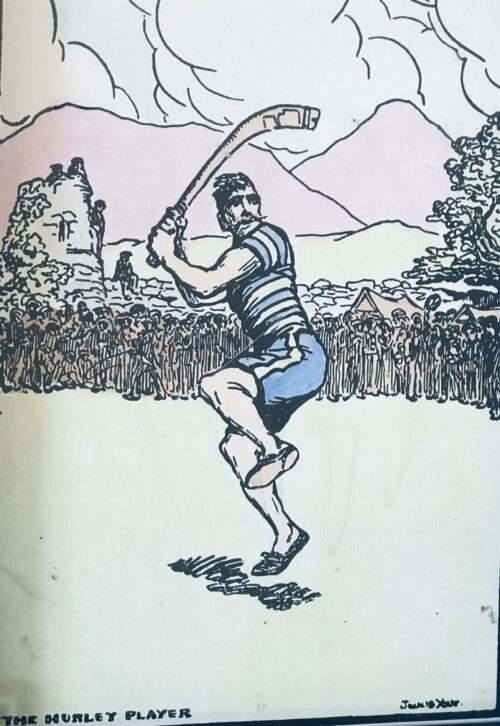
The Hurley Playerby Jack B Yeats in nice, offset frame.
33cm x 24cm
Jack Butler Yeats RHA (29 August 1871 – 28 March 1957) was an
Irish artist and Olympic medalist.
W. B. Yeats was his brother.
Butler's early style was that of an illustrator; he only began to work regularly in
oils in 1906.
His early pictures are simple lyrical depictions of
landscapes and figures, predominantly from the west of Ireland—especially of his boyhood home of
Sligo. Yeats's work contains elements of
Romanticism. He later would adopt the style of
Expressionism
Biography
Yeats was born in
London, England. He was the youngest son of Irish portraitist
John Butler Yeats and the brother of
W. B. Yeats, who received the 1923
Nobel Prize in Literature. He grew up in
Sligo with his maternal grandparents, before returning to his parents' home in London in 1887. Early in his career he worked as an illustrator for magazines like the
Boy's Own Paper and
Judy, drew comic strips, including the
Sherlock Holmes parody "Chubb-Lock Homes" for
Comic Cuts, and wrote articles for
Punch under the pseudonym "W. Bird".
In 1894 he married Mary Cottenham, also a native of England and two years his senior, and resided in Wicklow according to the
Census of Ireland, 1911.
From around 1920, he developed into an intensely
Expressionist artist, moving from illustration to
Symbolism. He was sympathetic to the
Irish Republican cause, but not politically active. However, he believed that 'a painter must be part of the land and of the life he paints', and his own artistic development, as a
Modernist and
Expressionist, helped articulate a modern
Dublin of the 20th century, partly by depicting specifically Irish subjects, but also by doing so in the light of universal themes such as the loneliness of the individual, and the universality of the plight of man.
Samuel Beckett wrote that "Yeats is with the great of our time... because he brings light, as only the great dare to bring light, to the issueless predicament of existence."
The Marxist art critic and author
John Berger also paid tribute to Yeats from a very different perspective, praising the artist as a "great painter" with a "sense of the future, an awareness of the possibility of a world other than the one we know".
His favourite subjects included the Irish landscape, horses, circus and travelling players. His early paintings and drawings are distinguished by an energetic simplicity of line and colour, his later paintings by an extremely vigorous and experimental treatment of often thickly applied paint. He frequently abandoned the brush altogether, applying paint in a variety of different ways, and was deeply interested in the expressive power of colour. Despite his position as the most important Irish artist of the 20th century (
and the first to sell for over £1m), he took no pupils and allowed no one to watch him work, so he remains a unique figure. The artist closest to him in style is his friend, the Austrian painter,
Oskar Kokoschka.
Besides painting, Yeats had a significant interest in
theatre and in
literature. He was a close friend of
Samuel Beckett. He designed sets for the
Abbey Theatre, and three of his own plays were also produced there. He wrote novels in a
stream of consciousness style that
Joyce acknowledged, and also many essays. His literary works include
The Careless Flower,
The Amaranthers (much admired by Beckett),
Ah Well, A Romance in Perpetuity,
And To You Also, and
The Charmed Life. Yeats's paintings usually bear poetic and evocative titles. Indeed, his father recognized that Jack was a far better painter than he, and also believed that 'some day I will be remembered as the father of a great poet, and the poet is Jack'.He was elected a member of the
Royal Hibernian Academy in 1916.
He died in Dublin in 1957, and was buried in
Mount Jerome Cemetery.
Yeats holds the distinction of being Ireland's first medalist at the
Olympic Games in the wake of creation of the
Irish Free State. At the
1924 Summer Olympics in Paris, Yeats' painting
The Liffey Swim won a silver medal in the
arts and culture segment of the Games. In the competition records the painting is simply entitled
Swimming.
