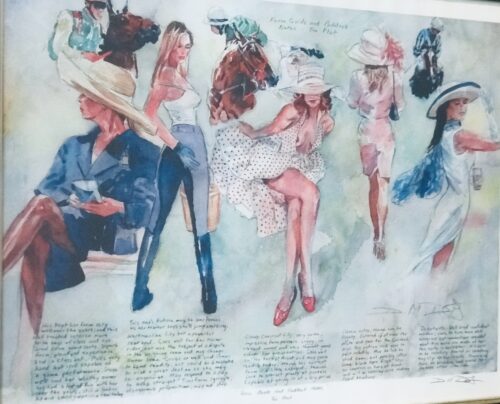
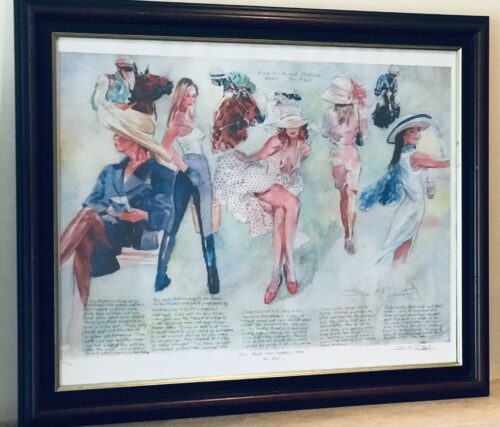
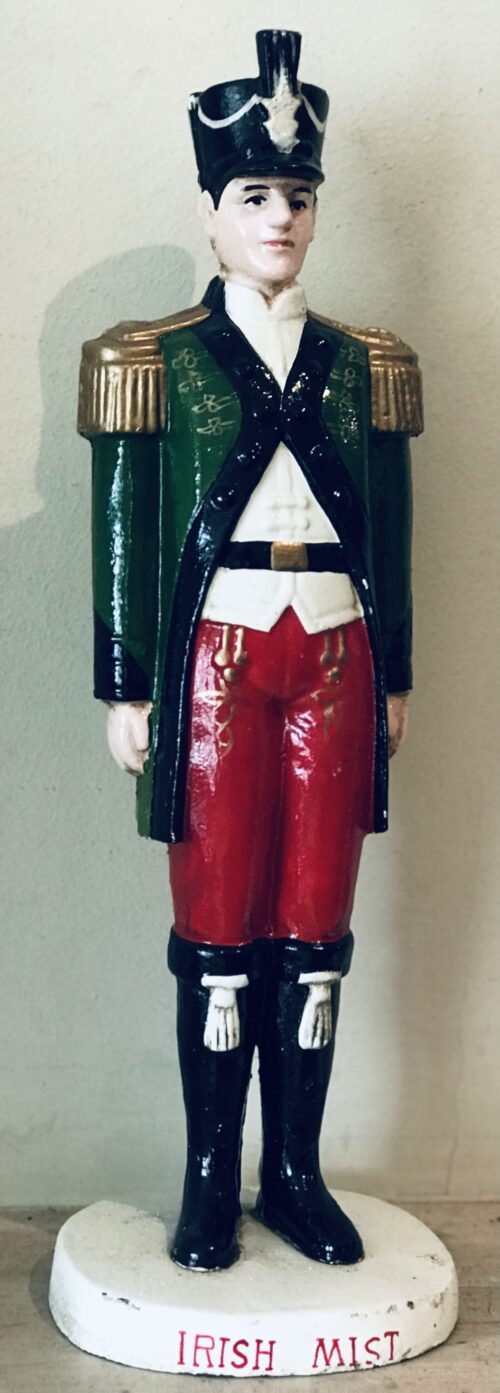
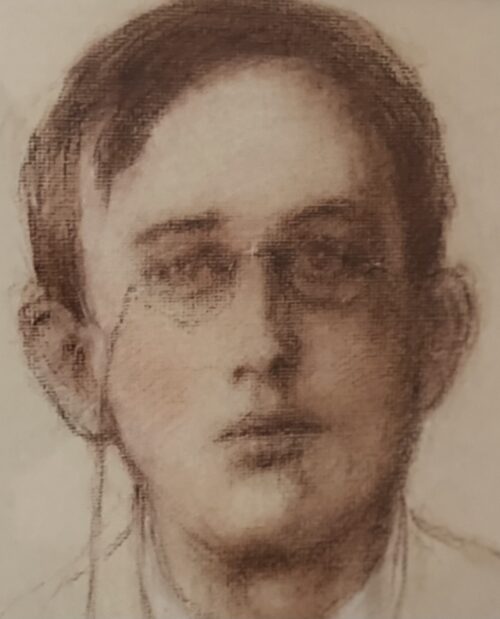
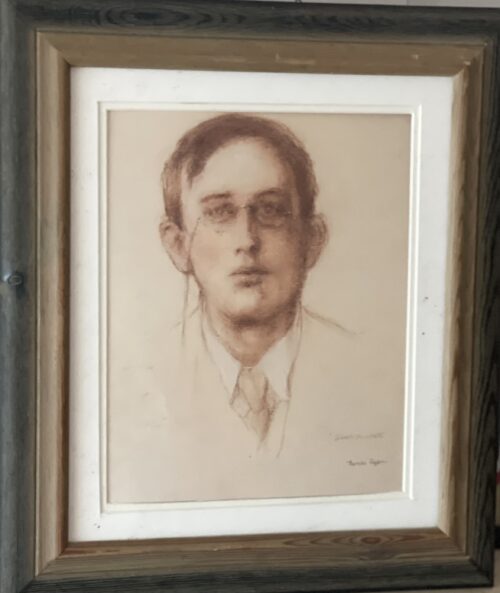
