-

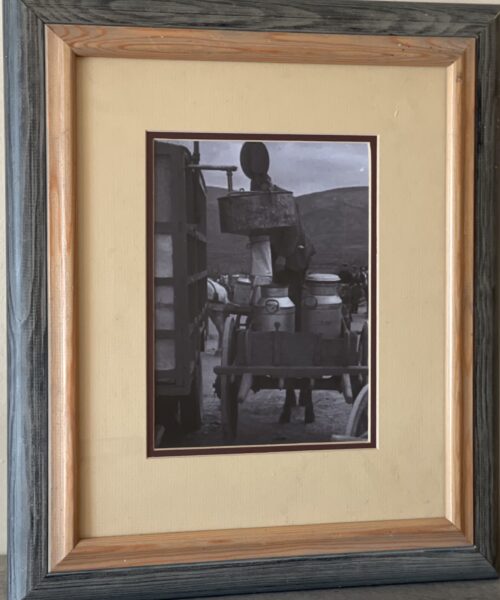
 45cm x 35cm Thurles Co Tipperary The 1913 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship Final was the 26th All-Ireland Final and the culmination of the 1913 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship, an inter-county hurling tournament for the top teams in Ireland. The match was held at Croke Park, Dublin, on 2 November 1913, between Kilkenny, represented by a club side from Mooncoin, and Tipperary, represented by club side Toomevara. The Munster champions lost to their Leinster opponents on a score line of 2–4 to 1–2.
45cm x 35cm Thurles Co Tipperary The 1913 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship Final was the 26th All-Ireland Final and the culmination of the 1913 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship, an inter-county hurling tournament for the top teams in Ireland. The match was held at Croke Park, Dublin, on 2 November 1913, between Kilkenny, represented by a club side from Mooncoin, and Tipperary, represented by club side Toomevara. The Munster champions lost to their Leinster opponents on a score line of 2–4 to 1–2. -
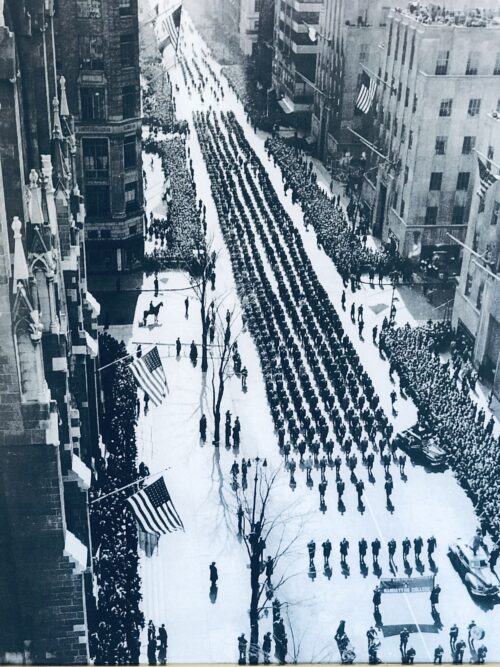

 36cm x 30cm New York Wonderful elevated shot of the 1950 New York St Patricks Day Parade from high above 5th Avenue as the procession passes St Patricks Cathedral. The St. Patrick’s Day Parade is one of New York City’s greatest traditions. On this day, everyone is Irish in the Big Apple! The Parade marched for the first time on March 17, 1762 – fourteen Years before the Declaration of Independence was adopted and today it is the largest Parade in the World. This annual parade has been held for the past 257 years in honor of the Patron Saint of Ireland and the Archdiocese of New York. The Parade is reviewed from the steps of Saint Patrick’s Cathedral by His Eminence, Timothy Cardinal Dolan, Archbishop of New York in the same manner as the Archbishop of New York did in the early days of the Parade at the Old St. Patrick’s Cathedral in Lower Manhattan before the new St Patrick’s was built on Fifth Avenue. Often regarded as the most popular parade in New York City, the Parade is the largest and most famous of the many parades held in the city each year. The Parade starts at 44th Street at 11 am and is held every March 17th except when March 17th falls on a Sunday; it is celebrated the day before, Saturday the 16th, because of religious observances. The parade marches up Fifth Avenue past St. Patrick’s Cathedral at 50th Street all the way up 79th Street, where the parade finishes around 4:30 – 5:00 pm To this day, the St. Patrick’s Day Parade remains true to its roots as a true marchers Parade by not allowing floats, automobiles and other commercial aspects in the Parade. Every year the Parade Committee hosts the 150,000- 250,000 marchers, along with many great bands; bagpipes, high school bands and the ever-present politicians in front of the approx 2 million spectators lining Fifth Avenue. The Parade is televised for four hours on WNBC Channel Four to over half a million households and was web streamed live for the first time in 2008. Today, the coverage has expanded to seven additional internet based platforms and can easily be viewed on mobile devices. The first St. Patrick’s Day Parade in New York was held on lower Broadway in 1762 by a band of homesick Irish ex-patriots and Irish military serving with the British Army stationed in the American colonies in New York City. This was a time when the wearing of green was a sign of Irish pride and was banned in Ireland. The parade participants reveled in the freedom to speak Irish, wear green, sing Irish songs and play the pipes to Irish tunes that were very meaningful to the Irish immigrants who had fled their homeland. For the first few years of its existence, the parade was organized by military units. After the war of 1812, the Irish fraternal and benevolent societies took over the duties of hosting and sponsoring the event. Originally, the Irish societies joined together at their respective meeting places and moved in a procession toward Old St. Patrick’s Cathedral in Lower Manhattan on Mott & Prince Streets where the Archbishop of New York would then address the crowd before revelers dispersed to celebrate. Around 1851 the individual societies merged under a single grand marshal and the size of the parade grew sharply. This was when the “Irish” 69th Regiment began to lead the marchers and the Ancient Order of Hibernians became the official sponsor. In the early 90’s, the Parade was attacked for its traditional values and in the resulting lawsuits the organizers rights were up held all the way to the US Supreme court. In 1992 the National AOH directed all AOH organizations to form separate corporations to run events such as the Parade. The Parade is run today by members of the AOH under a separate corporation, St Patrick’s Day Parade Inc. Since the first Parade, 257 years ago, the Parade today is still escorted by a unit of soldiers; and for the past 165 years “The Irish Infantry” National Guard 69th Regiment have led the Parade up Fifth Avenue, and they are followed by the various Irish societies of the city, the thirty two Irish county societies, and various schools, colleges, Emerald Societies, Irish-language, and Nationalist Societies. The 2002 parade was dedicated to the ‘Heroes of 9/11, ‘ honoring the police, fire and all rescue workers. At midday, the entire parade paused for two minutes, the Parade at that time stretched one and a half miles and the entire Parade turned around and faced South towards the “TWIN TOWERS” as the Cardinal said a prayer for all the victims of 9/11. This was the first time in history, in the City that never sleeps, one could hear a pin drop on Fifth Avenue, a fitting tribute to the men and women who lost their lives on that fateful day in 2001. The 2002 Parade was the largest Parade to date with an estimated 300,000 marchers and three million spectators lining Fifth Avenue. This was the first time in history; the President of Ireland reviewed a St. Patrick’s Day Parade outside Ireland on March 17th.
36cm x 30cm New York Wonderful elevated shot of the 1950 New York St Patricks Day Parade from high above 5th Avenue as the procession passes St Patricks Cathedral. The St. Patrick’s Day Parade is one of New York City’s greatest traditions. On this day, everyone is Irish in the Big Apple! The Parade marched for the first time on March 17, 1762 – fourteen Years before the Declaration of Independence was adopted and today it is the largest Parade in the World. This annual parade has been held for the past 257 years in honor of the Patron Saint of Ireland and the Archdiocese of New York. The Parade is reviewed from the steps of Saint Patrick’s Cathedral by His Eminence, Timothy Cardinal Dolan, Archbishop of New York in the same manner as the Archbishop of New York did in the early days of the Parade at the Old St. Patrick’s Cathedral in Lower Manhattan before the new St Patrick’s was built on Fifth Avenue. Often regarded as the most popular parade in New York City, the Parade is the largest and most famous of the many parades held in the city each year. The Parade starts at 44th Street at 11 am and is held every March 17th except when March 17th falls on a Sunday; it is celebrated the day before, Saturday the 16th, because of religious observances. The parade marches up Fifth Avenue past St. Patrick’s Cathedral at 50th Street all the way up 79th Street, where the parade finishes around 4:30 – 5:00 pm To this day, the St. Patrick’s Day Parade remains true to its roots as a true marchers Parade by not allowing floats, automobiles and other commercial aspects in the Parade. Every year the Parade Committee hosts the 150,000- 250,000 marchers, along with many great bands; bagpipes, high school bands and the ever-present politicians in front of the approx 2 million spectators lining Fifth Avenue. The Parade is televised for four hours on WNBC Channel Four to over half a million households and was web streamed live for the first time in 2008. Today, the coverage has expanded to seven additional internet based platforms and can easily be viewed on mobile devices. The first St. Patrick’s Day Parade in New York was held on lower Broadway in 1762 by a band of homesick Irish ex-patriots and Irish military serving with the British Army stationed in the American colonies in New York City. This was a time when the wearing of green was a sign of Irish pride and was banned in Ireland. The parade participants reveled in the freedom to speak Irish, wear green, sing Irish songs and play the pipes to Irish tunes that were very meaningful to the Irish immigrants who had fled their homeland. For the first few years of its existence, the parade was organized by military units. After the war of 1812, the Irish fraternal and benevolent societies took over the duties of hosting and sponsoring the event. Originally, the Irish societies joined together at their respective meeting places and moved in a procession toward Old St. Patrick’s Cathedral in Lower Manhattan on Mott & Prince Streets where the Archbishop of New York would then address the crowd before revelers dispersed to celebrate. Around 1851 the individual societies merged under a single grand marshal and the size of the parade grew sharply. This was when the “Irish” 69th Regiment began to lead the marchers and the Ancient Order of Hibernians became the official sponsor. In the early 90’s, the Parade was attacked for its traditional values and in the resulting lawsuits the organizers rights were up held all the way to the US Supreme court. In 1992 the National AOH directed all AOH organizations to form separate corporations to run events such as the Parade. The Parade is run today by members of the AOH under a separate corporation, St Patrick’s Day Parade Inc. Since the first Parade, 257 years ago, the Parade today is still escorted by a unit of soldiers; and for the past 165 years “The Irish Infantry” National Guard 69th Regiment have led the Parade up Fifth Avenue, and they are followed by the various Irish societies of the city, the thirty two Irish county societies, and various schools, colleges, Emerald Societies, Irish-language, and Nationalist Societies. The 2002 parade was dedicated to the ‘Heroes of 9/11, ‘ honoring the police, fire and all rescue workers. At midday, the entire parade paused for two minutes, the Parade at that time stretched one and a half miles and the entire Parade turned around and faced South towards the “TWIN TOWERS” as the Cardinal said a prayer for all the victims of 9/11. This was the first time in history, in the City that never sleeps, one could hear a pin drop on Fifth Avenue, a fitting tribute to the men and women who lost their lives on that fateful day in 2001. The 2002 Parade was the largest Parade to date with an estimated 300,000 marchers and three million spectators lining Fifth Avenue. This was the first time in history; the President of Ireland reviewed a St. Patrick’s Day Parade outside Ireland on March 17th. -
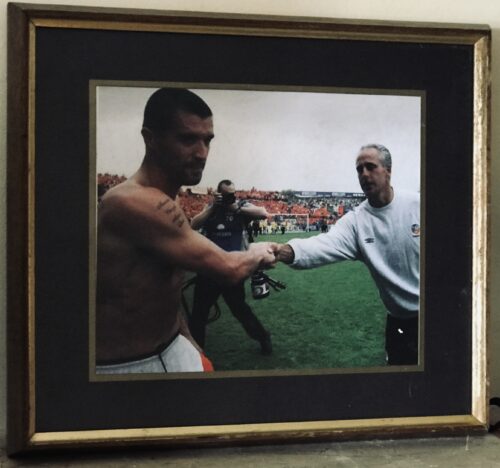
 Cork City 33cm x 38cm The Infamous Handshake between Roy Keane and Mick McCarthy that said it all
Cork City 33cm x 38cm The Infamous Handshake between Roy Keane and Mick McCarthy that said it all"Footballers are pragmatists. You play for the manager you have."
This is a quote from Roy Keane's autobiography [Page 76]. He was referring specifically to the Irish soccer players when Jack Charlton was the Republic of Ireland team manager, and to footballers in general. It would appear however that Keane had limits to his own pragmatism when it came to playing for Mick McCarthy as Irish manager.
The dynamics of the relationship between Roy Keane and Mick McCarthy are central to the whole Saipan incident. Clearly the two did not get on with each other. The question is - why? Keane and McCarthy are the only ones who can give a definitive answer to this but based upon the available evidence it appears to be primarily due to an intense dislike of McCarthy by Keane.
Roy Keane and Mick McCarthy Have a Row in Boston in 1992
Roy Keane and Mick McCarthy only played together for Ireland on two occasions, in September 1991 and May 1992. There are no generally known reports of any issues arising between the two men as players on the football pitch. However it was while Mick McCarthy was the Republic of Ireland team captain that the first instance of some discord between the two has been documented. During the fateful squad meeting, that led to the expulsion of Keane from the Irish World Cup squad, the Irish captain brought up an incident that had occurred a full ten years earlier. The now infamous Boston 1992 row.
It now seems that this otherwise innocuous event appears to have coloured the Keane and McCarthy relationship
from that time onward. A drunken 20 year old Keane had turned up late for the team bus at the end of a soccer tournament in the US. When the team captain Mick McCarthy challenged Keane about being late a heated row ensued. Roy Keane seems to have taken extreme exception to this. It is difficult to believe that such an event would even register the next day with Keane who seems to have spent his entire life going from one scrape to another. Keane admits in his autobiography that he has had hundreds or thousands of rows throughout his soccer career. Why should this one have been so significant to him?One possible explanation is that when Keane is drunk his, already low, tolerance levels become even lower. Any perceived slight is magnified disproportionately. Keane's autobiography is littered with stories about him getting into angry and violent situations when he was drunk. By his own admission there were many situations when he knew he should have walked away but his own sense of offence prevented him doing just that. These events seem to have made an indelible mark on his brain as they are recounted with real clarity in his book. It seems that a run of the mill, for footballers, exchange between McCarthy and Keane in 1992, magnified in intensity by his drunken state, soured Keane's view of McCarthy from that point on.
"Let Bygones be Bygones" - Roy Keane
There do not appear to have been any further meaningful interactions between the two until McCarthy was appointed as manager of the Republic of Ireland football team in 1996. In his autobiography [Page 246] Keane reveals an antipathy towards McCarthy that seems, to some extent, to be born out of Roy Keane's relationship with Jack Charlton. In his book Keane makes it clear that he had no time for Charlton "...I found it impossible to relate to him as a man or as a coach." [Page 54]. When commenting on McCarthy's appointment as Irish manager he said "McCarthy was part of the Charlton legend. Captain Fantastic...he didn't convince me. Still, when he got the job, I thought: let bygones be bygones." What bygones? Presumably the exchange between the pair in Boston six years earlier?
In his World Cup Diary McCarthy makes a case that he had gone to some lengths as manager of Ireland to accommodate Keane and his sensitivities. He had made Keane the captain of Ireland at the first opportunity. He allowed Keane to turn up later than the other players for international matches. Keane was the only player in the Irish squad that roomed alone. He also says that he put up "...with the odd tantrum from Keane here and there...". McCarthy contends that if he was holding a grudge towards Keane from 1992 he would not have gone to these lengths.
Roy Keane's first match for Ireland with Mick McCarthy as manager was an inauspicious occasion for the Manchester United player. Earning his 30th cap and wearing the captain's armband in place of the substituted Andy Townsend, Keane was sent off late in the match for kicking a Russian player.
Lack of Direct Communication Between Roy Keane & Mick McCarthy
The next notable point of conflict between Keane and McCarthy was on the occasion of a Republic of Ireland trip to the USA for an end of season international tournament in 1996. Keane decided that he didn't want to go as he was too tired after the season just ended. [Page 246]. Rather than contact McCarthy or anyone else in the Irish set up, Keane left it to someone at Old Trafford to inform the FAI. "As a result I got off to a bad start with McCarthy. He felt I should have spoken to him personally. He expressed this opinion, casting me in a bad light. What he didn't tell the media that if we had that sort of conversation on this occasion, it would have been our first." [Page 247]. This begs the question, why couldn't Keane contact McCarthy directly? Why would this have been the first such discussion between the two men as manager and team captain? It certainly doesn't suggest that Keane had, in reality, let bygones be bygones.
In his World Cup Diary McCarthy refers to the the 1996 USA trip. "I was never that bothered if he (Keane) went to America or not...it became a big media story...We have had a few chats to sort things out but it has all dragged on since then in the press." [Page 33].
In his autobiography Keane complains bitterly about the poor Republic of Ireland set up especially when compared to that of Manchester United. After the draw for the 2002 World Cup qualifiers was made Keane says that he met with McCarthy"...to level with him, to make the case for a reformed approach...We discussed the problems. He agreed with me...It was not and easy conversation - we're not not buddy-buddy...I thought we had a deal."[Page 250]. Interestingly this meeting took place at Keane's house in Manchester.
What is clear is that there was an unusual relationship between the Irish manager and his captain. Direct communication between McCarthy and Keane was kept to an absolute minimum. All of the available evidence is that was the way Keane wanted it. Keane admitted this in his interview with Tom Humphries in Saipan "I spoke to Mick Byrne, who's the middle man for me, really." For a man who has very admirable communication skills this is somewhat strange. Why would he need a middle man? The only possible explanation is that Roy Keane did not like Mick McCarthy and couldn't bear to be anywhere near him or have anything to do with him. During McCarthy's tenure as Irish manager Roy Keane took every opportunity to minimise his time with the Irish squad. "I dreaded the prospect of international weeks."[Page 250].
Conclusion
With the benefit of hindsight and with the insights afforded by Keane's autobiography it is clear that there was no way possible that Roy Keane could maintain an even keel while being away with Ireland for the duration of the World Cup campaign. All of his complaints about the crowded airport, the missing training gear, the poor training facilities, the goalkeeper row, were just symptoms. Clearly McCarthy and the FAI could have done better but the inescapable conclusion to be drawn is that even if conditions and facilities had been perfect Keane simply could not endure being in such close proximity to Mick McCarthy for such a protracted period of time. A Saipan incidentwas inevitable even before Roy Keane set foot on the plane to that Pacific island.
NOTE: Unless stated otherwise all quotations are from: Keane: The Autobiography; Roy Keane with Eamon Dunphy (2002); Michael Joseph Ltd
-
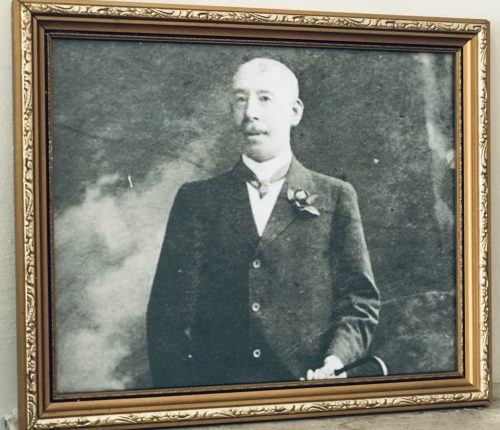 23cm x 28cm Drimoleague Co Cork Patrick J. O’Flaherty, better known as Paddy, sold what became his namesake whiskey in pubs across Ireland for an incredible four decades, spanning the turn of the 20th century. Magnetic, outgoing and generous, Paddy bought rounds and made friends everywhere he went, always making sure everyone had a great time. Kind and wise, with a good natured, rapier wit, Paddy was always welcomed and was by all accounts universally beloved. After 40 years of service, the whiskey he sold took on his name. Traversing the beautiful southern tip of Ireland from East to West and back for 40 years on foot, with horse and buggy or by train, Paddy was always on the move. From coast to coast, he was the life of the party—one filled with music, laughter, good times and great whiskey. Paddy’s good humour and revelry proved a winning combination, and before long, the brand name was forgotten. Everyone simply ordered more Paddy whiskey. Word got around, and not just in Ireland. Today, from continent to continent, the tradition Paddy started is alive and well.
23cm x 28cm Drimoleague Co Cork Patrick J. O’Flaherty, better known as Paddy, sold what became his namesake whiskey in pubs across Ireland for an incredible four decades, spanning the turn of the 20th century. Magnetic, outgoing and generous, Paddy bought rounds and made friends everywhere he went, always making sure everyone had a great time. Kind and wise, with a good natured, rapier wit, Paddy was always welcomed and was by all accounts universally beloved. After 40 years of service, the whiskey he sold took on his name. Traversing the beautiful southern tip of Ireland from East to West and back for 40 years on foot, with horse and buggy or by train, Paddy was always on the move. From coast to coast, he was the life of the party—one filled with music, laughter, good times and great whiskey. Paddy’s good humour and revelry proved a winning combination, and before long, the brand name was forgotten. Everyone simply ordered more Paddy whiskey. Word got around, and not just in Ireland. Today, from continent to continent, the tradition Paddy started is alive and well.NEARLY A QUARTER-MILLENNIUM OF ENDURING QUALITY
Paddy Irish Whiskey traces its roots all the way back to 1779, but it started simple, and the recipe remained consistent. As its popularity grew across Ireland, Paddy eventually made it overseas. A century later, it won first-prize medals in Philadelphia (1876), Sydney (1879) and Cork (1883), along with a gold medal at the World’s Fair in Paris (1878). By 1930, Paddy could be found in cosmopolitan cities like Milan, Shanghai and Bangkok, and in 80+ countries worldwide.
ADDY IRISH WHISKEY
Light, well-balanced and pure.
An approachable Irish whiskey comprised of a triple-distilled blend of grain, malt and pot-still, Paddy is mild and yet crisp, with a hint of honey. Paddy is the perfect session spirit for gathering ‘round for good times with friends. Triple-distilled from the finest barley and water from County Cork’s Irish countryside, Paddy matures for years in three types of oaken casks, acquiring its distinctively rich and golden color in dark, aromatic warehouses before being bottled and shipped directly from Ireland.Theres a reason Paddy has been triple distilled the same way in County Cork Ireland for nearly a quarter-millennium. Some good things don’t come to an end.
Nose Malty, fresh, woody. Hints of spice, honey, vanilla. Taste Light and crisp. Hints of nuts, malt, charred wood. Finish A gently fading sweetness. A lingering of mild, woody malt. -
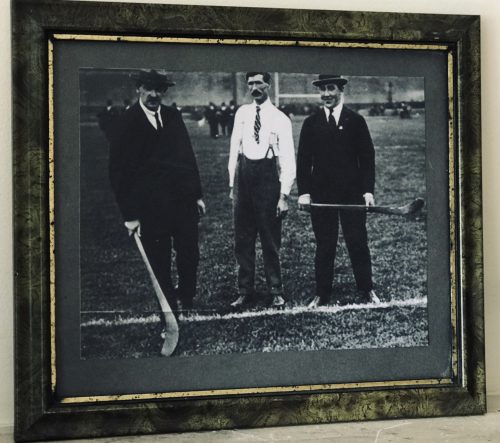 Iconic GAA photograph of a Hurley holding Michael Collins with Harry Boland in Croke Park in 1921 with an unknown gentleman. 30cm x 35cm Bantry Co Cork Michael Collins was a revolutionary, soldier and politician who was a leading figure in the early-20th-century Irish struggle for independence. He was Chairman of the Provisional Government of the Irish Free State from January 1922 until his assassination in August 1922. Collins was born in Woodfield, County Cork, the youngest of eight children, and his family had republican connections reaching back to the 1798 rebellion. He moved to London in 1906, to become a clerk in the Post Office Savings Bank at Blythe House. He was a member of the London GAA, through which he became associated with the Irish Republican Brotherhood and the Gaelic League. He returned to Ireland in 1916 and fought in the Easter Rising. He was subsequently imprisoned in the Frongoch internment camp as a prisoner of war, but was released in December 1916. Collins rose through the ranks of the Irish Volunteers and Sinn Féin after his release from Frongoch. He became a Teachta Dála for South Cork in 1918, and was appointed Minister for Finance in the First Dáil. He was present when the Dáil convened on 21 January 1919 and declared the independence of the Irish Republic. In the ensuing War of Independence, he was Director of Organisation and Adjutant General for the Irish Volunteers, and Director of Intelligence of the Irish Republican Army. He gained fame as a guerrilla warfare strategist, planning and directing many successful attacks on British forces, such as the assassination of key British intelligence agents in November 1920. After the July 1921 ceasefire, Collins and Arthur Griffith were sent to London by Éamon de Valera to negotiate peace terms. The resulting Anglo-Irish Treaty established the Irish Free State but depended on an Oath of Allegiance to the Crown, a condition that de Valera and other republican leaders could not reconcile with. Collins viewed the Treaty as offering "the freedom to achieve freedom", and persuaded a majority in the Dáil to ratify the Treaty. A provisional government was formed under his chairmanship in early 1922 but was soon disrupted by the Irish Civil War, in which Collins was commander-in-chief of the National Army. He was shot and killed in an ambush by anti-Treaty on 22nd August 1922.
