorabilia.Such is our affinity with the US in particular, that often you see American sports and other pieces of memorabilia on display.And over time we have added such nuggets to our extensive collection.This framed collage of memories from the Boston Garden originated from a pub in Kerry,the owners of which had plenty of family connections in Boston,some of whom actually worked at the Garden.Hence this lovely piece getting sent across the Atlantic. This wonderful poster depicts many of the great events that took place in the Garden over the years.
Boston Garden was an arena in Boston, Massachusetts. Designed by boxing promoter Tex Rickard, who also built the third iteration of New York's Madison Square Garden, it opened on November 17, 1928 as "Boston Madison Square Garden" (later shortened to just "Boston Garden") and outlived its original namesake by 30 years. It was above North Station, a train station which was originally a hub for the Boston and Maine Railroad and is now a hub for MBTA Commuter Rail and Amtrak trains. The Garden hosted home games for the Boston Bruins of the National Hockey League (NHL) and the Boston Celtics of the National Basketball Association (NBA), as well as rock concerts, amateur sports, boxing and professional wrestling matches, circuses, and ice shows. It was also used as an exposition hall for political rallies such as the speech by John F. Kennedy in November 1960. Boston Garden was demolished in 1998, three years after the completion of its new successor arena, TD Garden.Boston Garden "The Garden" Boston Garden viewed from Causeway Street 1994
Boston Garden viewed from Causeway Street 1994
Former names Boston Madison Square Garden Address 150 Causeway Street Location Boston, Massachusetts Owner Boston and Maine Corporation(1928–1965) Linnell & Cox (1965]–1973) Storer Broadcasting (1973–1975) Delaware North (1975–1997) Operator Madison Square GardenCorporation (1928–1934) Boston Garden-Arena Corporation(1934–1973) Storer Broadcasting (1973–1975) Delaware North (1975–1997) Capacity Ice hockey: 14,448 Basketball: 14,890 Concerts: 15,909 Surface Ice / Parquet floor Construction Broke ground December 1927 Opened November 17, 1928 Closed September 28, 1995 Demolished March 1998 Construction cost $4 million ($59.6 million in 2019 dollars) Architect Tex Rickard Funk & Wilcox Company General contractor Dwight P. Robinson Company, Inc. Tenants Boston Bruins (NHL) (1928–1995) Boston Celtics (BAA/NBA) (1946–1995) Boston Braves (AHL) (1971–1974) New England Whalers (WHA) (1973–1974) Boston Blazers (MILL) (1992–1995) History
Tex Rickard, the noted entrepreneur and boxing promoter who built and operated the third Madison Square Garden, sought to expand his empire by building seven "Madison Square Gardens" around the country. On November 15, 1927, Homer Loring, chairman of the Boston & Maine Railroad, announced that plans had been finalized for the construction of a new North Station facility, which would include a sports arena. A group led by Rickard, John S. Hammond, and William F. Carey of the Madison Square Garden Corporation, as well as Boston businessmen Charles F. Adamsand Huntington Hardwick, signed a 25-year lease for the arena. Sheldon Fairbanks was chosen to be the arena's first general manager. Boston & Maine shareholder Edmund D. Codman challenged the legality of the railroad constructing a non-railroad building. The Massachusetts General Court passed legislation expanding the corporate powers of the Boston & Maine Railroad which was signed by Governor Alvan T. Fuller on March 6, 1928. Codman's Bill in equity was dismissed by Massachusetts Supreme Court Justice John B. Crosby in October 1928. Built at a cost of $10 million – over double the cost for New York's arena three years earlier – Boston Garden turned out to be the last of Rickard's proposed series, a decision fueled by high costs and Rickard's death in 1929. The Garden's first event was on November 17, 1928, a boxing card headlined by Boston Native "Honey Boy" Dick Finnegan's defeat of Andre Routis.The first team sporting event was held three days later, an ice hockey game between the Bruins and the archrival Montreal Canadiens, won by the Canadiens 1–0. The game was attended by 17,000 fans, 2,000 over capacity, as fans without tickets stormed their way in. The game started 25 minutes late. Windows and doors were broken by the fans in the action. The first non-sporting event, a conclave featuring evangelist Rodney "Gipsy" Smith, was held on March 24, 1929.Early years
During the Boston Garden's early years, the arena was owned by the Boston and Maine Corporation and controlled by Rickard and the Madison Square Garden. In 1934, the Madison Square Garden Corporation sold its interest in the Boston Garden to the Boston Arena Corporation, led by Henry G. Lapham. This resulted in the creation of the Boston Garden-Arena Corporation.George V. Brown served as general manager of the Garden under the Boston Garden-Arena Corporation until his death in 1937, when he was succeeded by his son, Walter A. Brown. During the early years of the Boston Garden, the building's main draws were boxing, wrestling, and Bruins hockey. Johnny Indrisano, Lou Brouillard, Ernie Schaaf, Al Mello, and Jack Sharkey were among the boxers who fought at the Boston Garden. Wrestling became big due to the popularity of Gus Sonnenberg. Sonnenberg defeated Ed "Strangler" Lewis at the Garden in 1929 in a fight that set an attendance record for a wrestling match (19,500) and drew a record gate ($77,000). Paul Bowser promoted wrestling in Boston at this time and when the sport began to lose popularity, he brought Danno O'Mahony from Ireland to Boston. O'Mahony became a popular draw at the Garden. In 1930, construction on the Hotel Manger, a 500-room hotel connected to the Boston Garden through an elevated skyway, was completed. The hotel (later known as the Hotel Madison) closed in 1976 and was demolished in 1983.73 x 104cm 7kgThe Garden suffered economically during the Great Depression. Boxing was at a low point in Boston, as fighters chose to work in other cities, wrestling attendance was down, and hockey attendance waned after Ace Bailey suffered a severe head injury at the hands of Bruin Eddie Shore in 1933. During this period Sonja Henie's Hollywood Ice Revue and the Ice Follies were successful draws and kept the Garden afloat. In 1939, a financial dispute between Henie and her managers led Walter Brown and eight other arena managers to found the Ice Capades.Design
Rickard built the arena specifically with boxing in mind, believing every seat should be close enough to see the "sweat on the boxers' brows". Because of this design theme, fans were much closer to the players during Bruins and Celtics games than in most arenas, leading to a distinct hometown advantage. This physical proximity also created spectacular acoustic effects, much like the Chicago Stadium. When teams made playoff appearances, and a sold-out crowd was chanting or screaming, the impact was enormous. Due to the success of the Celtics in the 1980s, the Boston Garden was one of the most difficult buildings for visiting NBA teams. During the 1985–86 season, the Celtics were 40–1 at home, setting the NBA record for home court mastery (before the San Antonio Spurs tied the record 30 years later in the 2015–16 season). They also finished the post-season undefeated at home. Combined with the following regular season, the Celtics' Garden record was an amazing 79-3 between the 1985–86 and 1986–87 regular seasons. While the parquet floor was an important part of the history of the Celtics,[38] it was not originally part of the Garden. The parquet floor was built and installed in the aforementioned Boston Arena(first home of the Bruins hockey team) and moved to the Garden in 1952. It is said the Celtics knew which way the basketball would bounce off any section