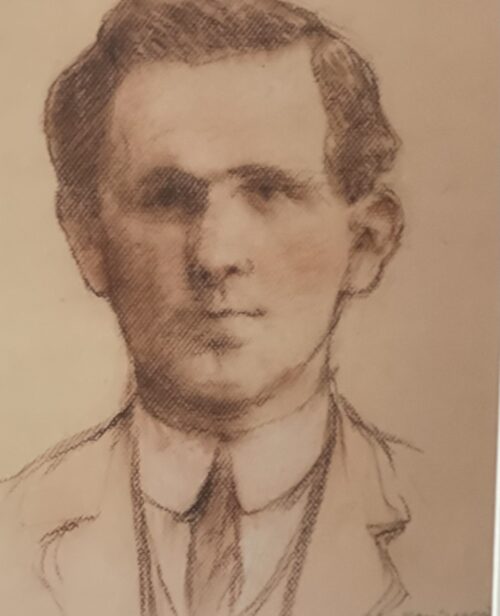
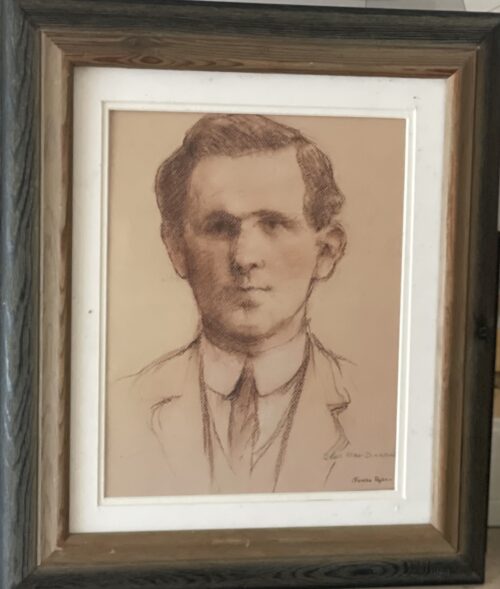
Classy 1980s Bombay Dry Gin mirror in fantastic oak frame.Please contact us directly at irishpubemporium@gmail.com for pricing and shipment quotation.
