-

 26cm diametre Nazi dictator Adolf Hitler loved Irish folk music, and historical photographs reveal that famous Irish musician Sean Dempsey played for him in 1936. Dempsey, an uileann piper, was invited to play for Hitler and propaganda chief Joseph Goebbels during a visit to Berlin in 1936 after being told that Hitler was an Irish folk music fan. When he arrived to play, however, there was no room for him to sit, which he needed to do to play, and it looked like it would be canceled. However, Hitler jumped up and demanded that an S.S. member get down on his hands and knees and that Dempsey sit astride him while he played. Dempsey played what was described as a "haunting air" as Hitler listened with rapt attention. After he performed, Hitler presented him with a gold fountain pen while Goebbels clapped wildly. The bizarre scene was revealed for the first time in a 2010 exhibition of Irish photographs from that era called "Ceol na Cathra." The exhibition opened in Dublin and was collected by legendary fiddle player Mick O’Connor. Also in the exhibit were rare photographs from the early days of The Chieftains and Sean O'Riada, the father of modern Irish folk music.
26cm diametre Nazi dictator Adolf Hitler loved Irish folk music, and historical photographs reveal that famous Irish musician Sean Dempsey played for him in 1936. Dempsey, an uileann piper, was invited to play for Hitler and propaganda chief Joseph Goebbels during a visit to Berlin in 1936 after being told that Hitler was an Irish folk music fan. When he arrived to play, however, there was no room for him to sit, which he needed to do to play, and it looked like it would be canceled. However, Hitler jumped up and demanded that an S.S. member get down on his hands and knees and that Dempsey sit astride him while he played. Dempsey played what was described as a "haunting air" as Hitler listened with rapt attention. After he performed, Hitler presented him with a gold fountain pen while Goebbels clapped wildly. The bizarre scene was revealed for the first time in a 2010 exhibition of Irish photographs from that era called "Ceol na Cathra." The exhibition opened in Dublin and was collected by legendary fiddle player Mick O’Connor. Also in the exhibit were rare photographs from the early days of The Chieftains and Sean O'Riada, the father of modern Irish folk music. -

 Lovely set of 4 sepia toned hand printed framed photographs of Limerick City scenes taken from the original glass plates of the well known photographer W.Lawrence.The four scenes depict the Treaty Stone,St Marys Cathedral & ,A steamboat docked at Limerick Quays and a busy O'Connell Street scene. Origins : Co Clare Dimensions :16cm x 18cm 3kg (set of 4)
Lovely set of 4 sepia toned hand printed framed photographs of Limerick City scenes taken from the original glass plates of the well known photographer W.Lawrence.The four scenes depict the Treaty Stone,St Marys Cathedral & ,A steamboat docked at Limerick Quays and a busy O'Connell Street scene. Origins : Co Clare Dimensions :16cm x 18cm 3kg (set of 4) -

 26cm x 32cm Nice,enlarged example of the labels used by bottling pubs in Ireland back in the day. The (nearly) Lost Art of Irish Whiskey Bonding It may seem extraordinary considering the system we have now, but during the 19th century Irish distillers did not bottle and sell their own whiskey. They simply produced the spirit, put it in casks and then sold it on to retailers directly, who would then supply the public as they wished. These spirits merchants were known as bonders, from the practice of holding whiskey “in bond” (i.e. without duties paid on it) in their specialised bonded warehouses. Many pubs also doubled as bonders, which meant they could, supply their patrons with whiskey of which they were assured the provenance. Provenance and dishonesty were the main problem with this system as distilleries had no control over what happened to their whiskey after it left their premises. This lead some of the more unscrupulous proprietors to adulterate the whiskey coming from the cask or lie about how old it was, meaning that a distillery might end up with a bad name for their product through no fault of their own. However, some whiskey bonders of the era were renowned for their dedication to the art of maturing and blending, such that their names and products have today become some of the most important in Irish whiskey. Mitchell & Sons (Spot Whiskeys) Though beginning life in 1805 as a tea shop and confectionary business, it was in 1887 that the Mitchell family made their mark on Irish spirit history. That was the year they decided to go into the whiskey bonding, following a period as solely wine merchants. The ingenious idea must have seemed quite obvious, they had lots of empty wine and sherry casks so why not send them across the river to Jameson’s Bow Street distillery to be filled with new make single pot still whiskey. Once in the bonded warehouse the casks were given a coloured dash or spot, depending on how long they were due to be aged for, blue for seven years, green for 10, yellow for 12 and red for 15. This led to its renown as “Spot Whiskey” which became hugely popular with the high society of the time and had no lesser proponent than Samuel Beckett, who would order casks to be delivered to his Parisian literary atelier. Thankfully, Mitchell and Son are still going strong, and aged single pot still whiskey from Midleton, in the form of Green and Yellow Spot is widely available. Gilbey’s (Redbreast) A huge wine and spirit retailer, Gilbey’s Irish operation had stores of Irish, particularly Dublin, pot still that could only be matched by the distilleries themselves. At the turn of the 19th century for example they held over 700,000 gallons of Jameson whiskey. Its most famous brand at the time was its 6-year old “Castle Whiskey”, which was discontinued in the 30s (the castle having a negative political connotation in the Republic of Ireland). It was in 1912 however that its lasting legacy on Irish whiskey was founded, when it introduced its 12-year old single pot still, Redbreast. This was to last under the Gilbey’s name until the 1980s, more than a decade after the Jameson Distillery in Dublin had actually stopped producing, relying on stocks that had been built up. Today, after a joining with Irish Distillers and being produced in Midleton, Redbreast is still the preeminent expression of single pot still whiskey and a testament to the enduring good name of quality bonding. Chapel Gate (JJ Corry – ‘The Gael’) The resurgent life force affecting all other aspects of Irish whiskey has also laid its hands on the art of whiskey bonding. Chapel Gate, in west Clare, have resurrected the practice of buying whiskey straight from distilleries, casking it in their own barrels and maturing it and blending it as they wish. Their JJ Corry ’The Gael’ is their first release and contains a blend of whiskey up to 26 years old, with the majority being 11 to 15 year single malt. With the wild Atlantic air providing a perfect climate for maturing whiskey we can expect them to be continuing this great Irish whiskey tradition for a long time into the future. If you would like to see what the art of bonding has endowed to Irish whiskey, you can try the excellent Green and Yellow Spots from Mitchell and Son, or the wonderful Redbreast including an original Gilbey’s bottling.
26cm x 32cm Nice,enlarged example of the labels used by bottling pubs in Ireland back in the day. The (nearly) Lost Art of Irish Whiskey Bonding It may seem extraordinary considering the system we have now, but during the 19th century Irish distillers did not bottle and sell their own whiskey. They simply produced the spirit, put it in casks and then sold it on to retailers directly, who would then supply the public as they wished. These spirits merchants were known as bonders, from the practice of holding whiskey “in bond” (i.e. without duties paid on it) in their specialised bonded warehouses. Many pubs also doubled as bonders, which meant they could, supply their patrons with whiskey of which they were assured the provenance. Provenance and dishonesty were the main problem with this system as distilleries had no control over what happened to their whiskey after it left their premises. This lead some of the more unscrupulous proprietors to adulterate the whiskey coming from the cask or lie about how old it was, meaning that a distillery might end up with a bad name for their product through no fault of their own. However, some whiskey bonders of the era were renowned for their dedication to the art of maturing and blending, such that their names and products have today become some of the most important in Irish whiskey. Mitchell & Sons (Spot Whiskeys) Though beginning life in 1805 as a tea shop and confectionary business, it was in 1887 that the Mitchell family made their mark on Irish spirit history. That was the year they decided to go into the whiskey bonding, following a period as solely wine merchants. The ingenious idea must have seemed quite obvious, they had lots of empty wine and sherry casks so why not send them across the river to Jameson’s Bow Street distillery to be filled with new make single pot still whiskey. Once in the bonded warehouse the casks were given a coloured dash or spot, depending on how long they were due to be aged for, blue for seven years, green for 10, yellow for 12 and red for 15. This led to its renown as “Spot Whiskey” which became hugely popular with the high society of the time and had no lesser proponent than Samuel Beckett, who would order casks to be delivered to his Parisian literary atelier. Thankfully, Mitchell and Son are still going strong, and aged single pot still whiskey from Midleton, in the form of Green and Yellow Spot is widely available. Gilbey’s (Redbreast) A huge wine and spirit retailer, Gilbey’s Irish operation had stores of Irish, particularly Dublin, pot still that could only be matched by the distilleries themselves. At the turn of the 19th century for example they held over 700,000 gallons of Jameson whiskey. Its most famous brand at the time was its 6-year old “Castle Whiskey”, which was discontinued in the 30s (the castle having a negative political connotation in the Republic of Ireland). It was in 1912 however that its lasting legacy on Irish whiskey was founded, when it introduced its 12-year old single pot still, Redbreast. This was to last under the Gilbey’s name until the 1980s, more than a decade after the Jameson Distillery in Dublin had actually stopped producing, relying on stocks that had been built up. Today, after a joining with Irish Distillers and being produced in Midleton, Redbreast is still the preeminent expression of single pot still whiskey and a testament to the enduring good name of quality bonding. Chapel Gate (JJ Corry – ‘The Gael’) The resurgent life force affecting all other aspects of Irish whiskey has also laid its hands on the art of whiskey bonding. Chapel Gate, in west Clare, have resurrected the practice of buying whiskey straight from distilleries, casking it in their own barrels and maturing it and blending it as they wish. Their JJ Corry ’The Gael’ is their first release and contains a blend of whiskey up to 26 years old, with the majority being 11 to 15 year single malt. With the wild Atlantic air providing a perfect climate for maturing whiskey we can expect them to be continuing this great Irish whiskey tradition for a long time into the future. If you would like to see what the art of bonding has endowed to Irish whiskey, you can try the excellent Green and Yellow Spots from Mitchell and Son, or the wonderful Redbreast including an original Gilbey’s bottling. -
