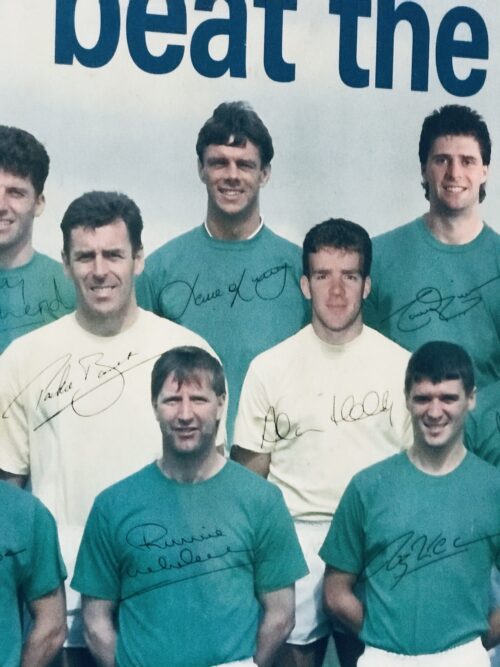
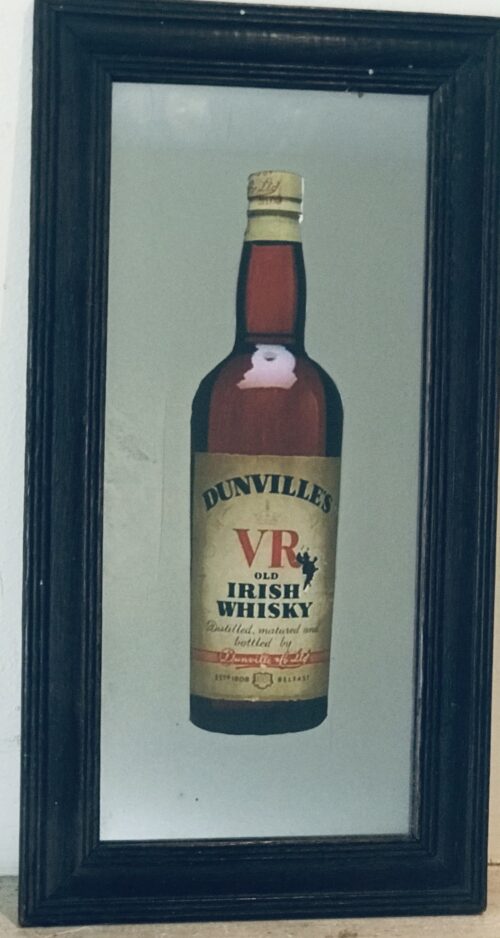
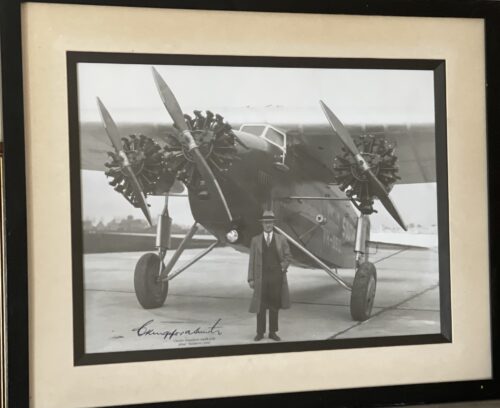
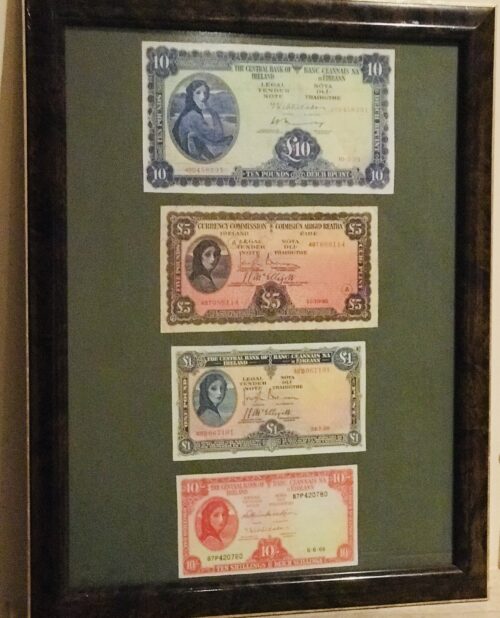
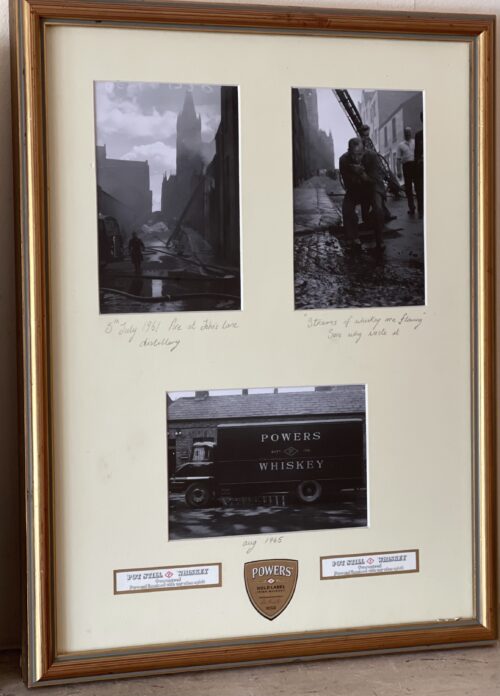
Power's Pure Pot Still Whiskey display depicting scenes after the 1961 Fire at Johns Lane distillery, when the burned whiskey barrels were literally overflowing down the street and thirsty onlookers were drinking it off the ground as you can see in these iconic photographs
44cm x 34cm Thomas St Dublin
In 1791 James Power, an innkeeper from
Dublin, established a small distillery at his public house at 109 Thomas St., Dublin.
The distillery, which had an output of about 6,000 gallons in its first year of operation,
initially traded as James Power and Son, but by 1822 had become John Power & Son,
and had moved to a new premises at John's Lane, a side street off Thomas Street.
At the time the distillery had three pot stills, though only one, a 500-gallon still is thought to have been in use.
Following reform of the distilling laws in 1823, the distillery expanded rapidly. In 1827, production was reported at 160,270 gallons,
and by 1833 had grown to 300,000 gallons per annum.
As the distillery grew, so too did the stature of the family. In 1841, John Power, grandson of the founder was awarded a
baronet, a hereditary title.
In 1855, his son Sir James Power, laid the foundation stone for the
O'Connell Monument,
and in 1859 became High Sheriff of Dublin.
In 1871, the distillery was expanded and rebuilt in the Victorian style, becoming one of the most impressive sights in Dublin.
After expansion, output at the distillery rose to 700,000 gallons per annum, and by the 1880s, had reached about 900,000 gallons per annum, at which point the distillery covered over six acres of central Dublin, and had a staff of about 300 people.

The Still House at John's Lane Distillery, as it looked when
Alfred Barnard visited in the 1800s.
During this period, when the Dublin whiskey distilleries were amongst the largest in the world, the family run firms of John Powers, along with
