-

 Wooden Jameson Irish Whiskey Show Card pointing the way of the Beer Garden & toilets of a once famous pub in the west of Ireland. 70cm x 45cm. Achill Island Co Mayo John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it maintained for four consecutive years.
Wooden Jameson Irish Whiskey Show Card pointing the way of the Beer Garden & toilets of a once famous pub in the west of Ireland. 70cm x 45cm. Achill Island Co Mayo John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it maintained for four consecutive years. -

 Team photograph of the Irish Rugby Team that played Wales in the first ever Rugby International ever held in Limerick in the County Cricket Grounds (now the Limerick Lawn Tennis Club) Ennis Road on the 19th March 1898. 42cm x 30cm Parnell St Limerick City
Team photograph of the Irish Rugby Team that played Wales in the first ever Rugby International ever held in Limerick in the County Cricket Grounds (now the Limerick Lawn Tennis Club) Ennis Road on the 19th March 1898. 42cm x 30cm Parnell St Limerick City
 44cm x 22cm Dublin Nice 1990s retro Smithwicks clock The old Smithwicks brewery is on the site of a Franciscan abbey, where monks had brewed ale since the 14th century, and ruins of the original abbey still remain on its grounds. The old brewery has since been renovated and now hosts "The Smithwick's Experience Kilkenny" visitor attraction and centre.At the time of its closure, it was Ireland's oldest operating brewery. John Smithwick was an orphan who had settled in Kilkenny. Shortly after his arrival, Smithwick went into the brewing business with Richard Cole on a piece of land that Cole had leased from the Duke of Ormond in 1705. Five years later, John Smithwick became the owner of the land. The brewery stayed small, servicing a loyal local following while John Smithwick diversified. Following John Smithwick's death, the brewery temporarily fell out of family hands. John Smithwick's great grandson, Edmond bought the brewery land back freehold and worked to reshape its future. Edmond concentrated on discovering new markets and successfully building export trade. Drinkers in England, Scotland and Wales developed a taste for Smithwick's brews and output increased fivefold. As a result of substantial contributions made to St Mary's Cathedral, Edmond became great friends with Irish liberal Daniel O'Connell, who later became godfather to one of his sons. Edmond Smithwick became well known and respected by the people of Kilkenny who elected him town mayor four times. In 1800, export sales began to fall and the brewing industry encountered difficulty. To combat this, the Smithwick family increased production in their maltings, began selling mineral water and delivered butter with the ale from the back of their drays.By 1900, output was at an all-time low and the then owner James Smithwick was advised by auditors to shut the doors of the brewery. Instead, James reduced the range of beers they produced and set out to find new markets. He secured military contracts and soon after saw output increase again. James' son, Walter, took control in 1930 and steered the brewery to success through the hardships of both World War II and increasingly challenging weather conditions.By January 1950, Smithwick's was exporting ale to Boston.Smithwick's was purchased from Walter Smithwick in 1965 by Guinness and is now, along with Guinness, part of Diageo. Together, Guinness & Co. and Smithwick's developed and launched Smithwick's Draught Ale in 1966. By 1979, half a million barrels were sold each year.In 1980, Smithwick's began exporting to France. In 1993, Smithwick's Draught became Canada's leading imported ale.By 2010, Smithwick's continued to be brewed in Dundalk and Kilkenny with tankers sent to Dublin to be kegged for the on trade market. Cans and bottles were packaged by IBC in Belfast.Production in the Kilkenny brewery finished on 31 December 2013 and Smithwicks brands are now produced in the Diageo St.James' Gate brewery in Dublin.The original Kilkenny site was sold to Kilkenny County Council, with a small portion of the site dedicated to the opening of a visitor's centre, the "Smithwick's Experience Kilkenny".
44cm x 22cm Dublin Nice 1990s retro Smithwicks clock The old Smithwicks brewery is on the site of a Franciscan abbey, where monks had brewed ale since the 14th century, and ruins of the original abbey still remain on its grounds. The old brewery has since been renovated and now hosts "The Smithwick's Experience Kilkenny" visitor attraction and centre.At the time of its closure, it was Ireland's oldest operating brewery. John Smithwick was an orphan who had settled in Kilkenny. Shortly after his arrival, Smithwick went into the brewing business with Richard Cole on a piece of land that Cole had leased from the Duke of Ormond in 1705. Five years later, John Smithwick became the owner of the land. The brewery stayed small, servicing a loyal local following while John Smithwick diversified. Following John Smithwick's death, the brewery temporarily fell out of family hands. John Smithwick's great grandson, Edmond bought the brewery land back freehold and worked to reshape its future. Edmond concentrated on discovering new markets and successfully building export trade. Drinkers in England, Scotland and Wales developed a taste for Smithwick's brews and output increased fivefold. As a result of substantial contributions made to St Mary's Cathedral, Edmond became great friends with Irish liberal Daniel O'Connell, who later became godfather to one of his sons. Edmond Smithwick became well known and respected by the people of Kilkenny who elected him town mayor four times. In 1800, export sales began to fall and the brewing industry encountered difficulty. To combat this, the Smithwick family increased production in their maltings, began selling mineral water and delivered butter with the ale from the back of their drays.By 1900, output was at an all-time low and the then owner James Smithwick was advised by auditors to shut the doors of the brewery. Instead, James reduced the range of beers they produced and set out to find new markets. He secured military contracts and soon after saw output increase again. James' son, Walter, took control in 1930 and steered the brewery to success through the hardships of both World War II and increasingly challenging weather conditions.By January 1950, Smithwick's was exporting ale to Boston.Smithwick's was purchased from Walter Smithwick in 1965 by Guinness and is now, along with Guinness, part of Diageo. Together, Guinness & Co. and Smithwick's developed and launched Smithwick's Draught Ale in 1966. By 1979, half a million barrels were sold each year.In 1980, Smithwick's began exporting to France. In 1993, Smithwick's Draught became Canada's leading imported ale.By 2010, Smithwick's continued to be brewed in Dundalk and Kilkenny with tankers sent to Dublin to be kegged for the on trade market. Cans and bottles were packaged by IBC in Belfast.Production in the Kilkenny brewery finished on 31 December 2013 and Smithwicks brands are now produced in the Diageo St.James' Gate brewery in Dublin.The original Kilkenny site was sold to Kilkenny County Council, with a small portion of the site dedicated to the opening of a visitor's centre, the "Smithwick's Experience Kilkenny".
 38cm x 8cm Limerick City
38cm x 8cm Limerick CityThe former beer of choice of An Taoiseach Bertie Ahern,the Bass Ireland Brewery operated on the Glen Road in West Belfast for 107 years until its closure in 2004.But despite its popularity, this ale would be the cause of bitter controversy in the 1930s as you can learn below.
Founded in 1777 by William Bass in Burton-upon-Trent, Staffordshire, England.The main brand was Bass Pale Ale, once the highest-selling beer in the UK.By 1877, Bass had become the largest brewery in the world, with an annual output of one million barrels.Its pale ale was exported throughout the British Empire, and the company's distinctive red triangle became the UK's first registered trade mark. In the early 1930s republicans in Dublin and elsewhere waged a campaign of intimidation against publicans who sold Bass ale, which involved violent tactics and grabbed headlines at home and further afield. This campaign occurred within a broader movement calling for the boycott of British goods in Ireland, spearheaded by the IRA. Bass was not alone a British product, but republicans took issue with Colonel John Gretton, who was chairman of the company and a Conservative politician in his day.In Britain,Ireland and the Second World War, Ian Woods notes that the republican newspaper An Phoblacht set the republican boycott of Bass in a broader context , noting that there should be “No British ales. No British sweets or chocolate. Shoulder to shoulder for a nationwide boycott of British goods. Fling back the challenge of the robber empire.”
In late 1932, Irish newspapers began to report on a sustained campaign against Bass ale, which was not strictly confined to Dublin. On December 5th 1932, The Irish Times asked:
Will there be free beer in the Irish Free State at the end of this week? The question is prompted by the orders that are said to have been given to publicans in Dublin towards the end of last week not to sell Bass after a specified date.
The paper went on to claim that men visited Dublin pubs and told publicans “to remove display cards advertising Bass, to dispose of their stock within a week, and not to order any more of this ale, explaining that their instructions were given in furtherance of the campaign to boycott British goods.” The paper proclaimed a ‘War on English Beer’ in its headline. The same routine, of men visiting and threatening public houses, was reported to have happened in Cork.
It was later reported that on November 25th young men had broken into the stores owned by Bass at Moore Lane and attempted to do damage to Bass property. When put before the courts, it was reported that the republicans claimed that “Colonel Gretton, the chairman of the company, was a bitter enemy of the Irish people” and that he “availed himself of every opportunity to vent his hate, and was an ardent supporter of the campaign of murder and pillage pursued by the Black and Tans.” Remarkably, there were cheers in court as the men were found not guilty, and it was noted that they had no intention of stealing from Bass, and the damage done to the premises amounted to less than £5.
A campaign of intimidation carried into January 1933, when pubs who were not following the boycott had their signs tarred, and several glass signs advertising the ale were smashed across the city. ‘BOYCOTT BRITISH GOODS’ was painted across several Bass advertisements in the city.
Throughout 1933, there were numerous examples of republicans entering pubs and smashing the supply of Bass bottles behind the counter. This activity was not confined to Dublin,as this report from late August shows. It was noted that the men publicly stated that they belonged to the IRA.
September appears to have been a particularly active period in the boycott, with Brian Hanley identifying Dublin, Tralee, Naas, Drogheda and Waterford among the places were publicans were targetted in his study The IRA: 1926-1936. One of the most interesting incidents occurring in Dun Laoghaire. There, newspapers reported that on September 4th 1933 “more than fifty young men marched through the streets” before raiding the premises of Michael Moynihan, a local publican. Bottles of Bass were flung onto the roadway and advertisements destroyed. Five young men were apprehended for their role in the disturbances, and a series of court cases nationwide would insure that the Bass boycott was one of the big stories of September 1933.
The young men arrested in Dun Laoghaire refused to give their name or any information to the police, and on September 8th events at the Dublin District Court led to police baton charging crowds. The Irish Times reported that about fifty supporters of the young men gathered outside the court with placards such as ‘Irish Goods for Irish People’, and inside the court a cry of ‘Up The Republic!’ led to the judge slamming the young men, who told him they did not recognise his court. The night before had seen some anti-Bass activity in the city, with the smashing of Bass signs at Burgh Quay. This came after attacks on pubs at Lincoln Place and Chancery Street. It wasn’t long before Mountjoy and other prisons began to home some of those involved in the Boycott Bass campaign, which the state was by now eager to suppress.

An undated image of a demonstration to boycott British goods. Credit: http://irishmemory.blogspot.ie/
This dramatic court appearance was followed by similar scenes in Kilmainham, where twelve men were brought before the courts for a raid on the Dead Man’s Pub, near to Palmerstown in West Dublin. Almost all in their 20s, these men mostly gave addresses in Clondalkin. Their court case was interesting as charges of kidnapping were put forward, as Michael Murray claimed the men had driven him to the Featherbed mountain. By this stage, other Bass prisoners had begun a hungerstrike, and while a lack of evidence allowed the men to go free, heavy fines were handed out to an individual who the judge was certain had been involved.
The decision to go on hungerstrike brought considerable attention on prisoners in Mountjoy, and Maud Gonne MacBride spoke to the media on their behalf, telling the Irish Press on September 18th that political treatment was sought by the men. This strike had begun over a week previously on the 10th, and by the 18th it was understood that nine young men were involved. Yet by late September, it was evident the campaign was slowing down, particularly in Dublin.
The controversy around the boycott Bass campaign featured in Dáil debates on several occasions. In late September Eamonn O’Neill T.D noted that he believed such attacks were being allowed to be carried out “with a certain sort of connivance from the Government opposite”, saying:
I suppose the Minister is aware that this campaign against Bass, the destruction of full bottles of Bass, the destruction of Bass signs and the disfigurement of premises which Messrs. Bass hold has been proclaimed by certain bodies to be a national campaign in furtherance of the “Boycott British Goods” policy. I put it to the Minister that the compensation charges in respect of such claims should be made a national charge as it is proclaimed to be a national campaign and should not be placed on the overburdened taxpayers in the towns in which these terrible outrages are allowed to take place with a certain sort of connivance from the Government opposite.
Another contribution in the Dáil worth quoting came from Daniel Morrissey T.D, perhaps a Smithwicks man, who felt it necessary to say that we were producing “an ale that can compare favourably with any ale produced elsewhere” while condemning the actions of those targeting publicans:
I want to say that so far as I am concerned I have no brief good, bad, or indifferent, for Bass’s ale. We are producing in this country at the moment—and I am stating this quite frankly as one who has a little experience of it—an ale that can compare favourably with any ale produced elsewhere. But let us be quite clear that if we are going to have tariffs or embargoes, no tariffs or embargoes can be issued or given effect to in this country by any person, any group of persons, or any organisation other than the Government elected by the people of the country.
Tim Pat Coogan claims in his history of the IRA that this boycott brought the republican movement into conflict with the Army Comrades Association, later popularly known as the ‘Blueshirts’. He claims that following attacks in Dublin in December 1932, “the Dublin vitners appealed to the ACA for protection and shipments of Bass were guarded by bodyguards of ACA without further incident.” Yet it is undeniable there were many incidents of intimidation against suppliers and deliverers of the product into 1933.
Not all republicans believed the ‘Boycott Bass’ campaign had been worthwhile. Patrick Byrne, who would later become secretary within the Republican Congress group, later wrote that this was a time when there were seemingly bigger issues, like mass unemployment and labour disputes in Belfast, yet:
In this situation, while the revolution was being served up on a plate in Belfast, what was the IRA leadership doing? Organising a ‘Boycott Bass’ Campaign. Because of some disparaging remarks the Bass boss, Colonel Gretton, was reported to have made about the Irish, some IRA leaders took umbrage and sent units out onto the streets of Dublin and elsewhere to raid pubs, terrify the customers, and destroy perfectly good stocks of bottled Bass, an activity in which I regret to say I was engaged.
Historian Brian Hanley has noted by late 1933 “there was little effort to boycott anything except Bass and the desperation of the IRA in hoping violence would revive the campaign was in fact an admission of its failure. At the 1934 convention the campaign was quietly abandoned.”
Interestingly, this wasn’t the last time republicans would threaten Bass. In 1986 The Irish Times reported that Bass and Guinness were both threatened on the basis that they were supplying to British Army bases and RUC stations, on the basis of providing a service to security forces.
Origins : Co Galway
Dimensions:35 cm x 45cm

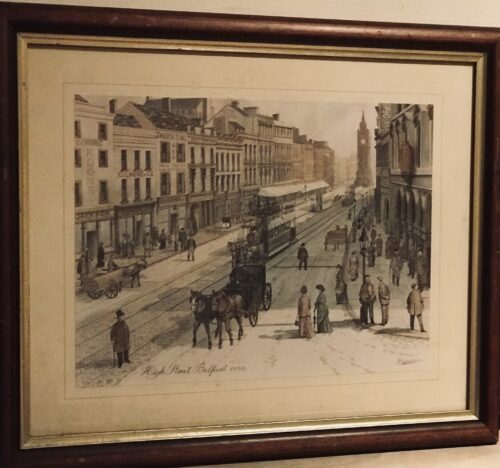 45cm x 55cm Belfast The history of Belfast as a settlement goes back to the Iron Age, but its status as a major urban centre dates to the 18th century. Belfast today is the capital of Northern Ireland. Belfast was throughout its modern history a major commercial and industrial centre, but the late 20th century saw a decline in its traditional industries, particularly shipbuilding. The city's history has been marked by violent conflict between Catholics and Protestants which has caused many working class areas of the city to be split into Catholic and Protestant areas. In recent years the city has been relatively peaceful and major redevelopment has occurred, especially in the inner city and dock areas. During the Great Famine, a potato blight that originated in America spread to Europe decimated crops in Ireland. A Belfast newspaper predicted the devastating effect the blight would have on the common people of Ireland, particularly in rural areas. The potato crop in 1845 largely failed all-over Ireland with the exception of the west coast and parts of Ulster. One-third of the crop was inedible and fears that those spuds in storage were contaminated were soon realized. In October 1846, a Belfast journal The Vindicator made an appeal on behalf of the starving, writing that their universal cry was "give us food or we perish". The publication went on to scold the United Kingdom for not meeting the basic needs of its people. By 1847, the British government were feeding 3 million famine victims a day, though many were still succumbing to disease brought on by starvation. Many of the poor moved eastward from rural areas into Belfast and Dublin, bringing with them famine-related diseases. Dr. Andrew Malcolm, who was working in Belfast at the time, wrote of the influx of the starving into the town, their horrific appearance and the "plague breath" they carried with them. The Belfast Newsletter reported in July 1847 that the town's hospitals were overflowing and that some of the emaciated were stretched out on the streets, dead or dying.On 10 July 1849, the Belfast Harbour commissioners, members of the council, gentry, merchants and the 13th Regiment officially opened the Victoria Channel aboard the royal steamer Prince of Wales. This new waterway allowed for large vessels to come up the River Lagan regardless of tide level. After a signal was given, a flotilla of sea craft moved up the channel to the adulation of the large crowds that had gathered to watch the event. The spectacle was concluded by a cannon salute and a resounding chorus of "Rule Britannia" by all those present.This new channel fed the growth of Belfast industry enabling new development, despite being completed during the last years of the Great Famine. Queen Victoria and Prince Albert along with the Prince of Wales visited Belfast in August 1849, sailing up Victoria Channel and venturing into the town. They were received jubilantly by the people of Belfast with fanfare and decorations adorning the streets. The Royal Family moved up High Street amidst rapturous cheers and well-wishing. On the same street, a 32-foot high arch had been built with a misspelled rendering of Irish Gaelic greeting "Céad Míle Fáilte" (a thousand welcomes) written on it. In the White Linen Hall, the Queen viewed an exhibition of Belfast's industrial goods. The Royals would make their way to the Lisburn Road and the Malone Turnpike where Victoria inspected the new Queen's College (later, University). After touring Mulholland's Mill, Victoria and her entourage returned to their vessel. Belfast was recovering from a cholera epidemic at the time of the Royal visit and many credited Victoria and Albert with lifting the spirits of the town during a difficult period.Conditions for the new working class were often squalid, with much of the population packed into overcrowded and unsanitary tenements. The city suffered from repeated cholera outbreaks in the mid-19th century. Though both Catholics and Protestants were often employed, Protestants would experience preferment over their Catholic counterparts. Hardly any of those in management were Catholic and Protestants would often receive promotion and desirable positions. Working class Catholics were the only group on the whole to experience adverse poverty during this period. Though there were Catholics and Protestants at all levels of society, it was often said "there are no Protestants in the slums". Conditions improved somewhat after a wholesale slum clearance programme in the 1900s. Belfast was becoming one of the greatest places for trade in the western world. In 1852, Belfast was the first port of Ireland, out pacing Dublin in both size, value and tonnage.[39] However, old sectarian tensions would soon come to the fore resulting in an almost annual cycle of summer rioting between Catholics and Protestants. On 12 July 1857, confrontations between crowds of Catholics and Protestants degraded into throwing stones on Albert Street with Catholics beating two Methodist ministers in the Millfield area with sticks. The next night, Protestants from Sandy Rowwent into Catholic areas, smashed windows and set houses on fire. The unrest turned into ten days of rioting, with many of the police force joining the Protestant side. There were also riots in Derry, Portadown and Lurgan. Firearms were produced with sporadic gunfire happening all over Belfast, the police could do little to mitigate the turmoil. The Riots of 1864 were so intense that reinforcements and two field guns were dispatched from Dublin Castle. A funeral for a victim of police gunfire was turned into a loyalist parade that unexpectedly went up through Donegall Place in the heart of Belfast. Police barely held as a barrier between the Protestants marching through Belfast's main streets and the irate Catholics who were massing at Castle Place. Continuous gunfire resounded throughout the city until a deluge of summer rain dispersed most of the crowd. The mud that was dredged up to dig the Victoria Channel was made into an artificial island, called Queen's Island, near east Belfast. Robert Hixon, an engineer from Liverpool who managed the arms work on Cromac Street, decided to use his surplus of iron ore to make ships. Hixon hired Edward Harlandfrom Newcastle-on-Tyne to assist in the endeavour. Harland launched his first ship in October 1855, his cutting-edge designs would go on to revolutionize the ship building world. In 1858, Harland would buy-out Hixon with the backing of Gustav Schwab. Schwab's nephew, Gustav Wolff had been working as an assistant to Harland. They formed the partnership of Harland & Wolff in 1861. Business was booming with the advent of American Civil War and the Confederacy purchasing steamers from Harland & Wolff. Gustav Schwab would go on to create the White Star Line in 1869, he ordered all of his ocean vessels from Harland & Wolff, setting the firm on the path to becoming the biggest ship building company in the world. Harland & Wolff would go on to build some of the world's most famous (and infamous) ships including HMHS Britannic, RMS Oceanic, RMS Olympic and, best known of all, the RMS Titanic.
