Early life
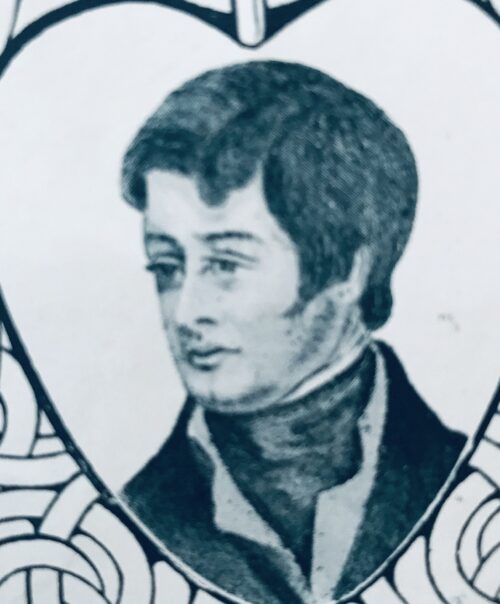
Emmet was born at 109 St. Stephen's Green, in Dublin on 4 March 1778. He was the youngest son of Dr Robert Emmet (1729–1802), a court physician, and his wife, Elizabeth Mason (1739–1803). The Emmets were financially comfortable, members of the Protestant Ascendancywith a house at St Stephen's Green and a country residence near Milltown. One of his elder brothers was an Irish Republican and Nationalist Thomas Addis Emmet, a close friend of Theobald Wolfe Tone, who was a frequent visitor to the house when Robert was a child. Emmet attended Oswald's school, in Dopping's-court, off Golden-lane.Emmet entered Trinity College Dublin in October 1793, at the age of fifteen. In December 1797 he joined the College Historical Society, a debating society.Career as a revolutionary
While Emmet was at college, his brother Thomas and some of his friends became involved in political activism. Robert became secretary of a secret United Irish Committee in college, and was expelled in April 1798 as a result. That same year he fled to France to avoid the many British arrests of nationalists that were taking place in Ireland. While in France, Emmet supposedly garnered the support of Napoleon, who had promised to lend support when the upcoming revolution started.However this pledged support existed in Emmet's imagination, as Napoleon was fully involved from early 1798 in organising the French invasion of Egypt. Napoleon was in Toulon from 9 May 1798, before the Irish Rebellion of 1798 had begun, yet there is no record of Emmet travelling to Toulon to see him. After the 1798 rising, Emmet was involved in reorganising the defeated United Irish Society. In April 1799 a warrant was issued for his arrest. He escaped and soon after travelled to the continent in the hope of securing French military aid, but his efforts were unsuccessful. The French Consulate dictatorship was however focused on new peace treaties, that resulted in the Treaty of Lunéville in 1801 and the Treaty of Amiens (March 1802). Emmet returned to Ireland in October 1802. In March the following year, he began preparations for another uprising. In the meantime, the French Consulate was holding on to Holland, Switzerland and Piedmont, in a manner contrary to the Treaty of Amiens, and so the treaty was ended by the British government in May 1803.1803 rebellion
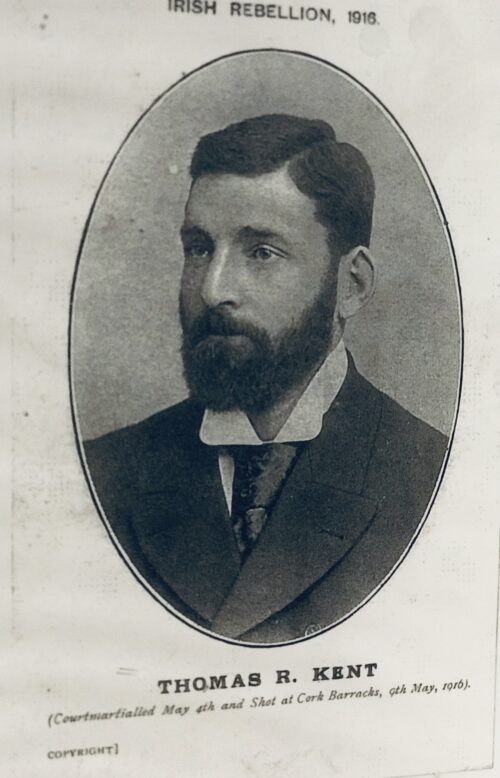
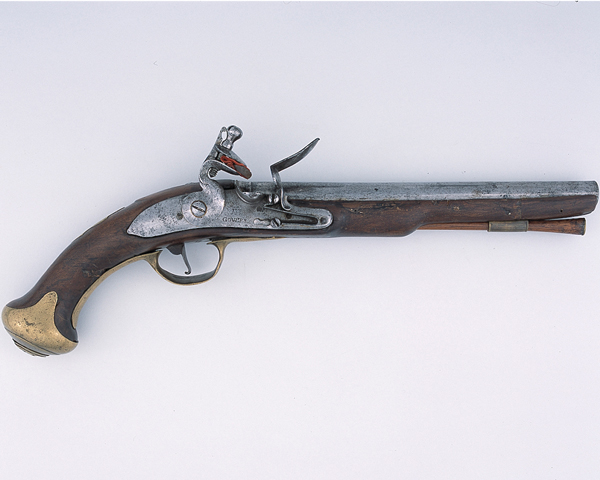
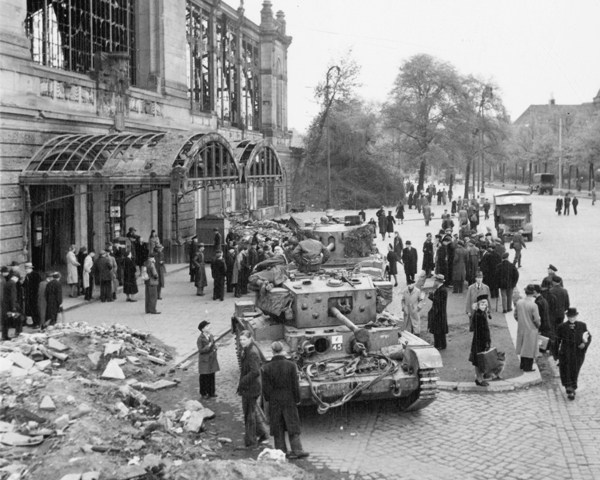
After his return to Ireland, Emmet began to prepare a new rebellion, with fellow revolutionaries Thomas Russell and James Hope. He began to manufacture weapons and explosives at a number of premises in Dublin and developed a folding pike fitted with a hinge that allowed it to be concealed under a cloak. Unlike in 1798, the revolutionaries concealed their preparations, but a premature explosion at one of Emmet's arms depots killed a man. Emmet was forced to advance the date of the rising before the authorities' suspicions were aroused. Emmet was unable to secure the help of Michael Dwyer's Wicklow rebels. Many rebels from Kildare turned back due to the scarcity of firearms they had been promised, but the rising went ahead in Dublin on the evening of 23 July 1803. About 10,000 copies were printed of a proclamation in the name of the "Provisional Government", which influenced the 1916 Proclamation; most were destroyed by the authorities. Emmet wore a uniform of a green coat with white facings, white breeches, top-boots, and a cocked hat with feathers.