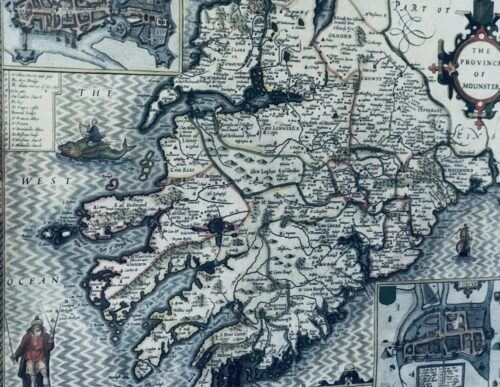
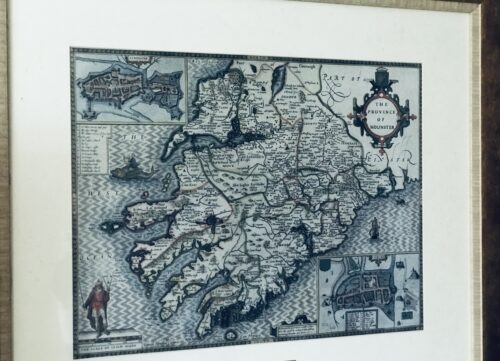
Cork City. 72cm x 60cm
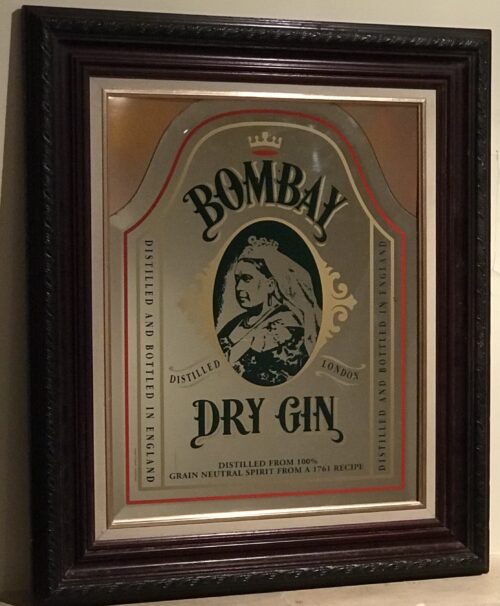
Bombay Sapphire is a brand of
gin that was first launched in 1986 by English
wine-merchant IDV. In 1997
Diageo sold the brand to
Bacardi.
Its name originates from the popularity of gin in
India during the
British Raj and "Sapphire" refers to the violet-blue
Star of Bombay which was mined from
Sri Lanka and is now on display at the
Smithsonian Institution.
Bombay Sapphire is marketed in a flat-sided, sapphire-coloured bottle that bears a picture of
Queen Victoria on the label.
The flavouring of the drink comes from a recipe of ten ingredients:
almond,
lemon peel,
liquorice,
juniper berries,
orris root,
angelica,
coriander,
cassia,
cubeb, and
grains of paradise. Alcohol brought in from another supplier is evaporated three times using a carterhead still, and the alcohol vapours are passed through a mesh/basket containing the ten botanicals, in order to gain flavour and aroma. This is felt to give the gin a lighter, more floral taste compared to those gins that are created using a copper
pot still. Water from
Lake Vyrnwy is added to bring the strength of Bombay Sapphire down to 40.0% (UK, the Nordics, several continental European markets, Canada and Australia).
The 47.0% version is the standard for sale at duty-free stores in all markets.
Production
In 2011, plans were announced to move the manufacturing process to a new facility at
Laverstoke Mill in
Whitchurch, Hampshire, including the restoration of the former
Portal's paper mill at the proposed site, and the construction of a visitor centre.
Planning permission was granted in February 2012, and the centre opened to the public in the autumn of 2014.
The visitor centre included a new construction by
Thomas Heatherwick of two glasshouses for plants used as botanicals in the production of Bombay Sapphire gin.
Production and bottling of the drink is contracted out by Bacardi to G&J Greenall.
