-

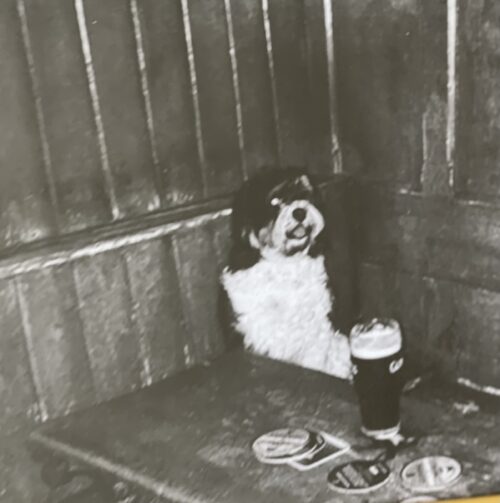
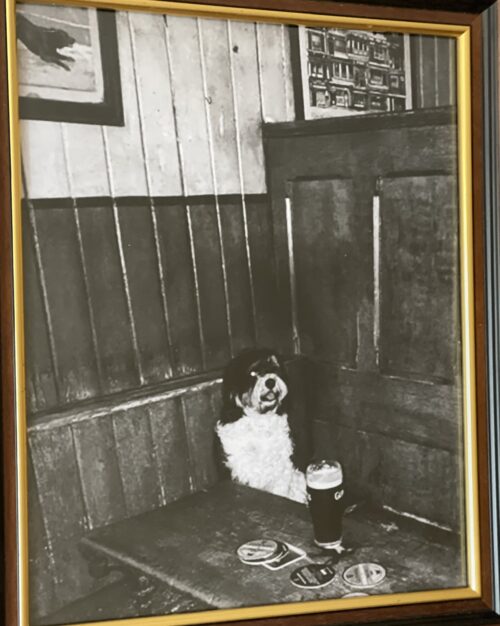
 Framed print of the famous Guinness battle of Hastings 1066-1966 advert. Dimensions : 40cmx 30cm Dublin Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.” Origins : Dublin Dimensions : 43cm x 35cm
Framed print of the famous Guinness battle of Hastings 1066-1966 advert. Dimensions : 40cmx 30cm Dublin Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.” Origins : Dublin Dimensions : 43cm x 35cm -

 Whimsical,retro Get together with Guinness advert from the 1970s. Dimensions : 40cmx 33cm Dublin Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.” Origins : Dublin Dimensions : 43cm x 35cm
Whimsical,retro Get together with Guinness advert from the 1970s. Dimensions : 40cmx 33cm Dublin Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.” Origins : Dublin Dimensions : 43cm x 35cm -

 Framed print of vintage Guinness advert extolling the delights of a pint being poured by draught.Draught Guinness was first introduced in 1959 Dimensions : 44cmx 37cm Dublin Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.” Origins : Dublin Dimensions : 43cm x 35cm
Framed print of vintage Guinness advert extolling the delights of a pint being poured by draught.Draught Guinness was first introduced in 1959 Dimensions : 44cmx 37cm Dublin Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.” Origins : Dublin Dimensions : 43cm x 35cm -
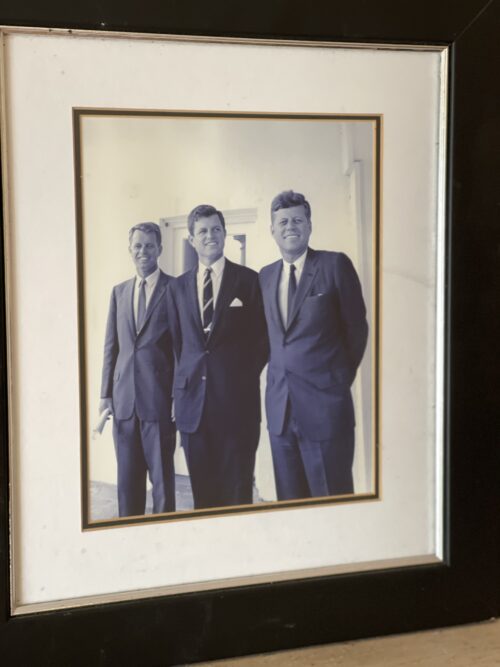
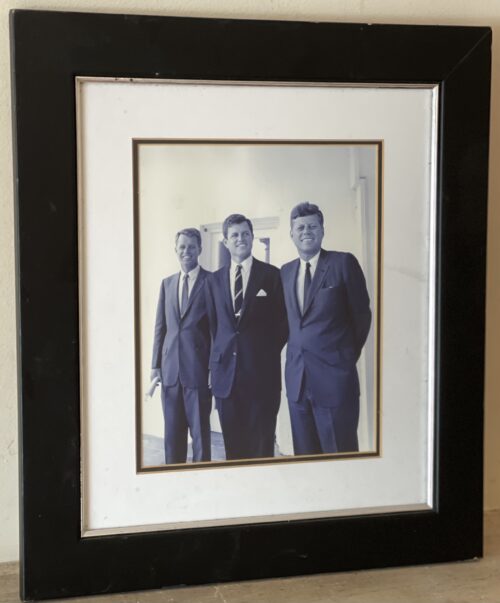
 Framed portrait of the three Kennedy Brothers from 1963 ,taken in the White House. 45cm x 35cm Bruree Co Limerick
Framed portrait of the three Kennedy Brothers from 1963 ,taken in the White House. 45cm x 35cm Bruree Co LimerickUlster is becoming Britain’s Vietnam,” Senator Edward M Kennedy, the youngest of three exceptionally accomplished brothers in the United States’ most famous Irish family, told the US Senate in the autumn of 1971.
This year marks an important anniversary for the Kennedys, the Irish and the world, for it was 50 years ago when Ted Kennedy set his sights on peace in Northern Ireland. And, from that moment to the miracle of Stormont, in 1998, that secured peace, Ted spearheaded the United States’ peace-making efforts. He pushed presidents, worked with key Senate and House members of Irish descent, testified before Congress, delivered speeches, wrote articles, visited the region and met leaders on both sides of the conflict.
Jack, Bobby and Ted Kennedy were all proudly Irish. They all spoke of the anti-Irish bigotry that had plagued their ancestors in the United States. Jack visited Ireland to trace his roots and, while there as president in 1963, called it “the land for which I hold the greatest affection”. Ted came in 1964 in grief after Jack’s murder, and he spent more time trying to end the Troubles in Northern Ireland than on any other global challenge.
Joe and Rose led discussions about the world with the boys over meals, and Joe invited prominent people, such as aviator Charles Lindbergh and media mogul Henry Luce, to dine with them and enrich the conversations
Ted’s peace-making in Northern Ireland, however, reflects far more than the proud Irishness that he shared with his brothers. It also reflects perhaps the most fascinating and consequential story about the Kennedy brothers that hardly anyone knows – a story with important lessons for the United States of today.
Most people know that Joe and Rose Kennedy groomed their sons for success. They started with Joe jnr, who died at war in 1944 at the age of 29, and continued through Jack, Bobby and Ted. What most people don’t know (and what I explore in my new book, The Kennedys in the World: How Jack, Bobby, and Ted Remade America’s Empire) is that, from the time the brothers were little boys, Joe and Rose pushed them not just to succeed but to look beyond the United States’ borders – to learn about the world, care about the world and, once they attained power, shape the United States’ role in the world.





-
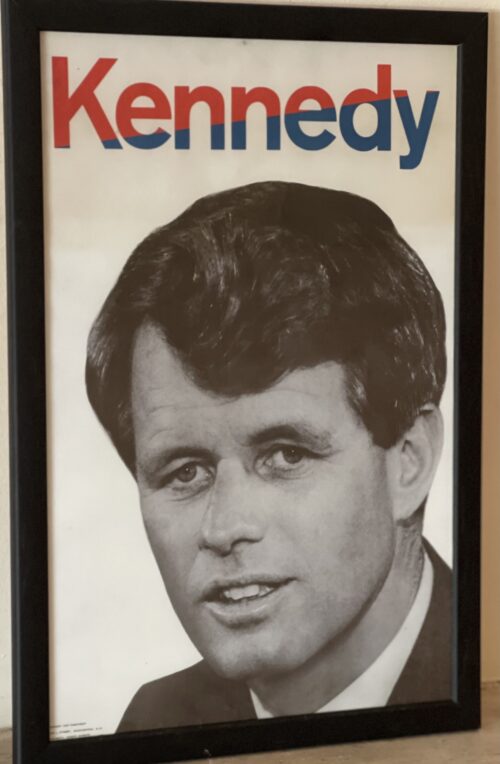

 RFK Election Poster from 1968. 60cm x 50cm Bruree Co Limerick
RFK Election Poster from 1968. 60cm x 50cm Bruree Co LimerickUlster is becoming Britain’s Vietnam,” Senator Edward M Kennedy, the youngest of three exceptionally accomplished brothers in the United States’ most famous Irish family, told the US Senate in the autumn of 1971.
This year marks an important anniversary for the Kennedys, the Irish and the world, for it was 50 years ago when Ted Kennedy set his sights on peace in Northern Ireland. And, from that moment to the miracle of Stormont, in 1998, that secured peace, Ted spearheaded the United States’ peace-making efforts. He pushed presidents, worked with key Senate and House members of Irish descent, testified before Congress, delivered speeches, wrote articles, visited the region and met leaders on both sides of the conflict.
Jack, Bobby and Ted Kennedy were all proudly Irish. They all spoke of the anti-Irish bigotry that had plagued their ancestors in the United States. Jack visited Ireland to trace his roots and, while there as president in 1963, called it “the land for which I hold the greatest affection”. Ted came in 1964 in grief after Jack’s murder, and he spent more time trying to end the Troubles in Northern Ireland than on any other global challenge.
Joe and Rose led discussions about the world with the boys over meals, and Joe invited prominent people, such as aviator Charles Lindbergh and media mogul Henry Luce, to dine with them and enrich the conversations
Ted’s peace-making in Northern Ireland, however, reflects far more than the proud Irishness that he shared with his brothers. It also reflects perhaps the most fascinating and consequential story about the Kennedy brothers that hardly anyone knows – a story with important lessons for the United States of today.
Most people know that Joe and Rose Kennedy groomed their sons for success. They started with Joe jnr, who died at war in 1944 at the age of 29, and continued through Jack, Bobby and Ted. What most people don’t know (and what I explore in my new book, The Kennedys in the World: How Jack, Bobby, and Ted Remade America’s Empire) is that, from the time the brothers were little boys, Joe and Rose pushed them not just to succeed but to look beyond the United States’ borders – to learn about the world, care about the world and, once they attained power, shape the United States’ role in the world.





-

 Tullamore Dew advert 40cm x 30cm Banagher Co Offaly Tullamore D.E.W. is a brand of Irish whiskey produced by William Grant & Sons. It is the second largest selling brand of Irish whiskey globally, with sales of over 950,000 cases per annum as of 2015.The whiskey was originally produced in the Tullamore, County Offaly, Ireland, at the old Tullamore Distillery which was established in 1829. Its name is derived from the initials of Daniel E. Williams (D.E.W.), a general manager and later owner of the original distillery. In 1954, the original distillery closed down, and with stocks of whiskey running low, the brand was sold to John Powers & Son, another Irish distiller in the 1960s, with production transferred to the Midleton Distillery, County Cork in the 1970s following a merger of three major Irish distillers.In 2010, the brand was purchased by William Grant & Sons, who constructed a new distillery on the outskirts of Tullamore. The new distillery opened in 2014, bringing production of the whiskey back to the town after a break of sixty years.
Tullamore Dew advert 40cm x 30cm Banagher Co Offaly Tullamore D.E.W. is a brand of Irish whiskey produced by William Grant & Sons. It is the second largest selling brand of Irish whiskey globally, with sales of over 950,000 cases per annum as of 2015.The whiskey was originally produced in the Tullamore, County Offaly, Ireland, at the old Tullamore Distillery which was established in 1829. Its name is derived from the initials of Daniel E. Williams (D.E.W.), a general manager and later owner of the original distillery. In 1954, the original distillery closed down, and with stocks of whiskey running low, the brand was sold to John Powers & Son, another Irish distiller in the 1960s, with production transferred to the Midleton Distillery, County Cork in the 1970s following a merger of three major Irish distillers.In 2010, the brand was purchased by William Grant & Sons, who constructed a new distillery on the outskirts of Tullamore. The new distillery opened in 2014, bringing production of the whiskey back to the town after a break of sixty years.Mick The Miller,as featured in this iconic advert, was the most famous greyhound of all time. He was born in 1926 in the village of Killeigh, County Offaly, Ireland at Millbrook House(only 5 miles from Tullamore), the home of parish curate, Fr Martin Brophy. When he was born Mick was the runt of the litter but Michael Greene, who worked for Fr Brophy, singled the little pup out as a future champion and insisted that he be allowed to rear him. With constant attention and regular exercise Mick The Miller developed into a racing machine. His first forays were on local coursing fields where he had some success but he showed his real talent on the track where he won 15 of his first 20 races.
.jpg)
In 1929 Fr Brophy decided to try Mick in English Greyhound Derby at White City, London. On his first trial-run, Mick equalled the track record. Then, in his first heat, he broke the world record, becoming the first greyhound ever to run 525 yards in under 30 seconds. Fr Brophy was inundated with offers and sold him to Albert Williams. Mick went on to win the 1929 Derby. Within a year he had changed hands again to Arundel H Kempton and won the Derby for a second time.
Over the course of his English career he won 36 of his 48 races, including the Derby (twice), the St Leger, the Cesarewitch, and the Welsh Derby. He set six new world records and two new track records. He was the first greyhound to win 19 races in a row. Several of his records went unbroken for over 40 years. He won, in total, almost £10,000 in prizemoney. But he also became the poster-dog for greyhound racing. He was a celebrity on a par with any sports person, muscisian or moviestar. The more famous he became, the more he attracted people to greyhound racing. Thousands thronged to watch him, providing a huge boost to the sport. It is said that he actually saved the sport of greyhound racing.
After retirement to stud his popularity continued. He starred in the film Wild Boy (based on his life-story) in 1934 which was shown in cinemas all across the UK. He was in huge demand on the celebrity circuit, opening shops, attending big races and even rubbing shoulder with royalty (such as the King and Queen) at charity events. When he died in 1939 aged 12, his owner donated his body to the British Natural History Museum in London. And Mick`s fame has continued ever since. In 1981 he was inducted into the American Hall of Fame (International Section). In 1990 English author Michael Tanner published a book, Mick The Miller - Sporting Icon Of the Depression. And in 2011 the people of Killeigh erected a monument on the village green to honour their most famous son. Mick The Miller is not just the most famous greyhound of all time but one of the most loved dogs that has ever lived.
-

 Kennedy for President -Leadership for the 60s-Election Poster 40cm x 27cm Bruree Co Limerick
Kennedy for President -Leadership for the 60s-Election Poster 40cm x 27cm Bruree Co LimerickUlster is becoming Britain’s Vietnam,” Senator Edward M Kennedy, the youngest of three exceptionally accomplished brothers in the United States’ most famous Irish family, told the US Senate in the autumn of 1971.
This year marks an important anniversary for the Kennedys, the Irish and the world, for it was 50 years ago when Ted Kennedy set his sights on peace in Northern Ireland. And, from that moment to the miracle of Stormont, in 1998, that secured peace, Ted spearheaded the United States’ peace-making efforts. He pushed presidents, worked with key Senate and House members of Irish descent, testified before Congress, delivered speeches, wrote articles, visited the region and met leaders on both sides of the conflict.
Jack, Bobby and Ted Kennedy were all proudly Irish. They all spoke of the anti-Irish bigotry that had plagued their ancestors in the United States. Jack visited Ireland to trace his roots and, while there as president in 1963, called it “the land for which I hold the greatest affection”. Ted came in 1964 in grief after Jack’s murder, and he spent more time trying to end the Troubles in Northern Ireland than on any other global challenge.
Joe and Rose led discussions about the world with the boys over meals, and Joe invited prominent people, such as aviator Charles Lindbergh and media mogul Henry Luce, to dine with them and enrich the conversations
Ted’s peace-making in Northern Ireland, however, reflects far more than the proud Irishness that he shared with his brothers. It also reflects perhaps the most fascinating and consequential story about the Kennedy brothers that hardly anyone knows – a story with important lessons for the United States of today.
Most people know that Joe and Rose Kennedy groomed their sons for success. They started with Joe jnr, who died at war in 1944 at the age of 29, and continued through Jack, Bobby and Ted. What most people don’t know (and what I explore in my new book, The Kennedys in the World: How Jack, Bobby, and Ted Remade America’s Empire) is that, from the time the brothers were little boys, Joe and Rose pushed them not just to succeed but to look beyond the United States’ borders – to learn about the world, care about the world and, once they attained power, shape the United States’ role in the world.





-
 29cm x 36cm. Dublin Famous picture during The Greatest's visit to Ireland of Muhammad Ali play fighting with two members of An Garda Siochana.Some memory for those officers to tell their grandchildren about ! July 19, 1972, Muhammad Ali fought Al 'Blue' Lewis at Croke Park in Dublin, causing quite a stir in Ireland.Decades later, an Irish documentary recounting the epic fight not only won awards but also won the approval of Ali's daughter Jamilah Ali. "When Ali Came to Ireland" is an Irish documentary that details Muhammad Ali's trip to Dublin for a fight against Al 'Blue' Lewis at Croke Park. In 2013 the film was screened at the Chicago film festival, where Jamilah Ali was in attendance. TheJournal.ie reported that following the screening, Jamilah said "I've seen so much footage of my father over the years but the amazing thing about watching this film was that I had seen none of the footage of him in Ireland... I loved the film from the beginning to the end." The film highlights a moment in Ali's career where he was set to stage a world comeback. He had been recently released from prison after refusing to join the Vietnam War as a conscientious objector. His opponent Al Lewis had also just been released on parole after serving time in Detroit for a murder charge, and he intended to use his boxing career as "a path to a new life." The movie that won an IFTA in 2013 documents the spectacle in Croke Park, Ali's presence in Ireland and how the public reacted to his being there. It also demonstrates how Ali came to be in Dublin for a fight in the first place, highlighting the involvement of "former Kerry strongman"Michael "Butty" Sugrue. Sugrue's story also proved to be revelatory to his family- in a quote from Ross Whittaker, co-director of the film, he speaks about how Sugrue's grandchildren had never had the chance to meet him. "We were amazed when we screened the film in London to find that Butty Sugrue's granddaughters had never heard their grandfather speak. He had died before they were born and they'd never seen footage of him in which he had spoken." After their 1972 meeting, however, Sugrue and Ali's fortunes took two divergent paths. Ali returned to the ring in America to further glories and fanfare before his retirement, while Sugrue lost a small fortune on the Dublin fight and after dying in London was laid to rest in an unmarked grave in his hometown of Killorglin, Co Kerry. The Louisville Lip was also incredibly proud of his County Clare roots. Today we recall the man's star quality and his Irish ancestry. The death of boxing legend Muhammad Ali at 74 in June 2016, from Parkinson’s, would have brought back many glorious memories of the greatest athlete of our times. At the height of his career, Ali was the most graceful, talented, and brilliant heavyweight boxer who ever stepped inside the ropes. I remember seeing him enter the room at the American Ireland Fund dinner in 2011 and grown men, including the Irish leader Enda Kenny, were simply awestruck that they were in the presence of the greatest living legend. Ali was more than a boxer, of course, he was a fighter who refused to become cannon fodder in the Vietnam War, the greatest mistaken war America entered until the invasion of Iraq. He was also a poet, a showman, a lover of many women, a devout Muslim, and simply a legend. Ali's stance to end the Vietnam War when he refused to be drafted cost us the best years of his sporting life. He came back still a brilliant boxer, but the man who could float like a butterfly could never quite recover that greatness. Still, the fights with Joe Frazier, the rope-a-dope that saw him defeat George Foreman in Zaire in the "Rumble in the Jungle" will forever enshrine his name in history.
29cm x 36cm. Dublin Famous picture during The Greatest's visit to Ireland of Muhammad Ali play fighting with two members of An Garda Siochana.Some memory for those officers to tell their grandchildren about ! July 19, 1972, Muhammad Ali fought Al 'Blue' Lewis at Croke Park in Dublin, causing quite a stir in Ireland.Decades later, an Irish documentary recounting the epic fight not only won awards but also won the approval of Ali's daughter Jamilah Ali. "When Ali Came to Ireland" is an Irish documentary that details Muhammad Ali's trip to Dublin for a fight against Al 'Blue' Lewis at Croke Park. In 2013 the film was screened at the Chicago film festival, where Jamilah Ali was in attendance. TheJournal.ie reported that following the screening, Jamilah said "I've seen so much footage of my father over the years but the amazing thing about watching this film was that I had seen none of the footage of him in Ireland... I loved the film from the beginning to the end." The film highlights a moment in Ali's career where he was set to stage a world comeback. He had been recently released from prison after refusing to join the Vietnam War as a conscientious objector. His opponent Al Lewis had also just been released on parole after serving time in Detroit for a murder charge, and he intended to use his boxing career as "a path to a new life." The movie that won an IFTA in 2013 documents the spectacle in Croke Park, Ali's presence in Ireland and how the public reacted to his being there. It also demonstrates how Ali came to be in Dublin for a fight in the first place, highlighting the involvement of "former Kerry strongman"Michael "Butty" Sugrue. Sugrue's story also proved to be revelatory to his family- in a quote from Ross Whittaker, co-director of the film, he speaks about how Sugrue's grandchildren had never had the chance to meet him. "We were amazed when we screened the film in London to find that Butty Sugrue's granddaughters had never heard their grandfather speak. He had died before they were born and they'd never seen footage of him in which he had spoken." After their 1972 meeting, however, Sugrue and Ali's fortunes took two divergent paths. Ali returned to the ring in America to further glories and fanfare before his retirement, while Sugrue lost a small fortune on the Dublin fight and after dying in London was laid to rest in an unmarked grave in his hometown of Killorglin, Co Kerry. The Louisville Lip was also incredibly proud of his County Clare roots. Today we recall the man's star quality and his Irish ancestry. The death of boxing legend Muhammad Ali at 74 in June 2016, from Parkinson’s, would have brought back many glorious memories of the greatest athlete of our times. At the height of his career, Ali was the most graceful, talented, and brilliant heavyweight boxer who ever stepped inside the ropes. I remember seeing him enter the room at the American Ireland Fund dinner in 2011 and grown men, including the Irish leader Enda Kenny, were simply awestruck that they were in the presence of the greatest living legend. Ali was more than a boxer, of course, he was a fighter who refused to become cannon fodder in the Vietnam War, the greatest mistaken war America entered until the invasion of Iraq. He was also a poet, a showman, a lover of many women, a devout Muslim, and simply a legend. Ali's stance to end the Vietnam War when he refused to be drafted cost us the best years of his sporting life. He came back still a brilliant boxer, but the man who could float like a butterfly could never quite recover that greatness. Still, the fights with Joe Frazier, the rope-a-dope that saw him defeat George Foreman in Zaire in the "Rumble in the Jungle" will forever enshrine his name in history.Muhammad Ali's Irish roots explained
The astonishing fact that he had Irish roots, being descended from Abe Grady, an Irishman from Ennis, County Clare, only became known later in life. He returned to Ireland where he had fought and defeated Al “Blue” Lewis in Croke Park in 1972 almost seven years ago in 2009 to help raise money for his non–profit Muhammad Ali Center, a cultural and educational center in Louisville, Kentucky, and other hospices. He was also there to become the first Freeman of the town. The boxing great is no stranger to Irish shores and previously made a famous trip to Ireland in 1972 when he sat down with Cathal O’Shannon of RTE for a fascinating television interview. What’s more, genealogist Antoinette O'Brien discovered that one of Ali’s great-grandfathers emigrated to the United States from County Clare, meaning that the three-time heavyweight world champion joins the likes of President Obama and Professor Henry Louis Gates Jr. as prominent African-Americans with Irish heritage. In the 1860s, Abe Grady left Ennis in County Clare to start a new life in America. He would make his home in Kentucky and marry a free African-American woman. The couple started a family, and one of their daughters was Odessa Lee Grady. Odessa met and married Cassius Clay, Sr. and on January 17, 1942, Cassius junior was born. Cassius Clay changed his name to Muhammad Ali when he became a Muslim in 1964. Ali, an Olympic gold medalist at the 1960 games in Rome, has been suffering from Parkinson's for some years but was committed to raising funds for his center During his visit to Clare, he was mobbed by tens of thousands of locals who turned out to meet him and show him the area where his great-grandfather came from.Tracing Muhammad Ali's roots back to County Clare
Historian Dick Eastman had traced Ali’s roots back to Abe Grady the Clare emigrant to Kentucky and the freed slave he married. Eastman wrote: “An 1855 land survey of Ennis, a town in County Clare, Ireland, contains a reference to John Grady, who was renting a house in Turnpike Road in the center of the town. His rent payment was fifteen shillings a month. A few years later, his son Abe Grady immigrated to the United States. He settled in Kentucky." Also, around the year 1855, a man and a woman who were both freed slaves, originally from Liberia, purchased land in or around Duck Lick Creek, Logan, Kentucky. The two married, raised a family and farmed the land. These free blacks went by the name, Morehead, the name of white slave owners of the area. Odessa Grady Clay, Cassius Clay's mother, was the great-granddaughter of the freed slave Tom Morehead and of John Grady of Ennis, whose son Abe had emigrated from Ireland to the United States. She named her son Cassius in honor of a famous Kentucky abolitionist of that time. When he changed his name to Muhammad Ali in 1964, the famous boxer remarked, "Why should I keep my white slavemaster name visible and my black ancestors invisible, unknown, unhonored?" Ali was not only the greatest sporting figure, but he was also the best-known person in the world at his height, revered from Africa to Asia and all over the world. To the end, he was a battler, shown rare courage fighting Parkinson’s Disease, and surviving far longer than most sufferers from the disease. -

 Framed Guinness ephemera -these are Guinnessentials- a guide to publicans selling the Black Stuff ! Dimensions : 43cm x 36cm Dublin Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.” Origins : Dublin Dimensions : 43cm x 35cm
Framed Guinness ephemera -these are Guinnessentials- a guide to publicans selling the Black Stuff ! Dimensions : 43cm x 36cm Dublin Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.” Origins : Dublin Dimensions : 43cm x 35cm -