45cm x 55cm Belfast The history of Belfast as a settlement goes back to the Iron Age, but its status as a major urban centre dates to the 18th century. Belfast today is the capital of Northern Ireland. Belfast was throughout its modern history a major commercial and industrial centre, but the late 20th century saw a decline in its traditional industries, particularly shipbuilding. The city's history has been marked by violent conflict between Catholics and Protestants which has caused many working class areas of the city to be split into Catholic and Protestant areas. In recent years the city has been relatively peaceful and major redevelopment has occurred, especially in the inner city and dock areas. During the Great Famine, a potato blight that originated in America spread to Europe decimated crops in Ireland. A Belfast newspaper predicted the devastating effect the blight would have on the common people of Ireland, particularly in rural areas. The potato crop in 1845 largely failed all-over Ireland with the exception of the west coast and parts of Ulster. One-third of the crop was inedible and fears that those spuds in storage were contaminated were soon realized. In October 1846, a Belfast journal The Vindicator made an appeal on behalf of the starving, writing that their universal cry was "give us food or we perish". The publication went on to scold the United Kingdom for not meeting the basic needs of its people. By 1847, the British government were feeding 3 million famine victims a day, though many were still succumbing to disease brought on by starvation. Many of the poor moved eastward from rural areas into Belfast and Dublin, bringing with them famine-related diseases. Dr. Andrew Malcolm, who was working in Belfast at the time, wrote of the influx of the starving into the town, their horrific appearance and the "plague breath" they carried with them. The Belfast Newsletter reported in July 1847 that the town's hospitals were overflowing and that some of the emaciated were stretched out on the streets, dead or dying.On 10 July 1849, the Belfast Harbour commissioners, members of the council, gentry, merchants and the 13th Regiment officially opened the Victoria Channel aboard the royal steamer Prince of Wales. This new waterway allowed for large vessels to come up the River Lagan regardless of tide level. After a signal was given, a flotilla of sea craft moved up the channel to the adulation of the large crowds that had gathered to watch the event. The spectacle was concluded by a cannon salute and a resounding chorus of "Rule Britannia" by all those present.This new channel fed the growth of Belfast industry enabling new development, despite being completed during the last years of the Great Famine. Queen Victoria and Prince Albert along with the Prince of Wales visited Belfast in August 1849, sailing up Victoria Channel and venturing into the town. They were received jubilantly by the people of Belfast with fanfare and decorations adorning the streets. The Royal Family moved up High Street amidst rapturous cheers and well-wishing. On the same street, a 32-foot high arch had been built with a misspelled rendering of Irish Gaelic greeting "Céad Míle Fáilte" (a thousand welcomes) written on it. In the White Linen Hall, the Queen viewed an exhibition of Belfast's industrial goods. The Royals would make their way to the Lisburn Road and the Malone Turnpike where Victoria inspected the new Queen's College (later, University). After touring Mulholland's Mill, Victoria and her entourage returned to their vessel. Belfast was recovering from a cholera epidemic at the time of the Royal visit and many credited Victoria and Albert with lifting the spirits of the town during a difficult period.Conditions for the new working class were often squalid, with much of the population packed into overcrowded and unsanitary tenements. The city suffered from repeated cholera outbreaks in the mid-19th century. Though both Catholics and Protestants were often employed, Protestants would experience preferment over their Catholic counterparts. Hardly any of those in management were Catholic and Protestants would often receive promotion and desirable positions. Working class Catholics were the only group on the whole to experience adverse poverty during this period. Though there were Catholics and Protestants at all levels of society, it was often said "there are no Protestants in the slums". Conditions improved somewhat after a wholesale slum clearance programme in the 1900s. Belfast was becoming one of the greatest places for trade in the western world. In 1852, Belfast was the first port of Ireland, out pacing Dublin in both size, value and tonnage.[39] However, old sectarian tensions would soon come to the fore resulting in an almost annual cycle of summer rioting between Catholics and Protestants. On 12 July 1857, confrontations between crowds of Catholics and Protestants degraded into throwing stones on Albert Street with Catholics beating two Methodist ministers in the Millfield area with sticks. The next night, Protestants from Sandy Rowwent into Catholic areas, smashed windows and set houses on fire. The unrest turned into ten days of rioting, with many of the police force joining the Protestant side. There were also riots in Derry, Portadown and Lurgan. Firearms were produced with sporadic gunfire happening all over Belfast, the police could do little to mitigate the turmoil. The Riots of 1864 were so intense that reinforcements and two field guns were dispatched from Dublin Castle. A funeral for a victim of police gunfire was turned into a loyalist parade that unexpectedly went up through Donegall Place in the heart of Belfast. Police barely held as a barrier between the Protestants marching through Belfast's main streets and the irate Catholics who were massing at Castle Place. Continuous gunfire resounded throughout the city until a deluge of summer rain dispersed most of the crowd. The mud that was dredged up to dig the Victoria Channel was made into an artificial island, called Queen's Island, near east Belfast. Robert Hixon, an engineer from Liverpool who managed the arms work on Cromac Street, decided to use his surplus of iron ore to make ships. Hixon hired Edward Harlandfrom Newcastle-on-Tyne to assist in the endeavour. Harland launched his first ship in October 1855, his cutting-edge designs would go on to revolutionize the ship building world. In 1858, Harland would buy-out Hixon with the backing of Gustav Schwab. Schwab's nephew, Gustav Wolff had been working as an assistant to Harland. They formed the partnership of Harland & Wolff in 1861. Business was booming with the advent of American Civil War and the Confederacy purchasing steamers from Harland & Wolff. Gustav Schwab would go on to create the White Star Line in 1869, he ordered all of his ocean vessels from Harland & Wolff, setting the firm on the path to becoming the biggest ship building company in the world. Harland & Wolff would go on to build some of the world's most famous (and infamous) ships including HMHS Britannic, RMS Oceanic, RMS Olympic and, best known of all, the RMS Titanic.Home Rule and the City Charter
In 1862 George Hamilton Chichester, 3rd Marquess of Donegall (a descendant of the Chichester family) built a new mansion on the slopes of Cavehill above the town. The named as the new Belfast Castle, it was designed by Charles Lanyon and construction was completed in 1870. By 1901, Belfast was the largest city in Ireland. The city's importance was evidenced by the construction of the lavish City Hall, completed in 1906. As noted, around 1840 its population included many Catholics, who originally settled in the west of city, around the area of today's Barrack Street which was known as the "Pound Loney". West Belfast remains the centre of the city's Catholic population (in contrast with the east of the city which remains predominantly Protestant). Other areas of Catholic settlement have included parts of the north of the city, especially Ardoyne and the Antrim Road, the Markets area immediately to the south of the city centre, and the Short Strand (a Catholic enclave in east Belfast). During the summer of 1872, about 30,000 Nationalists held a demonstration at Hannahstown in Belfast, campaigning for the release of Fenian prisoners, which lead to another series of riots between Catholics and Protestants. In 1874, the issue of Home Rule became mainstream in Irish politics, A conglomeration of MP's were denounced by the Belfast Newsletter on the eve of election, writing that "Home Rule was simply 'Rome Rule'" and that Protestants would not support a new Dublin parliament. In June 1886, Protestants celebrated the defeat of the First Home Rule Bill in the House of Commons, leading to rioting on the streets of Belfast and the deaths of seven people, with many more injured. In the same year, following The Twelfth Orange Institution parades, clashes took place between Catholics and Protestants, and also between Loyalists and police. Thirteen people were killed in a weekend of serious rioting which continued sporadically until mid-September with an official death toll of 31 people. Belfast City Hall during constructionAlthough the county borough of Belfast was created when it was granted city status by Queen Victoria in 1888,[42] the city continues to be viewed as straddling County Antrim and County Down with the River Lagan generally being seen as the line of demarcation.Charles Vane-Tempest-Stewart made a grand visit to Belfast on behalf of the Queen to give it official recognition as a city. Belfast at this time was Ireland's largest city and the third most important port (behind London and Liverpool) in the United Kingdom; the leader in world trade at the time.Belfast had become a world class industrial city and the center of linen production for the whole planet. In 1896, a Second Home Rule Bill passed through the House of Commons but was struck down in the House of Lords. Wary Protestants celebrated and, as had happened 7 years earlier, Catholics took exception to Protestant triumphalism and rioted. On 14 January 1899, large crowds gathered to watch the launch of the RMS Oceanic which had been ordered by the White Star Line for the trans-Atlantic passenger travel. The Oceanic was the largest man-made moving object that had ever been built up to that time. By the year 1900, Belfast had the world's largest tobacco factory, tea machinery and fan-making works, handkerchief factory, dry dock and color Christmascard printers. Belfast was also the world's leading manufacturer of "fizzy drinks" (soft drinks). Belfast was by far the greatest economic beneficiary in Ireland of the Act of Union and Industrial Revolution. The city saw a bitter strike by dock workers organised by radical trade unionist Jim Larkin, in 1907. The dispute saw 10,000 workers on strike and a mutiny by the police, who refused to disperse the striker's pickets. Eventually the Army had to be deployed to restore order. The strike was a rare instance of non-sectarian mobilisation in Ulster at the time.
Belfast City Hall during constructionAlthough the county borough of Belfast was created when it was granted city status by Queen Victoria in 1888,[42] the city continues to be viewed as straddling County Antrim and County Down with the River Lagan generally being seen as the line of demarcation.Charles Vane-Tempest-Stewart made a grand visit to Belfast on behalf of the Queen to give it official recognition as a city. Belfast at this time was Ireland's largest city and the third most important port (behind London and Liverpool) in the United Kingdom; the leader in world trade at the time.Belfast had become a world class industrial city and the center of linen production for the whole planet. In 1896, a Second Home Rule Bill passed through the House of Commons but was struck down in the House of Lords. Wary Protestants celebrated and, as had happened 7 years earlier, Catholics took exception to Protestant triumphalism and rioted. On 14 January 1899, large crowds gathered to watch the launch of the RMS Oceanic which had been ordered by the White Star Line for the trans-Atlantic passenger travel. The Oceanic was the largest man-made moving object that had ever been built up to that time. By the year 1900, Belfast had the world's largest tobacco factory, tea machinery and fan-making works, handkerchief factory, dry dock and color Christmascard printers. Belfast was also the world's leading manufacturer of "fizzy drinks" (soft drinks). Belfast was by far the greatest economic beneficiary in Ireland of the Act of Union and Industrial Revolution. The city saw a bitter strike by dock workers organised by radical trade unionist Jim Larkin, in 1907. The dispute saw 10,000 workers on strike and a mutiny by the police, who refused to disperse the striker's pickets. Eventually the Army had to be deployed to restore order. The strike was a rare instance of non-sectarian mobilisation in Ulster at the time. A 1907 stereoscope postcard depicting the construction of an ocean liner at the Harland and Wolff shipyard
A 1907 stereoscope postcard depicting the construction of an ocean liner at the Harland and Wolff shipyard
 Very well reproduced and quaint advertisement for the legendary Fair of Spancil Hill,held every year on the 23rd of June -with Jameson Whiskey sponsoring the advert. Ennis Co Clare. 50 cm x 60cm Spancilhill is a small settlement in East County Clare that hosts an annual horse fair on the 23rd of June. The Spancilhill Horse Fair is Ireland’s oldest having been chartered in 1641 by Charles II. It derives its name from the Irish, Cnoc Fhuar Choille or Cold Wood Hill. The name was misinterpreted as Cnoc Urchaill or Spancel Hill. A spancel is a type hobble and its association with a horse fair perpetuated this misinterpretation. The 1913 fair saw four thousand horses for sale. The British, Belgian, and French armies sought cavalry mounts. The British army purchased 1,175 horses and lead them tied head to tail to Ennis for rail transport. Horse Fairs gained a reputation for wild behavior and animal cruelty. The Friends of the Spancilhill Horse Fair formed in the 1980s with the aim of restructuring the event as an agricultural show. Michael Considine, who emigrated from the area in 1870, composed the popular Irish folk ballad, Spancil Hill. Buyers across Europe attend with hopes to find international showjumping prospects. Photographers find the event irresistible and nearly outnumber the horses in recent times.The aforementioned song written about the fair has almost become more famous than the fair itself in modern times. Robbie McMahon was a songwriter and singer whose rendition of Spancil Hill is widely regarded as the definitive version. He reckoned he sang it more than 10,000 times since he learned it as a teenager.
Very well reproduced and quaint advertisement for the legendary Fair of Spancil Hill,held every year on the 23rd of June -with Jameson Whiskey sponsoring the advert. Ennis Co Clare. 50 cm x 60cm Spancilhill is a small settlement in East County Clare that hosts an annual horse fair on the 23rd of June. The Spancilhill Horse Fair is Ireland’s oldest having been chartered in 1641 by Charles II. It derives its name from the Irish, Cnoc Fhuar Choille or Cold Wood Hill. The name was misinterpreted as Cnoc Urchaill or Spancel Hill. A spancel is a type hobble and its association with a horse fair perpetuated this misinterpretation. The 1913 fair saw four thousand horses for sale. The British, Belgian, and French armies sought cavalry mounts. The British army purchased 1,175 horses and lead them tied head to tail to Ennis for rail transport. Horse Fairs gained a reputation for wild behavior and animal cruelty. The Friends of the Spancilhill Horse Fair formed in the 1980s with the aim of restructuring the event as an agricultural show. Michael Considine, who emigrated from the area in 1870, composed the popular Irish folk ballad, Spancil Hill. Buyers across Europe attend with hopes to find international showjumping prospects. Photographers find the event irresistible and nearly outnumber the horses in recent times.The aforementioned song written about the fair has almost become more famous than the fair itself in modern times. Robbie McMahon was a songwriter and singer whose rendition of Spancil Hill is widely regarded as the definitive version. He reckoned he sang it more than 10,000 times since he learned it as a teenager.The ballad is named after a crossroads between Ennis and Tulla in east Clare, the site of a centuries-old horse fair held every June. In 1870 a young man from the locality, Michael Considine, bade farewell to his sweetheart Mary McNamara and left for the US. He hoped to earn sufficient money to enable her to join him.
However, he died in California in 1873. Before his death he wrote a poem dedicated to Mary which he posted to his six-year-old nephew, John, back home.
Seventy years later McMahon was given the words at a house party. His singing of the ballad was warmly received by those in attendance, who included the author’s nephew, then an elderly man.
Many singers have recorded the ballad, but McMahon insisted his was the authentic version. He told The Irish Times in 2006: “Nowadays the song is not sung correctly. Many singers put words that are not in it [at] all, singing stuff like ‘Johnny, I love you still’. There’s no ‘Johnny’ in that song.” The late writer Bryan MacMahon was an early admirer of his namesake’s talent and had high praise for his ability as a performer and entertainer.
Singer Maura O’Connell warmed to Robbie McMahon’s “great big personality”, and said that he made Spancil Hill his own.
Born in 1926, he was the third youngest of 11 children, one of whom died in childhood, and grew up on his father’s farm in Clooney, near Ennis. There was music in the family, and all the children sang. Young Robbie was something of a mischief-maker, hence the title of an album he recorded later in life – The Black Sheep.
He began singing in public at the age of 18, and went on to win 16 all-Ireland titles at fleadhanna around the country. In the 1950s, 1960s and 1970s he toured Britain and the US with a troupe of traditional musicians under the auspices of Comhaltas Ceoltóirí Éireann.
As a songwriter, he is best known for the Fleadh Down in Ennis, which celebrates the 1956 all-Ireland fleadh cheoil. Other compositions include Come on the Banner, the Red Cross Social and the Feakle Hurlers, in honour of the 1988 Clare county champions.
A lilter, he was renowned for his performance of the Mason’s Apron, in which he simulated the sound of both the fiddle and accompanying banjo.
Possessed of a store of jokes, ranging from the hilarious to the unprintable, he was as much a character as a singer and was more comfortable with the craic and banter of casual sessions than with formal concerts.
He was the subject of a film documentary Last Night As I Lay Dreaming. Clare County Council hosted a civic reception in his honour in 2010, and he was the recipient of the Fleadh Nua Gradam Ceoil in 2011.
He is survived by his wife Maura, daughters Fiona, Noleen and Dympna and son Donal.

 Classy advert depicting the magnificence of Dunluce Castle ,just down the road from the famed Bushmills Distillery. Portrush Co Antrim 52cm x 72cm In the 13th century, Richard Óg de Burgh, 2nd Earl of Ulster, built the first castle at Dunluce. It is first documented in the hands of the McQuillan family in 1513. The earliest features of the castle are two large drum towers about 9 metres (30 ft) in diameter on the eastern side, both relics of a stronghold built here by the McQuillans after they became lords of the Route. The McQuillans were the Lords of Route from the late 13th century until they were displaced by the MacDonnell after losing two major battles against them during the mid- and late-16th century. Later Dunluce Castle became the home of the chief of the Clan MacDonnell of Antrim and the Clan MacDonald of Dunnyveg from Scotland. Chief John Mor MacDonald was the second son of Good John of Islay, Lord of the Isles, 6th chief of Clan Donald in Scotland. John Mor MacDonald l was born through John of Islay's second marriage to Princess Margaret Stewart, daughter of King Robert II of Scotland. In 1584, on the death of James MacDonald the 6th chief of the Clan MacDonald of Antrim and Dunnyveg, the Antrim Glens were seized by Sorley Boy MacDonnell, one of his younger brothers. Sorley Boy took the castle, keeping it for himself and improving it in the Scottish style. Sorley Boy swore allegiance to Queen Elizabeth I and his son Randal was made 1st Earl of Antrim by King James I. Four years later, the Girona, a galleass from the Spanish Armada, was wrecked in a storm on the rocks nearby. The cannons from the ship were installed in the gatehouses and the rest of the cargo sold, the funds being used to restore the castle. MacDonnell's granddaughter Rose was born in the castle in 1613. A local legend states that at one point, part of the kitchen next to the cliff face collapsed into the sea, after which the wife of the owner refused to live in the castle any longer. According to a legend, when the kitchen fell into the sea, only a kitchen boy survived, as he was sitting in the corner of the kitchen which did not collapse. However, the kitchen is still intact and next to the manor house. You can still see the oven, fireplace and entry ways into it. It wasn't until some time in the 18th century that the north wall of the residence building collapsed into the sea. The east, west and south walls still stand. Dunluce Castle served as the seat of the Earl of Antrim until the impoverishment of the MacDonnells in 1690, following the Battle of the Boyne. Since that time, the castle has deteriorated and parts were scavenged to serve as materials for nearby buildings.
Classy advert depicting the magnificence of Dunluce Castle ,just down the road from the famed Bushmills Distillery. Portrush Co Antrim 52cm x 72cm In the 13th century, Richard Óg de Burgh, 2nd Earl of Ulster, built the first castle at Dunluce. It is first documented in the hands of the McQuillan family in 1513. The earliest features of the castle are two large drum towers about 9 metres (30 ft) in diameter on the eastern side, both relics of a stronghold built here by the McQuillans after they became lords of the Route. The McQuillans were the Lords of Route from the late 13th century until they were displaced by the MacDonnell after losing two major battles against them during the mid- and late-16th century. Later Dunluce Castle became the home of the chief of the Clan MacDonnell of Antrim and the Clan MacDonald of Dunnyveg from Scotland. Chief John Mor MacDonald was the second son of Good John of Islay, Lord of the Isles, 6th chief of Clan Donald in Scotland. John Mor MacDonald l was born through John of Islay's second marriage to Princess Margaret Stewart, daughter of King Robert II of Scotland. In 1584, on the death of James MacDonald the 6th chief of the Clan MacDonald of Antrim and Dunnyveg, the Antrim Glens were seized by Sorley Boy MacDonnell, one of his younger brothers. Sorley Boy took the castle, keeping it for himself and improving it in the Scottish style. Sorley Boy swore allegiance to Queen Elizabeth I and his son Randal was made 1st Earl of Antrim by King James I. Four years later, the Girona, a galleass from the Spanish Armada, was wrecked in a storm on the rocks nearby. The cannons from the ship were installed in the gatehouses and the rest of the cargo sold, the funds being used to restore the castle. MacDonnell's granddaughter Rose was born in the castle in 1613. A local legend states that at one point, part of the kitchen next to the cliff face collapsed into the sea, after which the wife of the owner refused to live in the castle any longer. According to a legend, when the kitchen fell into the sea, only a kitchen boy survived, as he was sitting in the corner of the kitchen which did not collapse. However, the kitchen is still intact and next to the manor house. You can still see the oven, fireplace and entry ways into it. It wasn't until some time in the 18th century that the north wall of the residence building collapsed into the sea. The east, west and south walls still stand. Dunluce Castle served as the seat of the Earl of Antrim until the impoverishment of the MacDonnells in 1690, following the Battle of the Boyne. Since that time, the castle has deteriorated and parts were scavenged to serve as materials for nearby buildings.Dunluce town
In 2011, major archaeological excavations found significant remains of the "lost town of Dunluce", which was razed to the ground in the Irish uprising of 1641. Lying adjacent to Dunluce Castle, the town was built around 1608 by Randall MacDonnell, the first Earl of Antrim, and pre-dates the official Plantation of Ulster.It may have contained the most revolutionary housing in Europe when it was built in the early 17th century, including indoor toilets which had only started to be introduced around Europe at the time, and a complex street network based on a grid system. 95% of the town is still to be discovered.Cultural references
- The castle inspired the orchestral tone poem Dunluce (1921) by Irish composer Norman Hay.
- Dunluce Castle is thought to be the inspiration for Cair Paravel in C. S. Lewis's Chronicles of Narnia (1950–54).
- Ron Moody menaced Jack Wild and Helen Raye at Dunluce Castle in Flight of the Doves, a 1971 film.
- In 1973 the castle appeared on the inner gatefold of the multi-million selling Led Zeppelin album Houses of the Holy.
- On the 1984 Gary Moore video "Emerald Aisles" on his return to Northern Ireland, he visits the castle and talks about the history of the castle. Cassette and CD versions of Gary Moore's 1989 album After the War feature an instrumental track titled "Dunluce" in one and two parts respectively.
- The castle is also the subject of a 1990s song named "Dunluce Castle" written by George Millar and sung by the Irish Rovers.
- The castle is mentioned and appears briefly in Michael Palin's 1994 episode of Great Railway Journeys, Derry to Kerry.
- The castle appeared as Snakehead's hideout under the name 'Ravens Keep' in the 2003 movie, The Medallion, which starred Jackie Chan.
- It is also featured on the cover of the album Glasgow Friday (2008) by American musician Jandek.
- The castle is the film location of the Game of Thrones Seat of House Greyjoy, the great castle of Pyke.The Old Bushmills Distillery is a distillery in Bushmills, County Antrim, Northern Ireland, owned by Casa Cuervo of Mexico. Bushmills Distillery uses water drawn from Saint Columb's Rill, which is a tributary of the River Bush. The distillery is a popular tourist attraction, with around 120,000 visitors per year.
The area has a long tradition with distillation. According to one story, as far back as 1276, an early settler called Sir Robert Savage of Ards, before defeating the Irish in battle, fortified his troops with "a mighty drop of acqua vitae".In 1608, a licence was granted to Sir Thomas Phillips by King James I to distil whiskey. The distillery in County Antrim.
The distillery in County Antrim.for the next seven years, within the countie of Colrane, otherwise called O Cahanes countrey, or within the territorie called Rowte, in Co. Antrim, by himselfe or his servauntes, to make, drawe, and distil such and soe great quantities of aquavite, usquabagh and aqua composita, as he or his assignes shall thinke fitt; and the same to sell, vent, and dispose of to any persons, yeeldinge yerelie the somme 13s 4d ...
The Bushmills Old Distillery Company itself was not established until 1784 by Hugh Anderson.Bushmills suffered many lean years with numerous periods of closure with no record of the distillery being in operation in the official records both in 1802 and in 1822. In 1860 a Belfast spirit merchant named Jame McColgan and Patrick Corrigan bought the distillery; in 1880 they formed a limited company. In 1885, the original Bushmills buildings were destroyed by fire but the distillery was swiftly rebuilt. In 1890, a steamship owned and operated by the distillery, SS Bushmills, made its maiden voyage across the Atlantic to deliver Bushmills whiskey to America. It called at Philadelphia and New York City before heading on to Singapore, Hong Kong, Shanghai and Yokohama. In the early 20th century, the U.S. was a very important market for Bushmills (and other Irish Whiskey producers). American Prohibition in 1920 came as a large blow to the Irish Whiskey industry, but Bushmills managed to survive. Wilson Boyd, Bushmills' director at the time, predicted the end of prohibition and had large stores of whiskey ready to export. After the Second World War, the distillery was bought by Isaac Wolfson, and, in 1972, it was taken over by Irish Distillers, meaning that Irish Distillers controlled the production of all Irish whiskey at the time. In June 1988, Irish Distillers was bought by French liquor group Pernod Ricard. In June 2005, the distillery was bought by Diageo for £200 million. Diageo have also announced a large advertising campaign in order to regain a market share for Bushmills. In May 2008, the Bank of Ireland issued a new series of sterling banknotes in Northern Ireland which all feature an illustration of the Old Bushmills Distillery on the obverse side, replacing the previous notes series which depicted Queen's University of Belfast. In November 2014 it was announced that Diageo had traded the Bushmills brand with Jose Cuervo in exchange for the 50% of the Don Julio brand of tequila that Diageo did not already own.
