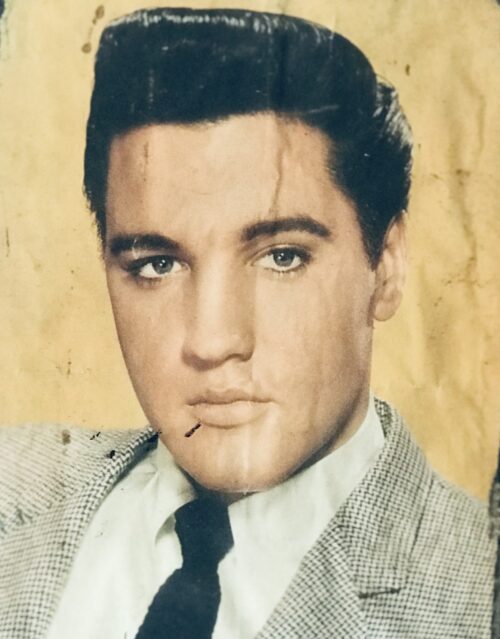
| Desert Orchid | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Sire | Grey Mirage |
| Grandsire | Double-U-Jay |
| Dam | Flower Child |
| Damsire | Brother |
| Sex | Gelding |
| Foaled | 11 April 1979 in Goadby, Leicestershire, England. |
| Country | Great Britain |
| Colour | Grey |
| Breeder | James Burridge |
| Owner | James Burridge, Midge Burridge, Richard Burridge, Simon Bullimore |
| Trainer | David Elsworth at Whitsbury Manor Racing Stables, Fordingbridge, Wiltshire |
| Record | 70: 34-11-8 |
| Earnings | £654,066 |
| Major wins | |
| Tolworth Hurdle (1984) Kingwell Hurdle (1984) Hurst Park Novices' Chase (1985) King George VI Chase (1986, 1988, 1989, 1990) Gainsborough Chase (1987, 1989, 1991) Martell Cup (1988) Whitbread Gold Cup (1988) Tingle Creek Chase (1988) Victor Chandler Chase (1989) Cheltenham Gold Cup (1989) Racing Post Chase (1990) Irish Grand National (1990) | |
| Awards | |
| Timeform rating: 187 | |
| Honours | |
| The Desert Orchid Chase at Wincanton Desert Orchid Chase at Kempton Park Racecourse Statue, ashes, headstone - Kempton Park Racecourse | |
-
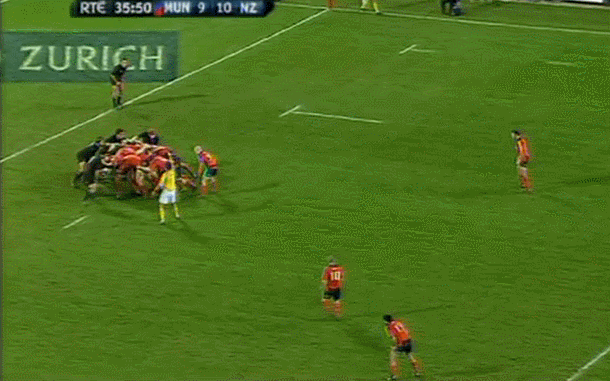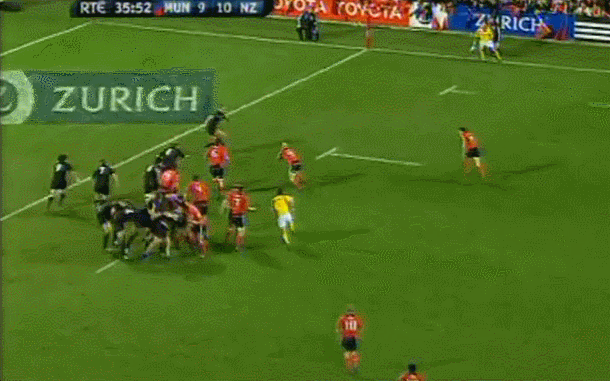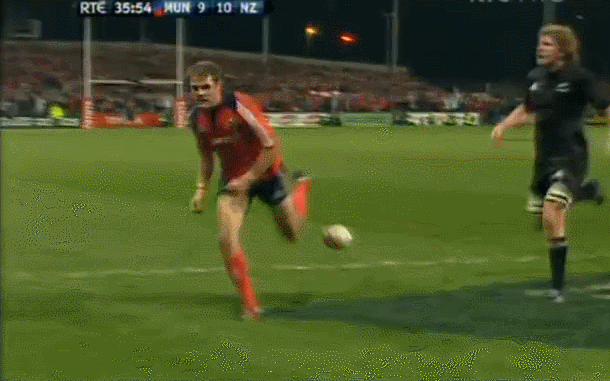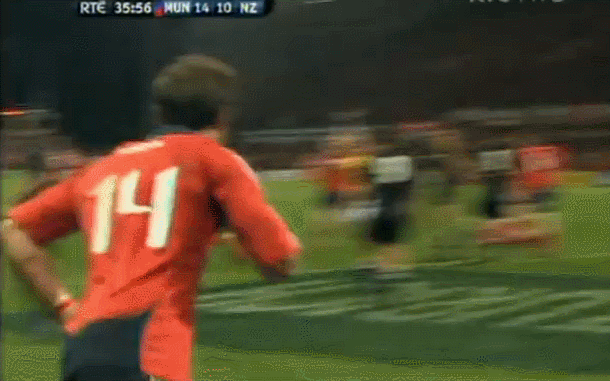
 Although Dessie had no Irish connection whatsoever ,we love a good horse in Ireland and by God Desert Orchid was some horse.Its said his appearance in Fairhouse when he own the Irish Grand National was akin to JFK or the Pope arriving ! Origins : Dunshaughlin Co Meath. Dimensions : 50cm x 65cm
Although Dessie had no Irish connection whatsoever ,we love a good horse in Ireland and by God Desert Orchid was some horse.Its said his appearance in Fairhouse when he own the Irish Grand National was akin to JFK or the Pope arriving ! Origins : Dunshaughlin Co Meath. Dimensions : 50cm x 65cm
Desert Orchid (11 April 1979 – 13 November 2006), known as Dessie, was an English racehorse. The grey achieved a revered and esteemed status within National Hunt racing, where he was much loved by supporters for his front-running attacking style, iron will and extreme versatility. He was rated the fifth best National Hunt horse of all time by Timeform. During his racing career he was partnered by five different jump jockeys: Colin Brown, Richard Linley, Simon Sherwood, Graham Bradley and Richard Dunwoody. -


struggle for independence, this month marks the 100-year anniversary of an important moment in Irish-US relations.
In June 1919, Éamon de Valera arrived in the United States for what was to be an 18-month visit. He had recently escaped from Lincoln jail in England in sensational fashion, after a duplicate key was smuggled into the jail in a cake and he escaped dressed as a woman.
A few months later he was a stowaway aboard the SS Lapland from Liverpool bound for America.
De Valera’s plan was to secure recognition for the emerging Irish nation, tap into the huge Irish-American community for funds, and to pressurise the US government to take a stance on Irish independence. Playing on his mind was the upcoming Versailles conference where the nascent League of Nations was preparing to guarantee “existing international borders” – a provision that would imply Ireland remaining within the United Kingdom.
De Valera also had a challenge in winning over President Woodrow Wilson, who was less than sympathetic to Ireland’s cause.
De Valera’s interest in America was of course personal. He was born in New York in 1882 and his US citizenship was one of the reasons he was spared execution after the 1916 rising.
Public speeches
At first Dev kept a low profile in America. Though he was greeted by Harry Boland and others when he docked in New York, he first went to Philadelphia and stayed with Joseph McGarrity, the Tyrone-born leader of Clan na Gael and a well-known figure in Irish America. He also quietly paid a visit to his mother in Rochester, upstate New York.
De Valera’s first major engagement was on June 23rd when he was unveiled to the American public at a press conference in the Waldorf-Astoria hotel in New York. Crowds thronged the streets around the hotel, and De Valera proclaimed: “I am in America as the official head of the Republic established by the will of the Irish people in accordance with the principle of self-determination.”