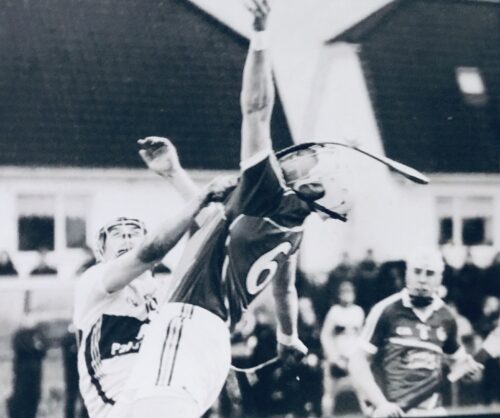

 26cm x 33cm Not so much the clash of the ash as the bend of the ash in this unbelievable action photograph as Clare and Limerick Hurlers do battle in a challenge game in Sixmilebridge.The art of Hurley making & the raw materials used have not changed a lot since time immemorial as this article demonstrates ; Cad a dhéanfaimid feasta gan adhmaid, tá deireadh na gcoillte ar lár…” seems an appropriate opening to an article about hurley making, as we speak to Pat Cronin in his workshop overlooking the Comeragh Mountains in Kilcash, Tipperary. “Over 90% of the timber used in hurley-making now is foreign. Irish ash is very scarce, although Coillte are working to change this”, explained Pat. “I get most of my timber from Coillte in Dundrum (Tipperary). This comes from Denmark and Sweden”. Although some makers have produced hurleys from 14 year old ash Pat believes this is too soon. “You might only get two or three slabs out of a tree that young. If you left it another five or more years you’d get more than double that. It’d really take up to 25 years to get a decent return.” Pat’s uncle, Larry Welsh, made hurleys, but Pat didn’t realise this when he started out. “John Joe O’Brien in Cahir taught me. I used to call to him to get a few now and then and it went from there. I started about 25 years ago and gave up working with Eircom to go at it full time five years ago. I’m kept busy throughout the year.” Brian Dowling’s “Star Hurleys” workshop is in the heart of Kilkenny. Despite the fact that his son Mark is also in the business they’re under constant pressure to meet demand. Brian, who served his time to become a carpenter, has been making hurleys since 1980. His father Ramie was a well known maker, who started in the early 1960’s with Brian’s grandfather Tom Neary. It probably takes about thirty minutes to make a hurley, if you were to go at it from start to finish. However, neither Pat nor Brian make them in this way. Both use copying machines to rough cut “slabs” three or four at a time. Each then finishes the hurleys by hand, to meet specific requirements. “You get phases of popularity in styles”, explained Pat Cronin, “Because of the O’Connor’s of Cork for instance, big bosses are in favour now. But there’s also a trend towards shorter and lighter sticks. There’s a risk if the hurley is too light it’ll snap more easily. And you don’t get the same distance on a puck out.” Brian, recently in Italy looking at a replacement for his aging copying machine, only cuts 33 inch sticks and bigger this way. “I do the smaller ones entirely by hand”. The style of hurling has changed over the years and naturally the hurley changes to reflect this. “Demands for particular styles naturally reflect the styles of the successful teams of the time”. Certainly the demand for personalised sticks has grown. Brian, who supplies most of the Kilkenny senior team, explains that most of them have specific demands. Every hurley maker will advise you differently about how best to look after your stick! wever, you need good quality timber to start with. Pat Cronin suggests that when you get your new hurley you should put it away for a while. “Some people hang them, rather than prop them against a wall, so they won’t warp. There are those who put them in water until they get the right weight. Then they’ll varnish or linseed oil them to keep them at that weight. Like a good wine it should also be stored somewhere cool! You definitely shouldn’t keep them in the kitchen or in the boot of your car, or they will dry out.” Brian suggests that it’s better to buy the stick unbanded. “You need to allow a bit of time for timber to settle. You might also put five or six coats of linseed oil on, or even drop them into a barrel of linseed oil for a while, to get more penetration. You have to remember that this will add weight ‘though. But whether you oil them or not, you should leave them for a good week or so before banding them. And don’t keep them in the house!” There is a Hurley Makers Guild, which was formed almost ten years ago when ash became scarce. Makers felt the need to organise themselves to address the problem. There are about fifty active members these days. Both Pat Cronin and Brian Dowling are curious to see how Jack Carey – brother of the illustrious DJ – gets on with his plan to import finished hurleys from Eastern Europe. This could have quite an impact on what might be regarded as a quintessentially Irish cottage industry. However, time will tell. Just to set up a workshop and kit it out here in Ireland would probably cost about half a million Euro, according to both Pat and Brian. Not a cheap business to get into! Little wonder the notion of foreign manufactured hurleys doesn’t seem that strange… Two great Craftsmen, continuing the wonderful tradition of hurley-making.
26cm x 33cm Not so much the clash of the ash as the bend of the ash in this unbelievable action photograph as Clare and Limerick Hurlers do battle in a challenge game in Sixmilebridge.The art of Hurley making & the raw materials used have not changed a lot since time immemorial as this article demonstrates ; Cad a dhéanfaimid feasta gan adhmaid, tá deireadh na gcoillte ar lár…” seems an appropriate opening to an article about hurley making, as we speak to Pat Cronin in his workshop overlooking the Comeragh Mountains in Kilcash, Tipperary. “Over 90% of the timber used in hurley-making now is foreign. Irish ash is very scarce, although Coillte are working to change this”, explained Pat. “I get most of my timber from Coillte in Dundrum (Tipperary). This comes from Denmark and Sweden”. Although some makers have produced hurleys from 14 year old ash Pat believes this is too soon. “You might only get two or three slabs out of a tree that young. If you left it another five or more years you’d get more than double that. It’d really take up to 25 years to get a decent return.” Pat’s uncle, Larry Welsh, made hurleys, but Pat didn’t realise this when he started out. “John Joe O’Brien in Cahir taught me. I used to call to him to get a few now and then and it went from there. I started about 25 years ago and gave up working with Eircom to go at it full time five years ago. I’m kept busy throughout the year.” Brian Dowling’s “Star Hurleys” workshop is in the heart of Kilkenny. Despite the fact that his son Mark is also in the business they’re under constant pressure to meet demand. Brian, who served his time to become a carpenter, has been making hurleys since 1980. His father Ramie was a well known maker, who started in the early 1960’s with Brian’s grandfather Tom Neary. It probably takes about thirty minutes to make a hurley, if you were to go at it from start to finish. However, neither Pat nor Brian make them in this way. Both use copying machines to rough cut “slabs” three or four at a time. Each then finishes the hurleys by hand, to meet specific requirements. “You get phases of popularity in styles”, explained Pat Cronin, “Because of the O’Connor’s of Cork for instance, big bosses are in favour now. But there’s also a trend towards shorter and lighter sticks. There’s a risk if the hurley is too light it’ll snap more easily. And you don’t get the same distance on a puck out.” Brian, recently in Italy looking at a replacement for his aging copying machine, only cuts 33 inch sticks and bigger this way. “I do the smaller ones entirely by hand”. The style of hurling has changed over the years and naturally the hurley changes to reflect this. “Demands for particular styles naturally reflect the styles of the successful teams of the time”. Certainly the demand for personalised sticks has grown. Brian, who supplies most of the Kilkenny senior team, explains that most of them have specific demands. Every hurley maker will advise you differently about how best to look after your stick! wever, you need good quality timber to start with. Pat Cronin suggests that when you get your new hurley you should put it away for a while. “Some people hang them, rather than prop them against a wall, so they won’t warp. There are those who put them in water until they get the right weight. Then they’ll varnish or linseed oil them to keep them at that weight. Like a good wine it should also be stored somewhere cool! You definitely shouldn’t keep them in the kitchen or in the boot of your car, or they will dry out.” Brian suggests that it’s better to buy the stick unbanded. “You need to allow a bit of time for timber to settle. You might also put five or six coats of linseed oil on, or even drop them into a barrel of linseed oil for a while, to get more penetration. You have to remember that this will add weight ‘though. But whether you oil them or not, you should leave them for a good week or so before banding them. And don’t keep them in the house!” There is a Hurley Makers Guild, which was formed almost ten years ago when ash became scarce. Makers felt the need to organise themselves to address the problem. There are about fifty active members these days. Both Pat Cronin and Brian Dowling are curious to see how Jack Carey – brother of the illustrious DJ – gets on with his plan to import finished hurleys from Eastern Europe. This could have quite an impact on what might be regarded as a quintessentially Irish cottage industry. However, time will tell. Just to set up a workshop and kit it out here in Ireland would probably cost about half a million Euro, according to both Pat and Brian. Not a cheap business to get into! Little wonder the notion of foreign manufactured hurleys doesn’t seem that strange… Two great Craftsmen, continuing the wonderful tradition of hurley-making. -
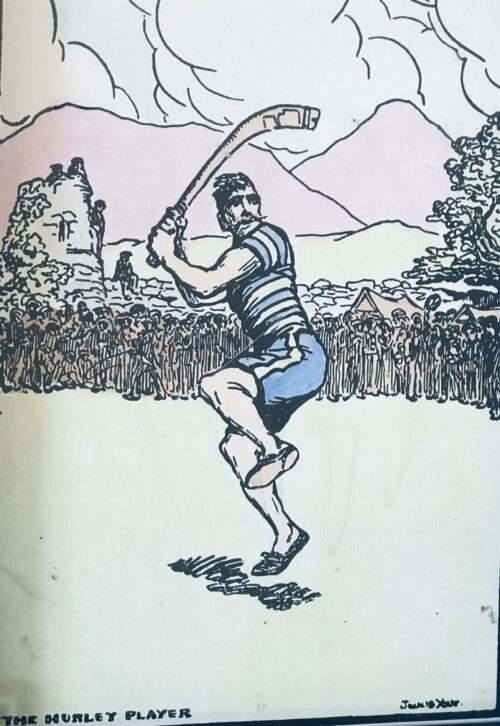

 The Hurley Playerby Jack B Yeats in nice, offset frame. 33cm x 24cm Jack Butler Yeats RHA (29 August 1871 – 28 March 1957) was an Irish artist and Olympic medalist. W. B. Yeats was his brother. Butler's early style was that of an illustrator; he only began to work regularly in oils in 1906. His early pictures are simple lyrical depictions of landscapes and figures, predominantly from the west of Ireland—especially of his boyhood home of Sligo. Yeats's work contains elements of Romanticism. He later would adopt the style of Expressionism
The Hurley Playerby Jack B Yeats in nice, offset frame. 33cm x 24cm Jack Butler Yeats RHA (29 August 1871 – 28 March 1957) was an Irish artist and Olympic medalist. W. B. Yeats was his brother. Butler's early style was that of an illustrator; he only began to work regularly in oils in 1906. His early pictures are simple lyrical depictions of landscapes and figures, predominantly from the west of Ireland—especially of his boyhood home of Sligo. Yeats's work contains elements of Romanticism. He later would adopt the style of ExpressionismBiography