 Old Dublin White Swan Irish Whiskey For Export-McManus,Fritch & Co.Advert. Francis St Dublin 50cm x 35cm We have found it difficult to discover precise details about the above advert- Old Dublin White Swan Whiskey ,produced for export. A Matthew MacManus did first found Kilbeggan distillery in 1757 who may have distilled elsewhere before founding Kilbeggan.The more unusual surname -Fritch - has yielded very little results even though the enterprise appears to have been a partnership.What is more likely is Macmanus & Fritch was a bonded warehouse or bonder. During the ‘golden age’ of Irish Whiskey (in the 19th and 20th centuries), there were hundreds of distilleries operating on the island of Ireland. Most did not have their own brands of whiskey at that time, however. These distilleries made their new whiskey spirit and sold it wholesale to the Bonders to age, blend and bottle. The Bonders were the publicans, grocers and mercantile owners. They would travel to their local distillery with their own barrels, fill them up with new make spirit and then cart them home for ageing and then blending. Bonders were present in every town in Ireland, giving rise to regional styles. Sadly, the Irish Whiskey Industry collapsed in the 1930s and the few remaining distilleries cut off the Bonders’ supply, leaving Irish Whiskey Bonding to die out.
Old Dublin White Swan Irish Whiskey For Export-McManus,Fritch & Co.Advert. Francis St Dublin 50cm x 35cm We have found it difficult to discover precise details about the above advert- Old Dublin White Swan Whiskey ,produced for export. A Matthew MacManus did first found Kilbeggan distillery in 1757 who may have distilled elsewhere before founding Kilbeggan.The more unusual surname -Fritch - has yielded very little results even though the enterprise appears to have been a partnership.What is more likely is Macmanus & Fritch was a bonded warehouse or bonder. During the ‘golden age’ of Irish Whiskey (in the 19th and 20th centuries), there were hundreds of distilleries operating on the island of Ireland. Most did not have their own brands of whiskey at that time, however. These distilleries made their new whiskey spirit and sold it wholesale to the Bonders to age, blend and bottle. The Bonders were the publicans, grocers and mercantile owners. They would travel to their local distillery with their own barrels, fill them up with new make spirit and then cart them home for ageing and then blending. Bonders were present in every town in Ireland, giving rise to regional styles. Sadly, the Irish Whiskey Industry collapsed in the 1930s and the few remaining distilleries cut off the Bonders’ supply, leaving Irish Whiskey Bonding to die out.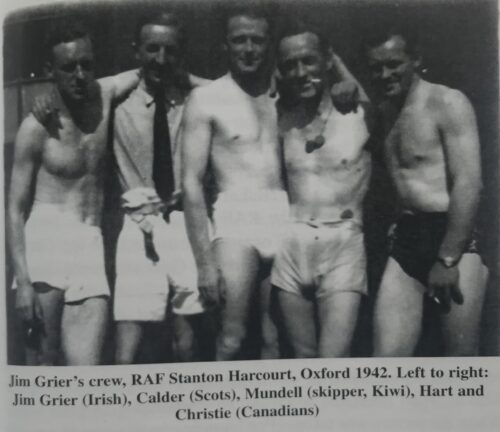
 An extraordinary piece of Irish Rugby memorabilia .A team photo of the 'Blarney Boys-Irish International Rugby XV' taken by Jim Grier from Granard Co Longford,who was an RAF pilot incarcerated in Stalag VIIIB Prisoner of War Camp in Lamsdorf,East Germany from 1942 to 1945.This amazing photograph was taken by the resident German Camp Photographer and presented to Jim. 36cm x 50cm Jim captained the Irish Team which was assembled during the summer of 1943 when the prisoners organised their own international rugby tournament comprising of the various nationalities incarcerated there.The Irish Team were mainly Army men.Their coach was the remarkable 'Pop' Press -50 years old and a Great War Veteran and Royal Marine (seen in the photo back row on left ).All teams were assigned full playing kit by their hosts with their country's emblem emblazoned on each. Stalag 344 was a large German P.O.W Camp ,100 miles south of Breslau and held between 12 & 15000 British troops, most of them taken prisoner at Dunkirk in 1940,Canadian & RAF Aircrew. The competition was limited to 12 a side as the pitches were small.Not surprisingly ,a New Zealand team emerged victorious who competed against the Home Nations.
An extraordinary piece of Irish Rugby memorabilia .A team photo of the 'Blarney Boys-Irish International Rugby XV' taken by Jim Grier from Granard Co Longford,who was an RAF pilot incarcerated in Stalag VIIIB Prisoner of War Camp in Lamsdorf,East Germany from 1942 to 1945.This amazing photograph was taken by the resident German Camp Photographer and presented to Jim. 36cm x 50cm Jim captained the Irish Team which was assembled during the summer of 1943 when the prisoners organised their own international rugby tournament comprising of the various nationalities incarcerated there.The Irish Team were mainly Army men.Their coach was the remarkable 'Pop' Press -50 years old and a Great War Veteran and Royal Marine (seen in the photo back row on left ).All teams were assigned full playing kit by their hosts with their country's emblem emblazoned on each. Stalag 344 was a large German P.O.W Camp ,100 miles south of Breslau and held between 12 & 15000 British troops, most of them taken prisoner at Dunkirk in 1940,Canadian & RAF Aircrew. The competition was limited to 12 a side as the pitches were small.Not surprisingly ,a New Zealand team emerged victorious who competed against the Home Nations.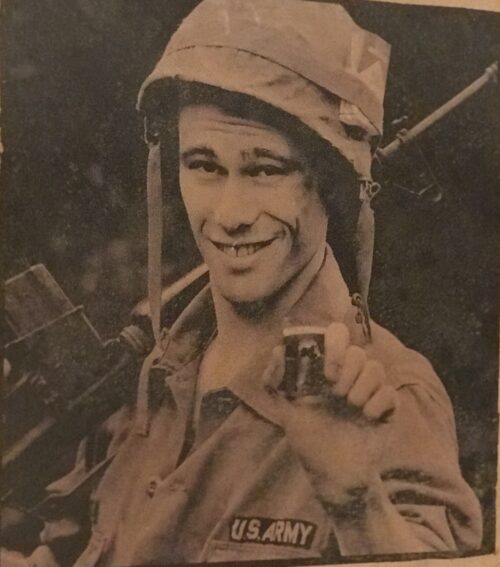
 Brilliantly conceived Murphys Stout advertisement depicting a WW2 American GI with the ubiquitous Zippo cigarette lighter. Cobh Co Cork 68cm x 48cm
Brilliantly conceived Murphys Stout advertisement depicting a WW2 American GI with the ubiquitous Zippo cigarette lighter. Cobh Co Cork 68cm x 48cmJAMES J. MURPHY
 Born on November 1825, James Jeremiah Murphy was the eldest son of fifteen children born to Jeremiah James Murphy and Catherine Bullen. James J. served his time in the family business interest and was also involved in the running of a local distillery in Cork. He sold his share in this distillery to fund his share of the set up costs of the brewery in 1856. James J. was the senior partner along with his four other brothers. It was James who guided to the brewery to success in its first forty years and he saw its output grow to 100,000 barrels before his death in 1897. James J. through his life had a keen interest in sport, rowing, sailing and GAA being foremost. He was a supporter of the Cork Harbour Rowing Club and the Royal Cork Yacht Club and the Cork County Board of the GAA. James J. philanthropic efforts were also well known in the city supporting hospitals, orphanages and general relief of distress in the city so much so on his death being described as a ‘prince in the charitable world’. It is James J. that epitomises the Murphy’s brand in stature and quality of character.1854
Born on November 1825, James Jeremiah Murphy was the eldest son of fifteen children born to Jeremiah James Murphy and Catherine Bullen. James J. served his time in the family business interest and was also involved in the running of a local distillery in Cork. He sold his share in this distillery to fund his share of the set up costs of the brewery in 1856. James J. was the senior partner along with his four other brothers. It was James who guided to the brewery to success in its first forty years and he saw its output grow to 100,000 barrels before his death in 1897. James J. through his life had a keen interest in sport, rowing, sailing and GAA being foremost. He was a supporter of the Cork Harbour Rowing Club and the Royal Cork Yacht Club and the Cork County Board of the GAA. James J. philanthropic efforts were also well known in the city supporting hospitals, orphanages and general relief of distress in the city so much so on his death being described as a ‘prince in the charitable world’. It is James J. that epitomises the Murphy’s brand in stature and quality of character.1854OUR LADY’S WELL BREWERY
 In 1854 James J. and his brothers purchased the buildings of the Cork foundling Hospital and on this site built the brewery. The brewery eventually became known as the Lady’s Well Brewery as it is situated adjacent to a famous ‘Holy Well’ and water source that had become a famous place of devotion during penal times.1856
In 1854 James J. and his brothers purchased the buildings of the Cork foundling Hospital and on this site built the brewery. The brewery eventually became known as the Lady’s Well Brewery as it is situated adjacent to a famous ‘Holy Well’ and water source that had become a famous place of devotion during penal times.1856THE BEGINNING
 James J. Murphy and his brothers found James J. Murphy & Co. and begin brewing.1861
James J. Murphy and his brothers found James J. Murphy & Co. and begin brewing.1861FROM STRENGTH TO STRENGTH
 In 1861 the brewery produced 42,990 barrels and began to impose itself as one of the major breweries in the country.1885
In 1861 the brewery produced 42,990 barrels and began to impose itself as one of the major breweries in the country.1885A FRIEND OF THE POOR, HURRAH
 James J. was a much loved figure in Cork, a noted philanthropist and indeed hero of the entire city at one point. The ‘Hurrah for the hero’ song refers to James J’s heroic efforts to save the local economy from ruin in the year of 1885. The story behind this is that when the key bank for the region the ‘Munster Bank’ was close to ruin, which could have led to an economic disaster for the entire country and bankruptcy for thousands, James J. stepped in and led the venture to establish a new bank the ‘Munster and Leinster’, saving the Munster Bank depositors and creditors from financial loss and in some cases, ruin. His exploits in saving the bank, led to the writing of many a poem and song in his honour including ‘Hurrah for the man who’s a friend of the poor’, which would have been sung in pubs for many years afterwards.1889
James J. was a much loved figure in Cork, a noted philanthropist and indeed hero of the entire city at one point. The ‘Hurrah for the hero’ song refers to James J’s heroic efforts to save the local economy from ruin in the year of 1885. The story behind this is that when the key bank for the region the ‘Munster Bank’ was close to ruin, which could have led to an economic disaster for the entire country and bankruptcy for thousands, James J. stepped in and led the venture to establish a new bank the ‘Munster and Leinster’, saving the Munster Bank depositors and creditors from financial loss and in some cases, ruin. His exploits in saving the bank, led to the writing of many a poem and song in his honour including ‘Hurrah for the man who’s a friend of the poor’, which would have been sung in pubs for many years afterwards.1889THE MALT HOUSE
 In 1889 a Malt House for the brewery was built at a cost of 4,640 pounds and was ‘built and arranged on the newest principle and fitted throughout with the latest appliances known to modern science”. Today the Malthouse is one of the most famous Cork landmarks and continues to function as offices for Murphy’s.1892
In 1889 a Malt House for the brewery was built at a cost of 4,640 pounds and was ‘built and arranged on the newest principle and fitted throughout with the latest appliances known to modern science”. Today the Malthouse is one of the most famous Cork landmarks and continues to function as offices for Murphy’s.1892MURPHY’S GOLD
 Murphy’s Stout wins the Gold medal at the Brewers and Allied Trades Exhibition in Dublin and again wins the supreme award when the exhibition is held in Manchester in 1895. These same medals feature on our Murphy’s packaging today. Murphy’s have continued it’s tradition of excellence in brewing winning Gold again at the Brewing Industry International awards in 2002 and also gaining medals in the subsequent two competitions.1893
Murphy’s Stout wins the Gold medal at the Brewers and Allied Trades Exhibition in Dublin and again wins the supreme award when the exhibition is held in Manchester in 1895. These same medals feature on our Murphy’s packaging today. Murphy’s have continued it’s tradition of excellence in brewing winning Gold again at the Brewing Industry International awards in 2002 and also gaining medals in the subsequent two competitions.1893MURPHY’S FOR STRENGTH
 Eugen Sandow the world famous ‘strongman’, endorses Murphy’s Stout: “From experience I can strongly recommend Messrs JJ Murphy’s Stout”. The famous Murphy’s image of Sandow lifting a horse was then created.1906
Eugen Sandow the world famous ‘strongman’, endorses Murphy’s Stout: “From experience I can strongly recommend Messrs JJ Murphy’s Stout”. The famous Murphy’s image of Sandow lifting a horse was then created.1906THE JUBILEE
 The Brewery celebrates its 50th anniversary. On Whit Monday the brewery workforce and their families are treated to an excursion by train to Killarney. Paddy Barrett the youngest of the workforce that day at 13 went on to become head porter for the brewery and could recall the day vividly 50 years later.1913
The Brewery celebrates its 50th anniversary. On Whit Monday the brewery workforce and their families are treated to an excursion by train to Killarney. Paddy Barrett the youngest of the workforce that day at 13 went on to become head porter for the brewery and could recall the day vividly 50 years later.1913SWIMMING IN STOUT
 In the year of 1913 the No.5 Vat at ‘Lady’s Well’ Brewery burst and sent 23,000 galleons of porter flooding through the brewey and out on to Leitrim Street. The Cork Constitution, the local newspaper of the time wrote that “a worker had a most exciting experience and in the onrush of porter he had to swim in it for about 40 yards to save himself from asphyxiation”1914
In the year of 1913 the No.5 Vat at ‘Lady’s Well’ Brewery burst and sent 23,000 galleons of porter flooding through the brewey and out on to Leitrim Street. The Cork Constitution, the local newspaper of the time wrote that “a worker had a most exciting experience and in the onrush of porter he had to swim in it for about 40 yards to save himself from asphyxiation”1914JOINING UP
 The First World War marked an era of dramatic change both in the countries fortune and on a much smaller scale that of the Brewery’s. On the 13 August James J. Murphy and Co. joined the other members of the Cork Employers Federation in promising that ‘all constant employees volunteering to join any of his Majesties forces for active service in compliance with the call for help by the Government will be facilitated and their places given back to them at the end of the war’. Eighteen of the Brewery’s workers joined up including one sixteen year old. Ten never returned.1915
The First World War marked an era of dramatic change both in the countries fortune and on a much smaller scale that of the Brewery’s. On the 13 August James J. Murphy and Co. joined the other members of the Cork Employers Federation in promising that ‘all constant employees volunteering to join any of his Majesties forces for active service in compliance with the call for help by the Government will be facilitated and their places given back to them at the end of the war’. Eighteen of the Brewery’s workers joined up including one sixteen year old. Ten never returned.1915THE FIRST LORRY IN IRELAND
 James J. Murphy & Co. purchase the first petrol lorry in the country.1920
James J. Murphy & Co. purchase the first petrol lorry in the country.1920THE BURNING OF CORK
 On the 11-12th December the centre of Cork city was extensively damaged by fire including four of the company’s tied houses (Brewery owned establishments). The company was eventually compensated for its losses by the British government.1921
On the 11-12th December the centre of Cork city was extensively damaged by fire including four of the company’s tied houses (Brewery owned establishments). The company was eventually compensated for its losses by the British government.1921MURPHY’S IN A BOTTLE
 In 1921 James J. Murphy and Co. open a bottling plant and bottle their own stout. A foreman and four ‘boys’ were installed to run the operation and the product quickly won ‘good trade’.1924
In 1921 James J. Murphy and Co. open a bottling plant and bottle their own stout. A foreman and four ‘boys’ were installed to run the operation and the product quickly won ‘good trade’.1924THE FIRST CAMPAIGNS
 In 1924 the Murphy’s Brewery began to embrace advertising. In the decades prior to this the attitude had been somewhat negative with one director stating ‘We do not hope to thrive on pushing and puffing; our sole grounds for seeking popular favour is the excellence of our product’.1940
In 1924 the Murphy’s Brewery began to embrace advertising. In the decades prior to this the attitude had been somewhat negative with one director stating ‘We do not hope to thrive on pushing and puffing; our sole grounds for seeking popular favour is the excellence of our product’.1940WWII
 In 1940 at the height of the London Blitz the Murphy’s auditing firm is completely destroyed. The war which had indirectly affected the firm in terms of shortages of fuel and materials now affected the brewery directly.1953
In 1940 at the height of the London Blitz the Murphy’s auditing firm is completely destroyed. The war which had indirectly affected the firm in terms of shortages of fuel and materials now affected the brewery directly.1953LT. COL JOHN FITZJAMES
 In 1953 the last direct descendant of James J. takes over Chairmanship of the firm. Affectionately known in the Brewery as the ‘Colonel’ he ran the company until 1981.1961
In 1953 the last direct descendant of James J. takes over Chairmanship of the firm. Affectionately known in the Brewery as the ‘Colonel’ he ran the company until 1981.1961THE IRON LUNG
 Complete replacement of old wooden barrels to aluminium lined vessels (kegs) known as ‘Iron lungs’ draws to an end the era of ‘Coopers’ the tradesmen who built the wooden barrels on site in the Brewery for so many decades.1979
Complete replacement of old wooden barrels to aluminium lined vessels (kegs) known as ‘Iron lungs’ draws to an end the era of ‘Coopers’ the tradesmen who built the wooden barrels on site in the Brewery for so many decades.1979MURPHY’S IN AMERICA

Murphy’s reaches Americans shores for the first time winning back many drinkers lost to emigration and a whole new generation of stout drinkers.
1985MURPHY’S GOES INTERNATIONAL
 Murphy’s Launched as a National and International Brand. Exports included UK, US and Canada. Introduction of the first 25cl long neck stout bottle.1994
Murphy’s Launched as a National and International Brand. Exports included UK, US and Canada. Introduction of the first 25cl long neck stout bottle.1994MURPHY’S OPEN
 Murphy’s commence sponsorship of the hugely successful Murphy’s Irish Open Golf Championship culminating in Colm Montgomery’s ‘Monty’s’ famous third win at ‘Fota Island’ in 2002.2005
Murphy’s commence sponsorship of the hugely successful Murphy’s Irish Open Golf Championship culminating in Colm Montgomery’s ‘Monty’s’ famous third win at ‘Fota Island’ in 2002.2005MURPHY’S GOLD
 Murphy’s wins Gold at the Brewing Industry International Awards a testament to it’s superior taste and quality. Indeed 2003 was the first of three successive wins in this competition.2006
Murphy’s wins Gold at the Brewing Industry International Awards a testament to it’s superior taste and quality. Indeed 2003 was the first of three successive wins in this competition.2006150 YEARS OF BREWING LEGEND
 The Murphy Brewery celebrates 150 years of brewing from 1856 to 2006 going from strength to strength; the now legendary stout is sold in over 40 countries and recognised worldwide as superior stout. We hope James J. would be proud.
The Murphy Brewery celebrates 150 years of brewing from 1856 to 2006 going from strength to strength; the now legendary stout is sold in over 40 countries and recognised worldwide as superior stout. We hope James J. would be proud.
 44cm x 55cm Dublin The Marrowbone Lane Distillery was an Irish whiskey distillery located on Marrowbone Lane, in Dublin, Ireland. One of the "big four" historical Dublin whiskey firms, it was run by William Jameson, a member of the Jameson whiskey dynasty. However, the whiskey now known as Jameson Irish Whiskey was not produced at this distillery, but at the separate enterprise run by John Jameson at the nearby Bow Street Distillery. The distillery closed in 1923 following financial difficulties.The precise origins of the distillery are uncertain, however, it was likely established in the 1750s (possibly 1752) and later acquired by the Stein family, relatives of the Jameson family circa 1780. An excise return in 1802 lists Stein and Jameson, however, by 1822 the company had become William Jameson & Co. Initially a small undertaking, with an output of just 30,000 gallons per annum, the distillery expanded over time, and by the time Alfred Barnard, a British historian visited the distillery in the 1880s, it had grown to cover some 14 acres. In his book, The Whisky Distilleries of the United Kingdom, Barnard described Marrowbone Lane as having some of the biggest distilling equipment in the world, including two mash tuns with capacities in excess of 100,000 gallons, which were the "said to be the largest in the United Kingdom". At its peak, the distillery was the second largest in Dublin (then one of the world's largest whiskey distilling centres), with an output of 900,000 gallons per annum, and a staff of 200, including 30 coopers. The whiskey produced at the distillery, known as "Dublin Whiskey" was chiefly exported to Australia, Canada, India and the United States. Later renamed the Dublin Distilling Company, the company entered financial difficulties in the late 1800s, and in 1891, merged with George Roe's Thomas Street Distillery and the Dublin Whiskey Distillery Company's Jones Road Distillery to form the Dublin Distilleries Company Ltd. Although, the amalgamated company had a potential production capacity of 3.5 million gallons per annum, it continued to endure severe financial difficulties, in particular, following the loss of both the American and British Commonwealth export markets during prohibition and the Anglo-Irish trade war in the 1920s. Both the Thomas Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries closed in 1923, with the Jones Road Distillery following suit in 1926. Though distilling may have continued at Jones Road until 1946. During the 1916 Easter uprising, both the Marrowbone Lane distillery and Roe's distillery at Thomas Street were used as strongpoints by a force of more than a hundred rebels.
44cm x 55cm Dublin The Marrowbone Lane Distillery was an Irish whiskey distillery located on Marrowbone Lane, in Dublin, Ireland. One of the "big four" historical Dublin whiskey firms, it was run by William Jameson, a member of the Jameson whiskey dynasty. However, the whiskey now known as Jameson Irish Whiskey was not produced at this distillery, but at the separate enterprise run by John Jameson at the nearby Bow Street Distillery. The distillery closed in 1923 following financial difficulties.The precise origins of the distillery are uncertain, however, it was likely established in the 1750s (possibly 1752) and later acquired by the Stein family, relatives of the Jameson family circa 1780. An excise return in 1802 lists Stein and Jameson, however, by 1822 the company had become William Jameson & Co. Initially a small undertaking, with an output of just 30,000 gallons per annum, the distillery expanded over time, and by the time Alfred Barnard, a British historian visited the distillery in the 1880s, it had grown to cover some 14 acres. In his book, The Whisky Distilleries of the United Kingdom, Barnard described Marrowbone Lane as having some of the biggest distilling equipment in the world, including two mash tuns with capacities in excess of 100,000 gallons, which were the "said to be the largest in the United Kingdom". At its peak, the distillery was the second largest in Dublin (then one of the world's largest whiskey distilling centres), with an output of 900,000 gallons per annum, and a staff of 200, including 30 coopers. The whiskey produced at the distillery, known as "Dublin Whiskey" was chiefly exported to Australia, Canada, India and the United States. Later renamed the Dublin Distilling Company, the company entered financial difficulties in the late 1800s, and in 1891, merged with George Roe's Thomas Street Distillery and the Dublin Whiskey Distillery Company's Jones Road Distillery to form the Dublin Distilleries Company Ltd. Although, the amalgamated company had a potential production capacity of 3.5 million gallons per annum, it continued to endure severe financial difficulties, in particular, following the loss of both the American and British Commonwealth export markets during prohibition and the Anglo-Irish trade war in the 1920s. Both the Thomas Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries closed in 1923, with the Jones Road Distillery following suit in 1926. Though distilling may have continued at Jones Road until 1946. During the 1916 Easter uprising, both the Marrowbone Lane distillery and Roe's distillery at Thomas Street were used as strongpoints by a force of more than a hundred rebels.
 Classic.John Jameson's JJ & S Whiskey Mirror.Excellent quality reproduction. 26cm x 26cm. John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it maintained for four consecutive years.
Classic.John Jameson's JJ & S Whiskey Mirror.Excellent quality reproduction. 26cm x 26cm. John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it maintained for four consecutive years.
