-
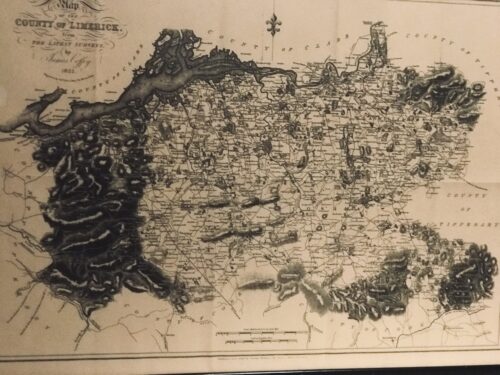
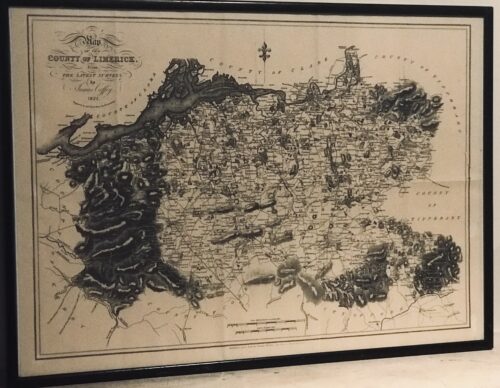 Very interesting map of Co Limerick from the 1825 surveys by the well known cartographer James Coffey.From the Latest Surveys. By James Coffey. 1825. Engraved by Sidney Hall, Bury Street, Bloomsbury. Published and sold by George McKern, 106, George Street, Limerick. Scale in Irish and English Miles. Framed and glazed. Bruree Co Limerick 45cm x 60cm
Very interesting map of Co Limerick from the 1825 surveys by the well known cartographer James Coffey.From the Latest Surveys. By James Coffey. 1825. Engraved by Sidney Hall, Bury Street, Bloomsbury. Published and sold by George McKern, 106, George Street, Limerick. Scale in Irish and English Miles. Framed and glazed. Bruree Co Limerick 45cm x 60cm -
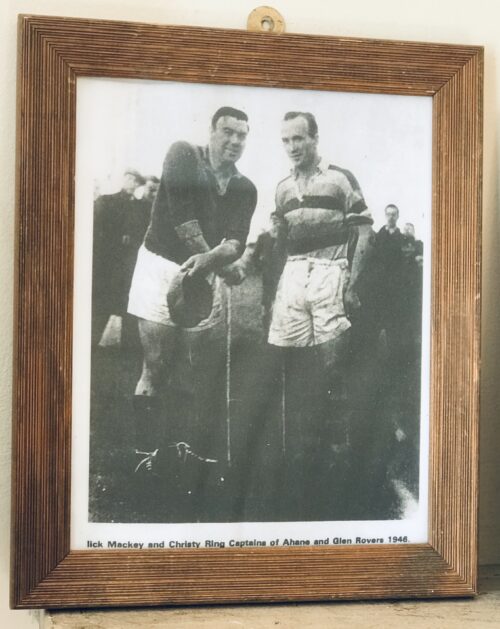
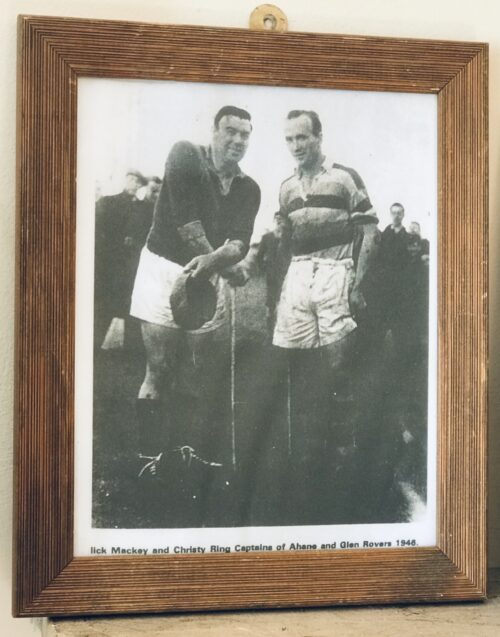
 Atmospheric photo from 1946 of two of the greatest hurlers in the history of the GAA in its original vintage frame -a veteran Mick Mackey of Limerick and a fresh faced Christy Ring of Cork.The only shame was they never met on the playing field while at the peak of their powers,Mackey being older and in decline when Ring was lording it on the pitch.Although they had their controversial moments together ,there was a massive mutual respect between the two men.this photo was taken after a challenge match between their respective clubs,Mackey's Ahane of Limerick and Ring's Glen Rovers of Cork - it proved to be the last time the two legends met on the field of play. Origins : Co Limerick Dimensions : 31cm x 25cm 1kg
Atmospheric photo from 1946 of two of the greatest hurlers in the history of the GAA in its original vintage frame -a veteran Mick Mackey of Limerick and a fresh faced Christy Ring of Cork.The only shame was they never met on the playing field while at the peak of their powers,Mackey being older and in decline when Ring was lording it on the pitch.Although they had their controversial moments together ,there was a massive mutual respect between the two men.this photo was taken after a challenge match between their respective clubs,Mackey's Ahane of Limerick and Ring's Glen Rovers of Cork - it proved to be the last time the two legends met on the field of play. Origins : Co Limerick Dimensions : 31cm x 25cm 1kg -

 Beautifully atmospheric lithograph of the pre match parade by the Cork and Dublin Hurlers in 1952.This lithograph was sponsored by the National Flour Mills Co.Ltd. 42cm x 46cm Douglas Cork
Beautifully atmospheric lithograph of the pre match parade by the Cork and Dublin Hurlers in 1952.This lithograph was sponsored by the National Flour Mills Co.Ltd. 42cm x 46cm Douglas Cork
The 1952 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship Final was the 65th All-Ireland Final and the culmination of the 1952 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship, an inter-county hurling tournament for the top teams in Ireland. The match was held at Croke Park, Dublin, on 7 September 1952, between Cork and Dublin. The Leinster champions lost to their Munster opponents on a score line of 2-14 to 0-7.1952 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Final 
Event 1952 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship Cork Dublin 2-14 0-7 Date 7 September 1952 Venue Croke Park, Dublin Referee W. O'Donoghue (Limerick) Attendance 71,195 Origins : Co CorkDimensions : 31cm x 36cm 1.5kg -
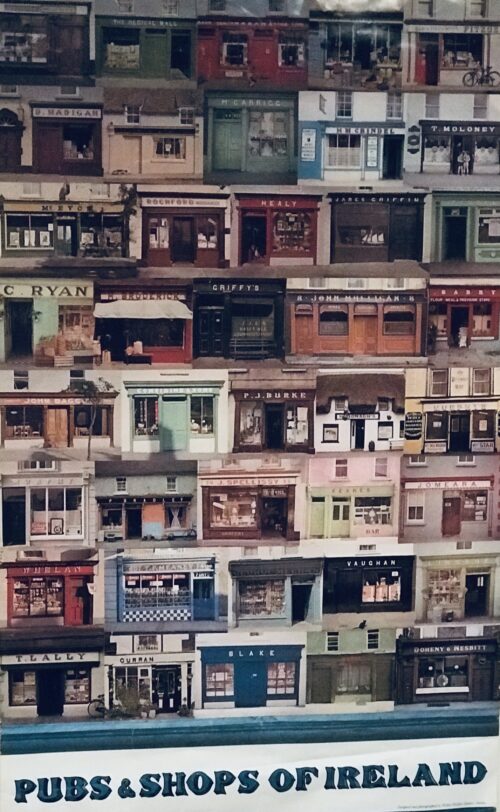
 88cm x 52cm In olden times the traditional Irish country pub also often functioned as a grocery,sweetshop,veterinary chemist,hardware store and haberdashery where patrons could partake in a soothing drink after shopping alongside displays of chocolate bars, tins of canned fruit, reels of hay bailer twine, and tubs of sheep dip.Sadly grocery bars are now few and far between but the ones that survive are a throwback to an old and innocent way of life.Dingle in Co Kerry is home to many of the best surviving examples of the pub-grocer.In the famous Currans on Main Street ,the pub always doubled as a general merchant.They sold everything and supplied the townspeople and farmers who would pile into the town on Fairday.The old ledgers still in existence are stuffed with billheads from all types of suppliers- everything was sold -ropes.twines,seeds,ales,buckets,hams,jams,fishing nets,flowers,ladies rubber heels and tights, cloth caps, shirts,boots- the list is endless.