Iconic GAA photograph of a Hurley holding Michael Collins with Harry Boland in Croke Park in 1921 with an unknown gentleman. 30cm x 35cm Bantry Co Cork Michael Collins was a revolutionary, soldier and politician who was a leading figure in the early-20th-century Irish struggle for independence. He was Chairman of the Provisional Government of the Irish Free State from January 1922 until his assassination in August 1922. Collins was born in Woodfield, County Cork, the youngest of eight children, and his family had republican connections reaching back to the 1798 rebellion. He moved to London in 1906, to become a clerk in the Post Office Savings Bank at Blythe House. He was a member of the London GAA, through which he became associated with the Irish Republican Brotherhood and the Gaelic League. He returned to Ireland in 1916 and fought in the Easter Rising. He was subsequently imprisoned in the Frongoch internment camp as a prisoner of war, but was released in December 1916. Collins rose through the ranks of the Irish Volunteers and Sinn Féin after his release from Frongoch. He became a Teachta Dála for South Cork in 1918, and was appointed Minister for Finance in the First Dáil. He was present when the Dáil convened on 21 January 1919 and declared the independence of the Irish Republic. In the ensuing War of Independence, he was Director of Organisation and Adjutant General for the Irish Volunteers, and Director of Intelligence of the Irish Republican Army. He gained fame as a guerrilla warfare strategist, planning and directing many successful attacks on British forces, such as the assassination of key British intelligence agents in November 1920. After the July 1921 ceasefire, Collins and Arthur Griffith were sent to London by Éamon de Valera to negotiate peace terms. The resulting Anglo-Irish Treaty established the Irish Free State but depended on an Oath of Allegiance to the Crown, a condition that de Valera and other republican leaders could not reconcile with. Collins viewed the Treaty as offering "the freedom to achieve freedom", and persuaded a majority in the Dáil to ratify the Treaty. A provisional government was formed under his chairmanship in early 1922 but was soon disrupted by the Irish Civil War, in which Collins was commander-in-chief of the National Army. He was shot and killed in an ambush by anti-Treaty on 22nd August 1922. -
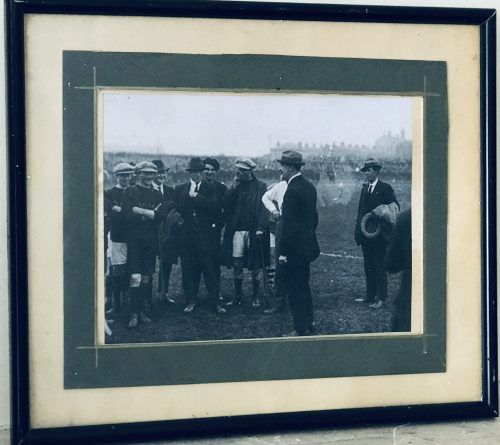 Atmospheric photograph of a moustached Michael Collins meeting the Kilkenny hurling team in advance of the 1921 Leinster hurling final, played at Croke Park on September 11, 1921. Dublin won the match on the score of Dublin 4-04 Kilkenny 1-05. 30cm x 40cm Durrow Co Laois Michael Collins was a revolutionary, soldier and politician who was a leading figure in the early-20th-century Irish struggle for independence. He was Chairman of the Provisional Government of the Irish Free State from January 1922 until his assassination in August 1922. Collins was born in Woodfield, County Cork, the youngest of eight children, and his family had republican connections reaching back to the 1798 rebellion. He moved to London in 1906, to become a clerk in the Post Office Savings Bank at Blythe House. He was a member of the London GAA, through which he became associated with the Irish Republican Brotherhood and the Gaelic League. He returned to Ireland in 1916 and fought in the Easter Rising. He was subsequently imprisoned in the Frongoch internment camp as a prisoner of war, but was released in December 1916. Collins rose through the ranks of the Irish Volunteers and Sinn Féin after his release from Frongoch. He became a Teachta Dála for South Cork in 1918, and was appointed Minister for Finance in the First Dáil. He was present when the Dáil convened on 21 January 1919 and declared the independence of the Irish Republic. In the ensuing War of Independence, he was Director of Organisation and Adjutant General for the Irish Volunteers, and Director of Intelligence of the Irish Republican Army. He gained fame as a guerrilla warfare strategist, planning and directing many successful attacks on British forces, such as the assassination of key British intelligence agents in November 1920. After the July 1921 ceasefire, Collins and Arthur Griffith were sent to London by Éamon de Valera to negotiate peace terms. The resulting Anglo-Irish Treaty established the Irish Free State but depended on an Oath of Allegiance to the Crown, a condition that de Valera and other republican leaders could not reconcile with. Collins viewed the Treaty as offering "the freedom to achieve freedom", and persuaded a majority in the Dáil to ratify the Treaty. A provisional government was formed under his chairmanship in early 1922 but was soon disrupted by the Irish Civil War, in which Collins was commander-in-chief of the National Army. He was shot and killed in an ambush by anti-Treaty on 22nd August 1922.
Atmospheric photograph of a moustached Michael Collins meeting the Kilkenny hurling team in advance of the 1921 Leinster hurling final, played at Croke Park on September 11, 1921. Dublin won the match on the score of Dublin 4-04 Kilkenny 1-05. 30cm x 40cm Durrow Co Laois Michael Collins was a revolutionary, soldier and politician who was a leading figure in the early-20th-century Irish struggle for independence. He was Chairman of the Provisional Government of the Irish Free State from January 1922 until his assassination in August 1922. Collins was born in Woodfield, County Cork, the youngest of eight children, and his family had republican connections reaching back to the 1798 rebellion. He moved to London in 1906, to become a clerk in the Post Office Savings Bank at Blythe House. He was a member of the London GAA, through which he became associated with the Irish Republican Brotherhood and the Gaelic League. He returned to Ireland in 1916 and fought in the Easter Rising. He was subsequently imprisoned in the Frongoch internment camp as a prisoner of war, but was released in December 1916. Collins rose through the ranks of the Irish Volunteers and Sinn Féin after his release from Frongoch. He became a Teachta Dála for South Cork in 1918, and was appointed Minister for Finance in the First Dáil. He was present when the Dáil convened on 21 January 1919 and declared the independence of the Irish Republic. In the ensuing War of Independence, he was Director of Organisation and Adjutant General for the Irish Volunteers, and Director of Intelligence of the Irish Republican Army. He gained fame as a guerrilla warfare strategist, planning and directing many successful attacks on British forces, such as the assassination of key British intelligence agents in November 1920. After the July 1921 ceasefire, Collins and Arthur Griffith were sent to London by Éamon de Valera to negotiate peace terms. The resulting Anglo-Irish Treaty established the Irish Free State but depended on an Oath of Allegiance to the Crown, a condition that de Valera and other republican leaders could not reconcile with. Collins viewed the Treaty as offering "the freedom to achieve freedom", and persuaded a majority in the Dáil to ratify the Treaty. A provisional government was formed under his chairmanship in early 1922 but was soon disrupted by the Irish Civil War, in which Collins was commander-in-chief of the National Army. He was shot and killed in an ambush by anti-Treaty on 22nd August 1922. -
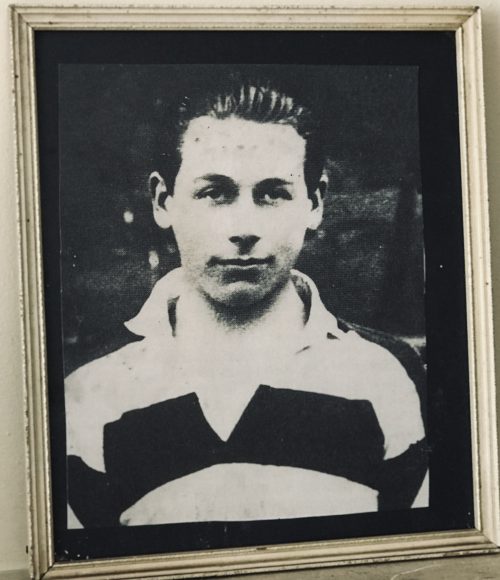 The iconic portrait of a teenage Kevin Barry,one of our most celebrated republican martyrs-in the black and white hooped rugby jersey of Belvedere College SJ. 26cm x 30cm Dunmanway Co Cork Kevin Gerard Barry (20 January 1902 – 1 November 1920) was an Irish republican paramilitary who was executed by the British Government during the Irish War of Independence. He was sentenced to death for his part in an attack upon a British Army supply lorry which resulted in the deaths of three British soldiers. His execution inflamed nationalist public opinion in Ireland, largely because of his age. The timing of the execution, only days after the death by hunger strike of Terence MacSwiney, the republican Lord Mayor of Cork, brought public opinion to a fever-pitch. His death attracted international attention, and attempts were made by U.S. and Vatican officials to secure a reprieve. His execution and MacSwiney's death precipitated an escalation in violence as the Irish War of Independence entered its bloodiest phase, and Barry became an Irish republican martyr.
The iconic portrait of a teenage Kevin Barry,one of our most celebrated republican martyrs-in the black and white hooped rugby jersey of Belvedere College SJ. 26cm x 30cm Dunmanway Co Cork Kevin Gerard Barry (20 January 1902 – 1 November 1920) was an Irish republican paramilitary who was executed by the British Government during the Irish War of Independence. He was sentenced to death for his part in an attack upon a British Army supply lorry which resulted in the deaths of three British soldiers. His execution inflamed nationalist public opinion in Ireland, largely because of his age. The timing of the execution, only days after the death by hunger strike of Terence MacSwiney, the republican Lord Mayor of Cork, brought public opinion to a fever-pitch. His death attracted international attention, and attempts were made by U.S. and Vatican officials to secure a reprieve. His execution and MacSwiney's death precipitated an escalation in violence as the Irish War of Independence entered its bloodiest phase, and Barry became an Irish republican martyr.Early life
Kevin Barry was born on 20 January 1902, at 8 Fleet Street, Dublin, to Thomas and Mary (née Dowling) Barry. The fourth of seven children, two boys and five sisters, Kevin was baptised in St Andrew's Church, Westland Row. Thomas Barry Sr. worked on the family's farm at Tombeagh, Hacketstown, County Carlow, and ran a dairy business from Fleet Street. Thomas Barry Sr. died in 1908, aged 56. His mother came from Drumguin, County Carlow, and, upon the death of her husband, moved the family to nearby Tombeagh. As a child he went to the national school in Rathvilly. On returning to Dublin, he attended St Mary's College, Rathmines, until the school closed in the summer of 1916.When he was thirteen, he attended a commemoration for the Manchester Martyrs, who were hanged in England in 1867. Afterwards he wished to join Constance Markievicz's Fianna Éireann, but was reportedly dissuaded by his family.Belvedere College
From St Mary's College he transferred to Belvedere College, where he was a member of the championship Junior Rugby Cup team, and earned a place on the senior team. In 1918 he became secretary of the school hurling club which had just been formed, and was one of their most enthusiastic players.A Jesuit priest, Thomas Counihan, who was Barry's science and mathematics teacher, said of him: "He was a dour kind of lad. But once he got down to something he went straight ahead… There was no waving of flags with him, but he was sincere and intense." Notwithstanding his many activities, he did not neglect his studies. He won a merit-based scholarship given annually by Dublin Corporation, which allowed him to become a student of medicine at UCD.Medical student
He entered University College Dublin in 1919. His closest friend at college was Gerry MacAleer, from Dungannon, whom he had first met in Belvedere. Other friends included Frank Flood, Tom Kissane and Mick Robinson, who, unknown to many in the college, were, along with Barry, members of the Irish Volunteers.Volunteer activities
In October 1917, during his second year at Belvedere, aged 15, he joined the IRA. Assigned originally to ‘C’ Company 1st Battalion, based on the north side of Dublin, he later transferred to the newly formed ‘H’ Company, under the command of Capt. Seamus Kavanagh. His first job as a member of the IRA was delivering mobilisation orders around the city. Along with other volunteers, Barry trained in a number of locations in Dublin, including the building at 44 Parnell Square, the present day headquarters of Sinn Féin, now named Kevin Barry Hall. The IRA held Field exercises during this period which were conducted in north county Dublin and in areas such as Finglas.The following year, at the age of 16, he was introduced by Seán O'Neill and Bob O'Flanagan to the Clarke Luby Club of the IRB, which had been reorganised. He took part in a number of IRA operations in the years leading up to his capture. He was part of the unit which raided the Shamrock Works for weapons destined to be handed over to the R.I.C. He also took part in the raid on Mark's of Capel Street, looking for ammunition and explosives. On 1 June 1920, under Vice-Commandant Peadar Clancy, he played a notable part in the seizing of the King's Inn, capturing the garrison’s arms. The haul included 25 rifles, two light machine guns and large quantities of ammunition. The 25 British soldiers captured during the attack were released as the volunteers withdrew. In recognition of his dedication to duty he was promoted to Section Commander.Ambush
On the morning of 20 September 1920, Barry went to Mass, then joined a party of IRA volunteers on Bolton Street in Dublin. Their orders were to ambush a British army lorry as it picked up a delivery of bread from the bakery, and capture their weapons. The ambush was scheduled for 11:00am, which gave him enough time to take part in the operation and return to class in time for an examination he had at 2:00pm. The truck arrived late, and was under the command of Sergeant Banks. Armed with a .38 Mauser Parabellum, Barry and members of C Company were to surround the lorry, disarm the soldiers, take the weapons and escape. He covered the back of the vehicle and, when challenged, the five soldiers complied with the order to lay down their weapons. A shot was then fired; Terry Golway, author of For the Cause of Liberty, suggests it was possibly a warning shot from an uncovered soldier in the front. Barry and the rest of the ambush party then opened fire. His gun jammed twice and he dived for cover under the vehicle. His comrades fled and he was left behind. He was then spotted and arrested by the soldiers.One of the soldiers, Private Harold Washington, aged 15, had been shot dead. Two others, Privates Marshall Whitehead and Thomas Humphries, were both badly wounded and later died of their wounds. The British Army released the following statement on Monday afternoon:This morning a party of one N.C.O. and six men of the Duke of Wellington's Regiment were fired on by a body of civilians outside a bakery in Church Street, Dublin. One soldier was killed and four were wounded. A piquet of the Lancashire Fusiliers in the vicinity, hearing the shots, hurried to their comrades' assistance, and succeeded in arresting one of the aggressors. No arms or equipment were lost by the soldiers.
Much was made of Barry's age by Irish newspapers, but the British military pointed out that the three soldiers who had been killed were "much the same age as Barry". On 20 October, Major Reginald Ingram Marians OBE, Head of the Press Section of the General Staff, informed Basil Clarke, Head of Publicity, that Washington was "only 19 and that the other soldiers were of similar ages." General Macready was well aware of the "propaganda value of the soldier's ages." Macready informed General Sir Henry Wilson on the day that sentence was pronounced "of the three men who were killed by him (Barry) and his friends two were 19 and one 20 — official age so probably they were younger... so if you want propaganda there you are."It was later confirmed that Private Harold Washington was 15 years and 351 days old, having been born 4 October 1904. About this competing propaganda, Martin Doherty wrote in a magazine article entitled 'Kevin Barry & the Anglo-Irish Propaganda War':from the British point of view, therefore, the Anglo-Irish propaganda war was probably unwinable [sic]. Nationalist Ireland had decided that men like Kevin Barry fought to free their country, while British soldiers — young or not — sought to withhold that freedom. In these circumstances, to label Barry a murderer was merely to add insult to injury. The contrasting failure of British propaganda is graphically demonstrated by the simple fact that even in British newspapers Privates Whitehead, Washington and Humphries remained faceless names and numbers, for whom no songs were written.”
Capture and torture
Barry was placed in the back of the lorry with the young body of Private Harold Washington, and was subjected to some abuse by Washington's comrades. He was transported then to the North Dublin Union. Upon arrival at the barracks he was taken under military police escort to the defaulters' room where he was searched and handcuffed. A short while later, three sergeants of the Lancashire Fusiliers and two officers began the interrogation. He gave his name and an address of 58 South Circular Road, Dublin (his uncle's address), and his occupation as a medical student, but refused to answer any other questions. The officers continued to demand the names of other republicans involved in the ambush. At this time a publicity campaign was mounted by Sinn Féin. Barry received orders on 28 October from his brigade commander, Richard McKee, "to make a sworn affidavit concerning his torture in the North Dublin Union." Arrangements were made to deliver this through Barry's sister, Kathy, to Desmond Fitzgerald, director of publicity for Sinn Féin, "with the object of having it published in the World press, and particularly in the English papers, on Saturday 30th October." The affidavit, drawn up in Mountjoy Prison days before his execution, describes his treatment when the question of names was repeated:Sinn Féin's Dublin HQ at the Kevin Barry Memorial HallHe tried to persuade me to give the names, and I persisted in refusing. He then sent the sergeant out of the room for a bayonet. When it was brought in the sergeant was ordered by the same officer to point the bayonet at my stomach ... The sergeant then said that he would run the bayonet into me if I did not tell ... The same officer then said to me that if I persisted in my attitude he would turn me out to the men in the barrack square, and he supposed I knew what that meant with the men in their present temper. I said nothing. He ordered the sergeants to put me face down on the floor and twist my arm ... When I lay on the floor, one of the sergeants knelt on my back, the other two placed one foot each on my back and left shoulder, and the man who knelt on me twisted my right arm, holding it by the wrist with one hand, while he held my hair with the other to pull back my head. The arm was twisted from the elbow joint. This continued, to the best of my judgment, for five minutes. It was very painful ... I still persisted in refusing to answer these questions... A civilian came in and repeated the questions, with the same result. He informed me that if I gave all the information I knew I could get off.
On 28 October, the Irish Bulletin (organised by Dick McKee, the IRA Commandant of the Dublin Brigade), a news-sheet produced by Dáil Éireann's Department of Publicity,published Barry's statement alleging torture. The headline read: English Military Government Torture a Prisoner of War and are about to Hang him. The Irish Bulletin declared Barry to be a prisoner of war, suggesting a conflict of principles was at the heart of the conflict. The English did not recognise a war and treated all killings by the IRA as murder. Irish republicans claimed that they were at war and it was being fought between two opposing nations and therefore demanded prisoner of war status. Historian John Ainsworth, author of Kevin Barry, the Incident at Monk's bakery and the Making of an Irish Republican Legend, pointed out that Barry had been captured by the British not as a uniformed soldier but disguised as a civilian and in possession of flat-nosed "Dum-dum" bullets, which expand upon impact, maximising the amount of damage done to the "unfortunate individual" targeted, in contravention of the Hague Convention of 1899. Erskine Childers addressed the question of political status in a letter to the press on 29 October, which was published the day after Barry's execution.-
- This lad Barry was doing precisely what Englishmen would be doing under the same circumstances and with the same bitter and intolerable provocation — the suppression by military force of their country's liberty.
- To hang him for murder is an insulting outrage, and it is more: it is an abuse of power: an unworthy act of vengeance. contrasting ill with the forbearance and humanity invariably shown by the Irish Volunteers towards the prisoners captured by them when they have been successful in encounters similar to this one. These guerrilla combats with soldiers and constables — both classes do the same work with the same weapons; the work of military repression — are typical episodes in Ireland.
- Murder of individual constables, miscalled ‘police’, have been comparatively rare. The Government figure is 38, and it will not, to my knowledge, bear examination. I charge against the British Government 80 murders by soldiers and constables: murders of unarmed people, and for the most part wholly innocent people, including old men, women and boys.
- To hang Barry is to push to its logical extreme the hypocritical pretense that the national movement in Ireland unflinchingly supported by the great mass of the Irish people, is the squalid conspiracy of a ‘murder gang’.
- That is false; it is a natural uprising: a collision between two Governments, one resting on consent, the other on force. The Irish are struggling against overwhelming odds to defend their own elected institutions against extinction.
-
-
-
Under similar circumstances a body of Irish Volunteers captured on June 1 of the present year a party of 25 English military who were on duty at the King's Inns, Dublin. Having disarmed the party the Volunteers immediately released their prisoners. This was in strict accordance with the conduct of the Volunteers in all such encounters. Hundreds of members of the armed forces have been from time to time captured by the Volunteers and in no case was any prisoner maltreated even though Volunteers had been killed and wounded in the fighting, as in the case of Cloyne, Co. Cork, when, after a conflict in which one Volunteer was killed and two wounded, the whole of the opposing forces were captured, disarmed, and set at liberty.
-
-
Trial
The War Office ordered that Kevin Barry be tried by court-martial under the Restoration of Order in Ireland Act, which received Royal Assent on 9 August 1920. General Sir Nevil Macready, Commander-in-Chief of British forces in Ireland then nominated a court of nine officers under a Brigadier-General Onslow. On 20 October, at 10 o’clock, the nine officers of the court — ranging in rank from Brigadier to Lieutenant — took their places at an elevated table. At 10.25, Kevin Barry was brought into the room by a military escort. Then Seán Ó hUadhaigh sought a short adjournment to consult his client. The court granted this request. After the short adjournment Barry announced "As a soldier of the Irish Republic, I refuse to recognise the court." Brigadier Onslow explained the prisoner's "perilous situation" and that he was being tried on a capital charge. He did not reply. Ó hUadhaigh then rose to tell the court that since his client did not recognise the authority of the court he himself could take no further part in the proceedings. Barry was charged on three counts of the murder of Private Marshall Whitehead. One of the bullets taken from Whitehead's body was of .45 calibre, while all witnesses stated that Barry was armed with a .38 Mauser Parabellum. The Judge Advocate General informed the court that the Crown had only to prove that the accused was one of the party that killed three British soldiers, and every member of the party was technically guilty of murder. In accordance with military procedure the verdict was not announced in court. He was returned to Mountjoy, and at about 8 o’clock that night, the district court-martial officer entered his cell and read out the sentence: death by hanging. The public learned on 28 October that the date of execution had been fixed for 1 November.Execution
Barry spent the last day of his life preparing for death. His ordeal focused world attention on Ireland. According to Sean Cronin, author of a biography of Barry (Kevin Barry), he hoped for a firing squad rather than the gallows, as he had been condemned by a military court. A friend who visited him in Mountjoy prison after he received confirmation of the death sentence, said:He is meeting death as he met life with courage but with nothing of the braggart. He does not believe that he is doing anything wonderfully heroic. Again and again he has begged that no fuss be made about him.
