The
1951 All-Ireland Senior Football Championship Final was the 64th All-Ireland Final and the deciding match of the
1951 All-Ireland Senior Football Championship, an inter-county
Gaelic football tournament for the top teams in
Ireland.
Mayo and
Meath met to decide the destination of the
Sam Maguire Cup.
Mayo won their second title in a row with goals by Tom Langan and Joe Gilvarry.
This was Mayo's second consecutive All-Ireland football title. They have not won an All-Ireland football title since. It is said that a legendary curse overshadows Mayo football since 1951
Mayo players Willie Casey, Paddy Jordan and former
GAA President Dr
Mick Loftus belatedly received their All-Ireland senior football medals 55 years later. Though squad members, they had not appeared as substitutes in the final and had initially been denied their medals.
Croke Park (
Irish:
Páirc an Chrócaigh) is a
Gaelic games stadium located in
Dublin, Ireland. Named after Archbishop
Thomas Croke, it is sometimes called
Croker by GAA fans and locals.
It serves as both the principal stadium and headquarters of the
Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA). Since 1891
the site has been used by the GAA to host Gaelic sports, including the annual All-Ireland in
Gaelic football and
hurling.
A major
expansion and redevelopment of the stadium ran from 1991–2005, raising capacity to its current 82,300 spectators.
This makes Croke Park the
third-largest stadium in Europe, and the largest not usually used for
association football.
Other events held at the stadium include the opening and closing ceremonies of the
2003 Special Olympics, and numerous musical concerts. In 2012, Irish pop group
Westlife sold out the stadium in record-breaking time: less than 5 minutes. From 2007–10, Croke Park hosted home matches of the
Ireland national rugby union team and the
Republic of Ireland national football team, while their new
Aviva Stadium was constructed. This use of Croke Park for non-Gaelic sports
was controversial and required temporary changes to GAA rules. In June 2012, the stadium hosted the closing ceremony of the
50th International Eucharistic Congress during which
Pope Benedict XVI gave an address over video link.
City and Suburban Racecourse

A fireworks and light display was held in Croke Park in front of 79,161 fans on Saturday 31 January 2009 to mark the GAA's 125th anniversary
The area now known as Croke Park was owned in the 1880s by Maurice Butterly and known as the City and Suburban Racecourse, or Jones' Road sports ground. From 1890 it was also used by the
Bohemian Football Club. In 1901 Jones' Road hosted the
IFA Cup football final when
Cliftonville defeated
Freebooters.
History
Recognising the potential of the Jones' Road sports ground a journalist and GAA member, Frank Dineen, borrowed much of the £3,250 asking price and bought the ground in 1908. In 1913 the GAA came into exclusive ownership of the plot when they purchased it from Dineen for £3,500. The ground was then renamed Croke Park in honour of Archbishop
Thomas Croke, one of the GAA's first patrons.
In 1913, Croke Park had only two stands on what is now known as the Hogan stand side and grassy banks all round. In 1917, a grassy hill was constructed on the railway end of Croke Park to afford patrons a better view of the pitch. This terrace was known originally as Hill 60, later renamed Hill 16 in memory of the 1916
Easter Rising. It is erroneously believed to have been built from the ruins of the GPO, when it was constructed the previous year in 1915.
In the 1920s, the GAA set out to create a high capacity stadium at Croke Park. Following the Hogan Stand, the Cusack Stand, named after
Michael Cusack from Clare (who founded the GAA and served as its first secretary), was built in 1927. 1936 saw the first double-deck Cusack Stand open with 5,000 seats, and concrete terracing being constructed on Hill 16. In 1952 the Nally Stand was built in memorial of
Pat Nally, another of the GAA founders. Seven years later, to celebrate the 75th anniversary of the GAA, the first cantilevered "New Hogan Stand" was opened.
The highest attendance ever recorded at an All-Ireland Senior Football Championship Final was 90,556 for
Offaly v
Down in
1961. Since the introduction of seating to the Cusack stand in 1966, the largest crowd recorded has been 84,516.
Bloody Sunday

Bloody Sunday remembrance plaque
During the
Irish War of Independence on 21 November 1920 Croke Park was the scene of a massacre by the
Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC). The Police, supported by the
British Auxiliary Division, entered the ground and began shooting into the crowd, killing or fatally wounding 14 civilians during a
Dublin-
Tipperary Gaelic football match. The dead included 13 spectators and Tipperary player
Michael Hogan. Posthumously, the Hogan stand built in 1924 was named in his honour. These shootings, on the day which became known as
Bloody Sunday, were a reprisal for the killing of 15 people associated with the
Cairo Gang, a group of
British Intelligence officers, by
Michael Collins' '
squad' earlier that day.
Dublin Rodeo
In 1924, American
rodeo promoter,
Tex Austin, staged the Dublin Rodeo,
Ireland's first professional rodeo at Croke Park Stadium.
For seven days, with two shows each day from August 18 to August 24, sell out crowds saw cowboys and cowgirls from Canada, the United States, Mexico, Argentina and Australia compete for rodeo championship titles.
Canadian bronc riders such as Andy Lund and his brother Art Lund, trick riders such as Ted Elder
and Vera McGinnis were among the contestants.
British Pathe filmed some of the rodeo events.
Stadium design
In 1984 the organisation decided to investigate ways to increase the capacity of the old stadium. The design for an 80,000 capacity stadium was completed in 1991. Gaelic sports have special requirements as they take place on a large field. A specific requirement was to ensure the spectators were not too far from the field of play. This resulted in the three-tier design from which viewing games is possible: the main concourse, a premium level incorporating hospitality facilities and an upper concourse. The premium level contains restaurants, bars and conference areas. The project was split into four phases over a 14-year period. Such was the importance of Croke Park to the GAA for hosting big games, the stadium did not close during redevelopment. During each phase different parts of the ground were redeveloped, while leaving the rest of the stadium open. Big games, including the annual All-Ireland Hurling and Football finals, were played in the stadium throughout the development.
The outside of the Cusack Stand
Phase one – New Cusack Stand
The first phase of construction was to build a replacement for Croke Park's Cusack Stand. A lower deck opened for use in 1994. The upper deck opened in 1995. Completed at a cost of £35 million, the new stand is 180 metres long, 35 metres high, has a capacity for 27,000 people and contains 46 hospitality suites. The new Cusack Stand contains three tiers from which viewing games is possible: the main concourse, a premium level incorporating hospitality facilities and finally an upper concourse. One end of the pitch was closer to the stand after this phase, as the process of slightly re-aligning the pitch during the redevelopment of the stadium began. The works were carried out by
Sisk Group.