Yeats was born in London, England. He was the youngest son of Irish portraitist John Butler Yeats and the brother of W. B. Yeats, who received the 1923 Nobel Prize in Literature. He grew up in Sligo with his maternal grandparents, before returning to his parents' home in London in 1887. Early in his career he worked as an illustrator for magazines like the Boy's Own Paper and Judy, drew comic strips, including the Sherlock Holmes parody "Chubb-Lock Homes" for Comic Cuts, and wrote articles for Punch under the pseudonym "W. Bird".In 1894 he married Mary Cottenham, also a native of England and two years his senior, and resided in Wicklow according to the Census of Ireland, 1911. From around 1920, he developed into an intensely Expressionist artist, moving from illustration to Symbolism. He was sympathetic to the Irish Republican cause, but not politically active. However, he believed that 'a painter must be part of the land and of the life he paints', and his own artistic development, as a Modernist and Expressionist, helped articulate a modern Dublin of the 20th century, partly by depicting specifically Irish subjects, but also by doing so in the light of universal themes such as the loneliness of the individual, and the universality of the plight of man. Samuel Beckett wrote that "Yeats is with the great of our time... because he brings light, as only the great dare to bring light, to the issueless predicament of existence."The Marxist art critic and author John Berger also paid tribute to Yeats from a very different perspective, praising the artist as a "great painter" with a "sense of the future, an awareness of the possibility of a world other than the one we know". His favourite subjects included the Irish landscape, horses, circus and travelling players. His early paintings and drawings are distinguished by an energetic simplicity of line and colour, his later paintings by an extremely vigorous and experimental treatment of often thickly applied paint. He frequently abandoned the brush altogether, applying paint in a variety of different ways, and was deeply interested in the expressive power of colour. Despite his position as the most important Irish artist of the 20th century (and the first to sell for over £1m), he took no pupils and allowed no one to watch him work, so he remains a unique figure. The artist closest to him in style is his friend, the Austrian painter, Oskar Kokoschka. Besides painting, Yeats had a significant interest in theatre and in literature. He was a close friend of Samuel Beckett. He designed sets for the Abbey Theatre, and three of his own plays were also produced there. He wrote novels in a stream of consciousness style that Joyce acknowledged, and also many essays. His literary works include The Careless Flower, The Amaranthers (much admired by Beckett), Ah Well, A Romance in Perpetuity, And To You Also, and The Charmed Life. Yeats's paintings usually bear poetic and evocative titles. Indeed, his father recognized that Jack was a far better painter than he, and also believed that 'some day I will be remembered as the father of a great poet, and the poet is Jack'.He was elected a member of the Royal Hibernian Academy in 1916.He died in Dublin in 1957, and was buried in Mount Jerome Cemetery. Yeats holds the distinction of being Ireland's first medalist at the Olympic Games in the wake of creation of the Irish Free State. At the 1924 Summer Olympics in Paris, Yeats' painting The Liffey Swim won a silver medal in the arts and culture segment of the Games. In the competition records the painting is simply entitled Swimming.Works
In November 2010, one of Yeats's works, A Horseman Enters a Town at Night, painted in 1948 and previously owned by novelist Graham Greene, sold for nearly £350,000 at a Christie's auction in London. A smaller work, Man in a Room Thinking, painted in 1947, sold for £66,000 at the same auction. In 1999 the painting, The Wild Ones, had sold at Sotheby's in London for over £1.2m, the highest price yet paid for a Yeats painting. Adam's Auctioneers hold the Irish record sale price for a Yeats painting, A Fair Day, Mayo (1925), which sold for €1,000,000 in September 2011.Hosting museums
- The Hunt Museum, Limerick
- The National Gallery of Ireland, Dublin
- The Hugh Lane Gallery, Dublin
- Crawford Art Gallery, Cork
- Irish Museum of Modern Art, Dublin
- The National Gallery of Canada, Ottawa
- Walters Art Museum, Baltimore
- Model Arts and Niland Gallery, Sligo
- The Municipal Art Collection, Waterford
- Ulster Museum, Belfast
- The Snite Museum of Art, University of Notre Dame
The Geography of Hurling
Kevin Whelan Why is hurling currently popular in a compact region centred on east Munster and south Leinster, and in isolated pockets in the Glens of Antrim and in the Ards peninsula of County Down? The answer lies in an exploration of the interplay between culture, politics and environment over a long period of time. TWO VERSIONS By the eighteenth century it is quite clear that there were two principal, and regionally distinct,versions of the game. One was akin to modern field hockey, or shinty, in that it did not allow handling of the ball; it was played with a narrow, crooked stick; it used a hard wooden ball (the ‘crag’); it was mainly a winter game. This game, called camán (anglicised to ‘commons’), was confined to the northern half of the country; its southern limits were set sharply where the small farms of the drumlin belt petered out into the pastoral central lowlands. (Fig 1)
‘The Hurley Player’ by Jack B. Yeats
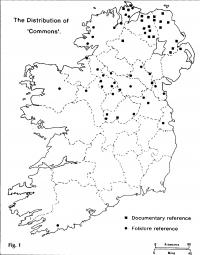 The second version of the game (iomán or báire) was of southern provenance. The ball could be handled or carried on the hurl, which was flat and round-headed; the ball (the sliothar) was soft and made of animal hair; the game was played in summer. Unlike commons, this form of hurling was patronised by the gentry, as a spectator and gambling sport, associated with fairs and other public gatherings, and involved a much greater degree of organisation (including advertising) than the more demotic ‘commons’. A 1742 advertisement for Ballyspellan Spa in Kilkenny noted that ‘horse racing, dancing and hurling will be provided for the pleasure of the quality at the spa’.
LANDLORD PATRONAGE
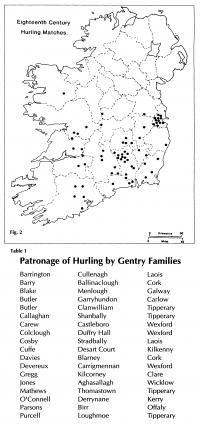
A number of factors determined the distribution of the southern game. (Fig. 2) The most important was the patronage of local gentry families, particularly those most closely embedded in the life of the local people. (Table 1) They picked the teams, arranged the hurling greens and supervised the matches, which were frequently organised as gambling events. The southern hurling zone coincides with the area where, in the late medieval period, the Norman and Gaelic worlds fused to produce a vigorous culture, reflected, for example, in the towerhouse as an architectural innovation. It coincides with well-drained, level terrain, seldom moving too far off the dry sod of limestone areas, which also happen to produce the best material for hurls – ash. It is closely linked to the distribution of big farms, where the relatively comfortable lifestyle afforded the leisure to pursue the sport.
Landlord patronage was essential to the well-being of the southern game; once it was removed, the structures it supported crumbled and the game collapsed into shapeless anarchy. The progressive separation of the manners and language of the élite from the common people was a pan-European phenomenon in the modern period. The gentry’s disengagement from immersion in the shared intimacies of daily life can be seen not just in hurling, but in other areas of language, music, sport and behaviour, as the gradual reception of metropolitan ideas eroded the older loyalties. As one hostile observer put it:
A hurling match is a scene of drunkenness, blasphemy and all kinds and manner of debauchery and faith, for my part, I would liken it to nothing else but to the idea I form of the Stygian regions where the daemonic inhabitants delight in torturing and afflicting each other.
DECLINE
By the mid nineteenth century, hurling had declined so steeply that it survived only in three pockets, around Cork city, in south-east Galway and in the area north of Wexford town. Amongst the reasons for decline were the withdrawal of gentry patronage in an age of political turbulence, sabbitudinarianism, modernisation and the dislocating impact of the Famine. Landlord, priest and magistrate all turned against the game. The older ‘moral economy’, which had linked landlord and tenant in bonds of patronage and deference, gave way to a sharper, adversarial relationship, especially in the 1790s, as the impact of the French Revolution in Ireland created a greater class-consciousness. Politicisation led to a growing anti-landlord feeling, which had been far more subdued in the heyday of gentry-sponsored hurling between the 1740s and 1760s.
The second version of the game (iomán or báire) was of southern provenance. The ball could be handled or carried on the hurl, which was flat and round-headed; the ball (the sliothar) was soft and made of animal hair; the game was played in summer. Unlike commons, this form of hurling was patronised by the gentry, as a spectator and gambling sport, associated with fairs and other public gatherings, and involved a much greater degree of organisation (including advertising) than the more demotic ‘commons’. A 1742 advertisement for Ballyspellan Spa in Kilkenny noted that ‘horse racing, dancing and hurling will be provided for the pleasure of the quality at the spa’.
LANDLORD PATRONAGE
A number of factors determined the distribution of the southern game. (Fig. 2) The most important was the patronage of local gentry families, particularly those most closely embedded in the life of the local people. (Table 1) They picked the teams, arranged the hurling greens and supervised the matches, which were frequently organised as gambling events. The southern hurling zone coincides with the area where, in the late medieval period, the Norman and Gaelic worlds fused to produce a vigorous culture, reflected, for example, in the towerhouse as an architectural innovation. It coincides with well-drained, level terrain, seldom moving too far off the dry sod of limestone areas, which also happen to produce the best material for hurls – ash. It is closely linked to the distribution of big farms, where the relatively comfortable lifestyle afforded the leisure to pursue the sport.
Landlord patronage was essential to the well-being of the southern game; once it was removed, the structures it supported crumbled and the game collapsed into shapeless anarchy. The progressive separation of the manners and language of the élite from the common people was a pan-European phenomenon in the modern period. The gentry’s disengagement from immersion in the shared intimacies of daily life can be seen not just in hurling, but in other areas of language, music, sport and behaviour, as the gradual reception of metropolitan ideas eroded the older loyalties. As one hostile observer put it:
A hurling match is a scene of drunkenness, blasphemy and all kinds and manner of debauchery and faith, for my part, I would liken it to nothing else but to the idea I form of the Stygian regions where the daemonic inhabitants delight in torturing and afflicting each other.
DECLINE
By the mid nineteenth century, hurling had declined so steeply that it survived only in three pockets, around Cork city, in south-east Galway and in the area north of Wexford town. Amongst the reasons for decline were the withdrawal of gentry patronage in an age of political turbulence, sabbitudinarianism, modernisation and the dislocating impact of the Famine. Landlord, priest and magistrate all turned against the game. The older ‘moral economy’, which had linked landlord and tenant in bonds of patronage and deference, gave way to a sharper, adversarial relationship, especially in the 1790s, as the impact of the French Revolution in Ireland created a greater class-consciousness. Politicisation led to a growing anti-landlord feeling, which had been far more subdued in the heyday of gentry-sponsored hurling between the 1740s and 1760s.