Varieties

Three of the Bombay varieties
Bacardi also markets Bombay Original London Dry Gin (or Bombay Original Dry). Eight botanical ingredients are used in the production of the Original Dry variety, as opposed to the ten in Bombay Sapphire.
Wine Enthusiast preferred it to Bombay Sapphire.
In September 2011, Bombay Sapphire East was launched in test markets in
New York and
Las Vegas. This variety has another two botanicals, lemongrass and black peppercorns, in addition to the original ten. It is bottled at 42% and was designed to counteract the sweetness of American
tonic water.
A special edition of Bombay gin called Star of Bombay was produced in 2015 for the UK market. It is bottled at 47.5% and is distilled from grain. It features bergamot and ambrette seeds in harmony with Bombay's signature botanicals. This version has later been extended to several other markets.
Another variety is Bombay Bramble, it’s Infused with fresh Black- and Raspberries and bottled at 37.5% ABV.
In summer 2019, Bacardi launched a limited edition gin called Bombay Sapphire English Estate, which features three additional English sourced botanicals: Pennyroyal Mint, rosehip and hazelnut. It is bottled at 41%.
Design connection
The brand started a series of
design collaborations. Their first step into the design world was a series of advertisements featuring work from currently popular designers. Their works, varying from
martini glasses to tiles and cloth patterns, are labelled as “Inspired by Bombay Sapphire”. The campaign featured designers such as
Marcel Wanders,
Yves Behar,
Karim Rashid,
Ulla Darni, and
Dror Benshetrit and performance artist Jurgen Hahn.
From the success of this campaign, the company began a series of events and sponsored locations. The best known is the Bombay Sapphire Designer Glass Competition, held each year, where design students from all over the world can participate by designing their own “inspired” martini cocktail glass. The finalists (one from each participating country) are then invited to the yearly Salone del Mobile, an international design fair in Milano, where the winner is chosen.
Bombay Sapphire also endorses glass artists and designers with the Bombay Sapphire Prize, which is awarded every year to an outstanding design which features glass. Bombay Sapphire also showcases the designers' work in the Bombay Sapphire endorsed blue room, which is a design exhibition touring the world each year.
From 2008 the Bombay Sapphire Designer Glass Competition final will be held at 100% Design in London, UK and the Bombay Sapphire Prize will take place in Milan at the Salone Del Mobile.
Evaluation
Bombay Sapphire has been reviewed by several outside
spirit ratings organizations to various degrees of success. Recently, it was awarded a score of 92 (on a 100-point scale) from the
Beverage Testing Institute. Ratings aggregator Proof66.com categorizes the Sapphire as a Tier 2 spirit, indicating highly favourable "expert" reviews.
Cultural references
|
Bombay Sapphire was used in the video work Victoria Day (Bombay Sapphire), 2002 by contemporary artists Marina Roy and Abbas Akhavan. |
- Long time sports radio personality Jim Rome is known for his love of Bombay Sapphire Gin, which he often refers to as "the Magic Blue".
- American hip-hop artist Wiz Khalifa and his "Taylor Gang" are also known for their love of Bombay Sapphire dry gin.
- Former Las Vegas, Nevada mayor Oscar Goodman is known for his love of Bombay Sapphire Gin, and he has served as a spokesman for the brand.
- American musician Robert Earl Keen references "a quart of Bombay gin" in the song "The Road Goes on Forever".
- American YouTuber/streamer Etika was known for drinking Bombay Sapphire, among other alcoholic drinks, during streams as a way to celebrate donations.
- In the Netflix series Bojack Horseman a bottle strongly resembling Bombay Sapphire can be seen in Princess Carolyn's office.
Gorgeous Gordon's -This is the Gin tin advertising sign.As the
Fantastic,rare antique tin Gordon's Gin Advertising sign from the 1940's.-manufactured by Sir Joseph Causton & Sons Ltd London (more information at bottom).At the top of the sign is the Royal Crest and By appointment Gin Distiller To H.M King George VI.