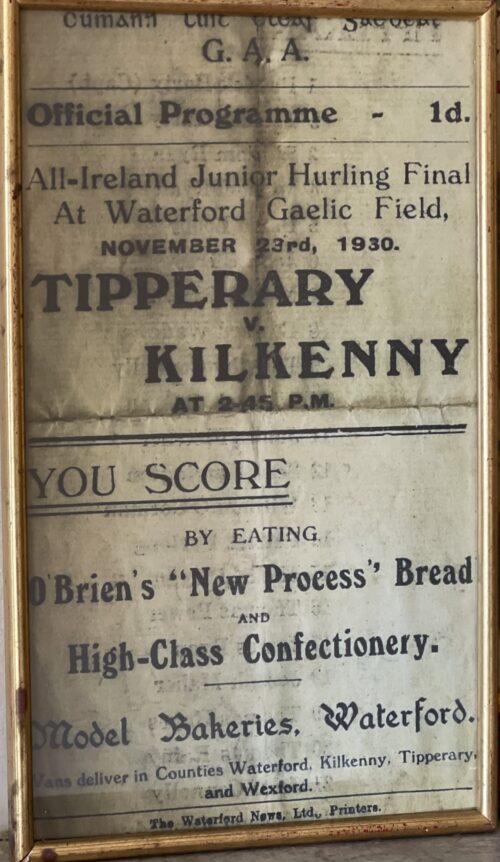 40cm x 23cm Thurles Co Tipperary The All-Ireland Junior Hurling Championship was a hurling competition organized by the Gaelic Athletic Association in Ireland. The competition was originally contested by the second teams of the strong counties, and the first teams of the weaker counties. In the years from 1961 to 1973 and from 1997 until now, the strong counties have competed for the All-Ireland Intermediate Hurling Championship instead. The competition was then restricted to the weaker counties. The competition was discontinued after 2004 as these counties now compete for the Nicky Rackard Cup instead. From 1974 to 1982, the original format of the competition was abandoned, and the competition was incorporated in Division 3 of the National Hurling League. The original format, including the strong hurling counties was re-introduced in 1983. 1930 – TIPPERARY: Paddy Harty (Captain), Tom Harty, Willie Ryan, Tim Connolly, Mick McGann, Martin Browne, Ned Wade, Tom Ryan, Jack Dwyer, Mick Ryan, Dan Looby, Pat Furlong, Bill O’Gorman, Joe Fletcher, Sean Harrington.
40cm x 23cm Thurles Co Tipperary The All-Ireland Junior Hurling Championship was a hurling competition organized by the Gaelic Athletic Association in Ireland. The competition was originally contested by the second teams of the strong counties, and the first teams of the weaker counties. In the years from 1961 to 1973 and from 1997 until now, the strong counties have competed for the All-Ireland Intermediate Hurling Championship instead. The competition was then restricted to the weaker counties. The competition was discontinued after 2004 as these counties now compete for the Nicky Rackard Cup instead. From 1974 to 1982, the original format of the competition was abandoned, and the competition was incorporated in Division 3 of the National Hurling League. The original format, including the strong hurling counties was re-introduced in 1983. 1930 – TIPPERARY: Paddy Harty (Captain), Tom Harty, Willie Ryan, Tim Connolly, Mick McGann, Martin Browne, Ned Wade, Tom Ryan, Jack Dwyer, Mick Ryan, Dan Looby, Pat Furlong, Bill O’Gorman, Joe Fletcher, Sean Harrington. -
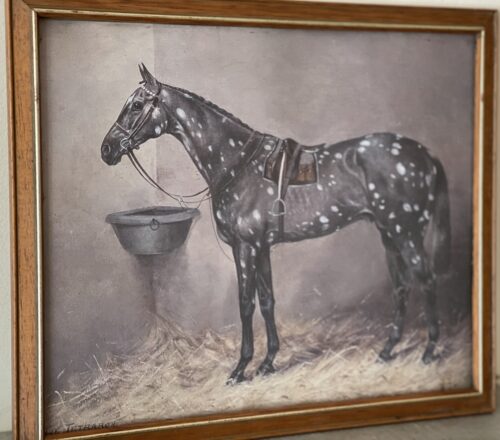
 40cm x 34cm LimerickUnfashionably – even eccentrically – bred, and strangely marked, he was a two-year-old of exceptional merit, a champion sire and, despite being sub-fertile and retired early from stud duties, he wielded tremendous influence on the breed. A racehorse of blinding speed, though bred to stay extreme distances. A stallion colossus who proved the cornerstone of an everlasting host of equine celebrities from flying machines to Grand National winners. The supreme nonpareil giant of turf history known as The Tetrarch was truly a freak of nature and, in his esteemed trainer’s words, “there will never be his likes again”.THE TETRARCH
40cm x 34cm LimerickUnfashionably – even eccentrically – bred, and strangely marked, he was a two-year-old of exceptional merit, a champion sire and, despite being sub-fertile and retired early from stud duties, he wielded tremendous influence on the breed. A racehorse of blinding speed, though bred to stay extreme distances. A stallion colossus who proved the cornerstone of an everlasting host of equine celebrities from flying machines to Grand National winners. The supreme nonpareil giant of turf history known as The Tetrarch was truly a freak of nature and, in his esteemed trainer’s words, “there will never be his likes again”.THE TETRARCHEarly Years
 Edward "Cub" KennedyBorn in 1911 on April 22nd at Edward “Cub” Kennedy’s Straffan Station Stud in Kildare, not far from where the present Goffs Sales complex is located. The Tetrarch was born chesnut with black “Bend Or spots” (so called after his Derby winning great-grandsire) which later transformed into his famous grey with splotches of white coat, that saddled him with the nickname “The Rocking Horse”. Every grey horse must have at least one grey parent and The Tetrarch inherited his colour from his sire. A direct line of his grey ancestors can be traced, like all grey thoroughbreds, back to one grey stallion in the original Weatherbys Stud Book named Alcocks Arabian, who was born around the turn of the 18th century and had his origins in Syria. When Cub Kennedy hastily arranged liaison of Roi Herode and Vahren in the late spring of 1910, he had been obsessed with the idea of reviving the apparently moribund male line of Herod. Could there be a more aptly named stallion for the job than Roi Herode? It was already nearly three months into the breeding season when Kennedy purchased his new stallion and he had little chance of attracting many outside mares, but he did have a couple due to foal late himself, one being Vahren. Kennedy decided to send the young Tetrarch to the 1912 Doncaster yearling sales and he knew that for make and shape there would be few to match him. Atty Persse duly had to go to 1,300gns to secure the colt for his patron Dermot McCalmont. When his jockey Steve Donoghue first saw him he described The Tetrarch as “a sort of elephant grey with big blotches, as though someone had splashed him with handfuls of wet lime”. However, once his brilliance on the racecourse became apparent, it wasn’t long before “The Rocking Horse” became “The Spotted Wonder”, a name that one hundred years on still resonates with horse racing aficionados around the world.THE TETRARCH
Edward "Cub" KennedyBorn in 1911 on April 22nd at Edward “Cub” Kennedy’s Straffan Station Stud in Kildare, not far from where the present Goffs Sales complex is located. The Tetrarch was born chesnut with black “Bend Or spots” (so called after his Derby winning great-grandsire) which later transformed into his famous grey with splotches of white coat, that saddled him with the nickname “The Rocking Horse”. Every grey horse must have at least one grey parent and The Tetrarch inherited his colour from his sire. A direct line of his grey ancestors can be traced, like all grey thoroughbreds, back to one grey stallion in the original Weatherbys Stud Book named Alcocks Arabian, who was born around the turn of the 18th century and had his origins in Syria. When Cub Kennedy hastily arranged liaison of Roi Herode and Vahren in the late spring of 1910, he had been obsessed with the idea of reviving the apparently moribund male line of Herod. Could there be a more aptly named stallion for the job than Roi Herode? It was already nearly three months into the breeding season when Kennedy purchased his new stallion and he had little chance of attracting many outside mares, but he did have a couple due to foal late himself, one being Vahren. Kennedy decided to send the young Tetrarch to the 1912 Doncaster yearling sales and he knew that for make and shape there would be few to match him. Atty Persse duly had to go to 1,300gns to secure the colt for his patron Dermot McCalmont. When his jockey Steve Donoghue first saw him he described The Tetrarch as “a sort of elephant grey with big blotches, as though someone had splashed him with handfuls of wet lime”. However, once his brilliance on the racecourse became apparent, it wasn’t long before “The Rocking Horse” became “The Spotted Wonder”, a name that one hundred years on still resonates with horse racing aficionados around the world.THE TETRARCHRacing Career
 The Tetrarch winning the Woodcote Stakes at EpsomAt the age of two The Tetrarch had developed into a magnificent individual and was showing phenomenal speed on the gallops. He made his first public appearance in a novice plate at Newmarket on April 17th 1913 – just five days short of his birthday and blew his twenty rivals away to win “in a canter” by 4 lengths. His second appearance was in the Woodcote Stakes at Epsom, traditionally the first six furlong juvenile race of the season, occurred the day before suffragette Emily Davison was fatally injured in the Derby. The Tetrarch took the race in hand rounding Tattenham Corner and won easily by three lengths, according to the British Bloodstock Review, “It was generally agreed that not since the days of Pretty Polly had a two-year-old accomplished a more impressive performance.” The Coventry Stakes at Royal Ascot was next, then run at five furlongs, and The Tetrarch won pulling up “with his mouth open”, his closest competitor trailed in 10 lengths behind. On July 19th to packed stands, he lined up for Britian’s richest two year old race, the National Breeders’ Produce Stakes (now the National Stakes) at Sandown. This was the only time The Tetrarch came close to defeat, scrambling home by a neck conceding 17 lbs to the runner-up. What onlookers didn’t know, as poor visibility obscured the view from the stands, was that The Tetrarch was severely hindered at the start. This is an account from jockey Steve Donoghue’s biography, “As the tapes went up, The Tetrarch got some of them tangled in his mouth, causing him to rear. On coming down he cannoned against another horse and fell to his knees. Although his plight had seemed hopeless, Steve set off in pursuit. The Tetrarch almost lifted him out of the saddle with his supercharged power as he came nearer and near his rivals with every stride”. Just twelve days later The Tetrarch stepped back up in distance to six furlongs at Glorious Goodwood for the Rous Memorial Stakes where he easily accounted for subsequent 1,000 Guineas and Oaks winner Princess Dorrie (in receipt of 13 lbs). He went on winning, the Champion Breeders Foal Stakes at Derby by four lengths, and what transpired to be his swansong in the Champagne Stakes at Doncaster by three lengths, where The Tetrarch treated Stornoway, his only credible rival for two-year-old honours, with contempt. Stornoway had previously won the Gimcrack and Norfolk (now Flying Childers) Stakes. His season was not meant to end there, but on the day before his intended start in the Imperial Produce Stakes at Kempton he struck into his off-fore fetlock joint, and was retired for the season. Crowned the Champion 2yo of 1913 and rated an unprecedented 10 lbs clear his nearest rival – that season’s Middle Park Stakes winner – The Tetrarch is still considered the greatest juvenile runner of all time. This view is backed by noted turf historians Tony Morris and John Randall, who rated the best juveniles of the 20th century in their book A Century of Champions, and have no doubt about which horse was top. Nearest to The Tetrarch, were Tudor Minstrel and The Tetrarch’s own son Tetratema.THE TETRARCH
The Tetrarch winning the Woodcote Stakes at EpsomAt the age of two The Tetrarch had developed into a magnificent individual and was showing phenomenal speed on the gallops. He made his first public appearance in a novice plate at Newmarket on April 17th 1913 – just five days short of his birthday and blew his twenty rivals away to win “in a canter” by 4 lengths. His second appearance was in the Woodcote Stakes at Epsom, traditionally the first six furlong juvenile race of the season, occurred the day before suffragette Emily Davison was fatally injured in the Derby. The Tetrarch took the race in hand rounding Tattenham Corner and won easily by three lengths, according to the British Bloodstock Review, “It was generally agreed that not since the days of Pretty Polly had a two-year-old accomplished a more impressive performance.” The Coventry Stakes at Royal Ascot was next, then run at five furlongs, and The Tetrarch won pulling up “with his mouth open”, his closest competitor trailed in 10 lengths behind. On July 19th to packed stands, he lined up for Britian’s richest two year old race, the National Breeders’ Produce Stakes (now the National Stakes) at Sandown. This was the only time The Tetrarch came close to defeat, scrambling home by a neck conceding 17 lbs to the runner-up. What onlookers didn’t know, as poor visibility obscured the view from the stands, was that The Tetrarch was severely hindered at the start. This is an account from jockey Steve Donoghue’s biography, “As the tapes went up, The Tetrarch got some of them tangled in his mouth, causing him to rear. On coming down he cannoned against another horse and fell to his knees. Although his plight had seemed hopeless, Steve set off in pursuit. The Tetrarch almost lifted him out of the saddle with his supercharged power as he came nearer and near his rivals with every stride”. Just twelve days later The Tetrarch stepped back up in distance to six furlongs at Glorious Goodwood for the Rous Memorial Stakes where he easily accounted for subsequent 1,000 Guineas and Oaks winner Princess Dorrie (in receipt of 13 lbs). He went on winning, the Champion Breeders Foal Stakes at Derby by four lengths, and what transpired to be his swansong in the Champagne Stakes at Doncaster by three lengths, where The Tetrarch treated Stornoway, his only credible rival for two-year-old honours, with contempt. Stornoway had previously won the Gimcrack and Norfolk (now Flying Childers) Stakes. His season was not meant to end there, but on the day before his intended start in the Imperial Produce Stakes at Kempton he struck into his off-fore fetlock joint, and was retired for the season. Crowned the Champion 2yo of 1913 and rated an unprecedented 10 lbs clear his nearest rival – that season’s Middle Park Stakes winner – The Tetrarch is still considered the greatest juvenile runner of all time. This view is backed by noted turf historians Tony Morris and John Randall, who rated the best juveniles of the 20th century in their book A Century of Champions, and have no doubt about which horse was top. Nearest to The Tetrarch, were Tudor Minstrel and The Tetrarch’s own son Tetratema.THE TETRARCHStud Career
 The Tetrarch was retired in 1915 to stand at his specially-built stallion box and covering shed at an initial fee of 300 guineas. However, due to the meditative state he would enter into when presented a mare, his owner eventually described the champion as “monastic in the extreme”. He only got 130 foals altogether, of which 80 were winners, but with such a dearth of opportunity, it is truly remarkable the number of brilliant racehorses The Tetrarch sired. Champion Sire in 1919, with only two crops of racing age, he was third on the list in 1920 and 1923. As might have been expected, a majority of his best progeny were outstanding two-year olds and sprinters such as: Tetratema Champion Sire and Champion Racehorse at 2, 3 & 4 years Winner of 13 races including 2,000 Guineas, Middle Park Stakes, King’s Stand Stakes and July Cup Mumtaz Mahal Champion 2yo Winner of 10 races including the Nunthorpe Stakes, King George Stakes, Champagne Stakes, Queen Mary Stakes and Molecomb Stakes (both by 10 lengths) The Satrap Champion 2yo Winner of 4 races including Chesham Stakes, July Stakes and Richmond Stakes Moti Mahal Champion 2yo Filly Winner of 6 races including the Coronation Stakes Paola Winner of the Cheveley Park Stakes and Coronation Stakes Stefan the Great Champion Broodmare Sire in Great Britain & Ireland Winner of 2 races including the Middle Park Plate
The Tetrarch was retired in 1915 to stand at his specially-built stallion box and covering shed at an initial fee of 300 guineas. However, due to the meditative state he would enter into when presented a mare, his owner eventually described the champion as “monastic in the extreme”. He only got 130 foals altogether, of which 80 were winners, but with such a dearth of opportunity, it is truly remarkable the number of brilliant racehorses The Tetrarch sired. Champion Sire in 1919, with only two crops of racing age, he was third on the list in 1920 and 1923. As might have been expected, a majority of his best progeny were outstanding two-year olds and sprinters such as: Tetratema Champion Sire and Champion Racehorse at 2, 3 & 4 years Winner of 13 races including 2,000 Guineas, Middle Park Stakes, King’s Stand Stakes and July Cup Mumtaz Mahal Champion 2yo Winner of 10 races including the Nunthorpe Stakes, King George Stakes, Champagne Stakes, Queen Mary Stakes and Molecomb Stakes (both by 10 lengths) The Satrap Champion 2yo Winner of 4 races including Chesham Stakes, July Stakes and Richmond Stakes Moti Mahal Champion 2yo Filly Winner of 6 races including the Coronation Stakes Paola Winner of the Cheveley Park Stakes and Coronation Stakes Stefan the Great Champion Broodmare Sire in Great Britain & Ireland Winner of 2 races including the Middle Park Plate Caligula, the St. Leger winner of 1920The Tetrarch was also capable of siring top class winners over longer distances: Snow Maiden Winner of 6 races including the Irish Oaks and 3rd Irish Derby Caligula Winner of 3 races including the St. Leger, Ascot Derby (now King Edward VII Stakes) and 3rd St James’s Palace Stakes Polemarch A leading sire in Argentina with 6 Classic winners Winner of 5 races including the St. Leger, Gimcrack Stakes and 3rd Middle Park Plate Salmon Trout A leading sire in Brazil Winner of 6 races including St. Leger, Princess of Wales’s Stakes, Dewhurst Stakes and 2nd Gold Cup The Tetrarch was also the sire of : Chief Ruler Twice Champion Sire in New Zealand Tractor A leading sire in New Zealand Arch-Gift Sire of Irish 2,000 Guineas winner Double Arch Ethnarch Sire of the ancestresses of Mill Reef and Blushing GroomMumtaz Mahal
Caligula, the St. Leger winner of 1920The Tetrarch was also capable of siring top class winners over longer distances: Snow Maiden Winner of 6 races including the Irish Oaks and 3rd Irish Derby Caligula Winner of 3 races including the St. Leger, Ascot Derby (now King Edward VII Stakes) and 3rd St James’s Palace Stakes Polemarch A leading sire in Argentina with 6 Classic winners Winner of 5 races including the St. Leger, Gimcrack Stakes and 3rd Middle Park Plate Salmon Trout A leading sire in Brazil Winner of 6 races including St. Leger, Princess of Wales’s Stakes, Dewhurst Stakes and 2nd Gold Cup The Tetrarch was also the sire of : Chief Ruler Twice Champion Sire in New Zealand Tractor A leading sire in New Zealand Arch-Gift Sire of Irish 2,000 Guineas winner Double Arch Ethnarch Sire of the ancestresses of Mill Reef and Blushing GroomMumtaz MahalLegacy
 Mumtaz MahalThe Tetrarch’s greatest legacy is undoubtedly through his daughter Mumtaz Mahal, purchased as a yearling for 9,100 guineas – the second highest price ever at the time – for the Aga Khan, such was her brilliant speed, she later became known as “The Flying Filly”. A champion 2yo on the track, she was to become one of the most influential broodmares of the 20th century. Her daughter Mumtaz Begum produced champion racehorse Nashrullah, who was a Champion sire in both Europe and the USA. His sons include Never Say Die, Nashua, Bold Ruler, Never Bend, Grey Sovereign and Red God. Her other efforts include champion 2yo filly Dodoma, who became the 4th dam of Shergar and Sun Princess, the dam of influential sire Royal Charger. Another daughter produced Abernant, champion 2yo and the greatest sprinter of modern times. Mumtaz Mahal best son was the Mirza, winner of the July and Coventry Stakes, who was seized by the Germans during invasion of Normandy in 1940, went on to numerous stakes winners including Skylarking ancestress of important sires Rahy, Singspiel and Devil’s Bag. Her other daughters Mah Mahal and Mah Iran, were also hugely influential. Mah Mahal’s son Mahmoud won the 1936 Derby in record time before being exported to America for stallion duties and becoming Champion Sire. His lasting legacy will be as the broodmare sire of Almahmoud – grandam of Northern Dancer. Her other descendants include French Champion Sire Arctic Tern, American Champion Sire Halo – sire of Japanese Champion Sire Sunday Silence, and Champion Australian and European Sire Danehill. Mah Iran was the second best two-year-old filly of 1941 and became the dam of Migoli, winner of the Prix de l’Arc de Triomphe, Eclipse Stakes, Champion Stakes, and second in the Derby. Migoli’s full-sister, Star of Iran produced the grey filly Petite Etoile, winner of the 1,000 Guineas, Oaks, Sussex Stakes, Champion Stakes and Coronation Cup. She is the fifth dam of Prix de l’Arc de Triomphe winner Zarkava. Other exceptional racehorses that descend directly from Mumtaz Mahal include Fillies’ Triple Crown winner Oh So Sharp, Champion Sprinter and Champion 3yo Habibti and Australian Champions Octagonal and Danewin.THE TETRARCHTetratema
Mumtaz MahalThe Tetrarch’s greatest legacy is undoubtedly through his daughter Mumtaz Mahal, purchased as a yearling for 9,100 guineas – the second highest price ever at the time – for the Aga Khan, such was her brilliant speed, she later became known as “The Flying Filly”. A champion 2yo on the track, she was to become one of the most influential broodmares of the 20th century. Her daughter Mumtaz Begum produced champion racehorse Nashrullah, who was a Champion sire in both Europe and the USA. His sons include Never Say Die, Nashua, Bold Ruler, Never Bend, Grey Sovereign and Red God. Her other efforts include champion 2yo filly Dodoma, who became the 4th dam of Shergar and Sun Princess, the dam of influential sire Royal Charger. Another daughter produced Abernant, champion 2yo and the greatest sprinter of modern times. Mumtaz Mahal best son was the Mirza, winner of the July and Coventry Stakes, who was seized by the Germans during invasion of Normandy in 1940, went on to numerous stakes winners including Skylarking ancestress of important sires Rahy, Singspiel and Devil’s Bag. Her other daughters Mah Mahal and Mah Iran, were also hugely influential. Mah Mahal’s son Mahmoud won the 1936 Derby in record time before being exported to America for stallion duties and becoming Champion Sire. His lasting legacy will be as the broodmare sire of Almahmoud – grandam of Northern Dancer. Her other descendants include French Champion Sire Arctic Tern, American Champion Sire Halo – sire of Japanese Champion Sire Sunday Silence, and Champion Australian and European Sire Danehill. Mah Iran was the second best two-year-old filly of 1941 and became the dam of Migoli, winner of the Prix de l’Arc de Triomphe, Eclipse Stakes, Champion Stakes, and second in the Derby. Migoli’s full-sister, Star of Iran produced the grey filly Petite Etoile, winner of the 1,000 Guineas, Oaks, Sussex Stakes, Champion Stakes and Coronation Cup. She is the fifth dam of Prix de l’Arc de Triomphe winner Zarkava. Other exceptional racehorses that descend directly from Mumtaz Mahal include Fillies’ Triple Crown winner Oh So Sharp, Champion Sprinter and Champion 3yo Habibti and Australian Champions Octagonal and Danewin.THE TETRARCHTetratemaLegacy
 Tetratema, in his paddock at BallylinchBorn at Ballylinch in 1917, Tetratema was a winner of all his twelve starts over sprint distances but also won the 2,000 Guineas for good measure. After an incredible debut in the National Breeders’ Produce Stakes, he took in the Molecomb Stakes, Champagne Stakes, Imperial Produce Plate and Middle Park Stakes on the way to being crowned Champion 2yo. He began his 3yo career as the first grey to win the 2,000 Guineas since 1838, but failed to stay in both the Derby and Eclipse Stakes. Dropping back to sprint distances he won the (now discontinued) Fern Hill Stakes at Royal Ascot and the King George Stakes at Glorious Goodwood, where he accounted for 1,000 Guineas winner and exceptional sprinter Diadem. As a four year old he won the King’s Stand Stakes at Royal Ascot, before taking the July Cup at Newmarket and repeating his win in the King George Stakes. Tetratema made his swansong in the five furlong Snailwell Stakes at Newmarket before retiring to Ballylinch in 1922 at the same initial fee as his sire, 300 guineas.THE TETRARCH
Tetratema, in his paddock at BallylinchBorn at Ballylinch in 1917, Tetratema was a winner of all his twelve starts over sprint distances but also won the 2,000 Guineas for good measure. After an incredible debut in the National Breeders’ Produce Stakes, he took in the Molecomb Stakes, Champagne Stakes, Imperial Produce Plate and Middle Park Stakes on the way to being crowned Champion 2yo. He began his 3yo career as the first grey to win the 2,000 Guineas since 1838, but failed to stay in both the Derby and Eclipse Stakes. Dropping back to sprint distances he won the (now discontinued) Fern Hill Stakes at Royal Ascot and the King George Stakes at Glorious Goodwood, where he accounted for 1,000 Guineas winner and exceptional sprinter Diadem. As a four year old he won the King’s Stand Stakes at Royal Ascot, before taking the July Cup at Newmarket and repeating his win in the King George Stakes. Tetratema made his swansong in the five furlong Snailwell Stakes at Newmarket before retiring to Ballylinch in 1922 at the same initial fee as his sire, 300 guineas.THE TETRARCH Mr. JinksIn 1929, he emulated his sire by becoming Champion Sire – the same year his daughter Tiffin became Champion 2yo and his son Mr. Jinks was the highest rated colt. In all, Tetratema was a top 7 sire on 11 occasions. Tiffin Champion 2yo Winner of the Cheveley Park Stakes and July Cup Mr Jinks Champion 2yo Colt Winner of the July Stakes, 2,000 Guineas and St. James’s Palace Stakes Myrobella Champion 2yo Winner of the Champagne Stakes, King George Stakes and July Cup Foray Champion 2yo Winner of the July Stakes, Champagne Stakes and King’s Stand Stakes Fourth Hand Winner of the Windsor Castle Stakes and Irish 2,000 Guineas Royal Minstrel Winner of the St. James’s Palace Stakes, Cork and Orrey (now Diamond Jubilee) Stakes and Eclipse Stakes Four Course Winner of the July Stakes, Richmond Stakes, Gimcrack Stakes and 1,000 Guineas Theft Five time Champion Sire in Japan Winner of the Windsor Castle Stakes and Jersey Stakes
Mr. JinksIn 1929, he emulated his sire by becoming Champion Sire – the same year his daughter Tiffin became Champion 2yo and his son Mr. Jinks was the highest rated colt. In all, Tetratema was a top 7 sire on 11 occasions. Tiffin Champion 2yo Winner of the Cheveley Park Stakes and July Cup Mr Jinks Champion 2yo Colt Winner of the July Stakes, 2,000 Guineas and St. James’s Palace Stakes Myrobella Champion 2yo Winner of the Champagne Stakes, King George Stakes and July Cup Foray Champion 2yo Winner of the July Stakes, Champagne Stakes and King’s Stand Stakes Fourth Hand Winner of the Windsor Castle Stakes and Irish 2,000 Guineas Royal Minstrel Winner of the St. James’s Palace Stakes, Cork and Orrey (now Diamond Jubilee) Stakes and Eclipse Stakes Four Course Winner of the July Stakes, Richmond Stakes, Gimcrack Stakes and 1,000 Guineas Theft Five time Champion Sire in Japan Winner of the Windsor Castle Stakes and Jersey Stakes -
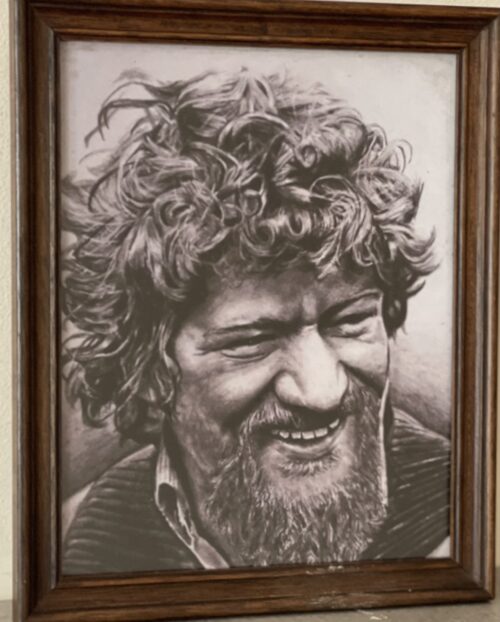 40cm x 30cm Luke Kelly (17 November 1940 – 30 January 1984) was an Irish singer, folk musician and actor from Dublin, Ireland. Born into a working-class household in Dublin city, Kelly moved to England in his late teens and by his early 20s had become involved in a folk music revival. Returning to Dublin in the 1960s, he is noted as a founding member of the band The Dubliners in 1962. Becoming known for his distinctive singing style, and sometimes political messages, the Irish Postand other commentators have regarded Kelly as one of Ireland's greatest folk singers. Early life Luke Kelly was born into a working-class family in Lattimore Cottages at 1 Sheriff Street.His maternal grandmother, who was a MacDonald from Scotland, lived with the family until her death in 1953. His father who was Irish- also named Luke- was shot and severely wounded as a child by British soldiers from the King's Own Scottish Borderers during the 1914 Bachelor's Walk massacre.His father worked all his life in Jacob's biscuit factory and enjoyed playing football. The elder Luke was a keen singer: Luke junior's brother Paddy later recalled that "he had this talent... to sing negro spirituals by people like Paul Robeson, we used to sit around and join in — that was our entertainment". After Dublin Corporation demolished Lattimore Cottages in 1942, the Kellys became the first family to move into the St. Laurence O’Toole flats, where Luke spent the bulk of his childhood, although the family were forced to move by a fire in 1953 and settled in the Whitehall area. Both Luke and Paddy played club Gaelic football and soccer as children. Kelly left school at thirteen and after a number of years of odd-jobbing, he went to England in 1958.[6] Working at steel fixing with his brother Paddy on a building site in Wolverhampton, he was apparently sacked after asking for higher pay. He worked a number of odd jobs, including a period as a vacuum cleaner salesman.Describing himself as a beatnik, he travelled Northern England in search of work, summarising his life in this period as "cleaning lavatories, cleaning windows, cleaning railways, but very rarely cleaning my face".
40cm x 30cm Luke Kelly (17 November 1940 – 30 January 1984) was an Irish singer, folk musician and actor from Dublin, Ireland. Born into a working-class household in Dublin city, Kelly moved to England in his late teens and by his early 20s had become involved in a folk music revival. Returning to Dublin in the 1960s, he is noted as a founding member of the band The Dubliners in 1962. Becoming known for his distinctive singing style, and sometimes political messages, the Irish Postand other commentators have regarded Kelly as one of Ireland's greatest folk singers. Early life Luke Kelly was born into a working-class family in Lattimore Cottages at 1 Sheriff Street.His maternal grandmother, who was a MacDonald from Scotland, lived with the family until her death in 1953. His father who was Irish- also named Luke- was shot and severely wounded as a child by British soldiers from the King's Own Scottish Borderers during the 1914 Bachelor's Walk massacre.His father worked all his life in Jacob's biscuit factory and enjoyed playing football. The elder Luke was a keen singer: Luke junior's brother Paddy later recalled that "he had this talent... to sing negro spirituals by people like Paul Robeson, we used to sit around and join in — that was our entertainment". After Dublin Corporation demolished Lattimore Cottages in 1942, the Kellys became the first family to move into the St. Laurence O’Toole flats, where Luke spent the bulk of his childhood, although the family were forced to move by a fire in 1953 and settled in the Whitehall area. Both Luke and Paddy played club Gaelic football and soccer as children. Kelly left school at thirteen and after a number of years of odd-jobbing, he went to England in 1958.[6] Working at steel fixing with his brother Paddy on a building site in Wolverhampton, he was apparently sacked after asking for higher pay. He worked a number of odd jobs, including a period as a vacuum cleaner salesman.Describing himself as a beatnik, he travelled Northern England in search of work, summarising his life in this period as "cleaning lavatories, cleaning windows, cleaning railways, but very rarely cleaning my face".Musical beginnings
Kelly had been interested in music during his teenage years: he regularly attended céilithe with his sister Mona and listened to American vocalists including: Fats Domino, Al Jolson, Frank Sinatra and Perry Como. He also had an interest in theatre and musicals, being involved with the staging of plays by Dublin's Marian Arts Society. The first folk club he came across was in the Bridge Hotel, Newcastle upon Tyne in early 1960.Having already acquired the use of a banjo, he started memorising songs. In Leeds he brought his banjo to sessions in McReady's pub. The folk revival was under way in England: at the centre of it was Ewan MacColl who scripted a radio programme called Ballads and Blues. A revival in the skiffle genre also injected a certain energy into folk singing at the time. Kelly started busking. On a trip home he went to a fleadh cheoil in Milltown Malbay on the advice of Johnny Moynihan. He listened to recordings of Woody Guthrie and Pete Seeger. He also developed his political convictions which, as Ronnie Drew pointed out after his death, he stuck to throughout his life. As Drew also pointed out, he "learned to sing with perfect diction". Kelly befriended Sean Mulready in Birmingham and lived in his home for a period.Mulready was a teacher who was forced from his job in Dublin because of his communist beliefs. Mulready had strong music links; a sister, Kathleen Moynihan was a founder member of Comhaltas Ceoltóirí Éireann, and he was related by marriage to Festy Conlon, the County Galway whistle player. Mulready's brother-in-law, Ned Stapleton, taught Kelly "The Rocky Road to Dublin".During this period he studied literature and politics under the tutelage of Mulready, his wife Mollie, and Marxist classicist George Derwent Thomson: Kelly later stated that his interest in music grew parallel to his interest in politics. Kelly bought his first banjo, which had five strings and a long neck, and played it in the style of Pete Seeger and Tommy Makem. At the same time, Kelly began a habit of reading, and also began playing golf on one of Birmingham's municipal courses. He got involved in the Jug O'Punch folk club run by Ian Campbell. He befriended Dominic Behan and they performed in folk clubs and Irish pubs from London to Glasgow. In London pubs, like "The Favourite", he would hear street singer Margaret Barry and musicians in exile like Roger Sherlock, Seamus Ennis, Bobby Casey and Mairtín Byrnes. Luke Kelly was by now active in the Connolly Association, a left-wing grouping strongest among the emigres in England, and he also joined the Young Communist League: he toured Irish pubs playing his set and selling the Connolly Association's newspaper The Irish Democrat. By 1962 George Derwent Thomson had offered him the opportunity to further his educational and political development by attending university in Prague. However, Kelly turned down the offer in favour of pursuing his career in folk music. He was also to start frequenting Ewan MacColl and Peggy Seeger's Singer Club in London.The Dubliners
In 1961 there was a folk music revival or "ballad boom", as it was later termed, in waiting in Ireland.The Abbey Tavern sessions in Howth were the forerunner to sessions in the Hollybrook, Clontarf, the International Bar and the Grafton Cinema. Luke Kelly returned to Dublin in 1962. O'Donoghue's Pub was already established as a session house and soon Kelly was singing with, among others, Ronnie Drew and Barney McKenna. Other early people playing at O'Donoghues included The Fureys, father and sons, John Keenan and Sean Og McKenna, Johnny Moynihan, Andy Irvine, Seamus Ennis, Willy Clancy and Mairtin Byrnes. A concert John Molloy organised in the Hibernian Hotel led to his "Ballad Tour of Ireland" with the Ronnie Drew Ballad Group (billed in one town as the Ronnie Drew Ballet Group). This tour led to the Abbey Tavern and the Royal Marine Hotel and then to jam-packed sessions in the Embankment, Tallaght. Ciarán Bourke joined the group, followed later by John Sheahan. They renamed themselves The Dubliners at Kelly's suggestion, as he was reading James Joyce's book of short stories, entitled Dubliners, at the time.Kelly was the leading vocalist for the group's eponymous debut album in 1964, which included his rendition of "The Rocky Road to Dublin". Barney McKenna later noted that Kelly was the only singer he'd heard sing it to the rhythm it was played on the fiddle. In 1964 Luke Kelly left the group for nearly two years and was replaced by Bobby Lynch and John Sheahan. Kelly went with Deirdre O'Connell, founder of the Focus Theatre, whom he was to marry the following year, back to London and became involved in Ewan MacColl's "gathering". The Critics, as it was called, was formed to explore folk traditions and help young singers. During this period he retained his political commitments, becoming increasingly active in the Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament. Kelly also met and befriended Michael O'Riordan, the General Secretary of the Irish Workers' Party, and the two developed a "personal-political friendship". Kelly endorsed O'Riordan for election, and held a rally in his name during campaigning in 1965.In 1965, he sang 'The Rocky Road to Dublin' with Liam Clancy on his first, self-titled solo album. Bobby Lynch left The Dubliners, John Sheahan and Kelly rejoined. They recorded an album in the Gate Theatre, Dublin, played the Cambridge Folk Festival and recorded Irish Night Out, a live album with, among others, exiles Margaret Barry, Michael Gorman and Jimmy Powers. They also played a concert in the National Stadium in Dublin with Pete Seeger as special guest. They were on the road to success: Top Twenty hits with "Seven Drunken Nights" and "The Black Velvet Band", The Ed Sullivan Show in 1968 and a tour of New Zealand and Australia. The ballad boom in Ireland was becoming increasingly commercialised with bar and pub owners building ever larger venues for pay-in performances. Ewan MacColl and Peggy Seeger on a visit to Dublin expressed concern to Kelly about his drinking.[citation needed] Christy Moore and Kelly became acquainted in the 1960s.During his Planxty days, Moore got to know Kelly well. In 1972 The Dubliners themselves performed in Richard's Cork Leg, based on the "incomplete works" of Brendan Behan. In 1973, Kelly took to the stage performing as King Herod in Jesus Christ Superstar. The arrival of a new manager for The Dubliners, Derry composer Phil Coulter, resulted in a collaboration that produced three of Kelly's most notable performances: “The Town I Loved So Well”, "Hand me Down my Bible", and “Scorn Not His Simplicity”, a song about Phil's son who had Down Syndrome.Kelly had such respect for the latter song that he only performed it once for a television recording and rarely, if ever, sang it at the Dubliners' often boisterous events. His interpretations of “On Raglan Road” and "Scorn Not His Simplicity" became significant points of reference in Irish folk music.His version of "Raglan Road" came about when the poem's author, Patrick Kavanagh, heard him singing in a Dublin pub, and approached Kelly to say that he should sing the poem (which is set to the tune of “The Dawning of the Day”). Kelly remained a politically engaged musician, becoming a supporter of the movement against South African apartheid and performing at benefit concerts for the Irish Traveller community,and many of the songs he recorded dealt with social issues, the arms race and the Cold War, trade unionism and Irish republicanism, ("The Springhill Disaster", "Joe Hill", "The Button Pusher", "Alabama 1958" and "God Save Ireland" all being examples of his concerns).Personal life
Luke Kelly married Deirdre O'Connell in 1965, but they separated in the early 1970s.Kelly spent the last eight years of his life living with his partner Madeleine Seiler, who is from Germany.Final years
Kelly's health deteriorated in the 1970s. Kelly himself spoke about his problems with alcohol. On 30 June 1980 during a concert in the Cork Opera House he collapsed on the stage. He had already suffered for some time from migraines and forgetfulness - including forgetting what country he was in whilst visiting Iceland - which had been ascribed to his intense schedule, alcohol consumption, and "party lifestyle". A brain tumour was diagnosed.Although Kelly toured with the Dubliners after enduring an operation, his health deteriorated further. He forgot lyrics and had to take longer breaks in concerts as he felt weak. In addition following his emergency surgery after his collapse in Cork, he became more withdrawn, preferring the company of Madeleine at home to performing.On his European tour he managed to perform with the band for most of the show in Carre for their Live in Carre album. However, in autumn 1983 he had to leave the stage in Traun, Austria and again in Mannheim, Germany. Shortly after this, he had to cancel the tour of southern Germany, and after a short stay in hospital in Heidelberg he was flown back to Dublin. After another operation he spent Christmas with his family but was taken into hospital again in the New Year, where he died on 30 January 1984.Kelly's funeral in Whitehall attracted thousands of mourners from across Ireland.His gravestone in Glasnevin Cemetery, Dublin, bears the inscription: Luke Kelly – Dubliner. Sean Cannon took Kelly's place in The Dubliners. He had been performing with the Dubliners since 1982,due to the deterioration of Kelly's health.Legacy
Luke Kelly's legacy and contributions to Irish music and culture have been described as "iconic" and have been captured in a number of documentaries and anthologies. The influence of his Scottish grandmother was influential in Kelly's help in preserving important traditional Scottish songs such as "Mormond Braes", the Canadian folk song "Peggy Gordon", "Robert Burns", "Parcel of Rogues", "Tibbie Dunbar", Hamish Henderson's "Freedom Come-All-Ye", and Thurso Berwick's "Scottish Breakaway". The Ballybough Bridge in the north inner city of Dublin was renamed the Luke Kelly Bridge, and in November 2004 Dublin City Council voted unanimously to erect a bronze statue of Luke Kelly. However, the Dublin Docklands Authority subsequently stated that it could no longer afford to fund the statue. In 2010, councillor Christy Burke of Dublin City Council appealed to members of the music community including Bono, Phil Coulter and Enya to help build it. Paddy Reilly recorded a tribute to Kelly entitled "The Dublin Minstrel". It featured on his Gold And Silver Years, Celtic Collections and the Essential Paddy Reilly CD's. The Dubliners recorded the song on their Live at Vicar Street DVD/CD. The song was composed by Declan O'Donoghue, the Racing Correspondent of The Irish Sun. At Christmas 2005 writer-director Michael Feeney Callan's documentary, Luke Kelly: The Performer, was released and outsold U2's latest DVD during the festive season and into 2006, acquiring platinum sales status. The documentary told Kelly's story through the words of the Dubliners, Donovan, Ralph McTell and others and featured full versions of rarely seen performances such as the early sixties' Ed Sullivan Show. A later documentary, Luke Kelly: Prince of the City, was also well received. Two statues of Kelly were unveiled in Dublin in January 2019, to mark the 35th anniversary of his death.One, a life-size seated bronze by John Coll, is on South King Street. The second sculpture, a marble portrait head by Vera Klute, is on Sheriff Street. The Klute sculpture was vandalised on several occasions in 2019 and 2020, in each case being restored by graffiti-removal specialists. Sculpture of Luke Kelly on Sheriff Street by Vera Klute. Unveiled in 2019
Sculpture of Luke Kelly on Sheriff Street by Vera Klute. Unveiled in 2019 -