Works
In November 2010, one of Yeats's works,
A Horseman Enters a Town at Night, painted in 1948 and previously owned by novelist
Graham Greene, sold for nearly £350,000 at a
Christie's auction in London. A smaller work,
Man in a Room Thinking, painted in 1947, sold for £66,000 at the same auction. In 1999 the painting,
The Wild Ones, had sold at
Sotheby's in London for over £1.2m, the highest price yet paid for a Yeats painting.
Adam's Auctioneers hold the Irish record sale price for a Yeats painting,
A Fair Day, Mayo (1925), which sold for €1,000,000 in September 2011.
Hosting museums
- The Hunt Museum, Limerick
- The National Gallery of Ireland, Dublin
- The Hugh Lane Gallery, Dublin
- Crawford Art Gallery, Cork
- Irish Museum of Modern Art, Dublin
- The National Gallery of Canada, Ottawa
- Walters Art Museum, Baltimore
- Model Arts and Niland Gallery, Sligo
- The Municipal Art Collection, Waterford
- Ulster Museum, Belfast
- The Snite Museum of Art, University of Notre Dame
The Geography of Hurling

‘The Hurley Player’ by Jack B. Yeats
Kevin Whelan
Why is hurling currently popular in a compact region centred on east Munster and south Leinster, and in isolated pockets in the Glens of Antrim and in the Ards peninsula of County Down? The answer lies in an exploration of the interplay between culture, politics and environment over a long period of time.
TWO VERSIONS
By the eighteenth century it is quite clear that there were two principal, and regionally distinct,versions of the game. One was akin to modern field hockey, or shinty, in that it did not allow handling of the ball; it was played with a narrow, crooked stick; it used a hard wooden ball (the ‘crag’); it was mainly a winter game. This game, called camán (anglicised to ‘commons’), was confined to the northern half of the country; its southern limits were set sharply where the small farms of the drumlin belt petered out into the pastoral central lowlands. (Fig 1)
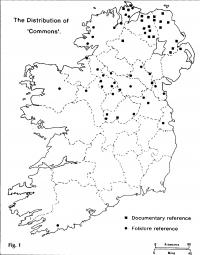
The second version of the game (iomán or báire) was of southern provenance. The ball could be handled or carried on the hurl, which was flat and round-headed; the ball (the sliothar) was soft and made of animal hair; the game was played in summer. Unlike commons, this form of hurling was patronised by the gentry, as a spectator and gambling sport, associated with fairs and other public gatherings, and involved a much greater degree of organisation (including advertising) than the more demotic ‘commons’. A 1742 advertisement for Ballyspellan Spa in Kilkenny noted that ‘horse racing, dancing and hurling will be provided for the pleasure of the quality at the spa’.
LANDLORD PATRONAGE
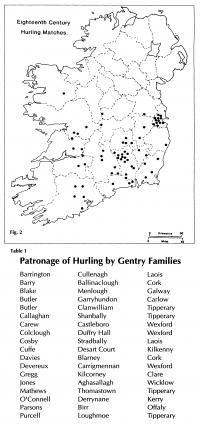
A number of factors determined the distribution of the southern game. (Fig. 2) The most important was the patronage of local gentry families, particularly those most closely embedded in the life of the local people. (Table 1) They picked the teams, arranged the hurling greens and supervised the matches, which were frequently organised as gambling events. The southern hurling zone coincides with the area where, in the late medieval period, the Norman and Gaelic worlds fused to produce a vigorous culture, reflected, for example, in the towerhouse as an architectural innovation. It coincides with well-drained, level terrain, seldom moving too far off the dry sod of limestone areas, which also happen to produce the best material for hurls – ash. It is closely linked to the distribution of big farms, where the relatively comfortable lifestyle afforded the leisure to pursue the sport.
Landlord patronage was essential to the well-being of the southern game; once it was removed, the structures it supported crumbled and the game collapsed into shapeless anarchy. The progressive separation of the manners and language of the élite from the common people was a pan-European phenomenon in the modern period. The gentry’s disengagement from immersion in the shared intimacies of daily life can be seen not just in hurling, but in other areas of language, music, sport and behaviour, as the gradual reception of metropolitan ideas eroded the older loyalties. As one hostile observer put it:
A hurling match is a scene of drunkenness, blasphemy and all kinds and manner of debauchery and faith, for my part, I would liken it to nothing else but to the idea I form of the Stygian regions where the daemonic inhabitants delight in torturing and afflicting each other.