 MICHAEL CUSACK & THE GAA
The model of élite participation in popular culture is a threefold process: first immersion, then withdrawal, and, finally rediscovery, invariably by an educated élite, and often with a nationalist agenda. ‘Rediscovery’ usually involves an invention of tradition, creating a packaged, homogenised and often false version of an idealised popular culture – as, for example, in the cult of the Highland kilt. The relationship of hurling and the newly established Gaelic Athletic Association in the 1880s shows this third phase with textbook clarity. Thus, when Michael Cusack set about reviving the game, he codified a synthetic version, principally modelled on the southern ‘iomán’ version that he had known as a child in Clare. Not surprisingly, this new game never caught on in the old ‘commons’ area, with the Glens of Antrim being the only major exception. Cusack and his GAA backers also wished to use the game as a nationalising idiom, a symbolic language of identity filling the void created by the speed of anglicisation. It had therefore to be sharply fenced off in organisational terms from competing ‘anglicised’ sports like cricket, soccer and rugby. Thus, from the beginning, the revived game had a nationalist veneer, its rules of association bristling like a porcupine with protective nationalist quills on which its perceived opponents would have to impale themselves. Its principal backers were those already active in the nationalist political culture of the time, classically the I.R.B. Its spread depended on the active support of an increasingly nationalist Catholic middle class – and as in every country concerned with the invention of tradition, its social constituency included especially journalists, publicans, schoolteachers, clerks, artisans and clerics. Thus, hurling’s early success was in south Leinster and east Munster, the very region which pioneered popular Irish nationalist politics – from the O’Connell campaign, to the devotional revolution in Irish Catholicism, from Fr. Matthews’ temperance campaign, to the Fenians, to the take-over of local government. The GAA was a classic example of the radical conservatism of this region – conservative in its ethos and ideology, radical in its techniques of organisation and mobilisation. The spread of hurling can be very closely matched to the spread of other radical conservative movements of this period – the diffusion of the indigenous Catholic teaching orders and the spread of co-operative dairying.
It would, however, be a mistake to see the spread of hurling under the aegis of the GAA solely in nationalist terms. The codification and success of gaelic games should be compared to the almost contemporaneous success in Britain of codified versions of soccer and rugby. All these were linked to rising spending power, a shortened working week (and the associated development of the ‘weekend’), improved and cheaper mass transport facilities which made spectator sports viable, expanded leisure time, the desire for organised sport among the working classes, and the commercialisation of leisure itself. The really distinctive feature of the GAA’s success was that it occurred in what was still a predominantly agrarian society. That success rested on the shrewd application of the principle of territoriality.
TERRITORIAL ALLEGIANCE
Irish rural life was essentially local life. Hurling was quintessentially a territorially based game – teams based on communities, parishes, counties, pitted one against the other. The painter Tony O’Malley has contrasted this tribal-territorial element in Irish sport to English attitudes:
If neighbours were playing like New Ross and Tullogher, there would be a real needle in it. When Carrickshock were playing, I once heard an old man shouting ‘come on the men that bate the tithe proctors’ and there was a tremor and real fervour in his voice. It was a battle cry, with hurleys as the swords, but with the same intensity.
Similar forces of territoriality have been identified behind the success of cricket in the West Indies and rugby in the Welsh valleys. The GAA tapped this deep-seated territorial loyalty, of the type which is beautifully captured in the rhetorical climax of the great underground classic of rural Ireland, Knocknagow or the Homes of Tipperary by Charles J. Kickham. Matt Donovan (Matt the Thrasher), the village hero, is competing against the outsider Captain French in a sledge-throwing contest. In the absence of steroids, Matt is pumping himself up before his throw:
Someone struck the big drum a single blow, as if by accident and, turning round quickly, the thatched roofs of the hamlet caught his eye. And, strange to say, those old mud walls and thatched roofs roused him as nothing else could. His breast heaved, as with glistening eyes, and that soft plaintive smile of his, he uttered the words, ‘For the credit of the little village!’ in a tone of the deepest tenderness. Then, grasping the sledge in his right hand, and drawing himself up to his full height, he measured the captain’s cast with his eye. The muscles of his arms seemed to start out like cords of steel as he wheeled slowly round and shot the ponderous hammer through the air. His eyes dilated as, with quivering nostrils, he watched its flight, till it fell so far beyond the best mark that even he himself started with astonishment. Then a shout of exultation burst from the excited throng; hands were convulsively grasped, and hats sent flying in the air; and in their wild joy they crushed around him and tried to lift him upon their shoulders.
The territorial allegiance and communal spirit celebrated and idealised by Kickham have died hard in Ireland. GAA club colours, for example were often drawn from old faction favours and, even now, an occasional faction slogan can still be heard. ‘If any man can, an Alley man can’. ‘Squeeze ‘em up Moycarkey and hang ‘em out to dry!’ Lingering animosities can sometimes surface in surprising ways: it is not unknown, for example, for an irate and disappointed Wexford hurling supporter (and what other kind of Wexford supporter is there?) to hurl abuse at Kilkenny, recalling an incident that occurred in Castlecomer to indignant Wexford United Irishmen: ‘Sure what good are they anyway? Didn’t they piss on the powder in ‘98?’ A possibly apocryphal incident occurred after a fiercely contested Cork-Tipperary match. Cork won but in Tipperary eyes that was solely due to a biased Limerick referee. When the disgruntled Tipperary supporters poured off the train at Thurles, they vented their frustrations on the only Limerick man they could find in the town – by tarring and feathering the statue of Archbishop Croke in the Square (presumably the only time in Irish history that a Catholic bishop has been tarred and feathered).
With the notable exception of Cork, the game has not been successfully transplanted into the cities. In Cork, close-knit working-class neighbourhoods like Blackrock and Gouldings Glen (home of Glen Rovers), and the strong antagonism between the hilly northside and the flat southside of the city, nourished the territoriality and community spirit so important to the game’s health. In Dublin, however, the modern suburbs, based on diversity, newness and mobility, have not proved hospitable receptacles of the game. Brendan Behan, brought up in the shadow of Croke Park, commented:
At home we played soccer in the street and sometimes a version of hurling, fast and sometimes savage, adapted from the long-pucking grace of Kilkenny and Tipperary to the crookeder, foreshortened, snappier brutality of the confines of a slum thoroughfare.
MICHAEL CUSACK & THE GAA
The model of élite participation in popular culture is a threefold process: first immersion, then withdrawal, and, finally rediscovery, invariably by an educated élite, and often with a nationalist agenda. ‘Rediscovery’ usually involves an invention of tradition, creating a packaged, homogenised and often false version of an idealised popular culture – as, for example, in the cult of the Highland kilt. The relationship of hurling and the newly established Gaelic Athletic Association in the 1880s shows this third phase with textbook clarity. Thus, when Michael Cusack set about reviving the game, he codified a synthetic version, principally modelled on the southern ‘iomán’ version that he had known as a child in Clare. Not surprisingly, this new game never caught on in the old ‘commons’ area, with the Glens of Antrim being the only major exception. Cusack and his GAA backers also wished to use the game as a nationalising idiom, a symbolic language of identity filling the void created by the speed of anglicisation. It had therefore to be sharply fenced off in organisational terms from competing ‘anglicised’ sports like cricket, soccer and rugby. Thus, from the beginning, the revived game had a nationalist veneer, its rules of association bristling like a porcupine with protective nationalist quills on which its perceived opponents would have to impale themselves. Its principal backers were those already active in the nationalist political culture of the time, classically the I.R.B. Its spread depended on the active support of an increasingly nationalist Catholic middle class – and as in every country concerned with the invention of tradition, its social constituency included especially journalists, publicans, schoolteachers, clerks, artisans and clerics. Thus, hurling’s early success was in south Leinster and east Munster, the very region which pioneered popular Irish nationalist politics – from the O’Connell campaign, to the devotional revolution in Irish Catholicism, from Fr. Matthews’ temperance campaign, to the Fenians, to the take-over of local government. The GAA was a classic example of the radical conservatism of this region – conservative in its ethos and ideology, radical in its techniques of organisation and mobilisation. The spread of hurling can be very closely matched to the spread of other radical conservative movements of this period – the diffusion of the indigenous Catholic teaching orders and the spread of co-operative dairying.
It would, however, be a mistake to see the spread of hurling under the aegis of the GAA solely in nationalist terms. The codification and success of gaelic games should be compared to the almost contemporaneous success in Britain of codified versions of soccer and rugby. All these were linked to rising spending power, a shortened working week (and the associated development of the ‘weekend’), improved and cheaper mass transport facilities which made spectator sports viable, expanded leisure time, the desire for organised sport among the working classes, and the commercialisation of leisure itself. The really distinctive feature of the GAA’s success was that it occurred in what was still a predominantly agrarian society. That success rested on the shrewd application of the principle of territoriality.
TERRITORIAL ALLEGIANCE
Irish rural life was essentially local life. Hurling was quintessentially a territorially based game – teams based on communities, parishes, counties, pitted one against the other. The painter Tony O’Malley has contrasted this tribal-territorial element in Irish sport to English attitudes:
If neighbours were playing like New Ross and Tullogher, there would be a real needle in it. When Carrickshock were playing, I once heard an old man shouting ‘come on the men that bate the tithe proctors’ and there was a tremor and real fervour in his voice. It was a battle cry, with hurleys as the swords, but with the same intensity.
Similar forces of territoriality have been identified behind the success of cricket in the West Indies and rugby in the Welsh valleys. The GAA tapped this deep-seated territorial loyalty, of the type which is beautifully captured in the rhetorical climax of the great underground classic of rural Ireland, Knocknagow or the Homes of Tipperary by Charles J. Kickham. Matt Donovan (Matt the Thrasher), the village hero, is competing against the outsider Captain French in a sledge-throwing contest. In the absence of steroids, Matt is pumping himself up before his throw:
Someone struck the big drum a single blow, as if by accident and, turning round quickly, the thatched roofs of the hamlet caught his eye. And, strange to say, those old mud walls and thatched roofs roused him as nothing else could. His breast heaved, as with glistening eyes, and that soft plaintive smile of his, he uttered the words, ‘For the credit of the little village!’ in a tone of the deepest tenderness. Then, grasping the sledge in his right hand, and drawing himself up to his full height, he measured the captain’s cast with his eye. The muscles of his arms seemed to start out like cords of steel as he wheeled slowly round and shot the ponderous hammer through the air. His eyes dilated as, with quivering nostrils, he watched its flight, till it fell so far beyond the best mark that even he himself started with astonishment. Then a shout of exultation burst from the excited throng; hands were convulsively grasped, and hats sent flying in the air; and in their wild joy they crushed around him and tried to lift him upon their shoulders.
The territorial allegiance and communal spirit celebrated and idealised by Kickham have died hard in Ireland. GAA club colours, for example were often drawn from old faction favours and, even now, an occasional faction slogan can still be heard. ‘If any man can, an Alley man can’. ‘Squeeze ‘em up Moycarkey and hang ‘em out to dry!’ Lingering animosities can sometimes surface in surprising ways: it is not unknown, for example, for an irate and disappointed Wexford hurling supporter (and what other kind of Wexford supporter is there?) to hurl abuse at Kilkenny, recalling an incident that occurred in Castlecomer to indignant Wexford United Irishmen: ‘Sure what good are they anyway? Didn’t they piss on the powder in ‘98?’ A possibly apocryphal incident occurred after a fiercely contested Cork-Tipperary match. Cork won but in Tipperary eyes that was solely due to a biased Limerick referee. When the disgruntled Tipperary supporters poured off the train at Thurles, they vented their frustrations on the only Limerick man they could find in the town – by tarring and feathering the statue of Archbishop Croke in the Square (presumably the only time in Irish history that a Catholic bishop has been tarred and feathered).