Phase two – Davin Stand
Phase Two of the development started in late 1998 and involved extending the new Cusack Stand to replace the existing Canal End terrace. It involved reacquiring a rugby pitch that had been sold to
Belvedere College in 1910 by Frank Dineen. In payment and part exchange, the college was given the nearby Distillery Road sportsgrounds.
[19]
It is now known as The Davin Stand (Irish:
Ardán Dáimhím), after
Maurice Davin, the first president of the GAA. This phase also saw the creation of a tunnel which was later named the Ali tunnel in honour of
Muhammad Ali and
his fight against Al Lewis in July 1972 in Croke Park.
Phase three – Hogan Stand
Phase Three saw the building of the new Hogan Stand. This required a greater variety of spectator categories to be accommodated including general spectators, corporate patrons, VIPs, broadcast and media services and operation staff. Extras included a fitted-out mezzanine level for VIP and Ard Comhairle (Where the dignitaries sit) along with a top-level press media facility. The end of Phase Three took the total spectator capacity of Croke Park to 82,000.
Phase four – Nally Stand & Nally End/Dineen Hill 16 terrace
After the 2003 Special Olympics, construction began in September 2003 on the final phase, Phase Four. This involved the redevelopment of the Nally Stand, named after the athlete
Pat Nally, and Hill 16 into a new Nally End/Dineen Hill 16 terrace. While the name Nally had been used for the stand it replaced, the use of the name Dineen was new, and was in honour of
Frank Dineen, who bought the original stadium for the GAA in 1908, giving it to them in 1913. The old Nally Stand was taken away and reassembled in Pairc Colmcille, home of Carrickmore GAA in
County Tyrone.
The phase four development was officially opened by the then GAA President
Seán Kelly on 14 March 2005. For logistical reasons (and, to a degree, historical reasons), and also to provide cheaper high-capacity space, the area is a terrace rather than a seated stand, the only remaining standing-room in Croke Park. Unlike the previous Hill, the new terrace was divided into separate sections – Hill A (Cusack stand side), Hill B (behind the goals) and the Nally terrace (on the site of the old Nally Stand). The fully redeveloped Hill has a capacity of around 13,200, bringing the overall capacity of the stadium to 82,300. This made the stadium the second biggest in the EU after the
Camp Nou, Barcelona. However, London's new Wembley stadium has since overtaken Croke Park in second place. The presence of terracing meant that for the brief period when Croke Park hosted international
association football during 2007–2009, the capacity was reduced to approximately 73,500, due to FIFA's statutes stating that competitive games must be played in all-seater stadiums.
Pitch

Croke Park floodlights in use during Six Nations Championship match
The pitch in Croke Park is a soil pitch that replaced the
Desso GrassMaster pitch laid in 2002.
This replacement was made after several complaints by players and managers that the pitch was excessively hard and far too slippery.
Since January 2006, a special growth and lighting system called the SGL Concept has been used to assist grass growing conditions, even in the winter months. The system, created by Dutch company SGL (Stadium Grow Lighting), helps in controlling and managing all pitch growth factors, such as light, temperature, CO
2, water, air and nutrients.
Floodlighting
With the
2007 Six Nations clash with
France and possibly other matches in subsequent years requiring lighting the GAA installed
floodlights in the stadium (after planning permission was granted). Indeed, many other GAA grounds around the country have started to erect floodlights as the organisation starts to hold games in the evenings, whereas traditionally major matches were played almost exclusively on Sunday afternoons. The first game to be played under these lights at Croke Park was a
National Football League Division One match between
Dublin and
Tyrone on 3 February 2007 with Tyrone winning in front of a capacity crowd of over 81,000 – which remains a record attendance for a National League game, with Ireland's Six Nations match with France following on 11 February.
Temporary floodlights were installed for the
American Bowl game between
Chicago Bears and
Pittsburgh Steelers on the pitch in 1997, and again for the
2003 Special Olympics.
Concert

U2's Vertigo Tour at Croke Park in 2005

U2's 360° Tour at Croke Park in 2009
| 29 June 1985 |
U2 |
In Tua Nua, R.E.M., The Alarm, Squeeze |
The Unforgettable Fire Tour |
57,000 |
First Irish act to have a headline concert. Part of the concert was filmed for the group's documentary Wide Awake in Dublin. |
| 28 June 1986 |
Simple Minds |
|
Once Upon A Time Tour |
|
Guest appearance by Bono |
| 27 June 1987 |
U2 |
Light A Big Fire, The Dubliners, The Pogues, Lou Reed |
The Joshua Tree Tour |
114,000 |
|
| 28 June 1987 |
Christy Moore, The Pretenders, Lou Reed, Hothouse Flowers |
|
| 28 June 1996 |
Tina Turner |
Brian Kennedy |
Wildest Dreams Tour |
40,000/40,000 |
|
| 16 May 1997 |
Garth Brooks |
|
World Tour II |
|
|
| 18 May 1997 |
|
|
| 29 May 1998 |
Elton John & Billy Joel |
|
Face to Face 1998 |
|
|
| 30 May 1998 |
|
|
|
| 24 June 2005 |
U2 |
The Radiators from Space, The Thrills, The Bravery, Snow Patrol, Paddy Casey, Ash |
Vertigo Tour |
246,743 |
|
| 25 June 2005 |
|
| 27 June 2005 |
|
| 20 May 2006 |
Bon Jovi |
Nickelback |
Have a Nice Day Tour |
81,327 |
|
| 9 June 2006 |
Robbie Williams |
Basement Jaxx |
Close Encounters Tour |
|
|
| 6 October 2007 |
The Police |
Fiction Plane |
The Police Reunion Tour |
81,640 |
Largest attendance of the tour. |
| 31 May 2008 |
Celine Dion |
Il Divo |
Taking Chances World Tour |
69,725 |
Largest attendance for a solo female act |
| 1 June 2008 |
Westlife |
Shayne Ward |
Back Home Tour |
85,000 |
Second Irish act to have a headline concert. Largest attendance of the tour. Part of the concert was filmed for the group's documentary and concert DVD 10 Years of Westlife - Live at Croke Park Stadium. |
| 14 June 2008 |
Neil Diamond |
|
|
|
|
| 13 June 2009 |
Take That |
The Script |
Take That Present: The Circus Live |
|
|
| 24 July 2009 |
U2 |
Glasvegas, Damien Dempsey |
U2 360° Tour |
243,198 |
|
| 25 July 2009 |
Kaiser Chiefs, Republic of Loose |
|
| 27 July 2009 |
Bell X1, The Script |