of the floor; this was one contributing factor to the Celtics' many NBA championships.The floor became as much a part of Boston sports lore as the Green Monster of Fenway Park. The parquet floor was used at the FleetCenter until December 22, 1999. Portions of the original floor are integrated with new parquet. The floor was cut into small pieces and sold as souvenirs along with seats and bricks. The Naden/Day Industries overhead scoreboard (which was electro-mechanical, not electronic, as more recent arenas used) hung in the Boston Garden-themed food court of the Arsenal Mall in Watertown until 2018, when the mall began to undergo renovations.The Celtics' old championship banners and retired numbers now hang at the team's now-former practice facility in Waltham; a new set of banners were made for the move to the FleetCenter (now TD Garden). The Celtics used to raise Eastern Division championship banners at Boston Garden in the 1960s, but stopped this practice by the 1970s. Likewise, the Bruins made a new set of banners when they moved to the FleetCenter, which were again replaced after the 2011 Stanley Cup Finals with six new banners, each using the contemporary logo of the Bruins when each Cup victory occurred. The Bruins also raised numerous Adams Division, Presidents' Trophy and Wales Conference championship banners at the old Garden, but due to lack of space, they consolidated them into one single banner each upon moving to TD GardenFlaws
The Garden's hockey rink was undersized at 191 by 83 feet (58.2 m × 25.3 m), some nine feet shorter and two feet narrower than standard (200 ft × 85 ft or 61 m × 26 m), due to the rink being built at a time when the NHL did not have a standard size for rinks. This size was even smaller than the original Boston Arena's standard-length 200-by-80-foot (61 m × 24 m) rink, still in use in the 21st century for college hockey with a new, widened 90-foot (27 m) upgrade in 1995, as the Boston Arena was the first rink to host the Bruins in 1924–25. Visiting players were frequently thrown off their games by the differing setup of the players' benches being on opposing sides of the ice, as well as the non-standard penalty box locations. This setup, still occasionally seen in college hockey, was done to ensure that each team could have a bench connected to their dressing room. Towards the end of the Garden's life as an arena, the NHL required all rinks to have both benches on the same side: the Garden obliged by moving the penalty boxes (formerly adjacent to the Bruins' bench) to the side vacated by the visitor's bench, and as such visiting teams were required to skate across the ice to head back to their rooms. The smaller ice surface allowed the Bruins to dump the puck in the offensive zone and then crush their opponents with checks along the boards. The shorter rink was well-suited to the rushing style of Bruins defenseman Bobby Orr; he was able to get from one end of the ice to another faster than in a standard-size rink. Its visitors' dressing room was notoriously small, hot, and underserved by plumbing. The Garden's earlier Bulova-crafted "Sports Timer" game clock system using the typical analog dial-type game clock design of that era, said to have been installed at the Garden early in the 1940s, and essentially identical in appearance and function to the one used in the Chicago Stadium until September 1975,was removed and replaced by an all-digital-display unit created by the Day Sign Company of Toronto in time for the 1970 Stanley Cup playoffs, and remained in use until the Garden's closure. The Garden had no air conditioning, resulting in fog forming over the ice during some Bruins' playoff games. During Game 5 of the 1984 NBA Finals, the 97 °F (36 °C) heat in the facility was so intense that oxygen tanks were provided to exhausted players. The Bruins' Stanley Cup finals appearances in 1988 and 1990 were both disrupted by power outages. On May 24, 1988, a power transformer in the North End blew up during Game 4 of the Finals between the Bruins and the Edmonton Oilers: the contest ended, being ruled as a 3–3 tie. Two years later, on May 15, 1990, the lights went out during an overtime finals game between the same two teams. However, the lights were on an automatic timer and could be turned back on this time with the game ending with a 3–2 triple overtime win for the visiting Oilers.Notable events
Music
Rudy Vallée and his orchestra performed at the Garden on April 21, 1932. Vallée returned to the Garden on October 23–24, 1938 for a "battle of the bands" with Benny Goodman that drew 25,000. The first rock concert held at the Garden was on November 30, 1956, when the building hosted Alan Freed's "Biggest Show of 1956". The Beatles played a show at the Garden during their first US/Canada tour on September 12, 1964, staying at the then-attached Hotel Madison. James Brown played a notable show at the Garden on April 5, 1968, the night after Martin Luther King Jr. was assassinated. Only 2,000 attended the sold-out show, because the mayor, Kevin White, and community leaders had encouraged people to obtain refunds on their tickets and instead to watch a hastily arranged television broadcast of the concert on the local public station WGBH-TV. Mayor White appeared on stage, asking the Garden audience and the city to peacefully remember King, and James Brown's words and presence was credited with helping to keep the peace in Boston. WGBH rebroadcast the concert twice that night, an action which helped keep people off of the street at a time other major cities were erupting in riots. The performance was released on DVD as Live at the Boston Garden: April 5, 1968. Elvis Presley performed in Boston only once, at the Garden on November 10, 1971 pulling a full crowd of about 16,500 and receiving high praise from Rolling Stone journalist Jon Landau for his performance. In 1972, The Rolling Stones were scheduled to perform at the Garden when two members were detained by Rhode Island police. Fearful that angry Stones fans (already in the Garden awaiting the show) would riot, mayor Kevin H. White intervened with the Rhode Island authorities and secured the musicians' release so they could play their set in Boston. The band had also played at the venue in 1965 and 1969 and would again in 1975. In 1973, The Who were scheduled to perform at the Garden and nearly didn't perform due to the band being detained by police after destroying a hotel room in Montreal, Quebec, Canada, where they'd appeared the previous evening. The band was eventually released from jail and managed to arrive at the Garden in time for their show and took out their frustrations for being arrested the night before by delivering a blistering set and taunting the Montreal police, dedicating their performance of "Won't Get Fooled Again" to them. Who drummer Keith Moon (for the rest of the Quadrophenia tour) changed one of the lyrics to the song "Bell Boy" from "remember the gaff where the doors we smashed" to "remember Montreal at the hotel we trashed" or variations of the band being arrested. Almost three years later in March 1976, Moon collapsed at his drum kit during the second song "Substitute" after downing muscle relaxers and brandy before the show. The band had to reschedule the performance for early April and the rescheduled performance turned out to be one of The Who's best performances of the 1976 tour. The Who's last performance at the Garden was in December 1979 on their first tour following Moon's death. That performance was almost canceled after several fans at a Who show in Cincinnatidied while trying to get in early for a general admission show. The Boston City Council held a televised hearing on whether to allow the show to go forward and decided to permit it because there was no general admission seating in Boston. The show was marred by a fan throwing a firecracker on