John Jameson,
William Jameson, and
George Roe, (collectively known as the "Big Four") came to dominate the Irish distilling landscape, introducing several innovations. In 1886, John Power & Son began bottling their own whiskey, rather than following the practice customary at the time, of selling whiskey directly to merchants and bonders who would bottle it themselves.
They were the first Dublin distillery to do so, and one of the first in the world.
A gold label adorned each bottle and it was from these that the whiskey got the name
Powers Gold Label.
When
Alfred Barnard, the British historian visited John's Lane in the late 1880s, he noted the elegance and cleanliness of the buildings, and the modernity of the distillery, describing it as "about as complete a work as it is possible to find anywhere".
At the time of his visit, the distillery was home to five pot stills, two of which with capacities of 25,000 gallons, were amongst the largest ever built.
In addition, Barnard was high in his praise for Powers whiskey, noting:"The old make, which we drank with our luncheon was delicious and finer than anything we had hitherto tasted.It was as perfect in flavour, and as pronounced in the ancient aroma of Irish Whiskey so dear to to the hearts of connoisseurs,as one could possibly desire and we found a small flask of it very useful afterwards on our travels."
The last member of the family to sit on the board was Sir Thomas Talbot Power,
who died in 1930,
and with him the
Power's Baronetcy. However, ownership remained in the family until 1966, and several descendants of his sisters remained at work with the company until recent times.
In 1961, a
Coffey still was installed in John's Lane Distillery, allowing the production of vodka and gin, in addition to the testing of grain whiskey for use in blended whiskey.
This was a notable departure for the firm, as for many years the big Dublin distilling dynasties had shunned the use of Coffey stills, questioning if their output, grain whiskey could even be termed whiskey.