DECLINE
By the mid nineteenth century, hurling had declined so steeply that it survived only in three pockets, around Cork city, in south-east Galway and in the area north of Wexford town. Amongst the reasons for decline were the withdrawal of gentry patronage in an age of political turbulence, sabbitudinarianism, modernisation and the dislocating impact of the Famine. Landlord, priest and magistrate all turned against the game. The older ‘moral economy’, which had linked landlord and tenant in bonds of patronage and deference, gave way to a sharper, adversarial relationship, especially in the 1790s, as the impact of the French Revolution in Ireland created a greater class-consciousness. Politicisation led to a growing anti-landlord feeling, which had been far more subdued in the heyday of gentry-sponsored hurling between the 1740s and 1760s.
 MICHAEL CUSACK & THE GAA
MICHAEL CUSACK & THE GAA
The model of élite participation in popular culture is a threefold process: first immersion, then withdrawal, and, finally rediscovery, invariably by an educated élite, and often with a nationalist agenda. ‘Rediscovery’ usually involves an invention of tradition, creating a packaged, homogenised and often false version of an idealised popular culture – as, for example, in the cult of the Highland kilt. The relationship of hurling and the newly established Gaelic Athletic Association in the 1880s shows this third phase with textbook clarity. Thus, when Michael Cusack set about reviving the game, he codified a synthetic version, principally modelled on the southern ‘iomán’ version that he had known as a child in Clare. Not surprisingly, this new game never caught on in the old ‘commons’ area, with the Glens of Antrim being the only major exception. Cusack and his GAA backers also wished to use the game as a nationalising idiom, a symbolic language of identity filling the void created by the speed of anglicisation. It had therefore to be sharply fenced off in organisational terms from competing ‘anglicised’ sports like cricket, soccer and rugby. Thus, from the beginning, the revived game had a nationalist veneer, its rules of association bristling like a porcupine with protective nationalist quills on which its perceived opponents would have to impale themselves. Its principal backers were those already active in the nationalist political culture of the time, classically the I.R.B. Its spread depended on the active support of an increasingly nationalist Catholic middle class – and as in every country concerned with the invention of tradition, its social constituency included especially journalists, publicans, schoolteachers, clerks, artisans and clerics. Thus, hurling’s early success was in south Leinster and east Munster, the very region which pioneered popular Irish nationalist politics – from the O’Connell campaign, to the devotional revolution in Irish Catholicism, from Fr. Matthews’ temperance campaign, to the Fenians, to the take-over of local government. The GAA was a classic example of the radical conservatism of this region – conservative in its ethos and ideology, radical in its techniques of organisation and mobilisation. The spread of hurling can be very closely matched to the spread of other radical conservative movements of this period – the diffusion of the indigenous Catholic teaching orders and the spread of co-operative dairying.
It would, however, be a mistake to see the spread of hurling under the aegis of the GAA solely in nationalist terms. The codification and success of gaelic games should be compared to the almost contemporaneous success in Britain of codified versions of soccer and rugby. All these were linked to rising spending power, a shortened working week (and the associated development of the ‘weekend’), improved and cheaper mass transport facilities which made spectator sports viable, expanded leisure time, the desire for organised sport among the working classes, and the commercialisation of leisure itself. The really distinctive feature of the GAA’s success was that it occurred in what was still a predominantly agrarian society. That success rested on the shrewd application of the principle of territoriality.
TERRITORIAL ALLEGIANCE
Irish rural life was essentially local life. Hurling was quintessentially a territorially based game – teams based on communities, parishes, counties, pitted one against the other. The painter Tony O’Malley has contrasted this tribal-territorial element in Irish sport to English attitudes:
If neighbours were playing like New Ross and Tullogher, there would be a real needle in it. When Carrickshock were playing, I once heard an old man shouting ‘come on the men that bate the tithe proctors’ and there was a tremor and real fervour in his voice. It was a battle cry, with hurleys as the swords, but with the same intensity.
Similar forces of territoriality have been identified behind the success of cricket in the West Indies and rugby in the Welsh valleys. The GAA tapped this deep-seated territorial loyalty, of the type which is beautifully captured in the rhetorical climax of the great underground classic of rural Ireland, Knocknagow or the Homes of Tipperary by Charles J. Kickham. Matt Donovan (Matt the Thrasher), the village hero, is competing against the outsider Captain French in a sledge-throwing contest. In the absence of steroids, Matt is pumping himself up before his throw:
Someone struck the big drum a single blow, as if by accident and, turning round quickly, the thatched roofs of the hamlet caught his eye. And, strange to say, those old mud walls and thatched roofs roused him as nothing else could. His breast heaved, as with glistening eyes, and that soft plaintive smile of his, he uttered the words, ‘For the credit of the little village!’ in a tone of the deepest tenderness. Then, grasping the sledge in his right hand, and drawing himself up to his full height, he measured the captain’s cast with his eye. The muscles of his arms seemed to start out like cords of steel as he wheeled slowly round and shot the ponderous hammer through the air. His eyes dilated as, with quivering nostrils, he watched its flight, till it fell so far beyond the best mark that even he himself started with astonishment. Then a shout of exultation burst from the excited throng; hands were convulsively grasped, and hats sent flying in the air; and in their wild joy they crushed around him and tried to lift him upon their shoulders.