stage, causing Pete Townshend to scream obscenities in the general direction of the source before getting on with the tension-filled show. In 1975, Led Zeppelin were banned from performing at the Boston Garden after concert fans were allowed in the lobby due to sub-freezing temperatures while waiting for tickets to go on sale for the band's show. Turning on the generosity of their hosts, some of the fans rioted, broke into the Garden and trashed the seating area, the ice, and most of the refreshment stands, leading then-mayor White to cancel the upcoming show and ban the group for five years. In 1976, KISS was banned from performing at the Garden because the band refused to comply with the venue's no pyrotechnic policy after fire marshals had watched their flamethrowers hit the ceiling at the Orpheum. Pink Floyd were the first band to perform at the Boston Garden with a stage set that cost over $1 million on their 1977 Animals tour (they first played there in 1975 on the band's Wish You Were Here tour). According to Pink Floyd drummer Nick Mason's book Inside Out: A Personal History of Pink Floyd, Pink Floyd almost got banned from the Boston Garden after their 1977 performances because the band, unknown to the venue's owners, used pyrotechnics during their performance (the exploding pig for "Pigs (Three Different Ones)" and firework displays on "Sheep" and "Money"). However, the band's road crew outsmarted the fire marshals by removing the pyro props quickly after they used them in the shows to prevent the band from being banned and also according to Mason's book since their manager had an Irish name (Steve O'Rourke), the band escaped being arrested. The band decided not to play at the venue again, instead opting for the Providence Civic Center and Foxboro Stadium on their 1987/1988 and 1994 tours, respectively. The Grateful Dead performed at the Boston Garden more times than any other band, with 24 performances from 1973 to 1994 (as an opener or middle of bill or headliner), and were intended to be the last band to play the Garden, with six shows scheduled for September 13th, 14th, 15th,17th, 18th, and 19th 1995, which were canceled due to the death of Jerry Garcia on August 9, 1995. The ticket for the 19th stated "lets tear this old building down" referencing the song "Samson and Delilah". The Dead did not play at the Garden for a number of years following an incident in which they were caught grilling lobsters on a fire escape before a performance.The Grateful Dead have released Dick's Picks Volume 12 and 17 culled from performances at the Garden on June 28, 1974 and September 25, 1991. Detroit rocker Bob Seger recorded a bulk of his 1981 double live album Nine Tonight at The Boston Garden in October 1980. Five years before, The J. Geils Band recorded most of their November 1975 show at The Boston Garden for their 1976 double live album Blow Your Face Out. The Geils band returned again, and had the historical distinction of being the first band in history to sell out a three-night stand in 1982 at the Garden featuring hometown favorites Jon Butcher Axis as opening act. Hometown band Aerosmith performed at the Boston Garden ten times from 1975 to 1995 and twice played New Year's shows there, ringing in the 1990 and 1994 New Years. Other acts that performed at the Garden include Pavarotti, Frank Sinatra, Liberace, Duke Ellington, Judy Garland, Arthur Fiedler and the Boston Pops, U2, Bruce Springsteen, Guns N' Roses, Grace Slick with Jefferson Airplane, Jethro Tull (who had 15 headlining performances there between 1971 and 1980 which is the most for a band, their last being on 1980's A Tour before switching to the Worcester Centrum in 1982), Bob Dylan with The Band, Diana Ross & the Supremes, The Jackson 5, Queen, Rush, Styx and George Burns and Gracie Allen among others. The opening of the Worcester Centrum and the Great Woods Amphitheater caused a massive drop in concerts at the Garden from the early 1980s until the early 1990s. The age of glam metalpractically passed the Garden by completely, as most bands from that era played the Centrum in the winter and Great Woods in the summer. Poor acoustics, a busy sports schedule, expensive booking fees, and difficulty with local unions all contributed to the migration to more modern venues outside of Boston. Under new Garden President Larry Moulter, bands started returning to the Garden in the late 1980s and early 1990s, highlighted by Pearl Jam's multi-night stand in 1994, and the Dead's lengthy residences there before the Garden finally closed. The final New Year's Eve show at the Boston Garden was performed by the Vermont band Phish on December 31, 1994. On that night, the band rode a giant hot dog float above the audience; the hot dog is now in the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in Cleveland.Sports
The facility hosted games in the 1929, 1930, 1932, 1939, 1941, 1943, 1946, 1953, 1957, 1958, 1970, 1972, 1974, 1977, 1978, 1988, and 1990 Stanley Cup Finals where the Bruins won two of their championships at the Garden in 1939 and 1970. The 1929 Stanley Cup championship was won at New York's Madison Square Garden (III). The 1941 Stanley Cup championship was won at Detroit's Olympia Stadium. The 1972 Stanley Cup championship was won at New York's Madison Square Garden. The Montreal Canadiens claimed the Stanley Cup at the Garden in 1958, 1977 and 1978, while the Detroit Red Wings won the cup there in 1943. In 1990, the Edmonton Oilers claimed their fifth Stanley Cup at the Garden. The 1932 series did not involve the Bruins; Game 2 between the Toronto Maple Leafs and New York Rangers was played there due to a scheduling conflict at MSG III. The facility has also hosted games in the 1957, 1958, 1959, 1960, 1961, 1962, 1963, 1964, 1965, 1966, 1968, 1969, 1974, 1976, 1981, 1984, 1985, 1986, and 1987 NBA Finals, in which the Celtics won nine of their championships on home court in 1957, 1960, 1961, 1962, 1964, 1965, 1966, 1984, and 1986. The only visitor to claim the NBA championship at the Garden were the Los Angeles Lakers, who won the 1985 Finals. In addition to championship rounds, the Garden also hosted the NBA All-Star Game in 1951, 1952, 1957, and 1964, and the NHL All-Star Game in 1971. The NCAA Frozen Four was contested there from 1972 to 1974. Starting in 1955, the Beanpot tournament, featuring the four major college hockey programs in the Boston area, was held at the Garden annually on the first week of February. Boston Garden was the first arena to host the Stanley Cup Final and NBA Finals at the same time in 1957. It occurred again in 1958 and 1974. The Boston Garden was a frequent host of Vince McMahon's WWF for many years throughout the 1970s and 1980s, in the form of wrestling "house shows" (non-televised matches), and superstars like Hulk Hogan, André the Giant, Randy "Macho Man" Savage, Tito Santana, Ricky "The Dragon" Steamboat and many others would regularly appear there. But despite this relationship, the Boston Garden was host to only one pro wrestling pay-per-view in its history: the 1993 Survivor Series. The WWF held their final house show in the Boston Garden on May 13, 1995.Rallies and speeches
The Boston Garden hosted many religious conclaves. Evangelists who appeared at the Garden include Aimee McPherson (1931), Billy Graham (1950) Bishop Fulton J. Sheen (1953), and Jimmy Swaggart (July 29–31, 1983). The Garden was also the site of a number of political rallies. 20,000 people attended a 55th birthday celebration for President Franklin D. Roosevelt on January 29, 1937. FDR also drew another 20,000 for a political rally 1940. On May 2, 1943, the night after the Hollywood Victory Caravan came through town, a Jewish anti-Nazi rally was held at the Garden. The United War Fund hosted a rally headlined by Jimmy Durante, Greer Garson, and the Boston Symphony Orchestra. The day before the 1960 presidential election, a rally for John F. Kennedy drew 20,000 while police estimated that there were another 100,000 people in the streets outside the Garden. Other politicians to hold rallies at the Garden include presidential candidates Thomas Dewey and Dwight D. Eisenhower and former Boston mayor and Massachusetts governor James Michael Curley. Former Irish Prime Minister and President Éamon de Valera spoke at the Garden On March 24, 1948 (Easter Sunday). British Prime Minister Winston Churchill spoke there March 31, 1949 as part of a Massachusetts Institute of Technology Convocation.Final years