[5] Failing to seize Dublin Castle, which was lightly defended, the rising of some 200 men amounted to a large-scale disturbance in the Thomas Street area. Emmet saw a dragoon being pulled from his horse and piked to death, the sight of which prompted him to call off the rising to avoid further bloodshed. But, he had lost all control of his followers. In one incident, the Lord Chief Justice of Ireland, Lord Kilwarden, was dragged from his carriage and stabbed by pikes. Found still alive, he was taken to a watch-house where he died shortly thereafter. He had been reviled as chief prosecutor of William Orr in 1797, but he was also the judge who granted habeas corpus to Wolfe Tone in 1798. Kilwarden's nephew, the Rev. Mr. Wolfe, was also murdered. Sporadic clashes continued into the night until finally quelled by British military forces.Capture and trial
Emmet fled into hiding, moving from Rathfarnham to Harold's Cross so that he could be near his sweetheart, Sarah Curran. He likely could have escaped to France, had he not insisted upon returning with Anne Devlin in order to take leave of Sarah Curran, to whom he was engaged. She was daughter of John Philpot Curran.Emmet was captured on 25 August and taken to the Castle, then removed to Kilmainham. Vigorous but ineffectual efforts were made to procure his escape. He was tried for treason on 19 September; the Crown repaired the weaknesses in its case by secretly buying the assistance of Emmet's defense attorney, Leonard McNally, for £200 and a pension.But McNally's assistant Peter Burrowes could not be bought and he pleaded the case as best he could. On 19 September, Emmet was found guilty of high treason. Before sentencing Emmet delivered a speech, the Speech from the Dock. It is especially remembered for its closing sentences and secured his posthumous fame among executed Irish republicans. It was printed in 1835 in Manchester for the bookseller TP Carlile.Let no man write my epitaph; for as no man who knows my motives dare now vindicate them, let not prejudice or ignorance, asperse them. Let them and me rest in obscurity and peace, and my tomb remain un-inscribed, and my memory in oblivion, until other times and other men can do justice to my character. When my country takes her place among the nations of the earth, then and not till then, let my epitaph be written. I have done.An earlier and more credible version of the speech was published in 1818, taken from the notes of his counsel Peter Burrowes, in a biography on Sarah Curran's father John, emphasising that Emmet's epitaph should be written on the future vindication of his character, and not specifically when Ireland took its place as a nation. It closed:
I am here ready to die. I am not allowed to vindicate my character; no man shall dare to vindicate my character; and when I am prevented from vindicating myself, let no man dare to calumniate me. Let my character and my motives repose in obscurity and peace, till other times and other men can do them justice. Then shall my character be vindicated; then may my epitaph be written.The modern historian Patrick Geoghehan wrote in 2003: "At last count there are over seventy different versions of the text, but most of these are later reworkings and have little claim to acceptance." Chief Justice Lord Norbury sentenced Emmet to be hanged, drawn and quartered, as was customary for conviction of treason. The following day, 20 September, Emmet was executed in Thomas Street in front of St. Catherine's. He was hanged and then beheaded once dead. As family members and friends of Robert had also been arrested, including some who had nothing to do with the rebellion, no one came forward to claim his remains out of fear of arrest. Robert Emmet is described as slight in person; his features were regular, his forehead high, his eyes bright and full of expression, his nose sharp, thin, and straight, the lower part of his face slightly pock-marked, his complexion sallow.[5]
Burial
Emmet's remains were first delivered to Newgate Prison and then back to Kilmainham Gaol, where the jailer was under instructions that if no one claimed them they were to be buried in a nearby hospital's burial grounds called 'Bully's Acre' in Kilmainham. A later search there found no remains. It is claimed that Emmet's remains were secretly removed from Bully's Acre and reinterred in St Michan's, a Dublin church with strong United Irish associations, though it was never confirmed.Speculation has continued regarding the whereabouts of Emmet's remains. It was suspected that they were buried secretly in the vault of a Dublin Anglican church. When the vault was inspected in the 1950s a headless corpse was found, suspected of being Emmet's, but could not be identified. Widely accepted is the theory that Emmet's remains were transferred to St Peter's Church in Aungier St. under cover of the burial of Robert's sister, Mary Anne Holmes, in 1804. In the 1980s the church was de-consecrated and all the coffins were removed from the vaults. The church has since been demolished.Legacy

Robert Emmet was honoured on two Irish postage stamps issued in 1953, commemorating the 150th anniversary of his death
Representation in popular culture
Robert Emmet wrote a letter from his cell in Kilmainham Gaol, Dublin on 8 September 1803. He addressed it to "Miss Sarah Curran, the Priory, Rathfarnham" and handed it to a prison warden, George Dunn, whom he trusted to deliver it. Dunn betrayed him and gave the letter to the government authorities. Due to Emmet's attempt to hide near Curran, which cost him his life, and his parting letter to her, Emmet became known as a legendary romantic character, appealing to the Victorian Era's appetite for Romanticism. His story was the subject of stage melodramas during the 19th century, most notably Dion Boucicault's inaccurate 1884 play Robert Emmet. He mistakenly portrayed Emmet and Curran as Roman Catholics (they were both Protestants), her father John Philpot Curran being portrayed as a Unionist, and Emmet being killed onstage by firing squad. Robert's friend from Trinity College, Thomas Moore, championed his cause by writing popular ballads about him and Sarah Curran, such as- Oh breathe not his name! let it sleep in the shade,
- Where cold and unhonoured his relics are laid!