Gordon's is a brand of London dry
gin first produced in 1769. The top markets for Gordon's are (in descending order) the United Kingdom, the United States and Greece.
It is owned by the British spirits company
Diageo and, in the UK, is made at
Cameron Bridge Distillery in
Fife, Scotland (although flavourings may be added elsewhere).It is the world's best-selling London dry gin.
Gordon's has been the UK's number one gin since the late 19th century.
A 40%
ABV version for the North American market is distilled in Canada.
Gordon's London Dry Gin was developed by Alexander Gordon, a Londoner of Scots descent.
He opened a distillery in the Southwark area in 1769, later moving in 1786 to
Clerkenwell.
The
Special London Dry Gin he developed proved successful, and its recipe remains unchanged to this day.
Its popularity with the
Royal Navy saw bottles of the product distributed all over the world.
In 1898 Gordon & Co. amalgamated with
Charles Tanqueray & Co. to form Tanqueray Gordon & Co. All production moved to the Gordon's
Goswell Roadsite. In 1899,
Charles Gordon died, ending the family association with the business.
In 1904 the distinctive square-faced, green bottle for the home market was introduced. In 1906 Gordon's Sloe Gin went into production. The earliest evidence in recipe books for the production of Gordon's Special Old Tom was in 1921.
In 1922 Tanqueray Gordon & Co. was acquired by the
Distillers Company. In 1924 Gordon's began production of a 'Ready-to-Serve' Shaker Cocktail range, each in an individual shaker bottle.
In 1925 Gordon's was awarded its first
Royal Warrant by
King George V.
In 1929 Gordon's released an orange gin followed by a lemon variety in 1931.
In 1934 Gordon's opened its first distillery in the US, at
Linden, New Jersey.
By 1962 at least it was the world's highest selling gin.
In 1984 British production was moved to
Laindon in Essex. In 1998 production was moved to Fife in Scotland, where it remains to this day.
Every label and bottle top of Gordon's gin bears a depiction of a
wild boar. According to legend a member of
Clan Gordon saved the
King of Scotland from the animal while hunting.
Products

An export bottle of Gordon's London Dry Gin
According to the manufacturer, Gordon's gin is triple-distilled and contains juniper berries, coriander seeds, angelica root, licorice, orris root, orange, and lemon peel, though the exact recipe has remained a closely guarded secret since 1769. It differed from others at the time in that it didn't add sugar, which made it a "dry" gin.
It takes ten days' distillation after receiving the wheat to create a finished product of a bottle of Gordon's Gin.
In the UK Gordon's is sold in a green glass bottle, but in export markets, it is sold in a clear bottle.
Some airport duty-free shops sell it in plastic bottles in the 75cl size.
Gordon's is sold in several different strengths depending on the market. In the US, the strength is 40% ABV. Until 1992, the ABV in the UK was 40%, but it was reduced to 37.5% to bring Gordon's gin into line with other white spirits such as white rum and vodka, and also reduce production costs
(the other leading brands of gin in the UK,
Beefeater gin and
Bombay Sapphire, are both 40% ABV in the UK). In continental Europe and in some duty-free stores, a 47.3% ABV version (Traveller's Edition) is available in addition to the 37.5% one, while in New Zealand and Australia, as of 2011, it is sold at 37.2% ABV,
and in South Africa, it is 43% ABV.
In addition to the main product line, Gordon's also produces a
sloe gin; a vodka (US & Venezuela only), two
alcopop variants, Space and Spark; three vodka liqueur variants, Cranberry, Parchita and Limon (Venezuela only) and a canned, pre-mixed gin and tonic as well as a canned Gordon's and Grapefruit (500ml - Russia only).
On 11 February 2013, Gordon's announced the release of Gordon's Crisp Cucumber, a flavored gin, which blends the original gin with
cucumber flavor.
In early 2014, Gordon's Elderflower was added to their "flavored" gin collection, and is made in much the same way, with a natural
elderflower flavoring being added to the original recipe.
In August 2017, Gordon's began selling Gordons Pink, a pink-colored gin flavored with several types of red berries.