By the early 1970s, Boston Garden was deteriorating. The building had no air conditioning and some seats were obstructed by structural pillars. The seats were decades old and terribly cramped. With a capacity of less than 15,000, it was one of the country's smallest major league sports arenas. The Garden also lacked luxury suites, which had become an important and much-needed source of revenue for teams in professional sports. In 1972, Boston Mayor Kevin White announced plans for a new 18,000-seat arena to be built near South Station. Plans for the arena fell through when Storer Broadcasting, then-owner of the Boston Garden and the Bruins, announced they would not be able to pay the $24 to $28 million required for the new arena. In 1977 the Boston Celtics negotiated with the city of Quincy to have a $30 million, 21,000-seat arena built there. In 1979, Boston Celtics owner Harry T. Mangurian, Jr. threatened to build a new arena unless the Boston Bruins, who owned the Garden, agreed to lower the rent. The team met with Ogden Corp., owners of Suffolk Downs, who proposed a $20 million, 18,000-seat arena to be built near the racetrack. They also met with the Boston Redevelopment Authority, who proposed $40 million, 15,000-seat arena that would be built behind the existing Garden and paid for with state bonds.]The Bruins meanwhile announced plans to move to a proposed $50 million sports complex on the site of the then closed Rockingham Park in Salem, New Hampshire. The plans for the Salem site were eventually killed by the New Hampshire General Court. Meanwhile, the track remained closed until May 26, 1984. In response to the Bruins' plans to leave the state, U.S. Senator Paul Tsongas established a committee to put forward a plan for a new Boston arena. The committee, chaired by Tsongas, proposed a $56.8 million, 16,000 seat arena that would be paid for by tax-exempt bonds floated by an Arena Authority and by raising the commonwealth's hotel tax from 5.7% to 8%. The naming rights to the proposed arena were sold to Sheraton for $2 million.Tsongas' proposal died in the state legislature. While a preservation study conducted by the Boston Landmarks Commission found the North Station/Boston Garden complex to be a significant example of Art Deco, the Massachusetts Historical Commission did not consider it eligible for listing in the National Register. In 1985, Garden-owner Delaware North and developer Rosalind Gorin each submitted proposals for a new arena, hotel, and office development. Both proposals were rejected by the Boston Redevelopment Authority and Mayor Raymond Flynn.The two groups later resubmitted plans, with Delaware North's calling for a renovation of the Garden instead of having it demolished.Gorin's plan called for the city to claim the Garden by eminent domain, as Delaware North refused to sell the Bruins and the Garden to a group led by Gorin, Paul Tsongas, and former Bruins Wayne Cashman and Bobby Orr.Delaware North was awarded the rights to construct the new arena, but poor economic conditions delayed the project. On May 8, 1992, Delaware North announced they had secured funding for a new arena in the form of $120 million worth of loans evenly split among Bank of Boston, Fleet Bank of Massachusetts, and Shawmut National Corporation. That December, a bill approving construction of the new arena was killed in the Massachusetts Senate by Senate President William M. Bulger. Legislative leaders and Delaware North attempted to reach an agreement on plans for the new arena, but in February 1993 Delaware North owner Jeremy Jacobs announced he was backing out of the project as a result of the legislature's demand his company pay $3.5 million in "linkage payments".Two weeks later, after a new series of negotiations, the two sides came to an agreement, and on February 26 the Legislature passed a bill that allowed for construction of a new sports arena.[68] Construction began on April 29, 1993. Shawmut Bank purchased the naming rights for the new building with the intent of calling it the "Shawmut Center", but it was purchased by FleetBank before the new arena opened, and thus the "FleetCenter" opened on September 30, 1995. In 2005, the FleetCenter was renamed the "TD Banknorth Garden", as Bank of America had acquired Fleet Bank and relinquished its predecessor's naming rights, selling them to TD Banknorth. As of 2009, it is known as TD Garden.[69][70] The Grateful Dead were scheduled to play September 13th, 14th, 15th, 17th, 18th and the 19th being the final event at the garden. The ticket for the 19th featured "lets tear this old building down" referencing the song Samson and Delilah. These shows were cancelled upon Jerry Garcia's death. The last official game played at the Garden took place on Sunday, May 14, 1995. It was game five of an NHL Eastern Conference quarterfinal series between the Boston Bruins and New Jersey Devils where the New Jersey Devils beat the Bruins, 3–2, winning the series four games to one and eliminating the Bruins from the 1995 Stanley Cup Playoffs. The last event at the Boston Garden was a preseason game between the Boston Bruins and the Montreal Canadiens on September 26, 1995.[71] In a special post-game ceremony, which included many former Bruins greats, the banners and retired numbers were removed. The Garden sat vacant for three years before it was demolished in 1998. The site where the building once stood is currently under construction for a commercial development known as The Hub on Causeway.References
-
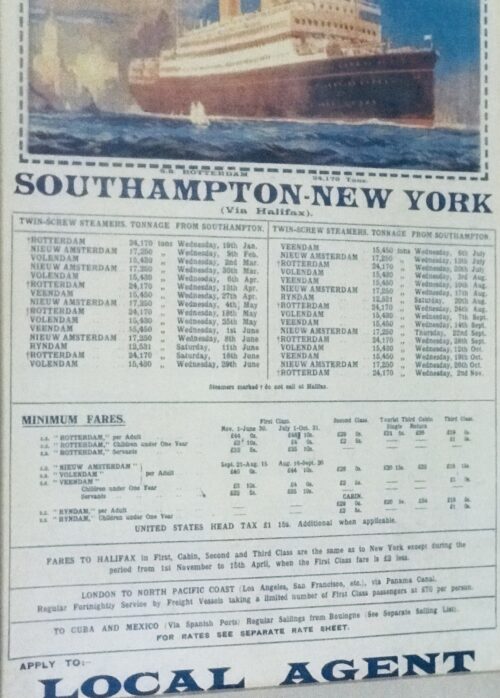
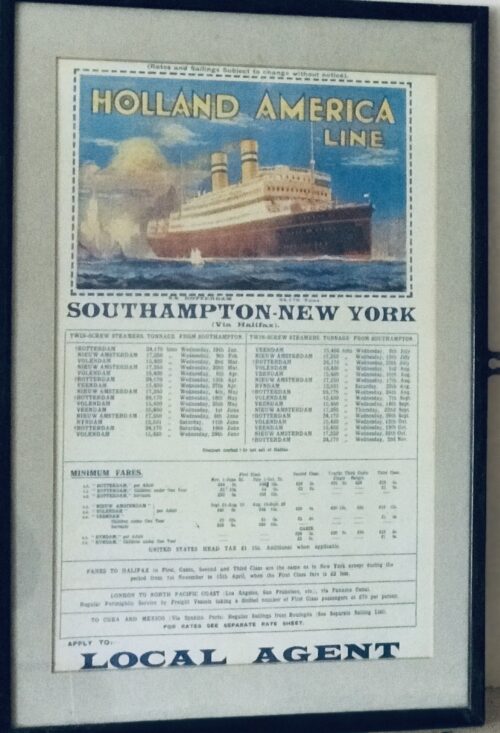 50cm x 35cm Birr Co Offaly "The Holland-America Line, a steamship company with passenger and freight steamers plying between Rotterdam and New York, is the only steamship line carrying emigrants from the Netherlands to the United States of America. Emigrants from the interior of the continent of Europe, who purchase their steamship tickets from the branch offices of the Holland-America Line in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and Italy, arrive in Rotterdam on international trains, in which several cars have been set apart for their accommodation, from five to six days before the departure of the steamer on which they expect to sail; while emigrants from parts not far distant from this city, like southern Germany and the interior of the Netherlands, arrive at Rotterdam by train and river boat until the day previous to the departure of the steamer. All emigrants for the Holland-America Line are met at the railway station and boat landing at Rotterdam by runners of the line, who conduct them, immediately upon arrival, per steam tug to the NASM Hotel, the emigrant hotel owned and controlled by the Holland-America Line and situated opposite to the line's wharf. Here the emigrants remain until the departure of the steamer on which they are to sail or, in case they should be found undesirable immigrants by one of the medical inspectors, by the steamship company, or by the consul-general or vice-consul-general, until the time that they are returned again to the countries whence they came. The NASM Hotel was designed and built exclusively for the accommodation of the immigrants traveling per Holland-America Line. In the construction, besides the comfort of the