With the notable exception of Cork, the game has not been successfully transplanted into the cities. In Cork, close-knit working-class neighbourhoods like Blackrock and Gouldings Glen (home of Glen Rovers), and the strong antagonism between the hilly northside and the flat southside of the city, nourished the territoriality and community spirit so important to the game’s health. In Dublin, however, the modern suburbs, based on diversity, newness and mobility, have not proved hospitable receptacles of the game. Brendan Behan, brought up in the shadow of Croke Park, commented:
At home we played soccer in the street and sometimes a version of hurling, fast and sometimes savage, adapted from the long-pucking grace of Kilkenny and Tipperary to the crookeder, foreshortened, snappier brutality of the confines of a slum thoroughfare.
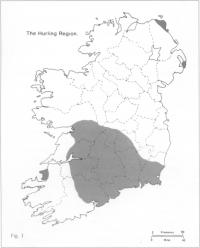 THE PRESENT HURLING REGION
If one looks at the present hurling core region, it is remarkably compact. It also exhibits striking continuity with the earlier ‘iomán’ region. (Fig. 3) The hurling heartland is focused on the three counties of Cork, Tipperary and Kilkenny, with a supporting cast of adjacent counties – Limerick, Clare, Galway, Offaly, Laois, Waterford and Wexford. In the hurling core, the game is king, and very closely stitched into the fabric of the community. Describing the situation in Rathnure, Billy Rackard claimed that in the absence of hurling, ‘the parish would commit suicide, if a parish could commit suicide!’ The boundaries of the hurling region are surprisingly well-defined. To the north, the midland bogs act, as in a way they have done throughout history, as a buffer zone, resolutely impervious to the spread of cultural influences from further south. The western edge of the hurling zone can be traced over a long distance. In County Galway, for example, its boundaries run along a line from Ballinasloe to the city; north of this line is the Tuam-Dunmore area, and west of it is Connemara, both footballing territories. In County Clare, the boundary runs from Tubber on the Galway border through Corofin and Kilmaley to Labasheeda on the Shannon estuary. Last summer, the tremendous achievement of Clare in winning a Munster football championship was most thoroughly relished in the footballing bastion of west Clare, from Kilkee and Doonbeg to Milltown Malbay. One could easily establish this pattern by looking at the thickening density of the forest of flags as one drove from east to west in August.
Across the Shannon in Limerick, the football-hurling divide runs clearly along the scarp dividing hilly west Limerick from the lush limestone lowlands of east Limerick. West of this is an enclave of hurling parishes in the footballing
kingdom of Kerry in the area north of Tralee, in Ardfert, Bally heigue, Causeway and Ballyduff. From Limerick, the hurling boundary loops through County Cork from Mallow to the city and then to the coast at Cloyne – home to the maestro Christy Ring, who famously expressed his strategy for promoting the game in Cork – by stabbing a knife through every football found east of that line. Outside this core region, there are only the hurling enclaves in the Glens of Antrim and on the tip of the Ards peninsula, where the clubs of Ballycran, Ballygalget and Portaferry backbone Down’s hurling revival.
The interesting question then is how these boundaries formed. In almost every case, that boundary divides big farm and small farm areas and marks the transition from fertile, drift-covered limestone lowland to hillier, hungrier, wetter shales, flagstones, grits and granites. In County Galway, for example, hurling has not put down roots in the bony granite outcrops of Connemara, and in Clare the poorly drained flagstone deposits are equally inhospitable. If ash is emblematic of hurling areas, the rush is the distinctive symbol of football territory.
CONCLUSION
This brief case study illustrates the interplay of what the French call la longue durée – the long evolution of history – and les évenements – the specific, precise incidents and personalities which intervene and alter that evolution. Hurling offers a classic Irish example, and the current game demonstrates that, beneath the superficial breaks, fractures and discontinuities, there are sometimes surprisingly stable, deep structures. If the idiom of the game has changed, its grammar stays the same.
THE PRESENT HURLING REGION
If one looks at the present hurling core region, it is remarkably compact. It also exhibits striking continuity with the earlier ‘iomán’ region. (Fig. 3) The hurling heartland is focused on the three counties of Cork, Tipperary and Kilkenny, with a supporting cast of adjacent counties – Limerick, Clare, Galway, Offaly, Laois, Waterford and Wexford. In the hurling core, the game is king, and very closely stitched into the fabric of the community. Describing the situation in Rathnure, Billy Rackard claimed that in the absence of hurling, ‘the parish would commit suicide, if a parish could commit suicide!’ The boundaries of the hurling region are surprisingly well-defined. To the north, the midland bogs act, as in a way they have done throughout history, as a buffer zone, resolutely impervious to the spread of cultural influences from further south. The western edge of the hurling zone can be traced over a long distance. In County Galway, for example, its boundaries run along a line from Ballinasloe to the city; north of this line is the Tuam-Dunmore area, and west of it is Connemara, both footballing territories. In County Clare, the boundary runs from Tubber on the Galway border through Corofin and Kilmaley to Labasheeda on the Shannon estuary. Last summer, the tremendous achievement of Clare in winning a Munster football championship was most thoroughly relished in the footballing bastion of west Clare, from Kilkee and Doonbeg to Milltown Malbay. One could easily establish this pattern by looking at the thickening density of the forest of flags as one drove from east to west in August.
Across the Shannon in Limerick, the football-hurling divide runs clearly along the scarp dividing hilly west Limerick from the lush limestone lowlands of east Limerick. West of this is an enclave of hurling parishes in the footballing
kingdom of Kerry in the area north of Tralee, in Ardfert, Bally heigue, Causeway and Ballyduff. From Limerick, the hurling boundary loops through County Cork from Mallow to the city and then to the coast at Cloyne – home to the maestro Christy Ring, who famously expressed his strategy for promoting the game in Cork – by stabbing a knife through every football found east of that line. Outside this core region, there are only the hurling enclaves in the Glens of Antrim and on the tip of the Ards peninsula, where the clubs of Ballycran, Ballygalget and Portaferry backbone Down’s hurling revival.
The interesting question then is how these boundaries formed. In almost every case, that boundary divides big farm and small farm areas and marks the transition from fertile, drift-covered limestone lowland to hillier, hungrier, wetter shales, flagstones, grits and granites. In County Galway, for example, hurling has not put down roots in the bony granite outcrops of Connemara, and in Clare the poorly drained flagstone deposits are equally inhospitable. If ash is emblematic of hurling areas, the rush is the distinctive symbol of football territory.
CONCLUSION
This brief case study illustrates the interplay of what the French call la longue durée – the long evolution of history – and les évenements – the specific, precise incidents and personalities which intervene and alter that evolution. Hurling offers a classic Irish example, and the current game demonstrates that, beneath the superficial breaks, fractures and discontinuities, there are sometimes surprisingly stable, deep structures. If the idiom of the game has changed, its grammar stays the same. -
Out of stock
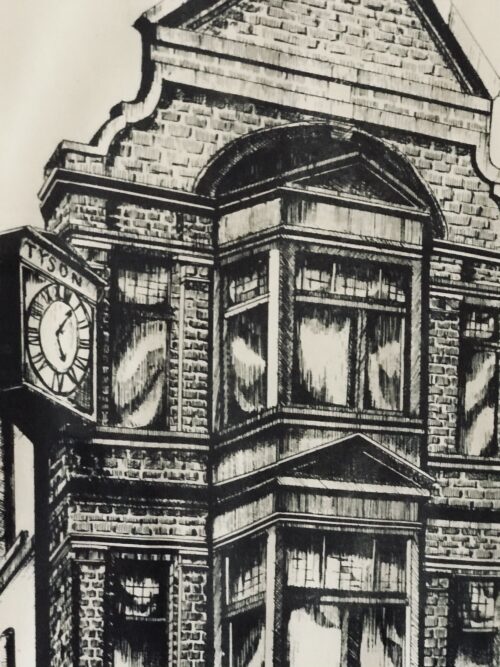
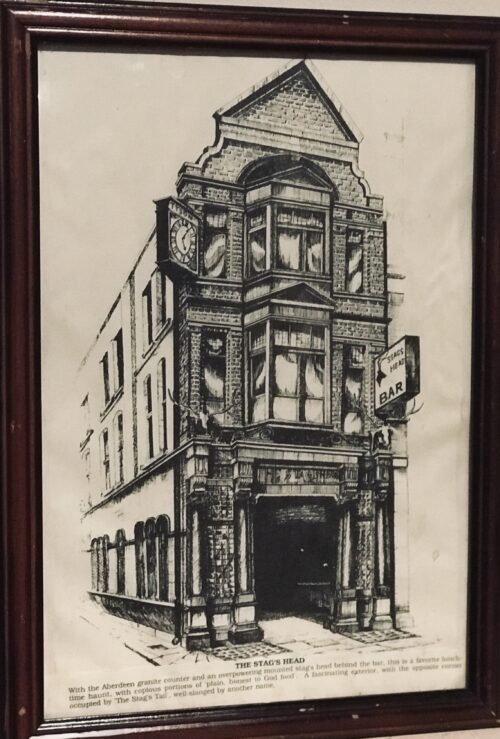
 An attractive drawing of the legendary Stags Head Public House in Dublin."With the Aberdeen granite counter and an overpowering mounted stag's head behind the bar,this is a favourite lunch-time haunt, with copious portions of 'plain ,honest to god food'.A fascinating exterior, with the opposite corner occupied by 'The Stag's Tail",well slanged by another name. 40cm x 30cm Dame St Dublin The Stag's Head is a pub on the corner of Dame Court and Dame Lane in Dublin, Ireland.Records of a pub on the site of the Stag's Head date to 1770 (original construction by a Mr. Tyson) and 1895 (extensive rebuilding).The pub is known for the preservation of its Victorian interior and the restored advertising mosaic on the footpath on Dame Street, some distance from the pub's doors.The name "Tyson", and Mr. Tyson's initials, decorate the old clock and the wrought-iron of the exterior. Mr. Tyson is also believed to have contributed to the construction of a permanent pavement over Dame Lane. There is a stuffed fox on the ground floor snug of the Stag's Head, while a large stag's head decorates the main bar. The pub has appeared in many films, notably A Man of No Importance, starring Albert Finney and Educating Rita starring Michael Caine and Julie Walters. Filming for Penny Dreadful also took place both inside and outside the pub in February 2014. The establishment was sold in 2005 for €5.8M and bought by the Louis Fitzgerald Group. A number of changes have made to the pub since the sale, most notably the introduction of a television set to the bar area.