He reported Barry as saying "It is nothing, to give one's life for Ireland. I'm not the first and maybe I won't be the last. What's my life compared with the cause?" Barry joked about his death with his sister Kathy. "Well, they are not going to let me like a soldier fall… But I must say they are going to hang me like a gentleman." This was, according to Cronin, a reference to George Bernard Shaw's The Devil's Disciple, the last play Kevin and his sister had seen together. On 31 October, he was allowed three visits of three people each, the last of which was taken by his mother, brother and sisters. In addition to the two Auxiliaries with him, there were five or six warders in the boardroom. As his family were leaving, they met Canon John Waters, on the way in, who said, "This boy does not seem to realise he is going to die in the morning." Mrs Barry asked him what he meant. He said: "He is so gay and light-hearted all the time. If he fully realised it, he would be overwhelmed." Mrs Barry replied, "Canon Waters, I know you are not a Republican. But is it impossible for you to understand that my son is actually proud to die for the Republic?" Canon Waters became somewhat flustered as they parted. The Barry family recorded that they were upset by this encounter because they considered the chief chaplain "the nearest thing to a friend that Kevin would see before his death, and he seemed so alien." Kevin Barry was hanged on 1 November, after hearing two Masses in his cell. Canon Waters, who walked with him to the scaffold, wrote to Barry's mother later, "You are the mother, my dear Mrs Barry, of one of the bravest and best boys I have ever known. His death was one of the most holy, and your dear boy is waiting for you now, beyond the reach of sorrow or trial." Dublin Corporation met on the Monday, and passed a vote of sympathy with the Barry family, and adjourned the meeting as a mark of respect. The Chief Secretary's office in Dublin Castle, on the Monday night, released the following communiqué:The sentence of death by hanging passed by court-martial upon Kevin Barry, or Berry, medical student, aged 18½ years, for the murder of Private Whitehead in Dublin on September 20, was duly executed this morning at Mountjoy Prison, Dublin. At a military court of inquiry, held subsequently in lieu of an inquest, medical evidence was given to the effect that death was instantaneous. The court found that the sentence had been carried out in accordance with law.
Barry's body was buried at 1.30 p.m, in a plot near the women's prison. His comrade and fellow-student Frank Flood was buried alongside him four months later. A plain cross marked their graves and those of Patrick Moran, Thomas Whelan, Thomas Traynor, Patrick Doyle, Thomas Bryan, Bernard Ryan, Edmond Foley and Patrick Maher who were hanged in the same prison before the Anglo-Irish Treaty of July 1921 which ended hostilities between Irish republicans and the British.The men had been buried in unconsecrated ground on the jail property and their graves went unidentified until 1934.They became known as The Forgotten Ten by republicans campaigning for the bodies to be reburied with honour and proper rites.On 14 October 2001, the remains of these ten men were given a state funeral and moved from Mountjoy Prison to be re-interred at Glasnevin Cemetery in Dublin.Aftermath
 Kevin Barry monument in Rathvilly, County CarlowThe only full-length biography of Kevin Barry was written by his nephew, journalist Donal O'Donovan, published in 1989 as Kevin Barry and his Time. In 1965, Sean Cronin wrote a short biography, simply entitled "Kevin Barry"; this was published by The National Publications Committee, Cork, to which Tom Barry provided a foreword. Barry is remembered in a well-known song about his imprisonment and execution, written shortly after his death and still sung today. The tune to "Kevin Barry" was taken from the sea-shanty "Rolling Home".[17] The execution reportedly inspired Thomas MacGreevy's surrealist poem, "Homage to Hieronymus Bosch". MacGreevy had unsuccessfully petitioned the Provost of Trinity College Dublin, John Henry Bernard, to make representations on Barry's behalf.
Kevin Barry monument in Rathvilly, County CarlowThe only full-length biography of Kevin Barry was written by his nephew, journalist Donal O'Donovan, published in 1989 as Kevin Barry and his Time. In 1965, Sean Cronin wrote a short biography, simply entitled "Kevin Barry"; this was published by The National Publications Committee, Cork, to which Tom Barry provided a foreword. Barry is remembered in a well-known song about his imprisonment and execution, written shortly after his death and still sung today. The tune to "Kevin Barry" was taken from the sea-shanty "Rolling Home".[17] The execution reportedly inspired Thomas MacGreevy's surrealist poem, "Homage to Hieronymus Bosch". MacGreevy had unsuccessfully petitioned the Provost of Trinity College Dublin, John Henry Bernard, to make representations on Barry's behalf. On 14 October 2001 the remains of Kevin Barry and nine other volunteers from the War of Independence were given a state funeral and moved from Mountjoy Prison to be re-interred at Glasnevin Cemetery in Dublin. Barry's grave is the first on the left.
On 14 October 2001 the remains of Kevin Barry and nine other volunteers from the War of Independence were given a state funeral and moved from Mountjoy Prison to be re-interred at Glasnevin Cemetery in Dublin. Barry's grave is the first on the left.Legacy[edit]
A commemorative stamp was issued by An Post to mark the 50th anniversary of Barry's death in 1970.[18] The University College Dublin and National University of Ireland, Galway branches of Ógra Fianna Fáil are named after him.[19] Derrylaughan Kevin Barry's GAA club was founded in Clonoe, County Tyrone. In 1930, Irish immigrants in Hartford, Connecticut, created a hurling club and named it after Barry. The club later disappeared for decades, but was revived in 2011 by more recently arrived Irish immigrants and local Irish-Americans in the area.[20] In 1934, a large stained-glass window commemorating Barry was unveiled in Earlsfort Terrace, then the principal campus of University College Dublin. It was designed by Richard King of the Harry Clarke Studio. In 2007, UCD completed its relocation to the Belfield campus some four miles away and a fund was collected by graduates to defray the cost (estimated at close to €250,000) of restoring and moving the window to this new location.[21] A grandnephew of Kevin Barry is Irish historian Eunan O'Halpin.[22] There is an Irish republican flute band named after him, the "Volunteer Kevin Barry Republican Flute Band", which operates out of the Calton area of the city.[citation needed] Barry's execution is mentioned in the folk song "Rifles of the I.R.A." written by Dominic Behan in 1968. A ballad bearing Barry's name, relating the story of his execution, has been sung by artists as diverse as Paul Robeson,[23] Leonard Cohen,[24] Lonnie Donegan, and The Dubliners. At the place where Kevin Barry was captured (North King Street/Church Street, Dublin), there are two blocks of flats named after him. -
-
 22cm x 28cm Quite hilarious now (but deadly serious at the time) political cartoon advertising the distinctions between a "True Gael" and a "West Briton",This was published in An Phoblacht in the 1930s,which was the media arm of Sinn Fein and its chief source of distributing propaganda. West Brit, an abbreviation of West Briton, is a derogatory term for an Irish person who is perceived as being anglophilic in matters of culture or politics.[1][2][3] West Britain is a description of Ireland emphasising it as under British influence.
22cm x 28cm Quite hilarious now (but deadly serious at the time) political cartoon advertising the distinctions between a "True Gael" and a "West Briton",This was published in An Phoblacht in the 1930s,which was the media arm of Sinn Fein and its chief source of distributing propaganda. West Brit, an abbreviation of West Briton, is a derogatory term for an Irish person who is perceived as being anglophilic in matters of culture or politics.[1][2][3] West Britain is a description of Ireland emphasising it as under British influence.History
"West Britain" was used with reference to the Acts of Union 1800 which united the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland into the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. Similarly "North Britain" for Scotland used after the 1603 Union of the Crowns and the Acts of Union 1707 connected it to the Kingdom of England ("South Britain"). In 1800 Thomas Grady, a Limerick unionist, published a collection of light verse called The West Briton, while an anti-union cartoon depicted an official offering bribes and proclaiming "God save the King & his Majesty's subjects of west Britain that is to be!"In 1801 the Latin description of George III on the Great Seal of the Realm was changed from MAGNÆ BRITANNIÆ FRANCIÆ ET HIBERNIÆ REX "King of Great Britain, France and Ireland" to BRITANNIARUM REX "King of the Britains", dropping the claim to the French throne and describing Great Britain and Ireland as "the Britains". Irish unionist MP Thomas Spring Rice (later Lord Monteagle of Brandon) said on 23 April 1834 in the House of Commons in opposing Daniel O'Connell's motion for Repeal of the Union, "I should prefer the name of West Britain to that of Ireland".Rice was derided by Henry Grattan later in the same debate: "He tells us, that he belongs to England, and designates himself as a West Briton."Daniel O'Connell himself used the phrase at a pro-Repeal speech in Dublin in February 1836:The people of Ireland are ready to become a portion of the empire, provided they be made so in reality and not in name alone; they are ready to become a kind of West Britons, if made so in benefits and justice; but if not, we are Irishmen again.
Here, O'Connell was hoping that Ireland would soon become as prosperous as "North Britain" had become after 1707, but if the Union did not deliver this, then some form of Irish home rule was essential. The Dublin administration as conducted in the 1830s was, by implication, an unsatisfactory halfway house between these two ideals, and as a prosperous "West Britain" was unlikely, home rule was the rational best outcome for Ireland. "West Briton" next came to prominence in a pejorative sense during the land struggle of the 1880s. D. P. Moran, who founded The Leader in 1900, used the term frequently to describe those who he did not consider sufficiently Irish. It was synonymous with those he described as "Sourfaces", who had mourned the death of the Queen Victoria in 1901. It included virtually all Church of Ireland Protestants and those Catholics who did not measure up to his definition of "Irish Irelanders". In 1907, Canon R. S. Ross-Lewin published a collection of loyal Irish poems under the pseudonym "A County of Clare West Briton", explaining the epithet in the foreword:Now, what is the exact definition and up-to-date meaning of that term? The holder of the title may be descended from O'Connors and O'Donelans and ancient Irish Kings. He may have the greatest love for his native land, desirous to learn the Irish language, and under certain conditions to join the Gaelic League. He may be all this, and rejoice in the victory of an Irish horse in the "Grand National", or an Irish dog at "Waterloo", or an Irish tug-of-war team of R.I.C. giants at Glasgow or Liverpool, but, if he does not at the same time hate the mere Saxon, and revel in the oft resuscitated pictures of long past periods, and the horrors of the penal laws he is a mere "West Briton", his Irish blood, his Irish sympathies go for nothing. He misses the chief qualifications to the ranks of the "Irish best", if he remains an imperialist, and sees no prospect of peace or happiness or return of prosperity in the event of the Union being severed. In this sense, Lord Roberts, Lord Charles Beresford and hundreds of others, of whom all Irishmen ought to be proud, are "West Britons", and thousands who have done nothing for the empire, under the just laws of which they live, who, perhaps, are mere descendants of Cromwell's soldiers, and even of Saxon lineage, with very little Celtic blood in their veins, are of the "Irish best".
Ernest Augustus Boyd's 1924 collection Portraits: real and imaginary included "A West Briton", which gave a table of West-Briton responses to keywords:-
-
Word Response Sinn Féin Pro-German Irish Vulgar England Mother-country Green Red Nationality Disloyalty Patriotism O.B.E. Self-determination Czecho-Slovakia
-
Contemporary usage
"Brit" meaning "British person", attested in 1884, is pejorative in Irish usage, though used as a value-neutral colloquialism in Great Britain. During the Troubles, among nationalists "the Brits" specifically meant the British Army in Northern Ireland. "West Brit" is today used by Irish people, chiefly within Ireland, to criticise a variety of perceived faults of other Irish people:- "Revisionism" (compare historical revisionism and historical negationism):
- Criticism of historical Irish uprisings. (State policy is to praise the patriotism of rebels up to the revolutionary period, while condemning later physical force republicans as antidemocratic.)
- highlighting perceived benefits of British influence in Ireland
- downplaying British culpability for historical disasters or atrocities
- Antipathy to Irish rebel songs.
- Anglophilia: following British popular culture; admiration for the British royal family; support for the Republic of Ireland rejoining the Commonwealth of Nations; highlighting positive British influence in the world, past or present
- Cultural cringe: appearing embarrassed by or disdainful of aspects of Irish culture, such as the Irish language, Hiberno-English, Gaelic games, or Irish traditional music
- Partitionism: Opposition or indifference to a United Ireland; neo-unionism
I'm an effete, urban Irishman. I was an avid radio listener as a boy, but it was the BBC, not RTÉ. I was a West Brit from the start. ... I'm a kind of child of the Pale. ... I think I was born to succeed here [in the UK]; I have much more freedom than I had in Ireland.
Wogan became a dual citizen of Ireland and the UK, and was eventually knighted by Queen Elizabeth II.Similar terms
Castle Catholic was applied more specifically by Republicans to middle-class Catholics assimilated into the pro-British establishment, after Dublin Castle, the centre of the British administration. Sometimes the exaggerated pronunciation spelling Cawtholic was used to suggest an accent imitative of British Received Pronunciation. These identified Catholic unionists whose involvement in the British system was the whole aim of O'Connell's Emancipation Act of 1829. Having and exercising their new legal rights under the Act, Castle Catholics were then rather illogically being pilloried by other Catholics for exercising them to the full. The old-fashioned word shoneen (from Irish: Seoinín, diminutive of Seán, thus literally 'Little John', and apparently a reference to John Bull) was applied to those who emulated the homes, habits, lifestyle, pastimes, clothes, and zeitgeist of the Protestant Ascendancy. P. W. Joyce's English As We Speak It in Ireland defines it as "a gentleman in a small way: a would-be gentleman who puts on superior airs." A variant since c. 1840, jackeen ('Little Jack'), was used in the countryside in reference to Dubliners with British sympathies; it is a pun, substituting the nickname Jack for John, as a reference to the Union Jack, the British flag. In the 20th century, jackeen took on the more generalized meaning of "a self-assertive worthless fellow".Antonyms
The term is sometimes contrasted with Little Irelander, a derogatory term for an Irish person who is seen as excessively nationalistic, Anglophobic and xenophobic, sometimes also practising a strongly conservative form of Roman Catholicism. This term was popularised by Seán Ó Faoláin."Little Englander" had been an equivalent term in British politics since about 1859. An antonym of jackeen, in its modern sense of an urban (and strongly British-influenced) Dubliner, is culchie, referring to a stereotypical Irish person of the countryside (and rarely pro-British). -
-
 Superb print depicting the spectacular and historic Rock of Cashel in the heart of Co Tipperary. 25cm x 35cm Killenaule Co Tipperary The Rock of Cashel , also known as Cashel of the Kings and St. Patrick's Rock, is a historic site located at Cashel, County Tipperary, Ireland
Superb print depicting the spectacular and historic Rock of Cashel in the heart of Co Tipperary. 25cm x 35cm Killenaule Co Tipperary The Rock of Cashel , also known as Cashel of the Kings and St. Patrick's Rock, is a historic site located at Cashel, County Tipperary, IrelandHistory
According to local legends, the Rock of Cashel originated in the Devil's Bit, a mountain 20 miles (30 km) north of Cashel when St. Patrick banished Satan from a cave, resulting in the Rock's landing in Cashel.[1] Cashel is reputed to be the site of the conversion of the King of Munster by St. Patrick in the 5th century. The Rock of Cashel was the traditional seat of the kings of Munster for several hundred years prior to the Norman invasion. In 1101, the King of Munster, Muirchertach Ua Briain, donated his fortress on the Rock to the Church. The picturesque complex has a character of its own and is one of the most remarkable collections of Celtic art and medieval architecture to be found anywhere in Europe.Few remnants of the early structures survive; the majority of buildings on the current site date from the 12th and 13th centuries.Buildings on the Rock
The oldest and tallest of the buildings is the well preserved round tower (28 metres, or 90 feet), dating from c.1100. Its entrance is 12 feet (3.7 m) from the ground, necessitated by a shallow foundation (about 3 feet) typical of round towers. The tower was built using the dry stone method. Modern conservationists have filled in some of the tower with mortar for safety reasons. Cormac's Chapel, the chapel of King Cormac Mac Carthaigh, was begun in 1127 and consecrated in 1134. It is a sophisticated structure, with vaulted ceilings and wide arches, drawing on contemporary European architecture and infusing unique native elements. The Irish Abbot of Regensburg, Dirmicius of Regensburg, sent two of his carpenters to help in the work and the twin towers on either side of the junction of the nave and chancel are strongly suggestive of their Germanic influence, as this feature is otherwise unknown in Ireland. Other notable features of the building include interior and exterior arcading, a barrel-vaulted roof, a carved tympanum over both doorways, the magnificent north doorway and chancel arch and the oldest stairs in Ireland. It contains one of the best-preserved Irish frescoes from this time period. The Chapel was constructed primarily of sandstone which has become waterlogged over the centuries, significantly damaging the interior frescoes. Restoration and preservation required the chapel be completely enclosed in a rain-proof structure with interior dehumidifiers to dry out the stone. It is now open for limited tours to the public. The Cathedral, built between 1235 and 1270, is an aisleless building of cruciform plan, having a central tower and terminating westwards in a massive residential castle. The Hall of the Vicars Choral was built in the 15th century. The vicars choral were laymen (sometimes minor canons) appointed to assist in chanting the cathedral services. At Cashel, there were originally eight vicars choral with their own seal. This was later reduced to five honorary vicars choral who appointed singing-men as their deputies, a practice which continued until 1836. The restoration of the Hall was undertaken by the Office of Public Works as a project in connection with the European Architectural Heritage Year, 1975. Through it visitors now enter the site. In 1647, during the Irish Confederate Wars, Cashel was sacked by English Parliamentarian troops under Murrough O'Brien, 1st Earl of Inchiquin. The Irish Confederate troops there were massacred, as were the Catholic clergy, including Theobald Stapleton. Inchiquin's troops looted or destroyed many important religious artefacts. In 1749, the main cathedral roof was removed by Arthur Price, the Anglican Archbishop of Cashel.] Today, what remains of the Rock of Cashel has become a tourist attraction. Price's decision to remove the roof on what had been called the jewel among Irish church buildings was criticised before and since. Queen Elizabeth II visited the Rock of Cashel during her 2011 visit to Ireland. The entire plateau on which the buildings and graveyard lie is walled. In the grounds around the buildings an extensive graveyard includes a number of high crosses. Scully's Cross, one of the largest and most famous high crosses here, originally constructed in 1867 to commemorate the Scully family, was destroyed in 1976 when lightning struck a metal rod that ran the length of the cross. The remains of the top of the cross now lie at the base of the cross adjacent to the rock wall.Burials
-
 36cm x 29cm The An Post GAA Hurling Team of the Millennium was chosen in 2000 to comprise, as a fifteen-member side divided as one goalkeeper, three full-backs, three half-backs, two midfielders, three half-forwards and three full-forwards, the best hurling team of all-time. The team, announced by GAA President Seán McCague on 24 July 2000 at a special function in Croke Park, was selected by a special committee, comprising five past GAA presidents - Joe McDonagh, Con Murphy, Paddy Buggy, Pat Fanning and Séamus Ó Riain - as well as GAA director-general Liam Mulvihill and four Gaelic games journalists: Paddy Downey, Mick Dunne, Seán Óg Ó Ceallacháin and Jim O'Sullivan. The initiative was sponsored by An Post, who issued special commemorative stamps of the millennium team members.
36cm x 29cm The An Post GAA Hurling Team of the Millennium was chosen in 2000 to comprise, as a fifteen-member side divided as one goalkeeper, three full-backs, three half-backs, two midfielders, three half-forwards and three full-forwards, the best hurling team of all-time. The team, announced by GAA President Seán McCague on 24 July 2000 at a special function in Croke Park, was selected by a special committee, comprising five past GAA presidents - Joe McDonagh, Con Murphy, Paddy Buggy, Pat Fanning and Séamus Ó Riain - as well as GAA director-general Liam Mulvihill and four Gaelic games journalists: Paddy Downey, Mick Dunne, Seán Óg Ó Ceallacháin and Jim O'Sullivan. The initiative was sponsored by An Post, who issued special commemorative stamps of the millennium team members.Controversy
While universal agreement on such a team would prove impossible, the selection committee came in for some criticism regarding omissions and changes from the earlier GAA Hurling Team of the Century. Kilkenny's D. J. Carey was seen as a shock omission from the team. As the holder of a then record seven All-Stars, Carey, whose inter-county career began in 1989, was seen as one of the greatest goal-scorers of his era and was hotly tipped to get one of the half-forward spots for which he was nominated. The 1990s were regarded as a golden age of hurling with many new teams emerging, however, this was not reflected in the team. Clare's Brian Lohan had been tipped for full-back but Wexford's Nick O'Donnell held on. There were no places for any of the Clare team that emerged to win two championships in the nineties. Brian Whelehan was the only player from the previous 20 years to make the team. An absence of players from Galway also sparked off major controversy in that county where the selection committee were accused of belittling the county by not recognising any of its heroes. There was anger too in Wexford over the dropping of full-forward Nicky Rackard from the Team of the Century. Former midfielder Dave Bernie, who won an All-Ireland medal in 1968, when Rackard was a selector, said Wexford fans were stunned by the news he had not been included. -
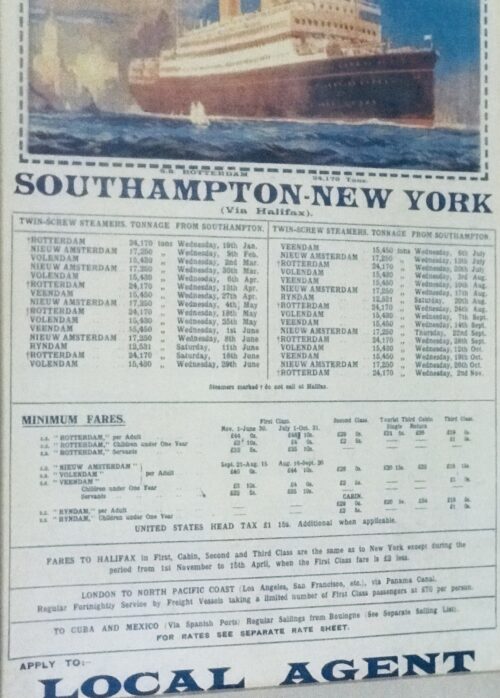
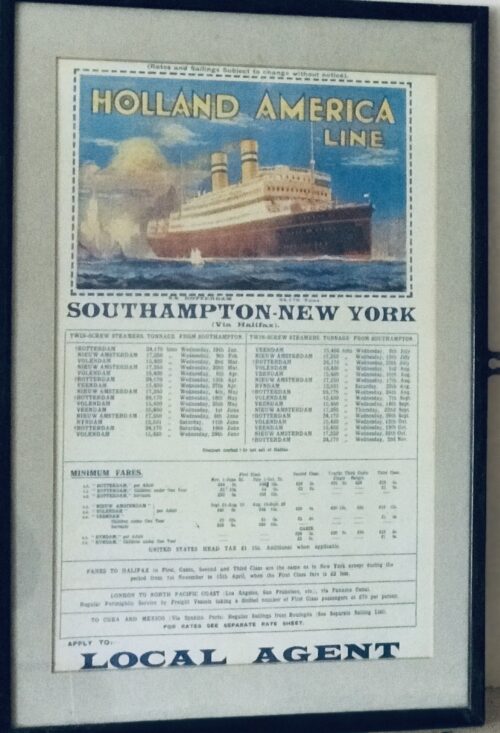 50cm x 35cm Birr Co Offaly "The Holland-America Line, a steamship company with passenger and freight steamers plying between Rotterdam and New York, is the only steamship line carrying emigrants from the Netherlands to the United States of America. Emigrants from the interior of the continent of Europe, who purchase their steamship tickets from the branch offices of the Holland-America Line in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and Italy, arrive in Rotterdam on international trains, in which several cars have been set apart for their accommodation, from five to six days before the departure of the steamer on which they expect to sail; while emigrants from parts not far distant from this city, like southern Germany and the interior of the Netherlands, arrive at Rotterdam by train and river boat until the day previous to the departure of the steamer. All emigrants for the Holland-America Line are met at the railway station and boat landing at Rotterdam by runners of the line, who conduct them, immediately upon arrival, per steam tug to the NASM Hotel, the emigrant hotel owned and controlled by the Holland-America Line and situated opposite to the line's wharf. Here the emigrants remain until the departure of the steamer on which they are to sail or, in case they should be found undesirable immigrants by one of the medical inspectors, by the steamship company, or by the consul-general or vice-consul-general, until the time that they are returned again to the countries whence they came. The NASM Hotel was designed and built exclusively for the accommodation of the immigrants traveling per Holland-America Line. In the construction, besides the comfort of the emigrants, the sanitary requirements for a building of its kind have been given due consideration. The dining rooms and coffee or conversation rooms are, though necessarily somewhat sober in appearance in order to insure cleanliness, bright, spacious, and pleasant. The dormitories are spacious, clean, and airy. Sleeping apartments, open on top, each containing from four to six iron berths, similar to those used in the steerage of the company's twin-screw steamers, have been partitioned off along the walls. This gives the immigrants the desired privacy, besides the advantage of being together with the members of their family in one apartment. Between the partitions a wide space is left in the center of the dormitories for chairs, tables, etc., while windows and ventilators provide light and air on every side. There are separate dormitories for families, for men, and for women. Spacious wash and bath rooms, with modern appointments, are located on the vestibules conveniently close to each dormitory. The hotel has been constructed in such a manner that, should the need at any time arise, it would be possible to quarantine 800 passengers within its walls as effectually as though they were on shipboard. This possibility of isolation before sailing is a great sanitary advantage. With reference to this hotel, Consul Listoe wrote in his dispatch to the Department of State, under date of April 6, 1900: The company's claim that it is furnishing good lodging and board for emigrants at a low figure and at the same time protecting them against low, boardinghouse runners and sharpers, who would fleece them, is correct, and the Holland America Line is entitled to a great deal of credit for the humane manner in which it treats and cares for its emigrants. What is of more importance, though, from a United States point of view, is the facilities furnished the examining physician at the NASM Hotel for inspecting the emigrants as well as the arrangements for cleaning, bathing, and disinfecting the latter, and taking other sanitary measures in connection with those prospective citizens of the United States. At the hotel the emigrants are, at the instance of the Holland America Line, daily subjected to a medical inspection by a Dutch physician in the employ of the line. One day before sailing the emigrants are inspected at the hotel by a prominent Rotterdam oculist, engaged by the steamship company for its own protection,' to prevent emigrants suffering from infectious eye diseases sailing on its steamers. As the medical inspections referred to are not those prescribed by the United States Quarantine Regulations, they are not witnessed by a consular officer. The work of consular inspection is carried on as follows: The day previous to the departure of a passenger steamer, the baggage of all steerage passengers is inspected by the consul-general or his deputy. Among this baggage large quantities of mildewed and otherwise spoiled eatables are found. These are taken out, this having been the practice of the Marine-Hospital surgeon formerly detailed at Rotterdam. All feather pillows and beds are taken from the baggage and undergo a steam disinfection of 1000 Cel. As many as 60 beds can be disinfected at the same time by the Holland-America Line's disinfection plants, and each disinfection will require about one and one-half hours, viz, half an hour for getting up the required steam heat, half an hour for the disinfection, and half an hour for drying purposes. When there are 200 beds or more to be disinfected, which is frequently the case, supervision of the disinfection will keep a consular officer engaged for several hours. The inspection of the baggage takes from two to four hours, according to the number of packages to be inspected. The last medical and general inspection of the emigrants at which the consul-general or vice-consul-general is present is the inspection prescribed by the Quarantine Regulations, page I5, paragraph 5. It takes place in the hotel of the Holland-American Line or in the line's covered warehouse and· begins from three to six hours before the departure of the steamer. The emigrants pass in single file before the ship's surgeon, an American physician, who inspects them in the presence of the consular officer, who, for his part, looks over their inspection cards, prescribed by the Quarantine Regulations, page 19, paragraph 40, and stamps the same with a consular rubber seal, for all emigrants approved of. There are also present an officer of the State commission controlling the transit of emigrants through the Netherlands, who tallies their numbers, and a Rotterdam police officer, who watches for fugitives from justice among them reported to the Netherlands police authorities. Immediately after the inspection, the emigrants in possession of inspection cards bearing the consular stamp board the steamer and enter the steerage, which has previously been inspected by the consul. A few minutes before departure, after looking over the freight manifests of the vessel to see if all the requirements of the Quarantine Regulations and of the regulations of the Department of Agriculture have been complied with reference to disinfection certificates and certificates of healthy origin, the bill of health is issued. The emigrants are vaccinated by the ship's surgeon as soon as practicable after the departure of the vessel. Of late years no emigrants from infected districts have passed through Rotterdam on their way to the United States. Should such occur at any time, then they can be effectually quarantined in the hotel of the Holland-America Line for the periods prescribed by the Quarantine Regulations. AIRE H. VOORWINDEN, Vice and Deputy Consul- Gtneral. In a letter by Mr. Voorwinden to Mr. Peirce. CONSULATE-GENERAL, UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, Rotterdam, Netherlands, September 23 1903.