-
 e famed brand, Dewar’s was established in 1846 by John Dewar Sr as a wine and spirits merchant on Perth High Street. John sold blended whisky with his own name on the bottles, a rare thing at the time and it was not long before he was supplying bars and hotels throughout Scotland with his product. John’s son, John Alexander Dewar, joined the business in 1871, becoming a partner eight years later. John Alexander inherited the business following his father’s death in 1880. Thomas ‘Tommy’ Dewar joined the business in 1884 and the brand was quickly expanded, starting with a serious introduction to the London market. Dewar’s was introduced to the American market in style, for in 1891 their whisky was delivered to the White House when Andrew Carnegie ordered a keg for President Benjamin Harrison. The President was later criticized for not supporting American products. The American subsequent demand was impressive. In 1893, Queen Victoria bestowed a Royal Warrant, indeed Dewar’s has received a Royal Warrant from every British monarch since. The regal involvement continued for in 1902, Tommy Dewar was knighted by King Edward VI. Today, Dewar’s own five distilleries, including Aberfeldy which the company built in 1896. The company also have a range of popular blends including Dewar’s White Label, an amalgam of around forty single malt Scotch whiskies. Origins:Co Louth Dimensions:33cm x 25cm
e famed brand, Dewar’s was established in 1846 by John Dewar Sr as a wine and spirits merchant on Perth High Street. John sold blended whisky with his own name on the bottles, a rare thing at the time and it was not long before he was supplying bars and hotels throughout Scotland with his product. John’s son, John Alexander Dewar, joined the business in 1871, becoming a partner eight years later. John Alexander inherited the business following his father’s death in 1880. Thomas ‘Tommy’ Dewar joined the business in 1884 and the brand was quickly expanded, starting with a serious introduction to the London market. Dewar’s was introduced to the American market in style, for in 1891 their whisky was delivered to the White House when Andrew Carnegie ordered a keg for President Benjamin Harrison. The President was later criticized for not supporting American products. The American subsequent demand was impressive. In 1893, Queen Victoria bestowed a Royal Warrant, indeed Dewar’s has received a Royal Warrant from every British monarch since. The regal involvement continued for in 1902, Tommy Dewar was knighted by King Edward VI. Today, Dewar’s own five distilleries, including Aberfeldy which the company built in 1896. The company also have a range of popular blends including Dewar’s White Label, an amalgam of around forty single malt Scotch whiskies. Origins:Co Louth Dimensions:33cm x 25cm -
 Really distressed looking retro Guinness advert.Will help lend that crucial authenticity to any pub or home bar! 38cm x 32cm Castleconnell Co Limerick Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.”
Really distressed looking retro Guinness advert.Will help lend that crucial authenticity to any pub or home bar! 38cm x 32cm Castleconnell Co Limerick Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.” -
Out of stock
 Really distressed looking retro Guinness advert.Will help lend that crucial authenticity to any pub or home bar! 45cm x 34cm Castleconnell Co Limerick Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.”
Really distressed looking retro Guinness advert.Will help lend that crucial authenticity to any pub or home bar! 45cm x 34cm Castleconnell Co Limerick Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.” -
 Deliberately distressed Guinness is good for you advert. Origins ; Co Louth Dimensions :40cm x 53cm Glazed Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.”
Deliberately distressed Guinness is good for you advert. Origins ; Co Louth Dimensions :40cm x 53cm Glazed Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.” -

 45cm x 30cm Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.”
45cm x 30cm Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.” -
 This beautiful Degas print once hung in a pub in the horse racing crazy county of Kildare and we couldn't resist bringing it home with us.Beautifully framed, it is a wonderful example of the great impressionists work. Naas Co Kildare 46cm x 50cm Edgar Degas born Hilaire-Germain-Edgar De Gas; 19 July 1834 – 27 September 1917) was a French artist famous for his paintings, sculptures, prints, and drawings. He is especially identified with the subject of dance; more than half of his works depict dancers. Regarded as one of the founders of Impressionism, he rejected the term, preferring to be called a realist.He was a superb draftsman, and particularly masterly in depicting movement, as can be seen in his rendition of dancers, racecourse subjects and female nudes. His portraits are notable for their psychological complexity and for their portrayal of human isolation At the beginning of his career, Degas wanted to be a history painter, a calling for which he was well prepared by his rigorous academic training and close study of classical art. In his early thirties, he changed course, and by bringing the traditional methods of a history painter to bear on contemporary subject matter, he became a classical painter of modern life.
This beautiful Degas print once hung in a pub in the horse racing crazy county of Kildare and we couldn't resist bringing it home with us.Beautifully framed, it is a wonderful example of the great impressionists work. Naas Co Kildare 46cm x 50cm Edgar Degas born Hilaire-Germain-Edgar De Gas; 19 July 1834 – 27 September 1917) was a French artist famous for his paintings, sculptures, prints, and drawings. He is especially identified with the subject of dance; more than half of his works depict dancers. Regarded as one of the founders of Impressionism, he rejected the term, preferring to be called a realist.He was a superb draftsman, and particularly masterly in depicting movement, as can be seen in his rendition of dancers, racecourse subjects and female nudes. His portraits are notable for their psychological complexity and for their portrayal of human isolation At the beginning of his career, Degas wanted to be a history painter, a calling for which he was well prepared by his rigorous academic training and close study of classical art. In his early thirties, he changed course, and by bringing the traditional methods of a history painter to bear on contemporary subject matter, he became a classical painter of modern life. -

 20cm diametre Dublin In the 1980s and 1990s, a number of areas in the Republic of Ireland held year-long festivals commemorating historic anniversaries. The country was in an economic depression at the time and these were excuses for some civic pride; the anniversaries chosen were often rather arbitrary and were chosen by the relevant local authority to promote tourism. The "Dublin millennium" was proposed by city manager Frank Feely to be held in 1988, commemorating Gaelic King Mael Seachlainn II's conquest of the Viking city of Dublin.The corporation agreed in December 1985, prompting a historian to point out that the conquest had actually occurred in 989 and to suggest the year "was chosen quite arbitrarily for the 'millennium' because it is coming up soon, not long after the Galway 500 and the Cork 800". A commemorative 50 pence piece was minted for general circulationFounding and early history of Dublin The earliest reference to Dublin is sometimes said to be found in the writings of Claudius Ptolemaeus (Ptolemy), the Egyptian-Greek astronomer and cartographer, around the year 140, who refers to a settlement called Eblana. This would seem to give Dublin a just claim to nearly two thousand years of antiquity, as the settlement must have existed a considerable time before Ptolemy became aware of it. Recently, however, doubt has been cast on the identification of Eblana with Dublin, and the similarity of the two names is now thought to be coincidental. It is now thought that the Viking settlement was preceded by a Christian ecclesiastical settlement known as Duiblinn, from which Dyflin took its name. Beginning in the 9th and 10th century, there were two settlements where the modern city stands. The Viking settlement of about 841 was known as Dyflin, from the Irish Duiblinn (or "Black Pool", referring to a dark tidal pool where the River Poddle entered the Liffey on the site of the Castle Gardens at the rear of Dublin Castle), and a Gaelic settlement, Áth Cliath ("ford of hurdles") was further upriver, at the present day Father Mathew Bridge at the bottom of Church Street. The Celtic settlement's name is still used as the Irish name of the modern city, though the first written evidence of it is found in the Annals of Ulster of 1368. The modern English name came from the Viking settlement of Dyflin, which derived its name from the Irish Duiblinn. The Vikings, or Ostmen as they called themselves, ruled Dublin for almost three centuries, although they were expelled in 902 only to return in 917 and notwithstanding their defeat by the Irish High King Brian Boru at the Battle of Clontarf in 1014. From that date, the Norse were a minor political force in Ireland, firmly opting for a commercial life. Viking rule of Dublin would end completely in 1171 when the city was captured by King Dermot MacMurrough of Leinster, with the aid of Cambro-Norman mercenaries. An attempt was made by the last Norse King of Dublin, Ascall mac Ragnaill, to recapture the city with an army he raised among his relations in the Scottish Highlands, where he was forced to flee after the city was taken, but the attempted reconquest failed and Ascall was killed.The Thingmote was a raised mound, 40-foot (12 m) high and 240-foot (73 m) in circumference, where the Norsemen assembled and made their laws. It stood on the south of the river, adjacent to Dublin Castle, until 1685.[4] Viking Dublin had a large slave market. Thralls were captured and sold, not only by the Norse but also by warring Irish chiefs.b Dublin celebrated its millennium in 1988 with the slogan Dublin's great in '88'. The city is far older than that, but in that year, the Norse King Glun Iarainnrecognised Máel Sechnaill II (Máel Sechnaill Mór), High King of Ireland, and agreed to pay taxes and accept Brehon Law.a That date was celebrated, but might not be accurate: in 989 (not 988), Mael Seachlainn laid siege to the city for 20 days and captured it. This was not his first attack on the city.[citation needed] Dublin became the centre of English power in Ireland after the Norman invasion of the southern half of Ireland (Munster and Leinster) in 1169–71, replacing Tara in Meath – seat of the Gaelic High Kings of Ireland – as the focal point of Ireland's polity. On 15 May 1192 Dublin's first written Charter of Liberties was granted by John, Lord of Ireland, and was addressed to all his "French, English, Irish and Welsh subjects and friends". On 15 June 1229 his son Henrygranted the citizens the right to elect a mayor who was to be assisted by two provosts.[5] By 1400, however, many of the Anglo-Norman conquerors were absorbed into the Gaelic culture, adopting the Irish language and customs, leaving only a small area of Leinster around Dublin, known as the Pale, under direct English control. Origins : Dublin Dimensions :Skudelev II, a large Viking Age warship built in the Dublin area c. 1042