The territorial allegiance and communal spirit celebrated and idealised by Kickham have died hard in Ireland. GAA club colours, for example were often drawn from old faction favours and, even now, an occasional faction slogan can still be heard. ‘If any man can, an Alley man can’. ‘Squeeze ‘em up Moycarkey and hang ‘em out to dry!’ Lingering animosities can sometimes surface in surprising ways: it is not unknown, for example, for an irate and disappointed Wexford hurling supporter (and what other kind of Wexford supporter is there?) to hurl abuse at Kilkenny, recalling an incident that occurred in Castlecomer to indignant Wexford United Irishmen: ‘Sure what good are they anyway? Didn’t they piss on the powder in ‘98?’ A possibly apocryphal incident occurred after a fiercely contested Cork-Tipperary match. Cork won but in Tipperary eyes that was solely due to a biased Limerick referee. When the disgruntled Tipperary supporters poured off the train at Thurles, they vented their frustrations on the only Limerick man they could find in the town – by tarring and feathering the statue of Archbishop Croke in the Square (presumably the only time in Irish history that a Catholic bishop has been tarred and feathered).
With the notable exception of Cork, the game has not been successfully transplanted into the cities. In Cork, close-knit working-class neighbourhoods like Blackrock and Gouldings Glen (home of Glen Rovers), and the strong antagonism between the hilly northside and the flat southside of the city, nourished the territoriality and community spirit so important to the game’s health. In Dublin, however, the modern suburbs, based on diversity, newness and mobility, have not proved hospitable receptacles of the game. Brendan Behan, brought up in the shadow of Croke Park, commented:
At home we played soccer in the street and sometimes a version of hurling, fast and sometimes savage, adapted from the long-pucking grace of Kilkenny and Tipperary to the crookeder, foreshortened, snappier brutality of the confines of a slum thoroughfare.
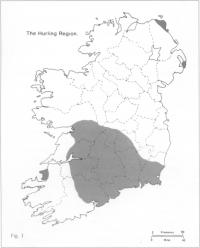 THE PRESENT HURLING REGION
THE PRESENT HURLING REGION
If one looks at the present hurling core region, it is remarkably compact. It also exhibits striking continuity with the earlier ‘iomán’ region. (Fig. 3) The hurling heartland is focused on the three counties of Cork, Tipperary and Kilkenny, with a supporting cast of adjacent counties – Limerick, Clare, Galway, Offaly, Laois, Waterford and Wexford. In the hurling core, the game is king, and very closely stitched into the fabric of the community. Describing the situation in Rathnure, Billy Rackard claimed that in the absence of hurling, ‘the parish would commit suicide, if a parish could commit suicide!’ The boundaries of the hurling region are surprisingly well-defined. To the north, the midland bogs act, as in a way they have done throughout history, as a buffer zone, resolutely impervious to the spread of cultural influences from further south. The western edge of the hurling zone can be traced over a long distance. In County Galway, for example, its boundaries run along a line from Ballinasloe to the city; north of this line is the Tuam-Dunmore area, and west of it is Connemara, both footballing territories. In County Clare, the boundary runs from Tubber on the Galway border through Corofin and Kilmaley to Labasheeda on the Shannon estuary. Last summer, the tremendous achievement of Clare in winning a Munster football championship was most thoroughly relished in the footballing bastion of west Clare, from Kilkee and Doonbeg to Milltown Malbay. One could easily establish this pattern by looking at the thickening density of the forest of flags as one drove from east to west in August.
Across the Shannon in Limerick, the football-hurling divide runs clearly along the scarp dividing hilly west Limerick from the lush limestone lowlands of east Limerick. West of this is an enclave of hurling parishes in the footballing

‘The Hurley Player’ by Jack B. Yeats
kingdom of Kerry in the area north of Tralee, in Ardfert, Bally heigue, Causeway and Ballyduff. From Limerick, the hurling boundary loops through County Cork from Mallow to the city and then to the coast at Cloyne – home to the maestro Christy Ring, who famously expressed his strategy for promoting the game in Cork – by stabbing a knife through every football found east of that line. Outside this core region, there are only the hurling enclaves in the Glens of Antrim and on the tip of the Ards peninsula, where the clubs of Ballycran, Ballygalget and Portaferry backbone Down’s hurling revival.
The interesting question then is how these boundaries formed. In almost every case, that boundary divides big farm and small farm areas and marks the transition from fertile, drift-covered limestone lowland to hillier, hungrier, wetter shales, flagstones, grits and granites. In County Galway, for example, hurling has not put down roots in the bony granite outcrops of Connemara, and in Clare the poorly drained flagstone deposits are equally inhospitable. If ash is emblematic of hurling areas, the rush is the distinctive symbol of football territory.