 45cm x 34cm Aer Lingus was founded on 15 April 1936, with a capital of £100,000. Its first chairman was Seán Ó hUadhaigh.Pending legislation for Government investment through a parent company, Aer Lingus was associated with Blackpool and West Coast Air Services which advanced the money for the first aircraft, and operated with Aer Lingus under the common title "Irish Sea Airways". Aer Lingus Teoranta was registered as an airline on 22 May 1936.The name Aer Lingus was proposed by Richard F O'Connor, who was County Cork Surveyor, as well as an aviation enthusiast. On 27 May 1936, five days after being registered as an airline, its first service began between Baldonnel Airfield in Dublin and Bristol (Whitchurch) Airport, the United Kingdom, using a six-seater de Havilland DH.84 Dragon biplane (registration EI-ABI), named Iolar (Eagle). Later that year, the airline acquired its second aircraft, a four-engined biplane de Havilland DH.86 Express named "Éire", with a capacity of 14 passengers. This aircraft provided the first air link between Dublin and London by extending the Bristol service to Croydon. At the same time, the DH.84 Dragon was used to inaugurate an Aer Lingus service on the Dublin-Liverpool route. The airline was established as the national carrier under the Air Navigation and Transport Act (1936). In 1937, the Irish government created Aer Rianta (now called Dublin Airport Authority), a company to assume financial responsibility for the new airline and the entire country's civil aviation infrastructure. In April 1937, Aer Lingus became wholly owned by the Irish government via Aer Rianta. The airline's first General Manager was Dr J.F. (Jeremiah known as 'Jerry') Dempsey, a chartered accountant, who joined the company on secondment from Kennedy Crowley & Co (predecessor to KPMG as Company Secretary in 1936 (aged 30) and was appointed to the role of General Manager in 1937. He retired 30 years later in 1967 at the age of 60. In 1938, a de Havilland DH.89 Dragon Rapide replaced Iolar, and the company purchased a second DH.86B. Two Lockheed 14s arrived in 1939, Aer Lingus' first all-metal aircraft.In January 1940, a new airport opened in the Dublin suburb of Collinstown and Aer Lingus moved its operations there. It purchased a new DC-3 and inaugurated new services to Liverpool and an internal service to Shannon. The airline's services were curtailed during World War II with the sole route being to Liverpool or Barton Aerodrome Manchester depending on the fluctuating security situation.
45cm x 34cm Aer Lingus was founded on 15 April 1936, with a capital of £100,000. Its first chairman was Seán Ó hUadhaigh.Pending legislation for Government investment through a parent company, Aer Lingus was associated with Blackpool and West Coast Air Services which advanced the money for the first aircraft, and operated with Aer Lingus under the common title "Irish Sea Airways". Aer Lingus Teoranta was registered as an airline on 22 May 1936.The name Aer Lingus was proposed by Richard F O'Connor, who was County Cork Surveyor, as well as an aviation enthusiast. On 27 May 1936, five days after being registered as an airline, its first service began between Baldonnel Airfield in Dublin and Bristol (Whitchurch) Airport, the United Kingdom, using a six-seater de Havilland DH.84 Dragon biplane (registration EI-ABI), named Iolar (Eagle). Later that year, the airline acquired its second aircraft, a four-engined biplane de Havilland DH.86 Express named "Éire", with a capacity of 14 passengers. This aircraft provided the first air link between Dublin and London by extending the Bristol service to Croydon. At the same time, the DH.84 Dragon was used to inaugurate an Aer Lingus service on the Dublin-Liverpool route. The airline was established as the national carrier under the Air Navigation and Transport Act (1936). In 1937, the Irish government created Aer Rianta (now called Dublin Airport Authority), a company to assume financial responsibility for the new airline and the entire country's civil aviation infrastructure. In April 1937, Aer Lingus became wholly owned by the Irish government via Aer Rianta. The airline's first General Manager was Dr J.F. (Jeremiah known as 'Jerry') Dempsey, a chartered accountant, who joined the company on secondment from Kennedy Crowley & Co (predecessor to KPMG as Company Secretary in 1936 (aged 30) and was appointed to the role of General Manager in 1937. He retired 30 years later in 1967 at the age of 60. In 1938, a de Havilland DH.89 Dragon Rapide replaced Iolar, and the company purchased a second DH.86B. Two Lockheed 14s arrived in 1939, Aer Lingus' first all-metal aircraft.In January 1940, a new airport opened in the Dublin suburb of Collinstown and Aer Lingus moved its operations there. It purchased a new DC-3 and inaugurated new services to Liverpool and an internal service to Shannon. The airline's services were curtailed during World War II with the sole route being to Liverpool or Barton Aerodrome Manchester depending on the fluctuating security situation. An Aer Lingus Douglas DC-3 at Manchester Airport in 1948 wearing the first postwar livery.
An Aer Lingus Douglas DC-3 at Manchester Airport in 1948 wearing the first postwar livery.Post-war expansion
On 9 November 1945, regular services were resumed with an inaugural flight to London. From this point Aer Lingus aircraft, initially mostly Douglas DC-3s, were painted in a silver and green livery. The airline introduced its first flight attendants. In 1946, a new Anglo-Irish agreement gave Aer Lingus exclusive UK traffic rights from Ireland in exchange for a 40% holding by British Overseas Airways Corporation (BOAC) and British European Airways (BEA). Because of Aer Lingus' growth the airline bought seven new Vickers Viking aircraft in 1947, however, these proved to be uneconomical and were soon sold.In 1947, Aerlínte Éireann came into existence to operate transatlantic flights to New York City from Ireland. The airline ordered five new Lockheed L-749 Constellations, but a change of government and a financial crisis prevented the service from starting. John A Costello, the incoming Fine Gael Taoiseach (Prime Minister), was not a keen supporter of air travel and thought that flying the Atlantic was too grandiose a scheme for a small airline from a small country like Ireland. A Bristol 170 Freighter at Manchester Airport in 1953.During the late 1940s and early 1950s, Aer Lingus introduced routes to Brussels, Amsterdam via Manchester and to Rome. Because of the expanding route structure, the airline became one of the early purchasers of Vickers Viscount 700s in 1951, which were placed in service in April 1954. In 1952, the airline expanded its all-freight services and acquired a small fleet of Bristol 170 Freighters, which remained in service until 1957. Prof. Patrick Lynch was appointed the chairman of Aer Lingus and Aer Rianta in 1954 and served in the position until 1975. In 1956, Aer Lingus introduced a new, green-top livery with a white lightning flash down the windows and the Irish flag displayed on the fin.
A Bristol 170 Freighter at Manchester Airport in 1953.During the late 1940s and early 1950s, Aer Lingus introduced routes to Brussels, Amsterdam via Manchester and to Rome. Because of the expanding route structure, the airline became one of the early purchasers of Vickers Viscount 700s in 1951, which were placed in service in April 1954. In 1952, the airline expanded its all-freight services and acquired a small fleet of Bristol 170 Freighters, which remained in service until 1957. Prof. Patrick Lynch was appointed the chairman of Aer Lingus and Aer Rianta in 1954 and served in the position until 1975. In 1956, Aer Lingus introduced a new, green-top livery with a white lightning flash down the windows and the Irish flag displayed on the fin. A Vickers Viscount 808 in "green top" livery at Manchester Airport in 1963.
A Vickers Viscount 808 in "green top" livery at Manchester Airport in 1963.First transatlantic service
On 28 April 1958, Aerlínte Éireann operated its first transatlantic service from Shannon to New York.In 1960, Aerlínte Éireann was renamed Aer Lingus. Aer Lingus bought seven Fokker F27 Friendships, which were delivered between November 1958 and May 1959. These were used in short-haul services to the UK, gradually replacing the Dakotas, until Aer Lingus replaced them in 1966 with secondhand Viscount 800s. The airline entered the jet age on 14 December 1960 when it received three Boeing 720 for use on the New York route and the newest Aer Lingus destination Boston. In 1963, Aer Lingus added Aviation Traders Carvairs to the fleet. These aircraft could transport five cars which were loaded into the fuselage through the nose of the aircraft. The Carvair proved to be uneconomical for the airline partly due to the rise of auto ferry services, and the aircraft were used for freight services until disposed of. The Boeing 720s proved to be a success for the airline on the transatlantic routes. To supplement these, Aer Lingus took delivery of its first larger Boeing 707 in 1964, and the type continued to serve the airline until 1986. A Boeing 720 in Aer Lingus-Irish International livery in 1965.
A Boeing 720 in Aer Lingus-Irish International livery in 1965.Jet aircraft
Conversion of the European fleet to jet equipment began in 1965 when the BAC One-Eleven started services on continental Europe.The airline adopted a new livery in the same year, with a large green shamrock on the fin. In 1966, the remainder of the company's shares held by Aer Rianta were transferred to the Minister for Finance. A Fokker F27 Friendship at Manchester Airport in 1965. The F27 was used on short-haul services between 1958 and 1966.In 1966, the company added routes to Montreal and Chicago. In 1968, flights from Belfast, in Northern Ireland, to New York City started, however, it was soon suspended due to the beginning of the Troubles.Aer Lingus introduced Boeing 737s to its fleet in 1969 to cope with the high demand for flights between Dublin and London. Later, Aer Lingus extended the 737 flights to all of its European networks. In 1967, after 30 years of service, General Manager Dr J.F. Dempsey signed the contract for the airline's first two Boeing 747 aircraft before he retired later that year.
A Fokker F27 Friendship at Manchester Airport in 1965. The F27 was used on short-haul services between 1958 and 1966.In 1966, the company added routes to Montreal and Chicago. In 1968, flights from Belfast, in Northern Ireland, to New York City started, however, it was soon suspended due to the beginning of the Troubles.Aer Lingus introduced Boeing 737s to its fleet in 1969 to cope with the high demand for flights between Dublin and London. Later, Aer Lingus extended the 737 flights to all of its European networks. In 1967, after 30 years of service, General Manager Dr J.F. Dempsey signed the contract for the airline's first two Boeing 747 aircraft before he retired later that year. An Aviation Traders Carvair that was used as a vehicle freighter is seen loading a car at Bristol Airport in 1964.
An Aviation Traders Carvair that was used as a vehicle freighter is seen loading a car at Bristol Airport in 1964. -

 40cm x 34cm Hurling (Irish: iománaíocht, iomáint) is an outdoor team game of ancient Gaelic Irish origin, played by men. One of Ireland's native Gaelic games, it shares a number of features with Gaelic football, such as the field and goals, the number of players, and much terminology. There is a similar game for women called camogie (camógaíocht). It shares a common Gaelic root. The objective of the game is for players to use an ash wood stick called a hurley (in Irish a camán, pronounced /ˈkæmən/or /kəˈmɔːn/) to hit a small ball called a sliotar /ˈʃlɪtər/ between the opponents' goalposts either over the crossbar for one point, or under the crossbar into a net guarded by a goalkeeper for three points. The sliotar can be caught in the hand and carried for not more than four steps, struck in the air, or struck on the ground with the hurley. It can be kicked, or slapped with an open hand (the hand pass) for short-range passing. A player who wants to carry the ball for more than four steps has to bounce or balance the sliotar on the end of the stick, and the ball can only be handled twice while in the player’s possession. Provided that a player has at least one foot on the ground, a player may make a shoulder-to-shoulder charge on an opponent who is in possession of the ball or is playing the ball or when both players are moving in the direction of the ball to play it. No protective padding is worn by players. A plastic protective helmet with a faceguard is mandatory for all age groups, including senior level, as of 2010. The game has been described as "a bastion of humility", with player names absent from jerseys and a player's number decided by his position on the field. Hurling is administered by the Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA). It is played throughout the world, and is popular among members of the Irish diaspora in North America, Europe, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, Argentina, and South Korea. In many parts of Ireland, however, hurling is a fixture of life.It has featured regularly in art forms such as film, music and literature. The final of the All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship was listed in second place by CNN in its "10 sporting events you have to see live", after the Olympic Games and ahead of both the FIFA World Cup and UEFA European Championship.After covering the 1959 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship Final between Kilkenny and Waterford for BBC Television, English commentator Kenneth Wolstenholme was moved to describe hurling as his second favourite sport in the world after his first love, football.Alex Ferguson used footage of an All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship final in an attempt to motivate his players during his time as manager of Premier League football club Manchester United; the players winced at the standard of physicality and intensity in which the hurlers were engaged. In 2007, Forbes magazine described the media attention and population multiplication of Thurles town ahead of one of the game's annual provincial hurling finals as being "the rough equivalent of 30 million Americans watching a regional lacrosse game".Financial Times columnist Simon Kuper wrote after Stephen Bennett's performance in the 2020 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship Final that hurling was "the best sport ever and if the Irish had colonised the world, nobody would ever have heard of football" UNESCO lists hurling as an element of Intangible cultural heritage.
40cm x 34cm Hurling (Irish: iománaíocht, iomáint) is an outdoor team game of ancient Gaelic Irish origin, played by men. One of Ireland's native Gaelic games, it shares a number of features with Gaelic football, such as the field and goals, the number of players, and much terminology. There is a similar game for women called camogie (camógaíocht). It shares a common Gaelic root. The objective of the game is for players to use an ash wood stick called a hurley (in Irish a camán, pronounced /ˈkæmən/or /kəˈmɔːn/) to hit a small ball called a sliotar /ˈʃlɪtər/ between the opponents' goalposts either over the crossbar for one point, or under the crossbar into a net guarded by a goalkeeper for three points. The sliotar can be caught in the hand and carried for not more than four steps, struck in the air, or struck on the ground with the hurley. It can be kicked, or slapped with an open hand (the hand pass) for short-range passing. A player who wants to carry the ball for more than four steps has to bounce or balance the sliotar on the end of the stick, and the ball can only be handled twice while in the player’s possession. Provided that a player has at least one foot on the ground, a player may make a shoulder-to-shoulder charge on an opponent who is in possession of the ball or is playing the ball or when both players are moving in the direction of the ball to play it. No protective padding is worn by players. A plastic protective helmet with a faceguard is mandatory for all age groups, including senior level, as of 2010. The game has been described as "a bastion of humility", with player names absent from jerseys and a player's number decided by his position on the field. Hurling is administered by the Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA). It is played throughout the world, and is popular among members of the Irish diaspora in North America, Europe, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, Argentina, and South Korea. In many parts of Ireland, however, hurling is a fixture of life.It has featured regularly in art forms such as film, music and literature. The final of the All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship was listed in second place by CNN in its "10 sporting events you have to see live", after the Olympic Games and ahead of both the FIFA World Cup and UEFA European Championship.After covering the 1959 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship Final between Kilkenny and Waterford for BBC Television, English commentator Kenneth Wolstenholme was moved to describe hurling as his second favourite sport in the world after his first love, football.Alex Ferguson used footage of an All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship final in an attempt to motivate his players during his time as manager of Premier League football club Manchester United; the players winced at the standard of physicality and intensity in which the hurlers were engaged. In 2007, Forbes magazine described the media attention and population multiplication of Thurles town ahead of one of the game's annual provincial hurling finals as being "the rough equivalent of 30 million Americans watching a regional lacrosse game".Financial Times columnist Simon Kuper wrote after Stephen Bennett's performance in the 2020 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship Final that hurling was "the best sport ever and if the Irish had colonised the world, nobody would ever have heard of football" UNESCO lists hurling as an element of Intangible cultural heritage. -

 45cm x 34cm The Midland Great Western Railway (MGWR) was the third largest Irish gauge (1,600 mm (5 ft 3 in)) railway company in Ireland. It was incorporated in 1845 and absorbed into the Great Southern Railways in 1924. At its peak the MGWR had a network of 538 miles (866 km), making it Ireland's third largest network after the Great Southern and Western Railway(GS&WR) and the Great Northern Railway of Ireland. The MGWR served part of Leinster, County Cavan in Ulster and much of Connacht. Its network was entirely within what in 1922 became the Irish Free State.
45cm x 34cm The Midland Great Western Railway (MGWR) was the third largest Irish gauge (1,600 mm (5 ft 3 in)) railway company in Ireland. It was incorporated in 1845 and absorbed into the Great Southern Railways in 1924. At its peak the MGWR had a network of 538 miles (866 km), making it Ireland's third largest network after the Great Southern and Western Railway(GS&WR) and the Great Northern Railway of Ireland. The MGWR served part of Leinster, County Cavan in Ulster and much of Connacht. Its network was entirely within what in 1922 became the Irish Free State.Early development
The Midland Great Western Railway Act received the Royal Assent in July 1845, authorising it to raise £1,000,000 capitaland to build a railway from Dublin to Mullingar and Longford and to buy the Royal Canal. Construction of the main line began from Dublin in January 1846 and proceeded westwards in stages, supervised by chief engineer G. W. Hemans. It opened from Dublin Broadstoneas far as Enfield in May 1847,to Hill of Down in December 1847 and to Mullingar in October 1848Dublin to Galway
Rivalry existed between the MGWR and the GS&WR, each of which wanted to build the line to Galway. The MGWR extended its line from Mullingar and the GS&WR from its line at Portarlington. The MGWR was first, going via Athlone and reaching Galway, 126.5 miles (203.6 km) from Dublin, in August 1851.It was not until 1859 that the GS&WR got as far as Athlone. The GS&WR was obliged to operate its service over MGWR track between Athlone and Galway, paying the MGWR 65% of passenger and 55% of goods receipts. The GS&WR retained a separate station, which is now the sole operating station, as the last service to the MGWR station ran on 13 January 1985.. The branch is to be made into a rail trail as part of the Dublin-Galway Greenway by 2020.Galway to Clifden
In 1890 the Government granted the MGWR £264,000 to build a railway to Clifdenon the Atlantic coast of County Galway. It opened as far as Oughterard in January 1895 and to Clifden in July 1895.Due to its inland route it did not serve the bulk of the area's population, so the GSR closed it in 1935. A similar branch line was built at the same time from Westport to Achill on the Atlantic coast of County Mayo. The MGW built the first section, opening it as far as Newport in February 1894 and Mulranny in May 1894.The Board of Works built the section from Mulranny to Achill, which opened in May 1895.The GSR closed the line in 1937.Branch lines
At its peak the MGWR had a number of branch lines: Tunnel at Newport on the Westport to Achill branch line.
Tunnel at Newport on the Westport to Achill branch line.- Clonsilla to Navan (opened as the Dublin and Meath Railway 1862, leased to the MGWR 1869, sold to the MGWR 1888)
- extension from Navan to Kingscourt, (opened by the Navan and Kingscourt Railway 1865, sold to the MGWR 1888)
- Kilmessan Junction to Athboy (opened 1864, closed 1963)
- Nesbitt Junction (near Enfield) to Edenderry (opened 1877, closed 1963)
- Streamstown to Clara, County Offaly (opened 1863, closed 1963)
- Attymon Junction to Loughrea (light railway worked by the MGWR, opened 1890)
- Galway to Clifden (opened 1895, closed 1935)
- Westport to Achill (opened 1895, closed 1937)
- Inny Junction to Cavan Town (opened 1856, closed 1960)
- Kilfree Junction railway station to Ballaghaderreen (opened by the Sligo and Ballaghaderreen Railway 1874, sold to the MGWR 1877, closed 1963)
- Crossdoney to Killeshandra (opened 1886, closed 1960)
- Athlone to Westport (opened by the Great Northern and Western Railway 1860–66, leased to the MGWR 1870, sold to the MGWR 1890)
- Claremorris to Ballinrobe (light railway worked by the MGWR, opened 1892, closed 1960)
- Manulla to Ballina, County Mayo (opened 1873)
- extension from Ballina to Killala (opened 1893, closed 1937)
Consolidation
In 1924 the Oireachtas of the Irish Free State passed the Railways Act, which that November merged the MGWR with the Great Southern and Western Railway(GS&WR), Cork, Bandon and South Coast Railway to form the Great Southern Railway. In January 1925, that was joined by the Dublin and South Eastern Railwayto form the Great Southern Railways.Locomotives and rolling stock
Locomotives and rolling stock were maintained at MGWR's Broadstone works in Dublin.Livery
The MGWR painted all of its locomotives bright emeralduntil about 1902, when the first of the new Class A 4-4-0 express locomotives were outshopped in royal blue.This did not wear well and in 1905 the company adopted grass green. From about 1913 locos were painted gloss blackuntil the MGWR became part of the GSR in 1925. From then on, all locomotives were gradually repainted plain unlined dark grey. Passenger coaches were finished in varnish or brown paint until the blue livery was introduced in 1901. As on the locomotives this weathered badly and from 1905 the MGWR reverted to brown,which after 1910 was not so well-adorned with lining.From October 1918 coaches were painted a very dark Crimson and after 1924 the GSR used a similar shade for some years.Preservation
No MGWR locomotive has been preserved but several of its six-wheeled carriages exist.- No. 25 - Downpatrick and County Down Railway. Originally a full 2nd, this coach is on display in the carriage gallery awaiting restoration.
- No. 47 - Ulster Folk and Transport Museum. Built in 1844 and notable for being used as William Dargan's private saloon. Fully restored.
- No. 47M - This carriage used to be based at the DCDR, but unfortunately had to be scrapped.
- No. 53 - Downpatrick and County Down Railway. Originally a full 2nd, this coach is on display in the carriage gallery awaiting restoration.
- No. 62M - Railway Preservation Society of Ireland. A full 3rd, this carriage is meant to be under restoration for use at the DCDR.
- No. 84 - Clifden. Intended to be restored as part of the Station House Hotel's collection.
Present day
Those of the former MGWR's main lines that are still open are owned and operated by Iarnród Éireann. Routes between Dublin and Sligo, Athlone and Galway, Athlone and Westport and the Ballina branch remain open to passenger traffic. The Meath on Track campaign is campaigning to have the Navan — Clonsilla line (not to be confused with the former GNR Navan — Drogheda line) reopened earlier than the 2030 date announced under current Iarnród Éireann policy.The Edenderry, Clifden, Achill, Cavan, Killeshandra, Ballaghaderreen branch line, Ballinrobe, Killala and Loughrea branches lines are all closed. Rail Users Ireland proposed running some Galway — Dublin services via the MGWR station in Athlone and the disused route via Moate to Mullingar, reinstating the route of the first MGWR service via the former GS&WR line. The current Galway service runs from Dublin Heuston. This proposal will not go ahead as the railway is due to be replaced with the Dublin-Galway greenway starting from 2020. Three former MGWR stations are now hotels, two of which are called the "Station House Hotel" but are unconnected by ownership. They are the expanded former Clifden station in County Galway, Kilmessan Junction in County Meath and the Mullranny Park Hotel at Mulranny, County Mayo. The Great Western Greenway is a greenway rail trail that uses the route of the former Westport — Achill branch line. -
 45cm x 34cm The old Smithwicks brewery is on the site of a Franciscan abbey, where monks had brewed ale since the 14th century, and ruins of the original abbey still remain on its grounds. The old brewery has since been renovated and now hosts "The Smithwick's Experience Kilkenny" visitor attraction and centre.At the time of its closure, it was Ireland's oldest operating brewery. John Smithwick was an orphan who had settled in Kilkenny. Shortly after his arrival, Smithwick went into the brewing business with Richard Cole on a piece of land that Cole had leased from the Duke of Ormond in 1705. Five years later, John Smithwick became the owner of the land. The brewery stayed small, servicing a loyal local following while John Smithwick diversified. Following John Smithwick's death, the brewery temporarily fell out of family hands. John Smithwick's great grandson, Edmond bought the brewery land back freehold and worked to reshape its future. Edmond concentrated on discovering new markets and successfully building export trade. Drinkers in England, Scotland and Wales developed a taste for Smithwick's brews and output increased fivefold. As a result of substantial contributions made to St Mary's Cathedral, Edmond became great friends with Irish liberal Daniel O'Connell, who later became godfather to one of his sons. Edmond Smithwick became well known and respected by the people of Kilkenny who elected him town mayor four times. In 1800, export sales began to fall and the brewing industry encountered difficulty. To combat this, the Smithwick family increased production in their maltings, began selling mineral water and delivered butter with the ale from the back of their drays.By 1900, output was at an all-time low and the then owner James Smithwick was advised by auditors to shut the doors of the brewery. Instead, James reduced the range of beers they produced and set out to find new markets. He secured military contracts and soon after saw output increase again. James' son, Walter, took control in 1930 and steered the brewery to success through the hardships of both World War II and increasingly challenging weather conditions.By January 1950, Smithwick's was exporting ale to Boston.Smithwick's was purchased from Walter Smithwick in 1965 by Guinness and is now, along with Guinness, part of Diageo. Together, Guinness & Co. and Smithwick's developed and launched Smithwick's Draught Ale in 1966. By 1979, half a million barrels were sold each year.In 1980, Smithwick's began exporting to France. In 1993, Smithwick's Draught became Canada's leading imported ale.By 2010, Smithwick's continued to be brewed in Dundalk and Kilkenny with tankers sent to Dublin to be kegged for the on trade market. Cans and bottles were packaged by IBC in Belfast.Production in the Kilkenny brewery finished on 31 December 2013 and Smithwicks brands are now produced in the Diageo St.James' Gate brewery in Dublin.The original Kilkenny site was sold to Kilkenny County Council, with a small portion of the site dedicated to the opening of a visitor's centre, the "Smithwick's Experience Kilkenny".
45cm x 34cm The old Smithwicks brewery is on the site of a Franciscan abbey, where monks had brewed ale since the 14th century, and ruins of the original abbey still remain on its grounds. The old brewery has since been renovated and now hosts "The Smithwick's Experience Kilkenny" visitor attraction and centre.At the time of its closure, it was Ireland's oldest operating brewery. John Smithwick was an orphan who had settled in Kilkenny. Shortly after his arrival, Smithwick went into the brewing business with Richard Cole on a piece of land that Cole had leased from the Duke of Ormond in 1705. Five years later, John Smithwick became the owner of the land. The brewery stayed small, servicing a loyal local following while John Smithwick diversified. Following John Smithwick's death, the brewery temporarily fell out of family hands. John Smithwick's great grandson, Edmond bought the brewery land back freehold and worked to reshape its future. Edmond concentrated on discovering new markets and successfully building export trade. Drinkers in England, Scotland and Wales developed a taste for Smithwick's brews and output increased fivefold. As a result of substantial contributions made to St Mary's Cathedral, Edmond became great friends with Irish liberal Daniel O'Connell, who later became godfather to one of his sons. Edmond Smithwick became well known and respected by the people of Kilkenny who elected him town mayor four times. In 1800, export sales began to fall and the brewing industry encountered difficulty. To combat this, the Smithwick family increased production in their maltings, began selling mineral water and delivered butter with the ale from the back of their drays.By 1900, output was at an all-time low and the then owner James Smithwick was advised by auditors to shut the doors of the brewery. Instead, James reduced the range of beers they produced and set out to find new markets. He secured military contracts and soon after saw output increase again. James' son, Walter, took control in 1930 and steered the brewery to success through the hardships of both World War II and increasingly challenging weather conditions.By January 1950, Smithwick's was exporting ale to Boston.Smithwick's was purchased from Walter Smithwick in 1965 by Guinness and is now, along with Guinness, part of Diageo. Together, Guinness & Co. and Smithwick's developed and launched Smithwick's Draught Ale in 1966. By 1979, half a million barrels were sold each year.In 1980, Smithwick's began exporting to France. In 1993, Smithwick's Draught became Canada's leading imported ale.By 2010, Smithwick's continued to be brewed in Dundalk and Kilkenny with tankers sent to Dublin to be kegged for the on trade market. Cans and bottles were packaged by IBC in Belfast.Production in the Kilkenny brewery finished on 31 December 2013 and Smithwicks brands are now produced in the Diageo St.James' Gate brewery in Dublin.The original Kilkenny site was sold to Kilkenny County Council, with a small portion of the site dedicated to the opening of a visitor's centre, the "Smithwick's Experience Kilkenny". -