20cm diametre Dublin In the 1980s and 1990s, a number of areas in the Republic of Ireland held year-long festivals commemorating historic anniversaries. The country was in an economic depression at the time and these were excuses for some civic pride; the anniversaries chosen were often rather arbitrary and were chosen by the relevant local authority to promote tourism. The "Dublin millennium" was proposed by city manager Frank Feely to be held in 1988, commemorating Gaelic King Mael Seachlainn II's conquest of the Viking city of Dublin.The corporation agreed in December 1985, prompting a historian to point out that the conquest had actually occurred in 989 and to suggest the year "was chosen quite arbitrarily for the 'millennium' because it is coming up soon, not long after the Galway 500 and the Cork 800". A commemorative 50 pence piece was minted for general circulationFounding and early history of Dublin The earliest reference to Dublin is sometimes said to be found in the writings of Claudius Ptolemaeus (Ptolemy), the Egyptian-Greek astronomer and cartographer, around the year 140, who refers to a settlement called Eblana. This would seem to give Dublin a just claim to nearly two thousand years of antiquity, as the settlement must have existed a considerable time before Ptolemy became aware of it. Recently, however, doubt has been cast on the identification of Eblana with Dublin, and the similarity of the two names is now thought to be coincidental. It is now thought that the Viking settlement was preceded by a Christian ecclesiastical settlement known as Duiblinn, from which Dyflin took its name. Beginning in the 9th and 10th century, there were two settlements where the modern city stands. The Viking settlement of about 841 was known as Dyflin, from the Irish Duiblinn (or "Black Pool", referring to a dark tidal pool where the River Poddle entered the Liffey on the site of the Castle Gardens at the rear of Dublin Castle), and a Gaelic settlement, Áth Cliath ("ford of hurdles") was further upriver, at the present day Father Mathew Bridge at the bottom of Church Street. The Celtic settlement's name is still used as the Irish name of the modern city, though the first written evidence of it is found in the Annals of Ulster of 1368. The modern English name came from the Viking settlement of Dyflin, which derived its name from the Irish Duiblinn. The Vikings, or Ostmen as they called themselves, ruled Dublin for almost three centuries, although they were expelled in 902 only to return in 917 and notwithstanding their defeat by the Irish High King Brian Boru at the Battle of Clontarf in 1014. From that date, the Norse were a minor political force in Ireland, firmly opting for a commercial life. Viking rule of Dublin would end completely in 1171 when the city was captured by King Dermot MacMurrough of Leinster, with the aid of Cambro-Norman mercenaries. An attempt was made by the last Norse King of Dublin, Ascall mac Ragnaill, to recapture the city with an army he raised among his relations in the Scottish Highlands, where he was forced to flee after the city was taken, but the attempted reconquest failed and Ascall was killed.The Thingmote was a raised mound, 40-foot (12 m) high and 240-foot (73 m) in circumference, where the Norsemen assembled and made their laws. It stood on the south of the river, adjacent to Dublin Castle, until 1685.[4] Viking Dublin had a large slave market. Thralls were captured and sold, not only by the Norse but also by warring Irish chiefs.b Dublin celebrated its millennium in 1988 with the slogan Dublin's great in '88'. The city is far older than that, but in that year, the Norse King Glun Iarainnrecognised Máel Sechnaill II (Máel Sechnaill Mór), High King of Ireland, and agreed to pay taxes and accept Brehon Law.a That date was celebrated, but might not be accurate: in 989 (not 988), Mael Seachlainn laid siege to the city for 20 days and captured it. This was not his first attack on the city.[citation needed] Dublin became the centre of English power in Ireland after the Norman invasion of the southern half of Ireland (Munster and Leinster) in 1169–71, replacing Tara in Meath – seat of the Gaelic High Kings of Ireland – as the focal point of Ireland's polity. On 15 May 1192 Dublin's first written Charter of Liberties was granted by John, Lord of Ireland, and was addressed to all his "French, English, Irish and Welsh subjects and friends". On 15 June 1229 his son Henrygranted the citizens the right to elect a mayor who was to be assisted by two provosts.[5] By 1400, however, many of the Anglo-Norman conquerors were absorbed into the Gaelic culture, adopting the Irish language and customs, leaving only a small area of Leinster around Dublin, known as the Pale, under direct English control. Origins : Dublin Dimensions :Skudelev II, a large Viking Age warship built in the Dublin area c. 1042 -

 W & A Gilbey was founded in 1857 and began in small basement cellars at the corner of Oxford Street and Berwick Street in London. Gilbeys benefitted greatly from the introduction of the off-licence system introduced in 1860 and a commercial agreement between Britain and France in 1861, following which, the British Prime Minister Gladstone reduced duty on French wines from 12 shillings to 2 shillings. Gilbeys were successful from the start and, within a couple of years, had branches in Dublin, Belfast and Edinburgh.
W & A Gilbey was founded in 1857 and began in small basement cellars at the corner of Oxford Street and Berwick Street in London. Gilbeys benefitted greatly from the introduction of the off-licence system introduced in 1860 and a commercial agreement between Britain and France in 1861, following which, the British Prime Minister Gladstone reduced duty on French wines from 12 shillings to 2 shillings. Gilbeys were successful from the start and, within a couple of years, had branches in Dublin, Belfast and Edinburgh.
1861 Wine importers and distillers
By 1861 Gilbeys had premises at 31 Upper Sackville Street in Dublin (now called O’Connell Street), and were described as wine importers and distillers. They carried stocks of over 140 different wines and held between 700 and 1,000 wine casks under bond.
1866 A distinctive brand
In 1866, the company moved to new offices and stores at 46 & 47 Upper Sackville Street in the centre of Dublin (now O’Connell Street), which contained their own vaults. The buildings were previously the premises of Sneyd, French and Barton. The premises had its own tasting room and a small still for determining the alcoholic strength of wines and spirits. Gilbeys had their own patented bottle cases which could be easily stacked, a state of the art bottle washing machine and by this time, wax seals were replaced with their patented capsule seal. Gilbeys sold all their wines and spirits directly to consumers under their own distinctive brand.
1874 300,000 Gallons in bond
Initially famous for their wines, spirits were becoming a greater part of Gilbey’s business. By 1874, Gilbeys held a stock in bond of over 300,000 gallons of whiskey sourced from “the most celebrated Dublin Distilleries”. The proprietary brand at this time was Gilbey’s Castle Whiskey. They sold three main brands Castle U P Irish Whiskey 33% under proof (u.p.), Castle U V Irish Whiskey 17% u.p. and Castle D O Irish Whiskey at full proof strength.
1875 996,000 Bottles a year
At this point Gilbey’s held the largest stocks of Irish whiskey, outside of the distilleries themselves, of any company in the world. In 1875 they were selling 83,000 cases of Irish whiskey compared with only 38,000 of Scotch, a reflection of the pre-eminence of Irish Whiskey at the time. -
Out of stock
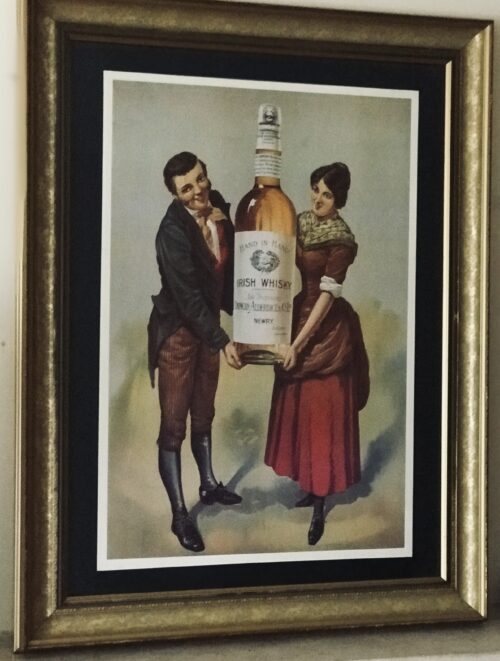
 80cm x 63cm. Newry Co Down Newry Co Down was synonymous with distilling until the business sadly and steadily died a commercial death.Now a local businessman Michael McKeown has acquired the old distillery site on Monaghan Street in February this year, the original location of D’Arcy’s Old Irish Whiskey since 1817 as well as many other brands over the centuries, including Duncan Alderdice & C0. Speaking at a press conference last week, McKeown said he had resurrected the title of Matthew D’Arcy & Company to honour the last distiller who occupied the site.The history of the site dates back to 1575 with research claiming that the tradition of distilling was said to have begun in the Cistercian Monastery which preceded the town of Newry. The distillery is thought to be a contender for the oldest distillery in Ireland.The distilling businesses operating in Newry before 1800 were Chapman, D’arcy, Caulfield and Thompson as well as Duncan Alderdice & Co as featured in the charming print here from the early 1890s.Chapman put his working distillery up for sale in 1802 and it is known that in 1817 all of these other parties were acting in partnership on two sites in Newry with the premises on Monaghan Street being one of those original sites. Plans for the site include the restoration of the 19th century buildings with the addition of a working distillery, a visitor’s centre, restaurant, theatre and a Victorian pub.The company aim to produce around 9000 cases per year of Old Newry single malt whiskey and to retain stocks for at least 10 years.McKeown has also registered the brand names from previous occupants of the site, such as Duncan, Alderdice & Company. The brands include The Blackthorn, The Native, Hand-in-Hand and Killeavy Cream.The distillery plans to be an “important” stop on the Irish Whiskey Trail currently being developed by Tourism Ireland, due to its location half-way between Belfast and Dublin.The distillery, which will provide a number of new jobs, is also looking to recruit a master distiller.