 67cm x 54cm Dublin The Sunday Press was a weekly newspaper published in Ireland from 1949 until 1995. It was launched by Éamon de Valera's Irish Press group following the defeat of his Fianna Fáil party in the 1948 Irish general election. Like its sister newspaper, the daily The Irish Press, politically the paper loyally supported Fianna Fáil. The future Taoiseach Seán Lemass was the managing editor of the Irish Press who spearheaded the launch of the Sunday paper, with the first editor Colonel Matt Feehan. Many of the Irish Press journalists contributed to the paper. 'When I open the pages, I duck' was Brendan Behan's description of reading The Sunday Press, for the habit of published memoirs of veterans (usually those aligned to Fianna Fáil) of the Irish War of Independence. It soon built up a large readership, and overtook its main competitor the Sunday Independent, which tended to support Fine Gael. At its peak The Sunday Press sold up to 475,000 copies every week, and had a readership of over one million, around one third of the Irish population. Like the Evening Press, the paper's readership held up better over the years than that of the flagship title in the group, The Irish Press, and it might have survived as a stand-alone title had it been sold. However, with the collapse of the Irish Press Newspapers group in May 1995, all three titles ceased publication immediately. The launch of Ireland on Sunday in 1997 was initially interpreted by many observers as an attempt to appeal to the former readership of The Sunday Press, seen as generally rural, fairly conservative Catholic, and with a traditional Irish nationalist political outlook. When Christmas Day fell on Sunday in 1949, 1955, 1960, 1966, 1977, 1983, 1988 and 1994 the paper came out on the Saturday. Vincent Jennings at the age of 31 became editor of The Sunday Press in 1968, serving until December 1986, when he became manager of the Irish Press Group. Journalists who worked at the press include Stephen Collins served as political editor his father Willie Collins was deputy editorand Michael Carwood became sports editor of The Sunday Press in 1988[5] until its closure in 1995.
67cm x 54cm Dublin The Sunday Press was a weekly newspaper published in Ireland from 1949 until 1995. It was launched by Éamon de Valera's Irish Press group following the defeat of his Fianna Fáil party in the 1948 Irish general election. Like its sister newspaper, the daily The Irish Press, politically the paper loyally supported Fianna Fáil. The future Taoiseach Seán Lemass was the managing editor of the Irish Press who spearheaded the launch of the Sunday paper, with the first editor Colonel Matt Feehan. Many of the Irish Press journalists contributed to the paper. 'When I open the pages, I duck' was Brendan Behan's description of reading The Sunday Press, for the habit of published memoirs of veterans (usually those aligned to Fianna Fáil) of the Irish War of Independence. It soon built up a large readership, and overtook its main competitor the Sunday Independent, which tended to support Fine Gael. At its peak The Sunday Press sold up to 475,000 copies every week, and had a readership of over one million, around one third of the Irish population. Like the Evening Press, the paper's readership held up better over the years than that of the flagship title in the group, The Irish Press, and it might have survived as a stand-alone title had it been sold. However, with the collapse of the Irish Press Newspapers group in May 1995, all three titles ceased publication immediately. The launch of Ireland on Sunday in 1997 was initially interpreted by many observers as an attempt to appeal to the former readership of The Sunday Press, seen as generally rural, fairly conservative Catholic, and with a traditional Irish nationalist political outlook. When Christmas Day fell on Sunday in 1949, 1955, 1960, 1966, 1977, 1983, 1988 and 1994 the paper came out on the Saturday. Vincent Jennings at the age of 31 became editor of The Sunday Press in 1968, serving until December 1986, when he became manager of the Irish Press Group. Journalists who worked at the press include Stephen Collins served as political editor his father Willie Collins was deputy editorand Michael Carwood became sports editor of The Sunday Press in 1988[5] until its closure in 1995.
 Limited Edition no 17/200 of the Republican Bulletin as issued by the Anti Treaty Side during the Irish Civil War.These pamphlets were distributed to the general public and sold at 1p per edition. 32cm x 54cm Limerick The Irish Civil War (28 June 1922 – 24 May 1923) was a conflict that followed the Irish War of Independence and accompanied the establishment of the Irish Free State, an entity independent from the United Kingdom but within the British Empire. The civil war was waged between two opposing groups, the pro-treaty Provisional Government and the anti-treaty Irish Republican Army (IRA), over the Anglo-Irish Treaty. The forces of the Provisional Government (which became the Free State in December 1922) supported the Treaty, while the anti-treaty opposition saw it as a betrayal of the Irish Republic (which had been proclaimed during the Easter Rising). Many of those who fought on both sides in the conflict had been members of the IRA during the War of Independence. The Civil War was won by the pro-treaty Free State forces, who benefited from substantial quantities of weapons provided by the British Government. The conflict may have claimed more lives than the War of Independence that preceded it, and left Irish society divided and embittered for generations. Today, two of the main political parties in the Republic of Ireland, Fine Gael and Fianna Fáil, are direct descendants of the opposing sides of the war.Out of stock
Limited Edition no 17/200 of the Republican Bulletin as issued by the Anti Treaty Side during the Irish Civil War.These pamphlets were distributed to the general public and sold at 1p per edition. 32cm x 54cm Limerick The Irish Civil War (28 June 1922 – 24 May 1923) was a conflict that followed the Irish War of Independence and accompanied the establishment of the Irish Free State, an entity independent from the United Kingdom but within the British Empire. The civil war was waged between two opposing groups, the pro-treaty Provisional Government and the anti-treaty Irish Republican Army (IRA), over the Anglo-Irish Treaty. The forces of the Provisional Government (which became the Free State in December 1922) supported the Treaty, while the anti-treaty opposition saw it as a betrayal of the Irish Republic (which had been proclaimed during the Easter Rising). Many of those who fought on both sides in the conflict had been members of the IRA during the War of Independence. The Civil War was won by the pro-treaty Free State forces, who benefited from substantial quantities of weapons provided by the British Government. The conflict may have claimed more lives than the War of Independence that preceded it, and left Irish society divided and embittered for generations. Today, two of the main political parties in the Republic of Ireland, Fine Gael and Fianna Fáil, are direct descendants of the opposing sides of the war.Out of stock
 32cm x 48cm Dublin Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.”
32cm x 48cm Dublin Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.”
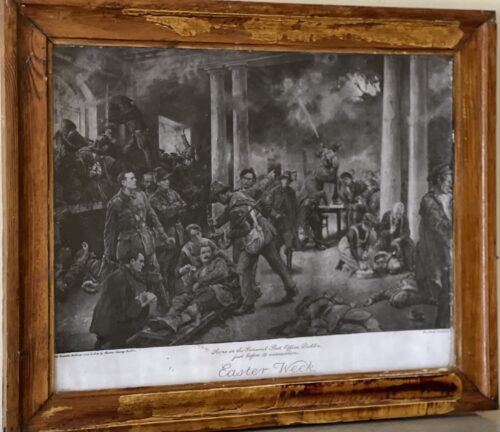 40cm x 50cm Dublin The Easter Rising (Irish: Éirí Amach na Cásca), also known as the Easter Rebellion, was an armed insurrection in Ireland during Easter Week in April 1916. The Rising was launched by Irish republicans against British rule in Ireland with the aim of establishing an independent Irish Republic while the United Kingdom was fighting the First World War. It was the most significant uprising in Ireland since the rebellion of 1798 and the first armed conflict of the Irish revolutionary period. Sixteen of the Rising's leaders were executed from May 1916. The nature of the executions, and subsequent political developments, ultimately contributed to an increase in popular support for Irish independence. Organised by a seven-man Military Council of the Irish Republican Brotherhood, the Rising began on Easter Monday, 24 April 1916 and lasted for six days. Members of the Irish Volunteers, led by schoolmaster and Irish language activist Patrick Pearse, joined by the smaller Irish Citizen Army of James Connolly and 200 women of Cumann na mBan, seized strategically important buildings in Dublin and proclaimed the Irish Republic. The British Army brought in thousands of reinforcements as well as artillery and a gunboat. There was street fighting on the routes into the city centre, where the rebels slowed the British advance and inflicted many casualties. Elsewhere in Dublin, the fighting mainly consisted of sniping and long-range gun battles. The main rebel positions were gradually surrounded and bombarded with artillery. There were isolated actions in other parts of Ireland; Volunteer leader Eoin MacNeill had issued a countermand in a bid to halt the Rising, which greatly reduced the number of rebels who mobilised. With much greater numbers and heavier weapons, the British Army suppressed the Rising. Pearse agreed to an unconditional surrender on Saturday 29 April, although sporadic fighting continued briefly. After the surrender, the country remained under martial law. About 3,500 people were taken prisoner by the British and 1,800 of them were sent to internment camps or prisons in Britain. Most of the leaders of the Rising were executed following courts-martial. The Rising brought physical force republicanism back to the forefront of Irish politics, which for nearly fifty years had been dominated by constitutional nationalism. Opposition to the British reaction to the Rising contributed to changes in public opinion and the move toward independence, as shown in the December 1918 election in Ireland which was won by the Sinn Féin party, which convened the First Dáil and declared independence. Of the 485 people killed, 260 were civilians, 143 were British military and police personnel, and 82 were Irish rebels, including 16 rebels executed for their roles in the Rising. More than 2,600 people were wounded. Many of the civilians were killed or wounded by British artillery fire or were mistaken for rebels. Others were caught in the crossfire during firefights between the British and the rebels. The shelling and resulting fires left parts of central Dublin in ruins.
40cm x 50cm Dublin The Easter Rising (Irish: Éirí Amach na Cásca), also known as the Easter Rebellion, was an armed insurrection in Ireland during Easter Week in April 1916. The Rising was launched by Irish republicans against British rule in Ireland with the aim of establishing an independent Irish Republic while the United Kingdom was fighting the First World War. It was the most significant uprising in Ireland since the rebellion of 1798 and the first armed conflict of the Irish revolutionary period. Sixteen of the Rising's leaders were executed from May 1916. The nature of the executions, and subsequent political developments, ultimately contributed to an increase in popular support for Irish independence. Organised by a seven-man Military Council of the Irish Republican Brotherhood, the Rising began on Easter Monday, 24 April 1916 and lasted for six days. Members of the Irish Volunteers, led by schoolmaster and Irish language activist Patrick Pearse, joined by the smaller Irish Citizen Army of James Connolly and 200 women of Cumann na mBan, seized strategically important buildings in Dublin and proclaimed the Irish Republic. The British Army brought in thousands of reinforcements as well as artillery and a gunboat. There was street fighting on the routes into the city centre, where the rebels slowed the British advance and inflicted many casualties. Elsewhere in Dublin, the fighting mainly consisted of sniping and long-range gun battles. The main rebel positions were gradually surrounded and bombarded with artillery. There were isolated actions in other parts of Ireland; Volunteer leader Eoin MacNeill had issued a countermand in a bid to halt the Rising, which greatly reduced the number of rebels who mobilised. With much greater numbers and heavier weapons, the British Army suppressed the Rising. Pearse agreed to an unconditional surrender on Saturday 29 April, although sporadic fighting continued briefly. After the surrender, the country remained under martial law. About 3,500 people were taken prisoner by the British and 1,800 of them were sent to internment camps or prisons in Britain. Most of the leaders of the Rising were executed following courts-martial. The Rising brought physical force republicanism back to the forefront of Irish politics, which for nearly fifty years had been dominated by constitutional nationalism. Opposition to the British reaction to the Rising contributed to changes in public opinion and the move toward independence, as shown in the December 1918 election in Ireland which was won by the Sinn Féin party, which convened the First Dáil and declared independence. Of the 485 people killed, 260 were civilians, 143 were British military and police personnel, and 82 were Irish rebels, including 16 rebels executed for their roles in the Rising. More than 2,600 people were wounded. Many of the civilians were killed or wounded by British artillery fire or were mistaken for rebels. Others were caught in the crossfire during firefights between the British and the rebels. The shelling and resulting fires left parts of central Dublin in ruins.
 91cm x 57cm The Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA) was set up in Hayes’s Hotel in Thurles, County Tipperary in November 1884. In an address to coincide with the GAA Annual Congress the Taoiseach Garret FitzGerald, speaking on behalf of the government and the Irish people, congratulated the GAA on reaching its centenary year. He commended the contribution the GAA has made to Irish life at home and abroad.
91cm x 57cm The Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA) was set up in Hayes’s Hotel in Thurles, County Tipperary in November 1884. In an address to coincide with the GAA Annual Congress the Taoiseach Garret FitzGerald, speaking on behalf of the government and the Irish people, congratulated the GAA on reaching its centenary year. He commended the contribution the GAA has made to Irish life at home and abroad.In a unique way, it has created a sense of community among Irish people both at home and abroad.
The GAA provided enormous pleasure to millions of people of all generations. The Taoiseach reflects on the important role the GAA has played in Irish culture reflected in the way people live, work and play. The sports of hurling and football are a major strand in the culture of Ireland. The impact that the GAA has on Irish life is far stronger than politics.No political event nowadays can assemble eighty thousand people filled with passion and excitement in one place.
Garret FitzGerald describes hurling as the game of the heroic age and it is appropriate that the GAA Congress in the centenary year should be held in Cú Chulainn’s Ulster. A hundred years ago, Gaelic sports were under threat of dying out and the GAA turned this threat around by making the games an integral part of Irish life again. Nine years after the establishment of the GAA, Eoin MacNeill and Douglas Hyde followed in the footsteps of Michael Cusack and founded the Gaelic League in 1893. The establishment of both organisations ensured that both the Irish language and games survived. The Taoiseach applauds the thousands of volunteers who have made the work of the GAA possible.May your work prosper and may this dimension of Irish culture that you cherish be as full of vitality a century hence as it is in this centenary year.
The GAA Centenary Taoiseach Special Message was broadcast on 22 April 1984.
 35cm x 57cm Imagination is something Guinness Advertising has never been short of… From John Gilroy’s hapless zookeeper and his menagerie of creatures to a Polynesian surfer and a herd of white horses; from messages in bottles setting sail across the ocean to a single, heart-stoppingly enormous wave. Guinness have been carving out their own creative path for almost a century with decades of extraordinary and enduring print, TV and digital campaigns to their name, and hopefully they will continue to push boundaries to tell stories to the world. Here’s to original thinking !
35cm x 57cm Imagination is something Guinness Advertising has never been short of… From John Gilroy’s hapless zookeeper and his menagerie of creatures to a Polynesian surfer and a herd of white horses; from messages in bottles setting sail across the ocean to a single, heart-stoppingly enormous wave. Guinness have been carving out their own creative path for almost a century with decades of extraordinary and enduring print, TV and digital campaigns to their name, and hopefully they will continue to push boundaries to tell stories to the world. Here’s to original thinking !
 68cm x 51cm In 1791 James Power, an innkeeper from Dublin, established a small distillery at his public house at 109 Thomas St., Dublin. The distillery, which had an output of about 6,000 gallons in its first year of operation, initially traded as James Power and Son, but by 1822 had become John Power & Son, and had moved to a new premises at John's Lane, a side street off Thomas Street. At the time the distillery had three pot stills, though only one, a 500-gallon still is thought to have been in use. Following reform of the distilling laws in 1823, the distillery expanded rapidly. In 1827, production was reported at 160,270 gallons,and by 1833 had grown to 300,000 gallons per annum. As the distillery grew, so too did the stature of the family. In 1841, John Power, grandson of the founder was awarded a baronet, a hereditary title. In 1855, his son Sir James Power, laid the foundation stone for the O'Connell Monument, and in 1859 became High Sheriff of Dublin. In 1871, the distillery was expanded and rebuilt in the Victorian style, becoming one of the most impressive sights in Dublin.After expansion, output at the distillery rose to 700,000 gallons per annum, and by the 1880s, had reached about 900,000 gallons per annum, at which point the distillery covered over six acres of central Dublin, and had a staff of about 300 people.During this period, when the Dublin whiskey distilleries were amongst the largest in the world, the family run firms of John Powers, along with John Jameson, William Jameson, and George Roe, (collectively known as the "Big Four") came to dominate the Irish distilling landscape, introducing several innovations. In 1886, John Power & Son began bottling their own whiskey, rather than following the practice customary at the time, of selling whiskey directly to merchants and bonders who would bottle it themselves. They were the first Dublin distillery to do so, and one of the first in the world.A gold label adorned each bottle and it was from these that the whiskey got the name Powers Gold Label. When Alfred Barnard, the British historian visited John's Lane in the late 1880s, he noted the elegance and cleanliness of the buildings, and the modernity of the distillery, describing it as "about as complete a work as it is possible to find anywhere". At the time of his visit, the distillery was home to five pot stills, two of which with capacities of 25,000 gallons, were amongst the largest ever built.In addition, Barnard was high in his praise for Powers whiskey, noting:"The old make, which we drank with our luncheon was delicious and finer than anything we had hitherto tasted.It was as perfect in flavour, and as pronounced in the ancient aroma of Irish Whiskey so dear to to the hearts of connoisseurs,as one could possibly desire and we found a small flask of it very useful afterwards on our travels." The last member of the family to sit on the board was Sir Thomas Talbot Power,who died in 1930,and with him the Power's Baronetcy. However, ownership remained in the family until 1966, and several descendants of his sisters remained at work with the company until recent times. In 1961, a Coffey still was installed in John's Lane Distillery, allowing the production of vodka and gin, in addition to the testing of grain whiskey for use in blended whiskey. This was a notable departure for the firm, as for many years the big Dublin distilling dynasties had shunned the use of Coffey stills, questioning if their output, grain whiskey could even be termed whiskey. However, with many of the Irish distilleries having closed in the early 20th century in part due to their failure to embrace a change in consumer preference towards blended whiskey, Powers were instrumental in convincing the remaining Irish distilleries to reconsider their stance on blended whiskey. In 1966, with the Irish whiskey industry still struggling following Prohibition in the United States, the Anglo-Irish Trade War and the rise of competition from Scotch whiskey, John Powers & Son joined forces with the only other remaining distillers in the Irish Republic, the Cork Distilleries Company and their Dublin rivals John Jameson & Son, to form Irish Distillers. Soon after, in a bold move, Irish Distillers decided to close all of their existing distilleries, and to consolidate production at a new purpose-built facility in Midleton (the New Midleton Distillery) alongside their existing Old Midleton Distillery. The new distillery opened in 1975, and a year later, production ceased at John's Lane Distillery and began anew in Cork, with Powers Gold Label and many other Irish whiskeys reformulated from single pot stills whiskeys to blends. In 1989, Irish Distillers itself became a subsidiary of Pernod-Ricard following a friendly takeover.Since the closure of the John's Lane distillery, many of the distillery buildings were demolished. However, some of the buildings have been incorporated into the National College of Art and Design, and are now protected structures. In addition, three of the distillery's pot stills were saved and now located in the college's Red Square. Origins : Dublin City Dimensions : 100cm x 70cm 20kg (specially constructed damage proof shipping container)
68cm x 51cm In 1791 James Power, an innkeeper from Dublin, established a small distillery at his public house at 109 Thomas St., Dublin. The distillery, which had an output of about 6,000 gallons in its first year of operation, initially traded as James Power and Son, but by 1822 had become John Power & Son, and had moved to a new premises at John's Lane, a side street off Thomas Street. At the time the distillery had three pot stills, though only one, a 500-gallon still is thought to have been in use. Following reform of the distilling laws in 1823, the distillery expanded rapidly. In 1827, production was reported at 160,270 gallons,and by 1833 had grown to 300,000 gallons per annum. As the distillery grew, so too did the stature of the family. In 1841, John Power, grandson of the founder was awarded a baronet, a hereditary title. In 1855, his son Sir James Power, laid the foundation stone for the O'Connell Monument, and in 1859 became High Sheriff of Dublin. In 1871, the distillery was expanded and rebuilt in the Victorian style, becoming one of the most impressive sights in Dublin.After expansion, output at the distillery rose to 700,000 gallons per annum, and by the 1880s, had reached about 900,000 gallons per annum, at which point the distillery covered over six acres of central Dublin, and had a staff of about 300 people.During this period, when the Dublin whiskey distilleries were amongst the largest in the world, the family run firms of John Powers, along with John Jameson, William Jameson, and George Roe, (collectively known as the "Big Four") came to dominate the Irish distilling landscape, introducing several innovations. In 1886, John Power & Son began bottling their own whiskey, rather than following the practice customary at the time, of selling whiskey directly to merchants and bonders who would bottle it themselves. They were the first Dublin distillery to do so, and one of the first in the world.A gold label adorned each bottle and it was from these that the whiskey got the name Powers Gold Label. When Alfred Barnard, the British historian visited John's Lane in the late 1880s, he noted the elegance and cleanliness of the buildings, and the modernity of the distillery, describing it as "about as complete a work as it is possible to find anywhere". At the time of his visit, the distillery was home to five pot stills, two of which with capacities of 25,000 gallons, were amongst the largest ever built.In addition, Barnard was high in his praise for Powers whiskey, noting:"The old make, which we drank with our luncheon was delicious and finer than anything we had hitherto tasted.It was as perfect in flavour, and as pronounced in the ancient aroma of Irish Whiskey so dear to to the hearts of connoisseurs,as one could possibly desire and we found a small flask of it very useful afterwards on our travels." The last member of the family to sit on the board was Sir Thomas Talbot Power,who died in 1930,and with him the Power's Baronetcy. However, ownership remained in the family until 1966, and several descendants of his sisters remained at work with the company until recent times. In 1961, a Coffey still was installed in John's Lane Distillery, allowing the production of vodka and gin, in addition to the testing of grain whiskey for use in blended whiskey. This was a notable departure for the firm, as for many years the big Dublin distilling dynasties had shunned the use of Coffey stills, questioning if their output, grain whiskey could even be termed whiskey. However, with many of the Irish distilleries having closed in the early 20th century in part due to their failure to embrace a change in consumer preference towards blended whiskey, Powers were instrumental in convincing the remaining Irish distilleries to reconsider their stance on blended whiskey. In 1966, with the Irish whiskey industry still struggling following Prohibition in the United States, the Anglo-Irish Trade War and the rise of competition from Scotch whiskey, John Powers & Son joined forces with the only other remaining distillers in the Irish Republic, the Cork Distilleries Company and their Dublin rivals John Jameson & Son, to form Irish Distillers. Soon after, in a bold move, Irish Distillers decided to close all of their existing distilleries, and to consolidate production at a new purpose-built facility in Midleton (the New Midleton Distillery) alongside their existing Old Midleton Distillery. The new distillery opened in 1975, and a year later, production ceased at John's Lane Distillery and began anew in Cork, with Powers Gold Label and many other Irish whiskeys reformulated from single pot stills whiskeys to blends. In 1989, Irish Distillers itself became a subsidiary of Pernod-Ricard following a friendly takeover.Since the closure of the John's Lane distillery, many of the distillery buildings were demolished. However, some of the buildings have been incorporated into the National College of Art and Design, and are now protected structures. In addition, three of the distillery's pot stills were saved and now located in the college's Red Square. Origins : Dublin City Dimensions : 100cm x 70cm 20kg (specially constructed damage proof shipping container) The Still House at John's Lane Distillery, as it looked when Alfred Barnard visited in the 1800s.
The Still House at John's Lane Distillery, as it looked when Alfred Barnard visited in the 1800s.