88cm x 52cm In olden times the traditional Irish country pub also often functioned as a grocery,sweetshop,veterinary chemist,hardware store and haberdashery where patrons could partake in a soothing drink after shopping alongside displays of chocolate bars, tins of canned fruit, reels of hay bailer twine, and tubs of sheep dip.Sadly grocery bars are now few and far between but the ones that survive are a throwback to an old and innocent way of life.Dingle in Co Kerry is home to many of the best surviving examples of the pub-grocer.In the famous Currans on Main Street ,the pub always doubled as a general merchant.They sold everything and supplied the townspeople and farmers who would pile into the town on Fairday.The old ledgers still in existence are stuffed with billheads from all types of suppliers- everything was sold -ropes.twines,seeds,ales,buckets,hams,jams,fishing nets,flowers,ladies rubber heels and tights, cloth caps, shirts,boots- the list is endless. -
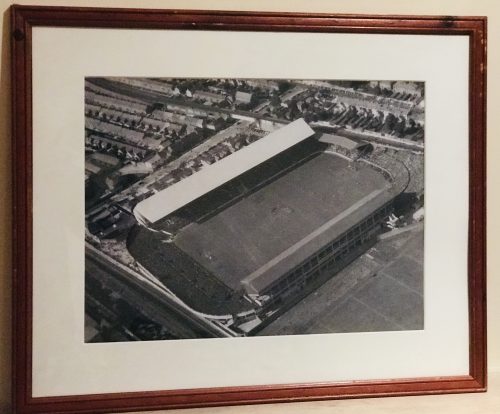 45cm x 52cm Broadford Co ClareCroke Park (Irish: Páirc an Chrócaigh) is a Gaelic games stadium located in Dublin, Ireland. Named after Archbishop Thomas Croke, it is sometimes called Croker by GAA fans and locals. It serves as both the principal stadium and headquarters of the Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA). Since 1891 the site has been used by the GAA to host Gaelic sports, including the annual All-Ireland in Gaelic football and hurling. A major expansion and redevelopment of the stadium ran from 1991–2005, raising capacity to its current 82,300 spectators. This makes Croke Park the third-largest stadium in Europe, and the largest not usually used for association football. Other events held at the stadium include the opening and closing ceremonies of the 2003 Special Olympics, and numerous musical concerts. In 2012, Irish pop group Westlife sold out the stadium in record-breaking time: less than 5 minutes. From 2007–10, Croke Park hosted home matches of the Ireland national rugby union team and the Republic of Ireland national football team, while their new Aviva Stadium was constructed. This use of Croke Park for non-Gaelic sports was controversial and required temporary changes to GAA rules. In June 2012, the stadium hosted the closing ceremony of the 50th International Eucharistic Congress during which Pope Benedict XVI gave an address over video link.
45cm x 52cm Broadford Co ClareCroke Park (Irish: Páirc an Chrócaigh) is a Gaelic games stadium located in Dublin, Ireland. Named after Archbishop Thomas Croke, it is sometimes called Croker by GAA fans and locals. It serves as both the principal stadium and headquarters of the Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA). Since 1891 the site has been used by the GAA to host Gaelic sports, including the annual All-Ireland in Gaelic football and hurling. A major expansion and redevelopment of the stadium ran from 1991–2005, raising capacity to its current 82,300 spectators. This makes Croke Park the third-largest stadium in Europe, and the largest not usually used for association football. Other events held at the stadium include the opening and closing ceremonies of the 2003 Special Olympics, and numerous musical concerts. In 2012, Irish pop group Westlife sold out the stadium in record-breaking time: less than 5 minutes. From 2007–10, Croke Park hosted home matches of the Ireland national rugby union team and the Republic of Ireland national football team, while their new Aviva Stadium was constructed. This use of Croke Park for non-Gaelic sports was controversial and required temporary changes to GAA rules. In June 2012, the stadium hosted the closing ceremony of the 50th International Eucharistic Congress during which Pope Benedict XVI gave an address over video link.
The 1951 All-Ireland Senior Football Championship Final was the 64th All-Ireland Final and the deciding match of the 1951 All-Ireland Senior Football Championship, an inter-county Gaelic football tournament for the top teams in Ireland. Mayo and Meath met to decide the destination of the Sam Maguire Cup. Mayo won their second title in a row with goals by Tom Langan and Joe Gilvarry. This was Mayo's second consecutive All-Ireland football title. They have not won an All-Ireland football title since. It is said that a legendary curse overshadows Mayo football since 1951 Mayo players Willie Casey, Paddy Jordan and former GAA President Dr Mick Loftus belatedly received their All-Ireland senior football medals 55 years later. Though squad members, they had not appeared as substitutes in the final and had initially been denied their medals.1951 All-Ireland Senior Football Final 
Event 1951 All-Ireland Senior Football Championship Mayo Meath 
2-8 0-9 Date 23 September 1951 Venue Croke Park, Dublin Attendance 78,201 City and Suburban Racecourse
The area now known as Croke Park was owned in the 1880s by Maurice Butterly and known as the City and Suburban Racecourse, or Jones' Road sports ground. From 1890 it was also used by the Bohemian Football Club. In 1901 Jones' Road hosted the IFA Cup football final when Cliftonville defeated Freebooters.History
Recognising the potential of the Jones' Road sports ground a journalist and GAA member, Frank Dineen, borrowed much of the £3,250 asking price and bought the ground in 1908. In 1913 the GAA came into exclusive ownership of the plot when they purchased it from Dineen for £3,500. The ground was then renamed Croke Park in honour of Archbishop Thomas Croke, one of the GAA's first patrons. In 1913, Croke Park had only two stands on what is now known as the Hogan stand side and grassy banks all round. In 1917, a grassy hill was constructed on the railway end of Croke Park to afford patrons a better view of the pitch. This terrace was known originally as Hill 60, later renamed Hill 16 in memory of the 1916 Easter Rising. It is erroneously believed to have been built from the ruins of the GPO, when it was constructed the previous year in 1915. In the 1920s, the GAA set out to create a high capacity stadium at Croke Park. Following the Hogan Stand, the Cusack Stand, named after Michael Cusack from Clare (who founded the GAA and served as its first secretary), was built in 1927. 1936 saw the first double-deck Cusack Stand open with 5,000 seats, and concrete terracing being constructed on Hill 16. In 1952 the Nally Stand was built in memorial of Pat Nally, another of the GAA founders. Seven years later, to celebrate the 75th anniversary of the GAA, the first cantilevered "New Hogan Stand" was opened. The highest attendance ever recorded at an All-Ireland Senior Football Championship Final was 90,556 for Offaly v Down in 1961. Since the introduction of seating to the Cusack stand in 1966, the largest crowd recorded has been 84,516.Bloody Sunday
During the Irish War of Independence on 21 November 1920 Croke Park was the scene of a massacre by the Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC). The Police, supported by the British Auxiliary Division, entered the ground and began shooting into the crowd, killing or fatally wounding 14 civilians during a Dublin-Tipperary Gaelic football match. The dead included 13 spectators and Tipperary player Michael Hogan. Posthumously, the Hogan stand built in 1924 was named in his honour. These shootings, on the day which became known as Bloody Sunday, were a reprisal for the killing of 15 people associated with the Cairo Gang, a group of British Intelligence officers, by Michael Collins' 'squad' earlier that day.Dublin Rodeo
In 1924, American rodeo promoter, Tex Austin, staged the Dublin Rodeo, Ireland's first professional rodeo at Croke Park Stadium. For seven days, with two shows each day from August 18 to August 24, sell out crowds saw cowboys and cowgirls from Canada, the United States, Mexico, Argentina and Australia compete for rodeo championship titles.Canadian bronc riders such as Andy Lund and his brother Art Lund, trick riders such as Ted Elder and Vera McGinnis were among the contestants. British Pathe filmed some of the rodeo events.Stadium design
In 1984 the organisation decided to investigate ways to increase the capacity of the old stadium. The design for an 80,000 capacity stadium was completed in 1991. Gaelic sports have special requirements as they take place on a large field. A specific requirement was to ensure the spectators were not too far from the field of play. This resulted in the three-tier design from which viewing games is possible: the main concourse, a premium level incorporating hospitality facilities and an upper concourse. The premium level contains restaurants, bars and conference areas. The project was split into four phases over a 14-year period. Such was the importance of Croke Park to the GAA for hosting big games, the stadium did not close during redevelopment. During each phase different parts of the ground were redeveloped, while leaving the rest of the stadium open. Big games, including the annual All-Ireland Hurling and Football finals, were played in the stadium throughout the development.Phase one – New Cusack Stand
The first phase of construction was to build a replacement for Croke Park's Cusack Stand. A lower deck opened for use in 1994. The upper deck opened in 1995. Completed at a cost of £35 million, the new stand is 180 metres long, 35 metres high, has a capacity for 27,000 people and contains 46 hospitality suites. The new Cusack Stand contains three tiers from which viewing games is possible: the main concourse, a premium level incorporating hospitality facilities and finally an upper concourse. One end of the pitch was closer to the stand after this phase, as the process of slightly re-aligning the pitch during the redevelopment of the stadium began. The works were carried out by Sisk Group.Phase two – Davin Stand