- No trump tells thy virtues—the grave where they rest
- With thy dust shall remain unpolluted by fame,
- Till thy foes, by the world and by fortune caressed,
- Shall pass like a mist from the light of thy name.
Honours
Places named after Emmet in the United States include Emmetsburg, Iowa; Emmet, Nebraska;Emmet County, Iowa; Emmett, Michigan and Emmet County, Michigan.[20] The Robert Emmet Elementary School in Chicago, Illinois was named for him. Two time All Ireland Club Camogie Champions Robert Emmet's GAC Slaughtneil is named after him. Emmet Park in Savannah, Georgia was named after Emmet after urging from the large Irish born population in the city. Statues were erected in his honour:- A life size bronze statue of Robert Emmet by Jerome Connor stands in St Stephen's Green, Dublin, the parkland beside which Emmet was born.
- A bronze statue of Emmet by Jerome Connor stands in Washington, DC on Embassy Row (Massachusetts Avenue NW and S Street NW). A public commemoration of Emmet's execution and legacy is held annually on the fourth Sunday in September by the Irish American Unity Conference.
- A copy of this statue was installed on the Music Concourse in front of the California Academy of Sciences in San Francisco's Golden Gate Park.
-
Bronze statue of Robert Emmet, 1916, by Jerome Connor, from the collection of the Smithsonian American Art Museum. It is installed in Washington, DC's Embassy Row.
-
Statue of Robert Emmet in St Stephens Green, Dublin
-
Reproduction of Robert Emmet statue in San Francisco's Golden Gate Park
- A statue of Robert Emmet is in the courthouse square in Emmetsburg, Iowa.