 58cm x 58cm John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it
58cm x 58cm John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it
 51cm x 63cm In 1929, Limerick city was the home to two large of tobacco factories Spillane’s and Clune’s who imported tobacco from the United States, Egypt and Turkey as well as locally grown tobacco to produce their famed products. Spillane’s Tobacco Factory on Sarsfield Street was started by John Spillane in 1829 and was known as ‘The House of Garryowen’. A hundred years later they were employing a hundred people. The famous Garryowen plug formed 80 per cent of the factories output while they had other products including Popular and Treaty bar plugs, Hazel Nut plug, Special Flake, Handy Cut Flake, snuffs, Cashel, High Toast, White Top and Craven A cigarettes. To meet a special demand from the North of Ireland the factory produced a type of plug known as Long Square. Spillane’s closed in 1958 with the loss of 150 jobs after the building was purchased by Murray Ltd, of Dublin the year previous. Their building is where the old Dunnes Stores building stands today. William Spillane who was the Mayor of Limerick in 1885 built the Spillane Tower which today is better known as the ‘Snuff Box’ on the banks of the Shannon river at Corkanree. The other large factory was Clune’s Tobacco Factory on Denmark Street. It opened in the late 1872 and had about 60 employees in 1929. The firm specialised in Big Bar Plug, every two ounces of which is stamped Thomond. They also excelled in the Far-Famed Limerick Twist. They were also known for Kincora Plug, Sarsfield Plug, Home Rule, Hibernian, Target, Ireland’s Pride and Two Flake. A popular item associated with tobacco factories are the cigarette cards. Cigarette cards were originally produced as a small piece of card which was designed to protect the individual cigarettes from being squashed as the original packaging was paper and not the card boxes that we know today. We must not forget M.Cahill’s of Wickham Street which housed a snuff factory in 1870 in the basement of the building and operated for over sixty years. The business was founded by Michael Cahill (c.1846-1918) who was also the director of the Limerick Race Company. Cahill’s became Ireland’s longest running tobacco store and is still in operation offering a selection of cigar, teas and “gentleman’s gifts” including Swiss army knives, hipflasks and pipes. Sharon Slater
51cm x 63cm In 1929, Limerick city was the home to two large of tobacco factories Spillane’s and Clune’s who imported tobacco from the United States, Egypt and Turkey as well as locally grown tobacco to produce their famed products. Spillane’s Tobacco Factory on Sarsfield Street was started by John Spillane in 1829 and was known as ‘The House of Garryowen’. A hundred years later they were employing a hundred people. The famous Garryowen plug formed 80 per cent of the factories output while they had other products including Popular and Treaty bar plugs, Hazel Nut plug, Special Flake, Handy Cut Flake, snuffs, Cashel, High Toast, White Top and Craven A cigarettes. To meet a special demand from the North of Ireland the factory produced a type of plug known as Long Square. Spillane’s closed in 1958 with the loss of 150 jobs after the building was purchased by Murray Ltd, of Dublin the year previous. Their building is where the old Dunnes Stores building stands today. William Spillane who was the Mayor of Limerick in 1885 built the Spillane Tower which today is better known as the ‘Snuff Box’ on the banks of the Shannon river at Corkanree. The other large factory was Clune’s Tobacco Factory on Denmark Street. It opened in the late 1872 and had about 60 employees in 1929. The firm specialised in Big Bar Plug, every two ounces of which is stamped Thomond. They also excelled in the Far-Famed Limerick Twist. They were also known for Kincora Plug, Sarsfield Plug, Home Rule, Hibernian, Target, Ireland’s Pride and Two Flake. A popular item associated with tobacco factories are the cigarette cards. Cigarette cards were originally produced as a small piece of card which was designed to protect the individual cigarettes from being squashed as the original packaging was paper and not the card boxes that we know today. We must not forget M.Cahill’s of Wickham Street which housed a snuff factory in 1870 in the basement of the building and operated for over sixty years. The business was founded by Michael Cahill (c.1846-1918) who was also the director of the Limerick Race Company. Cahill’s became Ireland’s longest running tobacco store and is still in operation offering a selection of cigar, teas and “gentleman’s gifts” including Swiss army knives, hipflasks and pipes. Sharon Slater
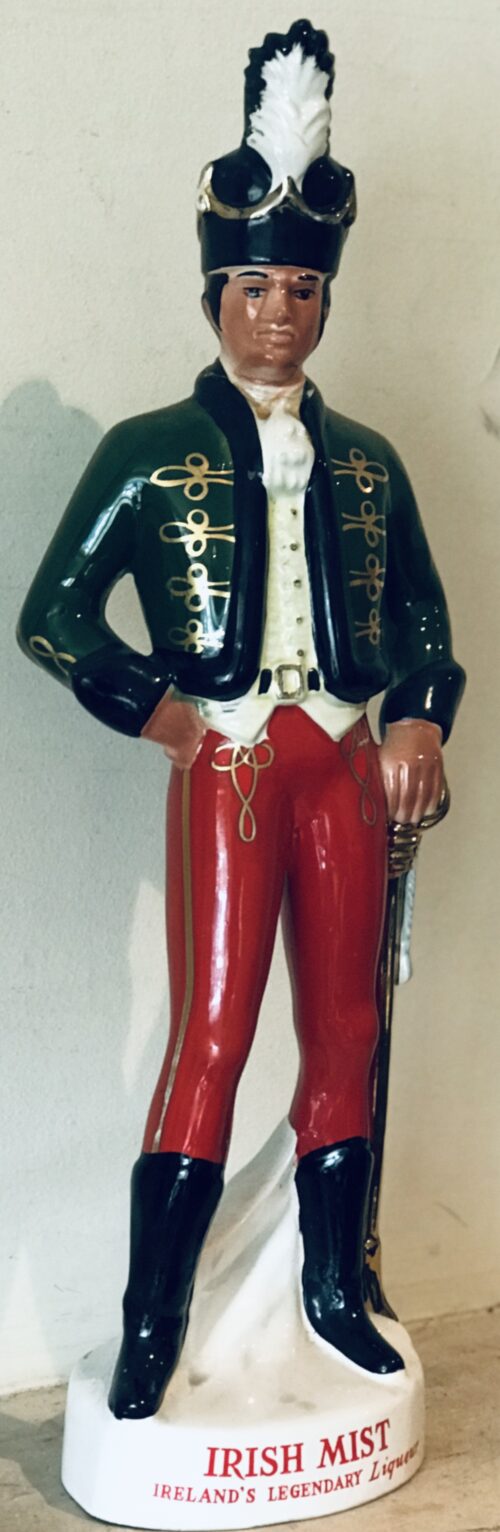 A beautiful original porcelain example of an Irish Mist Decanter bottle ,the iconic Irish soldier dressed in the traditional Irish Brigade of the Austrian Army uniform of 1750. cm x cm x cm Irish Mist is a brown Whiskey Liqueur produced in Dublin, Ireland, by the Irish Mist Liqueur Company Ltd. In September 2010 it was announced that the brand was being bought by Gruppo Campari from William Grant, only a few months after Grants had bought it from the C&C Group. It is made from aged Irish whiskey, heather and clover honey, aromatic herbs, and other spirits, blended to an ancient recipe claimed to be 1,000 years old.Though it was once 80 US proof (40% alcohol per volume), Irish Mist is now 35% or 70 US proof. The bottle shape has also been changed from a "decanter" style to a more traditional whiskey bottle shape. It is currently available in more than 40 countries. Irish Mist was the first liqueur to be produced in Ireland when commercial production began in 1947 at Tullamore, County Offaly. Tullamore is the hometown of the Williams family who were the original owners of Irish Mist. The company history goes back to 1829 when the Tullamore Distillery was founded to produce Irish whiskey. In the mid-1940s Desmond E. Williams began the search for an alternative yet related product, eventually deciding to produce a liqueur based on the ancient beverage known as heather wine.In 1985 the Cantrell & Cochrane Group purchased the Irish Mist Liqueur Company from the Williams family. In the summer of 2010 Irish Mist and the entire spirit division of C&C was bought by William Grant of Scotland. In September 2010 they in turn sold Irish Mist to Gruppo Campari.Irish Mist is typically served straight up or on ice, but also goes with coffee, vodka, or cranberry juice. Per the makers, Irish Mist's most popular recipe is Irish Mist with Cola and Lime. A Rusty Mist is an ounce of Irish Mist with an ounce of Drambuie Scotch whisky liqueur.A Black Nail is made from equal parts Irish Mist and Irish whiskey. Origins :Co Offaly Dimensions : 50cm x 15cm 4kg
A beautiful original porcelain example of an Irish Mist Decanter bottle ,the iconic Irish soldier dressed in the traditional Irish Brigade of the Austrian Army uniform of 1750. cm x cm x cm Irish Mist is a brown Whiskey Liqueur produced in Dublin, Ireland, by the Irish Mist Liqueur Company Ltd. In September 2010 it was announced that the brand was being bought by Gruppo Campari from William Grant, only a few months after Grants had bought it from the C&C Group. It is made from aged Irish whiskey, heather and clover honey, aromatic herbs, and other spirits, blended to an ancient recipe claimed to be 1,000 years old.Though it was once 80 US proof (40% alcohol per volume), Irish Mist is now 35% or 70 US proof. The bottle shape has also been changed from a "decanter" style to a more traditional whiskey bottle shape. It is currently available in more than 40 countries. Irish Mist was the first liqueur to be produced in Ireland when commercial production began in 1947 at Tullamore, County Offaly. Tullamore is the hometown of the Williams family who were the original owners of Irish Mist. The company history goes back to 1829 when the Tullamore Distillery was founded to produce Irish whiskey. In the mid-1940s Desmond E. Williams began the search for an alternative yet related product, eventually deciding to produce a liqueur based on the ancient beverage known as heather wine.In 1985 the Cantrell & Cochrane Group purchased the Irish Mist Liqueur Company from the Williams family. In the summer of 2010 Irish Mist and the entire spirit division of C&C was bought by William Grant of Scotland. In September 2010 they in turn sold Irish Mist to Gruppo Campari.Irish Mist is typically served straight up or on ice, but also goes with coffee, vodka, or cranberry juice. Per the makers, Irish Mist's most popular recipe is Irish Mist with Cola and Lime. A Rusty Mist is an ounce of Irish Mist with an ounce of Drambuie Scotch whisky liqueur.A Black Nail is made from equal parts Irish Mist and Irish whiskey. Origins :Co Offaly Dimensions : 50cm x 15cm 4kg
 Original oil on canvas painting of Bunratty Castle by the local artist Anne Byrne. 30cm x 36cm Limerick Bunratty -Caisleán Bhun Raithe, meaning "Castle at the Mouth of the Ratty") is a large 15th-century tower house in County Clare, Ireland. It is located in the centre of Bunratty village (Irish: Bun Ráite), by the N18 road between Limerick and Ennis, near Shannon Town and its airport. The castle and the adjoining folk park are run by Shannon Heritage as a major tourist attraction The name Bunratty, Bun Raite (or possibly, Bun na Raite) in Irish, means "river basin" of the 'Ratty' river. This river, alongside the castle, flows into the nearby Shannon estuary.The first recorded settlement at the site may have been a Norsemen settlement/trading camp reported in the Annals of the Four Masters to have been destroyed by Brian Boru in 977. According to local tradition, such a camp was located on a rise south-west of the current castle. However, since no actual remains of this settlement have yet been found, its exact location is unknown and its existence is not proven. Around 1250, King Henry III of England granted the cantred or district of Tradraighe (or Tradree) to Robert De Muscegros, who in 1251 cut down around 200 trees in the King's wood at Cratloe. These may have been used to construct a motte and bailey castle, which would have been the first castle at Bunratty, but again the exact position of this is unknown. A later reference in the state papers, dating to 1253 gives de Muscegros the right to hold markets and an annual fair at Bunratty. It has thus been assumed that the site was the centre of early Norman control in south-eastern Clare. Early 19th-century scholars put the structure to the north-west of the current castle. However, when a hotel was constructed there in 1959, John Huntexcavated the area and thought the remains to be that of a gun emplacement from the Confederate Wars (see below).
Original oil on canvas painting of Bunratty Castle by the local artist Anne Byrne. 30cm x 36cm Limerick Bunratty -Caisleán Bhun Raithe, meaning "Castle at the Mouth of the Ratty") is a large 15th-century tower house in County Clare, Ireland. It is located in the centre of Bunratty village (Irish: Bun Ráite), by the N18 road between Limerick and Ennis, near Shannon Town and its airport. The castle and the adjoining folk park are run by Shannon Heritage as a major tourist attraction The name Bunratty, Bun Raite (or possibly, Bun na Raite) in Irish, means "river basin" of the 'Ratty' river. This river, alongside the castle, flows into the nearby Shannon estuary.The first recorded settlement at the site may have been a Norsemen settlement/trading camp reported in the Annals of the Four Masters to have been destroyed by Brian Boru in 977. According to local tradition, such a camp was located on a rise south-west of the current castle. However, since no actual remains of this settlement have yet been found, its exact location is unknown and its existence is not proven. Around 1250, King Henry III of England granted the cantred or district of Tradraighe (or Tradree) to Robert De Muscegros, who in 1251 cut down around 200 trees in the King's wood at Cratloe. These may have been used to construct a motte and bailey castle, which would have been the first castle at Bunratty, but again the exact position of this is unknown. A later reference in the state papers, dating to 1253 gives de Muscegros the right to hold markets and an annual fair at Bunratty. It has thus been assumed that the site was the centre of early Norman control in south-eastern Clare. Early 19th-century scholars put the structure to the north-west of the current castle. However, when a hotel was constructed there in 1959, John Huntexcavated the area and thought the remains to be that of a gun emplacement from the Confederate Wars (see below). An Irish language plaque at Bunratty CastleThese lands were later handed back to (or taken back by) King Henry III and granted to Thomas De Clare, a descendant of Strongbow in 1276. De Clare built the first stone structure on the site (the second castle). This castle was occupied from 1278 to 1318 and consisted of a large single stone tower with lime white walls. It stood close to the river, on or near the site of the present Bunratty Castle. In the late 13th century, Bunratty had about 1,000 inhabitants. The castle was attacked several times by the O'Briens (or O'Brians) and their allies. In 1284, while De Clare was away in England, the site was captured and destroyed. On his return, in 1287, De Clare had the site rebuilt and a 140-yard (130 m) long fosse built around it. The castle was again attacked but it did not fall until 1318. In that year a major battle was fought at Dysert O'Dea as part of the Irish Bruce Wars, in which both Thomas De Clare and his son Richard were killed. Lady De Clare, on learning this, fled from Bunratty to Limerick after burning castle and town. The De Clare family never returned to the area and the remains of the castle eventually collapsed. As the stones were likely used for other local construction works, no traces remain of this second castle In the 14th century, Limerick was an important port for the English Crown. To guard access via the Shannon estuary against attacks from the Irish, the site was once again occupied. In 1353, Sir Thomas de Rokeby led an English army to conquer the MacNamaras and MacCarthys. A new castle (the third) was built at Bunratty, but once again, its exact location is unknown. Local tradition holds that it stood at the site where the Bunratty Castle Hotel was later constructed. However, the new structure was hardly finished before being captured by the Irish. Documents show that in 1355, King Edward III of England released Thomas Fitzjohn Fitzmaurice from prison in Limerick. He had been charged with letting the castle fall into the hands of Murtough O’Brien whilst serving as a Governor (Captain) of Bunratty. The fourth castle, the present structure, was built by the MacNamara family after around 1425. Its builder may have been one Maccon Sioda MacNamara, chieftain of Clann Cuilein (i.e. the MacNamaras). He died before the castle was completed which happened under his son Sean Finn (died in 1467). At around 1500, Bunratty Castle came into the hands of the O'Briens (or O'Brians), the most powerful clan in Munster and later Earls of Thomond. They expanded the site and eventually made it their chief seat, moving it there from Ennis. In 1558, the castle—now noted as one of the principal strongholds of Thomond—was taken by Thomas Radclyffe, the Lord-Lieutenant of Ireland from Donal O'Brien of Duagh, last King of Thomond (died 1579), and given to Donal's nephew, Connor O'Brien. Donogh O'Brien, Conor's son, may have been the one to move the seat of the family from Clonroad (Ennis) to Bunratty. He made various improvements to the castle including putting a new lead roof on it. During the Confederate Wars set off by the Irish Rebellion of 1641, Lord Forbes, commanding forces of the English Long Parliament, was allowed by the then Lord Barnabas O'Brien to occupy Bunratty in 1646. Barnabas did not want to commit to either side in the struggle, playing off royalists, rebels and roundheads against each other. He left for England, where he joined King Charles. Defence of the castle, whose position allowed those holding it to blockade maritime access to Limerick (held by the Confederates) and the river Shannon, was in the hands of Rear-Admiral Penn, the father of William Penn, founder of Pennsylvania. After a long siege, the Confederates took the castle. Penn surrendered but was allowed to sail away to Kinsale. Barnabas O'Brien died in 1657, but had apparently leased out the castle to one "John Cooper", possibly the same person married to Máire ní Mahon of Leamaneh Castle, widow of another O'Brien, Conor (died 1651). Bunratty Castle remained property of the O'Briens and in the 1680s the castle was still the principal seat of the Earls of Thomond. In 1712, Henry, the 8th and last Earl of Thomond (1688–1741) sold Bunratty Castle and 472 acres (191 ha) of land to Thomas Amory for £225 and an annual rent of £120. Amory in turn sold the castle to Thomas Studdert who moved in ca. 1720. The Studdert family left the castle (allowing it to fall into disrepair), to reside in the more comfortable and modern adjacent "Bunratty House" they had built in 1804. The reasons for the move are bound up in family arguments over the eldest son marrying his first cousin. For some time in the mid-19th century, the castle was used as a barracks by the Royal Irish Constabulary. In 1894, Bunratty was once again used by the Studdert family, as the seat of Captain Richard Studdert. In the late 19th century, the roof of the Great Hall collapsed. In 1956, the castle was purchased and restored by the 7th Viscount Gort, with assistance from the Office of Public Works.He reroofed the castle and saved it from ruin. The castle was opened to the public in 1960, sporting furniture, tapestries and works of art dating to around 1600. Today, the castle is a major tourist attraction, along with "Bunratty Folk Park". Both the castle and Bunratty House are open to the public. The castle is famous for its medieval banquets, offered since 1963, at which the "Bunratty Castle Entertainers" perform today. "Bunratty Folk Park" is an open-air museum featuring around 30 buildings, including the Ardcroney Church Of Ireland church, which moved here and reopened in 1998. Recently and controversially the Armada table of the O’Briens, princes of Thomond, was sold at auction for the princely sum of €360,000. Made from the timbers of a ship from the Spanish Armada which was wrecked off the coast of Co Clare in 1588 it had been placed for sale with Adam’s auction house yesterday, guiding between €100,000 and €200,000. In the end it sold to an undisclosed Irish buyer for €360,000.
An Irish language plaque at Bunratty CastleThese lands were later handed back to (or taken back by) King Henry III and granted to Thomas De Clare, a descendant of Strongbow in 1276. De Clare built the first stone structure on the site (the second castle). This castle was occupied from 1278 to 1318 and consisted of a large single stone tower with lime white walls. It stood close to the river, on or near the site of the present Bunratty Castle. In the late 13th century, Bunratty had about 1,000 inhabitants. The castle was attacked several times by the O'Briens (or O'Brians) and their allies. In 1284, while De Clare was away in England, the site was captured and destroyed. On his return, in 1287, De Clare had the site rebuilt and a 140-yard (130 m) long fosse built around it. The castle was again attacked but it did not fall until 1318. In that year a major battle was fought at Dysert O'Dea as part of the Irish Bruce Wars, in which both Thomas De Clare and his son Richard were killed. Lady De Clare, on learning this, fled from Bunratty to Limerick after burning castle and town. The De Clare family never returned to the area and the remains of the castle eventually collapsed. As the stones were likely used for other local construction works, no traces remain of this second castle In the 14th century, Limerick was an important port for the English Crown. To guard access via the Shannon estuary against attacks from the Irish, the site was once again occupied. In 1353, Sir Thomas de Rokeby led an English army to conquer the MacNamaras and MacCarthys. A new castle (the third) was built at Bunratty, but once again, its exact location is unknown. Local tradition holds that it stood at the site where the Bunratty Castle Hotel was later constructed. However, the new structure was hardly finished before being captured by the Irish. Documents show that in 1355, King Edward III of England released Thomas Fitzjohn Fitzmaurice from prison in Limerick. He had been charged with letting the castle fall into the hands of Murtough O’Brien whilst serving as a Governor (Captain) of Bunratty. The fourth castle, the present structure, was built by the MacNamara family after around 1425. Its builder may have been one Maccon Sioda MacNamara, chieftain of Clann Cuilein (i.e. the MacNamaras). He died before the castle was completed which happened under his son Sean Finn (died in 1467). At around 1500, Bunratty Castle came into the hands of the O'Briens (or O'Brians), the most powerful clan in Munster and later Earls of Thomond. They expanded the site and eventually made it their chief seat, moving it there from Ennis. In 1558, the castle—now noted as one of the principal strongholds of Thomond—was taken by Thomas Radclyffe, the Lord-Lieutenant of Ireland from Donal O'Brien of Duagh, last King of Thomond (died 1579), and given to Donal's nephew, Connor O'Brien. Donogh O'Brien, Conor's son, may have been the one to move the seat of the family from Clonroad (Ennis) to Bunratty. He made various improvements to the castle including putting a new lead roof on it. During the Confederate Wars set off by the Irish Rebellion of 1641, Lord Forbes, commanding forces of the English Long Parliament, was allowed by the then Lord Barnabas O'Brien to occupy Bunratty in 1646. Barnabas did not want to commit to either side in the struggle, playing off royalists, rebels and roundheads against each other. He left for England, where he joined King Charles. Defence of the castle, whose position allowed those holding it to blockade maritime access to Limerick (held by the Confederates) and the river Shannon, was in the hands of Rear-Admiral Penn, the father of William Penn, founder of Pennsylvania. After a long siege, the Confederates took the castle. Penn surrendered but was allowed to sail away to Kinsale. Barnabas O'Brien died in 1657, but had apparently leased out the castle to one "John Cooper", possibly the same person married to Máire ní Mahon of Leamaneh Castle, widow of another O'Brien, Conor (died 1651). Bunratty Castle remained property of the O'Briens and in the 1680s the castle was still the principal seat of the Earls of Thomond. In 1712, Henry, the 8th and last Earl of Thomond (1688–1741) sold Bunratty Castle and 472 acres (191 ha) of land to Thomas Amory for £225 and an annual rent of £120. Amory in turn sold the castle to Thomas Studdert who moved in ca. 1720. The Studdert family left the castle (allowing it to fall into disrepair), to reside in the more comfortable and modern adjacent "Bunratty House" they had built in 1804. The reasons for the move are bound up in family arguments over the eldest son marrying his first cousin. For some time in the mid-19th century, the castle was used as a barracks by the Royal Irish Constabulary. In 1894, Bunratty was once again used by the Studdert family, as the seat of Captain Richard Studdert. In the late 19th century, the roof of the Great Hall collapsed. In 1956, the castle was purchased and restored by the 7th Viscount Gort, with assistance from the Office of Public Works.He reroofed the castle and saved it from ruin. The castle was opened to the public in 1960, sporting furniture, tapestries and works of art dating to around 1600. Today, the castle is a major tourist attraction, along with "Bunratty Folk Park". Both the castle and Bunratty House are open to the public. The castle is famous for its medieval banquets, offered since 1963, at which the "Bunratty Castle Entertainers" perform today. "Bunratty Folk Park" is an open-air museum featuring around 30 buildings, including the Ardcroney Church Of Ireland church, which moved here and reopened in 1998. Recently and controversially the Armada table of the O’Briens, princes of Thomond, was sold at auction for the princely sum of €360,000. Made from the timbers of a ship from the Spanish Armada which was wrecked off the coast of Co Clare in 1588 it had been placed for sale with Adam’s auction house yesterday, guiding between €100,000 and €200,000. In the end it sold to an undisclosed Irish buyer for €360,000. South solar in Bunratty Castle
South solar in Bunratty Castle“The good news is, it will be staying in Ireland, ” says the managing director of Adam’s auction house, James O’Halloran. “That’s all we’ve been allowed to say for the moment, but we’re hoping that more information will be released fairly soon.” It’s understood that the State was outbid for the table and that the new owner is a private buyer.