50cm x 35cm Birr Co Offaly "The Holland-America Line, a steamship company with passenger and freight steamers plying between Rotterdam and New York, is the only steamship line carrying emigrants from the Netherlands to the United States of America. Emigrants from the interior of the continent of Europe, who purchase their steamship tickets from the branch offices of the Holland-America Line in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and Italy, arrive in Rotterdam on international trains, in which several cars have been set apart for their accommodation, from five to six days before the departure of the steamer on which they expect to sail; while emigrants from parts not far distant from this city, like southern Germany and the interior of the Netherlands, arrive at Rotterdam by train and river boat until the day previous to the departure of the steamer. All emigrants for the Holland-America Line are met at the railway station and boat landing at Rotterdam by runners of the line, who conduct them, immediately upon arrival, per steam tug to the NASM Hotel, the emigrant hotel owned and controlled by the Holland-America Line and situated opposite to the line's wharf. Here the emigrants remain until the departure of the steamer on which they are to sail or, in case they should be found undesirable immigrants by one of the medical inspectors, by the steamship company, or by the consul-general or vice-consul-general, until the time that they are returned again to the countries whence they came. The NASM Hotel was designed and built exclusively for the accommodation of the immigrants traveling per Holland-America Line. In the construction, besides the comfort of the emigrants, the sanitary requirements for a building of its kind have been given due consideration. The dining rooms and coffee or conversation rooms are, though necessarily somewhat sober in appearance in order to insure cleanliness, bright, spacious, and pleasant. The dormitories are spacious, clean, and airy. Sleeping apartments, open on top, each containing from four to six iron berths, similar to those used in the steerage of the company's twin-screw steamers, have been partitioned off along the walls. This gives the immigrants the desired privacy, besides the advantage of being together with the members of their family in one apartment. Between the partitions a wide space is left in the center of the dormitories for chairs, tables, etc., while windows and ventilators provide light and air on every side. There are separate dormitories for families, for men, and for women. Spacious wash and bath rooms, with modern appointments, are located on the vestibules conveniently close to each dormitory. The hotel has been constructed in such a manner that, should the need at any time arise, it would be possible to quarantine 800 passengers within its walls as effectually as though they were on shipboard. This possibility of isolation before sailing is a great sanitary advantage. With reference to this hotel, Consul Listoe wrote in his dispatch to the Department of State, under date of April 6, 1900: The company's claim that it is furnishing good lodging and board for emigrants at a low figure and at the same time protecting them against low, boardinghouse runners and sharpers, who would fleece them, is correct, and the Holland America Line is entitled to a great deal of credit for the humane manner in which it treats and cares for its emigrants. What is of more importance, though, from a United States point of view, is the facilities furnished the examining physician at the NASM Hotel for inspecting the emigrants as well as the arrangements for cleaning, bathing, and disinfecting the latter, and taking other sanitary measures in connection with those prospective citizens of the United States. At the hotel the emigrants are, at the instance of the Holland America Line, daily subjected to a medical inspection by a Dutch physician in the employ of the line. One day before sailing the emigrants are inspected at the hotel by a prominent Rotterdam oculist, engaged by the steamship company for its own protection,' to prevent emigrants suffering from infectious eye diseases sailing on its steamers. As the medical inspections referred to are not those prescribed by the United States Quarantine Regulations, they are not witnessed by a consular officer. The work of consular inspection is carried on as follows: The day previous to the departure of a passenger steamer, the baggage of all steerage passengers is inspected by the consul-general or his deputy. Among this baggage large quantities of mildewed and otherwise spoiled eatables are found. These are taken out, this having been the practice of the Marine-Hospital surgeon formerly detailed at Rotterdam. All feather pillows and beds are taken from the baggage and undergo a steam disinfection of 1000 Cel. As many as 60 beds can be disinfected at the same time by the Holland-America Line's disinfection plants, and each disinfection will require about one and one-half hours, viz, half an hour for getting up the required steam heat, half an hour for the disinfection, and half an hour for drying purposes. When there are 200 beds or more to be disinfected, which is frequently the case, supervision of the disinfection will keep a consular officer engaged for several hours. The inspection of the baggage takes from two to four hours, according to the number of packages to be inspected. The last medical and general inspection of the emigrants at which the consul-general or vice-consul-general is present is the inspection prescribed by the Quarantine Regulations, page I5, paragraph 5. It takes place in the hotel of the Holland-American Line or in the line's covered warehouse and· begins from three to six hours before the departure of the steamer. The emigrants pass in single file before the ship's surgeon, an American physician, who inspects them in the presence of the consular officer, who, for his part, looks over their inspection cards, prescribed by the Quarantine Regulations, page 19, paragraph 40, and stamps the same with a consular rubber seal, for all emigrants approved of. There are also present an officer of the State commission controlling the transit of emigrants through the Netherlands, who tallies their numbers, and a Rotterdam police officer, who watches for fugitives from justice among them reported to the Netherlands police authorities. Immediately after the inspection, the emigrants in possession of inspection cards bearing the consular stamp board the steamer and enter the steerage, which has previously been inspected by the consul. A few minutes before departure, after looking over the freight manifests of the vessel to see if all the requirements of the Quarantine Regulations and of the regulations of the Department of Agriculture have been complied with reference to disinfection certificates and certificates of healthy origin, the bill of health is issued. The emigrants are vaccinated by the ship's surgeon as soon as practicable after the departure of the vessel. Of late years no emigrants from infected districts have passed through Rotterdam on their way to the United States. Should such occur at any time, then they can be effectually quarantined in the hotel of the Holland-America Line for the periods prescribed by the Quarantine Regulations. AIRE H. VOORWINDEN, Vice and Deputy Consul- Gtneral. In a letter by Mr. Voorwinden to Mr. Peirce. CONSULATE-GENERAL, UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, Rotterdam, Netherlands, September 23 1903. -
Out of stock
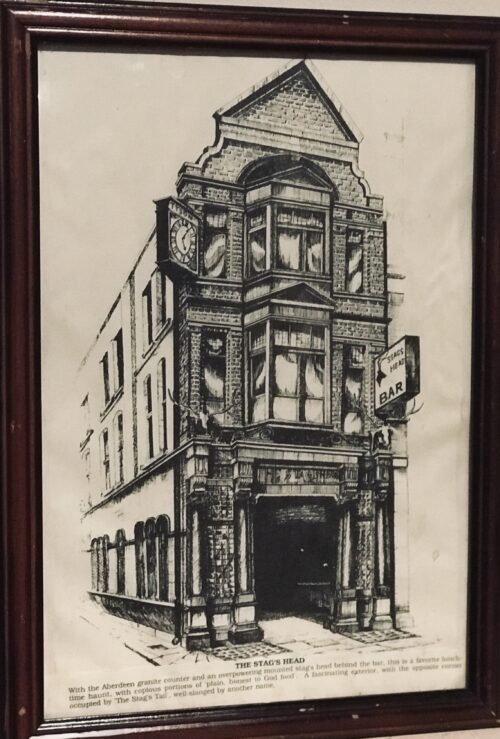
 An attractive drawing of the legendary Stags Head Public House in Dublin."With the Aberdeen granite counter and an overpowering mounted stag's head behind the bar,this is a favourite lunch-time haunt, with copious portions of 'plain ,honest to god food'.A fascinating exterior, with the opposite corner occupied by 'The Stag's Tail",well slanged by another name. 40cm x 30cm Dame St Dublin The Stag's Head is a pub on the corner of Dame Court and Dame Lane in Dublin, Ireland.Records of a pub on the site of the Stag's Head date to 1770 (original construction by a Mr. Tyson) and 1895 (extensive rebuilding).The pub is known for the preservation of its Victorian interior and the restored advertising mosaic on the footpath on Dame Street, some distance from the pub's doors.The name "Tyson", and Mr. Tyson's initials, decorate the old clock and the wrought-iron of the exterior. Mr. Tyson is also believed to have contributed to the construction of a permanent pavement over Dame Lane. There is a stuffed fox on the ground floor snug of the Stag's Head, while a large stag's head decorates the main bar. The pub has appeared in many films, notably A Man of No Importance, starring Albert Finney and Educating Rita starring Michael Caine and Julie Walters. Filming for Penny Dreadful also took place both inside and outside the pub in February 2014. The establishment was sold in 2005 for €5.8M and bought by the Louis Fitzgerald Group. A number of changes have made to the pub since the sale, most notably the introduction of a television set to the bar area.
An attractive drawing of the legendary Stags Head Public House in Dublin."With the Aberdeen granite counter and an overpowering mounted stag's head behind the bar,this is a favourite lunch-time haunt, with copious portions of 'plain ,honest to god food'.A fascinating exterior, with the opposite corner occupied by 'The Stag's Tail",well slanged by another name. 40cm x 30cm Dame St Dublin The Stag's Head is a pub on the corner of Dame Court and Dame Lane in Dublin, Ireland.Records of a pub on the site of the Stag's Head date to 1770 (original construction by a Mr. Tyson) and 1895 (extensive rebuilding).The pub is known for the preservation of its Victorian interior and the restored advertising mosaic on the footpath on Dame Street, some distance from the pub's doors.The name "Tyson", and Mr. Tyson's initials, decorate the old clock and the wrought-iron of the exterior. Mr. Tyson is also believed to have contributed to the construction of a permanent pavement over Dame Lane. There is a stuffed fox on the ground floor snug of the Stag's Head, while a large stag's head decorates the main bar. The pub has appeared in many films, notably A Man of No Importance, starring Albert Finney and Educating Rita starring Michael Caine and Julie Walters. Filming for Penny Dreadful also took place both inside and outside the pub in February 2014. The establishment was sold in 2005 for €5.8M and bought by the Louis Fitzgerald Group. A number of changes have made to the pub since the sale, most notably the introduction of a television set to the bar area. -
 32cm x 25cm Charles Stewart Parnell (1846-1891) will be remembered as one of the most iconic and indeed controversial politicians in Irish history.MP and Leader of the Irish Parliamentary or Home Rule Party from1882 to 1891 until revelations of his adulterous love affair with Kitty O'Shea forced his resignation.He died shortly afterwards from pneumonia in the arms of his newly divorced and remarried wife Katherine.His death was considered to be a direct result of the stresses he endured because of the Victorian era scandal and his subsequent funeral at Glasnevin Cemetery in Dublin was attended by more than 200000 people.His notability was such that his gravestone of unhewn Wicklow granite, erected in 1940,reads only Parnell. This faithful portrayal of Parnell,well over 130 years old, by the artist JG Wills dates to 1884 and is a beautiful homage to the "uncrowned king of Ireland".
32cm x 25cm Charles Stewart Parnell (1846-1891) will be remembered as one of the most iconic and indeed controversial politicians in Irish history.MP and Leader of the Irish Parliamentary or Home Rule Party from1882 to 1891 until revelations of his adulterous love affair with Kitty O'Shea forced his resignation.He died shortly afterwards from pneumonia in the arms of his newly divorced and remarried wife Katherine.His death was considered to be a direct result of the stresses he endured because of the Victorian era scandal and his subsequent funeral at Glasnevin Cemetery in Dublin was attended by more than 200000 people.His notability was such that his gravestone of unhewn Wicklow granite, erected in 1940,reads only Parnell. This faithful portrayal of Parnell,well over 130 years old, by the artist JG Wills dates to 1884 and is a beautiful homage to the "uncrowned king of Ireland". -

 34cm x 34cm The DMC DeLorean is a rear-engine two-passenger sports car manufactured and marketed by John DeLorean's DeLorean Motor Company (DMC) for the American market from 1981 until 1983—ultimately the only car brought to market by the fledgling company. The DeLorean is sometimes referred to by its internal DMC pre-production designation, DMC-12. However, the DMC-12 name was never used in sales or marketing materials for the production model. Designed by Giorgetto Giugiaro and noted for its gull-wing doors and brushed stainless-steel outer body panels, the sports car was also noted for a lack of power and performance incongruous with its looks and price. Though its production was short-lived, the DeLorean became widely known after it was featured as the time machine in the Back to the Future films. With the first production car completed on January 21, 1981, the design incorporated numerous minor revisions to the hood, wheels and interior before production ended in late December 1982, shortly after DMC filed for bankruptcy and after total production reached about 9,000 units. Despite the car having a reputation for poor build quality and an unsatisfactory driving experience, the DeLorean continues to have a strong following driven in part by the popularity of Back to the Future. 6,500 DeLoreans were estimated to still be on the road as of 2015.
34cm x 34cm The DMC DeLorean is a rear-engine two-passenger sports car manufactured and marketed by John DeLorean's DeLorean Motor Company (DMC) for the American market from 1981 until 1983—ultimately the only car brought to market by the fledgling company. The DeLorean is sometimes referred to by its internal DMC pre-production designation, DMC-12. However, the DMC-12 name was never used in sales or marketing materials for the production model. Designed by Giorgetto Giugiaro and noted for its gull-wing doors and brushed stainless-steel outer body panels, the sports car was also noted for a lack of power and performance incongruous with its looks and price. Though its production was short-lived, the DeLorean became widely known after it was featured as the time machine in the Back to the Future films. With the first production car completed on January 21, 1981, the design incorporated numerous minor revisions to the hood, wheels and interior before production ended in late December 1982, shortly after DMC filed for bankruptcy and after total production reached about 9,000 units. Despite the car having a reputation for poor build quality and an unsatisfactory driving experience, the DeLorean continues to have a strong following driven in part by the popularity of Back to the Future. 6,500 DeLoreans were estimated to still be on the road as of 2015. -

 30cm x 25cm Cork Michael Collins was a revolutionary, soldier and politician who was a leading figure in the early-20th-century Irish struggle for independence. He was Chairman of the Provisional Government of the Irish Free State from January 1922 until his assassination in August 1922. Collins was born in Woodfield, County Cork, the youngest of eight children, and his family had republican connections reaching back to the 1798 rebellion. He moved to London in 1906, to become a clerk in the Post Office Savings Bank at Blythe House. He was a member of the London GAA, through which he became associated with the Irish Republican Brotherhood and the Gaelic League. He returned to Ireland in 1916 and fought in the Easter Rising. He was subsequently imprisoned in the Frongoch internment camp as a prisoner of war, but was released in December 1916. Collins rose through the ranks of the Irish Volunteers and Sinn Féin after his release from Frongoch. He became a Teachta Dála for South Cork in 1918, and was appointed Minister for Finance in the First Dáil. He was present when the Dáil convened on 21 January 1919 and declared the independence of the Irish Republic. In the ensuing War of Independence, he was Director of Organisation and Adjutant General for the Irish Volunteers, and Director of Intelligence of the Irish Republican Army. He gained fame as a guerrilla warfare strategist, planning and directing many successful attacks on British forces, such as the assassination of key British intelligence agents in November 1920. After the July 1921 ceasefire, Collins and Arthur Griffith were sent to London by Éamon de Valera to negotiate peace terms. The resulting Anglo-Irish Treaty established the Irish Free State but depended on an Oath of Allegiance to the Crown, a condition that de Valera and other republican leaders could not reconcile with. Collins viewed the Treaty as offering "the freedom to achieve freedom", and persuaded a majority in the Dáil to ratify the Treaty. A provisional government was formed under his chairmanship in early 1922 but was soon disrupted by the Irish Civil War, in which Collins was commander-in-chief of the National Army. He was shot and killed in an ambush by anti-Treaty on 22nd August 1922.
30cm x 25cm Cork Michael Collins was a revolutionary, soldier and politician who was a leading figure in the early-20th-century Irish struggle for independence. He was Chairman of the Provisional Government of the Irish Free State from January 1922 until his assassination in August 1922. Collins was born in Woodfield, County Cork, the youngest of eight children, and his family had republican connections reaching back to the 1798 rebellion. He moved to London in 1906, to become a clerk in the Post Office Savings Bank at Blythe House. He was a member of the London GAA, through which he became associated with the Irish Republican Brotherhood and the Gaelic League. He returned to Ireland in 1916 and fought in the Easter Rising. He was subsequently imprisoned in the Frongoch internment camp as a prisoner of war, but was released in December 1916. Collins rose through the ranks of the Irish Volunteers and Sinn Féin after his release from Frongoch. He became a Teachta Dála for South Cork in 1918, and was appointed Minister for Finance in the First Dáil. He was present when the Dáil convened on 21 January 1919 and declared the independence of the Irish Republic. In the ensuing War of Independence, he was Director of Organisation and Adjutant General for the Irish Volunteers, and Director of Intelligence of the Irish Republican Army. He gained fame as a guerrilla warfare strategist, planning and directing many successful attacks on British forces, such as the assassination of key British intelligence agents in November 1920. After the July 1921 ceasefire, Collins and Arthur Griffith were sent to London by Éamon de Valera to negotiate peace terms. The resulting Anglo-Irish Treaty established the Irish Free State but depended on an Oath of Allegiance to the Crown, a condition that de Valera and other republican leaders could not reconcile with. Collins viewed the Treaty as offering "the freedom to achieve freedom", and persuaded a majority in the Dáil to ratify the Treaty. A provisional government was formed under his chairmanship in early 1922 but was soon disrupted by the Irish Civil War, in which Collins was commander-in-chief of the National Army. He was shot and killed in an ambush by anti-Treaty on 22nd August 1922. -
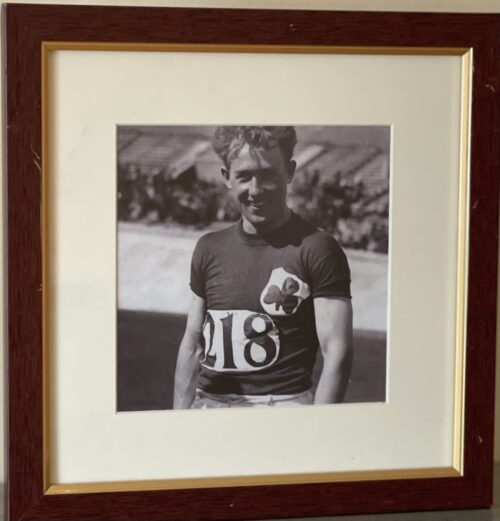
 30cm x 30cm Patrick "Pat" O'Callaghan (28 January 1906 – 1 December 1991) was an Irish athlete and Olympic gold medallist. He was the first athlete from Ireland to win an Olympic medal under the Irish flag rather than the British. In sport he then became regarded as one of Ireland's greatest-ever athletes.