The performances of "New Year's Day" and "I'll Go Crazy If I Don't Go Crazy Tonight" were recorded for the group's live album U22 and for the band's remix album Artificial Horizon and the live EP Wide Awake in Europe, respectively. |
| 5 June 2010 |
Westlife |
Wonderland, WOW, JLS, Jedward |
Where We Are Tour |
86,500 |
Largest attendance of the tour. |
| 18 June 2011 |
Take That |
Pet Shop Boys |
Progress Live |
154,828 |
|
| 19 June 2011 |
|
| 22 June 2012 |
Westlife |
Jedward, The Wanted, Lawson |
Greatest Hits Tour |
187,808[24] |
The 23 June 2012 date broke the stadium record for selling out its tickets in four minutes. Eleventh largest attendance at an outdoor stadium worldwide. Largest attendance of the tour and the band's music career history. Part of the concert was filmed for the group's documentary and concert DVD The Farewell Tour - Live in Croke Park. |
| 23 June 2012 |
| 26 June 2012 |
Red Hot Chili Peppers |
Noel Gallagher's High Flying Birds, The Vaccines |
I'm with You World Tour |
|
|
| 23 May 2014 |
One Direction |
5 Seconds of Summer |
Where We Are Tour |
235,008 |
|
| 24 May 2014 |
|
| 25 May 2014 |
|
| 20 June 2015 |
The Script & Pharrell Williams |
|
No Sound Without Silence Tour |
74,635 |
|
| 24 July 2015 |
Ed Sheeran |
|
x Tour |
162,308 |
|
| 25 July 2015 |
|
|
| 27 May 2016 |
Bruce Springsteen |
|
The River Tour 2016 |
160,188 |
|
| 29 May 2016 |
|
|
| 9 July 2016 |
Beyoncé |
Chloe x Halle, Ingrid Burley |
The Formation World Tour |
68,575 |
|
| 8 July 2017 |
Coldplay |
AlunaGeorge, Tove Lo |
A Head Full of Dreams Tour[25] |
80,398 |
|
| 22 July 2017 |
U2 |
Noel Gallagher's High Flying Birds |
The Joshua Tree Tour 2017 |
80,901 |
|
| 17 May 2018 |
The Rolling Stones |
The Academic |
No Filter Tour |
64,823 |
|
| 15 June 2018 |
Taylor Swift |
Camila Cabello, Charli XCX |
Taylor Swift's Reputation Stadium Tour |
136.000 |
Swift became the first woman headline two concerts in a row there. |
| 16 June 2018 |
| 7 July 2018 |
Michael Bublé |
Emeli Sandé |
|
|
| 24 May 2019 |
Spice Girls |
Jess Glynne |
Spice World - 2019 UK Tour |
|
|
| 5 July 2019 |
Westlife |
James Arthur
Wild Youth |
The 20 Touror The Twenty Tour |
|
The 5 July 2019 date sold out its tickets in six minutes. Second date released were also sold out in under forty-eight hours. |
| 6 July 2019 |
Non-Gaelic games
There was great debate in Ireland regarding the use of Croke Park for sports other than those of the GAA. As the GAA was founded as a
nationalist organisation to maintain and promote indigenous Irish sport, it has felt honour-bound throughout its history to oppose other, foreign (in practice, British), sports. In turn, nationalist groups supported the GAA as the prime example of purely Irish sporting culture.
Until its abolition in 1971, rule 27 of the GAA constitution stated that a member of the GAA could be banned from playing its games if found to be also playing association football, rugby or
cricket. That rule was abolished but
rule 42 still prohibited the use of GAA property for games with interests in conflict with the interests of the GAA. The belief was that rugby and association football were in competition with Gaelic football and hurling, and that if the GAA allowed these sports to use their ground it might be harmful to Gaelic games, while other sports, not seen as direct competitors with Gaelic football and hurling, were permitted, such as the two games of
American football (
Croke Park Classic college football game between
The University of Central Florida and
Penn State, and an
American Bowl NFL preseason game between the
Chicago Bears and the
Pittsburgh Steelers) on the Croke Park pitch during the 1990s.
[27]
On 16 April 2005, a motion to temporarily relax rule No. 42 was passed at the GAA Annual Congress. The motion gives the GAA Central Council the power to authorise the renting or leasing of Croke Park for events other than those controlled by the Association, during a period when
Lansdowne Road – the venue for international soccer and rugby matches – was closed for redevelopment. The final result was 227 in favour of the motion to 97 against, 11 votes more than the required two-thirds majority.
In January 2006, it was announced that the GAA had reached agreement with the
Football Association of Ireland (FAI) and
Irish Rugby Football Union (IRFU) to stage two Six Nations games and four soccer internationals at Croke Park in 2007 and in February 2007, use of the pitch by the FAI and the IRFU in 2008 was also agreed.
These agreements were within the temporary relaxation terms, as Lansdowne Road was still under redevelopment until 2010. Although the GAA had said that hosted use of Croke Park would not extend beyond 2008, irrespective of the redevelopment progress,
fixtures
for the
2009 Six Nations rugby tournament saw the Irish rugby team using Croke park for a third season. 11 February 2007 saw the first rugby union international to be played there. Ireland were leading France in a Six Nations clash, but lost 17–20 after conceding a last minute (converted) try.
Raphael Ibanez scored the first try in that match;
Ronan O'Gara scored Ireland's first ever try in Croke Park.
A second match between Ireland and
England on 24 February 2007 was politically symbolic because of the events of
Bloody Sunday in 1920.
There was considerable concern as to what reaction there would be to the singing of the British
national anthem "
God Save the Queen". Ultimately the anthem was sung without interruption or incident, and applauded by both sets of supporters at the match, which Ireland won by 43–13 (their largest ever win over England in rugby).
On 2 March 2010, Ireland played their final international rugby match against a Scotland team that was playing to avoid the wooden spoon and hadn't won a championship match against Ireland since 2001. Outside half, Dan Parks inspired the Scots to a 3-point victory and ended Irish Hopes of a triple crown.
On 24 March 2007, the first association football match took place at Croke Park. The
Republic of Ireland took on
Wales in
UEFA Euro 2008 qualifying Group D, with a
Stephen Ireland goal securing a
1–0 victory for the Irish in front of a crowd of 72,500. Prior to this, the
IFA Cup had been played at the then Jones' Road in 1901, but this was 12 years before the GAA took ownership.
Negotiations took place for the
NFL International Series's 2011 game to be held at Croke Park but the game was awarded to
Wembley Stadium.