CONCLUSION
This brief case study illustrates the interplay of what the French call la longue durée – the long evolution of history – and les évenements – the specific, precise incidents and personalities which intervene and alter that evolution. Hurling offers a classic Irish example, and the current game demonstrates that, beneath the superficial breaks, fractures and discontinuities, there are sometimes surprisingly stable, deep structures. If the idiom of the game has changed, its grammar stays the same.


















 Charlton had beaten late entrant Bob Paisley, a multiple trophy winner, to the FAI hot seat, and his introduction to the gathered press was a million miles away from the carefully staged managed productions of the modern day.
In fact, it almost turned into an impromptu David Haye and Tony Bellew pre-match fight when Charlton challenged hardened journalist and ex-international Eamon Dunphy’s line of questioning. That relationship turned increasingly sour as time went by.
Charlton had beaten late entrant Bob Paisley, a multiple trophy winner, to the FAI hot seat, and his introduction to the gathered press was a million miles away from the carefully staged managed productions of the modern day.
In fact, it almost turned into an impromptu David Haye and Tony Bellew pre-match fight when Charlton challenged hardened journalist and ex-international Eamon Dunphy’s line of questioning. That relationship turned increasingly sour as time went by.
 This was the blueprint – or greenprint – of the Irish national team for the next decade.
Former players like Johnny Giles thought this indicated a lack of trust in the ability of players. Charlton saw it as pragmatic. His idea was to keep information and instruction simple.
This was the blueprint – or greenprint – of the Irish national team for the next decade.
Former players like Johnny Giles thought this indicated a lack of trust in the ability of players. Charlton saw it as pragmatic. His idea was to keep information and instruction simple.
 After a 1-0 defeat to Wales in his first match in charge, Charlton got to work on qualifying for the 1988 European Championship in West Germany.
After a 1-0 defeat to Wales in his first match in charge, Charlton got to work on qualifying for the 1988 European Championship in West Germany.
 While England staggered to defeat against the USSR and Holland, the Irish matched both teams stride for stride. Houghton described the 1-1 draw against the Soviets as “one of the best performances I’ve ever been involved in with Jack’s teams”.
While England staggered to defeat against the USSR and Holland, the Irish matched both teams stride for stride. Houghton described the 1-1 draw against the Soviets as “one of the best performances I’ve ever been involved in with Jack’s teams”.
 A 1-1 draw with the Dutch meant both teams had identical records as all three of Holland, England and Ireland progressed, with the Irish benefiting from the drawing of lots to qualify as group runners-up
After three drab stalemates, the party only truly began in Genoa against Romania in the last 16 – after another goalless game, Bonner saved Romania’s fifth penalty, leaving David O’Leary to take the decisive kick.
RTE commentator George Hamilton uttered the most important seven words Irish fans remember: “A nation holds its breath… We’re there!”
How ironic that the hero was O’Leary, another more football-minded defender that was often overlooked by Charlton.
O’Leary recalled: “There were about 20,000 brilliant Irish supporters behind the goal. They were so still and the eruption of green afterwards when the ball hit the net was absolutely amazing. It’s a fantastic memory.”
A 1-1 draw with the Dutch meant both teams had identical records as all three of Holland, England and Ireland progressed, with the Irish benefiting from the drawing of lots to qualify as group runners-up
After three drab stalemates, the party only truly began in Genoa against Romania in the last 16 – after another goalless game, Bonner saved Romania’s fifth penalty, leaving David O’Leary to take the decisive kick.
RTE commentator George Hamilton uttered the most important seven words Irish fans remember: “A nation holds its breath… We’re there!”
How ironic that the hero was O’Leary, another more football-minded defender that was often overlooked by Charlton.
O’Leary recalled: “There were about 20,000 brilliant Irish supporters behind the goal. They were so still and the eruption of green afterwards when the ball hit the net was absolutely amazing. It’s a fantastic memory.”
 Ireland’s propensity to draw a large proportion of games (30 out of 93 under Charlton) cost them dearly in the 1992 Euro qualifying group as only eight teams could qualify for Sweden.
They finished behind Graham Taylor’s stodgy England team, despite drawing home and away against them.
However, the Republic were reaching a new peak, with a young Roy Keane and Denis Irwin introduced to the team.
“The worst thing about missing out on Euro 92 was that Denmark won it. It should have been Ireland.” recalled a frustrated manager.
Ireland’s propensity to draw a large proportion of games (30 out of 93 under Charlton) cost them dearly in the 1992 Euro qualifying group as only eight teams could qualify for Sweden.