Bidding on the table started at €70,000 but with one online bidder, three on the phone and one person in the room, it didn’t take long to sail past its lowest guide of €100,000, followed quickly by its top estimate of €200,000. “It got to €360,000 quite quickly,” O’Halloran says. “We thought it would do reasonably well, but because there was nothing to compare it to, we didn’t really know what to expect.”
The three-metre-long table was the property of Lord Inchiquin. Its rectangular top sits on a frieze of a dozen carved heads, with four carved heraldic lion corner supports and two figures of Hope and Charity, which would originally have been found on the stern of a galleon. It spent 300 years at Dromoland Castle before moving to Bunratty, where its elaborate series of carved masks became a key attraction.
When it was announced that the table – described by the Knight of Glin, Desmond FitzGerald, as “one of the most important and earliest pieces of Irish furniture” – was to be sold at Adam’s Country House Collections sale at Townley Hall, near Drogheda, Co Louth, there were calls for it to be kept in Ireland as it represents part of our cultural heritage. The only question now is, where will the table find its new home?




cm x cm Askeaton Co Limerick
‘Our seducers were our accusers’: the lurid tales of members of Askeaton Hellfire Club
The ruins of Askeaton Hellfire Club on an island in the River Deel, with the ruins of the Desmond Castle in the background (Photograph: Patrick Comerford, 2017) Patrick Comerford The ruins of Limerick Hellfire Club stand beside the ruins of the Desmond Castle on the island in the middle of the River Deel. As the fast-flowing waters of the river thunder past, making their way under the old narrow bridge, these ruins appear like a benign presence in the heart of the town, especially in the early evening as the sun sets behind them and the rooks and herons hover above the remains of this centuries-old crumbling structures. The ruins of the Hellfire Club stand within the bailey of Askeaton Castle. They date from 1636-1637, when this building was first erected as a detached barracks or tower. The barracks or tower was built by the builder and designer, Andrew Tucker, for Richard Boyle (1566-1643), the 1st Earl of Cork, who had recently acquired Askeaton Castle. The tower was built with battered walls with cut stone quoins, and the remains of a three-bay was built on top of the battered base later, some time in the mid-18th century. There is a bow to the south elevation of the house and a shallow projecting end-bay to the north elevation. The house is roofless, with a limestone eaves course. The course rubble limestone walls have tolled quoins, a brick stringcourse and brick quoins to the upper floors. There are square-headed door openings to the north elevation, a square-headed window opening to the bow with a brick architrave, and camber-headed window openings to the west, with brick voussoirs. The round-headed window opening to the east elevation has a brick surround, flanked by round-headed niches with brick surrounds and a continuous brick sill course. By 1740, the building belonged to the St Leger family, who may have engaged John Aheron to design the bow-sided house which was built on top of the base of the barracks. By then, this was the meeting place of the Askeaton Hell Fire Club, and the building was probably used by the club until the end of the 18th century. The club in Askeaton traced its origins to the first Hellfire Club, formed in 1719 by Philip Wharton (1698-1731), 1st Duke of Wharton. Wharton was a rake who gamble away Rathfarnham Castle in Dublin and most of his inheritance. In 1726, he married Maria Theresa O’Beirne (sometimes known as Maria Theresa Comerford). When he was in the advanced stages of alcoholism, the couple moved to a Cistercian abbey in Catalonia, where he died in 1731. His widow returned to London, and after his will was proved in court she lived comfortably in London society. The club continued long after Wharton’s death, and the club in Askeaton was founded around 1736-1740. Known as a satirical gentlemen’s club, the revelries of its members shocked their neighbours and the outside world. The two other clubs in Ireland were based on Montpelier Hill, south of Tallaght, and near Clonlara, Co Clare. In his recent book Blasphemers & Blackguards, The Irish Hellfire Clubs (2012), David Ryan examines the stories of these clubs. But, while local folklore recalls lurid tales of outrageous rituals, there is little actual information or evidence of the activities of the Askeaton Hellfire Club, and the name and supposedly lurid activities may have been opportunities to slight the church and to snub clerical authority, or mere excuses to hide their debauchery during evenings of wine, women and song. James Worsdale’s painting of the members of the Askeaton Hellfire Club One tradition recalls how a member of the club was thrown from one of the windows into the River Deel below during the course of a ‘drunken frolic.’ Evidence of the club and its members survives in a painting by James Worsdale (1692-1767) from sometime between 1736 and 1740. This painting shows a group of club members in Askeaton drinking, smoking and in conversation. Bottles of wine sit on a rack in the foreground, and there is a large bowl of punch on the table. Eleven men and one woman, as well as a boy, fill the painting. Some of the figures that have been identified include: Edward Croker of Ballingarde, his son John (died 1804); Wyndham Quin of Adare, father of the 1st Earl of Dunraven; Thomas Royce of Nantenan, near Askeaton; John Bayley of Debsborough, Nenagh, Co Tipperary; and Henry Prittie, father of Henry Prittie (1743-1801), father of Lord Dunalley. Worsdale, who was a founding member of the Dublin Hellfire Club, is on the far left of the painting, trying to attract the attention of the only woman in the painting. Most critics identify this woman as Margaret Blennerhassett, who was known as Celinda and who was the wife of Arthur Blennerhassett, a magistrate, of Riddlestown Park, Rathkeale. She was born Margaret Hayes, the eldest daughter of Jeremiah Hayes of Cahir Guillamore, Bruff. Celinda is said to have been the only woman who ever became a member of the Askeaton Hellfire Club. The story is told that in her curiosity she tried to find what the men did during their meetings at the club. She hid herself in the meeting room before the members arrived, and when they discovered her she was formally inducted as a member to ensure her silence. Later, her husband drowned in a boating tragedy in the Lakes of Killarney in 1775. Some critics, however, have identified the woman in this painting as Laetitia Pilkington, alongside her husband, the Revd Matthew Pilkington (1701-1774), one-time friends of Jonathan Swift, Dean of Saint Patrick’s Cathedral, Dublin. This would date the painting from some time before 1738. Matthew Pilkington moved to London, where he became friends with the painter James Worsley, led a dissolute life, divorced Laetitia, and was jailed in 1734. When he returned to Ireland, he enjoyed the patronage of Archbishop Michael Cobbe of Dublin and the Cobbe family of Newbridge House, Donabate. Laetitia Pilkington (1709-1750), was the daughter of a Dublin obstetrician, Dr John van Lewen. After Matthew fabricated the circumstances that led to their divorce, she was arrested for a debt of £2 and ended up in a debtors’ prison in London. If she was forced into discreet prostitute to earn a living later in life, she was also scathingly critical of the clergy of day. Speaking probably from the experience of her husband’s own lifestyle, she said ‘the holiness of their office gives them free admittance into every family’ and they abuse this so that ‘they are generally the first seducers of innocence.’ ‘Our seducers were our accusers,’ she wrote. The monument in Saint Ann’s Church, Dawson Street, Dublin, commemorating Laetitia Pilkington (Photograph: Patrick Comerford, 2017) When Laetitia Pilkington died in 1750, a monument was erected in Saint Ann’s Church, Dawson Street, Dublin, with clear references to the sufferings she had endured at the hands of her merciless husband. Less than a month after her death, Matthew Pilkington married his mistress Nancy Sandes. In 1811, an evangelical magazine published an obituary of Captain Perry, a carousing individual and likely member of a Hellfire Club. After a short lifetime of excessive living and radical thinking, he died an early death as he struggled to repent. It was a warning to readers of the dangers of being involved in such circles. The building was abandoned by the club sometime around 1840, and the club is inaccessible to the public, as the Office of Public Works continues work at stabilising the building. The Limerick Leader in May 1958 that James Worsdale’s painting of the members of the Askeaton Hellfire Club was being offered for sale to Limerick City Council for £350. It is now in the National Gallery of Ireland. Although the ruins of the Askeaton Hellfire Club have fallen into disrepair, the overall original form of this building is easily discerned, as are features such as the door and window openings. It retains many well-crafted features such as the brick window surrounds and limestone battered walls, and the high roof and the tall chimneys are of interest. The building has a curved bow at one side of each of the building’s two principal fronts, and one of them has a Venetian window. If, as is possible, the house dates from the 17th century, then this could be one of the earliest known examples of a Venetian window on a curve, not just in Ireland but anywhere else in Europe – which could just make it a far more interesting building than the myths and legends surrounding its rakish revellers. Sunset at Askeaton Castle and Hellfire Club, seen from Saint Mary’s Church (Photograph: Patrick Comerford, 2017)
 Fascinating map from 1610 as by the renowned cartographer John speed of the Province of Mounster(Munster!)-comprising the counties of Tipperary,Clare,Limerick,Cork,Kerry & Waterford.Includes miniature city layouts of both Limerick & Cork. 52cm x 65cm Beaufort Co Kerry John Speed (1551 or 1552 – 28 July 1629) was an English cartographer and historian. He is, alongside Christopher Saxton, one of the best known English mapmakers of the early modern period.
Fascinating map from 1610 as by the renowned cartographer John speed of the Province of Mounster(Munster!)-comprising the counties of Tipperary,Clare,Limerick,Cork,Kerry & Waterford.Includes miniature city layouts of both Limerick & Cork. 52cm x 65cm Beaufort Co Kerry John Speed (1551 or 1552 – 28 July 1629) was an English cartographer and historian. He is, alongside Christopher Saxton, one of the best known English mapmakers of the early modern period.Life
Speed was born in the Cheshire village of Farndon and went into his father Samuel Speed's tailoring later in life. While working in London, Speed was a tailor and member of a corresponding guild, and came to the attention of "learned" individuals. These individuals included Sir Fulke Greville, who subsequently made him an allowance to enable him to devote his whole attention to research. By 1598 he had enough patronage to leave his manual labour job and "engage in full-time scholarship". As a reward for his earlier efforts, Queen Elizabethgranted Speed the use of a room in the Custom House. Speed, was, by this point, as "tailor turned scholar" who had a highly developed "pictorial sense". In 1575, Speed married a woman named Susanna Draper in London, later having children with her. These children definitely included a son named John Speed, later a "learned" man with a doctorate, and an unknown number of others, since chroniclers and historians cannot agree on how many children they raised. Regardless, there is no doubt that the Speed family was relatively well-off. By 1595, Speed published a map of biblical Canaan, in 1598 he presented his maps to Queen Elizabeth, and in 1611–1612 he published maps of Great Britain, with his son perhaps assisting Speed in surveys of English towns. At age 77 or 78, in August 1629, Speed died. He was buried alongside his wife in London's St Giles-without-Cripplegate church on Fore Street. Later on, a memorial to John Speed was also erected behind the altar of the church.According to the church's website, "[His was] one of the few memorials [in the church] that survived the bombing" of London during The Blitz of 1940–1941 ... The website also notes that "[t]he cast for the niche in which the bust is placed was provided by the Merchant Taylors' Company, of which John Speed was a member". His memorial brass has ended up on display in the Burrell Collection near Glasgow.Works
Speed drew historical maps in 1601 and 1627 depicting the invasion of England and Ireland, depictions of the English Middle Ages, along with those depicting the current time, with rough originals but appealing, colourful final versions of his maps. It was with the encouragement of William Camden that Speed began his Historie of Great Britaine, which was published in 1611. Although he probably had access to historical sources that are now lost to us (he certainly used the work of Saxton and Norden), his work as a historian is now considered secondary in importance to his map-making, of which his most important contribution is probably his town plans, many of which provide the first visual record of the British towns they depict.In the years leading up to this point, while his atlas was being compiled, he sent letters to Robert Cotton, part of the British government to ask for assistance in gathering necessary materials.His atlas The Theatre of the Empire of Great Britaine was published in 1611 and 1612, and contained the first set of individual county maps of England and Wales besides maps of Ireland and a general map of Scotland. Tacked onto these maps was an introduction at the beginning when he addressed his "well affected and favourable reader", which had numerous Christian and religious undertones, admitting that there may be errors, but he made it the best he could, and stated his purpose for the atlas:my purpose...is to shew the situation of every Citie and Shire-town only [within Great Britain]...I have separated...[with] help of the tables...any Citie, Towne, Borough, Hamlet, or Place of Note...[it] may be affirmed, that there is not any one Kingdome in the world so exactly described...as is...Great Britaine...In shewing these things, I have chiefly sought to give satisfaction to all.
With maps as "proof impressions" and printed from copper plates, detail was engraved in reverse with writing having to be put on the map the correct way, while speed "copied, adapted and compiled the work of others", not doing much of the survey work on his own, which he acknowledged.The atlas was not above projections of his political opinions" Speed represented King James I as one who unified the "Kingdoms of the British isles". In 2016, the British Library published a book, introduced by former MP Nigel Nicolson and accompanied by commentaries by late medieval and early modern historian Alasdair Hawkyard, which reprinted this collection of maps on the British Isles, showing that Speed had drawn maps of areas ranging from Bedfordshire to Norfolk and Wales. Most, but not all, of the county maps have town plans on them; those showing a Scale of Passes being the places he had mapped himself. In 1627, two years before his death, Speed published Prospect of the Most Famous Parts of the World which was the first world atlas produced by an Englishman, costing 40 shillings, meaning that its circulation was limited to "richer customers and libraries", where many survive to this day. There is a fascinating text describing the areas shown on the back of the maps in English, although a rare edition of 1616 of the British maps has a Latin text – this is believed to have been produced for the Continental market. Much of the engraving was done in Amsterdam at the workshop of a Flemish man named Jodocus Hondius, with whom he collaborated with from 1598 until 1612, with Hondius's sudden death, a time period of 14 years.His maps of English and Welsh counties, often bordered with costumed figures ranging from nobility to country folk, are often found framed in homes throughout the United Kingdom. In 1611, he also published The genealogies recorded in the Sacred Scriptures according to euery family and tribe with the line of Our Sauior Jesus Christ obserued from Adam to the Blessed Virgin Mary, a biblical genealogy, reprinted several times during the 17th century. He also drew maps of the Channel Islands, Poland, and the Americas, the latter published only a few years before his death. On the year of his death, yet another collection of maps of Great Britain he had drawn the year before were published. Described as a "Protestant historian", "Puritan historian" or "Protestant propagandist" by some, Speed wrote about William Shakespeare, whom he called a "Superlative Monster" because of certain plays, Roman conquest, history of Chester, and explored "early modern concepts of national identity". As these writings indicate, he possibly saw Wales as English and not an independent entity. More concretely, there is evidence that Speed, in his chronicling of history, uses "theatrical metaphors" and his developed "historiographic skill" to work while he repeats myths from medieval times as part of his story.Legacy
Since his maps were used in many high circles, Speed's legacy has been long-reaching. After his death, in 1673 and 1676, some of his other maps on the British isles, the Chesapeake Bay region, specifically of Virginia and Maryland, the East Indies, the Russian Empire then ruled by Peter the Great, Jamaica, and Barbados, among other locations.With these printings and others, Speed's maps became the basis for world maps until at least the mid-eighteenth century, with his maps reprinted many times, and served as a major contribution to British topography for years to come. In later years, Speed would be called "our English Mercator", a person of "extraordinary industry and attainments in the study of antiques", an "honest and impartial historian", a "faithful Chronologer", and "our Cheshire historian...a scholar...a distinguished writer on history".He was also called a "celebrated chronologer and histographer", "cartographer", and much more. Even today, prints of his "beautiful maps" can be found in living rooms across the world, and sell for hundreds of thousands of pounds in rare art and map auctions, drawing in map collectors across the globe.Additionally, some use John Speed's maps, and connected commentary, to interpret William Shakespeare's plays; however, Speed did not like Shakespeare in the slightest, and called him a "papist".
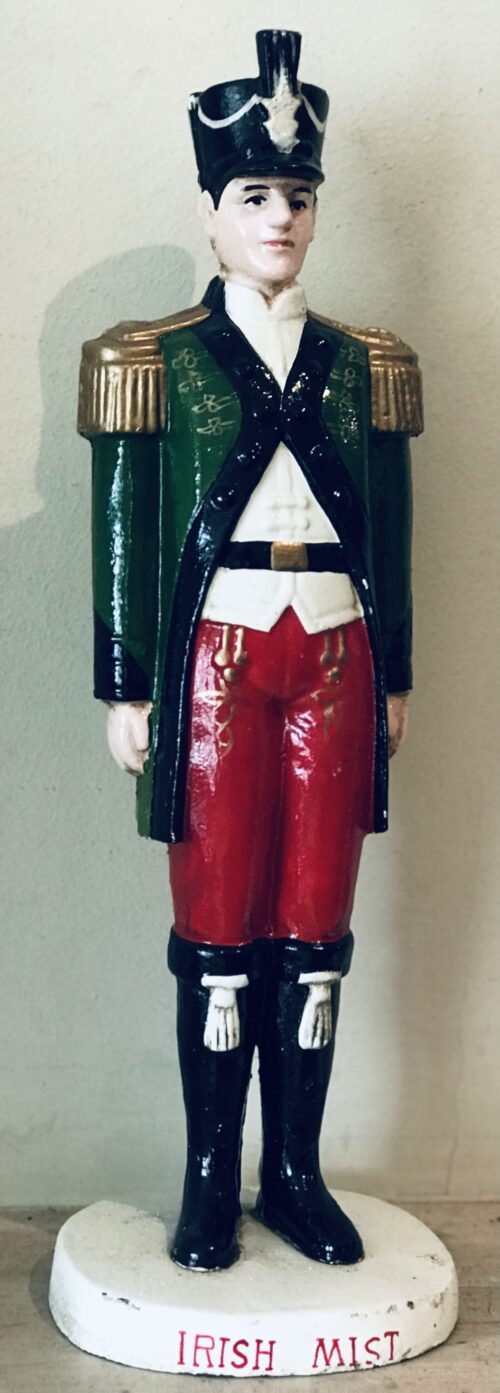 A beautiful and superbly made cast iron reproduction of an Irish Mist Decanter bottle ,the iconic Irish soldier dressed in the traditional Irish Brigade of the Austrian Army uniform of 1750. 39cm x 14cm x 12cm. 3kg Irish Mist is a brown Whiskey Liqueur produced in Dublin, Ireland, by the Irish Mist Liqueur Company Ltd. In September 2010 it was announced that the brand was being bought by Gruppo Campari from William Grant, only a few months after Grants had bought it from the C&C Group. It is made from aged Irish whiskey, heather and clover honey, aromatic herbs, and other spirits, blended to an ancient recipe claimed to be 1,000 years old.Though it was once 80 US proof (40% alcohol per volume), Irish Mist is now 35% or 70 US proof. The bottle shape has also been changed from a "decanter" style to a more traditional whiskey bottle shape. It is currently available in more than 40 countries. Irish Mist was the first liqueur to be produced in Ireland when commercial production began in 1947 at Tullamore, County Offaly. Tullamore is the hometown of the Williams family who were the original owners of Irish Mist. The company history goes back to 1829 when the Tullamore Distillery was founded to produce Irish whiskey. In the mid-1940s Desmond E. Williams began the search for an alternative yet related product, eventually deciding to produce a liqueur based on the ancient beverage known as heather wine.In 1985 the Cantrell & Cochrane Group purchased the Irish Mist Liqueur Company from the Williams family. In the summer of 2010 Irish Mist and the entire spirit division of C&C was bought by William Grant of Scotland. In September 2010 they in turn sold Irish Mist to Gruppo Campari.Irish Mist is typically served straight up or on ice, but also goes with coffee, vodka, or cranberry juice. Per the makers, Irish Mist's most popular recipe is Irish Mist with Cola and Lime. A Rusty Mist is an ounce of Irish Mist with an ounce of Drambuie Scotch whisky liqueur.A Black Nail is made from equal parts Irish Mist and Irish whiskey.
A beautiful and superbly made cast iron reproduction of an Irish Mist Decanter bottle ,the iconic Irish soldier dressed in the traditional Irish Brigade of the Austrian Army uniform of 1750. 39cm x 14cm x 12cm. 3kg Irish Mist is a brown Whiskey Liqueur produced in Dublin, Ireland, by the Irish Mist Liqueur Company Ltd. In September 2010 it was announced that the brand was being bought by Gruppo Campari from William Grant, only a few months after Grants had bought it from the C&C Group. It is made from aged Irish whiskey, heather and clover honey, aromatic herbs, and other spirits, blended to an ancient recipe claimed to be 1,000 years old.Though it was once 80 US proof (40% alcohol per volume), Irish Mist is now 35% or 70 US proof. The bottle shape has also been changed from a "decanter" style to a more traditional whiskey bottle shape. It is currently available in more than 40 countries. Irish Mist was the first liqueur to be produced in Ireland when commercial production began in 1947 at Tullamore, County Offaly. Tullamore is the hometown of the Williams family who were the original owners of Irish Mist. The company history goes back to 1829 when the Tullamore Distillery was founded to produce Irish whiskey. In the mid-1940s Desmond E. Williams began the search for an alternative yet related product, eventually deciding to produce a liqueur based on the ancient beverage known as heather wine.In 1985 the Cantrell & Cochrane Group purchased the Irish Mist Liqueur Company from the Williams family. In the summer of 2010 Irish Mist and the entire spirit division of C&C was bought by William Grant of Scotland. In September 2010 they in turn sold Irish Mist to Gruppo Campari.Irish Mist is typically served straight up or on ice, but also goes with coffee, vodka, or cranberry juice. Per the makers, Irish Mist's most popular recipe is Irish Mist with Cola and Lime. A Rusty Mist is an ounce of Irish Mist with an ounce of Drambuie Scotch whisky liqueur.A Black Nail is made from equal parts Irish Mist and Irish whiskey.