An attractive drawing of the legendary Stags Head Public House in Dublin."With the Aberdeen granite counter and an overpowering mounted stag's head behind the bar,this is a favourite lunch-time haunt, with copious portions of 'plain ,honest to god food'.A fascinating exterior, with the opposite corner occupied by 'The Stag's Tail",well slanged by another name. 40cm x 30cm Dame St Dublin The Stag's Head is a pub on the corner of Dame Court and Dame Lane in Dublin, Ireland.Records of a pub on the site of the Stag's Head date to 1770 (original construction by a Mr. Tyson) and 1895 (extensive rebuilding).The pub is known for the preservation of its Victorian interior and the restored advertising mosaic on the footpath on Dame Street, some distance from the pub's doors.The name "Tyson", and Mr. Tyson's initials, decorate the old clock and the wrought-iron of the exterior. Mr. Tyson is also believed to have contributed to the construction of a permanent pavement over Dame Lane. There is a stuffed fox on the ground floor snug of the Stag's Head, while a large stag's head decorates the main bar. The pub has appeared in many films, notably A Man of No Importance, starring Albert Finney and Educating Rita starring Michael Caine and Julie Walters. Filming for Penny Dreadful also took place both inside and outside the pub in February 2014. The establishment was sold in 2005 for €5.8M and bought by the Louis Fitzgerald Group. A number of changes have made to the pub since the sale, most notably the introduction of a television set to the bar area. -

 25cm x 35cm Limerick The Irish National Land League was an Irish political organisation of the late 19th century which sought to help poor tenant farmers. Its primary aim was to abolish landlordism in Ireland and enable tenant farmers to own the land they worked on. The period of the Land League's agitation is known as the Land War. Historian R. F. Foster argues that in the countryside the Land League "reinforced the politicization of rural Catholic nationalist Ireland, partly by defining that identity against urbanization, landlordism, Englishness and—implicitly—Protestantism."Foster adds that about a third of the activists were Catholic priests, and Archbishop Thomas Croke was one of its most influential champions.
25cm x 35cm Limerick The Irish National Land League was an Irish political organisation of the late 19th century which sought to help poor tenant farmers. Its primary aim was to abolish landlordism in Ireland and enable tenant farmers to own the land they worked on. The period of the Land League's agitation is known as the Land War. Historian R. F. Foster argues that in the countryside the Land League "reinforced the politicization of rural Catholic nationalist Ireland, partly by defining that identity against urbanization, landlordism, Englishness and—implicitly—Protestantism."Foster adds that about a third of the activists were Catholic priests, and Archbishop Thomas Croke was one of its most influential champions.Background
Following the founding meeting of the Mayo Tenants Defence Association in Castlebar, County Mayo on 26 October 1878 the demand for The Land of Ireland for the people of Ireland was reported in the Connaught Telegraph 2 November 1878. The first of many "monster meetings" of tenant farmers was held in Irishtown near Claremorris on 20 April 1879, with an estimated turnout of 15,000 to 20,000 people. This meeting was addressed by James Daly (who presided), John O'Connor Power, John Ferguson, Thomas Brennan, and J. J. Louden. The Connaught Telegraph's report of the meeting in its edition of 26 April 1879 began:Since the days of O'Connell a larger public demonstration has not been witnessed than that of Sunday last. About 1 o'clock the monster procession started from Claremorris, headed by several thousand men on foot – the men of each district wearing a laural leaf or green ribbon in hat or coat to distinguish the several contingents. At 11 o'clock a monster contingent of tenant-farmers on horseback drew up in front of Hughes's hotel, showing discipline and order that a cavalry regiment might feel proud of. They were led on in sections, each having a marshal who kept his troops well in hand. Messrs. P.W. Nally, J.W. Nally, H. French, and M. Griffin, wearing green and gold sashes, led on their different sections, who rode two deep, occupying, at least, over an Irish mile of the road. Next followed a train of carriages, brakes, cares, etc. led on by Mr. Martin Hughes, the spirited hotel proprietor, driving a pair of rare black ponies to a phæton, taking Messrs. J.J. Louden and J. Daly. Next came Messrs. O'Connor, J. Ferguson, and Thomas Brennan in a covered carriage, followed by at least 500 vehicles from the neighbouring towns. On passing through Ballindine the sight was truly imposing, the endless train directing its course to Irishtown – a neat little hamlet on the boundaries of Mayo, Roscommon, and Galway.
Evolving out of this a number of local land league organisations were set up to work against the excessive rents being demanded by landlords throughout Ireland, but especially in Mayo and surrounding counties. From 1874 agricultural prices in Europe had dropped, followed by some bad harvests due to wet weather during the Long Depression. The effect by 1878 was that many Irish farmers were unable to pay the rents that they had agreed, particularly in the poorer and wetter parts of Connacht. The localised 1879 Famine added to the misery. Unlike many other parts of Europe, the Irish land tenure system was inflexible in times of economic hardship.League founded
The Irish National Land League was founded at the Imperial Hotel in Castlebar, the County town of Mayo, on 21 October 1879. At that meeting Charles Stewart Parnell was elected president of the league. Andrew Kettle, Michael Davitt and Thomas Brennan were appointed as honorary secretaries. This united practically all the different strands of land agitation and tenant rights movements under a single organisation. The two aims of the Land League, as stated in the resolutions adopted in the meeting, were:..."first, to bring about a reduction of rack-rents; second, to facilitate the obtaining of the ownership of the soil by the occupiers". That the object of the League can be best attained by promoting organisation among the tenant-farmers; by defending those who may be threatened with eviction for refusing to pay unjust rents; by facilitating the working of the Bright clauses of the Irish Land Act during the winter; and by obtaining such reforms in the laws relating to land as will enable every tenant to become owner of his holding by paying a fair rent for a limited number of years".
Charles Stewart Parnell, John Dillon, Michael Davitt, and others then went to the United States to raise funds for the League with spectacular results. Branches were also set up in Scotland, where the Crofters Party imitated the League and secured a reforming Act in 1886. The government had introduced the first Land Act in 1870, which proved largely ineffective. It was followed by the marginally more effective Land Acts of 1880 and 1881. These established a Land Commission that started to reduce some rents. Parnell together with all of his party lieutenants, including Father Eugene Sheehyknown as "the Land League priest", went into a bitter verbal offensive and were imprisoned in October 1881 under the Irish Coercion Act in Kilmainham Jail for "sabotaging the Land Act", from where the No-Rent Manifesto was issued, calling for a national tenant farmer rent strike until "constitutional liberties" were restored and the prisoners freed. It had a modest success In Ireland, and mobilized financial and political support from the Irish Diaspora. Although the League discouraged violence, agrarian crimes increased widely. Typically a rent strike would be followed by eviction by the police and the bailiffs. Tenants who continued to pay the rent would be subject to a boycott, or as it was contemporaneously described in the US press, an "excommunication" by local League members.Where cases went to court, witnesses would change their stories, resulting in an unworkable legal system. This in turn led on to stronger criminal laws being passed that were described by the League as "Coercion Acts". The bitterness that developed helped Parnell later in his Home Rule campaign. Davitt's views as seen in his famous slogan: "The land of Ireland for the people of Ireland" was aimed at strengthening the hold on the land by the peasant Irish at the expense of the alien landowners.Parnell aimed to harness the emotive element, but he and his party were strictly constitutional. He envisioned tenant farmers as potential freeholders of the land they had rented. In the Encyclopedia Britannica, the League is considered part of the progressive "rise of fenianism".In the United States
The Land League had an equivalent organization in the United States, which raised hundreds of thousands of dollars both for famine relief and also for political action.The Clan na Gael attempted to infiltrate the Land League, with limited success.Land war
From 1879 to 1882, the "Land War" in pursuance of the "Three Fs" (Fair Rent, Fixity of Tenure and Free Sale) first demanded by the Tenant Right League in 1850, was fought in earnest. The League organised resistance to evictions, reductions in rents and aided the work of relief agencies. Landlords' attempts to evict tenants led to violence, but the Land League denounced excessive violence and destruction. Withholding of rent led on to evictions until "Ashbourne's Act" in 1885 made it unprofitable for most landlords to evict.By then agricultural prices had made a recovery, and rents had been fixed and could be reviewed downwards, but tenants found that holding out communally was the best option. Critics noted that the poorer sub-tenants were still expected to pay their rents to tenant farmers. The widespread upheavals and extensive evictions were accompanied by several years of bad weather and poor harvests, when the tenant farmers who were unable to pay the full arrears of rents resorted to a rent strike. A renewed Land War was waged under the Plan of Campaign from 1886 up until 1892 during which the League decided on a fair rent and then encouraged its members to offer this rent to the landlords. If this was refused, then the rent would be paid by tenants to the League and the landlord would not receive any money until he accepted a discount. The first target, ironically, was a member of the Catholic clergy, Canon Ulick Burke of Knock, who was eventually induced to reduce his rents by 25%. Many landlords resisted these tactics, often violently and there were deaths on either side of the dispute. The Royal Irish Constabulary, the national police force, largely made up of Irishmen, were charged with upholding the law and protecting both landlord and tenant against violence. Originally, the movement cut across some sectarian boundaries, with some meetings held in Orange halls in Ulster, but the tenancy system in effect there Ulster Custom was quite different and fairer to tenants and support drifted away. As a result of the Land War, the Irish National Land League was suppressed by the authorities. In October 1882, as its successor Parnell founded the Irish National League to campaign on broader issues including Home Rule.Many of the Scottish members formed the Scottish Land Restoration League. In 1881, the League started publishing United Ireland a weekly newspaper edited by William O'Brien, which continued until 1898.Outcomes