30cm x 30cm Patrick "Pat" O'Callaghan (28 January 1906 – 1 December 1991) was an Irish athlete and Olympic gold medallist. He was the first athlete from Ireland to win an Olympic medal under the Irish flag rather than the British. In sport he then became regarded as one of Ireland's greatest-ever athletes.Early and private life
Pat O'Callaghan was born in the townland of Knockaneroe, near Kanturk, County Cork, on 28 January 1906, the second of three sons born to Paddy O'Callaghan, a farmer, and Jane Healy. He began his education at the age of two at Derrygalun national school. O'Callaghan progressed to secondary school in Kanturk and at the age of fifteen he won a scholarship to the Patrician Academy in Mallow. During his year in the Patrician Academy he cycled the 32-mile round trip from Derrygalun every day and he never missed a class. O'Callaghan subsequently studied medicine at the Royal College of Surgeons in Dublin. Following his graduation in 1926 he joined the Royal Air Force Medical Service. He returned to Ireland in 1928 and set up his own medical practice in Clonmel, County Tipperary where he worked until his retirement in 1984.O'Callaghan was also a renowned field sports practitioner, greyhound trainer and storyteller.Sporting career
Early sporting life
O’Callaghan was born into a family that had a huge interest in a variety of different sports. His uncle, Tim Vaughan, was a national sprint champion and played Gaelic football with Cork in 1893. O’Callaghan's eldest brother, Seán, also enjoyed football as well as winning a national 440 yards hurdles title, while his other brother, Con, was also regarded as a gifted runner, jumper and thrower. O’Callaghan's early sporting passions included hunting, poaching and Gaelic football. He was regarded as an excellent midfielder on the Banteer football team, while he also lined out with the Banteer hurling team. At university in Dublin O’Callaghan broadened his sporting experiences by joining the local senior rugby club. This was at a time when the Gaelic Athletic Association ‘ban’ forbade players of Gaelic games from playing "foreign sports". It was also in Dublin that O’Callaghan first developed an interest in hammer-throwing. In 1926, he returned to his native Duhallow where he set up a training regime in hammer-throwing. Here he fashioned his own hammer by boring a one-inch hole through a 16 lb shot and filling it with the ball-bearing core of a bicycle pedal. He also set up a throwing circle in a nearby field where he trained. In 1927, O’Callaghan returned to Dublin where he won that year's hammer championship with a throw of 142’ 3”. In 1928, he retained his national title with a throw of 162’ 6”, a win which allowed him to represent the Ireland at the forthcoming Olympic Games in Amsterdam. On the same day, O’Callaghan's brother, Con, won the shot put and the decathlon and also qualified for the Olympic Games. Between winning his national title and competing in the Olympic Games O’Callaghan improved his throwing distance by recording a distance of 166’ 11” at the Royal Ulster ConstabularySports in Belfast.1928 Olympic Games
In the summer of 1928, the three O’Callaghan brothers paid their own fares when travelling to the Olympic Games in Amsterdam. Pat O’Callaghan finished in sixth place in the preliminary round and started the final with a throw of 155’ 9”. This put him in third place behind Ossian Skiöld of Sweden, but ahead of Malcolm Nokes, the favourite from Great Britain. For his second throw, O’Callaghan used the Swede's own hammer and recorded a throw of 168’ 7”. This was 4’ more than Skoeld's throw and resulted in a first gold medal for O’Callaghan and for Ireland. The podium presentation was particularly emotional as it was the first time at an Olympic Games that the Irish tricolour was raised and Amhrán na bhFiann was played.Success in Ireland
After returning from the Olympic Games, O’Callaghan cemented his reputation as a great athlete with additional successes between 1929 and 1932. In the national championships of 1930 he won the hammer, shot-putt, 56 lbs without follow, 56 lbs over-the-bar, discus and high jump. In the summer of 1930, O’Callaghan took part in a two-day invitation event in Stockholm where Oissian Skoeld was expected to gain revenge on the Irishman for the defeat in Amsterdam. On the first day of the competition, Skoeld broke his own European record with his very first throw. O’Callaghan followed immediately and overtook him with his own first throw and breaking the new record. On the second day of the event both O’Callaghan and Skoeld were neck-and-neck, when the former, with his last throw, set a new European record of 178’ 8” to win.1932 Summer Olympics
By the time the 1932 Summer Olympics came around O’Callaghan was regularly throwing the hammer over 170 feet. The Irish team were much better organised on that occasion and the whole journey to Los Angeles was funded by a church-gate collection. Shortly before departing on the 6,000-mile boat and train journey across the Atlantic O’Callaghan collected a fifth hammer title at the national championships. On arrival in Los Angeles O’Callaghan's preparations of the defence of his title came unstuck. The surface of the hammer circle had always been of grass or clay and throwers wore field shoes with steel spikes set into the heel and sole for grip. In Los Angeles, however, a cinder surface was to be provided. The Olympic Committee of Ireland had failed to notify O’Callaghan of this change. Consequently, he came to the arena with three pairs of spiked shoes for a grass or clay surface and time did not permit a change of shoe. He wore his shortest spikes, but found that they caught in the hard gritty slab and impeded his crucial third turn. In spite of being severely impeded, he managed to qualify for the final stage of the competition with his third throw of 171’ 3”. While the final of the 400m hurdles was delayed, O’Callaghan hunted down a hacksaw and a file in the groundskeeper's shack and he cut off the spikes. O’Callaghan's second throw reached a distance of 176’ 11”, a result which allowed him to retain his Olympic title. It was Ireland's second gold medal of the day as Bob Tisdall had earlier won a gold medal in the 400m hurdles.Retirement
Due to the celebrations after the Olympic Games O’Callaghan didn't take part in the national athletic championships in Ireland in 1933. In spite of that he still worked hard on his training and he experimented with a fourth turn to set a new European record at 178’ 9”. By this stage O’Callaghan was rated as the top thrower in the world by the leading international sports journalists. In the early 1930s controversy raged between the British AAA and the National Athletic and Cycling Association of Ireland (NACAI). The British AAA claimed jurisdiction in Northern Ireland while the NACAI claimed jurisdiction over the entire island of Ireland regardless of political division. The controversy came to a head in the lead-up to the 1936 Summer Olympics when the IAAF finally disqualified the NACAI. O’Callaghan remained loyal to the NACAI, a decision which effectively brought an end to his international athletic career. No Irish team travelled to the 1936 Olympic Games, however O’Callaghan travelled to Berlin as a private spectator. After Berlin, O’Callaghan's international career was over. He declined to join the new Irish Amateur Athletics Union (IAAU) or subsequent IOC recognised Amateur Athletics Union of Eire (AAUE) and continued to compete under NACAI rules. At Fermoy in 1937 he threw 195’ 4” – more than seven feet ahead of the world record set by his old friend Paddy 'Chicken' Ryan in 1913. This record, however, was not ratified by the AAUE or the IAAF. In retirement O’Callaghan remained interested in athletics. He travelled to every Olympic Games up until 1988 and enjoyed fishing and poaching in Clonmel. He died on 1 December 1991.Legacy
O'Callaghan was the flag bearer for Ireland at the 1932 Olympics. In 1960, he became the first person to receive the Texaco Hall of Fame Award. He was made a Freeman of Clonmel in 1984, and was honorary president of Commercials Gaelic Football Club. The Dr. Pat O'Callaghan Sports Complex at Cashel Rd, Clonmel which is the home of Clonmel Town Football Club is named after him, and in January 2007 his statue was raised in Banteer, County Cork. -
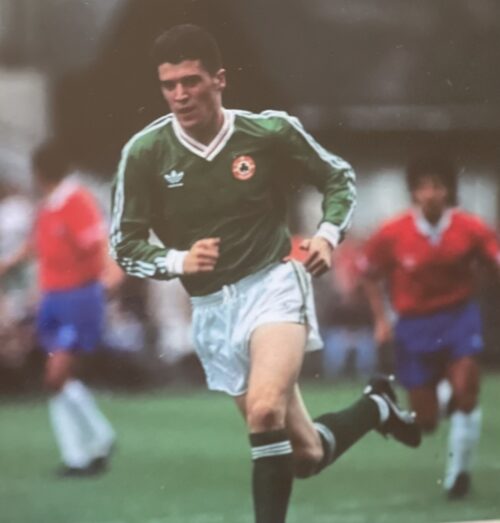
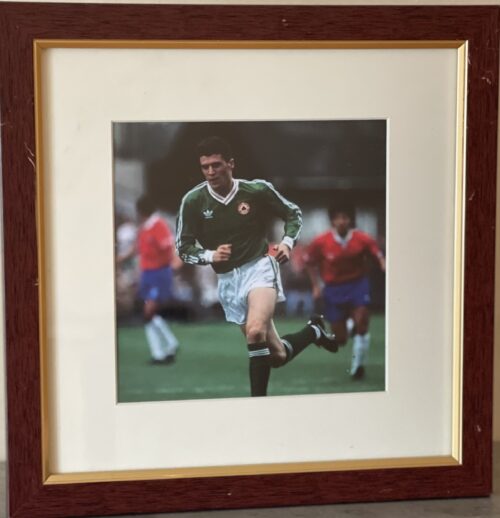
 I 30cm x 30cm Limerick Roy Maurice Keane (born 10 August 1971) is an Irish football manager and former professional player. He is the joint most successful Irish footballer of all time, having won 19 major trophies in his club career, 17 of which came during his time at English club Manchester United. He served as the assistant manager of the Republic of Ireland national teamfrom 2013 until 2018. Regarded as one of the best midfielders of his generation, he was named by Pelé in the FIFA 100 list of the world's greatest living players in 2004.Noted for his hardened and brash demeanour, he was ranked at No. 11 on The Times' list of the 50 "hardest" footballers in history in 2007. Keane was inducted into the Premier League Hall of Fame in 2021. In his 18-year playing career, Keane played for Cobh Ramblers, Nottingham Forest, and Manchester United, before ending his career at Celtic. He was a dominating box-to-box midfielder, noted for his aggressive and highly competitive style of play, an attitude that helped him excel as captain of Manchester United from 1997 until his departure in 2005. Keane helped United achieve a sustained period of success during his 12 years at the club. He then signed for Celtic, where he won a domestic double before he retired as a player in 2006. Keane played at the international level for the Republic of Ireland over 14 years, most of which he spent as captain. At the 1994 FIFA World Cup, he played in every Republic of Ireland game. He was sent home from the 2002 FIFA World Cup after a dispute with national coach Mick McCarthy over the team's training facilities. Keane was appointed manager of Sunderland shortly after his retirement as a player and took the club from 23rd position in the Football League Championship, in late August, to win the division title and gain promotion to the Premier League. He resigned in December 2008,and from April 2009 to January 2011, he was manager of Championship club Ipswich Town. In November 2013, he was appointed assistant manager of the Republic of Ireland national team by manager Martin O'Neill. Keane has also worked as a studio analyst for British channels ITV's and Sky Sportsfootball coverage.
I 30cm x 30cm Limerick Roy Maurice Keane (born 10 August 1971) is an Irish football manager and former professional player. He is the joint most successful Irish footballer of all time, having won 19 major trophies in his club career, 17 of which came during his time at English club Manchester United. He served as the assistant manager of the Republic of Ireland national teamfrom 2013 until 2018. Regarded as one of the best midfielders of his generation, he was named by Pelé in the FIFA 100 list of the world's greatest living players in 2004.Noted for his hardened and brash demeanour, he was ranked at No. 11 on The Times' list of the 50 "hardest" footballers in history in 2007. Keane was inducted into the Premier League Hall of Fame in 2021. In his 18-year playing career, Keane played for Cobh Ramblers, Nottingham Forest, and Manchester United, before ending his career at Celtic. He was a dominating box-to-box midfielder, noted for his aggressive and highly competitive style of play, an attitude that helped him excel as captain of Manchester United from 1997 until his departure in 2005. Keane helped United achieve a sustained period of success during his 12 years at the club. He then signed for Celtic, where he won a domestic double before he retired as a player in 2006. Keane played at the international level for the Republic of Ireland over 14 years, most of which he spent as captain. At the 1994 FIFA World Cup, he played in every Republic of Ireland game. He was sent home from the 2002 FIFA World Cup after a dispute with national coach Mick McCarthy over the team's training facilities. Keane was appointed manager of Sunderland shortly after his retirement as a player and took the club from 23rd position in the Football League Championship, in late August, to win the division title and gain promotion to the Premier League. He resigned in December 2008,and from April 2009 to January 2011, he was manager of Championship club Ipswich Town. In November 2013, he was appointed assistant manager of the Republic of Ireland national team by manager Martin O'Neill. Keane has also worked as a studio analyst for British channels ITV's and Sky Sportsfootball coverage. -

 Daniel Breen (11 August 1894 – 27 December 1969) was a volunteer in the Irish Republican Armyduring the Irish War of Independence and the Irish Civil War. In later years he was a Fianna Fáil politician.
Daniel Breen (11 August 1894 – 27 December 1969) was a volunteer in the Irish Republican Armyduring the Irish War of Independence and the Irish Civil War. In later years he was a Fianna Fáil politician.Background
Dan Breen was born in Grange, Donohill parish, County Tipperary. His father died when Breen was six, leaving the family very poor. He was educated locally, before becoming a plasterer and later a linesman on the Great Southern Railways.Irish Revolutionary Period
War of Independence
Breen was sworn into the Irish Republican Brotherhood in 1912 and the Irish Volunteers in 1914. On 21 January 1919, the day the First Dáil met in Dublin, Breen—who described himself as "a soldier first and foremost"—took part in the Soloheadbeg Ambush.The ambush party of eight men, nominally led by Séumas Robinson, attacked two Royal Irish Constabulary men who were escorting explosives to a quarry. The two policemen, James McDonnell and Patrick O’Connell, were fatally shot during the incident. The ambush is considered to be the first incident of the Irish War of Independence. Breen later recalled:"...we took the action deliberately, having thought over the matter and talked it over between us. [Seán] Treacyhad stated to me that the only way of starting a war was to kill someone, and we wanted to start a war, so we intended to kill some of the police whom we looked upon as the foremost and most important branch of the enemy forces ... The only regret that we had following the ambush was that there were only two policemen in it, instead of the six we had expected..."
During the conflict, the British put a £1,000 price on Breen's head, which was later raised to £10,000.He quickly established himself as a leader within the Irish Republican Army (IRA). He was known for his courage. On 13 May 1919, he helped rescue his comrade Seán Hogan at gunpoint from a heavily guarded train at Knocklong station in County Limerick. Breen, who was wounded, remembered how the battalion was "vehemently denounced as a cold-blooded assassins" and roundly condemned by the Catholic Church. After the fight, Seán Treacy, Séumas Robinson and Breen met Michael Collins in Dublin, where they were told to escape from the area. They agreed they would "fight it out, of course". Breen and Treacy shot their way out through a British military cordon in the northern suburb of Drumcondra (Fernside). They escaped, only for Treacy to be killed the next day. Breen was shot at least four times, twice in the lung. The British reaction was to make Tipperary a 'Special Military Area', with curfews and travel permits. Volunteer GHQ authorised enterprising attacks on barracks. Richard Mulcahy noted that British policy had "pushed rather turbulent spirits such as Breen and Treacy into the Dublin area". The inculcation of the principles of guerrilla warfare was to become an essential part of all training. They joined Collins' Squad of assassins, later known as the Dublin Guard, when Tipperary became "too hot for them". and Dublin was the centre of the war. Breen was present in December 1919 at the ambush in Ashtown beside Phoenix Park in Dublin where Martin Savage was killed while trying to assassinate the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland, Viscount French. The IRA men hid behind hedges and a dungheap as the convoy of vehicles came past. They had been instructed to ignore the first car, but this contained their target, Lord French. Their roadblock failed as a policeman removed the horse and cart intended to stop the car. Breen rejected the Anglo-Irish Treaty, which made him, like many others, angry and embittered:I would never have handled a gun or fired a shot… to obtain this Treaty… writing on the second anniversary of Martin Savage's death, do you suppose that he sacrificed his life in attempting to kill one British Governor-General to make room for another British Governor-General?
Regarding the continued existence of Northern Ireland from 1922, and an inevitable further war to conquer it to create a united Ireland, Breen commented:- "To me, a united Ireland of two million people would be preferable to an Ireland of four and a half million divided into three or four factions".
Irish Civil War
Breen was elected to Dáil Éireann at the 1923 general election as a Republican anti-Treaty Teachta Dála (TD) for the Tipperary constituency.Following the Anglo-Irish Treaty, Breen joined the Anti-Treaty IRA in the Civil War, fighting against those of his former comrades in arms who supported the Treaty. He was arrested by the National Army of the Irish Free State and interned at Limerick Prison. He spent two months there before going on hunger strike for six days, followed by a thirst strike of six days. Breen was released after he signed a document pleading to desist from attacking the Free State. Breen wrote a best-selling account of his guerrilla days, My Fight for Irish Freedom, in 1924, later republished by Rena Dardis and Anvil Press.Politics
Fianna Fáil TD
Breen represented Tipperary from the Fourth Dáil in 1923 as a Republican with Éamon de Valera and Frank Aiken.He was the first anti-Treaty TD to take his seat, in 1927. Standing as an Independent Republican he was defeated in the June 1927 general election. Thereafter Breen travelled to the United States, where he opened a speakeasy. He returned to Ireland in 1932 following the death of his mother,and regained his seat as a member of Fianna Fáil in the Dáil at that year's general election. He represented his Tipperary constituency without a break until his retirement at the 1965 election.Political views
Breen supported the Republican side during the Spanish Civil War. During World War II, he was said to hold largely pro-Axis views, with admiration for Erwin Rommel.When the fascist political party Ailtirí na hAiséirghe failed to win any seats in the 1944 Irish general election, he remarked that he was sorry that the party had not done better, as he had studied their programme and found a lot to commend. In 1946, Breen became secretary of the Save the German Children Society. He attended the funeral of Nazi spy Hermann Gortz on 27 May 1947.Irish-American John S. Monagan visited Breen in 1948, and was surprised to see two pictures of Adolf Hitler, a medallion of Napoleon and a Telefunken radio. Breen told him "the revolution didn't work out," and "to get the government they have now, I wouldn't have lost a night's sleep." He also said that he fought for freedom, but not for democracy.In 1943, Breen sent his "congratulations to the Führer. May he live long to lead Europe on the road to peace, security and happiness". After the end of World War II in Europe, the German Legation in Dublin was taken over by diplomats from the USA in May 1945, and ".. they found a recent letter from Breen asking the German minister to forward his birthday wishes to the Führer, just days before Hitler committed suicide." Breen was co-chairman of the anti-Vietnam War organisation "Irish Voice on Vietnam".Personal life
Breen was married on 12 June 1921, during the War of Independence, to Brigid Malone, a Dublin Cumann na mBan woman and sister of Lieutenant Michael Malone who was killed in action at the Battle of Mount Street Bridge during the 1916 Rising. They had met in Dublin when she helped to nurse him while he was recovering from a bullet wound. Seán Hogan was best man, and the bride's sister Aine Malone was the bridesmaid. Photographs of the wedding celebrations taken by 5th Battalion intelligence officer Séan Sharkey are published in The Tipperary Third Brigade a photographic record. Breen was, at the time, one of the most wanted men in Ireland, and South Tipperary was under martial law, yet a large celebration was held. The wedding took place at Purcell's, "Glenagat House", New Inn, County Tipperary. Many of the key members of the Third Tipperary Brigade attended, including flying column leaders Dinny Lacey and Hogan. Breen was the brother in-law of Commandant Theobald Wolfe Tone FitzGerald, the painter of the Irish Republic Flag that flew over the GPO during the Easter Rising in 1916. The Breens had two children, Donal and Granya. Breen was an atheist.Death
Breen died in Dublin in 1969, aged 75, and was buried in Donohill, near his birthplace. His funeral was the largest seen in west Tipperary since that of his close friend and comrade-in-arms, Seán Treacy, at Kilfeacle in October 1920. An estimated attendance of 10,000 mourners assembled in the tiny hamlet, giving ample testimony to the esteem in which he was held. Breen was the subject of a 2007 biography, Dan Breen and the IRA by Joe Ambrose.In popular culture
Breen is mentioned in the Irish folk ballad "The Galtee Mountain Boy", along with Seán Moylan, Dinny Lacey, and Seán Hogan. The song, written by Patsy Halloran, recalls some of the travels of a "Flying column" from Tipperary as they fought during the Irish War of Independence, and later against the pro-Treaty side during the Irish Civil War. The trophy for the Tipperary Senior Hurling Championship is named after him. -

 25cm x 30cm Glasgow
25cm x 30cm GlasgowThe Troubles, also called Northern Ireland conflict, violent sectarian conflict from about 1968 to 1998 in Northern Irelandbetween the overwhelmingly Protestantunionists (loyalists), who desired the province to remain part of the United Kingdom, and the overwhelmingly Roman Catholic nationalists (republicans), who wanted Northern Ireland to become part of the republic of Ireland. The other major players in the conflict were the British army, Royal Ulster Constabulary (RUC), and Ulster Defence Regiment (UDR; from 1992 called the Royal Irish Regiment), and their avowed purpose was to play a peacekeeping role, most prominently between the nationalist Irish Republican Army(IRA), which viewed the conflict as a guerrilla war for national independence, and the unionist paramilitary forces, which characterized the IRA’s aggression as terrorism. Marked by street fighting, sensational bombings, sniper attacks, roadblocks, and internment without trial, the confrontation had the characteristics of a civil war, notwithstanding its textbook categorization as a “low-intensity conflict.” Some 3,600 people were killed and more than 30,000 more were wounded before a peaceful solution, which involved the governments of both the United Kingdom and Ireland, was effectively reached in 1998, leading to a power-sharing arrangement in the Northern Ireland Assembly at Stormont.
Deep origins
The story of the Troubles is inextricably entwined with the history of Ireland as whole and, as such, can be seen as stemming from the first British incursion on the island, the Anglo-Norman invasion of the late 12th century, which left a wave of settlers whose descendants became known as the “Old English.” Thereafter, for nearly eight centuries, England and then Great Britain as a whole would dominate affairs in Ireland. Colonizing British landlords widely displaced Irish landholders. The most successful of these “plantations” began taking hold in the early 17th century in Ulster, the northernmost of Ireland’s four traditional provinces, previously a centre of rebellion, where the planters included English and Scottish tenants as well as British landlords. Because of the plantation of Ulster, as Irish history unfolded—with the struggle for the emancipation of the island’s Catholic majority under the supremacy of the Protestant ascendancy, along with the Irish nationalist pursuit of Home Rule and then independence after the island’s formal union with Great Britain in 1801—Ulster developed as a region where the Protestant settlers outnumbered the indigenousIrish. Unlike earlier English settlers, most of the 17th-century English and Scottish settlers and their descendants did not assimilate with the Irish. Instead, they held on tightly to British identity and remained steadfastly loyal to the British crown.
The formation of Northern Ireland, Catholic grievances, and the leadership of Terence O’Neill
Of the nine modern counties that constituted Ulster in the early 20th century, four—Antrim, Down, Armagh, and Londonderry (Derry)—had significant Protestant loyalist majorities; two—Fermanagh and Tyrone—had small Catholic nationalist majorities; and three—Donegal, Cavan, and Monaghan—had significant Catholic nationalist majorities. In 1920, during the Irish War of Independence (1919–21), the British Parliament, responding largely to the wishes of Ulster loyalists, enacted the Government of Ireland Act , which divided the island into two self-governing areas with devolved Home Rule-like powers. What would come to be known as Northern Ireland was formed by Ulster’s four majority loyalist counties along with Fermanagh and Tyrone. Donegal, Cavan, and Monaghan were combined with the island’s remaining 23 counties to form southern Ireland. The Anglo-Irish Treaty that ended the War of Independence then created the Irish Free State in the south, giving it dominion status within the British Empire. It also allowed Northern Ireland the option of remaining outside of the Free State, which it unsurprisingly chose to do.
Thus, in 1922 Northern Ireland began functioning as a self-governing region of the United Kingdom. Two-thirds of its population (about one million people) was Protestant and about one-third (roughly 500,000 people) was Catholic. Well before partition, Northern Ireland, particularly Belfast, had attracted economic migrants from elsewhere in Ireland seeking employment in its flourishing linen-making and shipbuilding industries. The best jobs had gone to Protestants, but the humming local economy still provided work for Catholics. Over and above the long-standing dominance of Northern Ireland politics that resulted for the Ulster Unionist Party (UUP) by virtue of the Protestants’ sheer numerical advantage, loyalist control of local politics was ensured by the gerrymandering of electoral districts that concentrated and minimized Catholic representation. Moreover, by restricting the franchise to ratepayers (the taxpaying heads of households) and their spouses, representation was further limited for Catholic households, which tended to be larger (and more likely to include unemployed adult children) than their Protestant counterparts. Those who paid rates for more than one residence (more likely to be Protestants) were granted an additional vote for each ward in which they held property (up to six votes). Catholics argued that they were discriminated against when it came to the allocation of public housing, appointments to public service jobs, and government investment in neighbourhoods. They were also more likely to be the subjects of police harassment by the almost exclusively Protestant RUC and Ulster Special Constabulary (B Specials).
The divide between Catholics and Protestants in Northern Ireland had little to do with theological differences but instead was grounded in culture and politics. Neither Irish history nor the Irish language was taught in schools in Northern Ireland, it was illegal to fly the flag of the Irish republic, and from 1956 to 1974 Sinn Féin, the party of Irish republicanism, also was banned in Northern Ireland. Catholics by and large identified as Irish and sought the incorporation of Northern Ireland into the Irish state. The great bulk of Protestants saw themselves as British and feared that they would lose their culture and privilege if Northern Ireland were subsumed by the republic. They expressed their partisan solidarity through involvement with Protestant unionist fraternal organizations such as the Orange Order, which found its inspiration in the victory of King William III (William of Orange) at the Battle of the Boyne in 1690 over his deposed Catholic predecessor, James II, whose siege of the Protestant community of Londonderry had earlier been broken by William. Despite these tensions, for 40 or so years after partition the status of unionist-dominated Northern Ireland was relatively stable.