World record attendance
On 2 May 2009, Croke Park was the venue for a
Heineken Cup rugby
semi-final, in which
Leinster defeated
Munster 25–6. The attendance of 82,208 set a new world record attendance for a club rugby union game.
[35] This record stood until 31 March 2012 when it was surpassed by an
English Premiership game between
Harlequins and
Saracens at
Wembley Stadium which hosted a crowd of 83,761.
This was beaten again in 2016 in the
Top 14 final at the
Nou Camp which hosted a crowd of 99,124
Skyline tour
A walkway,
known under a sponsorship deal as
Etihad Skyline Croke Park, opened on 1 June 2012.
From 44 metres above the ground, it offers views of Dublin city and the surrounding area.
The
Olympic Torch was brought to the stadium and along the walkway on 6 June 2012.
GAA Hall of Fame
On 11 February 2013, the GAA opened the Hall of Fame section in the Croke Park museum. The foundation of the award scheme is the Teams of the Millennium
the football team which was announced in 1999 and
the hurling team in 2000 and all 30 players were inducted into the hall of fame along with
Limerick hurler
Eamonn Cregan and
Offaly footballer
Tony McTague who were chosen by a GAA sub-committee from the years 1970–74.
New inductees will be chosen on an annual basis from the succeeding five-year intervals as well as from years preceding 1970.
In April 2014, Kerry legend Mick O'Dwyer, Sligo footballer Micheál Kerins, along with hurlers Noel Skehan of Kilkenny and Pat McGrath of Waterford became the second group of former players to receive hall of fame awards.
 The 1938 All-Ireland Football Final Replay on October 23rd, 1938 ended in the most bizarre fashion imaginable when with 2 minutes left to play, Galway supporters, mistakenly believing the referee had blown for full-time, invaded the pitch, causing a 20 minute delay before the final minutes could be played out.
Even more dramatic was the fact that by the time the pitch was cleared, most of the Kerry players seemed to have disappeared.
The 1938 All-Ireland Football Final Replay on October 23rd, 1938 ended in the most bizarre fashion imaginable when with 2 minutes left to play, Galway supporters, mistakenly believing the referee had blown for full-time, invaded the pitch, causing a 20 minute delay before the final minutes could be played out.
Even more dramatic was the fact that by the time the pitch was cleared, most of the Kerry players seemed to have disappeared.
 The confusion all began with a free awarded to Kerry by referee Peter Waters of Kildare with Galway leading the defending champions, by 2-4 to 0-6.
The referee placed the ball and blew his whistle for the kick to be taken while running towards the Galway goals. He looked round just as Sean Brosnan was taking the kick and seeing a Galway player too close he blew for the kick to be retaken.
Thinking that he had blown for full-time the jubilant Galway supporters invaded the pitch.
The confusion all began with a free awarded to Kerry by referee Peter Waters of Kildare with Galway leading the defending champions, by 2-4 to 0-6.
The referee placed the ball and blew his whistle for the kick to be taken while running towards the Galway goals. He looked round just as Sean Brosnan was taking the kick and seeing a Galway player too close he blew for the kick to be retaken.
Thinking that he had blown for full-time the jubilant Galway supporters invaded the pitch.
 It took all of twenty minutes to clear the pitch but only then did the real problems come to light. Jerry O’Leary Chairman of the Kerry Selection Committee outlined their dilemma.
It took all of twenty minutes to clear the pitch but only then did the real problems come to light. Jerry O’Leary Chairman of the Kerry Selection Committee outlined their dilemma.

 Somehow or other Kerry managed to re-field even if the team which played out the remaining minutes bore little resemblance to the starting fifteen.
Somehow or other Kerry managed to re-field even if the team which played out the remaining minutes bore little resemblance to the starting fifteen.
 More remarkable again was the fact that Kerry went on to add another point to their total before the referee finally blew for full-time with Galway winners by 2-4 to 0-7.
It was generally agreed that the confusion was of the crowd’s and not the referee’s making but questions remained about the total number of players Kerry had been permitted to use in those final few minutes.
More remarkable again was the fact that Kerry went on to add another point to their total before the referee finally blew for full-time with Galway winners by 2-4 to 0-7.
It was generally agreed that the confusion was of the crowd’s and not the referee’s making but questions remained about the total number of players Kerry had been permitted to use in those final few minutes.
 The National and Provincial papers and indeed all available Records to this day list only those 16 Kerry players who were involved prior to the 20 minute interruption but now (80 years on) for the first time all the players who played for Kerry in that October 23rd, 1938 All-Ireland Final Replay can be given their rightful place in the Record Books.
KERRY’s 24:
The National and Provincial papers and indeed all available Records to this day list only those 16 Kerry players who were involved prior to the 20 minute interruption but now (80 years on) for the first time all the players who played for Kerry in that October 23rd, 1938 All-Ireland Final Replay can be given their rightful place in the Record Books.
KERRY’s 24:

 That night, in front of a 1,500 crowd, at a Gaelic League organised Siamsa Mór in the Mansion House in Dawson Street, Art McCann presented the Galway team with their winners’ medals.
That night, in front of a 1,500 crowd, at a Gaelic League organised Siamsa Mór in the Mansion House in Dawson Street, Art McCann presented the Galway team with their winners’ medals.
 The Kerry players meanwhile joined 300 of their suppoeters at a Ceilidhe hosted by the Kerrymen’s Social Club in Rathmines Town Hall.
The National Newspapers may not always have reported the facts to Galway’s satisfaction but there can be no questioning the support of Galway County Council.
The Kerry players meanwhile joined 300 of their suppoeters at a Ceilidhe hosted by the Kerrymen’s Social Club in Rathmines Town Hall.
The National Newspapers may not always have reported the facts to Galway’s satisfaction but there can be no questioning the support of Galway County Council.
 Needless to say the Galway players received an unprecedented welcome on their return to Galway having first been feted along the way in Mullingar, Streamstown, Moate and Athlone.
GALWAY – 1938 ALL-IRELAND SENIOR FOOTBALL CHAMPIONS
Needless to say the Galway players received an unprecedented welcome on their return to Galway having first been feted along the way in Mullingar, Streamstown, Moate and Athlone.
GALWAY – 1938 ALL-IRELAND SENIOR FOOTBALL CHAMPIONS
 Back (L-R) Bobby Beggs, Ralph Griffin, John Burke, Jimmy McGauran, Charlie Connolly, Brendan Nestor, Dinny Sullivan, Mick Connaire, Martin Kelly. Front (L-R) Frank Cunniffe, Jackie Flavin, Mick Higgins, John ‘Tull’ Dunne (Capt), Ned Mulholland, Mick Raftery.