Within decades of the league's foundation, through the efforts of William O'Brien and George Wyndham (a descendant of Lord Edward FitzGerald), the 1902 Land Conference produced the Land Purchase (Ireland) Act 1903 which allowed Irish tenant farmers to buy out their freeholds with UK government loans over 68 years through the Land Commission (an arrangement that has never been possible in Britain itself). For agricultural labourers, D.D. Sheehanand the Irish Land and Labour Association secured their demands from the Liberal government elected in 1905 to pass the Labourers (Ireland) Act 1906, and the Labourers (Ireland) Act 1911, which paid County Councils to build over 40,000 new rural cottages, each on an acre of land. By 1914, 75% of occupiers were buying out their landlords, mostly under the two Acts. In all, under the pre-UK Land Acts over 316,000 tenants purchased their holdings amounting to 15 million acres (61,000 km2) out of a total of 20 million acres (81,000 km2) in the country. Sometimes the holdings were described as "uneconomic", but the overall sense of social justice was manifest. The major land reforms came when Parliament passed laws in 1870, 1881, 1903 and 1909 that enabled most tenant farmers to purchase their lands, and lowered the rents of the others. From 1870 and as a result of the Land War agitations and the Plan of Campaign of the 1880s, various British governments introduced a series of Irish Land Acts. William O'Brien played a leading role in the 1902 Land Conference to pave the way for the most advanced social legislation in Ireland since the Union, the Wyndham Land Purchase Act of 1903. This Act set the conditions for the break-up of large estates and gradually devolved to rural landholders, and tenants' ownership of the lands. It effectively ended the era of the absentee landlord, finally resolving the Irish Land Question. -
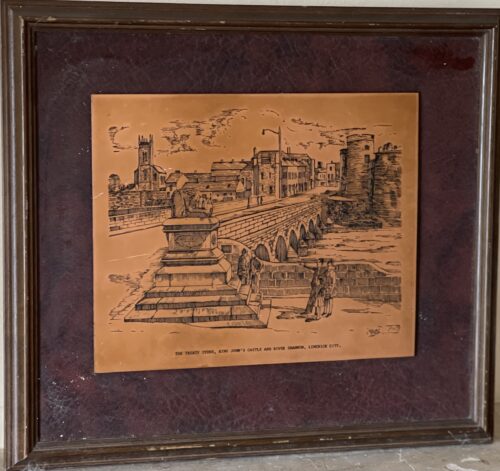
 34cm x 39cm Limerick CityThe Treaty Stone is the rock that the Treaty of Limerick was signed in 1691, marking the surrender of the city to William of Orange.King John's Castle is a 13th-century castle located on King's Island in Limerick, Ireland, next to the River Shannon.Although the site dates back to 922 when the Vikings lived on the Island, the castle itself was built on the orders of King John in 1200. One of the best preserved Norman castles in Europe, the walls, towers and fortifications remain today and are visitor attractions. The remains of a Viking settlement were uncovered during archaeological excavations at the site in 1900. Thomondgate was part of the “Northern” Liberties granted to Limerick in 1216. This area was the border between Munster and Connacht until County Clare, which was created in 1565, was annexed by Munster in 1602. TheThomondgate bridge was originally built in 1185 on the orders of King John and is said to have cost the hefty sum of £30. As a result of poor workmanship the bridge collapsed in 1292 causing the deaths of 80 people. Soon after, the bridge was rebuilt with the addition of two gate towers, one at each end. It partially collapsed in 1833 as a result of bad weather and was replaced with a bridge designed by brothers James and George Pain at a cost of £10,000.Limerick is known as the Treaty City, so called after the Treaty of Limerick signed on the 3rd of October 1691 after the war between William III of England (known as William of Orange) and his Father in Law King James II. Limericks role in the successful accession of William of Orange and his wife Mary Stuart, daughter of King James II to the throne of England cannot be understated. The Treaty, according to tradition was signed on a stone in the sight of both armies at the Clare end of Thomond Bridge on the 3rd of October 1691. The stone was for some years resting on the ground opposite its present location, where the old Ennis mail coach left to travel from the Clare end of Thomond Bridge, through Cratloe woods en route to Ennis. The Treaty stone of Limerick has rested on a plinth since 1865, at the Clare end of Thomond Bridge. The pedestal was erected in May 1865 by John Richard Tinsley, mayor of the city.
34cm x 39cm Limerick CityThe Treaty Stone is the rock that the Treaty of Limerick was signed in 1691, marking the surrender of the city to William of Orange.King John's Castle is a 13th-century castle located on King's Island in Limerick, Ireland, next to the River Shannon.Although the site dates back to 922 when the Vikings lived on the Island, the castle itself was built on the orders of King John in 1200. One of the best preserved Norman castles in Europe, the walls, towers and fortifications remain today and are visitor attractions. The remains of a Viking settlement were uncovered during archaeological excavations at the site in 1900. Thomondgate was part of the “Northern” Liberties granted to Limerick in 1216. This area was the border between Munster and Connacht until County Clare, which was created in 1565, was annexed by Munster in 1602. TheThomondgate bridge was originally built in 1185 on the orders of King John and is said to have cost the hefty sum of £30. As a result of poor workmanship the bridge collapsed in 1292 causing the deaths of 80 people. Soon after, the bridge was rebuilt with the addition of two gate towers, one at each end. It partially collapsed in 1833 as a result of bad weather and was replaced with a bridge designed by brothers James and George Pain at a cost of £10,000.Limerick is known as the Treaty City, so called after the Treaty of Limerick signed on the 3rd of October 1691 after the war between William III of England (known as William of Orange) and his Father in Law King James II. Limericks role in the successful accession of William of Orange and his wife Mary Stuart, daughter of King James II to the throne of England cannot be understated. The Treaty, according to tradition was signed on a stone in the sight of both armies at the Clare end of Thomond Bridge on the 3rd of October 1691. The stone was for some years resting on the ground opposite its present location, where the old Ennis mail coach left to travel from the Clare end of Thomond Bridge, through Cratloe woods en route to Ennis. The Treaty stone of Limerick has rested on a plinth since 1865, at the Clare end of Thomond Bridge. The pedestal was erected in May 1865 by John Richard Tinsley, mayor of the city. -

 23cm x 30cm Dublin We think small is beautiful when it comes to antique Irish Whiskey Mirrors and here is one magnificent example of one.A John Jameson Whiskey Mirror with the legendary Barrelman to the fore. WHY A BARRELMAN? In 1930 John Jameson made a barrelman mascot for aviator Sir C. Kingford-Smith. On June 24th 1930, the mascot took pride of place in the 'Southern Cross' plane that flew from Portmarnock, Ireland on the transatlantic odyssey to America. Since the making of this first lucky mascot, Jameson has revived the icon of the Barrelman, placing him front and centre on their communications. WHY AT THE DIRTY ONION? Constructed in the early 1800s, this was a busy Jameson warehouse long before it became a bar. Granted a bonded licence in 1921, it stored barrels and crates of Jameson in a warehouse known as 'Stack N'. The Barrelman is a tribute to those early adopters of Jameson who labored to bring the barrels to the city.John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it maintained for four consecutive years.
23cm x 30cm Dublin We think small is beautiful when it comes to antique Irish Whiskey Mirrors and here is one magnificent example of one.A John Jameson Whiskey Mirror with the legendary Barrelman to the fore. WHY A BARRELMAN? In 1930 John Jameson made a barrelman mascot for aviator Sir C. Kingford-Smith. On June 24th 1930, the mascot took pride of place in the 'Southern Cross' plane that flew from Portmarnock, Ireland on the transatlantic odyssey to America. Since the making of this first lucky mascot, Jameson has revived the icon of the Barrelman, placing him front and centre on their communications. WHY AT THE DIRTY ONION? Constructed in the early 1800s, this was a busy Jameson warehouse long before it became a bar. Granted a bonded licence in 1921, it stored barrels and crates of Jameson in a warehouse known as 'Stack N'. The Barrelman is a tribute to those early adopters of Jameson who labored to bring the barrels to the city.John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it maintained for four consecutive years.
-

 7Vintage advert for the 4 and 3 Seater Chevrolet (Agent ;The North Tipperary Motor Company P Flannery 6 & 7 McDonagh St Nenagh Co Tipperary).The 4 seater delivered complete cost £210 with the 3 seater English Body costing a heftier £280. 33cm x 44cm Nenagh Co Tipperary In November 3, 1911, Swiss race car driver and automotive engineer Louis Chevrolet co-founded the "Chevrolet Motor Company" in Detroit with William C. Durant and investment partners William Little (maker of the Little automobile), former Buick owner James H. Whiting,[6] Dr. Edwin R. Campbell (son-in-law of Durant) and in 1912 R. S. McLaughlin CEO of General Motors in Canada. Durant was cast out from the management of General Motors in 1910, a company which he had founded in 1908. In 1904 he had taken over the Flint Wagon Works and Buick Motor Company of Flint, Michigan. He also incorporated the Mason and Little companies. As head of Buick, Durant had hired Louis Chevrolet to drive Buicks in promotional races. Durant planned to use Chevrolet's reputation as a racer as the foundation for his new automobile company. The first factory location was in Flint, Michigan at the corner of Wilcox and Kearsley Street, now known as "Chevy Commons" at coordinates 43.00863°N 83.70991°W, along the Flint River, across the street from Kettering University. Actual design work for the first Chevy, the costly Series C Classic Six, was drawn up by Etienne Planche, following instructions from Louis. The first C prototype was ready months before Chevrolet was actually incorporated. However the first actual production wasn't until the 1913 model. So in essence there were no 1911 or 1912 production models, only the 1 pre-production model was made and fine tuned throughout the early part of 1912. Then in the fall of that year the new 1913 model was introduced at the New York auto show.Chevrolet first used the "bowtie emblem" logo in 1914 on the H series models (Royal Mail and Baby Grand) and The L Series Model (Light Six). It may have been designed from wallpaper Durant once saw in a French hotel room.More recent research by historian Ken Kaufmann presents a case that the logo is based on a logo of the "Coalettes" coal company.[10][11] An example of this logo as it appeared in an advertisement for Coalettes appeared in the Atlanta Constitution on November 12, 1911.Others claim that the design was a stylized Swiss cross, in tribute to the homeland of Chevrolet's parents. Over time, Chevrolet would use several different iterations of the bowtie logo at the same time, often using blue for passenger cars, gold for trucks, and an outline (often in red) for cars that had performance packages. Chevrolet eventually unified all vehicle models with the gold bowtie in 2004, for both brand cohesion as well as to differentiate itself from Ford (with its blue oval logo) and Toyota (who has often used red for its imaging), its two primary domestic rivals. Louis Chevrolet had differences with Durant over design and in 1914 sold Durant his share in the company. By 1916, Chevrolet was profitable enough with successful sales of the cheaper Series 490 to allow Durant to repurchase a controlling interest in General Motors. After the deal was completed in 1917, Durant became president of General Motors, and Chevrolet was merged into GM as a separate division. In 1919, Chevrolet's factories were located at Flint, Michigan; branch assembly locations were sited in Tarrytown, N.Y., Norwood, Ohio, St. Louis, Missouri, Oakland, California, Ft. Worth, Texas, and Oshawa, Ontario General Motors of Canada Limited. McLaughlin's were given GM Corporation stock for the proprietorship of their Company article September 23, 1933 Financial Post page 9.In the 1918 model year, Chevrolet introduced the Series D, a V8-powered model in four-passenger roadster and five-passenger tourer models. Sales were poor and it was dropped in 1919. Beginning also in 1919, GMC commercial grade trucks were rebranded as Chevrolet, and using the same chassis of Chevrolet passenger cars and building light-duty trucks. GMC commercial grade trucks were also rebranded as Chevrolet commercial grade trucks, sharing an almost identical appearance with GMC products.