They finished behind Graham Taylor’s stodgy England team, despite drawing home and away against them.
However, the Republic were reaching a new peak, with a young Roy Keane and Denis Irwin introduced to the team.
“The worst thing about missing out on Euro 92 was that Denmark won it. It should have been Ireland.” recalled a frustrated manager.
 In the USA, the party started early in New York as Italy were beaten in the Big Apple by a Houghton strike.
Patrick Barclay summed it up best in The Observer: “Ireland’s blanket defence rendered vain all the creative endeavours of Roberto Baggio, who adorned this marvellous occasion but was not allowed to influence it because for 90 mins Jack Charlton’s sweat-soaked soldiers stayed about as close as ranks can get.”
Unfortunately, Ireland’s performances tailed off dramatically for the remainder of the tournament.
Such draining tactics were hard to administer in the humidity of Orlando, and the manager was banned from the touchline for venting his fury at officials over the lack of water for his troops against Mexico.
After squeezing through the group following a goalless draw with Norway, the Green bus ran out of fuel against the Dutch in the last 16.
In the USA, the party started early in New York as Italy were beaten in the Big Apple by a Houghton strike.
Patrick Barclay summed it up best in The Observer: “Ireland’s blanket defence rendered vain all the creative endeavours of Roberto Baggio, who adorned this marvellous occasion but was not allowed to influence it because for 90 mins Jack Charlton’s sweat-soaked soldiers stayed about as close as ranks can get.”
Unfortunately, Ireland’s performances tailed off dramatically for the remainder of the tournament.
Such draining tactics were hard to administer in the humidity of Orlando, and the manager was banned from the touchline for venting his fury at officials over the lack of water for his troops against Mexico.
After squeezing through the group following a goalless draw with Norway, the Green bus ran out of fuel against the Dutch in the last 16.

 It is sometimes opined in retrospect that the Republic could have done better with the quality of players at their disposal. They only won one of nine World Cup matches, scoring just four goals.
After USA’ 94, Dunphy said: “The minority who know their football well enough to distinguish between fact and fantasy have long since decided that even though the show is great, the football of the Charlton era has been, too often, lousy.”
But would liberation have taken away the organisational pragmatism that was central to the Green Wall being breached just 41 times in 93 games? After all, this was a team that also beat Brazil at home and Germany in Hannover.
Niall Quinn said: “We were happy as we were – beautiful, skilled losers.”
Big Jack made them coarse but clinical winners on the pitch and a lot happier off it.
It is sometimes opined in retrospect that the Republic could have done better with the quality of players at their disposal. They only won one of nine World Cup matches, scoring just four goals.
After USA’ 94, Dunphy said: “The minority who know their football well enough to distinguish between fact and fantasy have long since decided that even though the show is great, the football of the Charlton era has been, too often, lousy.”
But would liberation have taken away the organisational pragmatism that was central to the Green Wall being breached just 41 times in 93 games? After all, this was a team that also beat Brazil at home and Germany in Hannover.
Niall Quinn said: “We were happy as we were – beautiful, skilled losers.”
Big Jack made them coarse but clinical winners on the pitch and a lot happier off it.































 As spirit merchants Power’s of Dungarvan had access to the freshest fortified wine casks, and in this letter we can see a distillery requesting access to that stock.
The records of Thomas Power & Company are far from complete, but as you can see below even in the late 50’s Power’s were importing hogsheads full of wine from Portugal.
As spirit merchants Power’s of Dungarvan had access to the freshest fortified wine casks, and in this letter we can see a distillery requesting access to that stock.
The records of Thomas Power & Company are far from complete, but as you can see below even in the late 50’s Power’s were importing hogsheads full of wine from Portugal.
 As well as importing barrels of wine and fortified wines, Power’s clearly had a need for the finest empty port pipes from Sandeman.
As well as importing barrels of wine and fortified wines, Power’s clearly had a need for the finest empty port pipes from Sandeman.
 Power’s bottled a lot of Guinness, and until the mid-1950’s the stout traveled to Dungarvan in wooden barrels.
Power’s bottled a lot of Guinness, and until the mid-1950’s the stout traveled to Dungarvan in wooden barrels.