However, with many of the Irish distilleries having closed in the early 20th century in part due to their failure to embrace a change in consumer preference towards blended whiskey, Powers were instrumental in convincing the remaining Irish distilleries to reconsider their stance on blended whiskey.
In 1966, with the Irish whiskey industry still struggling following
Prohibition in the United States, the
Anglo-Irish Trade War and the rise of competition from Scotch whiskey, John Powers & Son joined forces with the only other remaining distillers in the Irish Republic, the
Cork Distilleries Company and their Dublin rivals
John Jameson & Son, to form
Irish Distillers. Soon after, in a bold move, Irish Distillers decided to close all of their existing distilleries, and to consolidate production at a new purpose-built facility in Midleton (the
New Midleton Distillery) alongside their existing
Old Midleton Distillery. The new distillery opened in 1975, and a year later, production ceased at John's Lane Distillery and began anew in Cork,
with Powers Gold Label and many other Irish whiskeys reformulated from
single pot stills whiskeys to blends.
In 1989, Irish Distillers itself became a subsidiary of
Pernod-Ricard following a friendly takeover.Since the closure of the John's Lane distillery, many of the distillery buildings were demolished. However, some of the buildings have been incorporated into the
National College of Art and Design, and are now protected structures.
In addition, three of the distillery's pot stills were saved and now located in the college's Red Square.
Origins : Dublin City
Dimensions : 100cm x 70cm 20kg (specially constructed damage proof shipping container)
 Charlton had beaten late entrant Bob Paisley, a multiple trophy winner, to the FAI hot seat, and his introduction to the gathered press was a million miles away from the carefully staged managed productions of the modern day.
In fact, it almost turned into an impromptu David Haye and Tony Bellew pre-match fight when Charlton challenged hardened journalist and ex-international Eamon Dunphy’s line of questioning. That relationship turned increasingly sour as time went by.
Charlton had beaten late entrant Bob Paisley, a multiple trophy winner, to the FAI hot seat, and his introduction to the gathered press was a million miles away from the carefully staged managed productions of the modern day.
In fact, it almost turned into an impromptu David Haye and Tony Bellew pre-match fight when Charlton challenged hardened journalist and ex-international Eamon Dunphy’s line of questioning. That relationship turned increasingly sour as time went by.
 This was the blueprint – or greenprint – of the Irish national team for the next decade.
Former players like Johnny Giles thought this indicated a lack of trust in the ability of players. Charlton saw it as pragmatic. His idea was to keep information and instruction simple.
This was the blueprint – or greenprint – of the Irish national team for the next decade.
Former players like Johnny Giles thought this indicated a lack of trust in the ability of players. Charlton saw it as pragmatic. His idea was to keep information and instruction simple.
 After a 1-0 defeat to Wales in his first match in charge, Charlton got to work on qualifying for the 1988 European Championship in West Germany.
After a 1-0 defeat to Wales in his first match in charge, Charlton got to work on qualifying for the 1988 European Championship in West Germany.
 While England staggered to defeat against the USSR and Holland, the Irish matched both teams stride for stride. Houghton described the 1-1 draw against the Soviets as “one of the best performances I’ve ever been involved in with Jack’s teams”.
While England staggered to defeat against the USSR and Holland, the Irish matched both teams stride for stride. Houghton described the 1-1 draw against the Soviets as “one of the best performances I’ve ever been involved in with Jack’s teams”.
 A 1-1 draw with the Dutch meant both teams had identical records as all three of Holland, England and Ireland progressed, with the Irish benefiting from the drawing of lots to qualify as group runners-up
After three drab stalemates, the party only truly began in Genoa against Romania in the last 16 – after another goalless game, Bonner saved Romania’s fifth penalty, leaving David O’Leary to take the decisive kick.
RTE commentator George Hamilton uttered the most important seven words Irish fans remember: “A nation holds its breath… We’re there!”
How ironic that the hero was O’Leary, another more football-minded defender that was often overlooked by Charlton.
O’Leary recalled: “There were about 20,000 brilliant Irish supporters behind the goal. They were so still and the eruption of green afterwards when the ball hit the net was absolutely amazing. It’s a fantastic memory.”
A 1-1 draw with the Dutch meant both teams had identical records as all three of Holland, England and Ireland progressed, with the Irish benefiting from the drawing of lots to qualify as group runners-up
After three drab stalemates, the party only truly began in Genoa against Romania in the last 16 – after another goalless game, Bonner saved Romania’s fifth penalty, leaving David O’Leary to take the decisive kick.