80cm x 63cm. Newry Co Down Newry Co Down was synonymous with distilling until the business sadly and steadily died a commercial death.Now a local businessman Michael McKeown has acquired the old distillery site on Monaghan Street in February this year, the original location of D’Arcy’s Old Irish Whiskey since 1817 as well as many other brands over the centuries, including Duncan Alderdice & C0. Speaking at a press conference last week, McKeown said he had resurrected the title of Matthew D’Arcy & Company to honour the last distiller who occupied the site.The history of the site dates back to 1575 with research claiming that the tradition of distilling was said to have begun in the Cistercian Monastery which preceded the town of Newry. The distillery is thought to be a contender for the oldest distillery in Ireland.The distilling businesses operating in Newry before 1800 were Chapman, D’arcy, Caulfield and Thompson as well as Duncan Alderdice & Co as featured in the charming print here from the early 1890s.Chapman put his working distillery up for sale in 1802 and it is known that in 1817 all of these other parties were acting in partnership on two sites in Newry with the premises on Monaghan Street being one of those original sites. Plans for the site include the restoration of the 19th century buildings with the addition of a working distillery, a visitor’s centre, restaurant, theatre and a Victorian pub.The company aim to produce around 9000 cases per year of Old Newry single malt whiskey and to retain stocks for at least 10 years.McKeown has also registered the brand names from previous occupants of the site, such as Duncan, Alderdice & Company. The brands include The Blackthorn, The Native, Hand-in-Hand and Killeavy Cream.The distillery plans to be an “important” stop on the Irish Whiskey Trail currently being developed by Tourism Ireland, due to its location half-way between Belfast and Dublin.The distillery, which will provide a number of new jobs, is also looking to recruit a master distiller. -
Out of stock
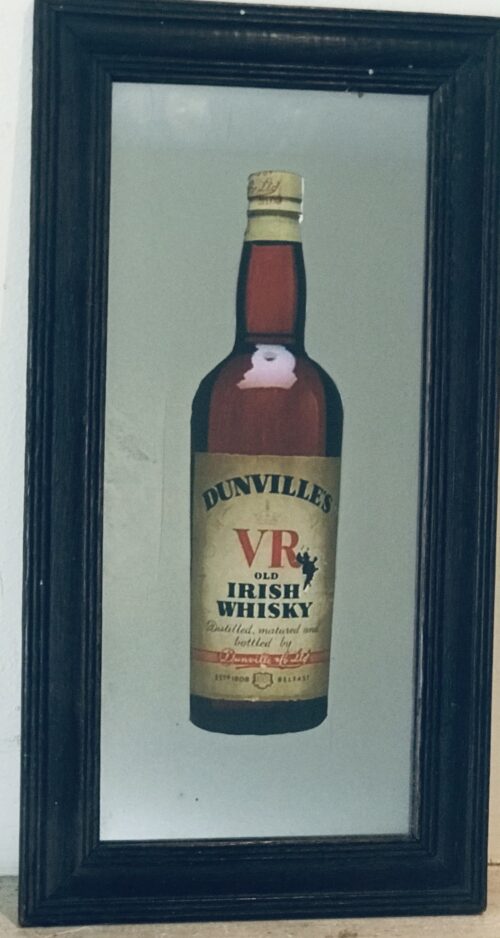
 Nice little reproduced Dunvilles mirror. 40cm x 20cm Dunville & Co. was a tea and spirits merchant company, based in Belfast, County Antrim. The company initially gained success as an Irish whiskey blender, but later produced and marketed its own whiskey, having constructed its own distillery. The company was founded by John Dumvill who joined William Napier of Napier & Co. The spelling of Dumvill was changed to Dunville and in 1825 the company name became Dunville & Co. In 1837, Dunville began producing its most popular whisky Dunville's VR. Dunville's was the main brand name of Dunville & Co, and was used in advertisements, on pub windows and pub mirrors such as the beautiful example featured here on the irishpubemporium.com and on whisky dispensers, water jugs, trays, match strikers, ash trays and playing cards.Although Dunville & Co was established and based in Ireland, before the Partition of Ireland, and Irish whiskey is normally spelt with an 'e' in 'whiskey', Dunville's Whisky was always spelt without an 'e' in 'Whisky'.In 2013, almost 80 years after the last Dunville's was distilled, the Echlinville Distillery revived the Dunville's brand, and began distilling at their facility in the Ards Peninsula. Previously they had purchased spirits from other distillers and aged it themselves. Dunville's VR Old Irish Whiskey and Dunville's Three Crowns Irish Whiskey from The Echlinville Distillery came on the market in 2016. Having gained success as a whiskey blender, Dunville & Co. constructed their own distillery, the Royal Irish Distilleries, on the edge of Belfast in 1869. When built, the distillery occupied an impressive four-storey red-brick building, and was amongst the most modern in Ireland.With production from five pot stills, and later a Coffey still, at its peak the distillery had a capacity of over 2.5 million gallons per annum, making it amongst the largest in the country.Much of the distillery's output was used in the company's whiskey blends, Dunville's VR and Dunville's Three Crowns. Although, like other Irish distilleries, Prohibition caused Dunville to lose access to the important American market, Dunville ended the 1920s in good financial health. However, when the last heir and chairman of Dunville, Robert Lambart Dunville, died in 1931, the company began to flounder, and left to its directors, in 1936 Dunville & Co. was liquidated. Incredibly, and almost uniquely amongst the Irish distilleries that closed in the 20th century, liquidation was not forced upon the firm, as Dunville was actually still profitable when it was wound up.The main brand name of Dunville & Co. was used in advertisements, on pub windows and pub mirrors, and on whisky dispensers, water jugs, trays, match strikers, ash trays and playing cards. Although Dunville & Co was established and based in Ireland, before the Partition of Ireland, and Irish whiskey is normally spelt with an 'e' in 'whiskey', Dunville's Whisky was always spelt without an 'e' in 'Whisky'. In 2013, almost 80 years after the last Dunville's was distilled, the Echlinville Distillery revived the Dunville's brand, and began distilling at their facility in the Ards Peninsula. Previously they had purchased spirits from other distillers and aged it themselves. Dunville's VR Old Irish Whiskey and Dunville's Three Crowns Irish Whiskey from The Echlinville Distillery came on the market in 2016.
Nice little reproduced Dunvilles mirror. 40cm x 20cm Dunville & Co. was a tea and spirits merchant company, based in Belfast, County Antrim. The company initially gained success as an Irish whiskey blender, but later produced and marketed its own whiskey, having constructed its own distillery. The company was founded by John Dumvill who joined William Napier of Napier & Co. The spelling of Dumvill was changed to Dunville and in 1825 the company name became Dunville & Co. In 1837, Dunville began producing its most popular whisky Dunville's VR. Dunville's was the main brand name of Dunville & Co, and was used in advertisements, on pub windows and pub mirrors such as the beautiful example featured here on the irishpubemporium.com and on whisky dispensers, water jugs, trays, match strikers, ash trays and playing cards.Although Dunville & Co was established and based in Ireland, before the Partition of Ireland, and Irish whiskey is normally spelt with an 'e' in 'whiskey', Dunville's Whisky was always spelt without an 'e' in 'Whisky'.In 2013, almost 80 years after the last Dunville's was distilled, the Echlinville Distillery revived the Dunville's brand, and began distilling at their facility in the Ards Peninsula. Previously they had purchased spirits from other distillers and aged it themselves. Dunville's VR Old Irish Whiskey and Dunville's Three Crowns Irish Whiskey from The Echlinville Distillery came on the market in 2016. Having gained success as a whiskey blender, Dunville & Co. constructed their own distillery, the Royal Irish Distilleries, on the edge of Belfast in 1869. When built, the distillery occupied an impressive four-storey red-brick building, and was amongst the most modern in Ireland.With production from five pot stills, and later a Coffey still, at its peak the distillery had a capacity of over 2.5 million gallons per annum, making it amongst the largest in the country.Much of the distillery's output was used in the company's whiskey blends, Dunville's VR and Dunville's Three Crowns. Although, like other Irish distilleries, Prohibition caused Dunville to lose access to the important American market, Dunville ended the 1920s in good financial health. However, when the last heir and chairman of Dunville, Robert Lambart Dunville, died in 1931, the company began to flounder, and left to its directors, in 1936 Dunville & Co. was liquidated. Incredibly, and almost uniquely amongst the Irish distilleries that closed in the 20th century, liquidation was not forced upon the firm, as Dunville was actually still profitable when it was wound up.The main brand name of Dunville & Co. was used in advertisements, on pub windows and pub mirrors, and on whisky dispensers, water jugs, trays, match strikers, ash trays and playing cards. Although Dunville & Co was established and based in Ireland, before the Partition of Ireland, and Irish whiskey is normally spelt with an 'e' in 'whiskey', Dunville's Whisky was always spelt without an 'e' in 'Whisky'. In 2013, almost 80 years after the last Dunville's was distilled, the Echlinville Distillery revived the Dunville's brand, and began distilling at their facility in the Ards Peninsula. Previously they had purchased spirits from other distillers and aged it themselves. Dunville's VR Old Irish Whiskey and Dunville's Three Crowns Irish Whiskey from The Echlinville Distillery came on the market in 2016. -
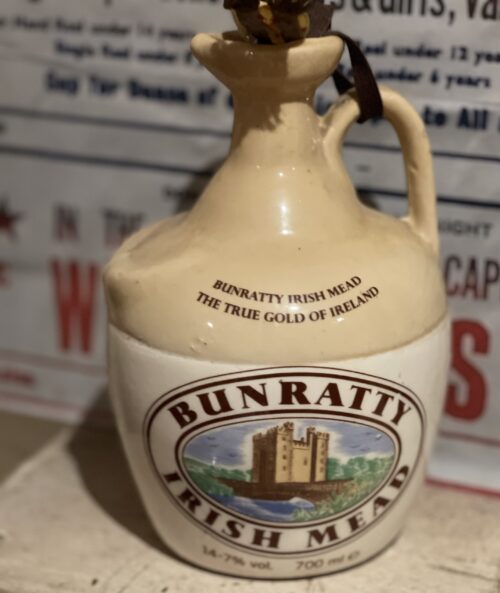
 26cm (empty)
26cm (empty)Bunratty Mead is a traditional wine, produced from an ancient Irish recipe of pure honey, fruit of the vine and natural herbs. It's a medium sweet wine, with a wide taste appeal, and suitable for all important occasions. As the drink of the ancient Celts, Mead derives much of its appeal through Irish Folklore, which is legendary of this mystical drink with strong attachments to Ireland.