emigrants, the sanitary requirements for a building of its kind have been given due consideration. The dining rooms and coffee or conversation rooms are, though necessarily somewhat sober in appearance in order to insure cleanliness, bright, spacious, and pleasant. The dormitories are spacious, clean, and airy. Sleeping apartments, open on top, each containing from four to six iron berths, similar to those used in the steerage of the company's twin-screw steamers, have been partitioned off along the walls. This gives the immigrants the desired privacy, besides the advantage of being together with the members of their family in one apartment. Between the partitions a wide space is left in the center of the dormitories for chairs, tables, etc., while windows and ventilators provide light and air on every side. There are separate dormitories for families, for men, and for women. Spacious wash and bath rooms, with modern appointments, are located on the vestibules conveniently close to each dormitory. The hotel has been constructed in such a manner that, should the need at any time arise, it would be possible to quarantine 800 passengers within its walls as effectually as though they were on shipboard. This possibility of isolation before sailing is a great sanitary advantage. With reference to this hotel, Consul Listoe wrote in his dispatch to the Department of State, under date of April 6, 1900: The company's claim that it is furnishing good lodging and board for emigrants at a low figure and at the same time protecting them against low, boardinghouse runners and sharpers, who would fleece them, is correct, and the Holland America Line is entitled to a great deal of credit for the humane manner in which it treats and cares for its emigrants. What is of more importance, though, from a United States point of view, is the facilities furnished the examining physician at the NASM Hotel for inspecting the emigrants as well as the arrangements for cleaning, bathing, and disinfecting the latter, and taking other sanitary measures in connection with those prospective citizens of the United States. At the hotel the emigrants are, at the instance of the Holland America Line, daily subjected to a medical inspection by a Dutch physician in the employ of the line. One day before sailing the emigrants are inspected at the hotel by a prominent Rotterdam oculist, engaged by the steamship company for its own protection,' to prevent emigrants suffering from infectious eye diseases sailing on its steamers. As the medical inspections referred to are not those prescribed by the United States Quarantine Regulations, they are not witnessed by a consular officer. The work of consular inspection is carried on as follows: The day previous to the departure of a passenger steamer, the baggage of all steerage passengers is inspected by the consul-general or his deputy. Among this baggage large quantities of mildewed and otherwise spoiled eatables are found. These are taken out, this having been the practice of the Marine-Hospital surgeon formerly detailed at Rotterdam. All feather pillows and beds are taken from the baggage and undergo a steam disinfection of 1000 Cel. As many as 60 beds can be disinfected at the same time by the Holland-America Line's disinfection plants, and each disinfection will require about one and one-half hours, viz, half an hour for getting up the required steam heat, half an hour for the disinfection, and half an hour for drying purposes. When there are 200 beds or more to be disinfected, which is frequently the case, supervision of the disinfection will keep a consular officer engaged for several hours. The inspection of the baggage takes from two to four hours, according to the number of packages to be inspected. The last medical and general inspection of the emigrants at which the consul-general or vice-consul-general is present is the inspection prescribed by the Quarantine Regulations, page I5, paragraph 5. It takes place in the hotel of the Holland-American Line or in the line's covered warehouse and· begins from three to six hours before the departure of the steamer. The emigrants pass in single file before the ship's surgeon, an American physician, who inspects them in the presence of the consular officer, who, for his part, looks over their inspection cards, prescribed by the Quarantine Regulations, page 19, paragraph 40, and stamps the same with a consular rubber seal, for all emigrants approved of. There are also present an officer of the State commission controlling the transit of emigrants through the Netherlands, who tallies their numbers, and a Rotterdam police officer, who watches for fugitives from justice among them reported to the Netherlands police authorities. Immediately after the inspection, the emigrants in possession of inspection cards bearing the consular stamp board the steamer and enter the steerage, which has previously been inspected by the consul. A few minutes before departure, after looking over the freight manifests of the vessel to see if all the requirements of the Quarantine Regulations and of the regulations of the Department of Agriculture have been complied with reference to disinfection certificates and certificates of healthy origin, the bill of health is issued. The emigrants are vaccinated by the ship's surgeon as soon as practicable after the departure of the vessel. Of late years no emigrants from infected districts have passed through Rotterdam on their way to the United States. Should such occur at any time, then they can be effectually quarantined in the hotel of the Holland-America Line for the periods prescribed by the Quarantine Regulations. AIRE H. VOORWINDEN, Vice and Deputy Consul- Gtneral. In a letter by Mr. Voorwinden to Mr. Peirce. CONSULATE-GENERAL, UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, Rotterdam, Netherlands, September 23 1903.
50cm x 35cm Birr Co Offaly "The Holland-America Line, a steamship company with passenger and freight steamers plying between Rotterdam and New York, is the only steamship line carrying emigrants from the Netherlands to the United States of America. Emigrants from the interior of the continent of Europe, who purchase their steamship tickets from the branch offices of the Holland-America Line in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and Italy, arrive in Rotterdam on international trains, in which several cars have been set apart for their accommodation, from five to six days before the departure of the steamer on which they expect to sail; while emigrants from parts not far distant from this city, like southern Germany and the interior of the Netherlands, arrive at Rotterdam by train and river boat until the day previous to the departure of the steamer. All emigrants for the Holland-America Line are met at the railway station and boat landing at Rotterdam by runners of the line, who conduct them, immediately upon arrival, per steam tug to the NASM Hotel, the emigrant hotel owned and controlled by the Holland-America Line and situated opposite to the line's wharf. Here the emigrants remain until the departure of the steamer on which they are to sail or, in case they should be found undesirable immigrants by one of the medical inspectors, by the steamship company, or by the consul-general or vice-consul-general, until the time that they are returned again to the countries whence they came. The NASM Hotel was designed and built exclusively for the accommodation of the immigrants traveling per Holland-America Line. In the construction, besides the comfort of the emigrants, the sanitary requirements for a building of its kind have been given due consideration. The dining rooms and coffee or conversation rooms are, though necessarily somewhat sober in appearance in order to insure cleanliness, bright, spacious, and pleasant. The dormitories are spacious, clean, and