In February 2020, Gordon’s launched two new flavours in lemon and peach.
In April 2020, it was announced that Gordon’s were launching an orange flavoured gin.
Discontinued products
Gins
- Gordon's special Old Tom Gin (1921–1987)
- Orange Gin (1929–1988, 2020–)
- Lemon Gin (1931–1988, 2020–)
- Spearmint gin (US only)
- Gordon's Distiller's Cut - A luxury version of the gin, released in 2004, with additional botanicals of lemongrass and ginger.
Shaker cocktails
A range of pre-mixed drinks:
- (1924–1967) Fifty-Fifty, Martini, Dry Martini, Perfect, Piccadilly, followed by Manhattan, San Martin, Dry San Martin and Bronx.
- (1930–1967) Rose, Paradise and Gimlet 1930-1967.
- (1924–1990) Dry/Extra Dry Martini
Other products
- Finest Old Jamaica Rum
- Orange Bitters (made from Seville Oranges)
In popular culture

1912 bottle of Gordon’s Gin
Gordon's Gin is specified by name in the recipe for the
Vesper Cocktail given by
James Bond in
Ian Fleming's 1953 novel
Casino Royale.
Gordon's was
Ernest Hemingway's favourite gin, which he claimed could "fortify, mollify and cauterize practically all internal and external injuries".
In the movie
The African Queen Katharine Hepburn's character pours
Humphrey Bogart's entire crate of Gordon's bottles into the river and floats away from the empties.
In the 14th episode of the anime series
Transformers: Super God Masterforce, towards the end of the episode, a hospital patient reveals that he snuck in a bottle of Gordon's Gin and the label was in its export colors.
In the film
The Sting,
Paul Newman's character drinks Gordon’s Gin whilst playing cards with
Robert Shaw's character.
In the film
The Big Heat,
Gloria Grahame's character mixes a cocktail with Gordon's Gin.
According to an eyewitness account cited in
A Night to Remember (book) by
Walter Lord, a passenger of the
RMS Titanic "drained" a bottle of Gordon's Gin and survived the sinking.
n 1863, Joseph Causton and his son, also named Joseph, developed the printing company which was to become the large and well known Joseph Causton & Sons Limited.
In 1867 the company was described as being a wholesale stationer and printer with a large warehouse at Southwark Street, London.
Joseph Causton was also a politician. He became a Councillor for Billingsgate, East London in 1868 and later Sheriff for London and Middlesex. The pinnacle of his career came when Queen Victoria opened Blackfriars Bridge and Holburn Viaduct in 1869 and he was knighted at Windsor Castle to mark the event. The company name now became Sir Joseph Causton & Sons Limited. Sir Joseph died just two years later but his sons, Joseph, Richard and James continued as partners of the firm.
The company moved to a large new printing works in Eastleigh, Hampshire in the 1930s. The printing works made labels for household brands including Marmite and Guiness. During The Second World War they printed secret maps for the government in a specially bricked off part of the building.
By the end of the 1960s Sir Joseph Causton & Sons Limited fortunes were in decline. In the mid 1970s the company was losing money but it was not until 1984 that the firm was taken over by Norton Opex. They in turn were acquired by Bowater and Sir Joseph Causton and Sons ceased trading.
The Causton name has survived only as Causton Envelopes Limited and Causton Cartons, which is a subsidiary of the Bowater Group, manufacturing cartons for the pharmaceutical industry.