Substitutes: (not in photograph) Mick Ryder and Pat McDonagh.
TIME ADDED ON:
Not far behind the controversy surrounding the last few minutes of 1938 All-Ireland Football Final Replay was the controversy surrounding the last few seconds of the drawn match played a month earlier.
Back (L-R) Bobby Beggs, Ralph Griffin, John Burke, Jimmy McGauran, Charlie Connolly, Brendan Nestor, Dinny Sullivan, Mick Connaire, Martin Kelly. Front (L-R) Frank Cunniffe, Jackie Flavin, Mick Higgins, John ‘Tull’ Dunne (Capt), Ned Mulholland, Mick Raftery.
Substitutes: (not in photograph) Mick Ryder and Pat McDonagh.
TIME ADDED ON:
Not far behind the controversy surrounding the last few minutes of 1938 All-Ireland Football Final Replay was the controversy surrounding the last few seconds of the drawn match played a month earlier.

 The sides were level, Kerry 2-06 Galway 3-03, when Kerry’s J.J. Landers sent the ball between the Galway uprights for what looked like the winning point. However the thousands of celebrating Kerry supporters making for the Croke Park exits were soon stopped in their tracks.
The sides were level, Kerry 2-06 Galway 3-03, when Kerry’s J.J. Landers sent the ball between the Galway uprights for what looked like the winning point. However the thousands of celebrating Kerry supporters making for the Croke Park exits were soon stopped in their tracks.
 It was cruel luck on Kerry and while there were many who criticised the referee, Tom Culhane from Glin, County Limerick, for blowing the final whistle while John Joe Landers was it the act of shooting, Kerry’s County Board Chairman Denis J. Bailey wasn’t among them.
At the next Central Council meeting, in a remarkably generous response to the Referee’s Report being read he stated that ‘they in Kerry were quite satisfied with the result’ and ‘They wished to pay a tribute to Galway for their sporting spirit and also to the referee who, in their opinion, carried out his duties very well.’
The Central Council then awarded the two counties £300 each towards the costs of the two-week Collective Training Camps both counties had planned in the lead up to the Replay on October 23rd. Munster Council granted Kerry (pictured here in Collective Training) an additional £100.
It was cruel luck on Kerry and while there were many who criticised the referee, Tom Culhane from Glin, County Limerick, for blowing the final whistle while John Joe Landers was it the act of shooting, Kerry’s County Board Chairman Denis J. Bailey wasn’t among them.
At the next Central Council meeting, in a remarkably generous response to the Referee’s Report being read he stated that ‘they in Kerry were quite satisfied with the result’ and ‘They wished to pay a tribute to Galway for their sporting spirit and also to the referee who, in their opinion, carried out his duties very well.’
The Central Council then awarded the two counties £300 each towards the costs of the two-week Collective Training Camps both counties had planned in the lead up to the Replay on October 23rd. Munster Council granted Kerry (pictured here in Collective Training) an additional £100.
 Prior to that Central Council meeting, General Secretary, Pádraig Ó’Caoimh, received a telephone call from the New York GAA suggesting the replay take place in New York but the request (which was successfully repeated nine years later in 1947) was on this occasion turned down.
However doubts about the Replay even going ahead were immediately raised.
Prior to that Central Council meeting, General Secretary, Pádraig Ó’Caoimh, received a telephone call from the New York GAA suggesting the replay take place in New York but the request (which was successfully repeated nine years later in 1947) was on this occasion turned down.
However doubts about the Replay even going ahead were immediately raised.
 Satisfactory transport arrangements were eventually agreed and the match went ahead although the Kerry supporters who left Tralee on the so-called ‘ghost’ train at 1am on the morning of the October 23rd may still have felt hard done by.
Satisfactory transport arrangements were eventually agreed and the match went ahead although the Kerry supporters who left Tralee on the so-called ‘ghost’ train at 1am on the morning of the October 23rd may still have felt hard done by.
 In the lead-up to the game the Galway selectors expressed their delight at the success of their forwards short hand-passing game against the Kerry backs in the drawn match although there were some worries that not all their players had been able to attend the first week of Collective Training and of course there was Kerry’s Replay record to be considered.
Kerry had previously played in 4 All-Ireland Replays and won them all, a great source of encouragement to the Kerry supporters.
However amid some reports of disharmony within the Kerry camp, following a ‘trial match’ on the Sunday before the Replay, the Kerry selection Committee dropped a real bombshell.
Joe Keohane (Dublin Geraldines) who had been Kerry’s regular full-back for the previous two years and was one of the stars of their 1937 All-Ireland win over Cavan was replaced by young Paddy ‘Bawn’ Brosnan a member of the 1938 Kerry Junior team.
A back injury to Kerry’s best forward, J.J. Landers made him an extreme doubt for the Replay with Martin Regan on stand-by to take his place if required which is exactly what happened before that fateful free-kick, that infamous 20 minute delay and Kerry’s unprecedented use of 24 players.
Most definitely an All-Ireland Final and Final Replay never to be forgotten.
In the lead-up to the game the Galway selectors expressed their delight at the success of their forwards short hand-passing game against the Kerry backs in the drawn match although there were some worries that not all their players had been able to attend the first week of Collective Training and of course there was Kerry’s Replay record to be considered.
Kerry had previously played in 4 All-Ireland Replays and won them all, a great source of encouragement to the Kerry supporters.
However amid some reports of disharmony within the Kerry camp, following a ‘trial match’ on the Sunday before the Replay, the Kerry selection Committee dropped a real bombshell.
Joe Keohane (Dublin Geraldines) who had been Kerry’s regular full-back for the previous two years and was one of the stars of their 1937 All-Ireland win over Cavan was replaced by young Paddy ‘Bawn’ Brosnan a member of the 1938 Kerry Junior team.
A back injury to Kerry’s best forward, J.J. Landers made him an extreme doubt for the Replay with Martin Regan on stand-by to take his place if required which is exactly what happened before that fateful free-kick, that infamous 20 minute delay and Kerry’s unprecedented use of 24 players.
Most definitely an All-Ireland Final and Final Replay never to be forgotten.