 48cm x 35cm Aer Lingus was founded on 15 April 1936, with a capital of £100,000. Its first chairman was Seán Ó hUadhaigh.Pending legislation for Government investment through a parent company, Aer Lingus was associated with Blackpool and West Coast Air Services which advanced the money for the first aircraft, and operated with Aer Lingus under the common title "Irish Sea Airways". Aer Lingus Teoranta was registered as an airline on 22 May 1936.The name Aer Lingus was proposed by Richard F O'Connor, who was County Cork Surveyor, as well as an aviation enthusiast. On 27 May 1936, five days after being registered as an airline, its first service began between Baldonnel Airfield in Dublin and Bristol (Whitchurch) Airport, the United Kingdom, using a six-seater de Havilland DH.84 Dragon biplane (registration EI-ABI), named Iolar (Eagle). Later that year, the airline acquired its second aircraft, a four-engined biplane de Havilland DH.86 Express named "Éire", with a capacity of 14 passengers. This aircraft provided the first air link between Dublin and London by extending the Bristol service to Croydon. At the same time, the DH.84 Dragon was used to inaugurate an Aer Lingus service on the Dublin-Liverpool route. The airline was established as the national carrier under the Air Navigation and Transport Act (1936). In 1937, the Irish government created Aer Rianta (now called Dublin Airport Authority), a company to assume financial responsibility for the new airline and the entire country's civil aviation infrastructure. In April 1937, Aer Lingus became wholly owned by the Irish government via Aer Rianta. The airline's first General Manager was Dr J.F. (Jeremiah known as 'Jerry') Dempsey, a chartered accountant, who joined the company on secondment from Kennedy Crowley & Co (predecessor to KPMG as Company Secretary in 1936 (aged 30) and was appointed to the role of General Manager in 1937. He retired 30 years later in 1967 at the age of 60. In 1938, a de Havilland DH.89 Dragon Rapide replaced Iolar, and the company purchased a second DH.86B. Two Lockheed 14s arrived in 1939, Aer Lingus' first all-metal aircraft.In January 1940, a new airport opened in the Dublin suburb of Collinstown and Aer Lingus moved its operations there. It purchased a new DC-3 and inaugurated new services to Liverpool and an internal service to Shannon. The airline's services were curtailed during World War II with the sole route being to Liverpool or Barton Aerodrome Manchester depending on the fluctuating security situation.
48cm x 35cm Aer Lingus was founded on 15 April 1936, with a capital of £100,000. Its first chairman was Seán Ó hUadhaigh.Pending legislation for Government investment through a parent company, Aer Lingus was associated with Blackpool and West Coast Air Services which advanced the money for the first aircraft, and operated with Aer Lingus under the common title "Irish Sea Airways". Aer Lingus Teoranta was registered as an airline on 22 May 1936.The name Aer Lingus was proposed by Richard F O'Connor, who was County Cork Surveyor, as well as an aviation enthusiast. On 27 May 1936, five days after being registered as an airline, its first service began between Baldonnel Airfield in Dublin and Bristol (Whitchurch) Airport, the United Kingdom, using a six-seater de Havilland DH.84 Dragon biplane (registration EI-ABI), named Iolar (Eagle). Later that year, the airline acquired its second aircraft, a four-engined biplane de Havilland DH.86 Express named "Éire", with a capacity of 14 passengers. This aircraft provided the first air link between Dublin and London by extending the Bristol service to Croydon. At the same time, the DH.84 Dragon was used to inaugurate an Aer Lingus service on the Dublin-Liverpool route. The airline was established as the national carrier under the Air Navigation and Transport Act (1936). In 1937, the Irish government created Aer Rianta (now called Dublin Airport Authority), a company to assume financial responsibility for the new airline and the entire country's civil aviation infrastructure. In April 1937, Aer Lingus became wholly owned by the Irish government via Aer Rianta. The airline's first General Manager was Dr J.F. (Jeremiah known as 'Jerry') Dempsey, a chartered accountant, who joined the company on secondment from Kennedy Crowley & Co (predecessor to KPMG as Company Secretary in 1936 (aged 30) and was appointed to the role of General Manager in 1937. He retired 30 years later in 1967 at the age of 60. In 1938, a de Havilland DH.89 Dragon Rapide replaced Iolar, and the company purchased a second DH.86B. Two Lockheed 14s arrived in 1939, Aer Lingus' first all-metal aircraft.In January 1940, a new airport opened in the Dublin suburb of Collinstown and Aer Lingus moved its operations there. It purchased a new DC-3 and inaugurated new services to Liverpool and an internal service to Shannon. The airline's services were curtailed during World War II with the sole route being to Liverpool or Barton Aerodrome Manchester depending on the fluctuating security situation. An Aer Lingus Douglas DC-3 at Manchester Airport in 1948 wearing the first postwar livery.
An Aer Lingus Douglas DC-3 at Manchester Airport in 1948 wearing the first postwar livery.Post-war expansion
On 9 November 1945, regular services were resumed with an inaugural flight to London. From this point Aer Lingus aircraft, initially mostly Douglas DC-3s, were painted in a silver and green livery. The airline introduced its first flight attendants. In 1946, a new Anglo-Irish agreement gave Aer Lingus exclusive UK traffic rights from Ireland in exchange for a 40% holding by British Overseas Airways Corporation (BOAC) and British European Airways (BEA). Because of Aer Lingus' growth the airline bought seven new Vickers Viking aircraft in 1947, however, these proved to be uneconomical and were soon sold.In 1947, Aerlínte Éireann came into existence to operate transatlantic flights to New York City from Ireland. The airline ordered five new Lockheed L-749 Constellations, but a change of government and a financial crisis prevented the service from starting. John A Costello, the incoming Fine Gael Taoiseach (Prime Minister), was not a keen supporter of air travel and thought that flying the Atlantic was too grandiose a scheme for a small airline from a small country like Ireland. A Bristol 170 Freighter at Manchester Airport in 1953.During the late 1940s and early 1950s, Aer Lingus introduced routes to Brussels, Amsterdam via Manchester and to Rome. Because of the expanding route structure, the airline became one of the early purchasers of Vickers Viscount 700s in 1951, which were placed in service in April 1954. In 1952, the airline expanded its all-freight services and acquired a small fleet of Bristol 170 Freighters, which remained in service until 1957. Prof. Patrick Lynch was appointed the chairman of Aer Lingus and Aer Rianta in 1954 and served in the position until 1975. In 1956, Aer Lingus introduced a new, green-top livery with a white lightning flash down the windows and the Irish flag displayed on the fin.
A Bristol 170 Freighter at Manchester Airport in 1953.During the late 1940s and early 1950s, Aer Lingus introduced routes to Brussels, Amsterdam via Manchester and to Rome. Because of the expanding route structure, the airline became one of the early purchasers of Vickers Viscount 700s in 1951, which were placed in service in April 1954. In 1952, the airline expanded its all-freight services and acquired a small fleet of Bristol 170 Freighters, which remained in service until 1957. Prof. Patrick Lynch was appointed the chairman of Aer Lingus and Aer Rianta in 1954 and served in the position until 1975. In 1956, Aer Lingus introduced a new, green-top livery with a white lightning flash down the windows and the Irish flag displayed on the fin. A Vickers Viscount 808 in "green top" livery at Manchester Airport in 1963.
A Vickers Viscount 808 in "green top" livery at Manchester Airport in 1963.First transatlantic service
On 28 April 1958, Aerlínte Éireann operated its first transatlantic service from Shannon to New York.In 1960, Aerlínte Éireann was renamed Aer Lingus. Aer Lingus bought seven Fokker F27 Friendships, which were delivered between November 1958 and May 1959. These were used in short-haul services to the UK, gradually replacing the Dakotas, until Aer Lingus replaced them in 1966 with secondhand Viscount 800s. The airline entered the jet age on 14 December 1960 when it received three Boeing 720 for use on the New York route and the newest Aer Lingus destination Boston. In 1963, Aer Lingus added Aviation Traders Carvairs to the fleet. These aircraft could transport five cars which were loaded into the fuselage through the nose of the aircraft. The Carvair proved to be uneconomical for the airline partly due to the rise of auto ferry services, and the aircraft were used for freight services until disposed of. The Boeing 720s proved to be a success for the airline on the transatlantic routes. To supplement these, Aer Lingus took delivery of its first larger Boeing 707 in 1964, and the type continued to serve the airline until 1986. A Boeing 720 in Aer Lingus-Irish International livery in 1965.
A Boeing 720 in Aer Lingus-Irish International livery in 1965.Jet aircraft
Conversion of the European fleet to jet equipment began in 1965 when the BAC One-Eleven started services on continental Europe.The airline adopted a new livery in the same year, with a large green shamrock on the fin. In 1966, the remainder of the company's shares held by Aer Rianta were transferred to the Minister for Finance. A Fokker F27 Friendship at Manchester Airport in 1965. The F27 was used on short-haul services between 1958 and 1966.In 1966, the company added routes to Montreal and Chicago. In 1968, flights from Belfast, in Northern Ireland, to New York City started, however, it was soon suspended due to the beginning of the Troubles.Aer Lingus introduced Boeing 737s to its fleet in 1969 to cope with the high demand for flights between Dublin and London. Later, Aer Lingus extended the 737 flights to all of its European networks. In 1967, after 30 years of service, General Manager Dr J.F. Dempsey signed the contract for the airline's first two Boeing 747 aircraft before he retired later that year.
A Fokker F27 Friendship at Manchester Airport in 1965. The F27 was used on short-haul services between 1958 and 1966.In 1966, the company added routes to Montreal and Chicago. In 1968, flights from Belfast, in Northern Ireland, to New York City started, however, it was soon suspended due to the beginning of the Troubles.Aer Lingus introduced Boeing 737s to its fleet in 1969 to cope with the high demand for flights between Dublin and London. Later, Aer Lingus extended the 737 flights to all of its European networks. In 1967, after 30 years of service, General Manager Dr J.F. Dempsey signed the contract for the airline's first two Boeing 747 aircraft before he retired later that year. An Aviation Traders Carvair that was used as a vehicle freighter is seen loading a car at Bristol Airport in 1964.
An Aviation Traders Carvair that was used as a vehicle freighter is seen loading a car at Bristol Airport in 1964. -

 48cm x 35cm
48cm x 35cmIt was Richie Connor in the early 1990s who first introduced me to the concept. For the Offaly team he captained, ultimately to the 1982 All-Ireland, beating Dublin in the 1980 Leinster final had he said been their most significant achievement.
This was because winning the province represented a longer journey from where the team under Eugene McGee had started than the distance from there to the Sam Maguire.
Maybe the reasoning was slightly different in Clare but it amounted to the same thing. In the few weeks that shimmered in the radiant summer of 1995 between winning Munster and the All-Ireland semi-final against Galway, manager Ger Loughnane was certainly of that view.
“In Clare, Munster is the Mount Everest. All along Munster was what was talked about. I remember stopping Nenagh on the way back from the League final and a man saying, ‘if only we could win Munster once, it would make up for everything’.
“The reaction to our winning Munster has been far greater than what would happen in other counties if they won an All-Ireland.”
Clare had got to the stage where they were being upstaged by their footballers whose first Munster title since 1917 had been sensationally won in 1992 leaving the hurlers by-passed.
Anthony Daly, prominent in 1995 as the exuberant captain of the hurlers, remembered the big-ball community’s notions. He went to support the footballers in their All-Ireland semi-final against Dublin three years previously. In a bar beforehand he was mocked for band-wagoning.
“Do you go to our matches at all,” asks Daly.
“I do, I do,” comes the response.
“And when you do, does anyone ever tell you to f*** off back to west Clare?”
Boom, boom.
Climbed Everest
Twenty-five years ago today (Thursday) the county hurlers climbed Everest and in unexpected style. Clare had qualified for a third successive Munster final but the previous two, against Limerick and Tipperary had ended in heavy defeats.
This season would be different. Loughnane’s elevation from selector to manager crystallised the potential that his predecessor Len Gaynor had harnessed to reach Munster finals in 1993 and ‘94. They had taken the lessons of losing to a Zen level.
I remember seeing Loughnane and his selectors Mike McNamara and Tony Considine sitting in the Queens Hotel in Ennis after a league match with a fairly full-strength Tipperary.

Clare’s James O’Connor is challenged by Limerick’s Gary Kirby during the 1995 Munster final. Photograph: Tom Honan/Inpho They were super-pleased with the win, one of a number of markers laid down in a season that ended with defeat in the final against Kilkenny after which the manager famously declared that they would win Munster. The approach had been clear: find some new players, get incredibly fit and start beating likely rivals.
The winter had been a time of slog under McNamara’s fundamentalist training but the late spring with its brightening nights would be a time for sharpening the hurling and adding speed to their playbook.
“In a way the League final was the best thing that happened us,” said Loughnane after the provincial success. “All the old failings were there. We were too tense: all frenzy, no method. We were going to have to use our heads. If we’d won the League we definitely wouldn’t have won the Munster championship.”
Limerick were in a valley season between two demoralising All-Ireland final defeats but were raging favourites, having beaten Tipperary while Clare had laboured to get past Cork.
Clare also had their past, 11 Munster final defeats since the previous win in 1932 and well beaten by Limerick the previous year. The League final defeat a mere two months previously didn’t help the argument that the team had the ability to win big matches.
As a match it doesn’t look great these days. There are too many errors and too much imprecision in the play. Limerick look lethargic and off-key. They play the first half with the advantage of a strong wind but trail at half-time.
In a low-scoring, scrappy affair Clare aren’t doing themselves justice either but for a team,who had been trimmed in their previous finals they’re hanging in there for most of the first half. In other words the match isn’t getting away from them, either - which is an improvement on the recent past.
Davy Fitzgerald
Goalkeeper Davy Fitzgerald’s expertly hit penalty edges Clare in front and tactically they have taken a grip. Fitzgerald is also excellent in goal producing a couple of saves that prevent Limerick from getting too involved.
Ollie Baker, of whom a lot had been expected when he was drafted into the team for the league, has a non-stop match, physically overshadowing the powerful Limerick pairing of Mike Houlihan and Seán O’Neill and beside him James O’Connor overcomes a difficult start and is on to everything, fast and fluent.
His six points include four from play and his only failure of marksmanship is a shot that hits the post late in the match. PJ O’Connell also gets four from play but is selected as MOTM for the job done on disorientating Ciarán Carey with his constant movement.

Clare captain Anthony Daly with the trophy after his side’s 1995 Munster final win over Limerick. Tom Honan/Inpho “I knew I had to keep Ciarán Carey away from the puck-outs,” he says afterwards, “so I kept him running around. I had done a lot of work for this and I knew I would not get winded or caught for pace. I just kept running him and I could see it was having an effect.”
Seán McMahon broke his collarbone in the semi-final against Cork and returns for the final a week earlier than ideal but thrives as Gary Kirby, who had destroyed him a year previously, falters.
Clare’s grip tightens. Limerick manage just four points in the second half, as the winners pull away steadily.
Stunning win
It’s a stunning win - a tribute to Loughnane, who in the years before the acid erosion of controversies and fallings-out is a charismatic leader, whose prescriptions were single-mindedly adopted by the players and embraced by the Clare public.
“The feeling was that at long last a barrier had been broken,” he said before the All-Ireland semi-final. “The atmosphere in the county was incredible. It was great for the footballers a couple of years ago but they hadn’t been waiting and failing the way the hurlers had for years and years and years. It was very emotional, more because it was so unexpected after Limerick trouncing Clare last year. A good few didn’t even go to Thurles because they were afraid.”

Clare captain Anthony Daly at the county’s homecoming in 1995. Photograph: Inpho For those few weeks, they are on the cusp of history, something almost spiritual. In the week before the Galway semi-final, Loughnane recounted how he had happened upon a car accident.
He hurries to check on the elderly motorist, who is shaken but not injured. They are joined by a third man.
“This other fella is looking at me and says, ‘Ger, isn’t it?’ I said, ‘yes’ and he says to the poor old man: ‘It’s Ger Loughnane! Isn’t that enough to make you better?’”
A nurse arrives with the ambulance and pauses to comment.
“I hope everything’s right for Sunday.”
Need she have asked in that summer of summers?
-

 45cm x 35cm I got this piece of interesting information from ‘The Unquiet Grave‘, The Development of Kerry’s Burial Grounds through the Ages – that very interesting book edited by Michael Connolly for Kerry County Council. The chapter on A Tale of Two Tombs tells the fascinating story of the rise and fall of the Donovan family of Tralee, who were wealthy merchants in the town through three generations in 1800’s. Some of you will remember that the Donovans also owned the Jeanie Johnston, which was the Donovan’s most important ship carrying emigrants on the outward journey to Quebec and bringing cargoes of timber back on the return voyage. John Donovan was the founding father and set up a hardware business initially in the Square, Tralee and then branched out leasing and owning shipping bringing iron, coal and slate to Tralee. His sons Nicholas and Henry followed him, they also became the leading political as well as the leading merchants in the town. There is a brilliant description of John’s funeral . He died in 1864 when he was 82 and we are told ‘All the stops were pulled out for the full pageantry of Victorian obsequies’. The Kerry Evening Post reported ‘an unusual grief had fallen upon the town’. According to the same newspaper there were 174 carriages, and there was an important extra little detail -‘the majority were drawn by two horses’ – a two-horse carriage indicated greater social standing than a one-horse carriage’ Try and get hold of this very interesting book from the County Council or log on here for the digital version. And were there any women there at all? Yes, but they were there with a purpose – to provide the all important keening that was then the expected norm at all funerals of all classes. At this funeral we are told ‘The poor of the town, beneficiaries of John Donovan’s generosity, congregated outside the house in The Square, and when the coffin was removed to the hearse, they set up an immense keening, which they continued as they followed the funeral all the way to Ballyseedy’. Another interesting fact relating to women and their own funerals at this time was that ‘while men were buried in the middle of the day, the women, on the other hand were buried early in the morning, regardless of the time of year’. John Donovan’s own wife Catherine was buried in the dark at 6am on a February morning and Nicholas’ wife was buried at the same time in December 1878. ‘Only Henry’s wife was buried in daylight and that was because the burial was at 8am on an August morning in 1885. The higher status of men was constantly affirmed. We have come a long way!
45cm x 35cm I got this piece of interesting information from ‘The Unquiet Grave‘, The Development of Kerry’s Burial Grounds through the Ages – that very interesting book edited by Michael Connolly for Kerry County Council. The chapter on A Tale of Two Tombs tells the fascinating story of the rise and fall of the Donovan family of Tralee, who were wealthy merchants in the town through three generations in 1800’s. Some of you will remember that the Donovans also owned the Jeanie Johnston, which was the Donovan’s most important ship carrying emigrants on the outward journey to Quebec and bringing cargoes of timber back on the return voyage. John Donovan was the founding father and set up a hardware business initially in the Square, Tralee and then branched out leasing and owning shipping bringing iron, coal and slate to Tralee. His sons Nicholas and Henry followed him, they also became the leading political as well as the leading merchants in the town. There is a brilliant description of John’s funeral . He died in 1864 when he was 82 and we are told ‘All the stops were pulled out for the full pageantry of Victorian obsequies’. The Kerry Evening Post reported ‘an unusual grief had fallen upon the town’. According to the same newspaper there were 174 carriages, and there was an important extra little detail -‘the majority were drawn by two horses’ – a two-horse carriage indicated greater social standing than a one-horse carriage’ Try and get hold of this very interesting book from the County Council or log on here for the digital version. And were there any women there at all? Yes, but they were there with a purpose – to provide the all important keening that was then the expected norm at all funerals of all classes. At this funeral we are told ‘The poor of the town, beneficiaries of John Donovan’s generosity, congregated outside the house in The Square, and when the coffin was removed to the hearse, they set up an immense keening, which they continued as they followed the funeral all the way to Ballyseedy’. Another interesting fact relating to women and their own funerals at this time was that ‘while men were buried in the middle of the day, the women, on the other hand were buried early in the morning, regardless of the time of year’. John Donovan’s own wife Catherine was buried in the dark at 6am on a February morning and Nicholas’ wife was buried at the same time in December 1878. ‘Only Henry’s wife was buried in daylight and that was because the burial was at 8am on an August morning in 1885. The higher status of men was constantly affirmed. We have come a long way! -

 42cm x 31cm
42cm x 31cmSpeaking to the Irish Times in 2007 about the Rolling Stones’s 1982 concert, Slane Castle owner Lord Henry Mount Charles said Ireland had never seen anything like it before.
“The weather was beautiful, the show was magic. Mick Jagger came down the Thursday before the show and had dinner in the castle and the production crew slept in the drawing room of the castle the night before the show. It had an almost gypsy-like quality about it.”
Some 70,000 music fans paid £12 each for a ticket in 1982. Thousands arrived the night before to camp out wherever they could find a pitch around the village. Fans complained of being charged £5 for a six-pack of beer and £1 for a can of Coke, with one newspaper report at the time remarking that “every kind of huckster, three-card-trick man and itinerant salesman had a stall in Slane”.
The day of the concert, July 24th, saw brilliant sunshine, with those who weren’t sprayed by two massive water hoses taking advantage of the lack of security to swim in the River Boyne.
After the warm-up acts, which included the Chieftains, the Rolling Stones bounded on, with Mick Jagger proclaiming: “It’s great to be back in Dublin. After 16 years, it’s very nice of you to come, so let’s spend the night together.” Jagger showed a hazy knowledge of Irish geography and also of the band’s own history. They had last played Ireland in 1965.

Aerial view of the 80,000-strong crowd at the Rolling Stones in Slane, July 1982. Photograph: Tom Lawlor Concert report, Slane, 1982, by Maev Kennedy
They were a pretty audience. They brought their babies and some of them brought their mammies.In the interminable gaps between the live music they shinned over the 10-foot fence to leap into the Boyne and every mother’s son and daughter of them was decently clothed. Some stripped down to pants, some modestly leaped in fully clothed.
A ferocious, savage, vicious, terrifying gang of Hell’s Angels, from the badlands of Waterford, sat in a reeking huddle on the grass, shunned by 20 yards by the rest of the crowd. Hunched menacingly in their colours, they were eating Choc-Ices.
The crowd got younger all the way into the centre. Half way down were the 20-year-olds, sprawled out on rugs with their wine, in plastic bottles as per instructions, and their dope. The worst crime they committed was to fall sound asleep in the hot sun, and some slept right through the Stones.
Only in the first 10 rows, damped down by fire hoses and at one ecstatic moment sprayed with fire hose by Mick Jagger HIMSELF was there that wild dangerous electric excitement the media associates with huge rock concerts. They leaped and shrieked and held up imploring arms.
“You’re all right!” Mick Jagger yelled at them. “You’re not too bad yourself!” they shouted back.
Up at the top of the hill, up at the top of a 60 foot pine tree, a lunatic fan leaped up and down hysterically.
“It’s great to be back in Dublin,” Jagger assured them. Nobody had the heart to correct him.
By the last chords of the opening Under My Thumb a steady stream of denim was pouring up the slopes and out the gate. They’d waited 10 hours to see the Rolling Stones, and they’d seen the Rolling Stones; they knew exactly what they were going to play, so they left, perfectly happy.
People kept comparing the Stones concert to the Pope’s visit, but nobody ever left a Papal gig before the Last Blessing.

Returning after 25 years to Slane Castle, Mick Jagger performs to a crowd of 70,000 on Saturday 18th August, 2007. Photograph: Kate Geraghty Concert report, Slane, August 2007
“Is it a bit much?” Mick Jagger asked while the central section of the massive stage, on which the Rolling Stones stood, levitated away from their backing band and moved through the awestruck crowd.
Excess is a term that has long been associated with the Stones, and their hi-tech, high energy performance seemed to strike the right chord with fans.
Concert goers who had paid some €60 extra for “Gold Circle” tickets, which entitled them to a standing space at front of the stage, most certainly got their money’s worth, as they stood a hair’s breadth away from their idols. Eventually the stage retracted and the show continued as before.
However, for some fans, the moment they stood beside the Rolling Stones will live long in memory.
Mick Jagger remains a remarkably competent frontman, with an impressive swagger, and his banter during the interludes had the crowd hanging on his every word.
He gave fans an obligatory few words “as Gaeilge” and to his credit, and much to the fans’ delight, his diction was spot on.
Another big cheer came when Jagger introduced guitarist Ronnie Wood to the crowd, describing him as a man from Naas, where Wood now has a home. Wood grabbed the microphone from his mate and bellowed “come on the Royals”, to a somewhat mixed reaction.
Dave Fanning: Slane 1982 was ‘a big circus’
Dave Fanning spoke to The Irish Times in 2007: “I remember the first Slane, standing backstage and watching Phil Lynott arrive by helicopter. There wasn’t such a big vibe about hanging around the castle – everyone was either in the crowd or backstage.
“1987 was memorable because I was seeing one of my favourite people fail miserably: David Bowie. That was also the year I got my binoculars nicked.
“The Rolling Stones in 1982 was like a great big circus, and the stage had these two big catwalks that spread right out into the crowd like a pair of wings. When Keith Richards walked down one of the catwalks, he was standing just 50 yards from us, and that was cool.“Bruce was the biggest thing going in 1985, but Slane was the biggest crowd he had played to up till then. Bob Dylan did a solid enough gig in ’84, but he played as if he was in the Baggot.
“Queen was the first Slane where it rained, and there was a bad vibe with the crowd down the front, because there were so many people there.”

Returning after 25 years to Slane Castle, Mick Jagger performs to a crowd of 70,000 on Saturday 18th August, 2007. Photograph: Kate Geraghty BP Fallon: 1982 wasn’t a patch on 2007
BP Fallon spoke to The Irish Times in 2007 about his memories of 1980s Slane: “Dylan was the most memorable one for me – he had a great band which included Mick Taylor (ex-Rolling Stones) and Ian McLagan (ex-Faces).
“The worst Slane was definitely David Bowie – all that Glass Spider rubbish and those dancers. Terrible. I didn’t go to Queen on principle, because they had played in South Africa during the apartheid regime. I saw The Rolling Stones gig, but it wasn’t a patch on the [2007] tour.”
-