In the days of old when knights were bold, the drink of choice was mead. Much more than an extraordinary legendary drink with strong attachments to Ireland, mead can be traced back as many centuries before Christ. It became the chief drink of the Irish and was often referred to in Gaelic poetry. Mead's influence was so great that the halls of Tara, where the High Kings of Ireland ruled, were called the house of the Mead Circle. Its fame spread quickly and soon a medieval banquet was not complete without it.


Even the church recognised the value of this fabulous drink. Legend has it that St. Finian lived for six days a week on bread and water, but on Sundays ate salmon and drank a full sup of mead. In addition, St. Bridget performed a miracle when mead could not be located for the king of Leinster. She blessed an empty vessel, which miraculously filled with Mead.

-

 Very well reproduced and quaint advertisement for the legendary Fair of Spancil Hill,held every year on the 23rd of June -with Jameson Whiskey sponsoring the advert. Ennis Co Clare. 50 cm x 60cm Spancilhill is a small settlement in East County Clare that hosts an annual horse fair on the 23rd of June. The Spancilhill Horse Fair is Ireland’s oldest having been chartered in 1641 by Charles II. It derives its name from the Irish, Cnoc Fhuar Choille or Cold Wood Hill. The name was misinterpreted as Cnoc Urchaill or Spancel Hill. A spancel is a type hobble and its association with a horse fair perpetuated this misinterpretation. The 1913 fair saw four thousand horses for sale. The British, Belgian, and French armies sought cavalry mounts. The British army purchased 1,175 horses and lead them tied head to tail to Ennis for rail transport. Horse Fairs gained a reputation for wild behavior and animal cruelty. The Friends of the Spancilhill Horse Fair formed in the 1980s with the aim of restructuring the event as an agricultural show. Michael Considine, who emigrated from the area in 1870, composed the popular Irish folk ballad, Spancil Hill. Buyers across Europe attend with hopes to find international showjumping prospects. Photographers find the event irresistible and nearly outnumber the horses in recent times.The aforementioned song written about the fair has almost become more famous than the fair itself in modern times. Robbie McMahon was a songwriter and singer whose rendition of Spancil Hill is widely regarded as the definitive version. He reckoned he sang it more than 10,000 times since he learned it as a teenager.
Very well reproduced and quaint advertisement for the legendary Fair of Spancil Hill,held every year on the 23rd of June -with Jameson Whiskey sponsoring the advert. Ennis Co Clare. 50 cm x 60cm Spancilhill is a small settlement in East County Clare that hosts an annual horse fair on the 23rd of June. The Spancilhill Horse Fair is Ireland’s oldest having been chartered in 1641 by Charles II. It derives its name from the Irish, Cnoc Fhuar Choille or Cold Wood Hill. The name was misinterpreted as Cnoc Urchaill or Spancel Hill. A spancel is a type hobble and its association with a horse fair perpetuated this misinterpretation. The 1913 fair saw four thousand horses for sale. The British, Belgian, and French armies sought cavalry mounts. The British army purchased 1,175 horses and lead them tied head to tail to Ennis for rail transport. Horse Fairs gained a reputation for wild behavior and animal cruelty. The Friends of the Spancilhill Horse Fair formed in the 1980s with the aim of restructuring the event as an agricultural show. Michael Considine, who emigrated from the area in 1870, composed the popular Irish folk ballad, Spancil Hill. Buyers across Europe attend with hopes to find international showjumping prospects. Photographers find the event irresistible and nearly outnumber the horses in recent times.The aforementioned song written about the fair has almost become more famous than the fair itself in modern times. Robbie McMahon was a songwriter and singer whose rendition of Spancil Hill is widely regarded as the definitive version. He reckoned he sang it more than 10,000 times since he learned it as a teenager.The ballad is named after a crossroads between Ennis and Tulla in east Clare, the site of a centuries-old horse fair held every June. In 1870 a young man from the locality, Michael Considine, bade farewell to his sweetheart Mary McNamara and left for the US. He hoped to earn sufficient money to enable her to join him.
However, he died in California in 1873. Before his death he wrote a poem dedicated to Mary which he posted to his six-year-old nephew, John, back home.
Seventy years later McMahon was given the words at a house party. His singing of the ballad was warmly received by those in attendance, who included the author’s nephew, then an elderly man.
Many singers have recorded the ballad, but McMahon insisted his was the authentic version. He told The Irish Times in 2006: “Nowadays the song is not sung correctly. Many singers put words that are not in it [at] all, singing stuff like ‘Johnny, I love you still’. There’s no ‘Johnny’ in that song.” The late writer Bryan MacMahon was an early admirer of his namesake’s talent and had high praise for his ability as a performer and entertainer.
Singer Maura O’Connell warmed to Robbie McMahon’s “great big personality”, and said that he made Spancil Hill his own.
Born in 1926, he was the third youngest of 11 children, one of whom died in childhood, and grew up on his father’s farm in Clooney, near Ennis. There was music in the family, and all the children sang. Young Robbie was something of a mischief-maker, hence the title of an album he recorded later in life – The Black Sheep.
He began singing in public at the age of 18, and went on to win 16 all-Ireland titles at fleadhanna around the country. In the 1950s, 1960s and 1970s he toured Britain and the US with a troupe of traditional musicians under the auspices of Comhaltas Ceoltóirí Éireann.
As a songwriter, he is best known for the Fleadh Down in Ennis, which celebrates the 1956 all-Ireland fleadh cheoil. Other compositions include Come on the Banner, the Red Cross Social and the Feakle Hurlers, in honour of the 1988 Clare county champions.
A lilter, he was renowned for his performance of the Mason’s Apron, in which he simulated the sound of both the fiddle and accompanying banjo.
Possessed of a store of jokes, ranging from the hilarious to the unprintable, he was as much a character as a singer and was more comfortable with the craic and banter of casual sessions than with formal concerts.
He was the subject of a film documentary Last Night As I Lay Dreaming. Clare County Council hosted a civic reception in his honour in 2010, and he was the recipient of the Fleadh Nua Gradam Ceoil in 2011.
He is survived by his wife Maura, daughters Fiona, Noleen and Dympna and son Donal.
-

 47cm x 35cm Barry's Tea is an Irish tea company founded in 1901 by James J. Barry in Cork. Until the 1960s, tea was sold from a shop in Prince's Street, but thereafter the company expanded its wholesaling and distribution operations. By the mid-1980s Barry's Tea had become a national brand. According to their website, they are currently responsible for 38% of all tea sales in the Irish market (which is worth an estimated €85 million annually). Today, Barry's Tea is also available in the United Kingdom, Spain, and in some areas of Canada, Australia, France, Luxembourg and the United States where there are significant Irish immigrant communities. Members of the Barry family been elected representatives for Fine Gael: the founder's son Anthony Barry (TD 1954–57 and 1961–65), Anthony's son Peter Barry (TD 1969–97) and Peter's daughter Deirdre Clune (TD 1997–2001 and 2007–11, and MEP since 2014).