Phase Two of the development started in late 1998 and involved extending the new Cusack Stand to replace the existing Canal End terrace. It involved reacquiring a rugby pitch that had been sold to Belvedere College in 1910 by Frank Dineen. In payment and part exchange, the college was given the nearby Distillery Road sportsgrounds.[19] It is now known as The Davin Stand (Irish: Ardán Dáimhím), after Maurice Davin, the first president of the GAA. This phase also saw the creation of a tunnel which was later named the Ali tunnel in honour of Muhammad Ali and his fight against Al Lewis in July 1972 in Croke Park.Phase three – Hogan Stand
Phase Three saw the building of the new Hogan Stand. This required a greater variety of spectator categories to be accommodated including general spectators, corporate patrons, VIPs, broadcast and media services and operation staff. Extras included a fitted-out mezzanine level for VIP and Ard Comhairle (Where the dignitaries sit) along with a top-level press media facility. The end of Phase Three took the total spectator capacity of Croke Park to 82,000.Phase four – Nally Stand & Nally End/Dineen Hill 16 terrace
After the 2003 Special Olympics, construction began in September 2003 on the final phase, Phase Four. This involved the redevelopment of the Nally Stand, named after the athlete Pat Nally, and Hill 16 into a new Nally End/Dineen Hill 16 terrace. While the name Nally had been used for the stand it replaced, the use of the name Dineen was new, and was in honour of Frank Dineen, who bought the original stadium for the GAA in 1908, giving it to them in 1913. The old Nally Stand was taken away and reassembled in Pairc Colmcille, home of Carrickmore GAA in County Tyrone. The phase four development was officially opened by the then GAA President Seán Kelly on 14 March 2005. For logistical reasons (and, to a degree, historical reasons), and also to provide cheaper high-capacity space, the area is a terrace rather than a seated stand, the only remaining standing-room in Croke Park. Unlike the previous Hill, the new terrace was divided into separate sections – Hill A (Cusack stand side), Hill B (behind the goals) and the Nally terrace (on the site of the old Nally Stand). The fully redeveloped Hill has a capacity of around 13,200, bringing the overall capacity of the stadium to 82,300. This made the stadium the second biggest in the EU after the Camp Nou, Barcelona. However, London's new Wembley stadium has since overtaken Croke Park in second place. The presence of terracing meant that for the brief period when Croke Park hosted international association football during 2007–2009, the capacity was reduced to approximately 73,500, due to FIFA's statutes stating that competitive games must be played in all-seater stadiums.Pitch
The pitch in Croke Park is a soil pitch that replaced the Desso GrassMaster pitch laid in 2002. This replacement was made after several complaints by players and managers that the pitch was excessively hard and far too slippery. Since January 2006, a special growth and lighting system called the SGL Concept has been used to assist grass growing conditions, even in the winter months. The system, created by Dutch company SGL (Stadium Grow Lighting), helps in controlling and managing all pitch growth factors, such as light, temperature, CO2, water, air and nutrients.Floodlighting
With the 2007 Six Nations clash with France and possibly other matches in subsequent years requiring lighting the GAA installed floodlights in the stadium (after planning permission was granted). Indeed, many other GAA grounds around the country have started to erect floodlights as the organisation starts to hold games in the evenings, whereas traditionally major matches were played almost exclusively on Sunday afternoons. The first game to be played under these lights at Croke Park was a National Football League Division One match between Dublin and Tyrone on 3 February 2007 with Tyrone winning in front of a capacity crowd of over 81,000 – which remains a record attendance for a National League game, with Ireland's Six Nations match with France following on 11 February. Temporary floodlights were installed for the American Bowl game between Chicago Bears and Pittsburgh Steelers on the pitch in 1997, and again for the 2003 Special Olympics.Concert
Date Performer(s) Opening act(s) Tour/Event Attendance Notes 29 June 1985 U2 In Tua Nua, R.E.M., The Alarm, Squeeze The Unforgettable Fire Tour 57,000 First Irish act to have a headline concert. Part of the concert was filmed for the group's documentary Wide Awake in Dublin. 28 June 1986 Simple Minds Once Upon A Time Tour Guest appearance by Bono 27 June 1987 U2 Light A Big Fire, The Dubliners, The Pogues, Lou Reed The Joshua Tree Tour 114,000 28 June 1987 Christy Moore, The Pretenders, Lou Reed, Hothouse Flowers 28 June 1996 Tina Turner Brian Kennedy Wildest Dreams Tour 40,000/40,000 16 May 1997 Garth Brooks World Tour II 18 May 1997 29 May 1998 Elton John & Billy Joel Face to Face 1998 30 May 1998 24 June 2005 U2 The Radiators from Space, The Thrills, The Bravery, Snow Patrol, Paddy Casey, Ash Vertigo Tour 246,743 25 June 2005 27 June 2005 20 May 2006 Bon Jovi Nickelback Have a Nice Day Tour 81,327 9 June 2006 Robbie Williams Basement Jaxx Close Encounters Tour 6 October 2007 The Police Fiction Plane The Police Reunion Tour 81,640 Largest attendance of the tour. 31 May 2008 Celine Dion Il Divo Taking Chances World Tour 69,725 Largest attendance for a solo female act 1 June 2008 Westlife Shayne Ward Back Home Tour 85,000 Second Irish act to have a headline concert. Largest attendance of the tour. Part of the concert was filmed for the group's documentary and concert DVD 10 Years of Westlife - Live at Croke Park Stadium. 14 June 2008 Neil Diamond 13 June 2009 Take That The Script Take That Present: The Circus Live 24 July 2009 U2 Glasvegas, Damien Dempsey U2 360° Tour 243,198 25 July 2009 Kaiser Chiefs, Republic of Loose 27 July 2009 Bell X1, The Script The performances of "New Year's Day" and "I'll Go Crazy If I Don't Go Crazy Tonight" were recorded for the group's live album U22 and for the band's remix album Artificial Horizon and the live EP Wide Awake in Europe, respectively. 5 June 2010 Westlife Wonderland, WOW, JLS, Jedward Where We Are Tour 86,500 Largest attendance of the tour. 18 June 2011 Take That Pet Shop Boys Progress Live 154,828 19 June 2011 22 June 2012 Westlife Jedward, The Wanted, Lawson Greatest Hits Tour 187,808[24] The 23 June 2012 date broke the stadium record for selling out its tickets in four minutes. Eleventh largest attendance at an outdoor stadium worldwide. Largest attendance of the tour and the band's music career history. Part of the concert was filmed for the group's documentary and concert DVD The Farewell Tour - Live in Croke Park. 23 June 2012 26 June 2012 Red Hot Chili Peppers Noel Gallagher's High Flying Birds, The Vaccines I'm with You World Tour 23 May 2014 One Direction 5 Seconds of Summer Where We Are Tour 235,008 24 May 2014 25 May 2014 20 June 2015 The Script & Pharrell Williams No Sound Without Silence Tour 74,635 24 July 2015 Ed Sheeran x Tour 162,308 25 July 2015 27 May 2016 Bruce Springsteen The River Tour 2016 160,188 29 May 2016 9 July 2016 Beyoncé Chloe x Halle, Ingrid Burley The Formation World Tour 68,575 8 July 2017 Coldplay AlunaGeorge, Tove Lo A Head Full of Dreams Tour[25] 80,398 22 July 2017 U2 Noel Gallagher's High Flying Birds The Joshua Tree Tour 2017 80,901 17 May 2018 The Rolling Stones The Academic No Filter Tour 64,823 15 June 2018 Taylor Swift Camila Cabello, Charli XCX Taylor Swift's Reputation Stadium Tour 136.000 Swift became the first woman headline two concerts in a row there. 16 June 2018 7 July 2018 Michael Bublé Emeli Sandé 24 May 2019 Spice Girls Jess Glynne Spice World - 2019 UK Tour 5 July 2019 Westlife James Arthur Wild Youth The 20 Touror The Twenty Tour The 5 July 2019 date sold out its tickets in six minutes. Second date released were also sold out in under forty-eight hours. 6 July 2019 Non-Gaelic games
There was great debate in Ireland regarding the use of Croke Park for sports other than those of the GAA. As the GAA was founded as a nationalist organisation to maintain and promote indigenous Irish sport, it has felt honour-bound throughout its history to oppose other, foreign (in practice, British), sports. In turn, nationalist groups supported the GAA as the prime example of purely Irish sporting culture. Until its abolition in 1971, rule 27 of the GAA constitution stated that a member of the GAA could be banned from playing its games if found to be also playing association football, rugby or cricket. That rule was abolished but rule 42 still prohibited the use of GAA property for games with interests in conflict with the interests of the GAA. The belief was that rugby and association football were in competition with Gaelic football and hurling, and that if the GAA allowed these sports to use their ground it might be harmful to Gaelic games, while other sports, not seen as direct competitors with Gaelic football and hurling, were permitted, such as the two games of American football (Croke Park Classic college football game between The University of Central Florida and Penn State, and an American Bowl NFL preseason game between the Chicago Bears and the Pittsburgh Steelers) on the Croke Park pitch during the 1990s.