IRA graffiti “IRA” spray-painted on a container, Derry (Londonderry), Northern Ireland.© Attila Jandi/Dreamstime.comRecognizing that any attempt to reinvigorate Northern Ireland’s declining industrial economy in the early 1960s would also need to address the province’s percolatingpolitical and social tensions, the newly elected prime minister of Northern Ireland, Terence O’Neill, not only reached out to the nationalist community but also, in early 1965, exchanged visits with Irish Taoiseach (Prime Minister) Seán Lemass—a radical step, given that the republic’s constitution included an assertion of sovereignty over the whole island. Nevertheless, O’Neill’s efforts were seen as inadequate by nationalists and as too conciliatory by loyalists, including the Rev. Ian Paisley, who became one of the most vehement and influential representatives of unionist reaction.
Civil rights activism, the Battle of Bogside, and the arrival of the British army
Contrary to the policies of UUP governments that disadvantaged Catholics, the Education Act that the Northern Ireland Parliament passed into law in 1947 increased educational opportunities for all citizens of the province. As a result, the generation of well-educated Catholics who came of age in the 1960s had new expectations for more equitable treatment. At a time when political activism was on the rise in Europe—from the events of May 1968 in France to the Prague Spring—and when the American civil rights movement was making great strides, Catholic activists in Northern Ireland such as John Humeand Bernadette Devlin came together to form civil rightsgroups such as the Northern Ireland Civil Rights Association (NICRA).
Although more than one violently disrupted political march has been pointed to as the starting point of the Troubles, it can be argued that the catalyzing event occurred on October 5, 1968, in Derry, where a march had been organized by the NICRA to protest discrimination and gerrymandering. The march was banned when unionists announced that they would be staging a counterdemonstration, but the NICRA decided to carry out their protest anyway. Rioting then erupted after the RUC violently suppressed the marchers with batons and a water cannon.
Similarly inflammatory were the events surrounding a march held by loyalists in Londonderry on August 12, 1969. Two days of rioting that became known as the Battle of Bogside (after the Catholic area in which the confrontation occurred) stemmed from the escalating clash between nationalists and the RUC, which was acting as a buffer between loyalist marchers and Catholic residents of the area. Rioting in support of the nationalists then erupted in Belfast and elsewhere, and the British army was dispatched to restore calm. Thereafter, violent confrontation only escalated, and the Troubles (a name that neither characterized the nature of the conflict nor assigned blame for it to one side or the other) had clearly begun.
The emergence of the Provisional IRA and the loyalist paramilitaries
Initially, the nationalists welcomed the British army as protectors and as a balance for the Protestant-leaning RUC. In time, however, the army would be viewed by nationalists as another version of the enemy, especially after its aggressive efforts to disarm republican paramilitaries. In the process, the Irish Republican Army (IRA) became the defender of the nationalist cause. From its base in Ireland(which had formally left the Commonwealth in 1949), the IRA had mounted an ineffectual guerrilla effort in support of Northern Ireland’s nationalists from 1956 to 1962, but, as the 1960s progressed, the IRA became less concerned with affairs in the north than with advancing a Marxist political agenda. As a result, a splinter group, the Provisional Irish Republican Army (Provos), which was prepared to use force to bring about unification, emerged as the champion of Northern Ireland’s nationalists. (The Official IRA would conduct operations in support of the republicans in Northern Ireland until undertaking a cease-fire in 1972, after which it effectively ceded the title of the IRA in the north to the Provos.) Believing that their fight was a continuation of the Irish War of Independence, the Provos adopted the tactics of guerrilla warfare, financed partly by members of the Irish diaspora in the United States and later supplied with arms and munitions by the government of Libyan strongman Muammar al-Qaddafi. Unionists also took up arms, swelling the numbers of loyalist paramilitary organizations, most notably the Ulster Volunteer Force (UVF) and Ulster Defence Association UDA).
British soldier in Northern Ireland Local people walking past a British soldier on guard in Northern Ireland, August 1969.Peter Kemp—AP/Shutterstock.comInternment, “peace walls,” and “Bloody Sunday”
In an attempt to address nationalist grievances, electoral boundaries were redrawn more fairly, efforts were made to rectify discrimination in housing and public employment, and the B Specials were decommissioned. At the same time, the government of Northern Ireland responded to the growing unrest by introducing increasingly stringent security measures, including internment (detention without trial). The overwhelming majority of those arrested, however, were nationalists.
As the 1970s progressed, rioting became more common in Belfast and Derry, bombings of public places (by both loyalists and republicans) increased, and both sides of the conflict perpetrated violent, deadly atrocities. Barbed wire laid by British soldiers to separate the sectarian communitiesevolved into brick and steel “peace walls,” some of which stood 45 feet (14 metres) high, segregating loyalist and republican enclaves, most famously the Falls Road Catholic community and the Shankill Protestant community of Belfast.
On January 30, 1972, the conflict reached a new level of intensity when British paratroopers fired on Catholic civil rights demonstrators in Londonderry, killing 13 and injuring 14 others (one of whom later died). The incident, which became known as “Bloody Sunday,” contributed to a spike in Provos recruitment and would remain controversial for decades, hinging on the question of which side fired first. In 2010 the Saville Report , the final pronouncement of a British government inquiry into the event, concluded that none of the victims had posed a threat to the troops and that their shooting had been unjustified. British Prime Minister David Cameron responded to the report by issuing a landmark apology for the shooting:
There is no point in trying to soften or equivocate what is in this report. It is clear from the tribunal’s authoritative conclusions that the events of Bloody Sunday were in no way justified….What happened should never, ever have happened….Some members of our armed forces acted wrongly. The government is ultimately responsible for the conduct of the armed forces and for that, on behalf of the government, indeed, on behalf of our country, I am deeply sorry.
In all, more than 480 people were killed as a result of the conflict in Northern Ireland in 1972, which proved to be the deadliest single year in the Troubles. That total included more than 100 fatalities for the British army, as the IRA escalated its onslaught. On July 21, “Bloody Friday,” nine people were killed and scores were injured when some two dozen bombs were detonated by the Provos in Belfast. Earlier, in March, frustrated with the Northern Ireland government’s failure to calm the situation, the British government suspended the Northern Ireland Parliament and reinstituted direct rule by Westminster.
Beginning in the mid-1970s, the IRA shifted the emphasis of its “Long War” from direct engagements with British troops to smaller-scale secretive operations, including the bombing of cities in Britain—a change of tactics the British military described as a shift from “insurgency” to “terrorism.” Similarly, the loyalist groups began setting off bombs in Ireland. Meanwhile, paramilitary violence at mid-decade (1974–76) resulted in the civilian deaths of some 370 Catholics and 88 Protestants.
Northern Ireland: peace movement Protesters against ongoing violence in Northern Ireland gathering on Shankill Road, Belfast, Northern Ireland, August 1976.Peace PeopleThe Sunningdale Agreement, hunger strikes, Bobby Sands, and the Brighton bombing
A glimmer of hope was offered by the Sunningdale Agreement , named for the English city in which it was negotiated in 1973. That agreement led to the creation of a new Northern Ireland Assembly, with proportional representation for all parties, and to the establishment of a Council of Ireland, which was to provide a role for Ireland in the affairs of Northern Ireland. Frustrated by the diminution of their political power and furious at the participation of the republic, loyalists scuttled the power-sharing plan with a general strike that brought the province to a halt in May 1974 and eventually forced a return to direct rule, which remained in place for some 25 years.
For the remainder of the decade, violence ebbed and flowed, cease-fires lingered and lapsed, and tit-for-tat bombings and assassinations continued, including the high-profile killing at sea in August 1979 of Lord Mountbatten, a relative of both Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip. In 1976 the opening of the specially designed Maze prison brought with it a shift in the treatment of IRA inmates from that of prisoners of war to that of common criminals. Seeking a return to their Special Category Status, the prisoners struck back, first staging the “blanket protest,” in which they refused to put on prison uniforms and instead wore only blankets, and then, in 1978, the “dirty protest,” in which inmates smeared the walls of their cells with excrement. The government of recently elected Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher refused to buckle, even in the face of hunger strikes in 1980–81 that led to the deaths of 10 prisoners, including Bobby Sands, who had won a seat in the British Parliament while incarcerated and fasting.
Sands’s election helped convince Sinn Féin, then operating as the political wing of the IRA, that the struggle for unification should be pursued at the ballot box as well as with the Armalite rifle. In June 1983 Sinn Féin leader Gerry Adams won a seat in Parliament representing West Belfast, though he refused to take it to avoid taking the compulsory oath of loyalty to the British queen.
The Anglo-Irish Agreement and Downing Street Declaration
In October 1984 an IRA bomb attack on the Conservative Party Conference in Brighton, England, took five lives and threatened that of Thatcher. Though she remained steadfast in the face of this attack, it was the “Iron Lady” who in November 1985 joined Irish Taoiseach Garret FitzGerald in signing the Anglo-Irish Agreement, under which both countries guaranteed that any change in the status of Northern Ireland would come about only with the consent of the majority of the people of Northern Ireland. The accordalso established the Intergovernmental Conference, which gave Ireland a consultative role in the political and security affairs of Northern Ireland for the first time. Finally, the agreement stipulated that power would be devolved back upon the government of Northern Ireland only if unionists and nationalists participated in power sharing.
Anglo-Irish Agreement (1985) Irish Taoiseach (Prime Minister) Garret FitzGerald and British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher signing the Anglo-Irish Agreement, November 15, 1985.Peter Kemp/APThe loyalists’ vehement opposition to the agreement included the resignation of all 15 unionist members of the House of Commons and a ramping up of violence. In the meantime, IRA bombings in London made headlines, and the reach of the British security forces extended to the killing of three Provos in Gibraltar. Behind the scenes, however, negotiations were underway. In 1993 British Prime Minister John Major and Irish Taoiseach Albert Reynolds issued the so-called Downing Street Declaration , which established a framework for all-party peace talks. A cease-fire declared by the Provos in 1994 and joined by the principal loyalist paramilitary groups fell apart in 1996 because Sinn Féin, which had replaced the more moderate Social Democratic and Labour Party (SDLP) as the leading nationalist party, had been excluded from peace talks because of the IRA’s continuing bombing campaign. Nevertheless, the unionists were at the table, prepared to consider a solution that included the participation of the republic of Ireland. After the IRA resumed its cease-fire in 1997, Sinn Féin was welcomed back to the talks, which now included the British and Irish governments, the SDLP, the Alliance Party of Northern Ireland, the UUP, and the Ulster Democratic Party, among others, though not the Paisley-led DUP, which was protesting the inclusion of Sinn Féin.
The Good Friday Agreement, the Omagh bombing, peace, and power sharing
Those talks, mediated by former U.S. senator George Mitchell, led to the Good Friday Agreement (Belfast Agreement), reached April 10, 1998. That landmark accordprovided for the creation of a power-sharing Northern Ireland Assembly, established an institutional arrangement for cross-border cooperation between the governments of Ireland and Northern Ireland on a range of issues, and lay the groundwork for continued consultation between the British and Irish governments. On May 22 Ireland and Northern Ireland held a joint referendum on the agreement, which was approved by 94 percent of those who voted in the republic and 71 percent of those voting in Northern Ireland, where Catholic approval of the accord (96 percent) was much higher than Protestant assent (52 per cent). Nonetheless, it was an IRA splinter group, the Real Irish Republican Army, which most dramatically violated the spirit of the agreement, with a bombing in Omagh in August that took 29 lives.
Elections for the new Assembly were held in June, but the IRA’s failure to decommission delayed the formation of the power-sharing Northern Ireland Executive until December 1999, when the IRA promised to fulfill its obligation to disarm. That month the republic of Ireland modified its constitution, removing its territorial claims to the whole of the island, and the United Kingdom yielded direct rule of Northern Ireland. Ostensibly the Troubles had come to end, but, though Northern Ireland began its most tranquil era in a generation, the peace was fragile. Sectarian antagonism persisted, the process of decommissioning was slow on both sides, and the rolling out of the new institutions was fitful, resulting in suspensions of devolution and the reimposition of direct rule.
In July 2005, however, the IRA announced that it had ordered all its units to “dump arms,” would henceforth pursue its goals only through peaceful means, and would work with international inspectors “to verifiably put its arms beyond use.” At a press conference in September, a spokesman for the Independent International Commission on Decommissioning stated, “We are satisfied that the arms decommissioned represent the totality of the IRA’s arsenal.” Decommissioning by unionist paramilitaries and other republican groups followed..
-

 25cm x 30cm Glasgow
25cm x 30cm GlasgowThe Troubles, also called Northern Ireland conflict, violent sectarian conflict from about 1968 to 1998 in Northern Irelandbetween the overwhelmingly Protestantunionists (loyalists), who desired the province to remain part of the United Kingdom, and the overwhelmingly Roman Catholic nationalists (republicans), who wanted Northern Ireland to become part of the republic of Ireland. The other major players in the conflict were the British army, Royal Ulster Constabulary (RUC), and Ulster Defence Regiment (UDR; from 1992 called the Royal Irish Regiment), and their avowed purpose was to play a peacekeeping role, most prominently between the nationalist Irish Republican Army(IRA), which viewed the conflict as a guerrilla war for national independence, and the unionist paramilitary forces, which characterized the IRA’s aggression as terrorism. Marked by street fighting, sensational bombings, sniper attacks, roadblocks, and internment without trial, the confrontation had the characteristics of a civil war, notwithstanding its textbook categorization as a “low-intensity conflict.” Some 3,600 people were killed and more than 30,000 more were wounded before a peaceful solution, which involved the governments of both the United Kingdom and Ireland, was effectively reached in 1998, leading to a power-sharing arrangement in the Northern Ireland Assembly at Stormont.
Deep origins
The story of the Troubles is inextricably entwined with the history of Ireland as whole and, as such, can be seen as stemming from the first British incursion on the island, the Anglo-Norman invasion of the late 12th century, which left a wave of settlers whose descendants became known as the “Old English.” Thereafter, for nearly eight centuries, England and then Great Britain as a whole would dominate affairs in Ireland. Colonizing British landlords widely displaced Irish landholders. The most successful of these “plantations” began taking hold in the early 17th century in Ulster, the northernmost of Ireland’s four traditional provinces, previously a centre of rebellion, where the planters included English and Scottish tenants as well as British landlords. Because of the plantation of Ulster, as Irish history unfolded—with the struggle for the emancipation of the island’s Catholic majority under the supremacy of the Protestant ascendancy, along with the Irish nationalist pursuit of Home Rule and then independence after the island’s formal union with Great Britain in 1801—Ulster developed as a region where the Protestant settlers outnumbered the indigenousIrish. Unlike earlier English settlers, most of the 17th-century English and Scottish settlers and their descendants did not assimilate with the Irish. Instead, they held on tightly to British identity and remained steadfastly loyal to the British crown.
The formation of Northern Ireland, Catholic grievances, and the leadership of Terence O’Neill
Of the nine modern counties that constituted Ulster in the early 20th century, four—Antrim, Down, Armagh, and Londonderry (Derry)—had significant Protestant loyalist majorities; two—Fermanagh and Tyrone—had small Catholic nationalist majorities; and three—Donegal, Cavan, and Monaghan—had significant Catholic nationalist majorities. In 1920, during the Irish War of Independence (1919–21), the British Parliament, responding largely to the wishes of Ulster loyalists, enacted the Government of Ireland Act , which divided the island into two self-governing areas with devolved Home Rule-like powers. What would come to be known as Northern Ireland was formed by Ulster’s four majority loyalist counties along with Fermanagh and Tyrone. Donegal, Cavan, and Monaghan were combined with the island’s remaining 23 counties to form southern Ireland. The Anglo-Irish Treaty that ended the War of Independence then created the Irish Free State in the south, giving it dominion status within the British Empire. It also allowed Northern Ireland the option of remaining outside of the Free State, which it unsurprisingly chose to do.
Thus, in 1922 Northern Ireland began functioning as a self-governing region of the United Kingdom. Two-thirds of its population (about one million people) was Protestant and about one-third (roughly 500,000 people) was Catholic. Well before partition, Northern Ireland, particularly Belfast, had attracted economic migrants from elsewhere in Ireland seeking employment in its flourishing linen-making and shipbuilding industries. The best jobs had gone to Protestants, but the humming local economy still provided work for Catholics. Over and above the long-standing dominance of Northern Ireland politics that resulted for the Ulster Unionist Party (UUP) by virtue of the Protestants’ sheer numerical advantage, loyalist control of local politics was ensured by the gerrymandering of electoral districts that concentrated and minimized Catholic representation. Moreover, by restricting the franchise to ratepayers (the taxpaying heads of households) and their spouses, representation was further limited for Catholic households, which tended to be larger (and more likely to include unemployed adult children) than their Protestant counterparts. Those who paid rates for more than one residence (more likely to be Protestants) were granted an additional vote for each ward in which they held property (up to six votes). Catholics argued that they were discriminated against when it came to the allocation of public housing, appointments to public service jobs, and government investment in neighbourhoods. They were also more likely to be the subjects of police harassment by the almost exclusively Protestant RUC and Ulster Special Constabulary (B Specials).
The divide between Catholics and Protestants in Northern Ireland had little to do with theological differences but instead was grounded in culture and politics. Neither Irish history nor the Irish language was taught in schools in Northern Ireland, it was illegal to fly the flag of the Irish republic, and from 1956 to 1974 Sinn Féin, the party of Irish republicanism, also was banned in Northern Ireland. Catholics by and large identified as Irish and sought the incorporation of Northern Ireland into the Irish state. The great bulk of Protestants saw themselves as British and feared that they would lose their culture and privilege if Northern Ireland were subsumed by the republic. They expressed their partisan solidarity through involvement with Protestant unionist fraternal organizations such as the Orange Order, which found its inspiration in the victory of King William III (William of Orange) at the Battle of the Boyne in 1690 over his deposed Catholic predecessor, James II, whose siege of the Protestant community of Londonderry had earlier been broken by William. Despite these tensions, for 40 or so years after partition the status of unionist-dominated Northern Ireland was relatively stable.
IRA graffiti “IRA” spray-painted on a container, Derry (Londonderry), Northern Ireland.© Attila Jandi/Dreamstime.comRecognizing that any attempt to reinvigorate Northern Ireland’s declining industrial economy in the early 1960s would also need to address the province’s percolatingpolitical and social tensions, the newly elected prime minister of Northern Ireland, Terence O’Neill, not only reached out to the nationalist community but also, in early 1965, exchanged visits with Irish Taoiseach (Prime Minister) Seán Lemass—a radical step, given that the republic’s constitution included an assertion of sovereignty over the whole island. Nevertheless, O’Neill’s efforts were seen as inadequate by nationalists and as too conciliatory by loyalists, including the Rev. Ian Paisley, who became one of the most vehement and influential representatives of unionist reaction.
Civil rights activism, the Battle of Bogside, and the arrival of the British army
Contrary to the policies of UUP governments that disadvantaged Catholics, the Education Act that the Northern Ireland Parliament passed into law in 1947 increased educational opportunities for all citizens of the province. As a result, the generation of well-educated Catholics who came of age in the 1960s had new expectations for more equitable treatment. At a time when political activism was on the rise in Europe—from the events of May 1968 in France to the Prague Spring—and when the American civil rights movement was making great strides, Catholic activists in Northern Ireland such as John Humeand Bernadette Devlin came together to form civil rightsgroups such as the Northern Ireland Civil Rights Association (NICRA).
Although more than one violently disrupted political march has been pointed to as the starting point of the Troubles, it can be argued that the catalyzing event occurred on October 5, 1968, in Derry, where a march had been organized by the NICRA to protest discrimination and gerrymandering. The march was banned when unionists announced that they would be staging a counterdemonstration, but the NICRA decided to carry out their protest anyway. Rioting then erupted after the RUC violently suppressed the marchers with batons and a water cannon.
Similarly inflammatory were the events surrounding a march held by loyalists in Londonderry on August 12, 1969. Two days of rioting that became known as the Battle of Bogside (after the Catholic area in which the confrontation occurred) stemmed from the escalating clash between nationalists and the RUC, which was acting as a buffer between loyalist marchers and Catholic residents of the area. Rioting in support of the nationalists then erupted in Belfast and elsewhere, and the British army was dispatched to restore calm. Thereafter, violent confrontation only escalated, and the Troubles (a name that neither characterized the nature of the conflict nor assigned blame for it to one side or the other) had clearly begun.
The emergence of the Provisional IRA and the loyalist paramilitaries
Initially, the nationalists welcomed the British army as protectors and as a balance for the Protestant-leaning RUC. In time, however, the army would be viewed by nationalists as another version of the enemy, especially after its aggressive efforts to disarm republican paramilitaries. In the process, the Irish Republican Army (IRA) became the defender of the nationalist cause. From its base in Ireland(which had formally left the Commonwealth in 1949), the IRA had mounted an ineffectual guerrilla effort in support of Northern Ireland’s nationalists from 1956 to 1962, but, as the 1960s progressed, the IRA became less concerned with affairs in the north than with advancing a Marxist political agenda. As a result, a splinter group, the Provisional Irish Republican Army (Provos), which was prepared to use force to bring about unification, emerged as the champion of Northern Ireland’s nationalists. (The Official IRA would conduct operations in support of the republicans in Northern Ireland until undertaking a cease-fire in 1972, after which it effectively ceded the title of the IRA in the north to the Provos.) Believing that their fight was a continuation of the Irish War of Independence, the Provos adopted the tactics of guerrilla warfare, financed partly by members of the Irish diaspora in the United States and later supplied with arms and munitions by the government of Libyan strongman Muammar al-Qaddafi. Unionists also took up arms, swelling the numbers of loyalist paramilitary organizations, most notably the Ulster Volunteer Force (UVF) and Ulster Defence Association UDA).
British soldier in Northern Ireland Local people walking past a British soldier on guard in Northern Ireland, August 1969.Peter Kemp—AP/Shutterstock.comInternment, “peace walls,” and “Bloody Sunday”
In an attempt to address nationalist grievances, electoral boundaries were redrawn more fairly, efforts were made to rectify discrimination in housing and public employment, and the B Specials were decommissioned. At the same time, the government of Northern Ireland responded to the growing unrest by introducing increasingly stringent security measures, including internment (detention without trial). The overwhelming majority of those arrested, however, were nationalists.
As the 1970s progressed, rioting became more common in Belfast and Derry, bombings of public places (by both loyalists and republicans) increased, and both sides of the conflict perpetrated violent, deadly atrocities. Barbed wire laid by British soldiers to separate the sectarian communitiesevolved into brick and steel “peace walls,” some of which stood 45 feet (14 metres) high, segregating loyalist and republican enclaves, most famously the Falls Road Catholic community and the Shankill Protestant community of Belfast.
On January 30, 1972, the conflict reached a new level of intensity when British paratroopers fired on Catholic civil rights demonstrators in Londonderry, killing 13 and injuring 14 others (one of whom later died). The incident, which became known as “Bloody Sunday,” contributed to a spike in Provos recruitment and would remain controversial for decades, hinging on the question of which side fired first. In 2010 the Saville Report , the final pronouncement of a British government inquiry into the event, concluded that none of the victims had posed a threat to the troops and that their shooting had been unjustified. British Prime Minister David Cameron responded to the report by issuing a landmark apology for the shooting:
There is no point in trying to soften or equivocate what is in this report. It is clear from the tribunal’s authoritative conclusions that the events of Bloody Sunday were in no way justified….What happened should never, ever have happened….Some members of our armed forces acted wrongly. The government is ultimately responsible for the conduct of the armed forces and for that, on behalf of the government, indeed, on behalf of our country, I am deeply sorry.