47cm x 35cm Barry's Tea is an Irish tea company founded in 1901 by James J. Barry in Cork. Until the 1960s, tea was sold from a shop in Prince's Street, but thereafter the company expanded its wholesaling and distribution operations. By the mid-1980s Barry's Tea had become a national brand. According to their website, they are currently responsible for 38% of all tea sales in the Irish market (which is worth an estimated €85 million annually). Today, Barry's Tea is also available in the United Kingdom, Spain, and in some areas of Canada, Australia, France, Luxembourg and the United States where there are significant Irish immigrant communities. Members of the Barry family been elected representatives for Fine Gael: the founder's son Anthony Barry (TD 1954–57 and 1961–65), Anthony's son Peter Barry (TD 1969–97) and Peter's daughter Deirdre Clune (TD 1997–2001 and 2007–11, and MEP since 2014). -

 52cm x 65cm Thomondgate Limerick This advertising print is as rare as a white rhino.Namely because one of Limerick City's only ever distillery's was Archibald Walkers located at Thomondgate on the banks of the River Shannon and it sadly closed in 1905.Originally owned by the Steins,who was we know were related to the Jamesons of Bow Street through marriage ,they sold the business to a Archibald Walker in 1879.Walker already owned the Vauxhall distillery in Liverpool and the Adelphi in Glasgow,making him the only distiller to ever simultaneously own a distillery in Scotland,England and Ireland.Walkers employed 70 men and produced 300,000 gallons of whiskey, which was much smaller than most of its competitors .The distillery did have a small local trade but most of the whiskey appears to have been exported to England.Business was badly affected by the economic downturn in 1900-1902 and was sold to Scottish Distillers Co,who within three years had closed down all of Archibalds Walkers three distilleries.Little or nothing of the distillery building remains today and bottles bearing the Limerick Whiskey label seem to have totally disappeared save a few mirrors and prints in a few old Limerick pubs - hence the absolute rarity value of this beautiful piece as it is well in excess of 115 years old.Please email us directly about this rare gem.
52cm x 65cm Thomondgate Limerick This advertising print is as rare as a white rhino.Namely because one of Limerick City's only ever distillery's was Archibald Walkers located at Thomondgate on the banks of the River Shannon and it sadly closed in 1905.Originally owned by the Steins,who was we know were related to the Jamesons of Bow Street through marriage ,they sold the business to a Archibald Walker in 1879.Walker already owned the Vauxhall distillery in Liverpool and the Adelphi in Glasgow,making him the only distiller to ever simultaneously own a distillery in Scotland,England and Ireland.Walkers employed 70 men and produced 300,000 gallons of whiskey, which was much smaller than most of its competitors .The distillery did have a small local trade but most of the whiskey appears to have been exported to England.Business was badly affected by the economic downturn in 1900-1902 and was sold to Scottish Distillers Co,who within three years had closed down all of Archibalds Walkers three distilleries.Little or nothing of the distillery building remains today and bottles bearing the Limerick Whiskey label seem to have totally disappeared save a few mirrors and prints in a few old Limerick pubs - hence the absolute rarity value of this beautiful piece as it is well in excess of 115 years old.Please email us directly about this rare gem. -

 45cm x 60cm Anticipation is an Irish advertisement launched by Guinness plc in 1994 to promote Guinness-brand draught stout. The advert, which appeared in print, posters, and cinema and television spots, was conceived by Irish advertising agency Arks, and starred relatively unknown Irish actor Joe McKinney as the 'Dancing Man' and Gordon Winter as the barman. It was the final part of the "Guinness Time" advertising campaign, which had been running in Ireland since the late 1980s. The advert was credited with increasing Guinness' sales, market share and brand awareness figures. However, controversy arose following claims of plagiarism raised by British director Mehdi Norowzian, who launched an unsuccessful lawsuit in 1998 seeking remuneration for the use of techniques and style from his 1992 short film Joy.
45cm x 60cm Anticipation is an Irish advertisement launched by Guinness plc in 1994 to promote Guinness-brand draught stout. The advert, which appeared in print, posters, and cinema and television spots, was conceived by Irish advertising agency Arks, and starred relatively unknown Irish actor Joe McKinney as the 'Dancing Man' and Gordon Winter as the barman. It was the final part of the "Guinness Time" advertising campaign, which had been running in Ireland since the late 1980s. The advert was credited with increasing Guinness' sales, market share and brand awareness figures. However, controversy arose following claims of plagiarism raised by British director Mehdi Norowzian, who launched an unsuccessful lawsuit in 1998 seeking remuneration for the use of techniques and style from his 1992 short film Joy.Sequence
The low-budget ad featured only two characters: a patron of a pub and the barman serving him. The patron (McKinney) orders a pint of Guinness stout and, while waiting for the pint to be poured, carries out a series of quirky dancing movements with the settling pint in the foreground, to the amusement of the barman (Winter). The piece ends with the patron taking his first sip of the freshly poured pint overlaid by the Guinness advertising slogan "No time like Guinness Time". The advert is set to Guaglione by Pérez Prado, and makes heavy use of jump cutting from a static camera to allow the dancer to make a series of movements that could not be achieved in reality.Reception
The distinctive jump cut editing techniques of Anticipation won the commercial critical acclaim and several awards from within the advertising industry, including the 1995 Institute of Creative Advertising & Design craft award for editing as well as a Gold Medal for editing and a Golden Shark award at the Kinsale International Advertising Festival. The success of the campaign led Guinness to re-broadcast it in the United Kingdom in 1995, as a transition between the campaign "The Man With the Guinness"/"Pure Genius", which had just concluded with Chain, and its new "Black and White" campaign, still in development.Though Chain was to be the last in the Pure Genius campaign, Anticipationwas tagged with the Pure Genius slogan in the UK instead of There's No Time Like Guinness Time. As a result of its featuring in the spot, Pérez Prado's Guaglione reached the Number 1 spot in the Irish music charts,and Number 2 in the British Top 40.Lawsuit
In 1992, British director Mehdi Norowzian submitted a show reel containing a number of short examples of his work to several prospective employers, including the Irish advertising agency Arks Ltd., in the hopes of being taken on to direct one or more of their commercials. Included on the reel was a short piece entitled Joy, which was shot using a static camera on a London rooftop and comprised a jump cut sequence of a man performing an extended dance of exuberance against a plain canvas background. Arks Ltd. were contracted by Guinness to produce an advertisement to run in Ireland. Among the ideas proposed was one based on a scene from the cinematic version of Roddy Doyle's novel, The Snapper, where a man rushes into a pub to celebrate the birth of his grandson with a pint of Guinness. The artistic director at Arks, thinking of possible ways to build on the concept, recalled Norowzian's submitted reel and came up with a script and storyboard based on Joy to present to Guinness. The idea was accepted, and Arks approached Norowzian to direct the commercial. Norowzian refused, as he was unwilling to simply "commercialise" an old idea, and wanted to create something new. The agency then took on Richie Smyth as director, urging him to create something "with an atmosphere broadly similar to that portrayed in Joy". Feeling that the original storyboard was too close to Joy, a new one was prepared. The result was Anticipation. Following the broadcast of the television spot in 1994, Norowzian lodged a complaint and ultimately a lawsuit against Arks Ltd. and Guinness, claiming that Anticipation breached his copyrights and accusing the agency of passing off. The plaintiff's claim for copyright infringement were based on a passage in the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988defining a dramatic work as including "recordings of a work of dance or mime", and that Anticipation was, or included, a copy of a substantial part of Joy. The case reached the High Court in 1997, where the claim of passing off was dropped. On 17 July 1998, Justice Rattee rendered his judgment that the jump cutting techniques used in Joy produced something qualitatively different from a recording of a dance or mime routine and that, as such, Joy was not in itself a dramatic work. It was therefore defined as an entrepreneurial work, a status which confers protection over only the physical recording of a work rather than the work itself. He also ruled that Anticipation did not reproduce either the whole or part of Joy. The decision was appealed, but while the Court of Appeal unanimously held that the content of a film (including the use of film and editing techniques) could enjoy copyright protection as a dramatic work, the presiding Justices ruled that Anticipation did not significantly copy any portion of Joy and dismissed the case. Ultimately, Norowzian was ordered to pay £200,000 in legal costs.As a result of the case, the Institute of Contemporary Arts called for reform of copyright law in the United Kingdom.Legacy
Actor Joe McKinney spent 1994–6 making personal appearances around Europe publicising Guinness. The lifestyle became too hectic and he gave up alcohol in 1997.He found it difficult to secure other roles due to typecasting as "the Guinness man", spending time in the US where the ad had not been broadcast. As one of the most recognisable Guinness advertisements of the 1990s, Anticipation has been mimicked or parodied in a number of more recent Guinness campaigns, including the Irish Waiting spot in 2004 promoting cans of Guinness draught beer,and director JJ Keith's British Eskimo commercial, which was part of an extended campaign promoting Guinness Extra Cold in summer 2004 and 2005. In March 2009, Guinness announced that Anticipation would be aired again as part of a "Classic Ads" campaign to mark the brewery's 250th anniversary. Imagination is something Guinness Advertising has never been short of… From John Gilroy’s hapless zookeeper and his menagerie of creatures to a Polynesian surfer and a herd of white horses; from messages in bottles setting sail across the ocean to a single, heart-stoppingly enormous wave. Guinness have been carving out their own creative path for almost a century with decades of extraordinary and enduring print, TV and digital campaigns to their name, and hopefully they will continue to push boundaries to tell stories to the world. Here’s to original thinking ! -
 Well framed Bogs of Ireland Print. We were very fortunate to acquire this very famous poster-The Bogs of Ireland.A collage of some very interesting toilets recorded for eternity by the renowned photographer John Morris.This poster is now completely out of print and is difficult to acquire.Makes a wonderful addition to anyone's favourite sanctuary and place of solitude! Dimensions : 65cm x 45cm
Well framed Bogs of Ireland Print. We were very fortunate to acquire this very famous poster-The Bogs of Ireland.A collage of some very interesting toilets recorded for eternity by the renowned photographer John Morris.This poster is now completely out of print and is difficult to acquire.Makes a wonderful addition to anyone's favourite sanctuary and place of solitude! Dimensions : 65cm x 45cm -

 45cm x 30cm Thurles Co Tipperary Classic commentary quote from the great Micheal O'Muircheartaigh. Micheal Ó Muircheartaigh (born 20 August 1930) is an Irish Gaelic games commentator for the Irish national radio and television, RTÉ. In a career that has spanned six decades he has come to be regarded as the "voice of Gaelic games." His prolific career has earned him a place in Guinness World Records Mícheál Ó Muircheartaigh was born in Dún Síon just outside Dingle, County Kerry in 1930.Ó Muircheartaigh grew up on the family farm and was educated locally in Dingle. In September 1945 he began studying at Coláiste Íosagáin in Baile Bhúirne in the County Cork Gaeltacht where he was in training to be a teacher. It was at this all-Irish school that his name changed from Michael Moriarty to the Irish version Mícheál Ó Muircheartaigh. In September 1948 he began the final year of his teacher training at St Patrick's College of Education in Drumcondra, Dublin.