 The Galway and Kerry players parade in front of the newly opened (1938) Cusack Stand
The Galway and Kerry players parade in front of the newly opened (1938) Cusack Stand
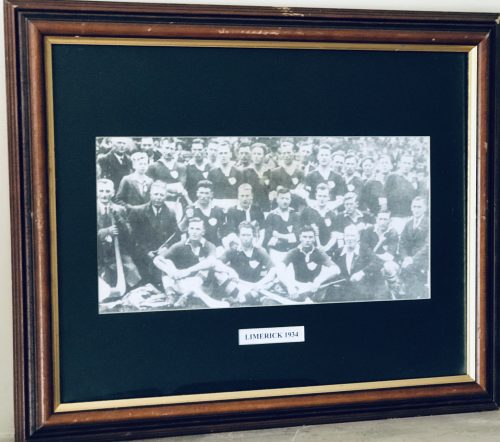
















 Limerick 5-2 Dublin 2-6
D Clohessy 4-0, M Mackey 1-1, J O’Connell 0-1
Limerick 5-2 Dublin 2-6
D Clohessy 4-0, M Mackey 1-1, J O’Connell 0-1
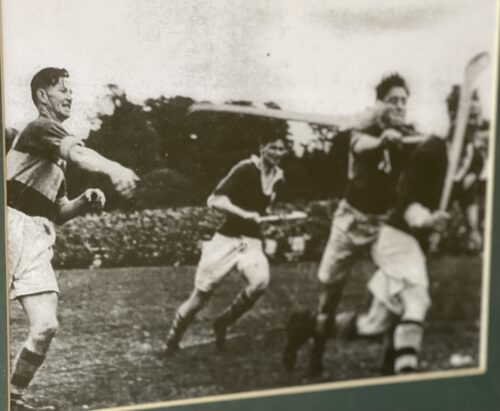
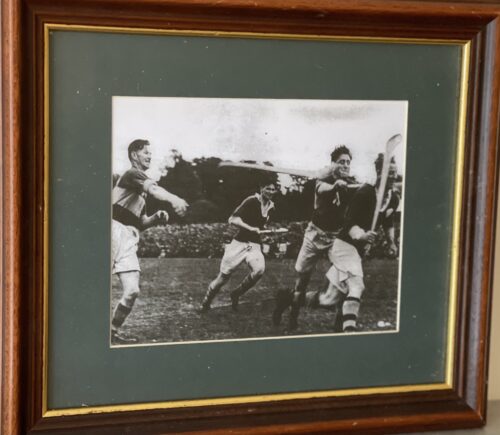
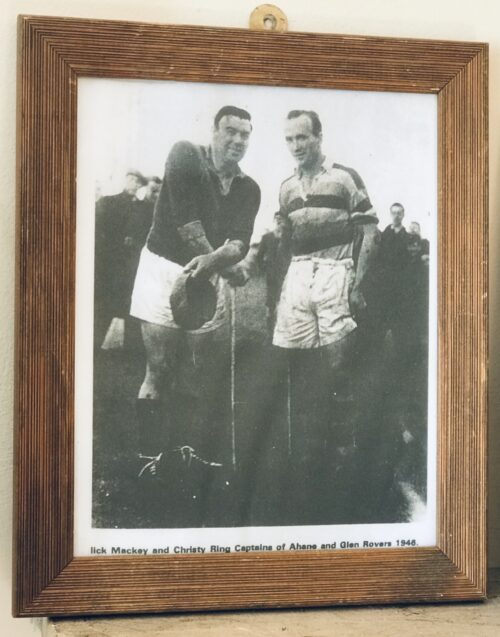
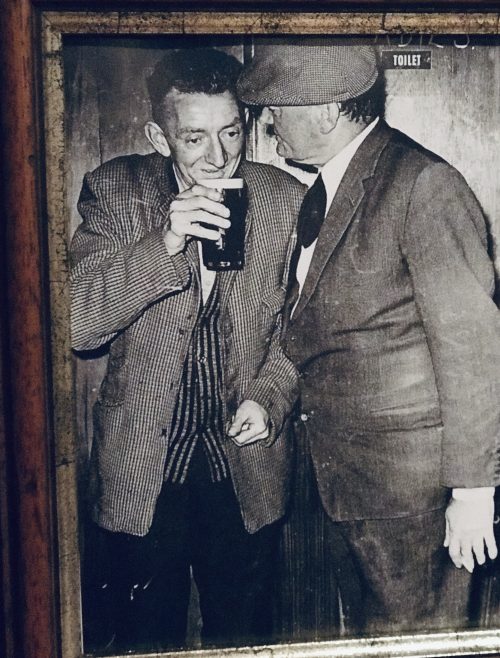
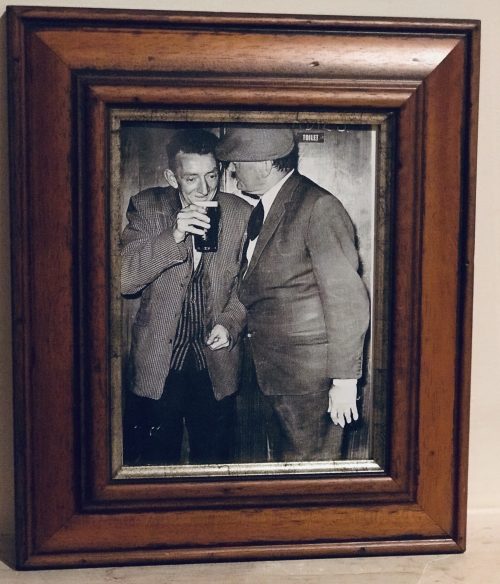














 Tom Moloughney, Jimmy Doyle, and Kieran Carey relax in the dressing room after Tipperary’s victory over Dublin in the 1961 All-Ireland final, a success that was to be repeated the following year. Picture from ‘The GAA — A People’s History’
Tom Moloughney, Jimmy Doyle, and Kieran Carey relax in the dressing room after Tipperary’s victory over Dublin in the 1961 All-Ireland final, a success that was to be repeated the following year. Picture from ‘The GAA — A People’s History’
















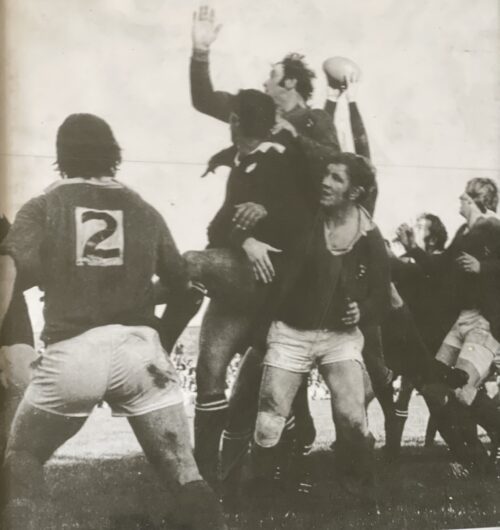
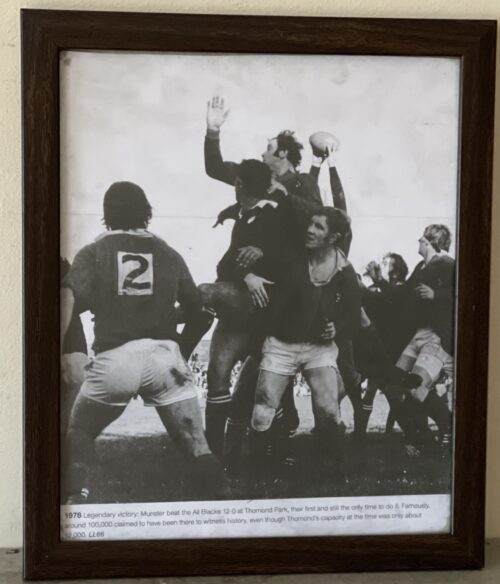
 Many years on, Stuart Wilson vividly recalled the Dennison tackles and spoke about them in remarkable detail and with commendable honesty: “The move involved me coming in from the blind side wing and it had been working very well on tour. It was a workable move and it was paying off so we just kept rolling it out. Against Munster, the gap opened up brilliantly as it was supposed to except that there was this little guy called Seamus Dennison sitting there in front of me.