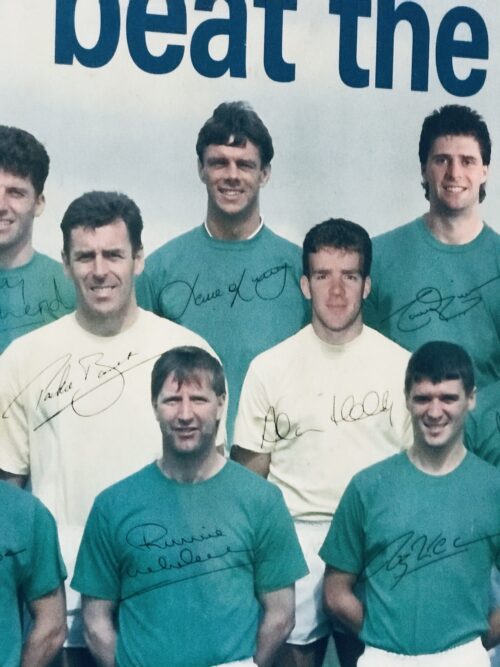








































 Charlton had beaten late entrant Bob Paisley, a multiple trophy winner, to the FAI hot seat, and his introduction to the gathered press was a million miles away from the carefully staged managed productions of the modern day.
In fact, it almost turned into an impromptu David Haye and Tony Bellew pre-match fight when Charlton challenged hardened journalist and ex-international Eamon Dunphy’s line of questioning. That relationship turned increasingly sour as time went by.
Charlton had beaten late entrant Bob Paisley, a multiple trophy winner, to the FAI hot seat, and his introduction to the gathered press was a million miles away from the carefully staged managed productions of the modern day.
In fact, it almost turned into an impromptu David Haye and Tony Bellew pre-match fight when Charlton challenged hardened journalist and ex-international Eamon Dunphy’s line of questioning. That relationship turned increasingly sour as time went by.
 This was the blueprint – or greenprint – of the Irish national team for the next decade.
Former players like Johnny Giles thought this indicated a lack of trust in the ability of players. Charlton saw it as pragmatic. His idea was to keep information and instruction simple.
This was the blueprint – or greenprint – of the Irish national team for the next decade.
Former players like Johnny Giles thought this indicated a lack of trust in the ability of players. Charlton saw it as pragmatic. His idea was to keep information and instruction simple.
 After a 1-0 defeat to Wales in his first match in charge, Charlton got to work on qualifying for the 1988 European Championship in West Germany.
After a 1-0 defeat to Wales in his first match in charge, Charlton got to work on qualifying for the 1988 European Championship in West Germany.
 While England staggered to defeat against the USSR and Holland, the Irish matched both teams stride for stride. Houghton described the 1-1 draw against the Soviets as “one of the best performances I’ve ever been involved in with Jack’s teams”.
While England staggered to defeat against the USSR and Holland, the Irish matched both teams stride for stride. Houghton described the 1-1 draw against the Soviets as “one of the best performances I’ve ever been involved in with Jack’s teams”.
 A 1-1 draw with the Dutch meant both teams had identical records as all three of Holland, England and Ireland progressed, with the Irish benefiting from the drawing of lots to qualify as group runners-up
After three drab stalemates, the party only truly began in Genoa against Romania in the last 16 – after another goalless game, Bonner saved Romania’s fifth penalty, leaving David O’Leary to take the decisive kick.
RTE commentator George Hamilton uttered the most important seven words Irish fans remember: “A nation holds its breath… We’re there!”
How ironic that the hero was O’Leary, another more football-minded defender that was often overlooked by Charlton.
O’Leary recalled: “There were about 20,000 brilliant Irish supporters behind the goal. They were so still and the eruption of green afterwards when the ball hit the net was absolutely amazing. It’s a fantastic memory.”
A 1-1 draw with the Dutch meant both teams had identical records as all three of Holland, England and Ireland progressed, with the Irish benefiting from the drawing of lots to qualify as group runners-up
After three drab stalemates, the party only truly began in Genoa against Romania in the last 16 – after another goalless game, Bonner saved Romania’s fifth penalty, leaving David O’Leary to take the decisive kick.
RTE commentator George Hamilton uttered the most important seven words Irish fans remember: “A nation holds its breath… We’re there!”
How ironic that the hero was O’Leary, another more football-minded defender that was often overlooked by Charlton.