In all, more than 480 people were killed as a result of the conflict in Northern Ireland in 1972, which proved to be the deadliest single year in the Troubles. That total included more than 100 fatalities for the British army, as the IRA escalated its onslaught. On July 21, “Bloody Friday,” nine people were killed and scores were injured when some two dozen bombs were detonated by the Provos in Belfast. Earlier, in March, frustrated with the Northern Ireland government’s failure to calm the situation, the British government suspended the Northern Ireland Parliament and reinstituted direct rule by Westminster.
Beginning in the mid-1970s, the IRA shifted the emphasis of its “Long War” from direct engagements with British troops to smaller-scale secretive operations, including the bombing of cities in Britain—a change of tactics the British military described as a shift from “insurgency” to “terrorism.” Similarly, the loyalist groups began setting off bombs in Ireland. Meanwhile, paramilitary violence at mid-decade (1974–76) resulted in the civilian deaths of some 370 Catholics and 88 Protestants.
Northern Ireland: peace movement Protesters against ongoing violence in Northern Ireland gathering on Shankill Road, Belfast, Northern Ireland, August 1976.Peace PeopleThe Sunningdale Agreement, hunger strikes, Bobby Sands, and the Brighton bombing
A glimmer of hope was offered by the Sunningdale Agreement , named for the English city in which it was negotiated in 1973. That agreement led to the creation of a new Northern Ireland Assembly, with proportional representation for all parties, and to the establishment of a Council of Ireland, which was to provide a role for Ireland in the affairs of Northern Ireland. Frustrated by the diminution of their political power and furious at the participation of the republic, loyalists scuttled the power-sharing plan with a general strike that brought the province to a halt in May 1974 and eventually forced a return to direct rule, which remained in place for some 25 years.
For the remainder of the decade, violence ebbed and flowed, cease-fires lingered and lapsed, and tit-for-tat bombings and assassinations continued, including the high-profile killing at sea in August 1979 of Lord Mountbatten, a relative of both Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip. In 1976 the opening of the specially designed Maze prison brought with it a shift in the treatment of IRA inmates from that of prisoners of war to that of common criminals. Seeking a return to their Special Category Status, the prisoners struck back, first staging the “blanket protest,” in which they refused to put on prison uniforms and instead wore only blankets, and then, in 1978, the “dirty protest,” in which inmates smeared the walls of their cells with excrement. The government of recently elected Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher refused to buckle, even in the face of hunger strikes in 1980–81 that led to the deaths of 10 prisoners, including Bobby Sands, who had won a seat in the British Parliament while incarcerated and fasting.
Sands’s election helped convince Sinn Féin, then operating as the political wing of the IRA, that the struggle for unification should be pursued at the ballot box as well as with the Armalite rifle. In June 1983 Sinn Féin leader Gerry Adams won a seat in Parliament representing West Belfast, though he refused to take it to avoid taking the compulsory oath of loyalty to the British queen.
The Anglo-Irish Agreement and Downing Street Declaration
In October 1984 an IRA bomb attack on the Conservative Party Conference in Brighton, England, took five lives and threatened that of Thatcher. Though she remained steadfast in the face of this attack, it was the “Iron Lady” who in November 1985 joined Irish Taoiseach Garret FitzGerald in signing the Anglo-Irish Agreement, under which both countries guaranteed that any change in the status of Northern Ireland would come about only with the consent of the majority of the people of Northern Ireland. The accordalso established the Intergovernmental Conference, which gave Ireland a consultative role in the political and security affairs of Northern Ireland for the first time. Finally, the agreement stipulated that power would be devolved back upon the government of Northern Ireland only if unionists and nationalists participated in power sharing.
Anglo-Irish Agreement (1985) Irish Taoiseach (Prime Minister) Garret FitzGerald and British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher signing the Anglo-Irish Agreement, November 15, 1985.Peter Kemp/APThe loyalists’ vehement opposition to the agreement included the resignation of all 15 unionist members of the House of Commons and a ramping up of violence. In the meantime, IRA bombings in London made headlines, and the reach of the British security forces extended to the killing of three Provos in Gibraltar. Behind the scenes, however, negotiations were underway. In 1993 British Prime Minister John Major and Irish Taoiseach Albert Reynolds issued the so-called Downing Street Declaration , which established a framework for all-party peace talks. A cease-fire declared by the Provos in 1994 and joined by the principal loyalist paramilitary groups fell apart in 1996 because Sinn Féin, which had replaced the more moderate Social Democratic and Labour Party (SDLP) as the leading nationalist party, had been excluded from peace talks because of the IRA’s continuing bombing campaign. Nevertheless, the unionists were at the table, prepared to consider a solution that included the participation of the republic of Ireland. After the IRA resumed its cease-fire in 1997, Sinn Féin was welcomed back to the talks, which now included the British and Irish governments, the SDLP, the Alliance Party of Northern Ireland, the UUP, and the Ulster Democratic Party, among others, though not the Paisley-led DUP, which was protesting the inclusion of Sinn Féin.
The Good Friday Agreement, the Omagh bombing, peace, and power sharing
Those talks, mediated by former U.S. senator George Mitchell, led to the Good Friday Agreement (Belfast Agreement), reached April 10, 1998. That landmark accordprovided for the creation of a power-sharing Northern Ireland Assembly, established an institutional arrangement for cross-border cooperation between the governments of Ireland and Northern Ireland on a range of issues, and lay the groundwork for continued consultation between the British and Irish governments. On May 22 Ireland and Northern Ireland held a joint referendum on the agreement, which was approved by 94 percent of those who voted in the republic and 71 percent of those voting in Northern Ireland, where Catholic approval of the accord (96 percent) was much higher than Protestant assent (52 per cent). Nonetheless, it was an IRA splinter group, the Real Irish Republican Army, which most dramatically violated the spirit of the agreement, with a bombing in Omagh in August that took 29 lives.
Elections for the new Assembly were held in June, but the IRA’s failure to decommission delayed the formation of the power-sharing Northern Ireland Executive until December 1999, when the IRA promised to fulfill its obligation to disarm. That month the republic of Ireland modified its constitution, removing its territorial claims to the whole of the island, and the United Kingdom yielded direct rule of Northern Ireland. Ostensibly the Troubles had come to end, but, though Northern Ireland began its most tranquil era in a generation, the peace was fragile. Sectarian antagonism persisted, the process of decommissioning was slow on both sides, and the rolling out of the new institutions was fitful, resulting in suspensions of devolution and the reimposition of direct rule.
In July 2005, however, the IRA announced that it had ordered all its units to “dump arms,” would henceforth pursue its goals only through peaceful means, and would work with international inspectors “to verifiably put its arms beyond use.” At a press conference in September, a spokesman for the Independent International Commission on Decommissioning stated, “We are satisfied that the arms decommissioned represent the totality of the IRA’s arsenal.” Decommissioning by unionist paramilitaries and other republican groups followed..
-

 25cm x 30cm Glasgow
25cm x 30cm GlasgowThe Troubles, also called Northern Ireland conflict, violent sectarian conflict from about 1968 to 1998 in Northern Irelandbetween the overwhelmingly Protestantunionists (loyalists), who desired the province to remain part of the United Kingdom, and the overwhelmingly Roman Catholic nationalists (republicans), who wanted Northern Ireland to become part of the republic of Ireland. The other major players in the conflict were the British army, Royal Ulster Constabulary (RUC), and Ulster Defence Regiment (UDR; from 1992 called the Royal Irish Regiment), and their avowed purpose was to play a peacekeeping role, most prominently between the nationalist Irish Republican Army(IRA), which viewed the conflict as a guerrilla war for national independence, and the unionist paramilitary forces, which characterized the IRA’s aggression as terrorism. Marked by street fighting, sensational bombings, sniper attacks, roadblocks, and internment without trial, the confrontation had the characteristics of a civil war, notwithstanding its textbook categorization as a “low-intensity conflict.” Some 3,600 people were killed and more than 30,000 more were wounded before a peaceful solution, which involved the governments of both the United Kingdom and Ireland, was effectively reached in 1998, leading to a power-sharing arrangement in the Northern Ireland Assembly at Stormont.
Deep origins
The story of the Troubles is inextricably entwined with the history of Ireland as whole and, as such, can be seen as stemming from the first British incursion on the island, the Anglo-Norman invasion of the late 12th century, which left a wave of settlers whose descendants became known as the “Old English.” Thereafter, for nearly eight centuries, England and then Great Britain as a whole would dominate affairs in Ireland. Colonizing British landlords widely displaced Irish landholders. The most successful of these “plantations” began taking hold in the early 17th century in Ulster, the northernmost of Ireland’s four traditional provinces, previously a centre of rebellion, where the planters included English and Scottish tenants as well as British landlords. Because of the plantation of Ulster, as Irish history unfolded—with the struggle for the emancipation of the island’s Catholic majority under the supremacy of the Protestant ascendancy, along with the Irish nationalist pursuit of Home Rule and then independence after the island’s formal union with Great Britain in 1801—Ulster developed as a region where the Protestant settlers outnumbered the indigenousIrish. Unlike earlier English settlers, most of the 17th-century English and Scottish settlers and their descendants did not assimilate with the Irish. Instead, they held on tightly to British identity and remained steadfastly loyal to the British crown.
The formation of Northern Ireland, Catholic grievances, and the leadership of Terence O’Neill
Of the nine modern counties that constituted Ulster in the early 20th century, four—Antrim, Down, Armagh, and Londonderry (Derry)—had significant Protestant loyalist majorities; two—Fermanagh and Tyrone—had small Catholic nationalist majorities; and three—Donegal, Cavan, and Monaghan—had significant Catholic nationalist majorities. In 1920, during the Irish War of Independence (1919–21), the British Parliament, responding largely to the wishes of Ulster loyalists, enacted the Government of Ireland Act , which divided the island into two self-governing areas with devolved Home Rule-like powers. What would come to be known as Northern Ireland was formed by Ulster’s four majority loyalist counties along with Fermanagh and Tyrone. Donegal, Cavan, and Monaghan were combined with the island’s remaining 23 counties to form southern Ireland. The Anglo-Irish Treaty that ended the War of Independence then created the Irish Free State in the south, giving it dominion status within the British Empire. It also allowed Northern Ireland the option of remaining outside of the Free State, which it unsurprisingly chose to do.
Thus, in 1922 Northern Ireland began functioning as a self-governing region of the United Kingdom. Two-thirds of its population (about one million people) was Protestant and about one-third (roughly 500,000 people) was Catholic. Well before partition, Northern Ireland, particularly Belfast, had attracted economic migrants from elsewhere in Ireland seeking employment in its flourishing linen-making and shipbuilding industries. The best jobs had gone to Protestants, but the humming local economy still provided work for Catholics. Over and above the long-standing dominance of Northern Ireland politics that resulted for the Ulster Unionist Party (UUP) by virtue of the Protestants’ sheer numerical advantage, loyalist control of local politics was ensured by the gerrymandering of electoral districts that concentrated and minimized Catholic representation. Moreover, by restricting the franchise to ratepayers (the taxpaying heads of households) and their spouses, representation was further limited for Catholic households, which tended to be larger (and more likely to include unemployed adult children) than their Protestant counterparts. Those who paid rates for more than one residence (more likely to be Protestants) were granted an additional vote for each ward in which they held property (up to six votes). Catholics argued that they were discriminated against when it came to the allocation of public housing, appointments to public service jobs, and government investment in neighbourhoods. They were also more likely to be the subjects of police harassment by the almost exclusively Protestant RUC and Ulster Special Constabulary (B Specials).
The divide between Catholics and Protestants in Northern Ireland had little to do with theological differences but instead was grounded in culture and politics. Neither Irish history nor the Irish language was taught in schools in Northern Ireland, it was illegal to fly the flag of the Irish republic, and from 1956 to 1974 Sinn Féin, the party of Irish republicanism, also was banned in Northern Ireland. Catholics by and large identified as Irish and sought the incorporation of Northern Ireland into the Irish state. The great bulk of Protestants saw themselves as British and feared that they would lose their culture and privilege if Northern Ireland were subsumed by the republic. They expressed their partisan solidarity through involvement with Protestant unionist fraternal organizations such as the Orange Order, which found its inspiration in the victory of King William III (William of Orange) at the Battle of the Boyne in 1690 over his deposed Catholic predecessor, James II, whose siege of the Protestant community of Londonderry had earlier been broken by William. Despite these tensions, for 40 or so years after partition the status of unionist-dominated Northern Ireland was relatively stable.
IRA graffiti “IRA” spray-painted on a container, Derry (Londonderry), Northern Ireland.© Attila Jandi/Dreamstime.comRecognizing that any attempt to reinvigorate Northern Ireland’s declining industrial economy in the early 1960s would also need to address the province’s percolatingpolitical and social tensions, the newly elected prime minister of Northern Ireland, Terence O’Neill, not only reached out to the nationalist community but also, in early 1965, exchanged visits with Irish Taoiseach (Prime Minister) Seán Lemass—a radical step, given that the republic’s constitution included an assertion of sovereignty over the whole island. Nevertheless, O’Neill’s efforts were seen as inadequate by nationalists and as too conciliatory by loyalists, including the Rev. Ian Paisley, who became one of the most vehement and influential representatives of unionist reaction.
Civil rights activism, the Battle of Bogside, and the arrival of the British army
Contrary to the policies of UUP governments that disadvantaged Catholics, the Education Act that the Northern Ireland Parliament passed into law in 1947 increased educational opportunities for all citizens of the province. As a result, the generation of well-educated Catholics who came of age in the 1960s had new expectations for more equitable treatment. At a time when political activism was on the rise in Europe—from the events of May 1968 in France to the Prague Spring—and when the American civil rights movement was making great strides, Catholic activists in Northern Ireland such as John Humeand Bernadette Devlin came together to form civil rightsgroups such as the Northern Ireland Civil Rights Association (NICRA).
Although more than one violently disrupted political march has been pointed to as the starting point of the Troubles, it can be argued that the catalyzing event occurred on October 5, 1968, in Derry, where a march had been organized by the NICRA to protest discrimination and gerrymandering. The march was banned when unionists announced that they would be staging a counterdemonstration, but the NICRA decided to carry out their protest anyway. Rioting then erupted after the RUC violently suppressed the marchers with batons and a water cannon.
Similarly inflammatory were the events surrounding a march held by loyalists in Londonderry on August 12, 1969. Two days of rioting that became known as the Battle of Bogside (after the Catholic area in which the confrontation occurred) stemmed from the escalating clash between nationalists and the RUC, which was acting as a buffer between loyalist marchers and Catholic residents of the area. Rioting in support of the nationalists then erupted in Belfast and elsewhere, and the British army was dispatched to restore calm. Thereafter, violent confrontation only escalated, and the Troubles (a name that neither characterized the nature of the conflict nor assigned blame for it to one side or the other) had clearly begun.
The emergence of the Provisional IRA and the loyalist paramilitaries
Initially, the nationalists welcomed the British army as protectors and as a balance for the Protestant-leaning RUC. In time, however, the army would be viewed by nationalists as another version of the enemy, especially after its aggressive efforts to disarm republican paramilitaries. In the process, the Irish Republican Army (IRA) became the defender of the nationalist cause. From its base in Ireland(which had formally left the Commonwealth in 1949), the IRA had mounted an ineffectual guerrilla effort in support of Northern Ireland’s nationalists from 1956 to 1962, but, as the 1960s progressed, the IRA became less concerned with affairs in the north than with advancing a Marxist political agenda. As a result, a splinter group, the Provisional Irish Republican Army (Provos), which was prepared to use force to bring about unification, emerged as the champion of Northern Ireland’s nationalists. (The Official IRA would conduct operations in support of the republicans in Northern Ireland until undertaking a cease-fire in 1972, after which it effectively ceded the title of the IRA in the north to the Provos.) Believing that their fight was a continuation of the Irish War of Independence, the Provos adopted the tactics of guerrilla warfare, financed partly by members of the Irish diaspora in the United States and later supplied with arms and munitions by the government of Libyan strongman Muammar al-Qaddafi. Unionists also took up arms, swelling the numbers of loyalist paramilitary organizations, most notably the Ulster Volunteer Force (UVF) and Ulster Defence Association UDA).
British soldier in Northern Ireland Local people walking past a British soldier on guard in Northern Ireland, August 1969.Peter Kemp—AP/Shutterstock.comInternment, “peace walls,” and “Bloody Sunday”
In an attempt to address nationalist grievances, electoral boundaries were redrawn more fairly, efforts were made to rectify discrimination in housing and public employment, and the B Specials were decommissioned. At the same time, the government of Northern Ireland responded to the growing unrest by introducing increasingly stringent security measures, including internment (detention without trial). The overwhelming majority of those arrested, however, were nationalists.
As the 1970s progressed, rioting became more common in Belfast and Derry, bombings of public places (by both loyalists and republicans) increased, and both sides of the conflict perpetrated violent, deadly atrocities. Barbed wire laid by British soldiers to separate the sectarian communitiesevolved into brick and steel “peace walls,” some of which stood 45 feet (14 metres) high, segregating loyalist and republican enclaves, most famously the Falls Road Catholic community and the Shankill Protestant community of Belfast.
On January 30, 1972, the conflict reached a new level of intensity when British paratroopers fired on Catholic civil rights demonstrators in Londonderry, killing 13 and injuring 14 others (one of whom later died). The incident, which became known as “Bloody Sunday,” contributed to a spike in Provos recruitment and would remain controversial for decades, hinging on the question of which side fired first. In 2010 the Saville Report , the final pronouncement of a British government inquiry into the event, concluded that none of the victims had posed a threat to the troops and that their shooting had been unjustified. British Prime Minister David Cameron responded to the report by issuing a landmark apology for the shooting:
There is no point in trying to soften or equivocate what is in this report. It is clear from the tribunal’s authoritative conclusions that the events of Bloody Sunday were in no way justified….What happened should never, ever have happened….Some members of our armed forces acted wrongly. The government is ultimately responsible for the conduct of the armed forces and for that, on behalf of the government, indeed, on behalf of our country, I am deeply sorry.
In all, more than 480 people were killed as a result of the conflict in Northern Ireland in 1972, which proved to be the deadliest single year in the Troubles. That total included more than 100 fatalities for the British army, as the IRA escalated its onslaught. On July 21, “Bloody Friday,” nine people were killed and scores were injured when some two dozen bombs were detonated by the Provos in Belfast. Earlier, in March, frustrated with the Northern Ireland government’s failure to calm the situation, the British government suspended the Northern Ireland Parliament and reinstituted direct rule by Westminster.
Beginning in the mid-1970s, the IRA shifted the emphasis of its “Long War” from direct engagements with British troops to smaller-scale secretive operations, including the bombing of cities in Britain—a change of tactics the British military described as a shift from “insurgency” to “terrorism.” Similarly, the loyalist groups began setting off bombs in Ireland. Meanwhile, paramilitary violence at mid-decade (1974–76) resulted in the civilian deaths of some 370 Catholics and 88 Protestants.
Northern Ireland: peace movement Protesters against ongoing violence in Northern Ireland gathering on Shankill Road, Belfast, Northern Ireland, August 1976.Peace PeopleThe Sunningdale Agreement, hunger strikes, Bobby Sands, and the Brighton bombing
A glimmer of hope was offered by the Sunningdale Agreement , named for the English city in which it was negotiated in 1973. That agreement led to the creation of a new Northern Ireland Assembly, with proportional representation for all parties, and to the establishment of a Council of Ireland, which was to provide a role for Ireland in the affairs of Northern Ireland. Frustrated by the diminution of their political power and furious at the participation of the republic, loyalists scuttled the power-sharing plan with a general strike that brought the province to a halt in May 1974 and eventually forced a return to direct rule, which remained in place for some 25 years.
For the remainder of the decade, violence ebbed and flowed, cease-fires lingered and lapsed, and tit-for-tat bombings and assassinations continued, including the high-profile killing at sea in August 1979 of Lord Mountbatten, a relative of both Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip. In 1976 the opening of the specially designed Maze prison brought with it a shift in the treatment of IRA inmates from that of prisoners of war to that of common criminals. Seeking a return to their Special Category Status, the prisoners struck back, first staging the “blanket protest,” in which they refused to put on prison uniforms and instead wore only blankets, and then, in 1978, the “dirty protest,” in which inmates smeared the walls of their cells with excrement. The government of recently elected Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher refused to buckle, even in the face of hunger strikes in 1980–81 that led to the deaths of 10 prisoners, including Bobby Sands, who had won a seat in the British Parliament while incarcerated and fasting.
Sands’s election helped convince Sinn Féin, then operating as the political wing of the IRA, that the struggle for unification should be pursued at the ballot box as well as with the Armalite rifle. In June 1983 Sinn Féin leader Gerry Adams won a seat in Parliament representing West Belfast, though he refused to take it to avoid taking the compulsory oath of loyalty to the British queen.
The Anglo-Irish Agreement and Downing Street Declaration
In October 1984 an IRA bomb attack on the Conservative Party Conference in Brighton, England, took five lives and threatened that of Thatcher. Though she remained steadfast in the face of this attack, it was the “Iron Lady” who in November 1985 joined Irish Taoiseach Garret FitzGerald in signing the Anglo-Irish Agreement, under which both countries guaranteed that any change in the status of Northern Ireland would come about only with the consent of the majority of the people of Northern Ireland. The accordalso established the Intergovernmental Conference, which gave Ireland a consultative role in the political and security affairs of Northern Ireland for the first time. Finally, the agreement stipulated that power would be devolved back upon the government of Northern Ireland only if unionists and nationalists participated in power sharing.
Anglo-Irish Agreement (1985) Irish Taoiseach (Prime Minister) Garret FitzGerald and British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher signing the Anglo-Irish Agreement, November 15, 1985.Peter Kemp/APThe loyalists’ vehement opposition to the agreement included the resignation of all 15 unionist members of the House of Commons and a ramping up of violence. In the meantime, IRA bombings in London made headlines, and the reach of the British security forces extended to the killing of three Provos in Gibraltar. Behind the scenes, however, negotiations were underway. In 1993 British Prime Minister John Major and Irish Taoiseach Albert Reynolds issued the so-called Downing Street Declaration , which established a framework for all-party peace talks. A cease-fire declared by the Provos in 1994 and joined by the principal loyalist paramilitary groups fell apart in 1996 because Sinn Féin, which had replaced the more moderate Social Democratic and Labour Party (SDLP) as the leading nationalist party, had been excluded from peace talks because of the IRA’s continuing bombing campaign. Nevertheless, the unionists were at the table, prepared to consider a solution that included the participation of the republic of Ireland. After the IRA resumed its cease-fire in 1997, Sinn Féin was welcomed back to the talks, which now included the British and Irish governments, the SDLP, the Alliance Party of Northern Ireland, the UUP, and the Ulster Democratic Party, among others, though not the Paisley-led DUP, which was protesting the inclusion of Sinn Féin.
The Good Friday Agreement, the Omagh bombing, peace, and power sharing
Those talks, mediated by former U.S. senator George Mitchell, led to the Good Friday Agreement (Belfast Agreement), reached April 10, 1998. That landmark accordprovided for the creation of a power-sharing Northern Ireland Assembly, established an institutional arrangement for cross-border cooperation between the governments of Ireland and Northern Ireland on a range of issues, and lay the groundwork for continued consultation between the British and Irish governments. On May 22 Ireland and Northern Ireland held a joint referendum on the agreement, which was approved by 94 percent of those who voted in the republic and 71 percent of those voting in Northern Ireland, where Catholic approval of the accord (96 percent) was much higher than Protestant assent (52 per cent). Nonetheless, it was an IRA splinter group, the Real Irish Republican Army, which most dramatically violated the spirit of the agreement, with a bombing in Omagh in August that took 29 lives.
Elections for the new Assembly were held in June, but the IRA’s failure to decommission delayed the formation of the power-sharing Northern Ireland Executive until December 1999, when the IRA promised to fulfill its obligation to disarm. That month the republic of Ireland modified its constitution, removing its territorial claims to the whole of the island, and the United Kingdom yielded direct rule of Northern Ireland. Ostensibly the Troubles had come to end, but, though Northern Ireland began its most tranquil era in a generation, the peace was fragile. Sectarian antagonism persisted, the process of decommissioning was slow on both sides, and the rolling out of the new institutions was fitful, resulting in suspensions of devolution and the reimposition of direct rule.