airy. Sleeping apartments, open on top, each containing from four to six iron berths, similar to those used in the steerage of the company's twin-screw steamers, have been partitioned off along the walls. This gives the immigrants the desired privacy, besides the advantage of being together with the members of their family in one apartment. Between the partitions a wide space is left in the center of the dormitories for chairs, tables, etc., while windows and ventilators provide light and air on every side. There are separate dormitories for families, for men, and for women. Spacious wash and bath rooms, with modern appointments, are located on the vestibules conveniently close to each dormitory. The hotel has been constructed in such a manner that, should the need at any time arise, it would be possible to quarantine 800 passengers within its walls as effectually as though they were on shipboard. This possibility of isolation before sailing is a great sanitary advantage. With reference to this hotel, Consul Listoe wrote in his dispatch to the Department of State, under date of April 6, 1900: The company's claim that it is furnishing good lodging and board for emigrants at a low figure and at the same time protecting them against low, boardinghouse runners and sharpers, who would fleece them, is correct, and the Holland America Line is entitled to a great deal of credit for the humane manner in which it treats and cares for its emigrants. What is of more importance, though, from a United States point of view, is the facilities furnished the examining physician at the NASM Hotel for inspecting the emigrants as well as the arrangements for cleaning, bathing, and disinfecting the latter, and taking other sanitary measures in connection with those prospective citizens of the United States. At the hotel the emigrants are, at the instance of the Holland America Line, daily subjected to a medical inspection by a Dutch physician in the employ of the line. One day before sailing the emigrants are inspected at the hotel by a prominent Rotterdam oculist, engaged by the steamship company for its own protection,' to prevent emigrants suffering from infectious eye diseases sailing on its steamers. As the medical inspections referred to are not those prescribed by the United States Quarantine Regulations, they are not witnessed by a consular officer. The work of consular inspection is carried on as follows: The day previous to the departure of a passenger steamer, the baggage of all steerage passengers is inspected by the consul-general or his deputy. Among this baggage large quantities of mildewed and otherwise spoiled eatables are found. These are taken out, this having been the practice of the Marine-Hospital surgeon formerly detailed at Rotterdam. All feather pillows and beds are taken from the baggage and undergo a steam disinfection of 1000 Cel. As many as 60 beds can be disinfected at the same time by the Holland-America Line's disinfection plants, and each disinfection will require about one and one-half hours, viz, half an hour for getting up the required steam heat, half an hour for the disinfection, and half an hour for drying purposes. When there are 200 beds or more to be disinfected, which is frequently the case, supervision of the disinfection will keep a consular officer engaged for several hours. The inspection of the baggage takes from two to four hours, according to the number of packages to be inspected. The last medical and general inspection of the emigrants at which the consul-general or vice-consul-general is present is the inspection prescribed by the Quarantine Regulations, page I5, paragraph 5. It takes place in the hotel of the Holland-American Line or in the line's covered warehouse and· begins from three to six hours before the departure of the steamer. The emigrants pass in single file before the ship's surgeon, an American physician, who inspects them in the presence of the consular officer, who, for his part, looks over their inspection cards, prescribed by the Quarantine Regulations, page 19, paragraph 40, and stamps the same with a consular rubber seal, for all emigrants approved of. There are also present an officer of the State commission controlling the transit of emigrants through the Netherlands, who tallies their numbers, and a Rotterdam police officer, who watches for fugitives from justice among them reported to the Netherlands police authorities. Immediately after the inspection, the emigrants in possession of inspection cards bearing the consular stamp board the steamer and enter the steerage, which has previously been inspected by the consul. A few minutes before departure, after looking over the freight manifests of the vessel to see if all the requirements of the Quarantine Regulations and of the regulations of the Department of Agriculture have been complied with reference to disinfection certificates and certificates of healthy origin, the bill of health is issued. The emigrants are vaccinated by the ship's surgeon as soon as practicable after the departure of the vessel. Of late years no emigrants from infected districts have passed through Rotterdam on their way to the United States. Should such occur at any time, then they can be effectually quarantined in the hotel of the Holland-America Line for the periods prescribed by the Quarantine Regulations. AIRE H. VOORWINDEN, Vice and Deputy Consul- Gtneral. In a letter by Mr. Voorwinden to Mr. Peirce. CONSULATE-GENERAL, UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, Rotterdam, Netherlands, September 23 1903. -
Out of stock

 Extremely rare photograph of the 1936 Limerick Hurlers as they embarked on a tour of the USA after winning the All Ireland. This photo was taken on board a transatlantic liner shows a very happy group setting sail for America where they would be feted as was customary for reigning All Ireland champions. 53cm x 65cm Castleconnell Co LimerickIn 1936, the Limerick GAA hurlers took on a New York team at Yankee Stadium.British Pathe has shared this amazing footage of the Limerick GAA hurling team taking on the New York-based hurling team on the hallowed grounds of Yankee Stadium in 1936. The historic footage, which unfortunately does not include sound, features the Limerick hurling team posing as a group on the pitch, as well as longshots of the match and the crowds in the grandstands.British Pathe noted that M. Mackey and T. Ryan scored for Limerick, and the final score was 16 points to 9 points, with Limerick as the victors.
Extremely rare photograph of the 1936 Limerick Hurlers as they embarked on a tour of the USA after winning the All Ireland. This photo was taken on board a transatlantic liner shows a very happy group setting sail for America where they would be feted as was customary for reigning All Ireland champions. 53cm x 65cm Castleconnell Co LimerickIn 1936, the Limerick GAA hurlers took on a New York team at Yankee Stadium.British Pathe has shared this amazing footage of the Limerick GAA hurling team taking on the New York-based hurling team on the hallowed grounds of Yankee Stadium in 1936. The historic footage, which unfortunately does not include sound, features the Limerick hurling team posing as a group on the pitch, as well as longshots of the match and the crowds in the grandstands.British Pathe noted that M. Mackey and T. Ryan scored for Limerick, and the final score was 16 points to 9 points, with Limerick as the victors. -

 Very rare example of a Jameson led advertising campaign extolling the delights of Ireland,in particular Bunratty Castle,the Shannon River as well as Jamesons old Irish Whiskey obviously! This delightful print demonstrates the unique old world charm of Ireland in the 1950s. 420cm x 60cm (unframed -limited edition poster form) John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it maintained for four consecutive years.