[27] On 16 April 2005, a motion to temporarily relax rule No. 42 was passed at the GAA Annual Congress. The motion gives the GAA Central Council the power to authorise the renting or leasing of Croke Park for events other than those controlled by the Association, during a period when Lansdowne Road – the venue for international soccer and rugby matches – was closed for redevelopment. The final result was 227 in favour of the motion to 97 against, 11 votes more than the required two-thirds majority. In January 2006, it was announced that the GAA had reached agreement with the Football Association of Ireland (FAI) and Irish Rugby Football Union (IRFU) to stage two Six Nations games and four soccer internationals at Croke Park in 2007 and in February 2007, use of the pitch by the FAI and the IRFU in 2008 was also agreed.These agreements were within the temporary relaxation terms, as Lansdowne Road was still under redevelopment until 2010. Although the GAA had said that hosted use of Croke Park would not extend beyond 2008, irrespective of the redevelopment progress, fixtures for the 2009 Six Nations rugby tournament saw the Irish rugby team using Croke park for a third season. 11 February 2007 saw the first rugby union international to be played there. Ireland were leading France in a Six Nations clash, but lost 17–20 after conceding a last minute (converted) try. Raphael Ibanez scored the first try in that match; Ronan O'Gara scored Ireland's first ever try in Croke Park. A second match between Ireland and England on 24 February 2007 was politically symbolic because of the events of Bloody Sunday in 1920.There was considerable concern as to what reaction there would be to the singing of the British national anthem "God Save the Queen". Ultimately the anthem was sung without interruption or incident, and applauded by both sets of supporters at the match, which Ireland won by 43–13 (their largest ever win over England in rugby). On 2 March 2010, Ireland played their final international rugby match against a Scotland team that was playing to avoid the wooden spoon and hadn't won a championship match against Ireland since 2001. Outside half, Dan Parks inspired the Scots to a 3-point victory and ended Irish Hopes of a triple crown. On 24 March 2007, the first association football match took place at Croke Park. The Republic of Ireland took on Wales in UEFA Euro 2008 qualifying Group D, with a Stephen Ireland goal securing a 1–0 victory for the Irish in front of a crowd of 72,500. Prior to this, the IFA Cup had been played at the then Jones' Road in 1901, but this was 12 years before the GAA took ownership. Negotiations took place for the NFL International Series's 2011 game to be held at Croke Park but the game was awarded to Wembley Stadium.World record attendance
On 2 May 2009, Croke Park was the venue for a Heineken Cup rugby semi-final, in which Leinster defeated Munster 25–6. The attendance of 82,208 set a new world record attendance for a club rugby union game.[35] This record stood until 31 March 2012 when it was surpassed by an English Premiership game between Harlequins and Saracens at Wembley Stadium which hosted a crowd of 83,761.This was beaten again in 2016 in the Top 14 final at the Nou Camp which hosted a crowd of 99,124Skyline tour
A walkway, known under a sponsorship deal as Etihad Skyline Croke Park, opened on 1 June 2012.From 44 metres above the ground, it offers views of Dublin city and the surrounding area.The Olympic Torch was brought to the stadium and along the walkway on 6 June 2012.GAA Hall of Fame
On 11 February 2013, the GAA opened the Hall of Fame section in the Croke Park museum. The foundation of the award scheme is the Teams of the Millennium the football team which was announced in 1999 and the hurling team in 2000 and all 30 players were inducted into the hall of fame along with Limerick hurler Eamonn Cregan and Offaly footballer Tony McTague who were chosen by a GAA sub-committee from the years 1970–74.New inductees will be chosen on an annual basis from the succeeding five-year intervals as well as from years preceding 1970. In April 2014, Kerry legend Mick O'Dwyer, Sligo footballer Micheál Kerins, along with hurlers Noel Skehan of Kilkenny and Pat McGrath of Waterford became the second group of former players to receive hall of fame awards. Statue of Michael Cusack outside the Croke Park GAA Museum
Statue of Michael Cusack outside the Croke Park GAA Museum -
 Beautiful artwork depicting the ultra talented but ill fated Derby Winner Shergar. Origins :Naas Co Kildare. Dimensions: 45cm x 55cm Glazed Shergar was an Irish-bred, British-trained Thoroughbred racehorse. After a very successful season in 1981 he was retired to the Ballymany Stud in County Kildare, Ireland. In 1983 he was stolen from the stud, and a ransom of £2 million was demanded; it was not paid, and negotiations were soon broken off by the thieves. In 1999 a supergrass, formerly in the Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA), stated they stole the horse. The IRA has never admitted any role in the theft. The Aga Khan, Shergar's owner, sent the horse for training in Britain in 1979 and 1980. Shergar began his first season of racing in September 1980 and ran two races that year, where he won one and came second in the other. In 1981 he ran in six races, winning five of them. In June that year he won the 202nd Epsom Derby by ten lengths—the longest winning margin in the race's history. Three weeks later he won the Irish Sweeps Derby by four lengths; a month after that he won the King George VI and Queen Elizabeth Stakes by four lengths. In his final race of the year he came in fourth, and the Aga Khan took the decision to retire him to stud in Ireland. After Shergar's Epsom Derby win, the Aga Khan sold 40 shares in the horse, valuing it at £10 million. Retaining six shares, he created an owners' syndicate with the remaining 34 members. Shergar was stolen from the Aga Khan's stud farm by an armed gang on 8 February 1983. Negotiations were conducted with the thieves, but the gang broke off all communication after four days when the syndicate did not accept as true the proof provided that the horse was still alive. In 1999 Sean O'Callaghan, a former member of the IRA, published details of the theft and stated that it was an IRA operation to raise money for arms. He said that very soon after the theft, Shergar had panicked and damaged his leg, which led to him being killed by the gang. An investigation by The Sunday Telegraph concluded that the horse was shot four days after the theft. No arrests have ever been made in relation to the theft. Shergar's body has never been recovered or identified; it is likely that the body was buried near Aughnasheelin, near Ballinamore, County Leitrim. In honour of Shergar, the Shergar Cup was inaugurated in 1999. His story has been made into two screen dramatisations, several books and two documentaries.
Beautiful artwork depicting the ultra talented but ill fated Derby Winner Shergar. Origins :Naas Co Kildare. Dimensions: 45cm x 55cm Glazed Shergar was an Irish-bred, British-trained Thoroughbred racehorse. After a very successful season in 1981 he was retired to the Ballymany Stud in County Kildare, Ireland. In 1983 he was stolen from the stud, and a ransom of £2 million was demanded; it was not paid, and negotiations were soon broken off by the thieves. In 1999 a supergrass, formerly in the Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA), stated they stole the horse. The IRA has never admitted any role in the theft. The Aga Khan, Shergar's owner, sent the horse for training in Britain in 1979 and 1980. Shergar began his first season of racing in September 1980 and ran two races that year, where he won one and came second in the other. In 1981 he ran in six races, winning five of them. In June that year he won the 202nd Epsom Derby by ten lengths—the longest winning margin in the race's history. Three weeks later he won the Irish Sweeps Derby by four lengths; a month after that he won the King George VI and Queen Elizabeth Stakes by four lengths. In his final race of the year he came in fourth, and the Aga Khan took the decision to retire him to stud in Ireland. After Shergar's Epsom Derby win, the Aga Khan sold 40 shares in the horse, valuing it at £10 million. Retaining six shares, he created an owners' syndicate with the remaining 34 members. Shergar was stolen from the Aga Khan's stud farm by an armed gang on 8 February 1983. Negotiations were conducted with the thieves, but the gang broke off all communication after four days when the syndicate did not accept as true the proof provided that the horse was still alive. In 1999 Sean O'Callaghan, a former member of the IRA, published details of the theft and stated that it was an IRA operation to raise money for arms. He said that very soon after the theft, Shergar had panicked and damaged his leg, which led to him being killed by the gang. An investigation by The Sunday Telegraph concluded that the horse was shot four days after the theft. No arrests have ever been made in relation to the theft. Shergar's body has never been recovered or identified; it is likely that the body was buried near Aughnasheelin, near Ballinamore, County Leitrim. In honour of Shergar, the Shergar Cup was inaugurated in 1999. His story has been made into two screen dramatisations, several books and two documentaries. -


Worldwide Duty Free selling is a $70 billion business, but it has its origins in the mind of one Clare man. And like many innovations, the concept of duty free, which first came to Shannon Airport in 1952, was born of necessity.Today the global travel retail business is a firm fixture at airports across the world, and the concept has made a lot of money for a lot of people.But not for Brendan O’Regan, the man with the idea.