 By 1832, George Roe had inherited both of these plants which were near to each other. George continued their expansion and leased additional premises in Mount Brown, which were used as maltings, kilns, and warehouses.By 1827, output of the Thomas Street Distillery was reported as being 244,279 gallons. George Roe’s two sons, Henry and George, succeeded to the ownership in 1862, by which point the firm was large and prosperous, and the Roes a family of wealth and influence. So much so that in 1878, the Roes could afford to donate £250,000, a very large sum in those days, to the restoration of
By 1832, George Roe had inherited both of these plants which were near to each other. George continued their expansion and leased additional premises in Mount Brown, which were used as maltings, kilns, and warehouses.By 1827, output of the Thomas Street Distillery was reported as being 244,279 gallons. George Roe’s two sons, Henry and George, succeeded to the ownership in 1862, by which point the firm was large and prosperous, and the Roes a family of wealth and influence. So much so that in 1878, the Roes could afford to donate £250,000, a very large sum in those days, to the restoration of 






 Many years on, Stuart Wilson vividly recalled the Dennison tackles and spoke about them in remarkable detail and with commendable honesty: “The move involved me coming in from the blind side wing and it had been working very well on tour. It was a workable move and it was paying off so we just kept rolling it out. Against Munster, the gap opened up brilliantly as it was supposed to except that there was this little guy called Seamus Dennison sitting there in front of me.
“He just basically smacked the living daylights out of me. I dusted myself off and thought, I don’t want to have to do that again. Ten minutes later, we called the same move again thinking we’d change it slightly but, no, it didn’t work and I got hammered again.”
The game was 11 minutes old when the most famous try in the history of Munster rugby was scored.
Tom Kiernan recalled: “It came from a great piece of anticipation by Bowen who in the first place had to run around his man to get to Ward’s kick ahead. He then beat two men and when finally tackled, managed to keep his balance and deliver the ball to Cantillon who went on to score. All of this was evidence of sharpness on Bowen’s part.”
Very soon it would be 9-0. In the first five minutes, a towering garryowen by skipper Canniffe had exposed the vulnerability of the New Zealand rearguard under the high ball. They were to be examined once or twice more but it was from a long range but badly struck penalty attempt by Ward that full-back Brian McKechnie knocked on some 15 yards from his line and close to where Cantillon had touched down a few minutes earlier. You could sense White, Whelan, McLoughlin and co in the front five of the Munster scrum smacking their lips as they settled for the scrum. A quick, straight put-in by Canniffe, a well controlled heel, a smart pass by the scrum-half to Ward and the inevitability of a drop goal. And that’s exactly what happened.
The All Blacks enjoyed the majority of forward possession but the harder they tried, the more they fell into the trap set by the wily Kiernan and so brilliantly carried out by every member of the Munster team.
The tourists might have edged the line-out contest through Andy Haden and Frank Oliver but scrum-half Mark Donaldson endured a miserable afternoon as the Munster forwards poured through and buried him in the Thomond Park turf.
As the minutes passed and the All Blacks became more and more unsure as to what to try next, the Thomond Park hordes chanted “Munster-Munster–Munster” to an ever increasing crescendo until with 12 minutes to go, the noise levels reached deafening proportions.
And then ... a deep, probing kick by Ward put Wilson under further pressure. Eventually, he stumbled over the ball as it crossed the line and nervously conceded a five-metre scrum. The Munster heel was disrupted but the ruck was won, Tucker gained possession and slipped a lovely little pass to Ward whose gifted feet and speed of thought enabled him in a twinkle to drop a goal although surrounded by a swarm of black jerseys. So the game entered its final 10 minutes with the All Blacks needing three scores to win and, of course, that was never going to happen.
Munster knew this, so, too, did the All Blacks. Stu Wilson admitted as much as he explained his part in Wardy’s second drop goal: “Tony Ward banged it down, it bounced a little bit, jigged here, jigged there, and I stumbled, fell over, and all of a sudden the heat was on me. They were good chasers. A kick is a kick — but if you have lots of good chasers on it, they make bad kicks look good. I looked up and realised — I’m not going to run out of here so I just dotted it down. I wasn’t going to run that ball back out at them because five of those mad guys were coming down the track at me and I’m thinking, I’m being hit by these guys all day and I’m looking after my body, thank you. Of course it was a five-yard scrum and Ward banged over another drop goal. That was it, there was the game”.
The final whistle duly sounded with Munster 12 points ahead but the heroes of the hour still had to get off the field and reach the safety of the dressing room. Bodies were embraced, faces were kissed, backs were pummelled, you name it, the gauntlet had to be walked. Even the All Blacks seemed impressed with the sense of joy being released all about them. Andy Haden recalled “the sea of red supporters all over the pitch after the game, you could hardly get off for the wave of celebration that was going on. The whole of Thomond Park glowed in the warmth that someone had put one over on the Blacks.”
Controversially, the All Blacks coach, Jack Gleeson (usually a man capable of accepting the good with the bad and who passed away of cancer within 12 months of the tour), in an unguarded (although possibly misunderstood) moment on the following day, let slip his innermost thoughts on the game.
“We were up against a team of kamikaze tacklers,” he lamented. “We set out on this tour to play 15-man rugby but if teams were to adopt the Munster approach and do all they could to stop the All Blacks from playing an attacking game, then the tour and the game would suffer.”