Very rare example of a Jameson led advertising campaign extolling the delights of Ireland,in particular Bunratty Castle,the Shannon River as well as Jamesons old Irish Whiskey obviously! This delightful print demonstrates the unique old world charm of Ireland in the 1950s. 420cm x 60cm (unframed -limited edition poster form) John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it maintained for four consecutive years. -
 90cm x 65cm Dublin A beautiful original souvenir Powers Whiskey poster advertising the company's participation at the 1893 World Fair held in Chicago to celebrate the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New World in 1492.The fair was an influential social and cultural event and had a profound effect on architecture,sanitation,the Arts,Chicago's self image and American Industrial optimism .Powers Whiskey itself was established in 1792 before moving to Johns Lane in 1822 and then expanding its ranks and production levels rapidly to become one of the most impressive architectural sights in Victorian Dublin-an overhead view of which is depicted in this beautiful print. In 1791 James Power, an innkeeper from Dublin, established a small distillery at his public house at 109 Thomas St., Dublin. The distillery, which had an output of about 6,000 gallons in its first year of operation, initially traded as James Power and Son, but by 1822 had become John Power & Son,and had moved to a new premises at John’s Lane, a side street off Thomas Street. At the time the distillery had three pot stills, though only one, a 500-gallon still is thought to have been in use. Following reform of the distilling laws in 1823, the distillery expanded rapidly. In 1827, production was reported at 160,270 gallons,and by 1833 had grown to 300,000 gallons per annum. As the distillery grew, so too did the stature of the family. In 1841, John Power, grandson of the founder was awarded a baronet, a hereditary title. In 1855, his son Sir James Power, laid the foundation stone for the O’Connell Monument, and in 1859 became High Sheriff of Dublin. In 1871, the distillery was expanded and rebuilt in the Victorian style, becoming one of the most impressive sights in Dublin.After expansion, output at the distillery rose to 700,000 gallons per annum, and by the 1880s, had reached about 900,000 gallons per annum, at which point the distillery covered over six acres of central Dublin, and had a staff of about 300 people.During this period, when the Dublin whiskey distilleries were amongst the largest in the world, the family run firms of John Powers, along with John Jameson, William Jameson, and George Roe, (collectively known as the “Big Four”) came to dominate the Irish distilling landscape, introducing several innovations. In 1886, John Power & Son began bottling their own whiskey, rather than following the practice customary at the time, of selling whiskey directly to merchants and bonders who would bottle it themselves. They were the first Dublin distillery to do so, and one of the first in the world.A gold label adorned each bottle and it was from these that the whiskey got the name Powers Gold Label. When Alfred Barnard, the British historian visited John’s Lane in the late 1880s, he noted the elegance and cleanliness of the buildings, and the modernity of the distillery, describing it as “about as complete a work as it is possible to find anywhere”. At the time of his visit, the distillery was home to five pot stills, two of which with capacities of 25,000 gallons, were amongst the largest ever built.In addition, Barnard was high in his praise for Powers whiskey, noting:”The old make, which we drank with our luncheon was delicious and finer than anything we had hitherto tasted.It was as perfect in flavour, and as pronounced in the ancient aroma of Irish Whiskey so dear to to the hearts of connoisseurs,as one could possibly desire and we found a small flask of it very useful afterwards on our travels.” The last member of the family to sit on the board was Sir Thomas Talbot Power,who died in 1930,and with him the Power’s Baronetcy. However, ownership remained in the family until 1966, and several descendants of his sisters remained at work with the company until recent times. In 1961, a Coffey still was installed in John’s Lane Distillery, allowing the production of vodka and gin, in addition to the testing of grain whiskey for use in blended whiskey. This was a notable departure for the firm, as for many years the big Dublin distilling dynasties had shunned the use of Coffey stills, questioning if their output, grain whiskey could even be termed whiskey. However, with many of the Irish distilleries having closed in the early 20th century in part due to their failure to embrace a change in consumer preference towards blended whiskey, Powers were instrumental in convincing the remaining Irish distilleries to reconsider their stance on blended whiskey. In 1966, with the Irish whiskey industry still struggling following Prohibition in the United States, the Anglo-Irish Trade War and the rise of competition from Scotch whiskey, John Powers & Son joined forces with the only other remaining distillers in the Irish Republic, the Cork Distilleries Company and their Dublin rivals John Jameson & Son, to form Irish Distillers. Soon after, in a bold move, Irish Distillers decided to close all of their existing distilleries, and to consolidate production at a new purpose-built facility in Midleton (the New Midleton Distillery) alongside their existing Old Midleton Distillery. The new distillery opened in 1975, and a year later, production ceased at John’s Lane Distillery and began anew in Cork, with Powers Gold Label and many other Irish whiskeys reformulated from single pot stills whiskeys to blends. In 1989, Irish Distillers itself became a subsidiary of Pernod-Ricard following a friendly takeover.Since the closure of the John’s Lane distillery, many of the distillery buildings were demolished. However, some of the buildings have been incorporated into the National College of Art and Design, and are now protected structures. In addition, three of the distillery’s pot stills were saved and now located in the college’s Red Square.
90cm x 65cm Dublin A beautiful original souvenir Powers Whiskey poster advertising the company's participation at the 1893 World Fair held in Chicago to celebrate the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New World in 1492.The fair was an influential social and cultural event and had a profound effect on architecture,sanitation,the Arts,Chicago's self image and American Industrial optimism .Powers Whiskey itself was established in 1792 before moving to Johns Lane in 1822 and then expanding its ranks and production levels rapidly to become one of the most impressive architectural sights in Victorian Dublin-an overhead view of which is depicted in this beautiful print. In 1791 James Power, an innkeeper from Dublin, established a small distillery at his public house at 109 Thomas St., Dublin. The distillery, which had an output of about 6,000 gallons in its first year of operation, initially traded as James Power and Son, but by 1822 had become John Power & Son,and had moved to a new premises at John’s Lane, a side street off Thomas Street. At the time the distillery had three pot stills, though only one, a 500-gallon still is thought to have been in use. Following reform of the distilling laws in 1823, the distillery expanded rapidly. In 1827, production was reported at 160,270 gallons,and by 1833 had grown to 300,000 gallons per annum. As the distillery grew, so too did the stature of the family. In 1841, John Power, grandson of the founder was awarded a baronet, a hereditary title. In 1855, his son Sir James Power, laid the foundation stone for the O’Connell Monument, and in 1859 became High Sheriff of Dublin. In 1871, the distillery was expanded and rebuilt in the Victorian style, becoming one of the most impressive sights in Dublin.After expansion, output at the distillery rose to 700,000 gallons per annum, and by the 1880s, had reached about 900,000 gallons per annum, at which point the distillery covered over six acres of central Dublin, and had a staff of about 300 people.During this period, when the Dublin whiskey distilleries were amongst the largest in the world, the family run firms of John Powers, along with John Jameson, William Jameson, and George Roe, (collectively known as the “Big Four”) came to dominate the Irish distilling landscape, introducing several innovations. In 1886, John Power & Son began bottling their own whiskey, rather than following the practice customary at the time, of selling whiskey directly to merchants and bonders who would bottle it themselves. They were the first Dublin distillery to do so, and one of the first in the world.A gold label adorned each bottle and it was from these that the whiskey got the name Powers Gold Label. When Alfred Barnard, the British historian visited John’s Lane in the late 1880s, he noted the elegance and cleanliness of the buildings, and the modernity of the distillery, describing it as “about as complete a work as it is possible to find anywhere”. At the time of his visit, the distillery was home to five pot stills, two of which with capacities of 25,000 gallons, were amongst the largest ever built.In addition, Barnard was high in his praise for Powers whiskey, noting:”The old make, which we drank with our luncheon was delicious and finer than anything we had hitherto tasted.It was as perfect in flavour, and as pronounced in the ancient aroma of Irish Whiskey so dear to to the hearts of connoisseurs,as one could possibly desire and we found a small flask of it very useful afterwards on our travels.” The last member of the family to sit on the board was Sir Thomas Talbot Power,who died in 1930,and with him the Power’s Baronetcy. However, ownership remained in the family until 1966, and several descendants of his sisters remained at work with the company until recent times. In 1961, a Coffey still was installed in John’s Lane Distillery, allowing the production of vodka and gin, in addition to the testing of grain whiskey for use in blended whiskey. This was a notable departure for the firm, as for many years the big Dublin distilling dynasties had shunned the use of Coffey stills, questioning if their output, grain whiskey could even be termed whiskey. However, with many of the Irish distilleries having closed in the early 20th century in part due to their failure to embrace a change in consumer preference towards blended whiskey, Powers were instrumental in convincing the remaining Irish distilleries to reconsider their stance on blended whiskey. In 1966, with the Irish whiskey industry still struggling following Prohibition in the United States, the Anglo-Irish Trade War and the rise of competition from Scotch whiskey, John Powers & Son joined forces with the only other remaining distillers in the Irish Republic, the Cork Distilleries Company and their Dublin rivals John Jameson & Son, to form Irish Distillers. Soon after, in a bold move, Irish Distillers decided to close all of their existing distilleries, and to consolidate production at a new purpose-built facility in Midleton (the New Midleton Distillery) alongside their existing Old Midleton Distillery. The new distillery opened in 1975, and a year later, production ceased at John’s Lane Distillery and began anew in Cork, with Powers Gold Label and many other Irish whiskeys reformulated from single pot stills whiskeys to blends. In 1989, Irish Distillers itself became a subsidiary of Pernod-Ricard following a friendly takeover.Since the closure of the John’s Lane distillery, many of the distillery buildings were demolished. However, some of the buildings have been incorporated into the National College of Art and Design, and are now protected structures. In addition, three of the distillery’s pot stills were saved and now located in the college’s Red Square. The Still House at John’s Lane Distillery, as it looked when Alfred Barnard visited in the 1800s.