“He just basically smacked the living daylights out of me. I dusted myself off and thought, I don’t want to have to do that again. Ten minutes later, we called the same move again thinking we’d change it slightly but, no, it didn’t work and I got hammered again.”
The game was 11 minutes old when the most famous try in the history of Munster rugby was scored.
Tom Kiernan recalled: “It came from a great piece of anticipation by Bowen who in the first place had to run around his man to get to Ward’s kick ahead. He then beat two men and when finally tackled, managed to keep his balance and deliver the ball to Cantillon who went on to score. All of this was evidence of sharpness on Bowen’s part.”
Very soon it would be 9-0. In the first five minutes, a towering garryowen by skipper Canniffe had exposed the vulnerability of the New Zealand rearguard under the high ball. They were to be examined once or twice more but it was from a long range but badly struck penalty attempt by Ward that full-back Brian McKechnie knocked on some 15 yards from his line and close to where Cantillon had touched down a few minutes earlier. You could sense White, Whelan, McLoughlin and co in the front five of the Munster scrum smacking their lips as they settled for the scrum. A quick, straight put-in by Canniffe, a well controlled heel, a smart pass by the scrum-half to Ward and the inevitability of a drop goal. And that’s exactly what happened.
The All Blacks enjoyed the majority of forward possession but the harder they tried, the more they fell into the trap set by the wily Kiernan and so brilliantly carried out by every member of the Munster team.
The tourists might have edged the line-out contest through Andy Haden and Frank Oliver but scrum-half Mark Donaldson endured a miserable afternoon as the Munster forwards poured through and buried him in the Thomond Park turf.
As the minutes passed and the All Blacks became more and more unsure as to what to try next, the Thomond Park hordes chanted “Munster-Munster–Munster” to an ever increasing crescendo until with 12 minutes to go, the noise levels reached deafening proportions.
And then ... a deep, probing kick by Ward put Wilson under further pressure. Eventually, he stumbled over the ball as it crossed the line and nervously conceded a five-metre scrum. The Munster heel was disrupted but the ruck was won, Tucker gained possession and slipped a lovely little pass to Ward whose gifted feet and speed of thought enabled him in a twinkle to drop a goal although surrounded by a swarm of black jerseys. So the game entered its final 10 minutes with the All Blacks needing three scores to win and, of course, that was never going to happen.
Munster knew this, so, too, did the All Blacks. Stu Wilson admitted as much as he explained his part in Wardy’s second drop goal: “Tony Ward banged it down, it bounced a little bit, jigged here, jigged there, and I stumbled, fell over, and all of a sudden the heat was on me. They were good chasers. A kick is a kick — but if you have lots of good chasers on it, they make bad kicks look good. I looked up and realised — I’m not going to run out of here so I just dotted it down. I wasn’t going to run that ball back out at them because five of those mad guys were coming down the track at me and I’m thinking, I’m being hit by these guys all day and I’m looking after my body, thank you. Of course it was a five-yard scrum and Ward banged over another drop goal. That was it, there was the game”.
The final whistle duly sounded with Munster 12 points ahead but the heroes of the hour still had to get off the field and reach the safety of the dressing room. Bodies were embraced, faces were kissed, backs were pummelled, you name it, the gauntlet had to be walked. Even the All Blacks seemed impressed with the sense of joy being released all about them. Andy Haden recalled “the sea of red supporters all over the pitch after the game, you could hardly get off for the wave of celebration that was going on. The whole of Thomond Park glowed in the warmth that someone had put one over on the Blacks.”
Controversially, the All Blacks coach, Jack Gleeson (usually a man capable of accepting the good with the bad and who passed away of cancer within 12 months of the tour), in an unguarded (although possibly misunderstood) moment on the following day, let slip his innermost thoughts on the game.
“We were up against a team of kamikaze tacklers,” he lamented. “We set out on this tour to play 15-man rugby but if teams were to adopt the Munster approach and do all they could to stop the All Blacks from playing an attacking game, then the tour and the game would suffer.”
It was interpreted by the majority of observers as a rare piece of sour grapes from a group who had accepted the defeat in good spirit and it certainly did nothing to diminish Munster respect for the All Blacks and their proud rugby tradition.
Many years on, Stuart Wilson vividly recalled the Dennison tackles and spoke about them in remarkable detail and with commendable honesty: “The move involved me coming in from the blind side wing and it had been working very well on tour. It was a workable move and it was paying off so we just kept rolling it out. Against Munster, the gap opened up brilliantly as it was supposed to except that there was this little guy called Seamus Dennison sitting there in front of me.
“He just basically smacked the living daylights out of me. I dusted myself off and thought, I don’t want to have to do that again. Ten minutes later, we called the same move again thinking we’d change it slightly but, no, it didn’t work and I got hammered again.”
The game was 11 minutes old when the most famous try in the history of Munster rugby was scored.
Tom Kiernan recalled: “It came from a great piece of anticipation by Bowen who in the first place had to run around his man to get to Ward’s kick ahead. He then beat two men and when finally tackled, managed to keep his balance and deliver the ball to Cantillon who went on to score. All of this was evidence of sharpness on Bowen’s part.”