He was born into “the first generation of free Irish men” in relatively well-off surroundings in Sixmilebridge, Co Clare in 1917. His father, James, was chairman of Clare County Council and a successful businessman. The family was in the hotel business, and for a time leased the renowned Falls Hotel in Ennistymon and the Old Ground in Ennis. Sent as a boarder to Blackrock College in Dublin in 1931, O’Regan enjoyed early renown when he requested that the college, which by then had given up on the camán, field a hurling team in the Leinster Colleges cup.
His next step after school was training in hotel management, an interest that brought him to Germany, France and the UK, before coming home to run The Falls. He then moved to the ailing St Stephen’s Green club in Dublin, before being appointed catering comptroller at Foynes flying boat base in Co Limerick, then a refuelling point for transatlantic seaplanes.
It was here his passion for travel took off, but it was his next move that sealed his legacy.
Shannon Airport
Rineanna on the Shannon estuary in Co Clare, chosen by then taoiseach Seán Lemass as the site for a new airport for both sea and land planes, opened in October 1945, when the first transatlantic commercial air service from Boston landed there. It soon became Europe’s most important transatlantic airport, handling more than 100,000 passengers in 1946, its first full year of operation.
When O’Regan joined the nascent airport, its future was by no means secure. The imminent arrival of jet planes, which meant US planes would no longer have to stop in Shannon to refuel, was of concern, while the political apparatus of the day favoured focusing efforts on one airport in Dublin.
Fearing “economic annihilation” for the new airport, O’Regan sought a new venture that would help secure its future. Inspiration struck when he was returning home by sea from a visit to the United States, arranged under the Marshall Plan to allow the Irish government to study US tourism.
As told in the recently published book Brendan O’Regan: Irish Innovator, Visionary and Peacemaker by Brian O’Connell and Cian O’Carroll, O’Regan had a “eureka” moment on board.
“I saw the shop that was selling duty-free goods and my brain said to me: “If they can do it when you are crossing the sea in a boat, you can surely be able to do [it] when you land for the first time.”
He had to convince the Department of Industry and Commerce and the Revenue Commissioners of the merits of forgoing tax on the sale of goods, while local traders also opposed the move.
Nonetheless, O’Regan got the go-ahead and by July 1950 he had set up an operation in a timber hut outside the terminal, selling whiskey for $1.50 a bottle. The following year, the first duty-free shop in the world opened, with a bottle of whiskey on sale for just 30s, compared with 10s 6d in a regular shop, while in 1954 a mail order service was included. It went on to become a vast operation, mailing to locations all around the world, quality items such as crystal, china, fashionable clothing and jewellery.
Contagious idea
The concept soon caught on. In 1957 Amsterdam became the next airport to open a duty free, with the concept making its way across the Atlantic in 1962. Prince Philip was an early admirer of the concept, and he wanted it extended to all the UK’s international airports.
O’Regan also inspired philanthropist Chuck Feeney, who took the idea of duty free and galloped ahead with it, founding Duty Free Shoppers Group (DFS) in Hawaii in 1962, which later became the largest duty-free retailer in the world.
These years also saw the invention of Irish coffee, after O’Regan asked chef Joe Sheridan to “come up with something special” to warm up transatlantic passengers tired and cold after their trip.
But duty free was only part of the equation. O’Regan’s big dream was to position Shannon as the European manufacturing basis for US companies, and to bring employment and prosperity to the region.

Senator TK Whitaker, Brendan O’Regan (centre) and Dr Jerry Dempsey. Photograph: Peter Thursfield Shaped by the devastating impact poverty and emigration had on the county of his birth, O’Regan often repeated his father’s maxim, that “the most important thing about life is to create work for others, if you can”.
In the 1950s, the post-war boom that lifted the US, Europe and the UK had missed Ireland, and emigration was running at the highest level since independence.
So O’Regan didn’t stop at the duty free.
In 1951, he established the Shannon College of Hotel Management, which is still operating today and the graduates of which have managed the world’s top hotels, while he also leveraged the area’s potential as a tourist hub. He identified the potential of Bunratty Castle as a tourist attraction and, with the co-operation of its owner, Lord Gort, it was renovated and opened to the public in 1960, with the first medieval banquet held shortly thereafter. O’Regan later chaired Bord Fáilte.
Great times
“He was very much a leader and innovative in the sense that he thought up ideas himself,” recalls O’Carroll, who worked alongside O’Regan as estates manager in the Shannon Free Airport Development Company Limited (SFADCO). “He would work very intensively until the project was launched, and then he would go on to the next project”.
It was a time of “brainstorming picnics”, and consultancy reports, to try and hit on a new idea.
“They were great times,” says O’Carroll. “If an idea came up, and it was any way worthwhile, it would stand a very good chance of implementation.”
The big move came in the establishment of the Shannon Free Zone, the world’s first free trade zone, in 1959, overseen by SFADCO. It operated a licensing system, offering qualifying companies a corporation tax rate of just 10 per cent; a model that would later be taken up by the IFSC.
O’Regan’s idea, inspired by the Free Zone in Colon, Panama, was greeted with much scepticism initially, but his ability to build good relationships, particularly with those in government, helped secure the initiative.
“He had the ability to short-circuit a lot of things in terms of procedures in getting approval,” says O’Carroll, adding that “this clearly annoyed civil servants at the time.”
Indeed his initials, BOR, in Shannon came to mean “Bash on regardless”.
So, on an “if you build it they will come” ambition, SFADCO set about building factories – without any tenants. A Dutch piano manufacturer owned by Johan J Rippen was the first real enterprise to come to Shannon, followed by Sony, and diamond company De Beers in 1960.
Tourism smarts
O’Regan also ramped up the region’s renown as a tourist destination, using his tools of persuasion to garner investment.
When Bernard McDonough, a wealthy Irish-American industrialist pulled out of a planned ball-bearing factory in the Shannon Free Zone, O’Regan told him about a nearby castle that was for sale. He took the bait and bought it; in 1963 Dromoland Castle opened as a five-star hotel. McDonough would later open a further three hotels in the area.
When he heard of a plan by German investors to acquire the land leading to the Cliffs of Moher, he rang then Clare county manager Joe Boland, who subsequently got the county council to buy it.
During the 1970s he moved away from his formal roles in Shannon, and turned his attention to the peace process, founding Co-operation North (now Co-operation Ireland) in 1979. He died in 2008, and a bronze bust sculpture was unveiled at Shannon Airport in May 2017 to mark the centenary of his birth.
A man of his time – as O’Carroll recalls, an “infinitely simpler” time – he nonetheless left a significant legacy.
As described when receiving an honorary degree from the National University of Ireland in 1978: “Rare is the man of whom it can be justly said that he transformed the social, economic and industrial life of a whole region”
The Shannon project was not just about creating jobs; it was also about providing homes for the workers who flocked there.
By the late 1950s the housing issue, which had plagued the development of the hub since the early days, was becoming a crisis. So, in 1960, a proposal was tabled for the creation of a new town; an innovation without precedent in post-war Ireland.
Inspired by the British new towns that arose after the war, including Crawleyin Sussex and Stevenage in Hertfordshire, Brendan O’Regan and his team sought to build a new hub for workers of the airport and the industrial zone.
The creation of the first new town in the history of the State was not without challenges; there were political ructions as to who would oversee the project – the government or SFADCO – while residents of nearby Limerick city accused Brendan O’Regan of “empire building”, as they rued the fact that the development did not happen in Limerick instead.
Nonetheless, by 1962 the first residents were moving in, all of whom were tenants of SFADCO and who had to work either in the airport or industrial area to qualify for affordable housing.
As SFADCO estates manager Cian O’Carroll recalls, building the houses so close to a place of huge employment was key, as was the fact that units were small – but even larger families were catered for.
“We often let them two houses and knocked them together,” he says.
Also key to its success was the fact that housing was affordable, and graded and related to people’s incomes. After some time a tenant purchase scheme was introduced, allowing people to buy their homes outright.
Today the town is home to some 10,000 residents, and remains one of the few examples of a new planned town in Ireland.
“It hasn’t grown as much as people might have expected, but it has its own social and economic viability,” says O’Carroll.