The Still House at John’s Lane Distillery, as it looked when Alfred Barnard visited in the 1800s.
-

 A very gracious and substantial Canadian Club Whiskey Mirror.Ok it might have originated from Windsor,Ontario when Hiram Walker moved his distillery across the Detroit River due to prohibition but we recovered this gem from a once famous public house in Killarney Co Kerry.The owner had returned from Canada to open his own pub in his native town and the first item he adorned his new pub was with this lovely mirror. Killarney Co Kerry (via Ontario) 53cm x 40cm
A very gracious and substantial Canadian Club Whiskey Mirror.Ok it might have originated from Windsor,Ontario when Hiram Walker moved his distillery across the Detroit River due to prohibition but we recovered this gem from a once famous public house in Killarney Co Kerry.The owner had returned from Canada to open his own pub in his native town and the first item he adorned his new pub was with this lovely mirror. Killarney Co Kerry (via Ontario) 53cm x 40cm -

 36cm x 44cm Tralee Co Kerry The Rose of Tralee Festival is held every August in Tralee, County Kerry, to choose a young woman to be crowned the Rose. The winner is the woman deemed best to match the attributes relayed in the song: "lovely and fair". She is selected on the basis of personality and should be a good role-model for the festival and ambassador for Ireland during her travels around the world. It is not a beauty pageant and the participants (Roses) are not judged on their appearances but on their personality and suitability to serve as ambassadors for the festival. The festival bills itself as a celebration of the "aspirations, ambitions, intellect, social responsibility and Irish heritage" of modern young women.Each of the 32 counties of the island of Ireland selects a Rose, and the international Roses, chosen from around the world, also participate in the qualifying rounds now staged in the Festival Dome in Tralee. Ultimately, 32 Roses are selected to appear in the televised selection finals on RTÉ One, out of whom one is crowned the Rose of Tralee.The festival overcame financial difficulties in 2004, and has strengthened with growing visitor numbers and maintaining strong viewer figures.Until the year 2008, unmarried mothers were not allowed to enter the contest.With very high TV ratings guaranteed every year,Guinness have been a long time corporate partner of the Festival.
36cm x 44cm Tralee Co Kerry The Rose of Tralee Festival is held every August in Tralee, County Kerry, to choose a young woman to be crowned the Rose. The winner is the woman deemed best to match the attributes relayed in the song: "lovely and fair". She is selected on the basis of personality and should be a good role-model for the festival and ambassador for Ireland during her travels around the world. It is not a beauty pageant and the participants (Roses) are not judged on their appearances but on their personality and suitability to serve as ambassadors for the festival. The festival bills itself as a celebration of the "aspirations, ambitions, intellect, social responsibility and Irish heritage" of modern young women.Each of the 32 counties of the island of Ireland selects a Rose, and the international Roses, chosen from around the world, also participate in the qualifying rounds now staged in the Festival Dome in Tralee. Ultimately, 32 Roses are selected to appear in the televised selection finals on RTÉ One, out of whom one is crowned the Rose of Tralee.The festival overcame financial difficulties in 2004, and has strengthened with growing visitor numbers and maintaining strong viewer figures.Until the year 2008, unmarried mothers were not allowed to enter the contest.With very high TV ratings guaranteed every year,Guinness have been a long time corporate partner of the Festival. -


On this day in 1963 JFK came to Ireland - What his historic trip meant to him and his ancestral home.
On this day (June 25) 1963, President John F. Kennedy arrived in Ireland on an emotional trip to his ancestral home. His speech is remembered for quoting the text of a Sinéad de Valera poem.
In June 1963, just five months before his assassination in Dallas, President John F. Kennedy made his historic trip to Ireland. On his last night in Ireland Kennedy was the guest of President de Valera and his wife Sinéad. Sinéad de Valera was an accomplished Irish writer, folklorist, and poet. During the evening she recited a poem of exile for the young president who was so impressed that he wrote it down on his place card. Over breakfast the next day, JFK memorized the poem and recited it in his last speech at Shannon as he departed.It reads: "'Tis the Shannon's brightly glancing stream, brightly gleaming, silent in the morning beam. Oh! the sight entrancing. Thus return from travels long, years of exile, years of pain to see Old Shannon's face again, O'er the waters glancing." Then he said, "Well, I am going to come back and see Old Shannon's face again, and I am taking, as I go back to America, all of you with me." Jackie Kennedy could not accompany her husband due to a difficult pregnancy with Patrick, her son who died soon after birth. Kennedy himself was suffering from physical stress and illness, a back condition and Addison's Disease to name but -two, but the vibrant face he showed to the world in Ireland would always be the lasting impression.Of course, he would never return to Ireland, struck down by an assassin's bullet 53 years ago. Yet, with each passing president, the JFK legend seems to grow larger. His popularity in America in the summer of 1963, just two and a half years into his presidency, seemed to make him a certainty for re-election. When he took his Irish trip, his approval rating was at an incredible 82 percent (Donald Trump is 45 percent at the moment; President Obama 63 percent) surpassing any president in history in a non-war situation. Kennedy was growing in stature, having faced down the Russians over Cuba, promising a man on the moon by 1970, and completing an amazing trip to Berlin where his speech “Ich Bin Ein Berliner” inspired a generation of separated Germans to come together again some 25-years later. Yet we will never know the full measure of the man. Two of his closest associates, Dave Powers and Kenneth O’Donnell, wrote a biography of Kennedy and entitled "Johnny We Hardly Knew You."President John F. Kennedy addresses a crowd at Redmond Place in Co. Wexford.
The title was taken from a sign someone held up when Kennedy was driving to Co. Wexford on his visit to his homestead. In 2013, the New Ross museum dedicated to Kennedy discovered the identity of the man holding up the sign and retrieved the sign for the museum. As sung by the Clancy Brothers and Tommy Makem, “Johnny We Hardly Knew You” is a fierce anti-war song which portrays an old lover meeting her former lover after he had fought in the Great War and was severely injured. He is now a cripple begging on the street. Here are some of the lyrics: “With your drums and guns and drums and guns, the enemy nearly slew ye, oh my darling dear, ye look so queer (strange). Johnny I hardly knew ye.” Ironically, of course, John F. Kennedy would have his own life cut short, suffering horrific injuries from an assassin's bullets just five months after the glorious Irish trip.He would never see 'Old Shannon’s' face again, but also he would never be forgotten by those who witnessed his visit.The emigrant and exile had returned home to a tiny country that revered and loved him. He was their stepping stone to the 21st century, but his own dreams died just months later. May he rest in peace.