 42cm x 31cm Limerick Here’s a quick, but loaded, question: Do you prefer Barry’s or Lyons? The Great Irish Tea War is the most intractable rivalry in the country. While Munster and Leinster have been known to put their differences aside for the sake of Irish rugby glory, tea drinkers are not so easily appeased. Mention a preference for the “wrong” tea and you can expect strong words at best – and definitely no biscuits. At worst, tea drinkers will go cup to cup in pitched battles, kettles angrily steaming, while insults like curdled milk sour friendships and family relationships. It’s more than just a battle of the brews. Barry’s Tea was founded the Rebel City in 1901 and is still one of Cork’s most famous brands. Lyons is originally from Dublin. Do you prefer Barry’s to Lyons? The yellow Snack or the purple one? Tayto or King Crisps? Cork or Dublin? Really, it is all a matter of taste… But there are many great reasons why anyone looking for a new job, or a whole new life, should consider a move to Cork.Lyons is a brand of tea belonging to Unilever that is sold in Ireland. It is one of the two dominant tea brands in the market within the Republic of Ireland, along with Barry's Tea. Lyons Tea was first produced by J. Lyons and Co., a catering empire created and built by the Salmons and Glucksteins, a German-Jewish immigrant family based in London. Starting in 1904, J Lyons began selling packaged tea through its network of teashops. Soon after, they began selling their own brand Lyons Tea through retailers in the UK, Ireland and around the world.In 1918, Lyons purchased Hornimans and in 1921 they moved their tea factory to J. Lyons and Co., Greenford at that time, the largest tea factory in Europe. In 1962, J Lyons and Company (Ireland) became Lyons Irish Holdings. After a merger with Allied Breweries in 1978, Lyons Irish Holdings became part of Allied Lyons (later Allied Domecq) who then sold the company to Unilever in 1996. Today, Lyons Tea is produced in England. Lyons Tea was a major advertiser in the early decades of RTÉ Television, featuring the "Lyons minstrels" and coupon-based prize competitions. The story of J Lyons is told in the book 'Legacy: One Family, a Cup of Tea and the Company that Took On the World' by Thomas Harding (writer)
42cm x 31cm Limerick Here’s a quick, but loaded, question: Do you prefer Barry’s or Lyons? The Great Irish Tea War is the most intractable rivalry in the country. While Munster and Leinster have been known to put their differences aside for the sake of Irish rugby glory, tea drinkers are not so easily appeased. Mention a preference for the “wrong” tea and you can expect strong words at best – and definitely no biscuits. At worst, tea drinkers will go cup to cup in pitched battles, kettles angrily steaming, while insults like curdled milk sour friendships and family relationships. It’s more than just a battle of the brews. Barry’s Tea was founded the Rebel City in 1901 and is still one of Cork’s most famous brands. Lyons is originally from Dublin. Do you prefer Barry’s to Lyons? The yellow Snack or the purple one? Tayto or King Crisps? Cork or Dublin? Really, it is all a matter of taste… But there are many great reasons why anyone looking for a new job, or a whole new life, should consider a move to Cork.Lyons is a brand of tea belonging to Unilever that is sold in Ireland. It is one of the two dominant tea brands in the market within the Republic of Ireland, along with Barry's Tea. Lyons Tea was first produced by J. Lyons and Co., a catering empire created and built by the Salmons and Glucksteins, a German-Jewish immigrant family based in London. Starting in 1904, J Lyons began selling packaged tea through its network of teashops. Soon after, they began selling their own brand Lyons Tea through retailers in the UK, Ireland and around the world.In 1918, Lyons purchased Hornimans and in 1921 they moved their tea factory to J. Lyons and Co., Greenford at that time, the largest tea factory in Europe. In 1962, J Lyons and Company (Ireland) became Lyons Irish Holdings. After a merger with Allied Breweries in 1978, Lyons Irish Holdings became part of Allied Lyons (later Allied Domecq) who then sold the company to Unilever in 1996. Today, Lyons Tea is produced in England. Lyons Tea was a major advertiser in the early decades of RTÉ Television, featuring the "Lyons minstrels" and coupon-based prize competitions. The story of J Lyons is told in the book 'Legacy: One Family, a Cup of Tea and the Company that Took On the World' by Thomas Harding (writer)Popular culture
A Lyons Tea sign is shown in the background in a scene in Castletown in The Quiet Man (1952), the iconic film directed by John Ford that starred John Wayne and Maureen O'Hara. Again in Ford’s ‘’How Green Was My Valley’’ (1941) an advertisement for Lyon’s Tea is to be seen in an early scene under the shop window near the church. In the BBC/RTÉ Mrs Brown's Boys TV series, there is a box of Lyons Tea sitting on top of the bread bin in Mrs Brown's kitchen. In Chariots of Fire, a Lyons sign is shown at Dover train station. -
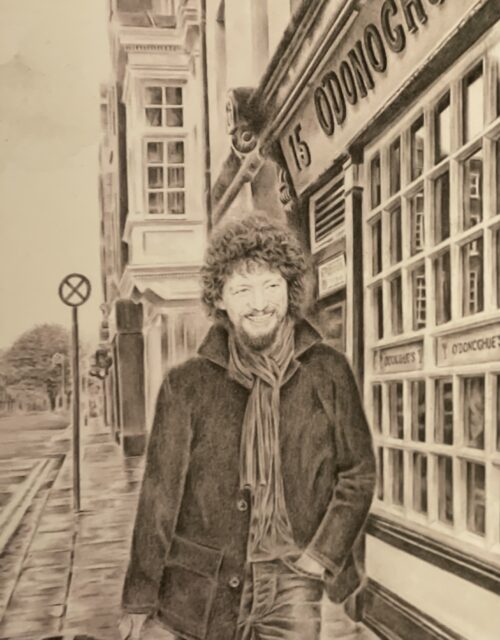
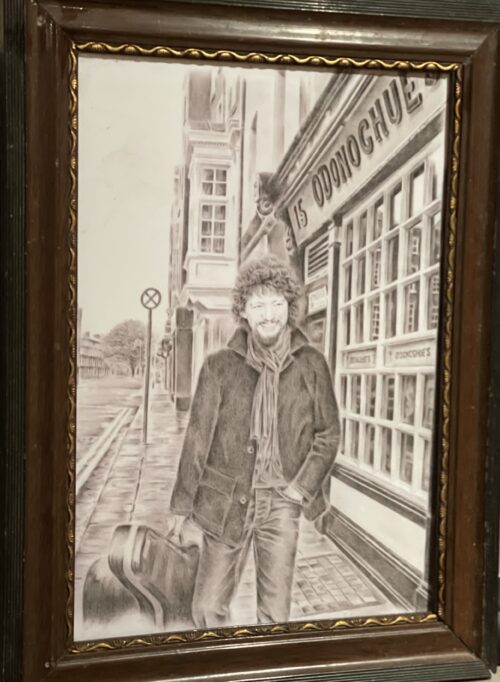
 40cm x 30cm Luke Kelly (17 November 1940 – 30 January 1984) was an Irish singer, folk musician and actor from Dublin, Ireland. Born into a working-class household in Dublin city, Kelly moved to England in his late teens and by his early 20s had become involved in a folk music revival. Returning to Dublin in the 1960s, he is noted as a founding member of the band The Dubliners in 1962. Becoming known for his distinctive singing style, and sometimes political messages, the Irish Postand other commentators have regarded Kelly as one of Ireland's greatest folk singers. Early life Luke Kelly was born into a working-class family in Lattimore Cottages at 1 Sheriff Street.His maternal grandmother, who was a MacDonald from Scotland, lived with the family until her death in 1953. His father who was Irish- also named Luke- was shot and severely wounded as a child by British soldiers from the King's Own Scottish Borderers during the 1914 Bachelor's Walk massacre.His father worked all his life in Jacob's biscuit factory and enjoyed playing football. The elder Luke was a keen singer: Luke junior's brother Paddy later recalled that "he had this talent... to sing negro spirituals by people like Paul Robeson, we used to sit around and join in — that was our entertainment". After Dublin Corporation demolished Lattimore Cottages in 1942, the Kellys became the first family to move into the St. Laurence O’Toole flats, where Luke spent the bulk of his childhood, although the family were forced to move by a fire in 1953 and settled in the Whitehall area. Both Luke and Paddy played club Gaelic football and soccer as children. Kelly left school at thirteen and after a number of years of odd-jobbing, he went to England in 1958.[6] Working at steel fixing with his brother Paddy on a building site in Wolverhampton, he was apparently sacked after asking for higher pay. He worked a number of odd jobs, including a period as a vacuum cleaner salesman.Describing himself as a beatnik, he travelled Northern England in search of work, summarising his life in this period as "cleaning lavatories, cleaning windows, cleaning railways, but very rarely cleaning my face".
40cm x 30cm Luke Kelly (17 November 1940 – 30 January 1984) was an Irish singer, folk musician and actor from Dublin, Ireland. Born into a working-class household in Dublin city, Kelly moved to England in his late teens and by his early 20s had become involved in a folk music revival. Returning to Dublin in the 1960s, he is noted as a founding member of the band The Dubliners in 1962. Becoming known for his distinctive singing style, and sometimes political messages, the Irish Postand other commentators have regarded Kelly as one of Ireland's greatest folk singers. Early life Luke Kelly was born into a working-class family in Lattimore Cottages at 1 Sheriff Street.His maternal grandmother, who was a MacDonald from Scotland, lived with the family until her death in 1953. His father who was Irish- also named Luke- was shot and severely wounded as a child by British soldiers from the King's Own Scottish Borderers during the 1914 Bachelor's Walk massacre.His father worked all his life in Jacob's biscuit factory and enjoyed playing football. The elder Luke was a keen singer: Luke junior's brother Paddy later recalled that "he had this talent... to sing negro spirituals by people like Paul Robeson, we used to sit around and join in — that was our entertainment". After Dublin Corporation demolished Lattimore Cottages in 1942, the Kellys became the first family to move into the St. Laurence O’Toole flats, where Luke spent the bulk of his childhood, although the family were forced to move by a fire in 1953 and settled in the Whitehall area. Both Luke and Paddy played club Gaelic football and soccer as children. Kelly left school at thirteen and after a number of years of odd-jobbing, he went to England in 1958.[6] Working at steel fixing with his brother Paddy on a building site in Wolverhampton, he was apparently sacked after asking for higher pay. He worked a number of odd jobs, including a period as a vacuum cleaner salesman.Describing himself as a beatnik, he travelled Northern England in search of work, summarising his life in this period as "cleaning lavatories, cleaning windows, cleaning railways, but very rarely cleaning my face".Musical beginnings
Kelly had been interested in music during his teenage years: he regularly attended céilithe with his sister Mona and listened to American vocalists including: Fats Domino, Al Jolson, Frank Sinatra and Perry Como. He also had an interest in theatre and musicals, being involved with the staging of plays by Dublin's Marian Arts Society. The first folk club he came across was in the Bridge Hotel, Newcastle upon Tyne in early 1960.Having already acquired the use of a banjo, he started memorising songs. In Leeds he brought his banjo to sessions in McReady's pub. The folk revival was under way in England: at the centre of it was Ewan MacColl who scripted a radio programme called Ballads and Blues. A revival in the skiffle genre also injected a certain energy into folk singing at the time. Kelly started busking. On a trip home he went to a fleadh cheoil in Milltown Malbay on the advice of Johnny Moynihan. He listened to recordings of Woody Guthrie and Pete Seeger. He also developed his political convictions which, as Ronnie Drew pointed out after his death, he stuck to throughout his life. As Drew also pointed out, he "learned to sing with perfect diction". Kelly befriended Sean Mulready in Birmingham and lived in his home for a period.Mulready was a teacher who was forced from his job in Dublin because of his communist beliefs. Mulready had strong music links; a sister, Kathleen Moynihan was a founder member of Comhaltas Ceoltóirí Éireann, and he was related by marriage to Festy Conlon, the County Galway whistle player. Mulready's brother-in-law, Ned Stapleton, taught Kelly "The Rocky Road to Dublin".During this period he studied literature and politics under the tutelage of Mulready, his wife Mollie, and Marxist classicist George Derwent Thomson: Kelly later stated that his interest in music grew parallel to his interest in politics. Kelly bought his first banjo, which had five strings and a long neck, and played it in the style of Pete Seeger and Tommy Makem. At the same time, Kelly began a habit of reading, and also began playing golf on one of Birmingham's municipal courses. He got involved in the Jug O'Punch folk club run by Ian Campbell. He befriended Dominic Behan and they performed in folk clubs and Irish pubs from London to Glasgow. In London pubs, like "The Favourite", he would hear street singer Margaret Barry and musicians in exile like Roger Sherlock, Seamus Ennis, Bobby Casey and Mairtín Byrnes. Luke Kelly was by now active in the Connolly Association, a left-wing grouping strongest among the emigres in England, and he also joined the Young Communist League: he toured Irish pubs playing his set and selling the Connolly Association's newspaper The Irish Democrat. By 1962 George Derwent Thomson had offered him the opportunity to further his educational and political development by attending university in Prague. However, Kelly turned down the offer in favour of pursuing his career in folk music. He was also to start frequenting Ewan MacColl and Peggy Seeger's Singer Club in London.The Dubliners
In 1961 there was a folk music revival or "ballad boom", as it was later termed, in waiting in Ireland.The Abbey Tavern sessions in Howth were the forerunner to sessions in the Hollybrook, Clontarf, the International Bar and the Grafton Cinema. Luke Kelly returned to Dublin in 1962. O'Donoghue's Pub was already established as a session house and soon Kelly was singing with, among others, Ronnie Drew and Barney McKenna. Other early people playing at O'Donoghues included The Fureys, father and sons, John Keenan and Sean Og McKenna, Johnny Moynihan, Andy Irvine, Seamus Ennis, Willy Clancy and Mairtin Byrnes. A concert John Molloy organised in the Hibernian Hotel led to his "Ballad Tour of Ireland" with the Ronnie Drew Ballad Group (billed in one town as the Ronnie Drew Ballet Group). This tour led to the Abbey Tavern and the Royal Marine Hotel and then to jam-packed sessions in the Embankment, Tallaght. Ciarán Bourke joined the group, followed later by John Sheahan. They renamed themselves The Dubliners at Kelly's suggestion, as he was reading James Joyce's book of short stories, entitled Dubliners, at the time.Kelly was the leading vocalist for the group's eponymous debut album in 1964, which included his rendition of "The Rocky Road to Dublin". Barney McKenna later noted that Kelly was the only singer he'd heard sing it to the rhythm it was played on the fiddle. In 1964 Luke Kelly left the group for nearly two years and was replaced by Bobby Lynch and John Sheahan. Kelly went with Deirdre O'Connell, founder of the Focus Theatre, whom he was to marry the following year, back to London and became involved in Ewan MacColl's "gathering". The Critics, as it was called, was formed to explore folk traditions and help young singers. During this period he retained his political commitments, becoming increasingly active in the Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament. Kelly also met and befriended Michael O'Riordan, the General Secretary of the Irish Workers' Party, and the two developed a "personal-political friendship". Kelly endorsed O'Riordan for election, and held a rally in his name during campaigning in 1965.In 1965, he sang 'The Rocky Road to Dublin' with Liam Clancy on his first, self-titled solo album. Bobby Lynch left The Dubliners, John Sheahan and Kelly rejoined. They recorded an album in the Gate Theatre, Dublin, played the Cambridge Folk Festival and recorded Irish Night Out, a live album with, among others, exiles Margaret Barry, Michael Gorman and Jimmy Powers. They also played a concert in the National Stadium in Dublin with Pete Seeger as special guest. They were on the road to success: Top Twenty hits with "Seven Drunken Nights" and "The Black Velvet Band", The Ed Sullivan Show in 1968 and a tour of New Zealand and Australia. The ballad boom in Ireland was becoming increasingly commercialised with bar and pub owners building ever larger venues for pay-in performances. Ewan MacColl and Peggy Seeger on a visit to Dublin expressed concern to Kelly about his drinking.[citation needed] Christy Moore and Kelly became acquainted in the 1960s.During his Planxty days, Moore got to know Kelly well. In 1972 The Dubliners themselves performed in Richard's Cork Leg, based on the "incomplete works" of Brendan Behan. In 1973, Kelly took to the stage performing as King Herod in Jesus Christ Superstar. The arrival of a new manager for The Dubliners, Derry composer Phil Coulter, resulted in a collaboration that produced three of Kelly's most notable performances: “The Town I Loved So Well”, "Hand me Down my Bible", and “Scorn Not His Simplicity”, a song about Phil's son who had Down Syndrome.Kelly had such respect for the latter song that he only performed it once for a television recording and rarely, if ever, sang it at the Dubliners' often boisterous events. His interpretations of “On Raglan Road” and "Scorn Not His Simplicity" became significant points of reference in Irish folk music.His version of "Raglan Road" came about when the poem's author, Patrick Kavanagh, heard him singing in a Dublin pub, and approached Kelly to say that he should sing the poem (which is set to the tune of “The Dawning of the Day”). Kelly remained a politically engaged musician, becoming a supporter of the movement against South African apartheid and performing at benefit concerts for the Irish Traveller community,and many of the songs he recorded dealt with social issues, the arms race and the Cold War, trade unionism and Irish republicanism, ("The Springhill Disaster", "Joe Hill", "The Button Pusher", "Alabama 1958" and "God Save Ireland" all being examples of his concerns).Personal life
Luke Kelly married Deirdre O'Connell in 1965, but they separated in the early 1970s.Kelly spent the last eight years of his life living with his partner Madeleine Seiler, who is from Germany.Final years
Kelly's health deteriorated in the 1970s. Kelly himself spoke about his problems with alcohol. On 30 June 1980 during a concert in the Cork Opera House he collapsed on the stage. He had already suffered for some time from migraines and forgetfulness - including forgetting what country he was in whilst visiting Iceland - which had been ascribed to his intense schedule, alcohol consumption, and "party lifestyle". A brain tumour was diagnosed.Although Kelly toured with the Dubliners after enduring an operation, his health deteriorated further. He forgot lyrics and had to take longer breaks in concerts as he felt weak. In addition following his emergency surgery after his collapse in Cork, he became more withdrawn, preferring the company of Madeleine at home to performing.On his European tour he managed to perform with the band for most of the show in Carre for their Live in Carre album. However, in autumn 1983 he had to leave the stage in Traun, Austria and again in Mannheim, Germany. Shortly after this, he had to cancel the tour of southern Germany, and after a short stay in hospital in Heidelberg he was flown back to Dublin. After another operation he spent Christmas with his family but was taken into hospital again in the New Year, where he died on 30 January 1984.Kelly's funeral in Whitehall attracted thousands of mourners from across Ireland.His gravestone in Glasnevin Cemetery, Dublin, bears the inscription: Luke Kelly – Dubliner. Sean Cannon took Kelly's place in The Dubliners. He had been performing with the Dubliners since 1982,due to the deterioration of Kelly's health.Legacy
Luke Kelly's legacy and contributions to Irish music and culture have been described as "iconic" and have been captured in a number of documentaries and anthologies. The influence of his Scottish grandmother was influential in Kelly's help in preserving important traditional Scottish songs such as "Mormond Braes", the Canadian folk song "Peggy Gordon", "Robert Burns", "Parcel of Rogues", "Tibbie Dunbar", Hamish Henderson's "Freedom Come-All-Ye", and Thurso Berwick's "Scottish Breakaway". The Ballybough Bridge in the north inner city of Dublin was renamed the Luke Kelly Bridge, and in November 2004 Dublin City Council voted unanimously to erect a bronze statue of Luke Kelly. However, the Dublin Docklands Authority subsequently stated that it could no longer afford to fund the statue. In 2010, councillor Christy Burke of Dublin City Council appealed to members of the music community including Bono, Phil Coulter and Enya to help build it. Paddy Reilly recorded a tribute to Kelly entitled "The Dublin Minstrel". It featured on his Gold And Silver Years, Celtic Collections and the Essential Paddy Reilly CD's. The Dubliners recorded the song on their Live at Vicar Street DVD/CD. The song was composed by Declan O'Donoghue, the Racing Correspondent of The Irish Sun. At Christmas 2005 writer-director Michael Feeney Callan's documentary, Luke Kelly: The Performer, was released and outsold U2's latest DVD during the festive season and into 2006, acquiring platinum sales status. The documentary told Kelly's story through the words of the Dubliners, Donovan, Ralph McTell and others and featured full versions of rarely seen performances such as the early sixties' Ed Sullivan Show. A later documentary, Luke Kelly: Prince of the City, was also well received. Two statues of Kelly were unveiled in Dublin in January 2019, to mark the 35th anniversary of his death.One, a life-size seated bronze by John Coll, is on South King Street. The second sculpture, a marble portrait head by Vera Klute, is on Sheriff Street. The Klute sculpture was vandalised on several occasions in 2019 and 2020, in each case being restored by graffiti-removal specialists. Sculpture of Luke Kelly on Sheriff Street by Vera Klute. Unveiled in 2019
Sculpture of Luke Kelly on Sheriff Street by Vera Klute. Unveiled in 2019 -

 48cm x 43cm The Irish Volunteers (Irish: Óglaigh na hÉireann), sometimes called the Irish Volunteer Force[3][4][5] or Irish Volunteer Army,was a military organisation established in 1913 by Irish nationalists and republicans. It was ostensibly formed in response to the formation of its Irish unionist/loyalist counterpart the Ulster Volunteers in 1912, and its declared primary aim was "to secure and maintain the rights and liberties common to the whole people of Ireland". The Volunteers included members of the Gaelic League, Ancient Order of Hibernians and Sinn Féin,and, secretly, the Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB). Increasing rapidly to a strength of nearly 200,000 by mid-1914, it split in September of that year over John Redmond's commitment to the British war effort, with the smaller group retaining the name of "Irish Volunteers".
48cm x 43cm The Irish Volunteers (Irish: Óglaigh na hÉireann), sometimes called the Irish Volunteer Force[3][4][5] or Irish Volunteer Army,was a military organisation established in 1913 by Irish nationalists and republicans. It was ostensibly formed in response to the formation of its Irish unionist/loyalist counterpart the Ulster Volunteers in 1912, and its declared primary aim was "to secure and maintain the rights and liberties common to the whole people of Ireland". The Volunteers included members of the Gaelic League, Ancient Order of Hibernians and Sinn Féin,and, secretly, the Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB). Increasing rapidly to a strength of nearly 200,000 by mid-1914, it split in September of that year over John Redmond's commitment to the British war effort, with the smaller group retaining the name of "Irish Volunteers".Formation
Home Rule for Ireland dominated political debate between the two countries since Prime Minister William Ewart Gladstoneintroduced the first Home Rule Bill in 1886, intended to grant a measure of self-government and national autonomy to Ireland, but which was rejected by the House of Commons. The second Home Rule Bill, seven years later having passed the House of Commons, was vetoed by the House of Lords. It would be the third Home Rule Bill, introduced in 1912, which would lead to the crisis in Ireland between the majority Nationalist population and the Unionists in Ulster. On 28 September 1912 at Belfast City Hall just over 450,000 Unionists signed the Ulster Covenant to resist the granting of Home Rule. This was followed in January 1913 with the formation of the Ulster Volunteers composed of adult male Unionists to oppose the passage and implementation of the bill by force of arms if necessary. The establishment of the Ulster Volunteers was (according to Eoin MacNeill) instigated, approved, and financed by English Tories with the other major British party, the Liberals, not finding "itself terribly distressed by that proceeding."Initiative
The initiative for a series of meetings leading up to the public inauguration of the Irish Volunteers came from the Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB).Bulmer Hobson, co-founder of the republican boy scouts, Fianna Éireann, and member of the Irish Republican Brotherhood, believed the IRB should use the formation of the Ulster Volunteers as an "excuse to try to persuade the public to form an Irish volunteer force".The IRB could not move in the direction of a volunteer force themselves, as any such action by known proponents of physical force would be suppressed, despite the precedent established by the Ulster Volunteers. They therefore confined themselves to encouraging the view that nationalists also ought to organise a volunteer force for the defence of Ireland. A small committee then began to meet regularly in Dublin from July 1913, who watched the growth of this opinion. They refrained however from any action until the precedent of Ulster should have first been established while waiting for the lead to come from a "constitutional" quarter. The IRB began the preparations for the open organisation of the Irish Volunteers in January 1913. James Stritch, an IRB member, had the Irish National Foresters build a hall at the back of 41 Parnell Square in Dublin, which was the headquarters of the Wolfe Tone Clubs. Anticipating the formation of the Volunteers they began to learn foot-drill and military movements.The drilling was conducted by Stritch together with members of Fianna Éireann. They began by drilling a small number of IRB associated with the Dublin Gaelic Athletic Association, led by Harry Boland. Michael Collins along with several other IRB members claim that the formation of the Irish Volunteers was not merely a "knee-jerk reaction" to the Ulster Volunteers, which is often supposed, but was in fact the "old Irish Republican Brotherhood in fuller force.""The North Began"
The IRB knew they would need a highly regarded figure as a public front that would conceal the reality of their control. The IRB found in Eoin MacNeill, Professor of Early and Medieval History at University College Dublin, the ideal candidate. McNeill's academic credentials and reputation for integrity and political moderation had widespread appeal. The O'Rahilly, assistant editor and circulation manager of the Gaelic League newspaper An Claidheamh Soluis, encouraged MacNeill to write an article for the first issue of a new series of articles for the paper. The O'Rahilly suggested to MacNeill that it should be on some wider subject than mere Gaelic pursuits. It was this suggestion which gave rise to the article entitled The North Began, giving the Irish Volunteers its public origins. On 1 November, MacNeill's article suggesting the formation of an Irish volunteer force was published.MacNeill wrote,There is nothing to prevent the other twenty-eight counties from calling into existence citizen forces to hold Ireland "for the Empire". It was precisely with this object that the Volunteers of 1782 were enrolled, and they became the instrument of establishing Irish self-government.
After the article was published, Hobson asked The O'Rahilly to see MacNeill, to suggest to him that a conference should be called to make arrangements for publicly starting the new movement.The article "threw down the gauntlet to nationalists to follow the lead given by Ulster unionists."MacNeill was unaware of the detailed planning which was going on in the background, but was aware of Hobson's political leanings. He knew the purpose as to why he was chosen, but he was determined not to be a puppet.Launch
With MacNeill willing to take part, O'Rahilly and Hobson sent out invitations for the first meeting at Wynn's Hotel in Abbey Street, Dublin, on 11 November. Hobson himself did not attend this meeting, believing his standing as an "extreme nationalist" might prove problematical.The IRB, however, was well represented by, among others, Seán Mac Diarmada and Éamonn Ceannt, who would prove to be substantially more extreme than Hobson.Several others meetings were soon to follow, as prominent nationalists planned the formation of the Volunteers, under the leadership of MacNeill.Meanwhile, labour leaders in Dublin began calling for the establishment of a citizens' defence force in the aftermath of the lock out of 19 August 1913.Thus formed the Irish Citizen Army, led by James Larkin and James Connolly, which, though it had similar aims, at this point had no connection with the Irish Volunteers (were later allies in the Easter Rising. The Volunteer organisation was publicly launched on 25 November, with their first public meeting and enrolment rally at the Rotunda in Dublin.The IRB organised this meeting to which all parties were invited,and brought 5000 enlistment blanks for distribution and handed out in books of one hundred each to each of the stewards. Every one of the stewards and officials wore on their lapel a small silken bow the centre of which was white, while on one side was green and on the other side orange and had long been recognised as the colours which the Irish Republican Brotherhood had adopted as the Irish national banner. The hall was filled to its 4,000 person capacity, with a further 3,000 spilling onto the grounds outside. Speakers at the rally included MacNeill, Patrick Pearse, and Michael Davitt, son of the Land League founder of the same name. Over the course of the following months the movement spread throughout the country, with thousands more joining every week.Organisation and leadership
The original members of the Provisional Committee were:Portfolio Name Organisation Political Party Honorary Secretaries Eoin Mac Néill Gaelic League Laurence Kettle Ancient Order of Hibernians Irish Parliamentary Party Honorary Treasurers The O'Rahilly Gaelic League Sinn Féin John Gore Ancient Order of Hibernians Irish Parliamentary Party - Members: Piaras Béaslaí (Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB)), Sir Roger Casement (GL), Éamonn Ceannt (IRB, GL, SF), John Fitzgibbon (GL, SF), Liam Gogan, Bulmer Hobson (IRB, Fianna Éireann (FÉ)), Michael J. Judge (AOH), Thomas Kettle (IPP, AOH), James Lenehan (AOH), Michael Lonergan (IRB, Fianna Éireann (FÉ)), Peter (Peadar) Macken (IRB, Labour leader, SF, GL), Seán Mac Diarmada (IRB, Irish Freedom), Thomas MacDonagh (GL), Liam Mellows (IRB), Maurice Moore (IPP, GL, Connaught Rangers), Séamus O'Connor (IRB), Colm O'Loughlin (IRB, St. Enda's School (SES)), Peter O'Reilly (Ancient Order of Hibernians (AOH)), Robert Page (IRB, Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA)), Patrick Pearse (GL, SES), Joseph M. Plunkett (GL, Irish Review), John Walsh (AOH), Peter White (Celtic Literary Society);
- Fianna Éireann representatives: Con Colbert (IRB), Eamon Martin (IRB), Patrick O'Riain (IRB).
John Redmond and the Irish Parliamentary Party
While the IRB was instrumental in the establishment of the Volunteers, they were never able to gain complete control of the organisation. This was compounded after John Redmond, leader of the Irish Parliamentary Party, took an active interest. Though some well known Redmond supporters had joined the Volunteers, the attitude of Redmond and the Party was largely one of opposition, though by the Summer of 1914, it was clear the IPP needed to control the Volunteers if they were not to be a threat to their authority.The majority of the IV members, like the nation as a whole, were supporters of Redmond (though this was not necessarily true of the organisation's leadership), and, armed with this knowledge, Redmond sought IPP influence, if not outright control of the Volunteers. Negotiations between MacNeil and Redmond over the latter's future role continued inconclusively for several weeks, until on 9 June Redmond issued an ultimatum, through the press, demanding the Provisional Committee co-opt twenty-five IPP nominees.With several IPP members and their supporters on the committee already, this would give them a majority of seats, and effective control. The more moderate members of the Volunteers' Provisional Committee did not like the idea, nor the way it was presented, but they were largely prepared to go along with it to prevent Redmond from forming a rival organisation, which would draw away most of their support. The IRB was completely opposed to Redmond's demands, as this would end any chance they had of controlling the Volunteers. Hobson, who simultaneously served in leadership roles in both the IRB and the Volunteers, was one of a few IRB members to reluctantly submit to Redmond's demands, leading to a falling out with the IRB leaders, notably Tom Clarke. In the end the Committee accepted Redmond's demands, by a vote of 18 to 9, most of the votes of dissent coming from members of the IRB. The new IPP members of the committee included MP Joseph Devlin and Redmond's son William, but were mostly composed of insignificant figures, believed to have been appointed as a reward for party loyalty.[46] Despite their numbers, they were never able to exert control over the organisation, which largely remained with its earlier officers. Finances remained fully in the hands of the treasurer, The O'Rahilly, his assistant, Éamonn Ceannt, and MacNeill himself, who retained his position as chairman, further diminishing the IPP's influence.Arming the Volunteers
Shortly after the formation of the Volunteers, the British Parliament banned the importation of weapons into Ireland. The "Curragh incident" (also referred to as the "Curragh Mutiny") of March 1914, indicated that the government could not rely on its army to ensure a smooth transition to Home Rule.Then in April 1914 the Ulster Volunteerssuccessfully imported 24,000 rifles in the Larne Gun Running event. The Irish Volunteers realised that it too would have to follow suit if they were to be taken as a serious force. Indeed, many contemporary observers commented on the irony of "loyal" Ulstermen arming themselves and threatening to defy the British government by force. Patrick Pearsefamously replied that "the Orangeman with a gun is not as laughable as the nationalist without one." Thus O'Rahilly, Sir Roger Casement and Bulmer Hobson worked together to co-ordinate a daylight gun-running expedition to Howth, just north of Dublin. The plan worked, and Erskine Childers brought nearly 1,000 rifles, purchased from Germany, to the harbour on 26 July and distributed them to the waiting Volunteers, without interference from the authorities. The remainder of the guns smuggled from Germany for the Irish Volunteers were landed at Kilcoole a week later by Sir Thomas Myles. As the Volunteers marched from Howth back to Dublin, however, they were met by a large patrol of the Dublin Metropolitan Police and the King's Own Scottish Borderers. The Volunteers escaped largely unscathed, but when the Borderers returned to Dublin they clashed with a group of unarmed civilians who had been heckling them at Bachelors Walk. Though no order was given, the soldiers fired on the civilians, killing four and further wounding 37. This enraged the populace, and during the outcry enlistments in the Volunteers soared.The Split
The outbreak of World War I in August 1914 provoked a serious split in the organisation. Redmond, in the interest of ensuring the enactment of the Home Rule Act 1914 then on the statute books, encouraged the Volunteers to support the British and Allied war commitment and join Irish regiments of the British New Army divisions, an action which angered the founding members. Given the wide expectation that the war was going to be a short one, the majority however supported the war effort and the call to restore the "freedom of small nations" on the European continent. They left to form the National Volunteers, some of whose members fought in the 10th and 16th (Irish) Division, side by side with their Ulster Volunteer counterparts from the 36th (Ulster) Division. A minority believed that the principles used to justify the Allied war cause were best applied in restoring the freedom to one small country in particular. They retained the name "Irish Volunteers", were led by MacNeill and called for Irish neutrality. The National Volunteers kept some 175,000 members, leaving the Irish Volunteers with an estimated 13,500. However, the National Volunteers declined rapidly, and the few remaining members reunited with the Irish Volunteers in October 1917.The split proved advantageous to the IRB, which was now back in a position to control the organisation. Following the split, the remnants of the Irish Volunteers were often, and erroneously, referred to as the "Sinn Féin Volunteers", or, by the British press, derisively as "Shinners", after Arthur Griffith's political organisation Sinn Féin. Although the two organisations had some overlapping membership, there was no official connection between Griffith's then moderate Sinn Féin and the Volunteers. The political stance of the remaining Volunteers was not always popular, and a 1,000-strong march led by Pearse through the garrison city of Limerick on Whit Sunday, 1915, was pelted with rubbish by a hostile crowd. Pearse explained the reason for the establishment of the new force when he said in May 1915:What if conscription be enforced on Ireland? What if a Unionist or a Coalition British Ministry repudiates the Home Rule Act? What if it be determined to dismember Ireland? The future is big with these and other possibilities.
After the departure of Redmond and his followers, the Volunteers adopted a constitution, which had been drawn up by the earlier provisional committee, and was ratified by a convention of 160 delegates on 25 October 1914. It called for general council of fifty members to meet monthly, as well as an executive of the president and eight elected members. In December a headquarters staff was appointed, consisting of Eoin MacNeill as chief of staff, The O'Rahilly as director of arms, Thomas MacDonagh as director of training, Patrick Pearse as director of military organisation, Bulmer Hobson as quartermaster, and Joseph Plunkett as director of military operations. The following year they were joined by Éamonn Ceannt as director of communications and J.J. O'Connell as chief of inspection. This reorganisation put the IRB is a stronger position, as four important military positions (director of training, director of military organisation, director of military operations, and director of communications) were held by men who were, or would soon be, members of the IRB, and who later become four of the seven signatories of the Easter Proclamation. (Hobson was also an IRB member, but had a falling out with the leadership after he supported Redmond's appointees to the provisional council, and hence played little role in the IRB thereafter.)Easter Rising, 1916
The official stance of the Irish Volunteers was that action would only be taken were the British authorities at Dublin Castle to attempt to disarm the Volunteers, arrest their leaders, or introduce conscription to Ireland.The IRB, however, was determined to use the Volunteers for offensive action while Britain was tied up in the First World War. Their plan was to circumvent MacNeill's command, instigating a Rising, and to get MacNeill on board once the rising was a fait accompli. Pearse issued orders for three days of parades and manoeuvres, a thinly disguised order for a general insurrection.MacNeill soon discovered the real intent behind the orders and attempted to stop all actions by the Volunteers. He succeeded only in putting the Rising off for a day, and limiting it to about 1,000 active participants within Dublin and a very limited action elsewhere. Almost all of the fighting was confined to Dublin - though the Volunteers were involved in engagements against RIC barracks in Ashbourne, County Meath, and there were actions in Enniscorthy, County Wexford and in County Galway.The Irish Citizen Army supplied slightly more than 200 personnel for the Dublin campaign.Reorganisation
Steps towards reorganising the Irish Volunteers were taken during 1917, and on 27 October 1917 a convention was held in Dublin. This convention was called to coincide with the Sinn Féin party conference. Nearly 250 people attended the convention; internment prevented many more from attending. The Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC) estimated that 162 companies of volunteers were active in the country, although other sources suggest a figure of 390. The proceedings were presided over by Éamon de Valera, who had been elected President of Sinn Féin the previous day. Also on the platform were Cathal Brugha and many others who were prominent in the reorganising of the Volunteers in the previous few months, many of them ex-prisoners. De Valera was elected president. A national executive was also elected, composed of representatives of all parts of the country. In addition, a number of directors were elected to head the various IRA departments. Those elected were: Michael Collins (Director for Organisation); Richard Mulcahy (Director of Training); Diarmuid Lynch (Director for Communications); Michael Staines (Director for Supply); Rory O'Connor (Director of Engineering). Seán McGarry was voted general secretary, while Cathal Brugha was made Chairman of the Resident Executive, which in effect made him Chief of Staff. The other elected members were: M. W. O'Reilly (Dublin); Austin Stack (Kerry); Con Collins (Limerick); Seán MacEntee (Belfast); Joseph O'Doherty (Donegal); Paul Galligan(Cavan); Eoin O'Duffy (Monaghan); Séamus Doyle (Wexford); Peadar Bracken (Offaly); Larry Lardner (Galway); Richard Walsh (Mayo) and another member from Connacht. There were six co-options to make-up the full number when the directors were named from within their ranks. The six were all Dublin men: Eamonn Duggan; Gearóid O'Sullivan; Fintan Murphy; Diarmuid O'Hegarty; Dick McKee and Paddy Ryan. Of the 26 elected, six were also members of the Sinn Féin National Executive, with Éamon de Valera president of both. Eleven of the 26 were elected Teachta Dála (members of the Dáil) in the 1918 general election and 13 in the May 1921 election.Relationship with Dáil Éireann
Sinn Féin MPs elected in 1918 fulfilled their election promise not to take their seats in Westminster but instead set up an independent "Assembly of Ireland", or Dáil Éireann, in the Irish language. In theory, the Volunteers were responsible to the Dáil and was the army of the Irish Republic. In practice, the Dáil had great difficulty controlling their actions; under their own constitution, the Volunteers were bound to obey their own executive and no other body. The fear was increased when, on the very day the new national parliament was meeting, 21 January 1919, members of the Third Tipperary Brigade led by Séumas Robinson, Seán Treacy, Dan Breen and Seán Hogan carried out the Soloheadbeg Ambush and seized a quantity of gelignite, killing two RIC constables and triggering the War of Independence. Technically, the men involved were considered to be in a serious breach of Volunteer discipline and were liable to be court-martialed, but it was considered more politically expedient to hold them up as examples of a rejuvenated militarism. The conflict soon escalated into guerrilla warfare by what were then known as the Flying Columns in remote areas. Attacks on remote RIC barracks continued throughout 1919 and 1920, forcing the police to consolidate defensively in the larger towns, effectively placing large areas of the countryside in the hands of the Republicans. Moves to make the Volunteers the army of the Dáil and not its rival had begun before the January attack, and were stepped up. On 31 January 1919 the Volunteer organ, An tÓglách ("The Volunteer") published a list of principles agreed between two representatives of the Aireacht, acting Príomh Aire Cathal Brugha and Richard Mulcahy and the Executive. It made first mention of the organisation treating "the armed forces of the enemy – whether soldiers or policemen – exactly as a national army would treat the members of an invading army". In the statement the new relationship between the Aireacht and the Volunteers – who increasingly became known as the Irish Republican Army (IRA) – was defined clearly.- The Government was defined as possessing the same power and authority as a normal government.
- It, and not the IRA, sanctions the IRA campaign;
- It explicitly spoke of a state of war.
Legacy
All organisations calling themselves the IRA, as well as the Irish Defence Forces (IDF), have their origins in the Irish Volunteers. The Irish name of the Volunteers, Óglaigh na hÉireann, was retained when the English name changed, and is the official Irish name of the IDF, as well as the various IRAs. The name of the Bengal Volunteers, an Indian revolutionary organization founded in 1928 and active against British rule in India, may have been inspired by the Irish organization. -
 The iconic portrait of a teenage Kevin Barry,one of our most celebrated republican martyrs-in the black and white hooped rugby jersey of Belvedere College SJ. 26cm x 30cm Dunmanway Co Cork Kevin Gerard Barry (20 January 1902 – 1 November 1920) was an Irish republican paramilitary who was executed by the British Government during the Irish War of Independence. He was sentenced to death for his part in an attack upon a British Army supply lorry which resulted in the deaths of three British soldiers. His execution inflamed nationalist public opinion in Ireland, largely because of his age. The timing of the execution, only days after the death by hunger strike of Terence MacSwiney, the republican Lord Mayor of Cork, brought public opinion to a fever-pitch. His death attracted international attention, and attempts were made by U.S. and Vatican officials to secure a reprieve. His execution and MacSwiney's death precipitated an escalation in violence as the Irish War of Independence entered its bloodiest phase, and Barry became an Irish republican martyr.
The iconic portrait of a teenage Kevin Barry,one of our most celebrated republican martyrs-in the black and white hooped rugby jersey of Belvedere College SJ. 26cm x 30cm Dunmanway Co Cork Kevin Gerard Barry (20 January 1902 – 1 November 1920) was an Irish republican paramilitary who was executed by the British Government during the Irish War of Independence. He was sentenced to death for his part in an attack upon a British Army supply lorry which resulted in the deaths of three British soldiers. His execution inflamed nationalist public opinion in Ireland, largely because of his age. The timing of the execution, only days after the death by hunger strike of Terence MacSwiney, the republican Lord Mayor of Cork, brought public opinion to a fever-pitch. His death attracted international attention, and attempts were made by U.S. and Vatican officials to secure a reprieve. His execution and MacSwiney's death precipitated an escalation in violence as the Irish War of Independence entered its bloodiest phase, and Barry became an Irish republican martyr.Early life
Kevin Barry was born on 20 January 1902, at 8 Fleet Street, Dublin, to Thomas and Mary (née Dowling) Barry. The fourth of seven children, two boys and five sisters, Kevin was baptised in St Andrew's Church, Westland Row. Thomas Barry Sr. worked on the family's farm at Tombeagh, Hacketstown, County Carlow, and ran a dairy business from Fleet Street. Thomas Barry Sr. died in 1908, aged 56. His mother came from Drumguin, County Carlow, and, upon the death of her husband, moved the family to nearby Tombeagh. As a child he went to the national school in Rathvilly. On returning to Dublin, he attended St Mary's College, Rathmines, until the school closed in the summer of 1916.When he was thirteen, he attended a commemoration for the Manchester Martyrs, who were hanged in England in 1867. Afterwards he wished to join Constance Markievicz's Fianna Éireann, but was reportedly dissuaded by his family.Belvedere College
From St Mary's College he transferred to Belvedere College, where he was a member of the championship Junior Rugby Cup team, and earned a place on the senior team. In 1918 he became secretary of the school hurling club which had just been formed, and was one of their most enthusiastic players.A Jesuit priest, Thomas Counihan, who was Barry's science and mathematics teacher, said of him: "He was a dour kind of lad. But once he got down to something he went straight ahead… There was no waving of flags with him, but he was sincere and intense." Notwithstanding his many activities, he did not neglect his studies. He won a merit-based scholarship given annually by Dublin Corporation, which allowed him to become a student of medicine at UCD.Medical student
He entered University College Dublin in 1919. His closest friend at college was Gerry MacAleer, from Dungannon, whom he had first met in Belvedere. Other friends included Frank Flood, Tom Kissane and Mick Robinson, who, unknown to many in the college, were, along with Barry, members of the Irish Volunteers.Volunteer activities
In October 1917, during his second year at Belvedere, aged 15, he joined the IRA. Assigned originally to ‘C’ Company 1st Battalion, based on the north side of Dublin, he later transferred to the newly formed ‘H’ Company, under the command of Capt. Seamus Kavanagh. His first job as a member of the IRA was delivering mobilisation orders around the city. Along with other volunteers, Barry trained in a number of locations in Dublin, including the building at 44 Parnell Square, the present day headquarters of Sinn Féin, now named Kevin Barry Hall. The IRA held Field exercises during this period which were conducted in north county Dublin and in areas such as Finglas.The following year, at the age of 16, he was introduced by Seán O'Neill and Bob O'Flanagan to the Clarke Luby Club of the IRB, which had been reorganised. He took part in a number of IRA operations in the years leading up to his capture. He was part of the unit which raided the Shamrock Works for weapons destined to be handed over to the R.I.C. He also took part in the raid on Mark's of Capel Street, looking for ammunition and explosives. On 1 June 1920, under Vice-Commandant Peadar Clancy, he played a notable part in the seizing of the King's Inn, capturing the garrison’s arms. The haul included 25 rifles, two light machine guns and large quantities of ammunition. The 25 British soldiers captured during the attack were released as the volunteers withdrew. In recognition of his dedication to duty he was promoted to Section Commander.Ambush
On the morning of 20 September 1920, Barry went to Mass, then joined a party of IRA volunteers on Bolton Street in Dublin. Their orders were to ambush a British army lorry as it picked up a delivery of bread from the bakery, and capture their weapons. The ambush was scheduled for 11:00am, which gave him enough time to take part in the operation and return to class in time for an examination he had at 2:00pm. The truck arrived late, and was under the command of Sergeant Banks. Armed with a .38 Mauser Parabellum, Barry and members of C Company were to surround the lorry, disarm the soldiers, take the weapons and escape. He covered the back of the vehicle and, when challenged, the five soldiers complied with the order to lay down their weapons. A shot was then fired; Terry Golway, author of For the Cause of Liberty, suggests it was possibly a warning shot from an uncovered soldier in the front. Barry and the rest of the ambush party then opened fire. His gun jammed twice and he dived for cover under the vehicle. His comrades fled and he was left behind. He was then spotted and arrested by the soldiers.One of the soldiers, Private Harold Washington, aged 15, had been shot dead. Two others, Privates Marshall Whitehead and Thomas Humphries, were both badly wounded and later died of their wounds. The British Army released the following statement on Monday afternoon:This morning a party of one N.C.O. and six men of the Duke of Wellington's Regiment were fired on by a body of civilians outside a bakery in Church Street, Dublin. One soldier was killed and four were wounded. A piquet of the Lancashire Fusiliers in the vicinity, hearing the shots, hurried to their comrades' assistance, and succeeded in arresting one of the aggressors. No arms or equipment were lost by the soldiers.
Much was made of Barry's age by Irish newspapers, but the British military pointed out that the three soldiers who had been killed were "much the same age as Barry". On 20 October, Major Reginald Ingram Marians OBE, Head of the Press Section of the General Staff, informed Basil Clarke, Head of Publicity, that Washington was "only 19 and that the other soldiers were of similar ages." General Macready was well aware of the "propaganda value of the soldier's ages." Macready informed General Sir Henry Wilson on the day that sentence was pronounced "of the three men who were killed by him (Barry) and his friends two were 19 and one 20 — official age so probably they were younger... so if you want propaganda there you are."It was later confirmed that Private Harold Washington was 15 years and 351 days old, having been born 4 October 1904. About this competing propaganda, Martin Doherty wrote in a magazine article entitled 'Kevin Barry & the Anglo-Irish Propaganda War':from the British point of view, therefore, the Anglo-Irish propaganda war was probably unwinable [sic]. Nationalist Ireland had decided that men like Kevin Barry fought to free their country, while British soldiers — young or not — sought to withhold that freedom. In these circumstances, to label Barry a murderer was merely to add insult to injury. The contrasting failure of British propaganda is graphically demonstrated by the simple fact that even in British newspapers Privates Whitehead, Washington and Humphries remained faceless names and numbers, for whom no songs were written.”
Capture and torture
Barry was placed in the back of the lorry with the young body of Private Harold Washington, and was subjected to some abuse by Washington's comrades. He was transported then to the North Dublin Union. Upon arrival at the barracks he was taken under military police escort to the defaulters' room where he was searched and handcuffed. A short while later, three sergeants of the Lancashire Fusiliers and two officers began the interrogation. He gave his name and an address of 58 South Circular Road, Dublin (his uncle's address), and his occupation as a medical student, but refused to answer any other questions. The officers continued to demand the names of other republicans involved in the ambush. At this time a publicity campaign was mounted by Sinn Féin. Barry received orders on 28 October from his brigade commander, Richard McKee, "to make a sworn affidavit concerning his torture in the North Dublin Union." Arrangements were made to deliver this through Barry's sister, Kathy, to Desmond Fitzgerald, director of publicity for Sinn Féin, "with the object of having it published in the World press, and particularly in the English papers, on Saturday 30th October." The affidavit, drawn up in Mountjoy Prison days before his execution, describes his treatment when the question of names was repeated:Sinn Féin's Dublin HQ at the Kevin Barry Memorial HallHe tried to persuade me to give the names, and I persisted in refusing. He then sent the sergeant out of the room for a bayonet. When it was brought in the sergeant was ordered by the same officer to point the bayonet at my stomach ... The sergeant then said that he would run the bayonet into me if I did not tell ... The same officer then said to me that if I persisted in my attitude he would turn me out to the men in the barrack square, and he supposed I knew what that meant with the men in their present temper. I said nothing. He ordered the sergeants to put me face down on the floor and twist my arm ... When I lay on the floor, one of the sergeants knelt on my back, the other two placed one foot each on my back and left shoulder, and the man who knelt on me twisted my right arm, holding it by the wrist with one hand, while he held my hair with the other to pull back my head. The arm was twisted from the elbow joint. This continued, to the best of my judgment, for five minutes. It was very painful ... I still persisted in refusing to answer these questions... A civilian came in and repeated the questions, with the same result. He informed me that if I gave all the information I knew I could get off.
On 28 October, the Irish Bulletin (organised by Dick McKee, the IRA Commandant of the Dublin Brigade), a news-sheet produced by Dáil Éireann's Department of Publicity,published Barry's statement alleging torture. The headline read: English Military Government Torture a Prisoner of War and are about to Hang him. The Irish Bulletin declared Barry to be a prisoner of war, suggesting a conflict of principles was at the heart of the conflict. The English did not recognise a war and treated all killings by the IRA as murder. Irish republicans claimed that they were at war and it was being fought between two opposing nations and therefore demanded prisoner of war status. Historian John Ainsworth, author of Kevin Barry, the Incident at Monk's bakery and the Making of an Irish Republican Legend, pointed out that Barry had been captured by the British not as a uniformed soldier but disguised as a civilian and in possession of flat-nosed "Dum-dum" bullets, which expand upon impact, maximising the amount of damage done to the "unfortunate individual" targeted, in contravention of the Hague Convention of 1899. Erskine Childers addressed the question of political status in a letter to the press on 29 October, which was published the day after Barry's execution.-
- This lad Barry was doing precisely what Englishmen would be doing under the same circumstances and with the same bitter and intolerable provocation — the suppression by military force of their country's liberty.
- To hang him for murder is an insulting outrage, and it is more: it is an abuse of power: an unworthy act of vengeance. contrasting ill with the forbearance and humanity invariably shown by the Irish Volunteers towards the prisoners captured by them when they have been successful in encounters similar to this one. These guerrilla combats with soldiers and constables — both classes do the same work with the same weapons; the work of military repression — are typical episodes in Ireland.
- Murder of individual constables, miscalled ‘police’, have been comparatively rare. The Government figure is 38, and it will not, to my knowledge, bear examination. I charge against the British Government 80 murders by soldiers and constables: murders of unarmed people, and for the most part wholly innocent people, including old men, women and boys.
- To hang Barry is to push to its logical extreme the hypocritical pretense that the national movement in Ireland unflinchingly supported by the great mass of the Irish people, is the squalid conspiracy of a ‘murder gang’.
- That is false; it is a natural uprising: a collision between two Governments, one resting on consent, the other on force. The Irish are struggling against overwhelming odds to defend their own elected institutions against extinction.
-
-
-
Under similar circumstances a body of Irish Volunteers captured on June 1 of the present year a party of 25 English military who were on duty at the King's Inns, Dublin. Having disarmed the party the Volunteers immediately released their prisoners. This was in strict accordance with the conduct of the Volunteers in all such encounters. Hundreds of members of the armed forces have been from time to time captured by the Volunteers and in no case was any prisoner maltreated even though Volunteers had been killed and wounded in the fighting, as in the case of Cloyne, Co. Cork, when, after a conflict in which one Volunteer was killed and two wounded, the whole of the opposing forces were captured, disarmed, and set at liberty.
-
-
Trial
The War Office ordered that Kevin Barry be tried by court-martial under the Restoration of Order in Ireland Act, which received Royal Assent on 9 August 1920. General Sir Nevil Macready, Commander-in-Chief of British forces in Ireland then nominated a court of nine officers under a Brigadier-General Onslow. On 20 October, at 10 o’clock, the nine officers of the court — ranging in rank from Brigadier to Lieutenant — took their places at an elevated table. At 10.25, Kevin Barry was brought into the room by a military escort. Then Seán Ó hUadhaigh sought a short adjournment to consult his client. The court granted this request. After the short adjournment Barry announced "As a soldier of the Irish Republic, I refuse to recognise the court." Brigadier Onslow explained the prisoner's "perilous situation" and that he was being tried on a capital charge. He did not reply. Ó hUadhaigh then rose to tell the court that since his client did not recognise the authority of the court he himself could take no further part in the proceedings. Barry was charged on three counts of the murder of Private Marshall Whitehead. One of the bullets taken from Whitehead's body was of .45 calibre, while all witnesses stated that Barry was armed with a .38 Mauser Parabellum. The Judge Advocate General informed the court that the Crown had only to prove that the accused was one of the party that killed three British soldiers, and every member of the party was technically guilty of murder. In accordance with military procedure the verdict was not announced in court. He was returned to Mountjoy, and at about 8 o’clock that night, the district court-martial officer entered his cell and read out the sentence: death by hanging. The public learned on 28 October that the date of execution had been fixed for 1 November.Execution
Barry spent the last day of his life preparing for death. His ordeal focused world attention on Ireland. According to Sean Cronin, author of a biography of Barry (Kevin Barry), he hoped for a firing squad rather than the gallows, as he had been condemned by a military court. A friend who visited him in Mountjoy prison after he received confirmation of the death sentence, said:He is meeting death as he met life with courage but with nothing of the braggart. He does not believe that he is doing anything wonderfully heroic. Again and again he has begged that no fuss be made about him.
He reported Barry as saying "It is nothing, to give one's life for Ireland. I'm not the first and maybe I won't be the last. What's my life compared with the cause?" Barry joked about his death with his sister Kathy. "Well, they are not going to let me like a soldier fall… But I must say they are going to hang me like a gentleman." This was, according to Cronin, a reference to George Bernard Shaw's The Devil's Disciple, the last play Kevin and his sister had seen together. On 31 October, he was allowed three visits of three people each, the last of which was taken by his mother, brother and sisters. In addition to the two Auxiliaries with him, there were five or six warders in the boardroom. As his family were leaving, they met Canon John Waters, on the way in, who said, "This boy does not seem to realise he is going to die in the morning." Mrs Barry asked him what he meant. He said: "He is so gay and light-hearted all the time. If he fully realised it, he would be overwhelmed." Mrs Barry replied, "Canon Waters, I know you are not a Republican. But is it impossible for you to understand that my son is actually proud to die for the Republic?" Canon Waters became somewhat flustered as they parted. The Barry family recorded that they were upset by this encounter because they considered the chief chaplain "the nearest thing to a friend that Kevin would see before his death, and he seemed so alien." Kevin Barry was hanged on 1 November, after hearing two Masses in his cell. Canon Waters, who walked with him to the scaffold, wrote to Barry's mother later, "You are the mother, my dear Mrs Barry, of one of the bravest and best boys I have ever known. His death was one of the most holy, and your dear boy is waiting for you now, beyond the reach of sorrow or trial." Dublin Corporation met on the Monday, and passed a vote of sympathy with the Barry family, and adjourned the meeting as a mark of respect. The Chief Secretary's office in Dublin Castle, on the Monday night, released the following communiqué:The sentence of death by hanging passed by court-martial upon Kevin Barry, or Berry, medical student, aged 18½ years, for the murder of Private Whitehead in Dublin on September 20, was duly executed this morning at Mountjoy Prison, Dublin. At a military court of inquiry, held subsequently in lieu of an inquest, medical evidence was given to the effect that death was instantaneous. The court found that the sentence had been carried out in accordance with law.
Barry's body was buried at 1.30 p.m, in a plot near the women's prison. His comrade and fellow-student Frank Flood was buried alongside him four months later. A plain cross marked their graves and those of Patrick Moran, Thomas Whelan, Thomas Traynor, Patrick Doyle, Thomas Bryan, Bernard Ryan, Edmond Foley and Patrick Maher who were hanged in the same prison before the Anglo-Irish Treaty of July 1921 which ended hostilities between Irish republicans and the British.The men had been buried in unconsecrated ground on the jail property and their graves went unidentified until 1934.They became known as The Forgotten Ten by republicans campaigning for the bodies to be reburied with honour and proper rites.On 14 October 2001, the remains of these ten men were given a state funeral and moved from Mountjoy Prison to be re-interred at Glasnevin Cemetery in Dublin.Aftermath
 Kevin Barry monument in Rathvilly, County CarlowThe only full-length biography of Kevin Barry was written by his nephew, journalist Donal O'Donovan, published in 1989 as Kevin Barry and his Time. In 1965, Sean Cronin wrote a short biography, simply entitled "Kevin Barry"; this was published by The National Publications Committee, Cork, to which Tom Barry provided a foreword. Barry is remembered in a well-known song about his imprisonment and execution, written shortly after his death and still sung today. The tune to "Kevin Barry" was taken from the sea-shanty "Rolling Home".[17] The execution reportedly inspired Thomas MacGreevy's surrealist poem, "Homage to Hieronymus Bosch". MacGreevy had unsuccessfully petitioned the Provost of Trinity College Dublin, John Henry Bernard, to make representations on Barry's behalf.
Kevin Barry monument in Rathvilly, County CarlowThe only full-length biography of Kevin Barry was written by his nephew, journalist Donal O'Donovan, published in 1989 as Kevin Barry and his Time. In 1965, Sean Cronin wrote a short biography, simply entitled "Kevin Barry"; this was published by The National Publications Committee, Cork, to which Tom Barry provided a foreword. Barry is remembered in a well-known song about his imprisonment and execution, written shortly after his death and still sung today. The tune to "Kevin Barry" was taken from the sea-shanty "Rolling Home".[17] The execution reportedly inspired Thomas MacGreevy's surrealist poem, "Homage to Hieronymus Bosch". MacGreevy had unsuccessfully petitioned the Provost of Trinity College Dublin, John Henry Bernard, to make representations on Barry's behalf. On 14 October 2001 the remains of Kevin Barry and nine other volunteers from the War of Independence were given a state funeral and moved from Mountjoy Prison to be re-interred at Glasnevin Cemetery in Dublin. Barry's grave is the first on the left.
On 14 October 2001 the remains of Kevin Barry and nine other volunteers from the War of Independence were given a state funeral and moved from Mountjoy Prison to be re-interred at Glasnevin Cemetery in Dublin. Barry's grave is the first on the left.Legacy[edit]
A commemorative stamp was issued by An Post to mark the 50th anniversary of Barry's death in 1970.[18] The University College Dublin and National University of Ireland, Galway branches of Ógra Fianna Fáil are named after him.[19] Derrylaughan Kevin Barry's GAA club was founded in Clonoe, County Tyrone. In 1930, Irish immigrants in Hartford, Connecticut, created a hurling club and named it after Barry. The club later disappeared for decades, but was revived in 2011 by more recently arrived Irish immigrants and local Irish-Americans in the area.[20] In 1934, a large stained-glass window commemorating Barry was unveiled in Earlsfort Terrace, then the principal campus of University College Dublin. It was designed by Richard King of the Harry Clarke Studio. In 2007, UCD completed its relocation to the Belfield campus some four miles away and a fund was collected by graduates to defray the cost (estimated at close to €250,000) of restoring and moving the window to this new location.[21] A grandnephew of Kevin Barry is Irish historian Eunan O'Halpin.[22] There is an Irish republican flute band named after him, the "Volunteer Kevin Barry Republican Flute Band", which operates out of the Calton area of the city.[citation needed] Barry's execution is mentioned in the folk song "Rifles of the I.R.A." written by Dominic Behan in 1968. A ballad bearing Barry's name, relating the story of his execution, has been sung by artists as diverse as Paul Robeson,[23] Leonard Cohen,[24] Lonnie Donegan, and The Dubliners. At the place where Kevin Barry was captured (North King Street/Church Street, Dublin), there are two blocks of flats named after him. -
-