It was interpreted by the majority of observers as a rare piece of sour grapes from a group who had accepted the defeat in good spirit and it certainly did nothing to diminish Munster respect for the All Blacks and their proud rugby tradition.
Many years on, Stuart Wilson vividly recalled the Dennison tackles and spoke about them in remarkable detail and with commendable honesty: “The move involved me coming in from the blind side wing and it had been working very well on tour. It was a workable move and it was paying off so we just kept rolling it out. Against Munster, the gap opened up brilliantly as it was supposed to except that there was this little guy called Seamus Dennison sitting there in front of me.
“He just basically smacked the living daylights out of me. I dusted myself off and thought, I don’t want to have to do that again. Ten minutes later, we called the same move again thinking we’d change it slightly but, no, it didn’t work and I got hammered again.”
The game was 11 minutes old when the most famous try in the history of Munster rugby was scored.
Tom Kiernan recalled: “It came from a great piece of anticipation by Bowen who in the first place had to run around his man to get to Ward’s kick ahead. He then beat two men and when finally tackled, managed to keep his balance and deliver the ball to Cantillon who went on to score. All of this was evidence of sharpness on Bowen’s part.”
Very soon it would be 9-0. In the first five minutes, a towering garryowen by skipper Canniffe had exposed the vulnerability of the New Zealand rearguard under the high ball. They were to be examined once or twice more but it was from a long range but badly struck penalty attempt by Ward that full-back Brian McKechnie knocked on some 15 yards from his line and close to where Cantillon had touched down a few minutes earlier. You could sense White, Whelan, McLoughlin and co in the front five of the Munster scrum smacking their lips as they settled for the scrum. A quick, straight put-in by Canniffe, a well controlled heel, a smart pass by the scrum-half to Ward and the inevitability of a drop goal. And that’s exactly what happened.
The All Blacks enjoyed the majority of forward possession but the harder they tried, the more they fell into the trap set by the wily Kiernan and so brilliantly carried out by every member of the Munster team.
The tourists might have edged the line-out contest through Andy Haden and Frank Oliver but scrum-half Mark Donaldson endured a miserable afternoon as the Munster forwards poured through and buried him in the Thomond Park turf.
As the minutes passed and the All Blacks became more and more unsure as to what to try next, the Thomond Park hordes chanted “Munster-Munster–Munster” to an ever increasing crescendo until with 12 minutes to go, the noise levels reached deafening proportions.
And then ... a deep, probing kick by Ward put Wilson under further pressure. Eventually, he stumbled over the ball as it crossed the line and nervously conceded a five-metre scrum. The Munster heel was disrupted but the ruck was won, Tucker gained possession and slipped a lovely little pass to Ward whose gifted feet and speed of thought enabled him in a twinkle to drop a goal although surrounded by a swarm of black jerseys. So the game entered its final 10 minutes with the All Blacks needing three scores to win and, of course, that was never going to happen.
Munster knew this, so, too, did the All Blacks. Stu Wilson admitted as much as he explained his part in Wardy’s second drop goal: “Tony Ward banged it down, it bounced a little bit, jigged here, jigged there, and I stumbled, fell over, and all of a sudden the heat was on me. They were good chasers. A kick is a kick — but if you have lots of good chasers on it, they make bad kicks look good. I looked up and realised — I’m not going to run out of here so I just dotted it down. I wasn’t going to run that ball back out at them because five of those mad guys were coming down the track at me and I’m thinking, I’m being hit by these guys all day and I’m looking after my body, thank you. Of course it was a five-yard scrum and Ward banged over another drop goal. That was it, there was the game”.
The final whistle duly sounded with Munster 12 points ahead but the heroes of the hour still had to get off the field and reach the safety of the dressing room. Bodies were embraced, faces were kissed, backs were pummelled, you name it, the gauntlet had to be walked. Even the All Blacks seemed impressed with the sense of joy being released all about them. Andy Haden recalled “the sea of red supporters all over the pitch after the game, you could hardly get off for the wave of celebration that was going on. The whole of Thomond Park glowed in the warmth that someone had put one over on the Blacks.”
Controversially, the All Blacks coach, Jack Gleeson (usually a man capable of accepting the good with the bad and who passed away of cancer within 12 months of the tour), in an unguarded (although possibly misunderstood) moment on the following day, let slip his innermost thoughts on the game.
“We were up against a team of kamikaze tacklers,” he lamented. “We set out on this tour to play 15-man rugby but if teams were to adopt the Munster approach and do all they could to stop the All Blacks from playing an attacking game, then the tour and the game would suffer.”
It was interpreted by the majority of observers as a rare piece of sour grapes from a group who had accepted the defeat in good spirit and it certainly did nothing to diminish Munster respect for the All Blacks and their proud rugby tradition.