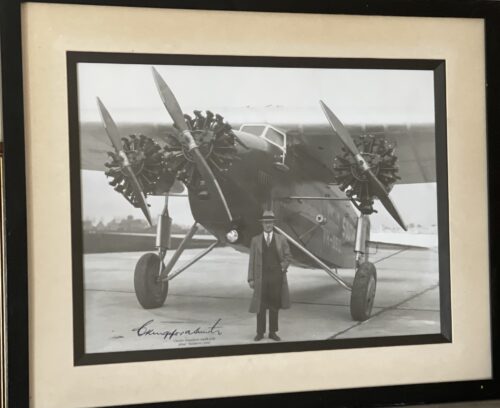 Excellent framed print of the world famous Australian aviator Sir Charles Kingsford Smith standing in front of his plane, the Southern Cross-have a read below of the links between the Jameson Whiskey Brand and the seminal trans Atlantic flight which took place from Portmarnock Beach,the home of the Jameson Family. 60cm x 50cm
Excellent framed print of the world famous Australian aviator Sir Charles Kingsford Smith standing in front of his plane, the Southern Cross-have a read below of the links between the Jameson Whiskey Brand and the seminal trans Atlantic flight which took place from Portmarnock Beach,the home of the Jameson Family. 60cm x 50cmJameson's Iconic Barrellman
The Story Behind the Barrellman
On every bottle of Jameson whiskey you fill find embossed on the glass the figure of a barrelman, there to symbolise the generations of workers who contributed to the success of the whiskey. In 1930 the Barrelman reached new heights (literally!) when a statuette was carried, as a mascot, on board the Southern Cross aircraft by Australian aviator Sir Charles Kingsford Smith when he took off from Portmarnock Strand in Dublin on his ground-breaking East – West crossing of the Atlantic. The original statuette is now on display in the Jameson Brand Home at Bow Street, and was most likely given to the aviators by one of the Jameson family of Portmarnock. Captain Saul, navigator on the flight, was the brother of one of Jameson’s sales reps in London and probably facilitated the Barrelman being welcomed aboard.

 Classic Power's Pure Pot Still Whiskey Advert 50cm x 60cm Thomas St Dublin In 1791 James Power, an innkeeper from Dublin, established a small distillery at his public house at 109 Thomas St., Dublin. The distillery, which had an output of about 6,000 gallons in its first year of operation, initially traded as James Power and Son, but by 1822 had become John Power & Son, and had moved to a new premises at John's Lane, a side street off Thomas Street. At the time the distillery had three pot stills, though only one, a 500-gallon still is thought to have been in use. Following reform of the distilling laws in 1823, the distillery expanded rapidly. In 1827, production was reported at 160,270 gallons,and by 1833 had grown to 300,000 gallons per annum. As the distillery grew, so too did the stature of the family. In 1841, John Power, grandson of the founder was awarded a baronet, a hereditary title. In 1855, his son Sir James Power, laid the foundation stone for the O'Connell Monument, and in 1859 became High Sheriff of Dublin. In 1871, the distillery was expanded and rebuilt in the Victorian style, becoming one of the most impressive sights in Dublin.After expansion, output at the distillery rose to 700,000 gallons per annum, and by the 1880s, had reached about 900,000 gallons per annum, at which point the distillery covered over six acres of central Dublin, and had a staff of about 300 people.During this period, when the Dublin whiskey distilleries were amongst the largest in the world, the family run firms of John Powers, along with John Jameson, William Jameson, and George Roe, (collectively known as the "Big Four") came to dominate the Irish distilling landscape, introducing several innovations. In 1886, John Power & Son began bottling their own whiskey, rather than following the practice customary at the time, of selling whiskey directly to merchants and bonders who would bottle it themselves. They were the first Dublin distillery to do so, and one of the first in the world.A gold label adorned each bottle and it was from these that the whiskey got the name Powers Gold Label. When Alfred Barnard, the British historian visited John's Lane in the late 1880s, he noted the elegance and cleanliness of the buildings, and the modernity of the distillery, describing it as "about as complete a work as it is possible to find anywhere". At the time of his visit, the distillery was home to five pot stills, two of which with capacities of 25,000 gallons, were amongst the largest ever built.In addition, Barnard was high in his praise for Powers whiskey, noting:"The old make, which we drank with our luncheon was delicious and finer than anything we had hitherto tasted.It was as perfect in flavour, and as pronounced in the ancient aroma of Irish Whiskey so dear to to the hearts of connoisseurs,as one could possibly desire and we found a small flask of it very useful afterwards on our travels." The last member of the family to sit on the board was Sir Thomas Talbot Power,who died in 1930,and with him the Power's Baronetcy. However, ownership remained in the family until 1966, and several descendants of his sisters remained at work with the company until recent times. In 1961, a Coffey still was installed in John's Lane Distillery, allowing the production of vodka and gin, in addition to the testing of grain whiskey for use in blended whiskey. This was a notable departure for the firm, as for many years the big Dublin distilling dynasties had shunned the use of Coffey stills, questioning if their output, grain whiskey could even be termed whiskey. However, with many of the Irish distilleries having closed in the early 20th century in part due to their failure to embrace a change in consumer preference towards blended whiskey, Powers were instrumental in convincing the remaining Irish distilleries to reconsider their stance on blended whiskey. In 1966, with the Irish whiskey industry still struggling following Prohibition in the United States, the Anglo-Irish Trade War and the rise of competition from Scotch whiskey, John Powers & Son joined forces with the only other remaining distillers in the Irish Republic, the Cork Distilleries Company and their Dublin rivals John Jameson & Son, to form Irish Distillers. Soon after, in a bold move, Irish Distillers decided to close all of their existing distilleries, and to consolidate production at a new purpose-built facility in Midleton (the New Midleton Distillery) alongside their existing Old Midleton Distillery. The new distillery opened in 1975, and a year later, production ceased at John's Lane Distillery and began anew in Cork, with Powers Gold Label and many other Irish whiskeys reformulated from single pot stills whiskeys to blends. In 1989, Irish Distillers itself became a subsidiary of Pernod-Ricard following a friendly takeover.Since the closure of the John's Lane distillery, many of the distillery buildings were demolished. However, some of the buildings have been incorporated into the National College of Art and Design, and are now protected structures. In addition, three of the distillery's pot stills were saved and now located in the college's Red Square. Origins : Dublin City Dimensions : 100cm x 70cm 20kg (specially constructed damage proof shipping container)
Classic Power's Pure Pot Still Whiskey Advert 50cm x 60cm Thomas St Dublin In 1791 James Power, an innkeeper from Dublin, established a small distillery at his public house at 109 Thomas St., Dublin. The distillery, which had an output of about 6,000 gallons in its first year of operation, initially traded as James Power and Son, but by 1822 had become John Power & Son, and had moved to a new premises at John's Lane, a side street off Thomas Street. At the time the distillery had three pot stills, though only one, a 500-gallon still is thought to have been in use. Following reform of the distilling laws in 1823, the distillery expanded rapidly. In 1827, production was reported at 160,270 gallons,and by 1833 had grown to 300,000 gallons per annum. As the distillery grew, so too did the stature of the family. In 1841, John Power, grandson of the founder was awarded a baronet, a hereditary title. In 1855, his son Sir James Power, laid the foundation stone for the O'Connell Monument, and in 1859 became High Sheriff of Dublin. In 1871, the distillery was expanded and rebuilt in the Victorian style, becoming one of the most impressive sights in Dublin.After expansion, output at the distillery rose to 700,000 gallons per annum, and by the 1880s, had reached about 900,000 gallons per annum, at which point the distillery covered over six acres of central Dublin, and had a staff of about 300 people.During this period, when the Dublin whiskey distilleries were amongst the largest in the world, the family run firms of John Powers, along with John Jameson, William Jameson, and George Roe, (collectively known as the "Big Four") came to dominate the Irish distilling landscape, introducing several innovations. In 1886, John Power & Son began bottling their own whiskey, rather than following the practice customary at the time, of selling whiskey directly to merchants and bonders who would bottle it themselves. They were the first Dublin distillery to do so, and one of the first in the world.A gold label adorned each bottle and it was from these that the whiskey got the name Powers Gold Label. When Alfred Barnard, the British historian visited John's Lane in the late 1880s, he noted the elegance and cleanliness of the buildings, and the modernity of the distillery, describing it as "about as complete a work as it is possible to find anywhere". At the time of his visit, the distillery was home to five pot stills, two of which with capacities of 25,000 gallons, were amongst the largest ever built.In addition, Barnard was high in his praise for Powers whiskey, noting:"The old make, which we drank with our luncheon was delicious and finer than anything we had hitherto tasted.It was as perfect in flavour, and as pronounced in the ancient aroma of Irish Whiskey so dear to to the hearts of connoisseurs,as one could possibly desire and we found a small flask of it very useful afterwards on our travels." The last member of the family to sit on the board was Sir Thomas Talbot Power,who died in 1930,and with him the Power's Baronetcy. However, ownership remained in the family until 1966, and several descendants of his sisters remained at work with the company until recent times. In 1961, a Coffey still was installed in John's Lane Distillery, allowing the production of vodka and gin, in addition to the testing of grain whiskey for use in blended whiskey. This was a notable departure for the firm, as for many years the big Dublin distilling dynasties had shunned the use of Coffey stills, questioning if their output, grain whiskey could even be termed whiskey. However, with many of the Irish distilleries having closed in the early 20th century in part due to their failure to embrace a change in consumer preference towards blended whiskey, Powers were instrumental in convincing the remaining Irish distilleries to reconsider their stance on blended whiskey. In 1966, with the Irish whiskey industry still struggling following Prohibition in the United States, the Anglo-Irish Trade War and the rise of competition from Scotch whiskey, John Powers & Son joined forces with the only other remaining distillers in the Irish Republic, the Cork Distilleries Company and their Dublin rivals John Jameson & Son, to form Irish Distillers. Soon after, in a bold move, Irish Distillers decided to close all of their existing distilleries, and to consolidate production at a new purpose-built facility in Midleton (the New Midleton Distillery) alongside their existing Old Midleton Distillery. The new distillery opened in 1975, and a year later, production ceased at John's Lane Distillery and began anew in Cork, with Powers Gold Label and many other Irish whiskeys reformulated from single pot stills whiskeys to blends. In 1989, Irish Distillers itself became a subsidiary of Pernod-Ricard following a friendly takeover.Since the closure of the John's Lane distillery, many of the distillery buildings were demolished. However, some of the buildings have been incorporated into the National College of Art and Design, and are now protected structures. In addition, three of the distillery's pot stills were saved and now located in the college's Red Square. Origins : Dublin City Dimensions : 100cm x 70cm 20kg (specially constructed damage proof shipping container) The Still House at John's Lane Distillery, as it looked when Alfred Barnard visited in the 1800s.
The Still House at John's Lane Distillery, as it looked when Alfred Barnard visited in the 1800s.

 Wonderful memento of the legendary Irish Traditional music ,the Chieftains . 54cm x 42cm Dublin The Chieftains are a traditional Irish band formed in Dublin in 1962, by Paddy Moloney, Sean Potts and Michael Tubridy. Their sound, which is almost entirely instrumental and largely built around uilleann pipes, has become synonymous with traditional Irish music and they are regarded as having helped popularise Irish music across the world.They have won six Grammys during their career and they were given a Lifetime Achievement Award at the prestigious BBC Radio 2 Folk Awards in 2002. Some music experts have credited The Chieftains with bringing traditional Irish music to a worldwide audience, so much so that the Irish government awarded them the honorary title of 'Ireland's Musical Ambassadors' in 1989.
Wonderful memento of the legendary Irish Traditional music ,the Chieftains . 54cm x 42cm Dublin The Chieftains are a traditional Irish band formed in Dublin in 1962, by Paddy Moloney, Sean Potts and Michael Tubridy. Their sound, which is almost entirely instrumental and largely built around uilleann pipes, has become synonymous with traditional Irish music and they are regarded as having helped popularise Irish music across the world.They have won six Grammys during their career and they were given a Lifetime Achievement Award at the prestigious BBC Radio 2 Folk Awards in 2002. Some music experts have credited The Chieftains with bringing traditional Irish music to a worldwide audience, so much so that the Irish government awarded them the honorary title of 'Ireland's Musical Ambassadors' in 1989.Name
The band's name came from the book Death of a Chieftain by Irish author John Montague.Assisted early on by Garech Browne, they signed with his company Claddagh Records. They needed financial success abroad, and succeeded in this, as within a few years their third album's sleeve note section was printed in three languages.Career
Origins
Paddy Moloney came out of Ceoltóirí Chualann, a group of musicians who specialised in instrumentals, and sought to form a new band. They had their first rehearsals at Moloney's house, with David Fallon and Martin Fay joining the original three. The group remained only semi-professional up until the 1970s and by then had achieved great success in Ireland and the United Kingdom.Rise to international fame
In 1973, their popularity began to spread to the United States when their previous albums were released there by Island Records. They received further acclaim when they worked on the Academy Award–winning soundtrack to Stanley Kubrick's 1975 film Barry Lyndon, which triggered their transition to the mainstream in the US.Successful career
The group continued to release successful records throughout the 1970s and 1980s, and their work with Van Morrison in 1988 resulted in the critically acclaimed album Irish Heartbeat. They went on to collaborate with many other well-known musicians and singers; among them Luciano Pavarotti, the Rolling Stones, Madonna, Sinéad O'Connor and Roger Daltrey.50th anniversary
In 2012, they celebrated their 50th anniversary with an ambitious album and tour. The album, Voice of Ages, was produced by T-Bone Burnett and featured the Chieftains collaborating with many musicians including Bon Iver, Paolo Nutini and The Decemberists. It also included a collaboration with NASA astronaut Catherine Coleman playing the flute aboard the International Space Station as it orbited the earth. The Chieftains performed at Carnegie Hall on March 17, 2012.The Irish Goodbye Tour
In February 2019, The Chieftains embarked on an extensive farewell tour entitled the "Irish Goodbye Tour", including a 2019 European leg, a 2020 Canadian leg and two 2019 and 2020 US legs. On 13 March 2020, the band announced that a few tour dates of their "Irish Goodbye Tour" had been postponed (until further notice) following the coronavirussituation.Collaborations
The band have become known for their vast work of collaborations with popular musicians of many genres, including country music, Galician traditional music, Newfoundland music, and rock and roll. Their widespread work as collaborators resulted in the Irish Government awarding the group the honorary title of Ireland's Musical Ambassadors in 1989. They have performed with (in alphabetical order): Paddy Moloney pictured with Bob Dylan, who is a fan of the band's work.In May 1986, they performed at Self Aid, a benefit concert held in Dublin that focused on the problem of chronic unemployment which was widespread in Ireland at that time. In 1994, they appeared in Roger Daltrey's production, album and video of A Celebration: The Music of Pete Townshend and The Who. They also performed with Canadian astronaut Cmdr. Chris Hadfield in Houston, TX on 15 February 2013. Cmdr. Hadfield sang and played guitar on "Moondance" from aboard the International Space Station.
Paddy Moloney pictured with Bob Dylan, who is a fan of the band's work.In May 1986, they performed at Self Aid, a benefit concert held in Dublin that focused on the problem of chronic unemployment which was widespread in Ireland at that time. In 1994, they appeared in Roger Daltrey's production, album and video of A Celebration: The Music of Pete Townshend and The Who. They also performed with Canadian astronaut Cmdr. Chris Hadfield in Houston, TX on 15 February 2013. Cmdr. Hadfield sang and played guitar on "Moondance" from aboard the International Space Station.- Moya Brennan
- Jackson Browne
- Rosanne Cash
- Ry Cooder
- Elvis Costello
- Roger Daltrey
- John Entwistle
- Marianne Faithfull
- Bela Fleck
- James Galway
- Art Garfunkel
- Glass Tiger
- Mike Gordon
- Great Big Sea
- Nanci Griffith
- Emmylou Harris
- Mick Jagger
- Tom Jones
- Kepa Junkera
- Mark Knopfler
- Diana Krall
- Alison Krauss
- Nolwenn Leroy
- Los Cenzontles
- Lyle Lovett
- Ashley MacIsaac
- Sarah McLachlan
- Natalie MacMaster
- Madonna
- Ziggy Marley
- Pink Martini
- Loreena McKennitt
- Natalie Merchant
- Gary Moore
- Van Morrison
- Willie Nelson
- Nickel Creek
- Punch Brothers
- Carlos Núñez
- Paolo Nutini
- Siobhán O'Brien
- Sinéad O'Connor
- Mike Oldfield
- Luciano Pavarotti
- The Pogues[14]
- Eros Ramazzotti
- Earl Scruggs
- Ricky Skaggs
- Sting
- The Civil Wars
- The Corrs
- The Decemberists
- The Dubliners
- The Low Anthem
- The Rolling Stones
- Ultravox
- Jim White
- John Williams
Success and legacy
The band has won six Grammy Awards and been nominated eighteen times. They have won an Emmy and a Genie and contributed tracks, including their highly praised version of the song Women of Ireland, to Leonard Rosenman's Oscar-winning score for Stanley Kubrick's 1975 film Barry Lyndon.In 2002 they were given a Lifetime Achievement Award by the UK's BBC Radio 2. Two of their singles have been minor hits in the UK Singles Chart. "Have I Told You Lately" (credited to The Chieftains with Van Morrison) reached No. 71 in 1995. "I Know My Love" (credited to The Chieftains featuring The Corrs) reached No. 37 in 1999. Dr. Gearóid Ó hAllmhuráin said the success of The Chieftains helped place Irish traditional music on a par with other musical genres in the world of popular entertainment. By collaborating with pop and rock musicians, they have taken Irish music to a much wider audience. They have become, in effect, musical ambassadors for Ireland. This de facto role was officially recognised by the Irish Government in 1989 when it awarded the group the honorary title of Ireland's Musical Ambassadors.Notable performances
They played in a concert for Pope John Paul II, before an audience of more than one million people in 1979 in Phoenix Park in Dublin, to mark the Papal visit to Ireland. In 1983, they were invited by the Chinese Government to perform with the Chinese Broadcasting Art Group in a concert on the Great Wall of China, becoming the first western musical group to do so.They were the first group to perform in the Capitol Building in Washington, D.C., invited by Senator Edward Kennedy and the former Speaker of the House, Tip O'Neill. In 2011, they performed at a concert in Dublin attended by President Mary McAleese and Queen Elizabeth II of Britain during her first ever official trip to the Republic of Ireland.Personnel
- Current members
- Paddy Moloney – uilleann pipes, tin whistle, button accordion, bodhrán (1962–present)
- Kevin Conneff – bodhrán, vocals (1976–present)
- Matt Molloy – flute, tin whistle (1979–present)
- Former members
- Seán Potts – tin whistle, bones, bodhrán (1962–1979; died 2014)
- Michael Tubridy – flute, concertina, tin whistle (1962–1979)
- David Fallon – bodhrán (1962–1966)
- Martin Fay – fiddle, bones (1962–2002; died 2012)
- Peadar Mercier – bodhrán, bones (1966–1976; died 1991)
- Seán Keane – fiddle, tin whistle (1968–2002; occasional performances thereafter)
- Derek Bell – Irish harp, keyboard instruments, oboe (1975–2002; died 2002)
- Ronnie McShane – bones, bodhrán (1975–1976; died 2017)
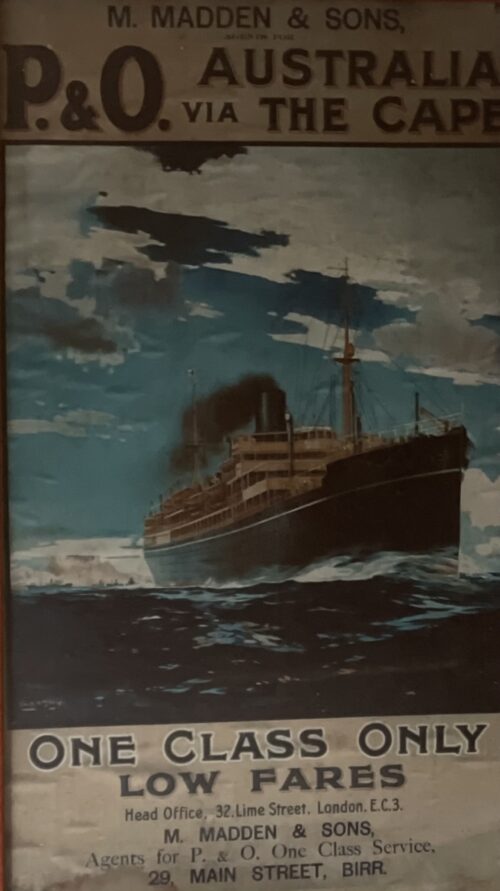

 64cm x 39cm
64cm x 39cmEarly years and expansion: 1822–1900
In 1822, Brodie McGhie Willcox, a London ship broker, and Arthur Anderson, a sailor from the Shetland Isles, went into partnership to operate a shipping line, primarily operating routes between England and Spain and Portugal. In 1835, Dublin shipowner Captain Richard Bourne joined the business, and the three men chartered the William Fawcett and started a regular steamer service between London and Spain and Portugal – the Iberian Peninsula – using the name Peninsular Steam Navigation Company, with services to Vigo, Oporto, Lisbon and Cádiz. As The Peninsular and Oriental Steam Navigation Company was incorporated in 1840 by a royal charter its name therefore included neither "plc" nor "Limited". The company flag colours are directly connected with the Peninsular flags: the white and blue represent the Portuguese flag in 1837, and the yellow and red the Spanish flag. At the height of the Carlist Wars the British lent their support to the legitimate heirs of Spain and Portugal and all three of P&O founders played their part, from gun running to chartering steamers. As a consequence of this association and involvement P&O officers are some of the few Merchant Navy officers entitled to wear swords, alongside the likes of Trinity House. Admission ticket to Lord Mayor Thomas Gabriel's reception of H.I.M. The Sultan Abd-ul-Aziz Khan at The Guildhall, 18 July 1867, issued to The Chairman of the P&O Steam Navigation Company.
Admission ticket to Lord Mayor Thomas Gabriel's reception of H.I.M. The Sultan Abd-ul-Aziz Khan at The Guildhall, 18 July 1867, issued to The Chairman of the P&O Steam Navigation Company. William Fane De Salis(1812–1896), joined P&O in 1849. Director 1851–1895, Chairman 1878–1881.In 1837, the business won a contract from the British Admiralty to deliver mail to the Iberian Peninsula and in 1840 they acquired a contract to deliver mail to Alexandria in Egypt. Brindisi, Italy was added to the route in the 1870s. P&O first introduced passenger services in 1844, with a leisure cruise departing from Southampton to the Mediterranean.These voyages were the first of their kind and the forerunner of modern cruise holidays. The company later introduced round trips to destinations such as Alexandria and Constantinople and underwent rapid expansion in the later half of the 19th century, with its ships becoming larger and more luxurious. One particularly notable ship of the era was the SS Ravenna, built in 1880, which became the first ship to be built with a total steel superstructure. In 1847, shortly after the Opium War, P&O entered the opium trade; shipping 642,000 chests of Bengal and Malwa opium in the next eleven years. They faced stiff competition from the incumbent shippers, Jardines and the Apcar Line.