 The iconic portrait of a teenage Kevin Barry,one of our most celebrated republican martyrs-in the black and white hooped rugby jersey of Belvedere College SJ. 26cm x 30cm Dunmanway Co Cork Kevin Gerard Barry (20 January 1902 – 1 November 1920) was an Irish republican paramilitary who was executed by the British Government during the Irish War of Independence. He was sentenced to death for his part in an attack upon a British Army supply lorry which resulted in the deaths of three British soldiers. His execution inflamed nationalist public opinion in Ireland, largely because of his age. The timing of the execution, only days after the death by hunger strike of Terence MacSwiney, the republican Lord Mayor of Cork, brought public opinion to a fever-pitch. His death attracted international attention, and attempts were made by U.S. and Vatican officials to secure a reprieve. His execution and MacSwiney's death precipitated an escalation in violence as the Irish War of Independence entered its bloodiest phase, and Barry became an Irish republican martyr.
The iconic portrait of a teenage Kevin Barry,one of our most celebrated republican martyrs-in the black and white hooped rugby jersey of Belvedere College SJ. 26cm x 30cm Dunmanway Co Cork Kevin Gerard Barry (20 January 1902 – 1 November 1920) was an Irish republican paramilitary who was executed by the British Government during the Irish War of Independence. He was sentenced to death for his part in an attack upon a British Army supply lorry which resulted in the deaths of three British soldiers. His execution inflamed nationalist public opinion in Ireland, largely because of his age. The timing of the execution, only days after the death by hunger strike of Terence MacSwiney, the republican Lord Mayor of Cork, brought public opinion to a fever-pitch. His death attracted international attention, and attempts were made by U.S. and Vatican officials to secure a reprieve. His execution and MacSwiney's death precipitated an escalation in violence as the Irish War of Independence entered its bloodiest phase, and Barry became an Irish republican martyr.Early life
Kevin Barry was born on 20 January 1902, at 8 Fleet Street, Dublin, to Thomas and Mary (née Dowling) Barry. The fourth of seven children, two boys and five sisters, Kevin was baptised in St Andrew's Church, Westland Row. Thomas Barry Sr. worked on the family's farm at Tombeagh, Hacketstown, County Carlow, and ran a dairy business from Fleet Street. Thomas Barry Sr. died in 1908, aged 56. His mother came from Drumguin, County Carlow, and, upon the death of her husband, moved the family to nearby Tombeagh. As a child he went to the national school in Rathvilly. On returning to Dublin, he attended St Mary's College, Rathmines, until the school closed in the summer of 1916.When he was thirteen, he attended a commemoration for the Manchester Martyrs, who were hanged in England in 1867. Afterwards he wished to join Constance Markievicz's Fianna Éireann, but was reportedly dissuaded by his family.Belvedere College
From St Mary's College he transferred to Belvedere College, where he was a member of the championship Junior Rugby Cup team, and earned a place on the senior team. In 1918 he became secretary of the school hurling club which had just been formed, and was one of their most enthusiastic players.A Jesuit priest, Thomas Counihan, who was Barry's science and mathematics teacher, said of him: "He was a dour kind of lad. But once he got down to something he went straight ahead… There was no waving of flags with him, but he was sincere and intense." Notwithstanding his many activities, he did not neglect his studies. He won a merit-based scholarship given annually by Dublin Corporation, which allowed him to become a student of medicine at UCD.Medical student
He entered University College Dublin in 1919. His closest friend at college was Gerry MacAleer, from Dungannon, whom he had first met in Belvedere. Other friends included Frank Flood, Tom Kissane and Mick Robinson, who, unknown to many in the college, were, along with Barry, members of the Irish Volunteers.Volunteer activities
In October 1917, during his second year at Belvedere, aged 15, he joined the IRA. Assigned originally to ‘C’ Company 1st Battalion, based on the north side of Dublin, he later transferred to the newly formed ‘H’ Company, under the command of Capt. Seamus Kavanagh. His first job as a member of the IRA was delivering mobilisation orders around the city. Along with other volunteers, Barry trained in a number of locations in Dublin, including the building at 44 Parnell Square, the present day headquarters of Sinn Féin, now named Kevin Barry Hall. The IRA held Field exercises during this period which were conducted in north county Dublin and in areas such as Finglas.The following year, at the age of 16, he was introduced by Seán O'Neill and Bob O'Flanagan to the Clarke Luby Club of the IRB, which had been reorganised. He took part in a number of IRA operations in the years leading up to his capture. He was part of the unit which raided the Shamrock Works for weapons destined to be handed over to the R.I.C. He also took part in the raid on Mark's of Capel Street, looking for ammunition and explosives. On 1 June 1920, under Vice-Commandant Peadar Clancy, he played a notable part in the seizing of the King's Inn, capturing the garrison’s arms. The haul included 25 rifles, two light machine guns and large quantities of ammunition. The 25 British soldiers captured during the attack were released as the volunteers withdrew. In recognition of his dedication to duty he was promoted to Section Commander.Ambush
On the morning of 20 September 1920, Barry went to Mass, then joined a party of IRA volunteers on Bolton Street in Dublin. Their orders were to ambush a British army lorry as it picked up a delivery of bread from the bakery, and capture their weapons. The ambush was scheduled for 11:00am, which gave him enough time to take part in the operation and return to class in time for an examination he had at 2:00pm. The truck arrived late, and was under the command of Sergeant Banks. Armed with a .38 Mauser Parabellum, Barry and members of C Company were to surround the lorry, disarm the soldiers, take the weapons and escape. He covered the back of the vehicle and, when challenged, the five soldiers complied with the order to lay down their weapons. A shot was then fired; Terry Golway, author of For the Cause of Liberty, suggests it was possibly a warning shot from an uncovered soldier in the front. Barry and the rest of the ambush party then opened fire. His gun jammed twice and he dived for cover under the vehicle. His comrades fled and he was left behind. He was then spotted and arrested by the soldiers.One of the soldiers, Private Harold Washington, aged 15, had been shot dead. Two others, Privates Marshall Whitehead and Thomas Humphries, were both badly wounded and later died of their wounds. The British Army released the following statement on Monday afternoon:This morning a party of one N.C.O. and six men of the Duke of Wellington's Regiment were fired on by a body of civilians outside a bakery in Church Street, Dublin. One soldier was killed and four were wounded. A piquet of the Lancashire Fusiliers in the vicinity, hearing the shots, hurried to their comrades' assistance, and succeeded in arresting one of the aggressors. No arms or equipment were lost by the soldiers.
Much was made of Barry's age by Irish newspapers, but the British military pointed out that the three soldiers who had been killed were "much the same age as Barry". On 20 October, Major Reginald Ingram Marians OBE, Head of the Press Section of the General Staff, informed Basil Clarke, Head of Publicity, that Washington was "only 19 and that the other soldiers were of similar ages." General Macready was well aware of the "propaganda value of the soldier's ages." Macready informed General Sir Henry Wilson on the day that sentence was pronounced "of the three men who were killed by him (Barry) and his friends two were 19 and one 20 — official age so probably they were younger... so if you want propaganda there you are."It was later confirmed that Private Harold Washington was 15 years and 351 days old, having been born 4 October 1904. About this competing propaganda, Martin Doherty wrote in a magazine article entitled 'Kevin Barry & the Anglo-Irish Propaganda War':from the British point of view, therefore, the Anglo-Irish propaganda war was probably unwinable [sic]. Nationalist Ireland had decided that men like Kevin Barry fought to free their country, while British soldiers — young or not — sought to withhold that freedom. In these circumstances, to label Barry a murderer was merely to add insult to injury. The contrasting failure of British propaganda is graphically demonstrated by the simple fact that even in British newspapers Privates Whitehead, Washington and Humphries remained faceless names and numbers, for whom no songs were written.”
Capture and torture
Barry was placed in the back of the lorry with the young body of Private Harold Washington, and was subjected to some abuse by Washington's comrades. He was transported then to the North Dublin Union. Upon arrival at the barracks he was taken under military police escort to the defaulters' room where he was searched and handcuffed. A short while later, three sergeants of the Lancashire Fusiliers and two officers began the interrogation. He gave his name and an address of 58 South Circular Road, Dublin (his uncle's address), and his occupation as a medical student, but refused to answer any other questions. The officers continued to demand the names of other republicans involved in the ambush. At this time a publicity campaign was mounted by Sinn Féin. Barry received orders on 28 October from his brigade commander, Richard McKee, "to make a sworn affidavit concerning his torture in the North Dublin Union." Arrangements were made to deliver this through Barry's sister, Kathy, to Desmond Fitzgerald, director of publicity for Sinn Féin, "with the object of having it published in the World press, and particularly in the English papers, on Saturday 30th October." The affidavit, drawn up in Mountjoy Prison days before his execution, describes his treatment when the question of names was repeated:Sinn Féin's Dublin HQ at the Kevin Barry Memorial HallHe tried to persuade me to give the names, and I persisted in refusing. He then sent the sergeant out of the room for a bayonet. When it was brought in the sergeant was ordered by the same officer to point the bayonet at my stomach ... The sergeant then said that he would run the bayonet into me if I did not tell ... The same officer then said to me that if I persisted in my attitude he would turn me out to the men in the barrack square, and he supposed I knew what that meant with the men in their present temper. I said nothing. He ordered the sergeants to put me face down on the floor and twist my arm ... When I lay on the floor, one of the sergeants knelt on my back, the other two placed one foot each on my back and left shoulder, and the man who knelt on me twisted my right arm, holding it by the wrist with one hand, while he held my hair with the other to pull back my head. The arm was twisted from the elbow joint. This continued, to the best of my judgment, for five minutes. It was very painful ... I still persisted in refusing to answer these questions... A civilian came in and repeated the questions, with the same result. He informed me that if I gave all the information I knew I could get off.
On 28 October, the Irish Bulletin (organised by Dick McKee, the IRA Commandant of the Dublin Brigade), a news-sheet produced by Dáil Éireann's Department of Publicity,published Barry's statement alleging torture. The headline read: English Military Government Torture a Prisoner of War and are about to Hang him. The Irish Bulletin declared Barry to be a prisoner of war, suggesting a conflict of principles was at the heart of the conflict. The English did not recognise a war and treated all killings by the IRA as murder. Irish republicans claimed that they were at war and it was being fought between two opposing nations and therefore demanded prisoner of war status. Historian John Ainsworth, author of Kevin Barry, the Incident at Monk's bakery and the Making of an Irish Republican Legend, pointed out that Barry had been captured by the British not as a uniformed soldier but disguised as a civilian and in possession of flat-nosed "Dum-dum" bullets, which expand upon impact, maximising the amount of damage done to the "unfortunate individual" targeted, in contravention of the Hague Convention of 1899. Erskine Childers addressed the question of political status in a letter to the press on 29 October, which was published the day after Barry's execution.-
- This lad Barry was doing precisely what Englishmen would be doing under the same circumstances and with the same bitter and intolerable provocation — the suppression by military force of their country's liberty.
- To hang him for murder is an insulting outrage, and it is more: it is an abuse of power: an unworthy act of vengeance. contrasting ill with the forbearance and humanity invariably shown by the Irish Volunteers towards the prisoners captured by them when they have been successful in encounters similar to this one. These guerrilla combats with soldiers and constables — both classes do the same work with the same weapons; the work of military repression — are typical episodes in Ireland.
- Murder of individual constables, miscalled ‘police’, have been comparatively rare. The Government figure is 38, and it will not, to my knowledge, bear examination. I charge against the British Government 80 murders by soldiers and constables: murders of unarmed people, and for the most part wholly innocent people, including old men, women and boys.
- To hang Barry is to push to its logical extreme the hypocritical pretense that the national movement in Ireland unflinchingly supported by the great mass of the Irish people, is the squalid conspiracy of a ‘murder gang’.
- That is false; it is a natural uprising: a collision between two Governments, one resting on consent, the other on force. The Irish are struggling against overwhelming odds to defend their own elected institutions against extinction.
-
-
-
Under similar circumstances a body of Irish Volunteers captured on June 1 of the present year a party of 25 English military who were on duty at the King's Inns, Dublin. Having disarmed the party the Volunteers immediately released their prisoners. This was in strict accordance with the conduct of the Volunteers in all such encounters. Hundreds of members of the armed forces have been from time to time captured by the Volunteers and in no case was any prisoner maltreated even though Volunteers had been killed and wounded in the fighting, as in the case of Cloyne, Co. Cork, when, after a conflict in which one Volunteer was killed and two wounded, the whole of the opposing forces were captured, disarmed, and set at liberty.
-
-
Trial
The War Office ordered that Kevin Barry be tried by court-martial under the Restoration of Order in Ireland Act, which received Royal Assent on 9 August 1920. General Sir Nevil Macready, Commander-in-Chief of British forces in Ireland then nominated a court of nine officers under a Brigadier-General Onslow. On 20 October, at 10 o’clock, the nine officers of the court — ranging in rank from Brigadier to Lieutenant — took their places at an elevated table. At 10.25, Kevin Barry was brought into the room by a military escort. Then Seán Ó hUadhaigh sought a short adjournment to consult his client. The court granted this request. After the short adjournment Barry announced "As a soldier of the Irish Republic, I refuse to recognise the court." Brigadier Onslow explained the prisoner's "perilous situation" and that he was being tried on a capital charge. He did not reply. Ó hUadhaigh then rose to tell the court that since his client did not recognise the authority of the court he himself could take no further part in the proceedings. Barry was charged on three counts of the murder of Private Marshall Whitehead. One of the bullets taken from Whitehead's body was of .45 calibre, while all witnesses stated that Barry was armed with a .38 Mauser Parabellum. The Judge Advocate General informed the court that the Crown had only to prove that the accused was one of the party that killed three British soldiers, and every member of the party was technically guilty of murder. In accordance with military procedure the verdict was not announced in court. He was returned to Mountjoy, and at about 8 o’clock that night, the district court-martial officer entered his cell and read out the sentence: death by hanging. The public learned on 28 October that the date of execution had been fixed for 1 November.Execution
Barry spent the last day of his life preparing for death. His ordeal focused world attention on Ireland. According to Sean Cronin, author of a biography of Barry (Kevin Barry), he hoped for a firing squad rather than the gallows, as he had been condemned by a military court. A friend who visited him in Mountjoy prison after he received confirmation of the death sentence, said:He is meeting death as he met life with courage but with nothing of the braggart. He does not believe that he is doing anything wonderfully heroic. Again and again he has begged that no fuss be made about him.
He reported Barry as saying "It is nothing, to give one's life for Ireland. I'm not the first and maybe I won't be the last. What's my life compared with the cause?" Barry joked about his death with his sister Kathy. "Well, they are not going to let me like a soldier fall… But I must say they are going to hang me like a gentleman." This was, according to Cronin, a reference to George Bernard Shaw's The Devil's Disciple, the last play Kevin and his sister had seen together. On 31 October, he was allowed three visits of three people each, the last of which was taken by his mother, brother and sisters. In addition to the two Auxiliaries with him, there were five or six warders in the boardroom. As his family were leaving, they met Canon John Waters, on the way in, who said, "This boy does not seem to realise he is going to die in the morning." Mrs Barry asked him what he meant. He said: "He is so gay and light-hearted all the time. If he fully realised it, he would be overwhelmed." Mrs Barry replied, "Canon Waters, I know you are not a Republican. But is it impossible for you to understand that my son is actually proud to die for the Republic?" Canon Waters became somewhat flustered as they parted. The Barry family recorded that they were upset by this encounter because they considered the chief chaplain "the nearest thing to a friend that Kevin would see before his death, and he seemed so alien." Kevin Barry was hanged on 1 November, after hearing two Masses in his cell. Canon Waters, who walked with him to the scaffold, wrote to Barry's mother later, "You are the mother, my dear Mrs Barry, of one of the bravest and best boys I have ever known. His death was one of the most holy, and your dear boy is waiting for you now, beyond the reach of sorrow or trial." Dublin Corporation met on the Monday, and passed a vote of sympathy with the Barry family, and adjourned the meeting as a mark of respect. The Chief Secretary's office in Dublin Castle, on the Monday night, released the following communiqué:The sentence of death by hanging passed by court-martial upon Kevin Barry, or Berry, medical student, aged 18½ years, for the murder of Private Whitehead in Dublin on September 20, was duly executed this morning at Mountjoy Prison, Dublin. At a military court of inquiry, held subsequently in lieu of an inquest, medical evidence was given to the effect that death was instantaneous. The court found that the sentence had been carried out in accordance with law.
Barry's body was buried at 1.30 p.m, in a plot near the women's prison. His comrade and fellow-student Frank Flood was buried alongside him four months later. A plain cross marked their graves and those of Patrick Moran, Thomas Whelan, Thomas Traynor, Patrick Doyle, Thomas Bryan, Bernard Ryan, Edmond Foley and Patrick Maher who were hanged in the same prison before the Anglo-Irish Treaty of July 1921 which ended hostilities between Irish republicans and the British.The men had been buried in unconsecrated ground on the jail property and their graves went unidentified until 1934.They became known as The Forgotten Ten by republicans campaigning for the bodies to be reburied with honour and proper rites.On 14 October 2001, the remains of these ten men were given a state funeral and moved from Mountjoy Prison to be re-interred at Glasnevin Cemetery in Dublin.Aftermath
 Kevin Barry monument in Rathvilly, County CarlowThe only full-length biography of Kevin Barry was written by his nephew, journalist Donal O'Donovan, published in 1989 as Kevin Barry and his Time. In 1965, Sean Cronin wrote a short biography, simply entitled "Kevin Barry"; this was published by The National Publications Committee, Cork, to which Tom Barry provided a foreword. Barry is remembered in a well-known song about his imprisonment and execution, written shortly after his death and still sung today. The tune to "Kevin Barry" was taken from the sea-shanty "Rolling Home".[17] The execution reportedly inspired Thomas MacGreevy's surrealist poem, "Homage to Hieronymus Bosch". MacGreevy had unsuccessfully petitioned the Provost of Trinity College Dublin, John Henry Bernard, to make representations on Barry's behalf.
Kevin Barry monument in Rathvilly, County CarlowThe only full-length biography of Kevin Barry was written by his nephew, journalist Donal O'Donovan, published in 1989 as Kevin Barry and his Time. In 1965, Sean Cronin wrote a short biography, simply entitled "Kevin Barry"; this was published by The National Publications Committee, Cork, to which Tom Barry provided a foreword. Barry is remembered in a well-known song about his imprisonment and execution, written shortly after his death and still sung today. The tune to "Kevin Barry" was taken from the sea-shanty "Rolling Home".[17] The execution reportedly inspired Thomas MacGreevy's surrealist poem, "Homage to Hieronymus Bosch". MacGreevy had unsuccessfully petitioned the Provost of Trinity College Dublin, John Henry Bernard, to make representations on Barry's behalf. On 14 October 2001 the remains of Kevin Barry and nine other volunteers from the War of Independence were given a state funeral and moved from Mountjoy Prison to be re-interred at Glasnevin Cemetery in Dublin. Barry's grave is the first on the left.
On 14 October 2001 the remains of Kevin Barry and nine other volunteers from the War of Independence were given a state funeral and moved from Mountjoy Prison to be re-interred at Glasnevin Cemetery in Dublin. Barry's grave is the first on the left.Legacy[edit]
A commemorative stamp was issued by An Post to mark the 50th anniversary of Barry's death in 1970.[18] The University College Dublin and National University of Ireland, Galway branches of Ógra Fianna Fáil are named after him.[19] Derrylaughan Kevin Barry's GAA club was founded in Clonoe, County Tyrone. In 1930, Irish immigrants in Hartford, Connecticut, created a hurling club and named it after Barry. The club later disappeared for decades, but was revived in 2011 by more recently arrived Irish immigrants and local Irish-Americans in the area.[20] In 1934, a large stained-glass window commemorating Barry was unveiled in Earlsfort Terrace, then the principal campus of University College Dublin. It was designed by Richard King of the Harry Clarke Studio. In 2007, UCD completed its relocation to the Belfield campus some four miles away and a fund was collected by graduates to defray the cost (estimated at close to €250,000) of restoring and moving the window to this new location.[21] A grandnephew of Kevin Barry is Irish historian Eunan O'Halpin.[22] There is an Irish republican flute band named after him, the "Volunteer Kevin Barry Republican Flute Band", which operates out of the Calton area of the city.[citation needed] Barry's execution is mentioned in the folk song "Rifles of the I.R.A." written by Dominic Behan in 1968. A ballad bearing Barry's name, relating the story of his execution, has been sung by artists as diverse as Paul Robeson,[23] Leonard Cohen,[24] Lonnie Donegan, and The Dubliners. At the place where Kevin Barry was captured (North King Street/Church Street, Dublin), there are two blocks of flats named after him. -
-