Early life
Wolfe Tone was born on 20 June 1763. His family were descended from a French Protestant family who fled to England from Gascony in the 16th century to escape religious persecution. A branch of the family settled in Dublin in the 17th century. Theobald's father, Peter Tone, was a coach-maker who had a farm near Sallins, County Kildare and belonged to the Church of Ireland. His mother came from a Catholic merchant family who converted to Protestantism after Theobald was born. His maternal grandfather was captain of a vessel in the West India trade. He was baptised as Theobald Wolfe Tone in honour of his godfather, Theobald Wolfe of Blackhall, County Kildare, a first cousin of Arthur Wolfe, 1st Viscount Kilwarden. However, it was widely believed that Tone was the son of Theobald Wolfe, which, if true, made him a half-brother of the poet Charles Wolfe. After his death, he was widely referred to as Wolfe Tone. In 1783, Tone found work as a tutor to Anthony and Robert, younger half-brothers of Richard Martin MP of Galway, a prominent supporter of Catholic emancipation, at Dangan, the Martin family home.Tone fell in love with Martin's wife, but later wrote that it came to nothing. During this period he briefly considered a career in the theatre as an actor. He studied law at Trinity College Dublin, where he became an active member in the College Historical Society debating club and was elected its auditor in 1785. He graduated BA in February 1786.He qualified as a barrister in King's Inns at the age of 26 after keeping the requisite terms as a student member of the Middle Temple in London. As a student, he eloped with Martha Witherington, daughter of William and Catherine Witherington (née Fanning) of Dublin.She would go on to change her name to Matilda, at Tone's request. When they married, Tone was 22, and Matilda was about 16. In 1796, while he was in France and she in Hamburg he wrote in his journal: "She is the delight of my eyes, the joy of my heart, the only object for which I wish to live. I doat upon her to distraction." Disappointed at finding no support for a plan that he had submitted to William Pitt the Younger, to found a military colony in Hawaii, Tone initially planned to enlist as a soldier in the East India Company, but applied too late in the year, when no more ships would be sent out until the following spring.Politician
In September 1791, Tone published An Argument on behalf of the Catholics of Ireland, signed "A Northern Whig". It displayed the growing breach between Whig patriots like Henry Flood and Henry Grattan, who sought Catholic emancipation and parliamentary reform without severing the tie to England. Tone expressed contempt for the constitution Grattan obtained from the British government in 1782. Himself an Anglican, Tone urged co-operation between the religions in Ireland as the only means of obtaining redress of Irish grievances. The British government had just passed the Roman Catholic Relief Act 1791, but the Dublin parliament was in no hurry to do so. In October 1791 Tone converted these ideas into practical policy by founding, in conjunction with Thomas Russell (1767–1803), Napper Tandy and others, the Society of the United Irishmen. Until 1794, this society aimed at no more than the formation of a political union between Catholics and Protestants, with a view to obtaining a liberal measure of parliamentary reform. In 1792 he was appointed an assistant secretary of the Catholic Committee. The Catholics involved were not united regarding the steps they were to take, and in December 1791, sixty-eight members withdrew, led by Lord Kenmare, with the support of the higher clergy. When the British government questioned the legality of the Catholic Convention called in December 1792, Tone drew up for the committee a statement of the case on which a favourable opinion of counsel was obtained. A petition was made to King George III early in 1793, and that year the re-enfranchisement of Catholics was enacted – if they owned property as "forty-shilling freeholders". They could again be called as barristers and serve as army officers. They could not, however, enter parliament or be made state officials above grand jurors. The Convention voted to Tone a sum of £1,500 with a gold medal and voted to dissolve. In this new climate of goodwill the Maynooth College Act 1795 was passed. Sectarian animosity threatened to undermine the United Irishmen movement: two secret societies in Ulster fought against each other: the agrarian Protestant Peep o' Day Boys and their Catholic opponents the Defenders. Tone's aim was to unite both into a revolutionary army of Irish "men of no property". Tone himself admitted that with him hatred of England had always been "rather an instinct than a principle," though until his views should become more generally accepted in Ireland he was prepared to work for reform as distinguished from revolution. But he desired to root out the popular respect for the names of Charlemont and Grattan, and to transfer to more violent leaders the conduct of the national movement. Wolfe Tone's principles were drawn from the French Convention, and he was a disciple of Georges Danton and Thomas Paine.Revolutionary in exile

Statue of Tone, Bantry, County Cork
Wolf Tone was sent to France to claim the support of the Directory, under the express condition that the French should come to Ireland as allies, and should act under direction of the new government, as Rochambeau had done in America. With this view, Tone had frequently conferences at Paris with Hoche; and the Directory finally determined to send from Brest a fleet of forty-five sail, with an army of fifteen thousand men, under the charge of this able general, December 15, 1796. England was saved by a violent tempest.
Hoche's Expedition and the 1798 Rebellion

In End of the Irish Invasion ; — or – the Destruction of the French Armada(1797), James Gillray caricatured the failure of Hoche's expedition.