7Vintage advert for the 4 and 3 Seater Chevrolet (Agent ;The North Tipperary Motor Company P Flannery 6 & 7 McDonagh St Nenagh Co Tipperary).The 4 seater delivered complete cost £210 with the 3 seater English Body costing a heftier £280. 33cm x 44cm Nenagh Co Tipperary In November 3, 1911, Swiss race car driver and automotive engineer Louis Chevrolet co-founded the "Chevrolet Motor Company" in Detroit with William C. Durant and investment partners William Little (maker of the Little automobile), former Buick owner James H. Whiting,[6] Dr. Edwin R. Campbell (son-in-law of Durant) and in 1912 R. S. McLaughlin CEO of General Motors in Canada. Durant was cast out from the management of General Motors in 1910, a company which he had founded in 1908. In 1904 he had taken over the Flint Wagon Works and Buick Motor Company of Flint, Michigan. He also incorporated the Mason and Little companies. As head of Buick, Durant had hired Louis Chevrolet to drive Buicks in promotional races. Durant planned to use Chevrolet's reputation as a racer as the foundation for his new automobile company. The first factory location was in Flint, Michigan at the corner of Wilcox and Kearsley Street, now known as "Chevy Commons" at coordinates 43.00863°N 83.70991°W, along the Flint River, across the street from Kettering University. Actual design work for the first Chevy, the costly Series C Classic Six, was drawn up by Etienne Planche, following instructions from Louis. The first C prototype was ready months before Chevrolet was actually incorporated. However the first actual production wasn't until the 1913 model. So in essence there were no 1911 or 1912 production models, only the 1 pre-production model was made and fine tuned throughout the early part of 1912. Then in the fall of that year the new 1913 model was introduced at the New York auto show.Chevrolet first used the "bowtie emblem" logo in 1914 on the H series models (Royal Mail and Baby Grand) and The L Series Model (Light Six). It may have been designed from wallpaper Durant once saw in a French hotel room.More recent research by historian Ken Kaufmann presents a case that the logo is based on a logo of the "Coalettes" coal company.[10][11] An example of this logo as it appeared in an advertisement for Coalettes appeared in the Atlanta Constitution on November 12, 1911.Others claim that the design was a stylized Swiss cross, in tribute to the homeland of Chevrolet's parents. Over time, Chevrolet would use several different iterations of the bowtie logo at the same time, often using blue for passenger cars, gold for trucks, and an outline (often in red) for cars that had performance packages. Chevrolet eventually unified all vehicle models with the gold bowtie in 2004, for both brand cohesion as well as to differentiate itself from Ford (with its blue oval logo) and Toyota (who has often used red for its imaging), its two primary domestic rivals. Louis Chevrolet had differences with Durant over design and in 1914 sold Durant his share in the company. By 1916, Chevrolet was profitable enough with successful sales of the cheaper Series 490 to allow Durant to repurchase a controlling interest in General Motors. After the deal was completed in 1917, Durant became president of General Motors, and Chevrolet was merged into GM as a separate division. In 1919, Chevrolet's factories were located at Flint, Michigan; branch assembly locations were sited in Tarrytown, N.Y., Norwood, Ohio, St. Louis, Missouri, Oakland, California, Ft. Worth, Texas, and Oshawa, Ontario General Motors of Canada Limited. McLaughlin's were given GM Corporation stock for the proprietorship of their Company article September 23, 1933 Financial Post page 9.In the 1918 model year, Chevrolet introduced the Series D, a V8-powered model in four-passenger roadster and five-passenger tourer models. Sales were poor and it was dropped in 1919. Beginning also in 1919, GMC commercial grade trucks were rebranded as Chevrolet, and using the same chassis of Chevrolet passenger cars and building light-duty trucks. GMC commercial grade trucks were also rebranded as Chevrolet commercial grade trucks, sharing an almost identical appearance with GMC products. Chevrolet plant in Tarrytown, NY, c. 1918Chevrolet continued into the 1920s, 1930s, and 1940s competing with Ford, and after the Chrysler Corporation formed Plymouth in 1928, Plymouth, Ford, and Chevrolet were known as the "Low-priced three".[16] In 1929 they introduced the famous "Stovebolt" overhead-valve inline six-cylinder engine, giving Chevrolet a marketing edge over Ford, which was still offering a lone flathead four ("A Six at the price of a Four"). In 1933 Chevrolet launched the Standard Six, which was advertised in the United States as the cheapest six-cylinder car on sale.[17] Chevrolet had a great influence on the American automobile market during the 1950s and 1960s. In 1953 it produced the Corvette, a two-seater sports car with a fiberglass body. In 1957 Chevy introduced its first fuel injected engine,[18] the Rochester Ramjet option on Corvette and passenger cars, priced at $484.[19] In 1960 it introduced the Corvair, with a rear-mounted air-cooled engine. In 1963 one out of every ten cars sold in the United States was a Chevrolet.[20]
Chevrolet plant in Tarrytown, NY, c. 1918Chevrolet continued into the 1920s, 1930s, and 1940s competing with Ford, and after the Chrysler Corporation formed Plymouth in 1928, Plymouth, Ford, and Chevrolet were known as the "Low-priced three".[16] In 1929 they introduced the famous "Stovebolt" overhead-valve inline six-cylinder engine, giving Chevrolet a marketing edge over Ford, which was still offering a lone flathead four ("A Six at the price of a Four"). In 1933 Chevrolet launched the Standard Six, which was advertised in the United States as the cheapest six-cylinder car on sale.[17] Chevrolet had a great influence on the American automobile market during the 1950s and 1960s. In 1953 it produced the Corvette, a two-seater sports car with a fiberglass body. In 1957 Chevy introduced its first fuel injected engine,[18] the Rochester Ramjet option on Corvette and passenger cars, priced at $484.[19] In 1960 it introduced the Corvair, with a rear-mounted air-cooled engine. In 1963 one out of every ten cars sold in the United States was a Chevrolet.[20] -

 35cm x 25cm Limerick"Danny Boy" is a ballad, written by English songwriter Frederic Weatherly in 1913, and set to the traditional Irish melody of "Londonderry Air".
35cm x 25cm Limerick"Danny Boy" is a ballad, written by English songwriter Frederic Weatherly in 1913, and set to the traditional Irish melody of "Londonderry Air".
In 1910, in Bath, Somerset, the English lawyer and lyricist Frederic Weatherly initially wrote the words to "Danny Boy" to a tune other than "Londonderry Air". After his Irish-born sister-in-law Margaret Enright Weatherly (known as Jess) in the United States sent him a copy of "Londonderry Air" in 1913 (an alternative version of the story has her singing the air to him in 1912 with different lyrics), Weatherly modified the lyrics of "Danny Boy" to fit the rhyme and meter of "Londonderry Air". Weatherly gave the song to the vocalist Elsie Griffin, who made it one of the most popular songs of the new century. In 1915, Ernestine Schumann-Heink produced the first recording of "Danny Boy". Jane Ross of Limavady is credited with collecting the melody of "Londonderry Air" in the mid-19th century from a musician she encountered."Danny Boy"  Danny Boy
Danny BoySong Published 1913 Genre Folk Songwriter(s) Frederic Weatherly (lyrics) in 1910 Recording Performed by Celtic Aire of the United States Air Force BandLyrics
The 1913 lyrics by Frederick E. Weatherly:Oh, Danny boy, the pipes, the pipes are calling From glen to glen, and down the mountain side. The summer's gone, and all the roses falling, It's you, It's you must go and I must bide. But come ye back when summer's in the meadow, Or when the valley's hushed and white with snow, It's I'll be there in sunshine or in shadow,— Oh, Danny boy, Oh Danny boy, I love you so! But when ye come, and all the flowers are dying, If I am dead, as dead I well may be, Ye'll come and find the place where I am lying, And kneel and say an Avé there for me. And I shall hear, though soft you tread above me, And all my grave will warmer, sweeter be, For you will bend and tell me that you love me, And I shall sleep in peace until you come to me!Meaning
There are various conjectures about the meaning of "Danny Boy".Some interpret the song to be a message from a parent to a son going off to war or participating in the Irish uprising (as suggested by the reference to "pipes calling glen to glen") or emigrating as part of the Irish diaspora. The 1918 version of the sheet music with Weatherly's printed signature included alternative lyrics ("Eily Dear"), with the instructions that "when sung by a man, the words in italic should be used; the song then becomes "Eily Dear", so that "Danny Boy" is only to be sung by a lady". Nonetheless, it is unclear whether this was Weatherly's intent.Usage
- Percy Grainger's Irish Tune from County Derry adapts the Danny Boy/Londonderry Air melody for wind ensemble in 1918.
- The song is popular for funerals; but the National Catholic Reporter wrote in 2001 that it "cannot be played during Mass."
Select recordings
"Danny Boy" has been recorded multiple times by a variety of performers. Several versions are listed below in chronological order.- 1940 Judy Garland Little Nellie Kelly soundtrack. Garland also sang it live at her concerts in Ireland and Scotland and most famously at her New York Palace Theatre debut in 1951.
- 1940 Glenn Miller and His Orchestra released a single that climbed to #17 in "Pop Memories 1890-1954" (not Billboard's charts);Arranged by Glenn Miller and pianist Chummy MacGregor.
- 1941 Bing Crosby Merry Christmas. "Danny Boy" was paired with "I'll Be Home for Christmas" on its original single. Recorded July 5, 1941.
- 1941 Deanna Durbin in the film It Started with Eve
- 1950 Al Hibbler released a single that rose to #9 on the R&B chart[12]
- 1959 Conway Twitty's version charted at #10 on the Billboard Hot 100, #18 on Top R&B.(banned by the BBC)
- 1961 Andy Williams used the song's title for his album Danny Boy and Other Songs I Love to Sing. The single hit #15 on the U.S. adult contemporary and #64 on the Hot 100 charts.
- 1964 Patti LaBelle and the Bluebelles released a single that peaked at #76 on the Hot 100.
- 1965 Jackie Wilson's version rose to #94 on the Hot 100 and #25 on the R&B charts.
- 1967 Ray Price's single hit #60 on the Hot 100 and #9 on the Country charts.
- 1992 Eric Clapton recorded an instrumental version released as a bonus track for Change the World [6]
- 1992 John McDermott released the song as an independent single.
- 1998 Sinéad O'Connor sang the song over Davy Spillane's uilleann pipes on Spillane's album The Sea of Dreams. Actor-filmmaker Gabriel Byrne said this version is his favourite.
- 2002 Johnny Cash recorded the song on his album American IV: The Man Comes Around, working with producer Rick Rubin in what would come to be the last album released during his lifetime. Cash had previously recorded the