As to why subsequent governments haven’t looked to emulate the success of Shannon – particularly given our housing shortages – O’Carroll suggests it’s due to an ideological shift away from the State doing things directly themselves, instead encouraging the private sector to do the same through tax incentives and other methods.
“It’s a shame,” he says.
-
 Unusual advertising print -History of Irish Whiskey -featuring a cartoon type character and a bottle of Jameson Whiskey(Cooper's Croze). 48cm x 60cm Kilmallock Co Limerick Named in honour of Jameson's Master Cooper, Ger Buckley. The aim of this whiskey is to showcase the diversity of the barrels used at Jameson and the influence of the oak on the whiskey. Fittingly this is aged in a variety of barrels including ex-Bourbon, ex-Sherry and some virgin oak barrels. According to Irish Distillers: 'The Cooper’s Croze is a carefully crafted whiskey that effortlessly carries vanilla sweetness, rich fruit flavours, floral and spice notes and the undeniable influence of oak. You can take whiskey out of wood but you can never take the wood out of whiskey.'
Unusual advertising print -History of Irish Whiskey -featuring a cartoon type character and a bottle of Jameson Whiskey(Cooper's Croze). 48cm x 60cm Kilmallock Co Limerick Named in honour of Jameson's Master Cooper, Ger Buckley. The aim of this whiskey is to showcase the diversity of the barrels used at Jameson and the influence of the oak on the whiskey. Fittingly this is aged in a variety of barrels including ex-Bourbon, ex-Sherry and some virgin oak barrels. According to Irish Distillers: 'The Cooper’s Croze is a carefully crafted whiskey that effortlessly carries vanilla sweetness, rich fruit flavours, floral and spice notes and the undeniable influence of oak. You can take whiskey out of wood but you can never take the wood out of whiskey.' Origins:Kilmaley Co Clare Dimensions : Glazed
Origins:Kilmaley Co Clare Dimensions : Glazed -
 Nearly a Che Guevera style to this poster of the rebel hero Sean South from Garryowen in the heart of Limerick City. Origins : Limerick. Dimensions : 54cm x 42cm Glazed Sean South ( c. 1928 – 1 January 1957)was a member of an IRA military column led by Sean Garland on a raid against a Royal Ulster Constabulary barracks in Brookeborough, County Fermanagh, Northern Ireland, on New Year's Day 1957.South, along with Fergal O'Hanlon, died of wounds sustained during the raid.
Nearly a Che Guevera style to this poster of the rebel hero Sean South from Garryowen in the heart of Limerick City. Origins : Limerick. Dimensions : 54cm x 42cm Glazed Sean South ( c. 1928 – 1 January 1957)was a member of an IRA military column led by Sean Garland on a raid against a Royal Ulster Constabulary barracks in Brookeborough, County Fermanagh, Northern Ireland, on New Year's Day 1957.South, along with Fergal O'Hanlon, died of wounds sustained during the raid.Early life
Seán South was born in Limerick where he was educated at Sexton Street Christian Brothers School, later working as a clerk in a local wood-importing company called McMahon's. He was a member of a number of organisations, including Clann na Poblachta, Sinn Féin, the Gaelic League and the Legion of Mary. In Limerick he founded the local branch of Maria Duce, a social Roman Catholic organisation, where he also edited both An Gath and An Giolla. He had received military training as a lieutenant of the Irish army reserve, the Local Defence Force (LDF), which would later become An Fórsa Cosanta Áitiúil (the FCA), before he became a volunteer in the Irish Republican Army. Being a member of An Réalt (the Irish-speaking chapter of the Legion of Mary),South was a devout Catholic and a conservative, even by the standards of the day.It was at a meeting of An Réalt that he met his only serious girlfriend, Máire de Paor. She was a schoolteacher from Limerick, and was a great lover of the Irish language. He was also a member of the Knights of Columbanus. In 1949, South wrote a series of letters to his local newspaper, the Limerick Leader. These letters condemned Hollywood films for what South regarded as their immoral messages. South accused these films of promoting a "stream of insidious propaganda which proceeds from Judeo-Masonic controlled sources, and which warps and corrupts the minds of our youth."South also claimed that the American film industry was controlled by "Jewish and Masonic executives dictating to Communist rank and file." In his letters, South also denounced Irish trade unions, and praised the activities of Senator Joseph McCarthy in the United States.Death
On New Year's Day 1957, 14 IRA volunteers crossed the border into County Fermanaghto launch an attack on a joint RUC/B Specials barracks in Brookeborough. During the attack a number of volunteers were injured, two fatally. South and Fergal O'Hanlon died of their wounds as they were making their escape. Their bodies were brought into an old sandstone barn by their comrades. The stone from the barn was used to build a memorial at the site. A young Catholic constable, John Scalley, was killed in the ensuing gun battle between the IRA unit and the RUC.Commemoration
The attack on the barracks inspired two popular rebel songs: ‘Seán South of Garryowen' and ‘The Patriot Game '.- "Sean South", also known as "Sean South of Garryowen", written by Sean Costelloe from County Limerick, to the tune of another republican ballad "Roddy McCorley" and made famous by the Wolfe Tones.
- South is also mentioned in the Rubberbandits' song "Up Da Ra", which pokes fun at the concept of armchair republicanism using the literary device of the unreliable narrator.
- There is a plaque dedicated to him outside his birthplace on Henry Street, Limerick.
-
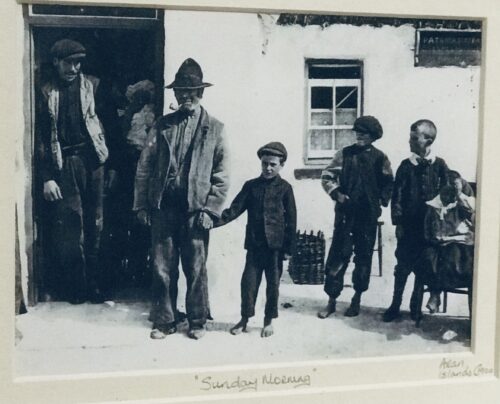
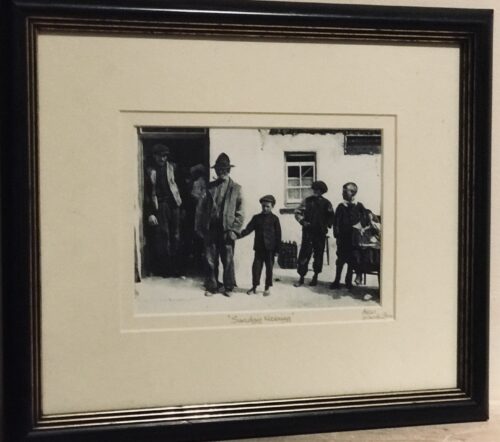
 30cm x 35cm These atmospheric prints dating from the early 20th century are from the Aran collection,a series of superbly photographed images depicting life on the Aran Islands at the turn of the last century. "The early part of the 20th century saw little change come to the Aran Islands so far removed from outside influences off the west coast of Ireland.As if time had stood still ,these unique photographs depict the islanders going about their daily lives as they had done for centuries in almost complete self sufficiency from the outside world and as a result form an integral part of our national heritage.
30cm x 35cm These atmospheric prints dating from the early 20th century are from the Aran collection,a series of superbly photographed images depicting life on the Aran Islands at the turn of the last century. "The early part of the 20th century saw little change come to the Aran Islands so far removed from outside influences off the west coast of Ireland.As if time had stood still ,these unique photographs depict the islanders going about their daily lives as they had done for centuries in almost complete self sufficiency from the outside world and as a result form an integral part of our national heritage.
Aran Islands: on the road to Synge’s Chair, on Inishmaan. Photograph: Andy Haslam/New York Times
-
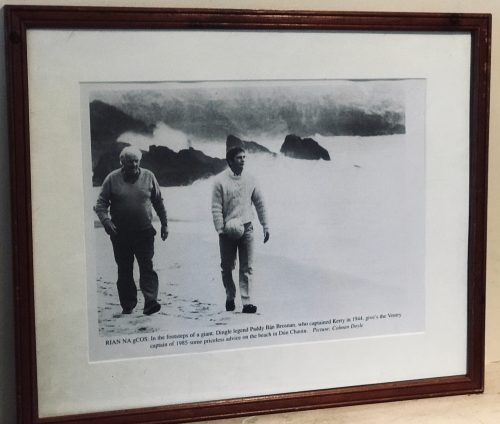 Rian na gCos (Gaelic for in the footsteps of a giant)Dingle legend Paddy Bán Brosnan,who captained Kerry in 1944 gives the 1985 Kerry captain Paidí O'Sé from Ventry some priceless advice on the beach at Dún Chaoin Iconic B&W photo taken by Colman Doyle of 2 of the all time Kerry football greats - Paidí O'Sé & Paddy Bawn Brosnan.This atmospheric image was captured as the 2 men walked along a stormy Atlantic shoreline on the beautiful Dingle Peninsula,.where both of these legends hailed from.Although from different eras both players encapsulated the essence of the Kerry Footballer-teak tough,ferocious,skillful and also well able to enjoy themselves when the opportunity presented itself ! Indeed Paddy Bawn had a very interesting family background as we discovered while researching his bio for this product description as you can now read.