45cm x 30cm Thurles Co Tipperary Classic commentary quote from the great Micheal O'Muircheartaigh. Micheal Ó Muircheartaigh (born 20 August 1930) is an Irish Gaelic games commentator for the Irish national radio and television, RTÉ. In a career that has spanned six decades he has come to be regarded as the "voice of Gaelic games." His prolific career has earned him a place in Guinness World Records Mícheál Ó Muircheartaigh was born in Dún Síon just outside Dingle, County Kerry in 1930.Ó Muircheartaigh grew up on the family farm and was educated locally in Dingle. In September 1945 he began studying at Coláiste Íosagáin in Baile Bhúirne in the County Cork Gaeltacht where he was in training to be a teacher. It was at this all-Irish school that his name changed from Michael Moriarty to the Irish version Mícheál Ó Muircheartaigh. In September 1948 he began the final year of his teacher training at St Patrick's College of Education in Drumcondra, Dublin.Broadcasting career
In early March 1949 Ó Muircheartaigh, along with ten other students from the college, and several from other colleges, did a test commentary on a hurling game at Croke Park. Each student had to commentate for five minutes in Irish and the most successful would be selected for further commentary work. Ó Muircheartaigh had never seen a game of hurling before in his life. But he knew that those adjudicators judging his commentary were not able to see the game:'Twas a new game to me. But I knew one person. He was in goal for UCD and his name was Tadhg Hurley. He went to school in Dingle and he had hurling because his father was a bank manager and had spent time in Tipperary or Cork. The moment my minute started, he was saving a fantastic shot. And he cleared it away out, I can still see it, out over the sideline, Cusack Stand side of the field, eighty yards out. But it was deflected out by a member of the opposition. The adjudicators couldn't see that that didn't happen. Who was called out to take the line-ball? The only person I knew, Tadhg Hurley. And he took a beautiful line-ball - Christy Ring never took better. He landed it down in front of the Railway goal, there was a dreadful foul on the full-forward, and there was a penalty. And who was called up to take the penalty? Tadhg Hurley. 'Twas the best individual display ever seen in Croke Park. It took him at least a minute to come from the Canal goal up. And while he was coming up I spoke about his brother Bob, who was in Donal's class, and his sister who used to come out to Dún Síon strand during the summer. So eventually he took the penalty. I've seen DJ Carey, I've seen Nicky Rackard, I've seen Christy Ring. None of them could ever equal the display he gave that day... Sin mar a thosaigh sé!
Ó Muircheartaigh was the one selected and his first assignment was to provide an all-Irish commentary on the 1949 Railway Cup final on St. Patrick's Day. He graduated from St. Patrick's College a little later and also completed a Bachelor of Arts degree from University College Dublin. He taught economics, accountancy and Irish in both primary and secondary schools throughout Dublin, the majority of which were run by the Christian Brothers. He continued teaching up until the 1980s, when he became a full-time broadcaster with Raidió Teilifís Éireann. For the early part of his broadcasting career Ó Muircheartaigh commentated on Minor GAA matches, in the Irish language. He also replaced the legendary Micheál O'Hehir when he was not available to commentate. Eventually when O'Hehir was forced to retire in the mid-1980s Ó Muircheartaigh took over as the station's premier radio commentator. He developed his own inimitable style of commentary and his accent is unmistakably that of a native Irish speaker. He is a true lover of Gaelic Athletic Association and it is reflected in the enthusiasm he brings to matches. His unusual turn of phrase has made him a much loved broadcaster and often imitated character. He has become particularly famous in Ireland for his unusual turns of phrase in the heat of the moment while commentating. Today he commentates on RTÉ Radio 1. In 2004 he published his autobiography, 'From Dún Sion to Croke Park'. Ó Muircheartaigh's commentaries for RTÉ Radio 1's Sunday Sport show won him a Jacob's Award in 1992. He was also the Parade Grand Marshal for the 2007 St. Patrick's Festival, having been given the honour by the chairman of the Festival in recognition and appreciation of his unique contribution to Irish culture. He will be the Parade Grand Marshal for the 2011 St. Patrick's Parade in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, also in recognition and appreciation of his unique contribution to Irish culture. On 16 September 2010 he announced his retirement from broadcasting. The last All-Ireland he commentated on was the 2010 All-Ireland Senior Football Championship Final on 19 September 2010.On 29 October 2010 it was announced that the 2nd International Rules test at Croke Park would be Ó Muircheartaigh's final broadcast as commentator on RTÉ Radio 1. On 30 October 2010 Micheál commentated his final commentary alongside RTÉ's pundit and former Meath footballer Bernard Flynn. He is contracted to officiate at the 2011–12 Volvo Ocean Race finish in Galway when he will commentate on the finish to the round the world race, to give it a uniquely Irish conclusion. Sailing has been a long time hobby of O Muircheartaigh. Ó Muircheartaigh writes a weekly sports column for Foinse, the Irish-language newspaper free with the Irish Independent each Wednesday. Ó Muircheartaigh was invited to read out a piece in Irish and in English at an event called "Laochra" in Croke Park on 24 April 2016 to commemorate the 100th anniversary of the Easter Rising.Other media
He is the main commentator in the 2005 video game Gaelic Games: Football for the PlayStation 2 and its 2007 sequel He was featured in the video "Mícheál Ó Muircheartaigh - Making a ham sandwich" which was posted on a Reddit forum, noting his "relaxing" voice.Honours
Mícheál was awarded an honorary doctorate by NUI Galway in 1999 for his lifetime service to broadcasting. -

 Fantastic framed photo of the famous Munster Haka performed by the New Zealand contingent wearing red- Doug Howlett,Lifemi Mafi,Jeremy Manning & Rua Tipoki. Limerick 45cm x60cm WHAT DO YOU remember most about this game? 12 years have passed now but what sticks out is how low-key the build-up was until the moment of the famous response to the haka from Munster’s New Zealand contingent. Low-key in the sense that not a whole lot was expected from the game itself. The occasion was always going to be a bit of crack with all the players from the epic day in ’78 being wheeled out to give interviews about the time they slayed the giant from the land of the long white cloud. But after all the clips and interviews with Seamus Dennison and Tony Ward were over, was anyone seriously expecting a proper contest from the game? Sure, it was an All Blacks ‘B’ side (although at the time, their second-string consisted of Cory Jane, Liam Messam, Kieran Read and Hosea Gear) but it was also a weakened Munster team, with Denis Leamy the only first choice forward available due to international commitments. The state of the two line-ups meant that two of rugby’s most well-worn clichés were put head-to-head: ‘There is no such thing as an All Blacks B team’ vs ‘you can never count out Munster’. Given what followed, you would probably say it was a push. The first sense that the game might channel the spirit of ’78 rather than just pay tribute to it was obviously during the haka. This would have been the perfect sporting moment if you could have erased Jeremy Manning’s Village People moustache out of there. The Thomond Park crowd rarely needs any encouragement but the ground was heaving after that introduction. Then the game started and the untested members of the Munster pack were the most tigerish. James Coughlan was basically a 28-year-old club player at the time but his ferocious display of carrying earned him a proper professional career. Donnacha Ryan exploded out of POC and DOC’s shadow with an commanding performance and Munster were clinical early on. It helped that out-half Paul Warwick was in the form of his life. These monster drop goals were a regular sight during that 2008-09 season. The All Blacks hit back with a try from Stephen ‘Beaver’ Donald but right on half time, Munster took a six point lead after this Barry Murphy try. This was one of those classic moments during an upset when you turn to a mate, nod vigorously and say ‘It’s on now' Half time came a moment later and with it, this nice gesture from Cory Jane. For most Irish fans, this was the first time they had seen Jane in action and this moment, coupled with his strong attacking performance marked him as one of the good guys. I can’t speak for anyone else, but the only thing I remember about the second half is Joe Rokocoko’s try – probably because Munster didn’t score in the second 40. Munster held out for 76 minutes until Rokocoko got the ball directly against his old teammate Doug Howlett. Should Howlett have made the tackle? It is hard to stop Smokin’ Joe when he plants that foot. And that was it. There was no heroic win. Unknown players like prop Timmy Ryan didn’t get to join the heroes of ’78 as regulars on the after-dinner speech circuit. What made this such a memorable occasion was how unexpected it was. It was played on a Tuesday, sandwiched between two other November Tests and although the pageantry was always going to be good fun, the fact that it exploded into life in the way it did makes it one of the most exciting games in the history of Irish rugby. It’s been six years now, but the memory of ‘It’s on’ is one that will never go away. Munster: Howlett; B Murphy, Tipoki, Mafi, Dowling; Warwick, Stringer; Pucciariello, Sheahan, Ryan; M O’Driscoll (capt), Ryan; Coughlan, Ronan, Leamy. Replacements: Buckley for Ryan 40, Fogarty for Sheahan 63, Holland for Leamy 24, Manning for Tipoki 52. Not used: Melbourne, O’Sullivan, Prendergast New Zealand: Jane; H Gear, Tuitavake, Toeava, Rokocoko; Donald, Weepu (capt); Mackintosh, Flynn, Franks, Filipo, Eaton, Thomson, Waldrom, Messam. Replacements: Elliott for Flynn 65, Afoa for Franks 70, B Thorn for Filipo 71, Read for Thomson 60, Mathewson for Weepu 63, Muliaina for Tuitavake 71. Not used: Kahui,