RTE commentator George Hamilton uttered the most important seven words Irish fans remember: “A nation holds its breath… We’re there!”
How ironic that the hero was O’Leary, another more football-minded defender that was often overlooked by Charlton.
O’Leary recalled: “There were about 20,000 brilliant Irish supporters behind the goal. They were so still and the eruption of green afterwards when the ball hit the net was absolutely amazing. It’s a fantastic memory.”
 Ireland’s propensity to draw a large proportion of games (30 out of 93 under Charlton) cost them dearly in the 1992 Euro qualifying group as only eight teams could qualify for Sweden.
They finished behind Graham Taylor’s stodgy England team, despite drawing home and away against them.
However, the Republic were reaching a new peak, with a young Roy Keane and Denis Irwin introduced to the team.
“The worst thing about missing out on Euro 92 was that Denmark won it. It should have been Ireland.” recalled a frustrated manager.
Ireland’s propensity to draw a large proportion of games (30 out of 93 under Charlton) cost them dearly in the 1992 Euro qualifying group as only eight teams could qualify for Sweden.
They finished behind Graham Taylor’s stodgy England team, despite drawing home and away against them.
However, the Republic were reaching a new peak, with a young Roy Keane and Denis Irwin introduced to the team.
“The worst thing about missing out on Euro 92 was that Denmark won it. It should have been Ireland.” recalled a frustrated manager.
 In the USA, the party started early in New York as Italy were beaten in the Big Apple by a Houghton strike.
Patrick Barclay summed it up best in The Observer: “Ireland’s blanket defence rendered vain all the creative endeavours of Roberto Baggio, who adorned this marvellous occasion but was not allowed to influence it because for 90 mins Jack Charlton’s sweat-soaked soldiers stayed about as close as ranks can get.”
Unfortunately, Ireland’s performances tailed off dramatically for the remainder of the tournament.
Such draining tactics were hard to administer in the humidity of Orlando, and the manager was banned from the touchline for venting his fury at officials over the lack of water for his troops against Mexico.
After squeezing through the group following a goalless draw with Norway, the Green bus ran out of fuel against the Dutch in the last 16.
In the USA, the party started early in New York as Italy were beaten in the Big Apple by a Houghton strike.
Patrick Barclay summed it up best in The Observer: “Ireland’s blanket defence rendered vain all the creative endeavours of Roberto Baggio, who adorned this marvellous occasion but was not allowed to influence it because for 90 mins Jack Charlton’s sweat-soaked soldiers stayed about as close as ranks can get.”
Unfortunately, Ireland’s performances tailed off dramatically for the remainder of the tournament.
Such draining tactics were hard to administer in the humidity of Orlando, and the manager was banned from the touchline for venting his fury at officials over the lack of water for his troops against Mexico.
After squeezing through the group following a goalless draw with Norway, the Green bus ran out of fuel against the Dutch in the last 16.

 It is sometimes opined in retrospect that the Republic could have done better with the quality of players at their disposal. They only won one of nine World Cup matches, scoring just four goals.
After USA’ 94, Dunphy said: “The minority who know their football well enough to distinguish between fact and fantasy have long since decided that even though the show is great, the football of the Charlton era has been, too often, lousy.”
But would liberation have taken away the organisational pragmatism that was central to the Green Wall being breached just 41 times in 93 games? After all, this was a team that also beat Brazil at home and Germany in Hannover.
Niall Quinn said: “We were happy as we were – beautiful, skilled losers.”
Big Jack made them coarse but clinical winners on the pitch and a lot happier off it.
11 of Jack Charlton’s best quotes: ‘Can we go now please? I’d like a beer’
It is sometimes opined in retrospect that the Republic could have done better with the quality of players at their disposal. They only won one of nine World Cup matches, scoring just four goals.
After USA’ 94, Dunphy said: “The minority who know their football well enough to distinguish between fact and fantasy have long since decided that even though the show is great, the football of the Charlton era has been, too often, lousy.”
But would liberation have taken away the organisational pragmatism that was central to the Green Wall being breached just 41 times in 93 games? After all, this was a team that also beat Brazil at home and Germany in Hannover.
Niall Quinn said: “We were happy as we were – beautiful, skilled losers.”
Big Jack made them coarse but clinical winners on the pitch and a lot happier off it.
11 of Jack Charlton’s best quotes: ‘Can we go now please? I’d like a beer’