O’Leary recalled: “There were about 20,000 brilliant Irish supporters behind the goal. They were so still and the eruption of green afterwards when the ball hit the net was absolutely amazing. It’s a fantastic memory.”
 Ireland’s propensity to draw a large proportion of games (30 out of 93 under Charlton) cost them dearly in the 1992 Euro qualifying group as only eight teams could qualify for Sweden.
They finished behind Graham Taylor’s stodgy England team, despite drawing home and away against them.
However, the Republic were reaching a new peak, with a young Roy Keane and Denis Irwin introduced to the team.
“The worst thing about missing out on Euro 92 was that Denmark won it. It should have been Ireland.” recalled a frustrated manager.
Ireland’s propensity to draw a large proportion of games (30 out of 93 under Charlton) cost them dearly in the 1992 Euro qualifying group as only eight teams could qualify for Sweden.
They finished behind Graham Taylor’s stodgy England team, despite drawing home and away against them.
However, the Republic were reaching a new peak, with a young Roy Keane and Denis Irwin introduced to the team.
“The worst thing about missing out on Euro 92 was that Denmark won it. It should have been Ireland.” recalled a frustrated manager.
 In the USA, the party started early in New York as Italy were beaten in the Big Apple by a Houghton strike.
Patrick Barclay summed it up best in The Observer: “Ireland’s blanket defence rendered vain all the creative endeavours of Roberto Baggio, who adorned this marvellous occasion but was not allowed to influence it because for 90 mins Jack Charlton’s sweat-soaked soldiers stayed about as close as ranks can get.”
Unfortunately, Ireland’s performances tailed off dramatically for the remainder of the tournament.
Such draining tactics were hard to administer in the humidity of Orlando, and the manager was banned from the touchline for venting his fury at officials over the lack of water for his troops against Mexico.
After squeezing through the group following a goalless draw with Norway, the Green bus ran out of fuel against the Dutch in the last 16.
In the USA, the party started early in New York as Italy were beaten in the Big Apple by a Houghton strike.
Patrick Barclay summed it up best in The Observer: “Ireland’s blanket defence rendered vain all the creative endeavours of Roberto Baggio, who adorned this marvellous occasion but was not allowed to influence it because for 90 mins Jack Charlton’s sweat-soaked soldiers stayed about as close as ranks can get.”
Unfortunately, Ireland’s performances tailed off dramatically for the remainder of the tournament.
Such draining tactics were hard to administer in the humidity of Orlando, and the manager was banned from the touchline for venting his fury at officials over the lack of water for his troops against Mexico.
After squeezing through the group following a goalless draw with Norway, the Green bus ran out of fuel against the Dutch in the last 16.

 It is sometimes opined in retrospect that the Republic could have done better with the quality of players at their disposal. They only won one of nine World Cup matches, scoring just four goals.
After USA’ 94, Dunphy said: “The minority who know their football well enough to distinguish between fact and fantasy have long since decided that even though the show is great, the football of the Charlton era has been, too often, lousy.”
But would liberation have taken away the organisational pragmatism that was central to the Green Wall being breached just 41 times in 93 games? After all, this was a team that also beat Brazil at home and Germany in Hannover.
Niall Quinn said: “We were happy as we were – beautiful, skilled losers.”
Big Jack made them coarse but clinical winners on the pitch and a lot happier off it.
It is sometimes opined in retrospect that the Republic could have done better with the quality of players at their disposal. They only won one of nine World Cup matches, scoring just four goals.
After USA’ 94, Dunphy said: “The minority who know their football well enough to distinguish between fact and fantasy have long since decided that even though the show is great, the football of the Charlton era has been, too often, lousy.”
But would liberation have taken away the organisational pragmatism that was central to the Green Wall being breached just 41 times in 93 games? After all, this was a team that also beat Brazil at home and Germany in Hannover.
Niall Quinn said: “We were happy as we were – beautiful, skilled losers.”
Big Jack made them coarse but clinical winners on the pitch and a lot happier off it.









