Fantastic framed photo of the famous Munster Haka performed by the New Zealand contingent wearing red- Doug Howlett,Lifemi Mafi,Jeremy Manning & Rua Tipoki. Limerick 45cm x60cm WHAT DO YOU remember most about this game? 12 years have passed now but what sticks out is how low-key the build-up was until the moment of the famous response to the haka from Munster’s New Zealand contingent. Low-key in the sense that not a whole lot was expected from the game itself. The occasion was always going to be a bit of crack with all the players from the epic day in ’78 being wheeled out to give interviews about the time they slayed the giant from the land of the long white cloud. But after all the clips and interviews with Seamus Dennison and Tony Ward were over, was anyone seriously expecting a proper contest from the game? Sure, it was an All Blacks ‘B’ side (although at the time, their second-string consisted of Cory Jane, Liam Messam, Kieran Read and Hosea Gear) but it was also a weakened Munster team, with Denis Leamy the only first choice forward available due to international commitments. The state of the two line-ups meant that two of rugby’s most well-worn clichés were put head-to-head: ‘There is no such thing as an All Blacks B team’ vs ‘you can never count out Munster’. Given what followed, you would probably say it was a push. The first sense that the game might channel the spirit of ’78 rather than just pay tribute to it was obviously during the haka. This would have been the perfect sporting moment if you could have erased Jeremy Manning’s Village People moustache out of there. The Thomond Park crowd rarely needs any encouragement but the ground was heaving after that introduction. Then the game started and the untested members of the Munster pack were the most tigerish. James Coughlan was basically a 28-year-old club player at the time but his ferocious display of carrying earned him a proper professional career. Donnacha Ryan exploded out of POC and DOC’s shadow with an commanding performance and Munster were clinical early on. It helped that out-half Paul Warwick was in the form of his life. These monster drop goals were a regular sight during that 2008-09 season. The All Blacks hit back with a try from Stephen ‘Beaver’ Donald but right on half time, Munster took a six point lead after this Barry Murphy try. This was one of those classic moments during an upset when you turn to a mate, nod vigorously and say ‘It’s on now' Half time came a moment later and with it, this nice gesture from Cory Jane. For most Irish fans, this was the first time they had seen Jane in action and this moment, coupled with his strong attacking performance marked him as one of the good guys. I can’t speak for anyone else, but the only thing I remember about the second half is Joe Rokocoko’s try – probably because Munster didn’t score in the second 40. Munster held out for 76 minutes until Rokocoko got the ball directly against his old teammate Doug Howlett. Should Howlett have made the tackle? It is hard to stop Smokin’ Joe when he plants that foot. And that was it. There was no heroic win. Unknown players like prop Timmy Ryan didn’t get to join the heroes of ’78 as regulars on the after-dinner speech circuit. What made this such a memorable occasion was how unexpected it was. It was played on a Tuesday, sandwiched between two other November Tests and although the pageantry was always going to be good fun, the fact that it exploded into life in the way it did makes it one of the most exciting games in the history of Irish rugby. It’s been six years now, but the memory of ‘It’s on’ is one that will never go away. Munster: Howlett; B Murphy, Tipoki, Mafi, Dowling; Warwick, Stringer; Pucciariello, Sheahan, Ryan; M O’Driscoll (capt), Ryan; Coughlan, Ronan, Leamy. Replacements: Buckley for Ryan 40, Fogarty for Sheahan 63, Holland for Leamy 24, Manning for Tipoki 52. Not used: Melbourne, O’Sullivan, Prendergast New Zealand: Jane; H Gear, Tuitavake, Toeava, Rokocoko; Donald, Weepu (capt); Mackintosh, Flynn, Franks, Filipo, Eaton, Thomson, Waldrom, Messam. Replacements: Elliott for Flynn 65, Afoa for Franks 70, B Thorn for Filipo 71, Read for Thomson 60, Mathewson for Weepu 63, Muliaina for Tuitavake 71. Not used: Kahui, -
 Iconic artwork of the famous tackle by Roy Keane on Marc Overmars at the start of the 2001 World Cup Qualifier between the Republic of Ireland and Holland at Lansdowne Road. 34cm x 30cm Limerick Roy Maurice Keane (born 10 August 1971) is an Irish football manager and former professional player. He is the joint most successful Irish footballer of all time, having won 19 major trophies in his club career, 17 of which came during his time at English club Manchester United. He served as the assistant manager of the Republic of Ireland national teamfrom 2013 until 2018. Regarded as one of the best midfielders of his generation, he was named by Pelé in the FIFA 100 list of the world's greatest living players in 2004.Noted for his hardened and brash demeanour, he was ranked at No. 11 on The Times' list of the 50 "hardest" footballers in history in 2007. Keane was inducted into the Premier League Hall of Fame in 2021. In his 18-year playing career, Keane played for Cobh Ramblers, Nottingham Forest, and Manchester United, before ending his career at Celtic. He was a dominating box-to-box midfielder, noted for his aggressive and highly competitive style of play, an attitude that helped him excel as captain of Manchester United from 1997 until his departure in 2005. Keane helped United achieve a sustained period of success during his 12 years at the club. He then signed for Celtic, where he won a domestic double before he retired as a player in 2006. Keane played at the international level for the Republic of Ireland over 14 years, most of which he spent as captain. At the 1994 FIFA World Cup, he played in every Republic of Ireland game. He was sent home from the 2002 FIFA World Cup after a dispute with national coach Mick McCarthy over the team's training facilities. Keane was appointed manager of Sunderland shortly after his retirement as a player and took the club from 23rd position in the Football League Championship, in late August, to win the division title and gain promotion to the Premier League. He resigned in December 2008,and from April 2009 to January 2011, he was manager of Championship club Ipswich Town. In November 2013, he was appointed assistant manager of the Republic of Ireland national team by manager Martin O'Neill. Keane has also worked as a studio analyst for British channels ITV's and Sky Sportsfootball coverage.
Iconic artwork of the famous tackle by Roy Keane on Marc Overmars at the start of the 2001 World Cup Qualifier between the Republic of Ireland and Holland at Lansdowne Road. 34cm x 30cm Limerick Roy Maurice Keane (born 10 August 1971) is an Irish football manager and former professional player. He is the joint most successful Irish footballer of all time, having won 19 major trophies in his club career, 17 of which came during his time at English club Manchester United. He served as the assistant manager of the Republic of Ireland national teamfrom 2013 until 2018. Regarded as one of the best midfielders of his generation, he was named by Pelé in the FIFA 100 list of the world's greatest living players in 2004.Noted for his hardened and brash demeanour, he was ranked at No. 11 on The Times' list of the 50 "hardest" footballers in history in 2007. Keane was inducted into the Premier League Hall of Fame in 2021. In his 18-year playing career, Keane played for Cobh Ramblers, Nottingham Forest, and Manchester United, before ending his career at Celtic. He was a dominating box-to-box midfielder, noted for his aggressive and highly competitive style of play, an attitude that helped him excel as captain of Manchester United from 1997 until his departure in 2005. Keane helped United achieve a sustained period of success during his 12 years at the club. He then signed for Celtic, where he won a domestic double before he retired as a player in 2006. Keane played at the international level for the Republic of Ireland over 14 years, most of which he spent as captain. At the 1994 FIFA World Cup, he played in every Republic of Ireland game. He was sent home from the 2002 FIFA World Cup after a dispute with national coach Mick McCarthy over the team's training facilities. Keane was appointed manager of Sunderland shortly after his retirement as a player and took the club from 23rd position in the Football League Championship, in late August, to win the division title and gain promotion to the Premier League. He resigned in December 2008,and from April 2009 to January 2011, he was manager of Championship club Ipswich Town. In November 2013, he was appointed assistant manager of the Republic of Ireland national team by manager Martin O'Neill. Keane has also worked as a studio analyst for British channels ITV's and Sky Sportsfootball coverage.