In July 2005, however, the IRA announced that it had ordered all its units to “dump arms,” would henceforth pursue its goals only through peaceful means, and would work with international inspectors “to verifiably put its arms beyond use.” At a press conference in September, a spokesman for the Independent International Commission on Decommissioning stated, “We are satisfied that the arms decommissioned represent the totality of the IRA’s arsenal.” Decommissioning by unionist paramilitaries and other republican groups followed..
-

 25cm x 35cm Limerick Major Michael John O'Leary VC (29 September 1890 – 2 August 1961) was an Irish recipient of the Victoria Cross, the most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth forces. O'Leary achieved his award for single-handedly charging and destroying two German barricades defended by machine gun positions near the French village of Cuinchy, in a localised operation on the Western Front during the First World War. At the time of his action, O'Leary was a nine-year veteran of the British armed forces and by the time he retired from the British Army in 1921, he had reached the rank of lieutenant. He served in the army again during the Second World War, although his later service was blighted by periods of ill-health. At his final retirement from the military in 1945, O'Leary was an Army major in command of a prisoner of war camp. Between the wars, O'Leary spent many years employed as a police officer in Canada and is sometimes considered to be a Canadian recipient of the Victoria Cross. Following the Second World War he worked as a building contractor in London, where he died in 1961.Early life O'Leary was born in 1890, one of four children of Daniel and Margaret O'Leary, who owned a farm at Inchigeela, near Macroom in County Cork, Ireland. Daniel O'Leary was a fervent Irish nationalist and keen sportsman who participated in competitive weightlifting and football. Aged 16 and unwilling to continue to work on his parent's land, Michael O'Leary joined the Royal Navy, serving at the shore establishment HMS Vivid at Devonport for several years until rheumatism in his knees forced his departure from the service. Within a few months however, O'Leary had again tired of the farm and joined the Irish Guards regiment of the British Army. O'Leary served three years with the Irish Guards, leaving in August 1913 to join the Royal North-West Mounted Police (RNWMP) in Saskatchewan, Canada. Operating from Regina, Constable O'Leary was soon commended for his bravery in capturing two criminals following a two-hour gunbattle, for which service he was presented with a gold ring. At the outbreak of the First World War in Europe during August 1914, O'Leary was given permission to leave the RNWMP and return to Britain in order to rejoin the army as an active reservist. On 22 October, O'Leary was mobilized and on 23 November he joined his regiment in France, then fighting with the British Expeditionary Force, entrenched in Flanders. First World War service During December 1914, O'Leary saw heavy fighting with the Irish Guards and was Mentioned in Despatches and subsequently promoted to lance corporal on 5 January 1915. Three weeks later, on 30 January, the Irish Guards were ordered to prepare for an attack on German positions near Cuinchy on the La Bassée Canal, a response to a successful German operation in the area five days before. The Germans attacked first however, and on the morning of 1 February seized a stretch of canal embankment on the western end of the 2nd Brigade line from a company of Coldstream Guards. This section, known as the Hollow, was tactically important as it defended a culvert that passed underneath a railway embankment. 4 Company of Irish Guards, originally in reserve, were tasked with joining the Coldstream Guards in retaking the position at 04:00, but the attack was met with heavy machine gun fire and most of the assault party, including all of the Irish Guards officers, were killed or wounded To replace these officers, Second Lieutenant Innes of 1 Company was ordered forward to gather the survivors and withdraw, forming up at a barricade on the edge of the Hollow. Innes regrouped the survivors and, following a heavy bombardment from supporting artillery and with his own company providing covering fire, assisted the Coldstream Guards in a second attack at 10:15.Weighed down with entrenching equipment, the attacking Coldstream Guardsmen faltered and began to suffer heavy casualties. Innes too came under heavy fire from a German barricade to their front equipped with a machine gun. O'Leary had been serving as Innes's orderly, and had joined him in the operations earlier in the morning and again in the second attack. Charging past the rest of the assault party, O'Leary closed with the first German barricade at the top of the railway embankment and fired five shots, killing the gun's crew. Continuing forward, O'Leary confronted a second barricade, also armed with a machine gun 60 yards (55 m) further on and again mounted the railway embankment, to avoid the marshy ground on either side. The Germans spotted his approach, but could not bring their gun to bear on him before he opened fire, killing three soldiers and capturing two others after he ran out of ammunition.Reportedly, O'Leary had made his advance on the second barricade "intent upon killing another German to whom he had taken a dislike". Having disabled both guns and enabled the recapture of the British position, O'Leary then returned to his unit with his prisoners, apparently "as cool as if he had been for a walk in the park." For his actions, O'Leary received a battlefield promotion to sergeant on 4 February and was recommended for the Victoria Cross, which was gazetted on 16 February: No. 3556 Lance-Corporal Michael O'Leary, 1st Battalion, Irish Guards For conspicuous bravery at Cuinchy on the 1st February, 1915. When forming one of the storming party which advanced against the enemy's barricades he rushed to the front and himself killed five Germans who were holding the first barricade, after which he attacked a second barricade, about 60 yards further on, which he captured, after killing three of the enemy and making prisoners of two more. Lance-Corporal O'Leary thus practically captured the enemy's position by himself and prevented the attacking party from being fired upon. The London Gazette, 16 February 1915 Returning to Britain to receive his medal from King George V at Buckingham Palace on 22 June 1915, O'Leary was given a grand reception attended by thousands of Londoners in Hyde Park on 10 July. He was also the subject of much patriotic writing, including a poem in the Daily Mail and the short play O'Flaherty V.C. by George Bernard Shaw.Tributes came from numerous prominent figures of the day, including Sir Arthur Conan Doyle who said that "No writer in fiction would dare to fasten such an achievement on any of his characters, but the Irish have always had a reputation of being wonderful fighters, and Lance-Corporal Michael O’Leary is clearly one of them." and Thomas Scanlan who said: "I heard early this week of the great achievements of the Irish Guards. All Ireland is proud of O’Leary. He fully deserves the high honour that has been conferred upon him. Ireland is grateful to him."His reception was repeated in Macroom when he visited Ireland, with crowds turning out to applaud him. Daniel O'Leary was interviewed in a local newspaper regarding his son's exploit but was reportedly unimpressed, commenting: "I am surprised he didn't do more. I often laid out twenty men myself with a stick coming from Macroom Fair, and it is a bad trial of Mick that he could kill only eight, and he having a rifle and bayonet." O'Leary was further rewarded for his service, being advanced to a commissioned rank as a second lieutenant with the Connaught Rangers,and he was also presented with a Russian decoration, the Cross of St. George (third class).Despite his popularity with the crowds in London and Macroom, he was jeered by Ulster Volunteers at a recruitment drive in Ballaghaderrin during the autumn of 1915. This treatment caused such a scandal that it was raised in the Houses of Parliament in December. In 1916, O'Leary travelled to Salonika with the 5th battalion of the Connaught Rangers to serve in the Balkans campaign, remaining in theatre until the end of the war, following which he was stationed in Dover with the 2nd battalion until demobilised in 1921.During his service in the Balkans, O'Leary contracted malaria, which was to have severe negative effects on his health for the rest of his life. O'Leary was in the same regiment as the British actor Stanley Holloway and they served together in France. After the war ended, they remained close friends and Holloway often stayed in The May Fair Hotel where O'Leary worked as a concierge. Later life Leaving his wife Greta and their two children in Britain, O'Leary returned to Canada in March 1921 with the purported intention of rejoining the RNWMP, newly renamed the Royal Canadian Mounted Police. For unknown reasons, this plan came to nothing and after some months giving lectures on his war service and working in a publishing house, O'Leary joined the Ontario Provincial Police, charged with enforcing the prohibition laws. In 1924, with his family recently arrived from England, O'Leary left the Ontario police force and became a police sergeant with the Michigan Central Railway in Bridgeburg, Ontario, receiving £33 a month. In 1925, O'Leary was the subject of several scandals, being arrested for smuggling illegal immigrants and later for irregularities in his investigations. Although he was acquitted both times, he spent a week in prison following the second arrest and lost his job with the railway. Several months later, the municipal authorities in Hamilton, Ontario loaned him £70 to pay for him and his family to return to Ireland. Although his family sailed on the SS Leticia, O'Leary remained in Ontario, working with the attorney general's office. With his health in serious decline, the British Legion arranged for O'Leary to return to Britain and work in their poppy factory. By 1932, O'Leary was living in Southborne Avenue in Colindale, had regained his health and found employment as a commissionaire at The May Fair Hotel in London, at which he was involved in charitable events for wounded servicemen. With the mobilisation of the British Army in 1939, O'Leary returned to military service as a captain in the Middlesex Regiment. O'Leary was sent to France as part of the British Expeditionary Force but had returned to Britain before the Battle of France due to a recurrence of his malaria. No longer fit for full active service, O'Leary was transferred to the Pioneer Corps and took command of a prisoner of war camp in Southern England. In 1945, he was discharged from the military as unfit for duty on medical grounds as a major and found work as a building contractor, in which career he remained until his retirement in 1954. Two of O'Leary's sons had also served in the military during the war, with both receiving the Distinguished Flying Cross for their actions. As a Victoria Cross recipient, O'Leary joined the VE day parade in 1946, but at the 1956 Centenary VC review his place was taken by an imposter travelling in a bath chair. With his health again declining, O'Leary moved to Limesdale Gardens in Edgware shortly before his death in 1961 at the Whittington Hospital in Islington. O'Leary was buried at Mill Hill Cemetery following a funeral service at the Roman Catholic Annunciation Church in Burnt Oak which was attended by an honour guard from the Irish Guards and six of his children. His medals were later presented to the Irish Guards, and are on display at the Regimental Headquarters. He is also remembered in his birthplace, the macroom-online website listing him as a prominent citizen and states that "while many might consider he was fighting with the wrong army, in the wrong war, he was nevertheless a very brave, resourceful and capable soldier who deserved the honours bestowed upon him."
25cm x 35cm Limerick Major Michael John O'Leary VC (29 September 1890 – 2 August 1961) was an Irish recipient of the Victoria Cross, the most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth forces. O'Leary achieved his award for single-handedly charging and destroying two German barricades defended by machine gun positions near the French village of Cuinchy, in a localised operation on the Western Front during the First World War. At the time of his action, O'Leary was a nine-year veteran of the British armed forces and by the time he retired from the British Army in 1921, he had reached the rank of lieutenant. He served in the army again during the Second World War, although his later service was blighted by periods of ill-health. At his final retirement from the military in 1945, O'Leary was an Army major in command of a prisoner of war camp. Between the wars, O'Leary spent many years employed as a police officer in Canada and is sometimes considered to be a Canadian recipient of the Victoria Cross. Following the Second World War he worked as a building contractor in London, where he died in 1961.Early life O'Leary was born in 1890, one of four children of Daniel and Margaret O'Leary, who owned a farm at Inchigeela, near Macroom in County Cork, Ireland. Daniel O'Leary was a fervent Irish nationalist and keen sportsman who participated in competitive weightlifting and football. Aged 16 and unwilling to continue to work on his parent's land, Michael O'Leary joined the Royal Navy, serving at the shore establishment HMS Vivid at Devonport for several years until rheumatism in his knees forced his departure from the service. Within a few months however, O'Leary had again tired of the farm and joined the Irish Guards regiment of the British Army. O'Leary served three years with the Irish Guards, leaving in August 1913 to join the Royal North-West Mounted Police (RNWMP) in Saskatchewan, Canada. Operating from Regina, Constable O'Leary was soon commended for his bravery in capturing two criminals following a two-hour gunbattle, for which service he was presented with a gold ring. At the outbreak of the First World War in Europe during August 1914, O'Leary was given permission to leave the RNWMP and return to Britain in order to rejoin the army as an active reservist. On 22 October, O'Leary was mobilized and on 23 November he joined his regiment in France, then fighting with the British Expeditionary Force, entrenched in Flanders. First World War service During December 1914, O'Leary saw heavy fighting with the Irish Guards and was Mentioned in Despatches and subsequently promoted to lance corporal on 5 January 1915. Three weeks later, on 30 January, the Irish Guards were ordered to prepare for an attack on German positions near Cuinchy on the La Bassée Canal, a response to a successful German operation in the area five days before. The Germans attacked first however, and on the morning of 1 February seized a stretch of canal embankment on the western end of the 2nd Brigade line from a company of Coldstream Guards. This section, known as the Hollow, was tactically important as it defended a culvert that passed underneath a railway embankment. 4 Company of Irish Guards, originally in reserve, were tasked with joining the Coldstream Guards in retaking the position at 04:00, but the attack was met with heavy machine gun fire and most of the assault party, including all of the Irish Guards officers, were killed or wounded To replace these officers, Second Lieutenant Innes of 1 Company was ordered forward to gather the survivors and withdraw, forming up at a barricade on the edge of the Hollow. Innes regrouped the survivors and, following a heavy bombardment from supporting artillery and with his own company providing covering fire, assisted the Coldstream Guards in a second attack at 10:15.Weighed down with entrenching equipment, the attacking Coldstream Guardsmen faltered and began to suffer heavy casualties. Innes too came under heavy fire from a German barricade to their front equipped with a machine gun. O'Leary had been serving as Innes's orderly, and had joined him in the operations earlier in the morning and again in the second attack. Charging past the rest of the assault party, O'Leary closed with the first German barricade at the top of the railway embankment and fired five shots, killing the gun's crew. Continuing forward, O'Leary confronted a second barricade, also armed with a machine gun 60 yards (55 m) further on and again mounted the railway embankment, to avoid the marshy ground on either side. The Germans spotted his approach, but could not bring their gun to bear on him before he opened fire, killing three soldiers and capturing two others after he ran out of ammunition.Reportedly, O'Leary had made his advance on the second barricade "intent upon killing another German to whom he had taken a dislike". Having disabled both guns and enabled the recapture of the British position, O'Leary then returned to his unit with his prisoners, apparently "as cool as if he had been for a walk in the park." For his actions, O'Leary received a battlefield promotion to sergeant on 4 February and was recommended for the Victoria Cross, which was gazetted on 16 February: No. 3556 Lance-Corporal Michael O'Leary, 1st Battalion, Irish Guards For conspicuous bravery at Cuinchy on the 1st February, 1915. When forming one of the storming party which advanced against the enemy's barricades he rushed to the front and himself killed five Germans who were holding the first barricade, after which he attacked a second barricade, about 60 yards further on, which he captured, after killing three of the enemy and making prisoners of two more. Lance-Corporal O'Leary thus practically captured the enemy's position by himself and prevented the attacking party from being fired upon. The London Gazette, 16 February 1915 Returning to Britain to receive his medal from King George V at Buckingham Palace on 22 June 1915, O'Leary was given a grand reception attended by thousands of Londoners in Hyde Park on 10 July. He was also the subject of much patriotic writing, including a poem in the Daily Mail and the short play O'Flaherty V.C. by George Bernard Shaw.Tributes came from numerous prominent figures of the day, including Sir Arthur Conan Doyle who said that "No writer in fiction would dare to fasten such an achievement on any of his characters, but the Irish have always had a reputation of being wonderful fighters, and Lance-Corporal Michael O’Leary is clearly one of them." and Thomas Scanlan who said: "I heard early this week of the great achievements of the Irish Guards. All Ireland is proud of O’Leary. He fully deserves the high honour that has been conferred upon him. Ireland is grateful to him."His reception was repeated in Macroom when he visited Ireland, with crowds turning out to applaud him. Daniel O'Leary was interviewed in a local newspaper regarding his son's exploit but was reportedly unimpressed, commenting: "I am surprised he didn't do more. I often laid out twenty men myself with a stick coming from Macroom Fair, and it is a bad trial of Mick that he could kill only eight, and he having a rifle and bayonet." O'Leary was further rewarded for his service, being advanced to a commissioned rank as a second lieutenant with the Connaught Rangers,and he was also presented with a Russian decoration, the Cross of St. George (third class).Despite his popularity with the crowds in London and Macroom, he was jeered by Ulster Volunteers at a recruitment drive in Ballaghaderrin during the autumn of 1915. This treatment caused such a scandal that it was raised in the Houses of Parliament in December. In 1916, O'Leary travelled to Salonika with the 5th battalion of the Connaught Rangers to serve in the Balkans campaign, remaining in theatre until the end of the war, following which he was stationed in Dover with the 2nd battalion until demobilised in 1921.During his service in the Balkans, O'Leary contracted malaria, which was to have severe negative effects on his health for the rest of his life. O'Leary was in the same regiment as the British actor Stanley Holloway and they served together in France. After the war ended, they remained close friends and Holloway often stayed in The May Fair Hotel where O'Leary worked as a concierge. Later life Leaving his wife Greta and their two children in Britain, O'Leary returned to Canada in March 1921 with the purported intention of rejoining the RNWMP, newly renamed the Royal Canadian Mounted Police. For unknown reasons, this plan came to nothing and after some months giving lectures on his war service and working in a publishing house, O'Leary joined the Ontario Provincial Police, charged with enforcing the prohibition laws. In 1924, with his family recently arrived from England, O'Leary left the Ontario police force and became a police sergeant with the Michigan Central Railway in Bridgeburg, Ontario, receiving £33 a month. In 1925, O'Leary was the subject of several scandals, being arrested for smuggling illegal immigrants and later for irregularities in his investigations. Although he was acquitted both times, he spent a week in prison following the second arrest and lost his job with the railway. Several months later, the municipal authorities in Hamilton, Ontario loaned him £70 to pay for him and his family to return to Ireland. Although his family sailed on the SS Leticia, O'Leary remained in Ontario, working with the attorney general's office. With his health in serious decline, the British Legion arranged for O'Leary to return to Britain and work in their poppy factory. By 1932, O'Leary was living in Southborne Avenue in Colindale, had regained his health and found employment as a commissionaire at The May Fair Hotel in London, at which he was involved in charitable events for wounded servicemen. With the mobilisation of the British Army in 1939, O'Leary returned to military service as a captain in the Middlesex Regiment. O'Leary was sent to France as part of the British Expeditionary Force but had returned to Britain before the Battle of France due to a recurrence of his malaria. No longer fit for full active service, O'Leary was transferred to the Pioneer Corps and took command of a prisoner of war camp in Southern England. In 1945, he was discharged from the military as unfit for duty on medical grounds as a major and found work as a building contractor, in which career he remained until his retirement in 1954. Two of O'Leary's sons had also served in the military during the war, with both receiving the Distinguished Flying Cross for their actions. As a Victoria Cross recipient, O'Leary joined the VE day parade in 1946, but at the 1956 Centenary VC review his place was taken by an imposter travelling in a bath chair. With his health again declining, O'Leary moved to Limesdale Gardens in Edgware shortly before his death in 1961 at the Whittington Hospital in Islington. O'Leary was buried at Mill Hill Cemetery following a funeral service at the Roman Catholic Annunciation Church in Burnt Oak which was attended by an honour guard from the Irish Guards and six of his children. His medals were later presented to the Irish Guards, and are on display at the Regimental Headquarters. He is also remembered in his birthplace, the macroom-online website listing him as a prominent citizen and states that "while many might consider he was fighting with the wrong army, in the wrong war, he was nevertheless a very brave, resourceful and capable soldier who deserved the honours bestowed upon him." -

 35cm x 25cm Limerick"Danny Boy" is a ballad, written by English songwriter Frederic Weatherly in 1913, and set to the traditional Irish melody of "Londonderry Air".
35cm x 25cm Limerick"Danny Boy" is a ballad, written by English songwriter Frederic Weatherly in 1913, and set to the traditional Irish melody of "Londonderry Air".
In 1910, in Bath, Somerset, the English lawyer and lyricist Frederic Weatherly initially wrote the words to "Danny Boy" to a tune other than "Londonderry Air". After his Irish-born sister-in-law Margaret Enright Weatherly (known as Jess) in the United States sent him a copy of "Londonderry Air" in 1913 (an alternative version of the story has her singing the air to him in 1912 with different lyrics), Weatherly modified the lyrics of "Danny Boy" to fit the rhyme and meter of "Londonderry Air". Weatherly gave the song to the vocalist Elsie Griffin, who made it one of the most popular songs of the new century. In 1915, Ernestine Schumann-Heink produced the first recording of "Danny Boy". Jane Ross of Limavady is credited with collecting the melody of "Londonderry Air" in the mid-19th century from a musician she encountered."Danny Boy"  Danny Boy
Danny BoySong Published 1913 Genre Folk Songwriter(s) Frederic Weatherly (lyrics) in 1910 Recording Performed by Celtic Aire of the United States Air Force BandLyrics
The 1913 lyrics by Frederick E. Weatherly:Oh, Danny boy, the pipes, the pipes are calling From glen to glen, and down the mountain side. The summer's gone, and all the roses falling, It's you, It's you must go and I must bide. But come ye back when summer's in the meadow, Or when the valley's hushed and white with snow, It's I'll be there in sunshine or in shadow,— Oh, Danny boy, Oh Danny boy, I love you so! But when ye come, and all the flowers are dying, If I am dead, as dead I well may be, Ye'll come and find the place where I am lying, And kneel and say an Avé there for me. And I shall hear, though soft you tread above me, And all my grave will warmer, sweeter be, For you will bend and tell me that you love me, And I shall sleep in peace until you come to me!Meaning
There are various conjectures about the meaning of "Danny Boy".Some interpret the song to be a message from a parent to a son going off to war or participating in the Irish uprising (as suggested by the reference to "pipes calling glen to glen") or emigrating as part of the Irish diaspora. The 1918 version of the sheet music with Weatherly's printed signature included alternative lyrics ("Eily Dear"), with the instructions that "when sung by a man, the words in italic should be used; the song then becomes "Eily Dear", so that "Danny Boy" is only to be sung by a lady". Nonetheless, it is unclear whether this was Weatherly's intent.Usage
- Percy Grainger's Irish Tune from County Derry adapts the Danny Boy/Londonderry Air melody for wind ensemble in 1918.
- The song is popular for funerals; but the National Catholic Reporter wrote in 2001 that it "cannot be played during Mass."
Select recordings
"Danny Boy" has been recorded multiple times by a variety of performers. Several versions are listed below in chronological order.- 1940 Judy Garland Little Nellie Kelly soundtrack. Garland also sang it live at her concerts in Ireland and Scotland and most famously at her New York Palace Theatre debut in 1951.
- 1940 Glenn Miller and His Orchestra released a single that climbed to #17 in "Pop Memories 1890-1954" (not Billboard's charts);Arranged by Glenn Miller and pianist Chummy MacGregor.
- 1941 Bing Crosby Merry Christmas. "Danny Boy" was paired with "I'll Be Home for Christmas" on its original single. Recorded July 5, 1941.
- 1941 Deanna Durbin in the film It Started with Eve
- 1950 Al Hibbler released a single that rose to #9 on the R&B chart[12]
- 1959 Conway Twitty's version charted at #10 on the Billboard Hot 100, #18 on Top R&B.(banned by the BBC)
- 1961 Andy Williams used the song's title for his album Danny Boy and Other Songs I Love to Sing. The single hit #15 on the U.S. adult contemporary and #64 on the Hot 100 charts.
- 1964 Patti LaBelle and the Bluebelles released a single that peaked at #76 on the Hot 100.
- 1965 Jackie Wilson's version rose to #94 on the Hot 100 and #25 on the R&B charts.
- 1967 Ray Price's single hit #60 on the Hot 100 and #9 on the Country charts.
- 1992 Eric Clapton recorded an instrumental version released as a bonus track for Change the World [6]
- 1992 John McDermott released the song as an independent single.
- 1998 Sinéad O'Connor sang the song over Davy Spillane's uilleann pipes on Spillane's album The Sea of Dreams. Actor-filmmaker Gabriel Byrne said this version is his favourite.
- 2002 Johnny Cash recorded the song on his album American IV: The Man Comes Around, working with producer Rick Rubin in what would come to be the last album released during his lifetime. Cash had previously recorded the



