William Fane De Salis(1812–1896), joined P&O in 1849. Director 1851–1895, Chairman 1878–1881.In 1837, the business won a contract from the British Admiralty to deliver mail to the Iberian Peninsula and in 1840 they acquired a contract to deliver mail to Alexandria in Egypt. Brindisi, Italy was added to the route in the 1870s. P&O first introduced passenger services in 1844, with a leisure cruise departing from Southampton to the Mediterranean.These voyages were the first of their kind and the forerunner of modern cruise holidays. The company later introduced round trips to destinations such as Alexandria and Constantinople and underwent rapid expansion in the later half of the 19th century, with its ships becoming larger and more luxurious. One particularly notable ship of the era was the SS Ravenna, built in 1880, which became the first ship to be built with a total steel superstructure. In 1847, shortly after the Opium War, P&O entered the opium trade; shipping 642,000 chests of Bengal and Malwa opium in the next eleven years. They faced stiff competition from the incumbent shippers, Jardines and the Apcar Line.Early 20th century years: 1900–1945
Mail contracts were the basis of P&O's prosperity until the Second World War, but the company also continued to become a major commercial shipping line and passenger liner operator. In 1914, it took over the British India Steam Navigation Company, which was then the largest British shipping line, owning 131 steamers. In 1918, it gained a controlling interest in the Orient Line, its partner in the England-Australia mail route. Further acquisitions followed and the fleet reached a peak of almost 500 ships in the mid-1920s. In 1920, the company also established a bank, P&O Bank, that it sold to Chartered Bank of India, Australia and China (now Standard Chartered Bank) in 1927. At this time it established a commercial relationship with Spinney's of Haifa, that developed into a major regional high-end grocery store chain, which eventually provided shipping services access to much of the Middle East. Until 1934 it operated liners from Key West, Florida to Havana; then it operated from Miamito Cuba until 1960. In 1932, P&O expanded their passenger operations to Australia, with the introduction of Strathaird, which departed on a cruise to Brisbane and Norfolk Island. Eighty-five of the company's ships were sunk in the First World War and 179 in the Second World War.Post war: 1945–2000
After 1945, the passenger market declined to India, but boomed to Australia with the advent of paid-passages for literate and healthy European immigrants known as Ten Pound Poms.P&O built 15 large passenger liners, including Himalaya, Chusan, Arcadia, and Iberia, culminating in Oriana and Canberra, which were an unprecedented speed and size.By 1968, over 1 million immigrants had arrived—many via P&O—and Australia ended the programme. P&O entered the cruise market and began to sell and scrap many of these liners. It concentrated mainly on cargo ships. It entered the tanker trade in 1959 and the roll-on roll-off (RORO) ferry business in the mid-1960s. P&O and Orient Line were formally merged in 1960 to form P&O-Orient Lines. In 1964, Orcades and Oronsay were transferred to the P&O fleet. The name Orient Line was dropped altogether in 1966 when Orsova and Oriana were also transferred to the P&O fleet.
 Brilliantly conceived Murphys Stout advertisement depicting a Blues harmonica player Cobh Co Cork 68cm x 48cm
Brilliantly conceived Murphys Stout advertisement depicting a Blues harmonica player Cobh Co Cork 68cm x 48cmJAMES J. MURPHY
 Born on November 1825, James Jeremiah Murphy was the eldest son of fifteen children born to Jeremiah James Murphy and Catherine Bullen. James J. served his time in the family business interest and was also involved in the running of a local distillery in Cork. He sold his share in this distillery to fund his share of the set up costs of the brewery in 1856. James J. was the senior partner along with his four other brothers. It was James who guided to the brewery to success in its first forty years and he saw its output grow to 100,000 barrels before his death in 1897. James J. through his life had a keen interest in sport, rowing, sailing and GAA being foremost. He was a supporter of the Cork Harbour Rowing Club and the Royal Cork Yacht Club and the Cork County Board of the GAA. James J. philanthropic efforts were also well known in the city supporting hospitals, orphanages and general relief of distress in the city so much so on his death being described as a ‘prince in the charitable world’. It is James J. that epitomises the Murphy’s brand in stature and quality of character.1854
Born on November 1825, James Jeremiah Murphy was the eldest son of fifteen children born to Jeremiah James Murphy and Catherine Bullen. James J. served his time in the family business interest and was also involved in the running of a local distillery in Cork. He sold his share in this distillery to fund his share of the set up costs of the brewery in 1856. James J. was the senior partner along with his four other brothers. It was James who guided to the brewery to success in its first forty years and he saw its output grow to 100,000 barrels before his death in 1897. James J. through his life had a keen interest in sport, rowing, sailing and GAA being foremost. He was a supporter of the Cork Harbour Rowing Club and the Royal Cork Yacht Club and the Cork County Board of the GAA. James J. philanthropic efforts were also well known in the city supporting hospitals, orphanages and general relief of distress in the city so much so on his death being described as a ‘prince in the charitable world’. It is James J. that epitomises the Murphy’s brand in stature and quality of character.1854OUR LADY’S WELL BREWERY
 In 1854 James J. and his brothers purchased the buildings of the Cork foundling Hospital and on this site built the brewery. The brewery eventually became known as the Lady’s Well Brewery as it is situated adjacent to a famous ‘Holy Well’ and water source that had become a famous place of devotion during penal times.1856
In 1854 James J. and his brothers purchased the buildings of the Cork foundling Hospital and on this site built the brewery. The brewery eventually became known as the Lady’s Well Brewery as it is situated adjacent to a famous ‘Holy Well’ and water source that had become a famous place of devotion during penal times.1856THE BEGINNING
 James J. Murphy and his brothers found James J. Murphy & Co. and begin brewing.1861
James J. Murphy and his brothers found James J. Murphy & Co. and begin brewing.1861FROM STRENGTH TO STRENGTH
 In 1861 the brewery produced 42,990 barrels and began to impose itself as one of the major breweries in the country.1885
In 1861 the brewery produced 42,990 barrels and began to impose itself as one of the major breweries in the country.1885A FRIEND OF THE POOR, HURRAH
 James J. was a much loved figure in Cork, a noted philanthropist and indeed hero of the entire city at one point. The ‘Hurrah for the hero’ song refers to James J’s heroic efforts to save the local economy from ruin in the year of 1885. The story behind this is that when the key bank for the region the ‘Munster Bank’ was close to ruin, which could have led to an economic disaster for the entire country and bankruptcy for thousands, James J. stepped in and led the venture to establish a new bank the ‘Munster and Leinster’, saving the Munster Bank depositors and creditors from financial loss and in some cases, ruin. His exploits in saving the bank, led to the writing of many a poem and song in his honour including ‘Hurrah for the man who’s a friend of the poor’, which would have been sung in pubs for many years afterwards.1889
James J. was a much loved figure in Cork, a noted philanthropist and indeed hero of the entire city at one point. The ‘Hurrah for the hero’ song refers to James J’s heroic efforts to save the local economy from ruin in the year of 1885. The story behind this is that when the key bank for the region the ‘Munster Bank’ was close to ruin, which could have led to an economic disaster for the entire country and bankruptcy for thousands, James J. stepped in and led the venture to establish a new bank the ‘Munster and Leinster’, saving the Munster Bank depositors and creditors from financial loss and in some cases, ruin. His exploits in saving the bank, led to the writing of many a poem and song in his honour including ‘Hurrah for the man who’s a friend of the poor’, which would have been sung in pubs for many years afterwards.1889THE MALT HOUSE
 In 1889 a Malt House for the brewery was built at a cost of 4,640 pounds and was ‘built and arranged on the newest principle and fitted throughout with the latest appliances known to modern science”. Today the Malthouse is one of the most famous Cork landmarks and continues to function as offices for Murphy’s.1892
In 1889 a Malt House for the brewery was built at a cost of 4,640 pounds and was ‘built and arranged on the newest principle and fitted throughout with the latest appliances known to modern science”. Today the Malthouse is one of the most famous Cork landmarks and continues to function as offices for Murphy’s.1892MURPHY’S GOLD
 Murphy’s Stout wins the Gold medal at the Brewers and Allied Trades Exhibition in Dublin and again wins the supreme award when the exhibition is held in Manchester in 1895. These same medals feature on our Murphy’s packaging today. Murphy’s have continued it’s tradition of excellence in brewing winning Gold again at the Brewing Industry International awards in 2002 and also gaining medals in the subsequent two competitions.1893
Murphy’s Stout wins the Gold medal at the Brewers and Allied Trades Exhibition in Dublin and again wins the supreme award when the exhibition is held in Manchester in 1895. These same medals feature on our Murphy’s packaging today. Murphy’s have continued it’s tradition of excellence in brewing winning Gold again at the Brewing Industry International awards in 2002 and also gaining medals in the subsequent two competitions.1893MURPHY’S FOR STRENGTH
 Eugen Sandow the world famous ‘strongman’, endorses Murphy’s Stout: “From experience I can strongly recommend Messrs JJ Murphy’s Stout”. The famous Murphy’s image of Sandow lifting a horse was then created.1906
Eugen Sandow the world famous ‘strongman’, endorses Murphy’s Stout: “From experience I can strongly recommend Messrs JJ Murphy’s Stout”. The famous Murphy’s image of Sandow lifting a horse was then created.1906THE JUBILEE
 The Brewery celebrates its 50th anniversary. On Whit Monday the brewery workforce and their families are treated to an excursion by train to Killarney. Paddy Barrett the youngest of the workforce that day at 13 went on to become head porter for the brewery and could recall the day vividly 50 years later.1913
The Brewery celebrates its 50th anniversary. On Whit Monday the brewery workforce and their families are treated to an excursion by train to Killarney. Paddy Barrett the youngest of the workforce that day at 13 went on to become head porter for the brewery and could recall the day vividly 50 years later.1913SWIMMING IN STOUT
 In the year of 1913 the No.5 Vat at ‘Lady’s Well’ Brewery burst and sent 23,000 galleons of porter flooding through the brewey and out on to Leitrim Street. The Cork Constitution, the local newspaper of the time wrote that “a worker had a most exciting experience and in the onrush of porter he had to swim in it for about 40 yards to save himself from asphyxiation”1914
In the year of 1913 the No.5 Vat at ‘Lady’s Well’ Brewery burst and sent 23,000 galleons of porter flooding through the brewey and out on to Leitrim Street. The Cork Constitution, the local newspaper of the time wrote that “a worker had a most exciting experience and in the onrush of porter he had to swim in it for about 40 yards to save himself from asphyxiation”1914JOINING UP
 The First World War marked an era of dramatic change both in the countries fortune and on a much smaller scale that of the Brewery’s. On the 13 August James J. Murphy and Co. joined the other members of the Cork Employers Federation in promising that ‘all constant employees volunteering to join any of his Majesties forces for active service in compliance with the call for help by the Government will be facilitated and their places given back to them at the end of the war’. Eighteen of the Brewery’s workers joined up including one sixteen year old. Ten never returned.1915
The First World War marked an era of dramatic change both in the countries fortune and on a much smaller scale that of the Brewery’s. On the 13 August James J. Murphy and Co. joined the other members of the Cork Employers Federation in promising that ‘all constant employees volunteering to join any of his Majesties forces for active service in compliance with the call for help by the Government will be facilitated and their places given back to them at the end of the war’. Eighteen of the Brewery’s workers joined up including one sixteen year old. Ten never returned.1915THE FIRST LORRY IN IRELAND
 James J. Murphy & Co. purchase the first petrol lorry in the country.1920
James J. Murphy & Co. purchase the first petrol lorry in the country.1920THE BURNING OF CORK
 On the 11-12th December the centre of Cork city was extensively damaged by fire including four of the company’s tied houses (Brewery owned establishments). The company was eventually compensated for its losses by the British government.1921
On the 11-12th December the centre of Cork city was extensively damaged by fire including four of the company’s tied houses (Brewery owned establishments). The company was eventually compensated for its losses by the British government.1921MURPHY’S IN A BOTTLE
 In 1921 James J. Murphy and Co. open a bottling plant and bottle their own stout. A foreman and four ‘boys’ were installed to run the operation and the product quickly won ‘good trade’.1924
In 1921 James J. Murphy and Co. open a bottling plant and bottle their own stout. A foreman and four ‘boys’ were installed to run the operation and the product quickly won ‘good trade’.1924THE FIRST CAMPAIGNS
 In 1924 the Murphy’s Brewery began to embrace advertising. In the decades prior to this the attitude had been somewhat negative with one director stating ‘We do not hope to thrive on pushing and puffing; our sole grounds for seeking popular favour is the excellence of our product’.1940
In 1924 the Murphy’s Brewery began to embrace advertising. In the decades prior to this the attitude had been somewhat negative with one director stating ‘We do not hope to thrive on pushing and puffing; our sole grounds for seeking popular favour is the excellence of our product’.1940WWII
 In 1940 at the height of the London Blitz the Murphy’s auditing firm is completely destroyed. The war which had indirectly affected the firm in terms of shortages of fuel and materials now affected the brewery directly.1953
In 1940 at the height of the London Blitz the Murphy’s auditing firm is completely destroyed. The war which had indirectly affected the firm in terms of shortages of fuel and materials now affected the brewery directly.1953LT. COL JOHN FITZJAMES
 In 1953 the last direct descendant of James J. takes over Chairmanship of the firm. Affectionately known in the Brewery as the ‘Colonel’ he ran the company until 1981.1961
In 1953 the last direct descendant of James J. takes over Chairmanship of the firm. Affectionately known in the Brewery as the ‘Colonel’ he ran the company until 1981.1961THE IRON LUNG
 Complete replacement of old wooden barrels to aluminium lined vessels (kegs) known as ‘Iron lungs’ draws to an end the era of ‘Coopers’ the tradesmen who built the wooden barrels on site in the Brewery for so many decades.1979
Complete replacement of old wooden barrels to aluminium lined vessels (kegs) known as ‘Iron lungs’ draws to an end the era of ‘Coopers’ the tradesmen who built the wooden barrels on site in the Brewery for so many decades.1979MURPHY’S IN AMERICA

Murphy’s reaches Americans shores for the first time winning back many drinkers lost to emigration and a whole new generation of stout drinkers.
1985MURPHY’S GOES INTERNATIONAL
 Murphy’s Launched as a National and International Brand. Exports included UK, US and Canada. Introduction of the first 25cl long neck stout bottle.1994
Murphy’s Launched as a National and International Brand. Exports included UK, US and Canada. Introduction of the first 25cl long neck stout bottle.1994MURPHY’S OPEN
 Murphy’s commence sponsorship of the hugely successful Murphy’s Irish Open Golf Championship culminating in Colm Montgomery’s ‘Monty’s’ famous third win at ‘Fota Island’ in 2002.2005
Murphy’s commence sponsorship of the hugely successful Murphy’s Irish Open Golf Championship culminating in Colm Montgomery’s ‘Monty’s’ famous third win at ‘Fota Island’ in 2002.2005MURPHY’S GOLD
 Murphy’s wins Gold at the Brewing Industry International Awards a testament to it’s superior taste and quality. Indeed 2003 was the first of three successive wins in this competition.2006
Murphy’s wins Gold at the Brewing Industry International Awards a testament to it’s superior taste and quality. Indeed 2003 was the first of three successive wins in this competition.2006150 YEARS OF BREWING LEGEND
 The Murphy Brewery celebrates 150 years of brewing from 1856 to 2006 going from strength to strength; the now legendary stout is sold in over 40 countries and recognised worldwide as superior stout. We hope James J. would be proud.
The Murphy Brewery celebrates 150 years of brewing from 1856 to 2006 going from strength to strength; the now legendary stout is sold in over 40 countries and recognised worldwide as superior stout. We hope James J. would be proud.
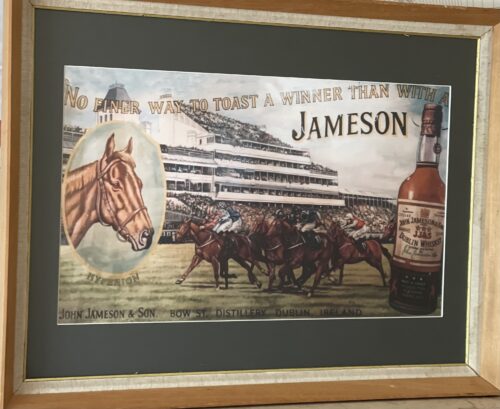 75cm x 65cm Hyperion (18 April 1930 – 9 December 1960) was a British-bred Thoroughbred, a dual classic winner and an outstanding sire. Owned by Edward Stanley, 17th Earl of Derby, Hyperion won GBP £29,509 during his racing career—a considerable sum at the time. His victories included the Epsom Derby and St Leger Stakes. He was the most successful British-bred sire of the 20th century and champion sire in Great Britain six times between 1940 and 1954. Hyperion was by the good sire Gainsborough, who was one of three wartime Triple Crown winners in Great Britain. His dam, Selene, was by Chaucer, a talented son of the undefeated St. Simon. Selene was also the dam of such good sires as Sickle (GB) (sireline ancestor of Native Dancer and Sea Bird), Pharamond (US), and Hunter's Moon (GB). Hyperion was inbred in the third and fourth generation to St. Simon, and was trained by George Lambton at Newmarket. Hyperion, who stood just 15.1 hands high, was one of the smallest horses to ever win a British Classic, but he had a good action and beautiful temperament. John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it maintained for four consecutive years.
75cm x 65cm Hyperion (18 April 1930 – 9 December 1960) was a British-bred Thoroughbred, a dual classic winner and an outstanding sire. Owned by Edward Stanley, 17th Earl of Derby, Hyperion won GBP £29,509 during his racing career—a considerable sum at the time. His victories included the Epsom Derby and St Leger Stakes. He was the most successful British-bred sire of the 20th century and champion sire in Great Britain six times between 1940 and 1954. Hyperion was by the good sire Gainsborough, who was one of three wartime Triple Crown winners in Great Britain. His dam, Selene, was by Chaucer, a talented son of the undefeated St. Simon. Selene was also the dam of such good sires as Sickle (GB) (sireline ancestor of Native Dancer and Sea Bird), Pharamond (US), and Hunter's Moon (GB). Hyperion was inbred in the third and fourth generation to St. Simon, and was trained by George Lambton at Newmarket. Hyperion, who stood just 15.1 hands high, was one of the smallest horses to ever win a British Classic, but he had a good action and beautiful temperament. John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it maintained for four consecutive years.
 Lovely Irish Mist Pub Mirror-the Worlds Most Luxurious Liqueur Pub Mirror . Edenderry Co Offaly. 60cm x 50cm Irish Mist is a brown Whiskey Liqueur produced in Dublin, Ireland, by the Irish Mist Liqueur Company Ltd. In September 2010 it was announced that the brand was being bought by Gruppo Campari from William Grant, only a few months after Grants had bought it from the C&C Group. It is made from aged Irish whiskey, heather and clover honey, aromatic herbs, and other spirits, blended to an ancient recipe claimed to be 1,000 years old.Though it was once 80 US proof (40% alcohol per volume), Irish Mist is now 35% or 70 US proof. The bottle shape has also been changed from a “decanter” style to a more traditional whiskey bottle shape. It is currently available in more than 40 countries. Irish Mist was the first liqueur to be produced in Ireland when commercial production began in 1947 at Tullamore, County Offaly. Tullamore is the hometown of the Williams family who were the original owners of Irish Mist. The company history goes back to 1829 when the Tullamore Distillery was founded to produce Irish whiskey. In the mid-1940s Desmond E. Williams began the search for an alternative yet related product, eventually deciding to produce a liqueur based on the ancient beverage known as heather wine.In 1985 the Cantrell & Cochrane Group purchased the Irish Mist Liqueur Company from the Williams family. In the summer of 2010 Irish Mist and the entire spirit division of C&C was bought by William Grant of Scotland. In September 2010 they in turn sold Irish Mist to Gruppo Campari.Irish Mist is typically served straight up or on ice, but also goes with coffee, vodka, or cranberry juice. Per the makers, Irish Mist’s most popular recipe is Irish Mist with Cola and Lime. A Rusty Mist is an ounce of Irish Mist with an ounce of Drambuie Scotch whisky liqueur.A Black Nail is made from equal parts Irish Mist and Irish whiskey.
Lovely Irish Mist Pub Mirror-the Worlds Most Luxurious Liqueur Pub Mirror . Edenderry Co Offaly. 60cm x 50cm Irish Mist is a brown Whiskey Liqueur produced in Dublin, Ireland, by the Irish Mist Liqueur Company Ltd. In September 2010 it was announced that the brand was being bought by Gruppo Campari from William Grant, only a few months after Grants had bought it from the C&C Group. It is made from aged Irish whiskey, heather and clover honey, aromatic herbs, and other spirits, blended to an ancient recipe claimed to be 1,000 years old.Though it was once 80 US proof (40% alcohol per volume), Irish Mist is now 35% or 70 US proof. The bottle shape has also been changed from a “decanter” style to a more traditional whiskey bottle shape. It is currently available in more than 40 countries. Irish Mist was the first liqueur to be produced in Ireland when commercial production began in 1947 at Tullamore, County Offaly. Tullamore is the hometown of the Williams family who were the original owners of Irish Mist. The company history goes back to 1829 when the Tullamore Distillery was founded to produce Irish whiskey. In the mid-1940s Desmond E. Williams began the search for an alternative yet related product, eventually deciding to produce a liqueur based on the ancient beverage known as heather wine.In 1985 the Cantrell & Cochrane Group purchased the Irish Mist Liqueur Company from the Williams family. In the summer of 2010 Irish Mist and the entire spirit division of C&C was bought by William Grant of Scotland. In September 2010 they in turn sold Irish Mist to Gruppo Campari.Irish Mist is typically served straight up or on ice, but also goes with coffee, vodka, or cranberry juice. Per the makers, Irish Mist’s most popular recipe is Irish Mist with Cola and Lime. A Rusty Mist is an ounce of Irish Mist with an ounce of Drambuie Scotch whisky liqueur.A Black Nail is made from equal parts Irish Mist and Irish whiskey.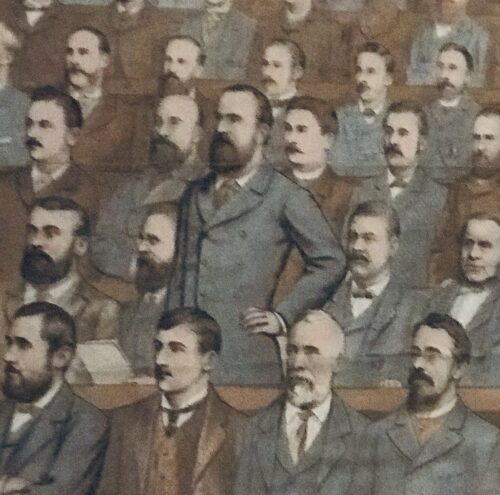
 Extremely rare,interesting print of the Irish Benches of the Irish Parliamentary Party in the House of Commons in 1885,with all members identified by name and number. Gort Co Galway 45 cm x 60cm The Irish Parliamentary Party or more commonly called the Irish Party or the Home Rule Party) was formed in 1874 by Isaac Butt, the leader of the Nationalist Party, replacing the Home Rule League, as official parliamentary party for Irish nationalist Members of Parliament (MPs) elected to the House of Commons at Westminster within the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland up until 1918. Its central objectives were legislative independence for Ireland and land reform. Its constitutional movement was instrumental in laying the groundwork for Irish self-government through three Irish Home Rule bills.Instrumental to the party's rise and fall was the iconic statesman,Charles Stewart Parnell.
Extremely rare,interesting print of the Irish Benches of the Irish Parliamentary Party in the House of Commons in 1885,with all members identified by name and number. Gort Co Galway 45 cm x 60cm The Irish Parliamentary Party or more commonly called the Irish Party or the Home Rule Party) was formed in 1874 by Isaac Butt, the leader of the Nationalist Party, replacing the Home Rule League, as official parliamentary party for Irish nationalist Members of Parliament (MPs) elected to the House of Commons at Westminster within the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland up until 1918. Its central objectives were legislative independence for Ireland and land reform. Its constitutional movement was instrumental in laying the groundwork for Irish self-government through three Irish Home Rule bills.Instrumental to the party's rise and fall was the iconic statesman,Charles Stewart Parnell.






