Rian na gCos (Gaelic for in the footsteps of a giant)Dingle legend Paddy Bán Brosnan,who captained Kerry in 1944 gives the 1985 Kerry captain Paidí O'Sé from Ventry some priceless advice on the beach at Dún Chaoin Iconic B&W photo taken by Colman Doyle of 2 of the all time Kerry football greats - Paidí O'Sé & Paddy Bawn Brosnan.This atmospheric image was captured as the 2 men walked along a stormy Atlantic shoreline on the beautiful Dingle Peninsula,.where both of these legends hailed from.Although from different eras both players encapsulated the essence of the Kerry Footballer-teak tough,ferocious,skillful and also well able to enjoy themselves when the opportunity presented itself ! Indeed Paddy Bawn had a very interesting family background as we discovered while researching his bio for this product description as you can now read.Paddy Bawn Brosnan & the American Civil War: The Famed Gaelic Footballer’s Links to Kerry’s Greatest Conflict
September 1947, New York witnessed a unique sporting occasion. In front of more than 30,000 people at the Polo Grounds in Manhattan, the Gaelic footballers of Kerry and Cavan did battle in what remains the only All-Ireland Football Championship Final ever to be held outside of Ireland. Among the men who donned the green and gold of Kerry that day was Paddy Bawn Brosnan of Dingle. Even in the annals of Ireland’s most famed footballing county, Paddy Bawn Brosnan remains special. Paddy had captained Kerry in 1944 when they lost the All-Ireland to Roscommon, and had taken home winner’s medals in 1940, 1941 and 1946. The New York match of 1947 was aimed at bringing this major event to the huge Irish-American community in the United States, 100 years after the Famine which had led so many to emigrate. But Paddy Bawn Brosnan had a special connection to New York and America. Indeed, had it not been for events that had taken place in a Prisoner of War camp in Georgia more than 80 years previously, it is unlikely that he would have ever had an opportunity to pull on the Kingdom’s colours. Footage of Cavan v Kerry from the Polo Grounds, Manhattan in 1947. You can access an RTE Radio 1 documentary on the background to the historic game by clicking here. Over recent years I have given many lectures around the country highlighting the extent of Irish involvement in the American Civil War. Many take the form of county-focused talks, using specific local individuals to illustrate just how major an event this was in Irish history. Interestingly, it is common for at least one attendee to have a known link to an ancestor who served in the Civil War– indicative both of the impact this conflict had on Irish people, and of the fact that not all 19th century emigration was permanent. Last July I gave just such a talk to Dingle Historical Society in Co. Kerry, and was fortunate to be contacted by local man Mossy Donegan. Mossy not only knew his own connections to the conflict, but through extensive research by both he and his sister Maeve had obtained copies of many of the historical files associated with those links. It is a familial story they share with Paddy Bawn Brosnan, and it is as a result of Mossy and Maeve’s endeavours that it can be related here. What then was Paddy Bawn Brosnan’s connection to the American Civil War? It is a narrative that directly involves his Grandmother, but can be traced back even further, to the marriage of Paddy Bawn’s Great-Grandparents (Mossy and Maeve’s Great-Great-Grandparents) Daniel Dowd and Mary Murphy. A few years shy of a century before Paddy Bawn took the field at the Polo Grounds, Father Eugene O’Sullivan married Daniel and Mary in Dingle Roman Catholic Church on 29th October 1853, A year later, on 8th October 1854, they celebrated the birth of their first child, Edward. At some point shortly after that, the Dowds decided their future lay across the Atlantic, and became just three of the more than 54,000 people who emigrated from Kerry between 1851 and 1860. (1)Denny Lyne, Paddy Bawn Brosnan, J J Nerney and Eddie Boland in action during the 1946 All Ireland Final between Kerry and Roscommon (The Kerryman) The favoured destination for Irish emigrants was New York, and that is where the young Dowd family arrived in the mid-1850s. A second child– a daughter Bridget– was born there about 1856. Bridget, or Biddy as she became known, came into the world on Long Island, and was Paddy Bawn Brosnan’s grandmother. If the Dowd family story had followed that of the majority of Irish immigrants to the United States in this period, Biddy Dowd would never have seen Ireland again, and Paddy Bawn Brosnan would never have been born. But seismic events intervened. By the 1860s the family had settled in Buffalo, where Daniel made the decision that changed all their lives forever, when on 6th September 1862 he enlisted in the Union army. (2) In 1862 Daniel Dowd became one of the c. 200,000 Irish-born men who would serve during the American Civil War. He was joined in the ranks by thousands of Kerrymen; there is little doubt that it was this conflict that saw more Kerrymen fight, and more Kerrymen die, than any other war in history. The Dingle native had decided not to join just any unit. Instead he enlisted in the 155th New York Infantry, one of the regiments that would form part of Corcoran’s Irish Legion. Its leader Brigadier-General Michael Corcoran from Carrowkeel, Co. Sligo was a noted Fenian, and many supporters of the cause of Ireland specifically chose to join his brigade. Whether Daniel was one of them, or simply wanted to serve close to his fellow Irishmen, remains unknown. (3)
Denny Lyne, Paddy Bawn Brosnan, J J Nerney and Eddie Boland in action during the 1946 All Ireland Final between Kerry and Roscommon (The Kerryman)
Daniel was mustered in as a private in Company I of the 155th New York at Newport News, Virginia on 19th November 1862. He was recorded as a 29 year old laborer who was 5 feet 5 inches in height, with a fair complexion, gray eyes and light hair. His surname was one that caused considerable confusion for recorders at the time. Sometimes recorded as Doud or Doody, Daniel was placed on the regimental roster as ‘Daniel Dout.’ It wasn’t long before he got his first taste of action in the Civil War, as in January his regiment was engaged the Battle of Deserted House, Virginia. Though only a mere skirmish in comparison to what the Legion would endure in 1864, it nonetheless must have had quite an impact on Daniel and the men of the 155th. (4) Private Daniel Dowd spent the next year in Virginia with his unit. On 17th December 1863 he found himself guarding a railroad bridge, part of a detachment of some 50 men of the Legion that were protecting the Orange & Alexandria line at Sangster’s Station. At a little after 6pm that evening they were set upon by a body of Confederate cavalry, who threatened to overrun them as they sought to burn the bridge. The Rebels attacked on a number of occasions, eventually getting around the flanks and rear of the Irishmen, succeeding in setting fire to their tents and forcing them into a retreat. Cut off, the detachment would normally have looked to their telegraph operator to call for reinforcements, but he was apparently so drunk he was unable to use his equipment. General Corcoran and the remainder of the Legion only learned of the attack around 8.30pm, when a local Unionist came to inform them of events. The relief force eventually re-established a connection with the detachment, but although the bridge was saved, a number of men had been captured. Among them was Dingle-native Daniel Dowd. (5) We have scant details of Daniel’s life as a prisoner-of-war, but initially he was likely held near Richmond. At some point in the spring or early summer of 1864 he was moved to the recently opened– and soon to be notorious– Camp Sumter, Georgia. Better known as Andersonville, between February 1864 and the close of the war almost 13,000 prisoners lost their lives in the unsheltered compound. Disease, much of it caused by malnutrition, was rife. On 3rd July 1864 Daniel was admitted to the camp hospital suffering from Chronic Diarrhoea. He must have been in an extremely severe state at the time, as he did not live through the day. Following the conflict his grave was identified, and today forms part of Andersonville National Cemetery, where he rests in Grave 2809. (6)
Soldiers of the 170th New York Infantry, one of the other regiments of Corcoran’s Irish Legion, during the Civil War (Library of Congress)
Shorn of her main support, the now widowed Mary decided to leave America behind and retrace her steps to Dingle, presumably to be close to family who could provide assistance. She returned to her home town with Edward and Biddy in tow; Edward must have had little or no-memory of Kerry, while Biddy was experiencing Ireland for the very first time. In 1869 Mary, now 45-years-old, went in search of a U.S. widow’s pension based on Daniel’s service to help support the children. Now living on the Strand, Dingle, she compiled information about her marriage and her children’s birth to send to Washington D.C. as part of her application. Unfortunately, the variant spellings of her husband’s name came back to haunt her. In the marriage record, Daniel’s surname had been written as ‘Doody’, sufficiently different from the ‘Dout’ recorded on the regimental roster to raise suspicions that this was not the same man. To compound matters there was also no available documentation relating to Biddy’s birth. Although the Commissioner of Emigration had written to every Catholic parish in Long Island in order to locate it, he met with no success. The combination of these two issues, together with the difficulty in dealing with the Washington authorities at such a remove, meant that Mary’s pension wasn’t granted. Her failure to provide the additional evidence requested meant that her claim was classified as ‘abandoned.’ Mary never fully gave up fully on the process; the last entry in her file is a letter she had written in the 1890s. Addressed from Waterside, Dingle on 4th July 1892, it was sent to the Secretary of the Claim Agent Office at the White House in Washington D.C.:
Andersonville as it appeared on 17th August 1864, a little over a month after Daniel died (Library of Congress)
Sir, I beg to state that I Mary Dowd now living here and aged about 65 am the widow of Daniel Dowd who served as a soldier in the late American war of 1863, and died a Prisoner of War in Richmond Prison Virginia [actually in Andersonville, Georgia]. Said Daniel Dowd served in the Army of the North. After his death, I deposited the necessary documents to prove my title to pension, in the hands of a Mr. Daniel McGillycuddy Solicitor Tralee, with the view to place them before the authorities in Washington , and he on 27th December 1873, forwarded the same to a Mr. Walsh a Claim Agent, for the purpose of lodging same. Since, I have not received a reply to my solicitor’s letters or received any pay nor pension or acknowledgement of claim. I also learn that my husband at his death had in his possession £100, which he left to Father Mc Coiney who prepared him for death, in trust for me, and which sum never reached me. I know no other course better, than apply to you, resting assured that you will cause my just claim to be sifted out, when justice will be measured to a poor Irish widow who is now working hard to maintain a long family. (7)
As was common at the time, Mary was illiterate– the letter was written for her by her solicitor McGillycuddy, and she made her mark with an ‘X’. It seems unlikely she ever received any monies as a result of it. Her American-born daughter Biddy grew to adulthood in Ireland. Her home had become Dingle, Co. Kerry rather than Buffalo, New York entirely as a result of her father’s death in a Prisoner of War camp more than 6,000 km from Ireland. Daniel’s fateful Civil War service also meant his daughter married and started a family in Ireland rather than America. Biddy’s husband was a fisherman, Patrick Johnson, and together the couple had seven children. One of them, Ellie, was Paddy Bawn Brosnan’s mother. Biddy died in 1945 and is buried in St. James’s Church in Dingle. Unlike her father’s resting place in Andersonville, it is not marked with a headstone. (8) The American Civil War had a long-lasting, inter-generational impact on tens of thousands of Irish people, both in Ireland and the United States. Had it not been for the Confederate decision to launch an attack at Sangster’s Station in Virginia in 1863, or Daniel’s incarceration in Georgia in 1864, it is unlikely that Paddy Bawn Brosnan would ever have been born. The story of the footballing legend’s family is evidence of the often unrecognised impact of what was the largest conflict in Kerry people’s history. One wonders did Paddy Bawn reflect on his own grandmother’s New York story as he made his own journey across the Atlantic to take part in that historic sporting occasion only two years after her death in 1947.*This post would not have been possible without the extensive research of Mossy and Maeve Donegan. They not only ordered his Great-Great-Grandmother’s unsuccessful pension application from Washington D.C. but also obtained Daniel’s service record. All the family history relating to the Brosnans in Dingle and Paddy Bawn’s connection to Biddy was provided by them, and I am grateful they shared their story with us. **Thanks to Donal Nolan and The Kerryman for permission to use the image of the 1946 Final, which originally appeared on the Terrace Talk website here. Also thanks to Kay Caball for Donal’s contact details. ***Thanks to Conn Crowley for a clarification with respect to the attendance at the Polo Grounds Final. (1) Daniel Dowd Widow’s Pension Application, Miller 1988: 570; (2) Daniel Dowd Service Record; (3) Daniel Dowd Service Record, 155th New York Roster; (4) Ibid., New York Civil War Muster Roll; (5) Official Records: 982-984, Daniel Dowd Widow’s Pension Application, Daniel Dowd Service Record, U.S. Register of Deaths of Volunteers, Records of Federal POWs Confined at Andersonville; (7) Daniel Dowd Widow’s Pension Application; (8) Daniel Dowd Widow’s Pension Application; References & Further Reading Daniel Dowd Widow’s Pension Application 180,808. Daniel Dowd Service Record. Roster of the 155th New York Infantry. Daniel Dowd Find A Grave Entry. New York State Archives, Cultural Education Center, Albany, New York; New York Civil War Muster Roll Abstracts, 1861-1900; Archive Collection #: 13775-83; Box #: 607; Roll #: 263 [Original scan, accessed via ancestry.com]. Selected Records of the War Department Commissary General of Prisoners Relating to Federal Prisoners of War Confined at Andersonville, GA, 1864-65; (National Archives Microfilm Publication M1303, 6 rolls); Records of the Commissary General of Prisoners, Record Group 249; National Archives, Washington, D.C. [Original scan, accessed via ancestry.com]. Registers of Deaths of Volunteers, compiled 1861–1865. ARC ID: 656639. Records of the Adjutant General’s Office, 1780’s–1917. Record Group 94. National Archives at Washington, D.C. [Original scan, accessed via ancestry.com]. Official Records of the War of the Rebellion Series 1, Volume 29, Part 1. December 17, 183 – Skirmish at Sangster’s Station, Va. Reports. Miller, Kerby A. 1988. Emigrants and Exiles: Ireland and the Irish Exodus to North America
Another image of Biddy, taken with some of the younger generations of her family. Without the events of the American Civil War, she would likely have never returned to Dingle, and Paddy Bawn Brosnan would never have been born (Mossy Donegan)
-
 A lovely little Bulmers moment here with its brightly coloured,ubiquitous Woodpecker ornament ( made from ceramic) Origins :Co Tipperary Dimensions: 20cm x 10cm x 10cm
A lovely little Bulmers moment here with its brightly coloured,ubiquitous Woodpecker ornament ( made from ceramic) Origins :Co Tipperary Dimensions: 20cm x 10cm x 10cm While the brand of cider produced locally in County Tipperary may be known as Bulmers to the people of the Irish republic, it is referred to as Magners everywhere in the world. Established in 1935 by a local from the town of Clonmel named William Magner, the cider factory there was later bought out by cider-makers H. P. Bulmer in 1946 After buying an orchard in County Tipperary, William Magner began to produce his own Irish cider in the mid-1930s. In 1937, he teamed up with the well-established H.P. Bulmer company from England, acquiring the right to produce under the Bulmers name in Ireland, and the brand became more widespread. Following almost ten successful years in partnership, Magner decided to sell his remaining fifty percent stake to his colleagues, seeing the factory become known as Bulmers Ltd Clonmel.
While the brand of cider produced locally in County Tipperary may be known as Bulmers to the people of the Irish republic, it is referred to as Magners everywhere in the world. Established in 1935 by a local from the town of Clonmel named William Magner, the cider factory there was later bought out by cider-makers H. P. Bulmer in 1946 After buying an orchard in County Tipperary, William Magner began to produce his own Irish cider in the mid-1930s. In 1937, he teamed up with the well-established H.P. Bulmer company from England, acquiring the right to produce under the Bulmers name in Ireland, and the brand became more widespread. Following almost ten successful years in partnership, Magner decided to sell his remaining fifty percent stake to his colleagues, seeing the factory become known as Bulmers Ltd Clonmel.Unfortunately for H.P. Bulmer, it wasn’t long before the company again changed hands. Coming out on the losing end of a legal dispute with the creators of Babycham sparkling perry over a competing product, they were forced to sell Bulmers Clonmel during the 1960s. Having become part of the C&C Group – a soft drinks and cider company then jointly owned by Guinness and Allied Breweries – production of Irish Bulmers was moved five years later to a modern complex at Annerville, outside Clonmel.

With the Tipperary cider greatly exceeding sales expectations in Ireland, the C&C Group sought during the late 1990s to sell it outside of its home country, particularly in the burgeoning international Irish bar market. But as H.P. Bulmer still owned the rights to that name everywhere other than Ireland, they decided to call the brand after its original owner when exporting it – bringing Magners Irish cider first to Spain, then to Germanyand the UK. In spite of the the differing name, the two products are identical.
Still produced at Annerville, today Irish Bulmers and Magners are made from 17 different kinds of apples, left to ferment and mature for up to two years. Continuing to grow in popularity, the cider can now be found in bars throughout Europe, Asia, North America, Australia and New Zealand.