 58cm x 42cm Quaint vintage poster of a jaunting car carrying a group around Phoenix Park- the giant Wellington monument can be seen in the background. The Wellington Monument or sometimes the Wellington Testimonial,is an obelisk located in the Phoenix Park, Dublin, Ireland. The testimonial is situated at the southeast end of the Park, overlooking Kilmainham and the River Liffey. The structure is 62 metres (203 ft) tall, making it the largest obelisk in Europe
58cm x 42cm Quaint vintage poster of a jaunting car carrying a group around Phoenix Park- the giant Wellington monument can be seen in the background. The Wellington Monument or sometimes the Wellington Testimonial,is an obelisk located in the Phoenix Park, Dublin, Ireland. The testimonial is situated at the southeast end of the Park, overlooking Kilmainham and the River Liffey. The structure is 62 metres (203 ft) tall, making it the largest obelisk in EuropeHistory
The Wellington Testimonial was built to commemorate the victories of Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington. Wellington, the British politician and general, also known as the 'Iron Duke', was born in Ireland. Originally planned to be located in Merrion Square, it was built in the Phoenix Park after opposition from the square's residents. The obelisk was designed by the architect Sir Robert Smirke and the foundation stone was laid in 1817. In 1820, the project ran out of construction funds and the structure remained unfinished until 18 June 1861 when it was opened to the public. There were also plans for a statue of Wellington on horseback, but a shortage of funds ruled that out.Features
There are four bronze plaques cast from cannons captured at Waterloo – three of which have pictorial representations of his career while the fourth has an inscription. The plaques depict 'Civil and Religious Liberty' by John Hogan, 'Waterloo' by Thomas Farrell and the 'Indian Wars' by Joseph Robinson Kirk. The inscription reads:- Asia and Europe, saved by thee, proclaim
- Invincible in war thy deathless name,
- Now round thy brow the civic oak we twine
- That every earthly glory may be thine.
Cultural references
The monument is referenced throughout James Joyce's Finnegans Wake. The first page of the novel alludes to a giant whose head is at "Howth Castle and Environs" and whose toes are at "a knock out in the park (p. 3)"; John Bishop extends the analogy, interpreting this centrally located obelisk as the prone giant's male member. A few pages later, the monument is the site of the fictional "Willingdone Museyroom" (p. 8). -

 Locke's Old Kilbeggan Pure Pot Still Whiskey Advert Origins: Kilbeggan Co Westmeath Dimensions: 32cm x 37cm The Kilbeggan Distillery (formerly Brusna Distillery and Locke's Distillery) is an Irish whiskey distillery situated on the River Brosna in Kilbeggan, County Westmeath, Ireland. It is owned by Beam Suntory. A small pot still distillery, the licence to distil dates to 1757, a copy of which can be seen in the distillery. Similar to many Irish distilleries, Kilbeggan endured financial difficulties during the early 20th century, and ceased operations in 1957. However, the distillery was later refurbished, with distilling recommencing on-site in 2007. Noted devotees of the distillery's whiskeys include British Prime Minister Sir Winston Churchill, and Myles na gCopaleen, the Irish playwright.
Locke's Old Kilbeggan Pure Pot Still Whiskey Advert Origins: Kilbeggan Co Westmeath Dimensions: 32cm x 37cm The Kilbeggan Distillery (formerly Brusna Distillery and Locke's Distillery) is an Irish whiskey distillery situated on the River Brosna in Kilbeggan, County Westmeath, Ireland. It is owned by Beam Suntory. A small pot still distillery, the licence to distil dates to 1757, a copy of which can be seen in the distillery. Similar to many Irish distilleries, Kilbeggan endured financial difficulties during the early 20th century, and ceased operations in 1957. However, the distillery was later refurbished, with distilling recommencing on-site in 2007. Noted devotees of the distillery's whiskeys include British Prime Minister Sir Winston Churchill, and Myles na gCopaleen, the Irish playwright.Early years
The distillery was founded in 1757 by Matthew MacManus, who may have distilled elsewhere before founding Kilbeggan.Although information about the early years of the distillery is scarce, documentation suggests that in its early years the distillery operated with a 232 gallon still, and an annual output of 1,500 gallons. By the early 19th century, the distillery was being run by a John and William Codd. In 1841, the distillery was put up for sale following the dissolution of the partnership between its then owners, William Codd and William Cuffee.The distillery at the time consisted of a brew house, still house with three pot stills (wash still: 8,000 gallons; low wine still, no. 1; 2,000 gallons; low wine still, no. 2: 1,500 gallons), run-room with five receivers, malt house, corn stores capable of storing 5,000 barrels, and oat-meal mills. Also listed in the sale were 400 tonnes of coal, and 10,000 boxes of turf - the latter reflecting the immense quantities of turf consumed at the distillery, so much so, that it was reported to have kept hundreds of poor people profitably employed in cutting, rearing, and drawing it to the town throughout the year.Locke's Distillery
In 1843, the distillery was taken over by John Locke, under whose stewardship the distillery flourished. Locke treated his staff well, and was held in high regard by both his workers and the people of the town. Informal records show that under Locke the distillery provided cottages for its employees, either for rent or purchase through a form of in-house mortgage scheme. In addition, all staff received a wagon load of coal at the start of each winter, the cost of which was deducted from salaries retrospectively on a weekly basis. Testimony of the respect with which he was held is offered by an incident in 1866. Following an accident on-site which had rendered a critical piece of equipment, the steam boiler, inoperable, the distillery had come to a standstill. With Locke unable to afford or obtain a loan to fund a replacement, the future of distillery lay in doubt.However, in a gesture of solidarity, the people of Kilbeggan came together and purchased a replacement boiler, which they presented to John Locke, along with the following public letter of appreciation, which was printed in several local newspapers at the time:An Address from the People of Kilbeggan to John Locke, Esq. Dear Sir - Permit us, your fellow townsmen, to assure of our deep and cordial sympathy in your loss and disappointment from the accident which occurred recently in your Distillery. Sincerely as we regret the accident, happily unattended with loss of life, we cannot but rejoice at the long-wished-for opportunity it affords us of testifying to you the high appreciation in which we hold you for your public and private worth. We are well aware that the restrictions imposed by recent legislation on that particular branch of Irish industry, with which you have been so long identified, have been attended with disastrous results to the trade, as is manifest in the long list of Distilleries now almost in ruins, and which were a few years ago centres of busy industry, affording remunerative employment to thousands of hands; and we are convinced the Kilbeggan Distillery would have long since swelled the dismal catalogue had it fallen into less energetic and enterprising hands. In such an event we would be compelled to witness the disheartening scene of a large number of our working population without employment during that period of the year when employment Is scarcest, and at the same time most essential to the poor. Independent then of what we owe you, on purely personal grounds, we feel we owe you a deep debt of gratitude for maintaining in our midst a manufacture which affords such extensive employment to our poor, and exercises so favourable an influence on the prosperity of the town. In conclusion, dear Sir, we beg your acceptance of a new steam boiler to replace the injured one, as testimony, inadequate though it is, of our unfeigned respect and esteems for you ; and we beg to present it with the ardent wish and earnest hope that, for many long years to come, it may contribute to enhance still more the deservedly high and increasing reputation of the Kilbeggan Distillery.
In a public response to mark the gift, also published in several newspapers, Locke thanked the people of Kilbeggan for their generosity, stating "...I feel this to be the proudest day of my life...". A plaque commemorating the event hangs in the distillery's restaurant today. In 1878, a fire broke out in the "can dip" (sampling) room of the distillery, and spread rapidly. Although, the fire was extinguished within an hour, it destroying a considerable portion of the front of the distillery and caused £400 worth of damage. Hundreds of gallons of new whiskey were also consumed in the blaze - however, the distillery is said to have been saved from further physical and financial ruin through the quick reaction of townsfolk who broke down the doors of the warehouses, and helped roll thousands of casks of ageing spirit down the street to safety. In 1887, the distillery was visited by Alfred Barnard, a British writer, as research for his book, "the Whiskey Distilleries of the United Kingdom". By then, the much enlarged distillery was being managed by John's sons, John Edward and James Harvey, who told Barnard that the distillery's output had more than doubled during the preceding ten years, and that they intended to install electric lighting.Barnard noted that the distillery, which he referred to as the "Brusna Distillery", named for the nearby river, was said to be the oldest in Ireland. According to Barnard, the distillery covered 5 acres, and employed a staff of about 70 men, with the aged and sick pensioned-off or assisted. At the time of his visit, the distillery was producing 157,200 proof gallons per annum, though it had the capacity to produce 200,000. The whiskey, which was sold primarily in Dublin, England, and "the Colonies", was "old pot still", produced using four pot stills (two wash stills: 10,320 / 8,436 gallons; and two spirit stills: 6,170 / 6,080 gallons), which had been installed by Millar and Company, Dublin. Barnard remarked that at the time of his visit over 2,000 casks of spirit were ageing in the distillery's bonded warehouses. In 1893, the distillery ceased to be privately held, and was converted a limited stock company, trading as John Locke & Co., Ltd., with nominal capital of £40,000.Decline and Closure
In the early part of the 20th century, Kilbeggan, like many Irish whiskey distilleries at the time, entered a period of decline. This was due to the combined effects of loss and hampering of market access - due to prohibition in the United States, the trade war with the British Empire, shipping difficulties during the world wars, and Irish Government export quotas; as well as competition from blended Scotch, and disruption to production during the Irish war of Independence. As a result, Kilbeggan was forced to cease production of new spirit for 7 years between 1924 and 1931, decimating the company's cash flow and finances.Most of the staff at the distillery were let go, and the distillery slowly sold off its stocks of aged whiskey. Distilling resumed in 1931, following the end of prohibition in the United States, and for a time the distillery's finances improved - with a loss of £83 in 1931, converted to a modest profit of £6,700 in 1939. In the 1920s, both of John sons passed away, John in 1920, and James in 1927, and ownership of the distillery passed to Locke's granddaughters, Mary Evelyn and Florence Emily.However, by then the distillery was in need to repair, with the turbulent economic conditions of the early 20th century having meant that no investment had been made in new plant since the 1890s. In 1947, the Lockes decided to put the distillery was put up for sale as a going concern. Although run down, the distillery had valuable stocks of mature whiskey, a valuable commodity in post-war Europe.An offer of £305,000 was received from a Swiss investor fronted by an Englishman, going by the name of Horace Smith.Their unstated interest, was not the business itself, but the 60,000 gallons of whiskey stocks, which they hoped to sell on the black market in England at £11 a gallon - thus, more than doubling their investment overnight. However, when they failed to come up with the deposit, the duo were arrested and promptly interrogated by Irish police. The Englishman, it turned out, was an impostor named Maximoe, who was wanted by Scotland Yard.]The Irish authorities placed Maximoe on a ferry back to England for extradition, but he jumped overboard and escaped with the help of unknown accomplices. An Irish opposition politician, Oliver J. Flanagan, subsequently alleged under parliamentary privilege that members of the governing Fianna Fáil political party were linked to the deal, accusing then Irish Taoiseach Éamon de Valera and his son of having accepted gold watches from the Swiss businessman. A tribunal of inquiry discounted the allegations but the damage contributed to Fianna Fáil's defeat in the 1948 election. In addition, as the scandal remained headline news in Ireland for several months, it discouraged interest from other investors in the distillery. Thus with no buyer found, operations continued at the distillery, with production averaging between 120,000 - 150,000 proof gallons per annum, and consumption running at between 15,000 - 20,000 barrels of barrel.In addition, although heavily indebted, investments were made in new plant and equipment. However, the death knell for the distillery came in April 1952, when the Irish Government introduced a 28% hike in the excise duties on spirits, causing a drastic decline in domestic whiskey sales. By November 1953, the distillery could not afford to pay the duty to release whiskey ordered for Christmas from bond, and production was forced to come to a halt. Although distilling had stopped, the firm struggled on until 27 November 1958, when a debenture issued in 1953 fell due, which the distillery could not afford to pay, forcing the bank to call in the receivers. Thus, bringing to an end 201 years of distilling in the town. In 1962, the distillery was purchased for £10,000 by Karl Heinz Moller, a German businessman, who owned a motor distribution company in Hamburg.Moller made a substantial profit on the deal, by selling off the whiskey stocks (about 100,000 gallons - worth tens of thousands of pounds alone) and a rare Mercedes Benz owned by the distillery. Much to the dismay of locals, Moller proceeded to convert the distillery into a pigsty, smashing thousands of Locke earthenware crocks (which would be worth a substantial amount at auction today) to create a hard-core base for the concrete floor. In 1969, the distillery was sold to Powerscreen, a firm which sold Volvo loading shovels, and in the early 1970s, the stills and worms were removed and sold for scrap.Distillery reopens
In 1982, almost thirty years after the distillery ceased operations, the Kilbeggan Preservation and Development Association was formed by locals in the town. Using funds raised locally, the Association restored the Distillery, and reopened it to the public as a whiskey distillery museum. Then, in 1987, the newly opened Cooley Distillery acquired the assets of Kilbeggan distillery, allowing Cooley to relaunch whiskeys under the Kilbeggan and Locke's Whiskey brands. Cooley later also took over the running of the museum, and began the process of re-establishing a working distillery on-site. Cooley were aided in the process by the fact that since the distillery's closure, each subsequent owner had faithfully paid the £5 annual fee to maintain the distilling licence. In 2007, the 250th anniversary of the distillery's founding, distillation recommenced at Kilbeggan. The official firing of the pot stills was witnessed by direct descendants of the three families, the McManuses, the Codds, and the Lockes, who had run the distillery during its 200 year distilling history. In a fitting nod to the long history of distilling at Kilbeggan, one of the two pot stills installed in the refurbished distillery was a 180-year old pot still, which had originally been installed at the Old Tullamore Distillery in the early 1800s.] It is the oldest working pot still producing whiskey in the world today. In 2010, with the installation of a mash tun and fermentation vats, Kilbeggan became a fully operational distillery once again.Present day
Today the distillery is known as Kilbeggan Distillery, and includes a restaurant, The Pantry Restaurant, and a 19th-century waterwheel that has been restored to working condition. The distillery can also be powered by a steam engine, which is in working condition but rarely used. It was installed to allow the distillery to continue operating in times of low water on the river. Prior to the recommencement of operations of Kilbeggan, the three brands associated with the distillery—Kilbeggan, Locke's Blend and Locke's Malt were produced at the Cooley Distillery in County Louth, before being transported to Kilbeggan, where they were to stored in a 200 year old granite warehouse. However, following recommencement of operations at Kilbeggan, new whiskey produced on-site has been sufficiently mature for market since around 2014. Since reopening, the distillery has launched a Kilbeggan Small Batch Rye, the first whiskey to be 100% distilled and matured on-site since the restoration was completed. Double-distilled, the whiskey is produced from a mash of malt, barley, and about 30% rye, said to reflect the traditional practice of using rye, which was common at 19th century Irish distilleries, but has since virtually died out. In late 2009, the distillery released small '3-pack' samples of its still-developing "new make spirit" at 1 month, 1 year, and 2 years of age (in Ireland, the spirit must be aged a minimum of three years before it can legally be called "whiskey"). The distillery's visitor centre was among the nominations in Whisky Magazine's Icons of Whisky visitor attraction category in 2008.Gallery
-

 Locke's Old Kilbeggan Pure Pot Still Whiskey Advert Origins: Kilbeggan Co Westmeath Dimensions: 32cm x 37cm The Kilbeggan Distillery (formerly Brusna Distillery and Locke's Distillery) is an Irish whiskey distillery situated on the River Brosna in Kilbeggan, County Westmeath, Ireland. It is owned by Beam Suntory. A small pot still distillery, the licence to distil dates to 1757, a copy of which can be seen in the distillery. Similar to many Irish distilleries, Kilbeggan endured financial difficulties during the early 20th century, and ceased operations in 1957. However, the distillery was later refurbished, with distilling recommencing on-site in 2007. Noted devotees of the distillery's whiskeys include British Prime Minister Sir Winston Churchill, and Myles na gCopaleen, the Irish playwright.
Locke's Old Kilbeggan Pure Pot Still Whiskey Advert Origins: Kilbeggan Co Westmeath Dimensions: 32cm x 37cm The Kilbeggan Distillery (formerly Brusna Distillery and Locke's Distillery) is an Irish whiskey distillery situated on the River Brosna in Kilbeggan, County Westmeath, Ireland. It is owned by Beam Suntory. A small pot still distillery, the licence to distil dates to 1757, a copy of which can be seen in the distillery. Similar to many Irish distilleries, Kilbeggan endured financial difficulties during the early 20th century, and ceased operations in 1957. However, the distillery was later refurbished, with distilling recommencing on-site in 2007. Noted devotees of the distillery's whiskeys include British Prime Minister Sir Winston Churchill, and Myles na gCopaleen, the Irish playwright.Early years
The distillery was founded in 1757 by Matthew MacManus, who may have distilled elsewhere before founding Kilbeggan.Although information about the early years of the distillery is scarce, documentation suggests that in its early years the distillery operated with a 232 gallon still, and an annual output of 1,500 gallons. By the early 19th century, the distillery was being run by a John and William Codd. In 1841, the distillery was put up for sale following the dissolution of the partnership between its then owners, William Codd and William Cuffee.The distillery at the time consisted of a brew house, still house with three pot stills (wash still: 8,000 gallons; low wine still, no. 1; 2,000 gallons; low wine still, no. 2: 1,500 gallons), run-room with five receivers, malt house, corn stores capable of storing 5,000 barrels, and oat-meal mills. Also listed in the sale were 400 tonnes of coal, and 10,000 boxes of turf - the latter reflecting the immense quantities of turf consumed at the distillery, so much so, that it was reported to have kept hundreds of poor people profitably employed in cutting, rearing, and drawing it to the town throughout the year.Locke's Distillery
In 1843, the distillery was taken over by John Locke, under whose stewardship the distillery flourished. Locke treated his staff well, and was held in high regard by both his workers and the people of the town. Informal records show that under Locke the distillery provided cottages for its employees, either for rent or purchase through a form of in-house mortgage scheme. In addition, all staff received a wagon load of coal at the start of each winter, the cost of which was deducted from salaries retrospectively on a weekly basis. Testimony of the respect with which he was held is offered by an incident in 1866. Following an accident on-site which had rendered a critical piece of equipment, the steam boiler, inoperable, the distillery had come to a standstill. With Locke unable to afford or obtain a loan to fund a replacement, the future of distillery lay in doubt.However, in a gesture of solidarity, the people of Kilbeggan came together and purchased a replacement boiler, which they presented to John Locke, along with the following public letter of appreciation, which was printed in several local newspapers at the time:An Address from the People of Kilbeggan to John Locke, Esq. Dear Sir - Permit us, your fellow townsmen, to assure of our deep and cordial sympathy in your loss and disappointment from the accident which occurred recently in your Distillery. Sincerely as we regret the accident, happily unattended with loss of life, we cannot but rejoice at the long-wished-for opportunity it affords us of testifying to you the high appreciation in which we hold you for your public and private worth. We are well aware that the restrictions imposed by recent legislation on that particular branch of Irish industry, with which you have been so long identified, have been attended with disastrous results to the trade, as is manifest in the long list of Distilleries now almost in ruins, and which were a few years ago centres of busy industry, affording remunerative employment to thousands of hands; and we are convinced the Kilbeggan Distillery would have long since swelled the dismal catalogue had it fallen into less energetic and enterprising hands. In such an event we would be compelled to witness the disheartening scene of a large number of our working population without employment during that period of the year when employment Is scarcest, and at the same time most essential to the poor. Independent then of what we owe you, on purely personal grounds, we feel we owe you a deep debt of gratitude for maintaining in our midst a manufacture which affords such extensive employment to our poor, and exercises so favourable an influence on the prosperity of the town. In conclusion, dear Sir, we beg your acceptance of a new steam boiler to replace the injured one, as testimony, inadequate though it is, of our unfeigned respect and esteems for you ; and we beg to present it with the ardent wish and earnest hope that, for many long years to come, it may contribute to enhance still more the deservedly high and increasing reputation of the Kilbeggan Distillery.
In a public response to mark the gift, also published in several newspapers, Locke thanked the people of Kilbeggan for their generosity, stating "...I feel this to be the proudest day of my life...". A plaque commemorating the event hangs in the distillery's restaurant today. In 1878, a fire broke out in the "can dip" (sampling) room of the distillery, and spread rapidly. Although, the fire was extinguished within an hour, it destroying a considerable portion of the front of the distillery and caused £400 worth of damage. Hundreds of gallons of new whiskey were also consumed in the blaze - however, the distillery is said to have been saved from further physical and financial ruin through the quick reaction of townsfolk who broke down the doors of the warehouses, and helped roll thousands of casks of ageing spirit down the street to safety. In 1887, the distillery was visited by Alfred Barnard, a British writer, as research for his book, "the Whiskey Distilleries of the United Kingdom". By then, the much enlarged distillery was being managed by John's sons, John Edward and James Harvey, who told Barnard that the distillery's output had more than doubled during the preceding ten years, and that they intended to install electric lighting.Barnard noted that the distillery, which he referred to as the "Brusna Distillery", named for the nearby river, was said to be the oldest in Ireland. According to Barnard, the distillery covered 5 acres, and employed a staff of about 70 men, with the aged and sick pensioned-off or assisted. At the time of his visit, the distillery was producing 157,200 proof gallons per annum, though it had the capacity to produce 200,000. The whiskey, which was sold primarily in Dublin, England, and "the Colonies", was "old pot still", produced using four pot stills (two wash stills: 10,320 / 8,436 gallons; and two spirit stills: 6,170 / 6,080 gallons), which had been installed by Millar and Company, Dublin. Barnard remarked that at the time of his visit over 2,000 casks of spirit were ageing in the distillery's bonded warehouses. In 1893, the distillery ceased to be privately held, and was converted a limited stock company, trading as John Locke & Co., Ltd., with nominal capital of £40,000.Decline and Closure
In the early part of the 20th century, Kilbeggan, like many Irish whiskey distilleries at the time, entered a period of decline. This was due to the combined effects of loss and hampering of market access - due to prohibition in the United States, the trade war with the British Empire, shipping difficulties during the world wars, and Irish Government export quotas; as well as competition from blended Scotch, and disruption to production during the Irish war of Independence. As a result, Kilbeggan was forced to cease production of new spirit for 7 years between 1924 and 1931, decimating the company's cash flow and finances.Most of the staff at the distillery were let go, and the distillery slowly sold off its stocks of aged whiskey. Distilling resumed in 1931, following the end of prohibition in the United States, and for a time the distillery's finances improved - with a loss of £83 in 1931, converted to a modest profit of £6,700 in 1939. In the 1920s, both of John sons passed away, John in 1920, and James in 1927, and ownership of the distillery passed to Locke's granddaughters, Mary Evelyn and Florence Emily.However, by then the distillery was in need to repair, with the turbulent economic conditions of the early 20th century having meant that no investment had been made in new plant since the 1890s. In 1947, the Lockes decided to put the distillery was put up for sale as a going concern. Although run down, the distillery had valuable stocks of mature whiskey, a valuable commodity in post-war Europe.An offer of £305,000 was received from a Swiss investor fronted by an Englishman, going by the name of Horace Smith.Their unstated interest, was not the business itself, but the 60,000 gallons of whiskey stocks, which they hoped to sell on the black market in England at £11 a gallon - thus, more than doubling their investment overnight. However, when they failed to come up with the deposit, the duo were arrested and promptly interrogated by Irish police. The Englishman, it turned out, was an impostor named Maximoe, who was wanted by Scotland Yard.]The Irish authorities placed Maximoe on a ferry back to England for extradition, but he jumped overboard and escaped with the help of unknown accomplices. An Irish opposition politician, Oliver J. Flanagan, subsequently alleged under parliamentary privilege that members of the governing Fianna Fáil political party were linked to the deal, accusing then Irish Taoiseach Éamon de Valera and his son of having accepted gold watches from the Swiss businessman. A tribunal of inquiry discounted the allegations but the damage contributed to Fianna Fáil's defeat in the 1948 election. In addition, as the scandal remained headline news in Ireland for several months, it discouraged interest from other investors in the distillery. Thus with no buyer found, operations continued at the distillery, with production averaging between 120,000 - 150,000 proof gallons per annum, and consumption running at between 15,000 - 20,000 barrels of barrel.In addition, although heavily indebted, investments were made in new plant and equipment. However, the death knell for the distillery came in April 1952, when the Irish Government introduced a 28% hike in the excise duties on spirits, causing a drastic decline in domestic whiskey sales. By November 1953, the distillery could not afford to pay the duty to release whiskey ordered for Christmas from bond, and production was forced to come to a halt. Although distilling had stopped, the firm struggled on until 27 November 1958, when a debenture issued in 1953 fell due, which the distillery could not afford to pay, forcing the bank to call in the receivers. Thus, bringing to an end 201 years of distilling in the town. In 1962, the distillery was purchased for £10,000 by Karl Heinz Moller, a German businessman, who owned a motor distribution company in Hamburg.Moller made a substantial profit on the deal, by selling off the whiskey stocks (about 100,000 gallons - worth tens of thousands of pounds alone) and a rare Mercedes Benz owned by the distillery. Much to the dismay of locals, Moller proceeded to convert the distillery into a pigsty, smashing thousands of Locke earthenware crocks (which would be worth a substantial amount at auction today) to create a hard-core base for the concrete floor. In 1969, the distillery was sold to Powerscreen, a firm which sold Volvo loading shovels, and in the early 1970s, the stills and worms were removed and sold for scrap.Distillery reopens
In 1982, almost thirty years after the distillery ceased operations, the Kilbeggan Preservation and Development Association was formed by locals in the town. Using funds raised locally, the Association restored the Distillery, and reopened it to the public as a whiskey distillery museum. Then, in 1987, the newly opened Cooley Distillery acquired the assets of Kilbeggan distillery, allowing Cooley to relaunch whiskeys under the Kilbeggan and Locke's Whiskey brands. Cooley later also took over the running of the museum, and began the process of re-establishing a working distillery on-site. Cooley were aided in the process by the fact that since the distillery's closure, each subsequent owner had faithfully paid the £5 annual fee to maintain the distilling licence. In 2007, the 250th anniversary of the distillery's founding, distillation recommenced at Kilbeggan. The official firing of the pot stills was witnessed by direct descendants of the three families, the McManuses, the Codds, and the Lockes, who had run the distillery during its 200 year distilling history. In a fitting nod to the long history of distilling at Kilbeggan, one of the two pot stills installed in the refurbished distillery was a 180-year old pot still, which had originally been installed at the Old Tullamore Distillery in the early 1800s.] It is the oldest working pot still producing whiskey in the world today. In 2010, with the installation of a mash tun and fermentation vats, Kilbeggan became a fully operational distillery once again.Present day
Today the distillery is known as Kilbeggan Distillery, and includes a restaurant, The Pantry Restaurant, and a 19th-century waterwheel that has been restored to working condition. The distillery can also be powered by a steam engine, which is in working condition but rarely used. It was installed to allow the distillery to continue operating in times of low water on the river. Prior to the recommencement of operations of Kilbeggan, the three brands associated with the distillery—Kilbeggan, Locke's Blend and Locke's Malt were produced at the Cooley Distillery in County Louth, before being transported to Kilbeggan, where they were to stored in a 200 year old granite warehouse. However, following recommencement of operations at Kilbeggan, new whiskey produced on-site has been sufficiently mature for market since around 2014. Since reopening, the distillery has launched a Kilbeggan Small Batch Rye, the first whiskey to be 100% distilled and matured on-site since the restoration was completed. Double-distilled, the whiskey is produced from a mash of malt, barley, and about 30% rye, said to reflect the traditional practice of using rye, which was common at 19th century Irish distilleries, but has since virtually died out. In late 2009, the distillery released small '3-pack' samples of its still-developing "new make spirit" at 1 month, 1 year, and 2 years of age (in Ireland, the spirit must be aged a minimum of three years before it can legally be called "whiskey"). The distillery's visitor centre was among the nominations in Whisky Magazine's Icons of Whisky visitor attraction category in 2008.Gallery
-