Very soon it would be 9-0. In the first five minutes, a towering garryowen by skipper Canniffe had exposed the vulnerability of the New Zealand rearguard under the high ball. They were to be examined once or twice more but it was from a long range but badly struck penalty attempt by Ward that full-back Brian McKechnie knocked on some 15 yards from his line and close to where Cantillon had touched down a few minutes earlier. You could sense White, Whelan, McLoughlin and co in the front five of the Munster scrum smacking their lips as they settled for the scrum. A quick, straight put-in by Canniffe, a well controlled heel, a smart pass by the scrum-half to Ward and the inevitability of a drop goal. And that’s exactly what happened.
The All Blacks enjoyed the majority of forward possession but the harder they tried, the more they fell into the trap set by the wily Kiernan and so brilliantly carried out by every member of the Munster team.
The tourists might have edged the line-out contest through Andy Haden and Frank Oliver but scrum-half Mark Donaldson endured a miserable afternoon as the Munster forwards poured through and buried him in the Thomond Park turf.
As the minutes passed and the All Blacks became more and more unsure as to what to try next, the Thomond Park hordes chanted “Munster-Munster–Munster” to an ever increasing crescendo until with 12 minutes to go, the noise levels reached deafening proportions.
And then ... a deep, probing kick by Ward put Wilson under further pressure. Eventually, he stumbled over the ball as it crossed the line and nervously conceded a five-metre scrum. The Munster heel was disrupted but the ruck was won, Tucker gained possession and slipped a lovely little pass to Ward whose gifted feet and speed of thought enabled him in a twinkle to drop a goal although surrounded by a swarm of black jerseys. So the game entered its final 10 minutes with the All Blacks needing three scores to win and, of course, that was never going to happen.
Munster knew this, so, too, did the All Blacks. Stu Wilson admitted as much as he explained his part in Wardy’s second drop goal: “Tony Ward banged it down, it bounced a little bit, jigged here, jigged there, and I stumbled, fell over, and all of a sudden the heat was on me. They were good chasers. A kick is a kick — but if you have lots of good chasers on it, they make bad kicks look good. I looked up and realised — I’m not going to run out of here so I just dotted it down. I wasn’t going to run that ball back out at them because five of those mad guys were coming down the track at me and I’m thinking, I’m being hit by these guys all day and I’m looking after my body, thank you. Of course it was a five-yard scrum and Ward banged over another drop goal. That was it, there was the game”.
The final whistle duly sounded with Munster 12 points ahead but the heroes of the hour still had to get off the field and reach the safety of the dressing room. Bodies were embraced, faces were kissed, backs were pummelled, you name it, the gauntlet had to be walked. Even the All Blacks seemed impressed with the sense of joy being released all about them. Andy Haden recalled “the sea of red supporters all over the pitch after the game, you could hardly get off for the wave of celebration that was going on. The whole of Thomond Park glowed in the warmth that someone had put one over on the Blacks.”
Controversially, the All Blacks coach, Jack Gleeson (usually a man capable of accepting the good with the bad and who passed away of cancer within 12 months of the tour), in an unguarded (although possibly misunderstood) moment on the following day, let slip his innermost thoughts on the game.
“We were up against a team of kamikaze tacklers,” he lamented. “We set out on this tour to play 15-man rugby but if teams were to adopt the Munster approach and do all they could to stop the All Blacks from playing an attacking game, then the tour and the game would suffer.”
It was interpreted by the majority of observers as a rare piece of sour grapes from a group who had accepted the defeat in good spirit and it certainly did nothing to diminish Munster respect for the All Blacks and their proud rugby tradition.
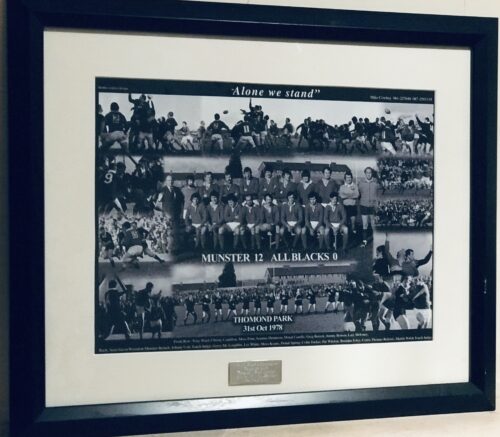
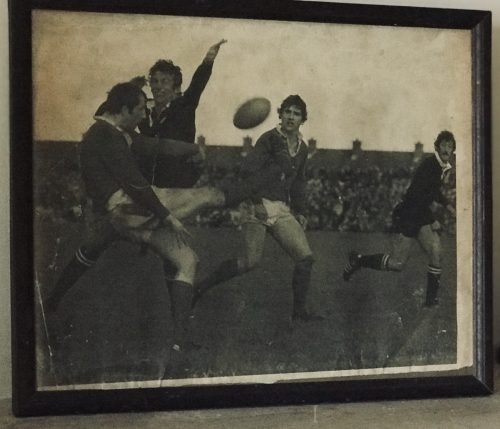
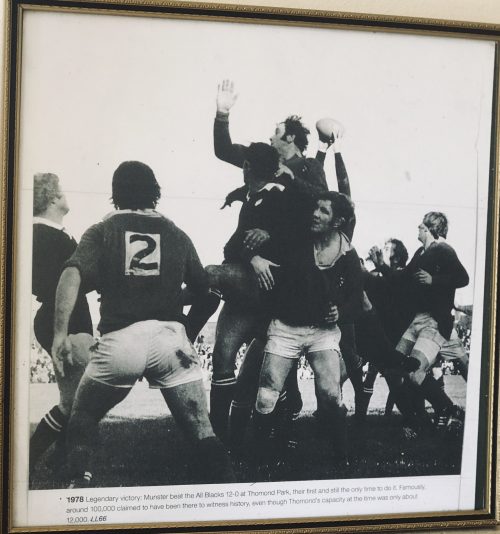




























 However, the Limerick players of 2007 will go down as heroes on Shannonside, regardless of a sub-standard performance on the first Sunday of September.
After an
However, the Limerick players of 2007 will go down as heroes on Shannonside, regardless of a sub-standard performance on the first Sunday of September.
After an  Henry Shefflin was the Cats captain that year and notched 1-2 for himself on the big day, while Eddie Brennan top-scored with a tally of 1-5.
Henry Shefflin was the Cats captain that year and notched 1-2 for himself on the big day, while Eddie Brennan top-scored with a tally of 1-5.