 46cm x 33cm
46cm x 33cmHistory
This pub is closely associated with Irish traditional music and was where the popular Irish folk group, The Dubliners, began performing in the early 1960s. Many other notable Irish musicians—including Séamus Ennis, Joe Heaney, Andy Irvine,Christy Moore, The Fureys and Phil Lynott—have played at O’Donoghue’s, and their photographs are displayed in the pub. Included are portraits of The Dubliners themselves: the five founding members Ronnie Drew, Luke Kelly, Ciarán Bourke, John Sheahan and Barney McKenna, as well as later members Eamonn Campbell and Seán Cannon; these photographs hang to the right of the entrance, where the nightly sessions are played.Andy Irvine wrote the tribute song "O'Donoghue's", in which he reminisces about his early days in Dublin—when he first started frequenting the pub in August 1962. The song was released on the album Changing Trains (2007). Dessie Hynes from Longford bought the bar from Paddy and Maureen O'Donoghue in 1977 and ran the pub with his family for 11 years. In 1988, O’Donoghue’s was purchased by publicans Oliver Barden and John Mahon. Barden is still the proprietor and continues to run the pub with his family and staff to this dayO’Donoghue’s
~ Andy Irvine, 2004It was August 1962 When I first set foot in O’Donoghue’s A world of music, friends and booze Opened up before me I never could’ve guessed as I walked through the door Just what the future had in store A crossroads for my life I saw Lying there to taunt me. -
Out of stock
 Irish pubs don't just decorate their space with Irish memorabilia.Such is our affinity with the US in particular, that often you see American sports and other pieces of memorabilia on display.And over time we have added such nuggets to our extensive collection.This framed collage of memories from the Boston Garden originated from a pub in Kerry,the owners of which had plenty of family connections in Boston,some of whom actually worked at the Garden.Hence this lovely piece getting sent across the Atlantic. This wonderful poster depicts many of the great events that took place in the Garden over the years.
Irish pubs don't just decorate their space with Irish memorabilia.Such is our affinity with the US in particular, that often you see American sports and other pieces of memorabilia on display.And over time we have added such nuggets to our extensive collection.This framed collage of memories from the Boston Garden originated from a pub in Kerry,the owners of which had plenty of family connections in Boston,some of whom actually worked at the Garden.Hence this lovely piece getting sent across the Atlantic. This wonderful poster depicts many of the great events that took place in the Garden over the years.
Boston Garden was an arena in Boston, Massachusetts. Designed by boxing promoter Tex Rickard, who also built the third iteration of New York's Madison Square Garden, it opened on November 17, 1928 as "Boston Madison Square Garden" (later shortened to just "Boston Garden") and outlived its original namesake by 30 years. It was above North Station, a train station which was originally a hub for the Boston and Maine Railroad and is now a hub for MBTA Commuter Rail and Amtrak trains. The Garden hosted home games for the Boston Bruins of the National Hockey League (NHL) and the Boston Celtics of the National Basketball Association (NBA), as well as rock concerts, amateur sports, boxing and professional wrestling matches, circuses, and ice shows. It was also used as an exposition hall for political rallies such as the speech by John F. Kennedy in November 1960. Boston Garden was demolished in 1998, three years after the completion of its new successor arena, TD Garden.Boston Garden "The Garden" Boston Garden viewed from Causeway Street 1994
Boston Garden viewed from Causeway Street 1994
Former names Boston Madison Square Garden Address 150 Causeway Street Location Boston, Massachusetts Owner Boston and Maine Corporation(1928–1965) Linnell & Cox (1965]–1973) Storer Broadcasting (1973–1975) Delaware North (1975–1997) Operator Madison Square GardenCorporation (1928–1934) Boston Garden-Arena Corporation(1934–1973) Storer Broadcasting (1973–1975) Delaware North (1975–1997) Capacity Ice hockey: 14,448 Basketball: 14,890 Concerts: 15,909 Surface Ice / Parquet floor Construction Broke ground December 1927 Opened November 17, 1928 Closed September 28, 1995 Demolished March 1998 Construction cost $4 million ($59.6 million in 2019 dollars) Architect Tex Rickard Funk & Wilcox Company General contractor Dwight P. Robinson Company, Inc. Tenants Boston Bruins (NHL) (1928–1995) Boston Celtics (BAA/NBA) (1946–1995) Boston Braves (AHL) (1971–1974) New England Whalers (WHA) (1973–1974) Boston Blazers (MILL) (1992–1995) History
Tex Rickard, the noted entrepreneur and boxing promoter who built and operated the third Madison Square Garden, sought to expand his empire by building seven "Madison Square Gardens" around the country. On November 15, 1927, Homer Loring, chairman of the Boston & Maine Railroad, announced that plans had been finalized for the construction of a new North Station facility, which would include a sports arena. A group led by Rickard, John S. Hammond, and William F. Carey of the Madison Square Garden Corporation, as well as Boston businessmen Charles F. Adamsand Huntington Hardwick, signed a 25-year lease for the arena. Sheldon Fairbanks was chosen to be the arena's first general manager. Boston & Maine shareholder Edmund D. Codman challenged the legality of the railroad constructing a non-railroad building. The Massachusetts General Court passed legislation expanding the corporate powers of the Boston & Maine Railroad which was signed by Governor Alvan T. Fuller on March 6, 1928. Codman's Bill in equity was dismissed by Massachusetts Supreme Court Justice John B. Crosby in October 1928. Built at a cost of $10 million – over double the cost for New York's arena three years earlier – Boston Garden turned out to be the last of Rickard's proposed series, a decision fueled by high costs and Rickard's death in 1929. The Garden's first event was on November 17, 1928, a boxing card headlined by Boston Native "Honey Boy" Dick Finnegan's defeat of Andre Routis.The first team sporting event was held three days later, an ice hockey game between the Bruins and the archrival Montreal Canadiens, won by the Canadiens 1–0. The game was attended by 17,000 fans, 2,000 over capacity, as fans without tickets stormed their way in. The game started 25 minutes late. Windows and doors were broken by the fans in the action. The first non-sporting event, a conclave featuring evangelist Rodney "Gipsy" Smith, was held on March 24, 1929.Early years
During the Boston Garden's early years, the arena was owned by the Boston and Maine Corporation and controlled by Rickard and the Madison Square Garden. In 1934, the Madison Square Garden Corporation sold its interest in the Boston Garden to the Boston Arena Corporation, led by Henry G. Lapham. This resulted in the creation of the Boston Garden-Arena Corporation.George V. Brown served as general manager of the Garden under the Boston Garden-Arena Corporation until his death in 1937, when he was succeeded by his son, Walter A. Brown. During the early years of the Boston Garden, the building's main draws were boxing, wrestling, and Bruins hockey. Johnny Indrisano, Lou Brouillard, Ernie Schaaf, Al Mello, and Jack Sharkey were among the boxers who fought at the Boston Garden. Wrestling became big due to the popularity of Gus Sonnenberg. Sonnenberg defeated Ed "Strangler" Lewis at the Garden in 1929 in a fight that set an attendance record for a wrestling match (19,500) and drew a record gate ($77,000). Paul Bowser promoted wrestling in Boston at this time and when the sport began to lose popularity, he brought Danno O'Mahony from Ireland to Boston. O'Mahony became a popular draw at the Garden. In 1930, construction on the Hotel Manger, a 500-room hotel connected to the Boston Garden through an elevated skyway, was completed. The hotel (later known as the Hotel Madison) closed in 1976 and was demolished in 1983.73 x 104cm 7kgThe Garden suffered economically during the Great Depression. Boxing was at a low point in Boston, as fighters chose to work in other cities, wrestling attendance was down, and hockey attendance waned after Ace Bailey suffered a severe head injury at the hands of Bruin Eddie Shore in 1933. During this period Sonja Henie's Hollywood Ice Revue and the Ice Follies were successful draws and kept the Garden afloat. In 1939, a financial dispute between Henie and her managers led Walter Brown and eight other arena managers to found the Ice Capades.Design
Rickard built the arena specifically with boxing in mind, believing every seat should be close enough to see the "sweat on the boxers' brows". Because of this design theme, fans were much closer to the players during Bruins and Celtics games than in most arenas, leading to a distinct hometown advantage. This physical proximity also created spectacular acoustic effects, much like the Chicago Stadium. When teams made playoff appearances, and a sold-out crowd was chanting or screaming, the impact was enormous. Due to the success of the Celtics in the 1980s, the Boston Garden was one of the most difficult buildings for visiting NBA teams. During the 1985–86 season, the Celtics were 40–1 at home, setting the NBA record for home court mastery (before the San Antonio Spurs tied the record 30 years later in the 2015–16 season). They also finished the post-season undefeated at home. Combined with the following regular season, the Celtics' Garden record was an amazing 79-3 between the 1985–86 and 1986–87 regular seasons. While the parquet floor was an important part of the history of the Celtics,[38] it was not originally part of the Garden. The parquet floor was built and installed in the aforementioned Boston Arena(first home of the Bruins hockey team) and moved to the Garden in 1952. It is said the Celtics knew which way the basketball would bounce off any section of the floor; this was one contributing factor to the Celtics' many NBA championships.The floor became as much a part of Boston sports lore as the Green Monster of Fenway Park. The parquet floor was used at the FleetCenter until December 22, 1999. Portions of the original floor are integrated with new parquet. The floor was cut into small pieces and sold as souvenirs along with seats and bricks. The Naden/Day Industries overhead scoreboard (which was electro-mechanical, not electronic, as more recent arenas used) hung in the Boston Garden-themed food court of the Arsenal Mall in Watertown until 2018, when the mall began to undergo renovations.The Celtics' old championship banners and retired numbers now hang at the team's now-former practice facility in Waltham; a new set of banners were made for the move to the FleetCenter (now TD Garden). The Celtics used to raise Eastern Division championship banners at Boston Garden in the 1960s, but stopped this practice by the 1970s. Likewise, the Bruins made a new set of banners when they moved to the FleetCenter, which were again replaced after the 2011 Stanley Cup Finals with six new banners, each using the contemporary logo of the Bruins when each Cup victory occurred. The Bruins also raised numerous Adams Division, Presidents' Trophy and Wales Conference championship banners at the old Garden, but due to lack of space, they consolidated them into one single banner each upon moving to TD GardenFlaws
The Garden's hockey rink was undersized at 191 by 83 feet (58.2 m × 25.3 m), some nine feet shorter and two feet narrower than standard (200 ft × 85 ft or 61 m × 26 m), due to the rink being built at a time when the NHL did not have a standard size for rinks. This size was even smaller than the original Boston Arena's standard-length 200-by-80-foot (61 m × 24 m) rink, still in use in the 21st century for college hockey with a new, widened 90-foot (27 m) upgrade in 1995, as the Boston Arena was the first rink to host the Bruins in 1924–25. Visiting players were frequently thrown off their games by the differing setup of the players' benches being on opposing sides of the ice, as well as the non-standard penalty box locations. This setup, still occasionally seen in college hockey, was done to ensure that each team could have a bench connected to their dressing room. Towards the end of the Garden's life as an arena, the NHL required all rinks to have both benches on the same side: the Garden obliged by moving the penalty boxes (formerly adjacent to the Bruins' bench) to the side vacated by the visitor's bench, and as such visiting teams were required to skate across the ice to head back to their rooms. The smaller ice surface allowed the Bruins to dump the puck in the offensive zone and then crush their opponents with checks along the boards. The shorter rink was well-suited to the rushing style of Bruins defenseman Bobby Orr; he was able to get from one end of the ice to another faster than in a standard-size rink. Its visitors' dressing room was notoriously small, hot, and underserved by plumbing. The Garden's earlier Bulova-crafted "Sports Timer" game clock system using the typical analog dial-type game clock design of that era, said to have been installed at the Garden early in the 1940s, and essentially identical in appearance and function to the one used in the Chicago Stadium until September 1975,was removed and replaced by an all-digital-display unit created by the Day Sign Company of Toronto in time for the 1970 Stanley Cup playoffs, and remained in use until the Garden's closure. The Garden had no air conditioning, resulting in fog forming over the ice during some Bruins' playoff games. During Game 5 of the 1984 NBA Finals, the 97 °F (36 °C) heat in the facility was so intense that oxygen tanks were provided to exhausted players. The Bruins' Stanley Cup finals appearances in 1988 and 1990 were both disrupted by power outages. On May 24, 1988, a power transformer in the North End blew up during Game 4 of the Finals between the Bruins and the Edmonton Oilers: the contest ended, being ruled as a 3–3 tie. Two years later, on May 15, 1990, the lights went out during an overtime finals game between the same two teams. However, the lights were on an automatic timer and could be turned back on this time with the game ending with a 3–2 triple overtime win for the visiting Oilers.Notable events
Music
Rudy Vallée and his orchestra performed at the Garden on April 21, 1932. Vallée returned to the Garden on October 23–24, 1938 for a "battle of the bands" with Benny Goodman that drew 25,000. The first rock concert held at the Garden was on November 30, 1956, when the building hosted Alan Freed's "Biggest Show of 1956". The Beatles played a show at the Garden during their first US/Canada tour on September 12, 1964, staying at the then-attached Hotel Madison. James Brown played a notable show at the Garden on April 5, 1968, the night after Martin Luther King Jr. was assassinated. Only 2,000 attended the sold-out show, because the mayor, Kevin White, and community leaders had encouraged people to obtain refunds on their tickets and instead to watch a hastily arranged television broadcast of the concert on the local public station WGBH-TV. Mayor White appeared on stage, asking the Garden audience and the city to peacefully remember King, and James Brown's words and presence was credited with helping to keep the peace in Boston. WGBH rebroadcast the concert twice that night, an action which helped keep people off of the street at a time other major cities were erupting in riots. The performance was released on DVD as Live at the Boston Garden: April 5, 1968. Elvis Presley performed in Boston only once, at the Garden on November 10, 1971 pulling a full crowd of about 16,500 and receiving high praise from Rolling Stone journalist Jon Landau for his performance. In 1972, The Rolling Stones were scheduled to perform at the Garden when two members were detained by Rhode Island police. Fearful that angry Stones fans (already in the Garden awaiting the show) would riot, mayor Kevin H. White intervened with the Rhode Island authorities and secured the musicians' release so they could play their set in Boston. The band had also played at the venue in 1965 and 1969 and would again in 1975. In 1973, The Who were scheduled to perform at the Garden and nearly didn't perform due to the band being detained by police after destroying a hotel room in Montreal, Quebec, Canada, where they'd appeared the previous evening. The band was eventually released from jail and managed to arrive at the Garden in time for their show and took out their frustrations for being arrested the night before by delivering a blistering set and taunting the Montreal police, dedicating their performance of "Won't Get Fooled Again" to them. Who drummer Keith Moon (for the rest of the Quadrophenia tour) changed one of the lyrics to the song "Bell Boy" from "remember the gaff where the doors we smashed" to "remember Montreal at the hotel we trashed" or variations of the band being arrested. Almost three years later in March 1976, Moon collapsed at his drum kit during the second song "Substitute" after downing muscle relaxers and brandy before the show. The band had to reschedule the performance for early April and the rescheduled performance turned out to be one of The Who's best performances of the 1976 tour. The Who's last performance at the Garden was in December 1979 on their first tour following Moon's death. That performance was almost canceled after several fans at a Who show in Cincinnatidied while trying to get in early for a general admission show. The Boston City Council held a televised hearing on whether to allow the show to go forward and decided to permit it because there was no general admission seating in Boston. The show was marred by a fan throwing a firecracker on stage, causing Pete Townshend to scream obscenities in the general direction of the source before getting on with the tension-filled show. In 1975, Led Zeppelin were banned from performing at the Boston Garden after concert fans were allowed in the lobby due to sub-freezing temperatures while waiting for tickets to go on sale for the band's show. Turning on the generosity of their hosts, some of the fans rioted, broke into the Garden and trashed the seating area, the ice, and most of the refreshment stands, leading then-mayor White to cancel the upcoming show and ban the group for five years. In 1976, KISS was banned from performing at the Garden because the band refused to comply with the venue's no pyrotechnic policy after fire marshals had watched their flamethrowers hit the ceiling at the Orpheum. Pink Floyd were the first band to perform at the Boston Garden with a stage set that cost over $1 million on their 1977 Animals tour (they first played there in 1975 on the band's Wish You Were Here tour). According to Pink Floyd drummer Nick Mason's book Inside Out: A Personal History of Pink Floyd, Pink Floyd almost got banned from the Boston Garden after their 1977 performances because the band, unknown to the venue's owners, used pyrotechnics during their performance (the exploding pig for "Pigs (Three Different Ones)" and firework displays on "Sheep" and "Money"). However, the band's road crew outsmarted the fire marshals by removing the pyro props quickly after they used them in the shows to prevent the band from being banned and also according to Mason's book since their manager had an Irish name (Steve O'Rourke), the band escaped being arrested. The band decided not to play at the venue again, instead opting for the Providence Civic Center and Foxboro Stadium on their 1987/1988 and 1994 tours, respectively. The Grateful Dead performed at the Boston Garden more times than any other band, with 24 performances from 1973 to 1994 (as an opener or middle of bill or headliner), and were intended to be the last band to play the Garden, with six shows scheduled for September 13th, 14th, 15th,17th, 18th, and 19th 1995, which were canceled due to the death of Jerry Garcia on August 9, 1995. The ticket for the 19th stated "lets tear this old building down" referencing the song "Samson and Delilah". The Dead did not play at the Garden for a number of years following an incident in which they were caught grilling lobsters on a fire escape before a performance.The Grateful Dead have released Dick's Picks Volume 12 and 17 culled from performances at the Garden on June 28, 1974 and September 25, 1991. Detroit rocker Bob Seger recorded a bulk of his 1981 double live album Nine Tonight at The Boston Garden in October 1980. Five years before, The J. Geils Band recorded most of their November 1975 show at The Boston Garden for their 1976 double live album Blow Your Face Out. The Geils band returned again, and had the historical distinction of being the first band in history to sell out a three-night stand in 1982 at the Garden featuring hometown favorites Jon Butcher Axis as opening act. Hometown band Aerosmith performed at the Boston Garden ten times from 1975 to 1995 and twice played New Year's shows there, ringing in the 1990 and 1994 New Years. Other acts that performed at the Garden include Pavarotti, Frank Sinatra, Liberace, Duke Ellington, Judy Garland, Arthur Fiedler and the Boston Pops, U2, Bruce Springsteen, Guns N' Roses, Grace Slick with Jefferson Airplane, Jethro Tull (who had 15 headlining performances there between 1971 and 1980 which is the most for a band, their last being on 1980's A Tour before switching to the Worcester Centrum in 1982), Bob Dylan with The Band, Diana Ross & the Supremes, The Jackson 5, Queen, Rush, Styx and George Burns and Gracie Allen among others. The opening of the Worcester Centrum and the Great Woods Amphitheater caused a massive drop in concerts at the Garden from the early 1980s until the early 1990s. The age of glam metalpractically passed the Garden by completely, as most bands from that era played the Centrum in the winter and Great Woods in the summer. Poor acoustics, a busy sports schedule, expensive booking fees, and difficulty with local unions all contributed to the migration to more modern venues outside of Boston. Under new Garden President Larry Moulter, bands started returning to the Garden in the late 1980s and early 1990s, highlighted by Pearl Jam's multi-night stand in 1994, and the Dead's lengthy residences there before the Garden finally closed. The final New Year's Eve show at the Boston Garden was performed by the Vermont band Phish on December 31, 1994. On that night, the band rode a giant hot dog float above the audience; the hot dog is now in the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in Cleveland.Sports
The facility hosted games in the 1929, 1930, 1932, 1939, 1941, 1943, 1946, 1953, 1957, 1958, 1970, 1972, 1974, 1977, 1978, 1988, and 1990 Stanley Cup Finals where the Bruins won two of their championships at the Garden in 1939 and 1970. The 1929 Stanley Cup championship was won at New York's Madison Square Garden (III). The 1941 Stanley Cup championship was won at Detroit's Olympia Stadium. The 1972 Stanley Cup championship was won at New York's Madison Square Garden. The Montreal Canadiens claimed the Stanley Cup at the Garden in 1958, 1977 and 1978, while the Detroit Red Wings won the cup there in 1943. In 1990, the Edmonton Oilers claimed their fifth Stanley Cup at the Garden. The 1932 series did not involve the Bruins; Game 2 between the Toronto Maple Leafs and New York Rangers was played there due to a scheduling conflict at MSG III. The facility has also hosted games in the 1957, 1958, 1959, 1960, 1961, 1962, 1963, 1964, 1965, 1966, 1968, 1969, 1974, 1976, 1981, 1984, 1985, 1986, and 1987 NBA Finals, in which the Celtics won nine of their championships on home court in 1957, 1960, 1961, 1962, 1964, 1965, 1966, 1984, and 1986. The only visitor to claim the NBA championship at the Garden were the Los Angeles Lakers, who won the 1985 Finals. In addition to championship rounds, the Garden also hosted the NBA All-Star Game in 1951, 1952, 1957, and 1964, and the NHL All-Star Game in 1971. The NCAA Frozen Four was contested there from 1972 to 1974. Starting in 1955, the Beanpot tournament, featuring the four major college hockey programs in the Boston area, was held at the Garden annually on the first week of February. Boston Garden was the first arena to host the Stanley Cup Final and NBA Finals at the same time in 1957. It occurred again in 1958 and 1974. The Boston Garden was a frequent host of Vince McMahon's WWF for many years throughout the 1970s and 1980s, in the form of wrestling "house shows" (non-televised matches), and superstars like Hulk Hogan, André the Giant, Randy "Macho Man" Savage, Tito Santana, Ricky "The Dragon" Steamboat and many others would regularly appear there. But despite this relationship, the Boston Garden was host to only one pro wrestling pay-per-view in its history: the 1993 Survivor Series. The WWF held their final house show in the Boston Garden on May 13, 1995.Rallies and speeches
The Boston Garden hosted many religious conclaves. Evangelists who appeared at the Garden include Aimee McPherson (1931), Billy Graham (1950) Bishop Fulton J. Sheen (1953), and Jimmy Swaggart (July 29–31, 1983). The Garden was also the site of a number of political rallies. 20,000 people attended a 55th birthday celebration for President Franklin D. Roosevelt on January 29, 1937. FDR also drew another 20,000 for a political rally 1940. On May 2, 1943, the night after the Hollywood Victory Caravan came through town, a Jewish anti-Nazi rally was held at the Garden. The United War Fund hosted a rally headlined by Jimmy Durante, Greer Garson, and the Boston Symphony Orchestra. The day before the 1960 presidential election, a rally for John F. Kennedy drew 20,000 while police estimated that there were another 100,000 people in the streets outside the Garden. Other politicians to hold rallies at the Garden include presidential candidates Thomas Dewey and Dwight D. Eisenhower and former Boston mayor and Massachusetts governor James Michael Curley. Former Irish Prime Minister and President Éamon de Valera spoke at the Garden On March 24, 1948 (Easter Sunday). British Prime Minister Winston Churchill spoke there March 31, 1949 as part of a Massachusetts Institute of Technology Convocation.Final years
By the early 1970s, Boston Garden was deteriorating. The building had no air conditioning and some seats were obstructed by structural pillars. The seats were decades old and terribly cramped. With a capacity of less than 15,000, it was one of the country's smallest major league sports arenas. The Garden also lacked luxury suites, which had become an important and much-needed source of revenue for teams in professional sports. In 1972, Boston Mayor Kevin White announced plans for a new 18,000-seat arena to be built near South Station. Plans for the arena fell through when Storer Broadcasting, then-owner of the Boston Garden and the Bruins, announced they would not be able to pay the $24 to $28 million required for the new arena. In 1977 the Boston Celtics negotiated with the city of Quincy to have a $30 million, 21,000-seat arena built there. In 1979, Boston Celtics owner Harry T. Mangurian, Jr. threatened to build a new arena unless the Boston Bruins, who owned the Garden, agreed to lower the rent. The team met with Ogden Corp., owners of Suffolk Downs, who proposed a $20 million, 18,000-seat arena to be built near the racetrack. They also met with the Boston Redevelopment Authority, who proposed $40 million, 15,000-seat arena that would be built behind the existing Garden and paid for with state bonds.]The Bruins meanwhile announced plans to move to a proposed $50 million sports complex on the site of the then closed Rockingham Park in Salem, New Hampshire. The plans for the Salem site were eventually killed by the New Hampshire General Court. Meanwhile, the track remained closed until May 26, 1984. In response to the Bruins' plans to leave the state, U.S. Senator Paul Tsongas established a committee to put forward a plan for a new Boston arena. The committee, chaired by Tsongas, proposed a $56.8 million, 16,000 seat arena that would be paid for by tax-exempt bonds floated by an Arena Authority and by raising the commonwealth's hotel tax from 5.7% to 8%. The naming rights to the proposed arena were sold to Sheraton for $2 million.Tsongas' proposal died in the state legislature. While a preservation study conducted by the Boston Landmarks Commission found the North Station/Boston Garden complex to be a significant example of Art Deco, the Massachusetts Historical Commission did not consider it eligible for listing in the National Register. In 1985, Garden-owner Delaware North and developer Rosalind Gorin each submitted proposals for a new arena, hotel, and office development. Both proposals were rejected by the Boston Redevelopment Authority and Mayor Raymond Flynn.The two groups later resubmitted plans, with Delaware North's calling for a renovation of the Garden instead of having it demolished.Gorin's plan called for the city to claim the Garden by eminent domain, as Delaware North refused to sell the Bruins and the Garden to a group led by Gorin, Paul Tsongas, and former Bruins Wayne Cashman and Bobby Orr.Delaware North was awarded the rights to construct the new arena, but poor economic conditions delayed the project. On May 8, 1992, Delaware North announced they had secured funding for a new arena in the form of $120 million worth of loans evenly split among Bank of Boston, Fleet Bank of Massachusetts, and Shawmut National Corporation. That December, a bill approving construction of the new arena was killed in the Massachusetts Senate by Senate President William M. Bulger. Legislative leaders and Delaware North attempted to reach an agreement on plans for the new arena, but in February 1993 Delaware North owner Jeremy Jacobs announced he was backing out of the project as a result of the legislature's demand his company pay $3.5 million in "linkage payments".Two weeks later, after a new series of negotiations, the two sides came to an agreement, and on February 26 the Legislature passed a bill that allowed for construction of a new sports arena.[68] Construction began on April 29, 1993. Shawmut Bank purchased the naming rights for the new building with the intent of calling it the "Shawmut Center", but it was purchased by FleetBank before the new arena opened, and thus the "FleetCenter" opened on September 30, 1995. In 2005, the FleetCenter was renamed the "TD Banknorth Garden", as Bank of America had acquired Fleet Bank and relinquished its predecessor's naming rights, selling them to TD Banknorth. As of 2009, it is known as TD Garden.[69][70] The Grateful Dead were scheduled to play September 13th, 14th, 15th, 17th, 18th and the 19th being the final event at the garden. The ticket for the 19th featured "lets tear this old building down" referencing the song Samson and Delilah. These shows were cancelled upon Jerry Garcia's death. The last official game played at the Garden took place on Sunday, May 14, 1995. It was game five of an NHL Eastern Conference quarterfinal series between the Boston Bruins and New Jersey Devils where the New Jersey Devils beat the Bruins, 3–2, winning the series four games to one and eliminating the Bruins from the 1995 Stanley Cup Playoffs. The last event at the Boston Garden was a preseason game between the Boston Bruins and the Montreal Canadiens on September 26, 1995.[71] In a special post-game ceremony, which included many former Bruins greats, the banners and retired numbers were removed. The Garden sat vacant for three years before it was demolished in 1998. The site where the building once stood is currently under construction for a commercial development known as The Hub on Causeway.References
-

 37cm x 37cm Naas Co Kildare Original John Gilroy pub print depicting the beleaguered zookeeper with yet another zoo inmate -this time a kangaroo-causing him more consternation. Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain. Arthur Guinness started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.”
37cm x 37cm Naas Co Kildare Original John Gilroy pub print depicting the beleaguered zookeeper with yet another zoo inmate -this time a kangaroo-causing him more consternation. Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain. Arthur Guinness started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.” -

 Superb Smithwicks sponsored team photograph of the 1981 All Ireland Hurling Champions -Offaly.The authenticity of this print and its worn appearance makes for an excellent addition to any GAA wall collection. 32cm x 47cm. Birr Co Offaly The 1981 All Ireland Hurling Final was the 94th All-Ireland Final and the culmination of the 1981 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship, an inter-county hurling tournament for the top teams in Ireland. The match was held at Croke Park, Dublin, on 6 September 1981, between Galway and Offaly. The reigning champions lost to their Leinster opponents, who won their first ever senior hurling title, on a score line of 2-12 to 0-15. Johnny Flaherty scored a handpassed goal in this game; this was before the handpassed goal was ruled out of the game as hurling's technical standards improved.
Superb Smithwicks sponsored team photograph of the 1981 All Ireland Hurling Champions -Offaly.The authenticity of this print and its worn appearance makes for an excellent addition to any GAA wall collection. 32cm x 47cm. Birr Co Offaly The 1981 All Ireland Hurling Final was the 94th All-Ireland Final and the culmination of the 1981 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship, an inter-county hurling tournament for the top teams in Ireland. The match was held at Croke Park, Dublin, on 6 September 1981, between Galway and Offaly. The reigning champions lost to their Leinster opponents, who won their first ever senior hurling title, on a score line of 2-12 to 0-15. Johnny Flaherty scored a handpassed goal in this game; this was before the handpassed goal was ruled out of the game as hurling's technical standards improved.

































