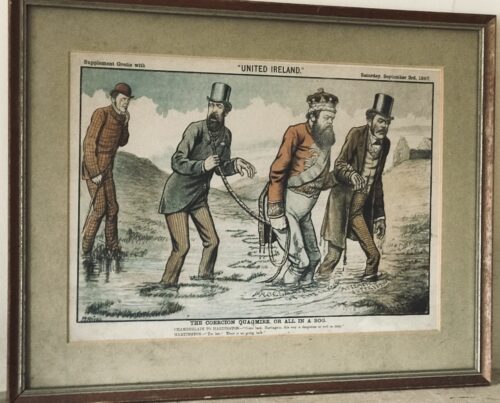
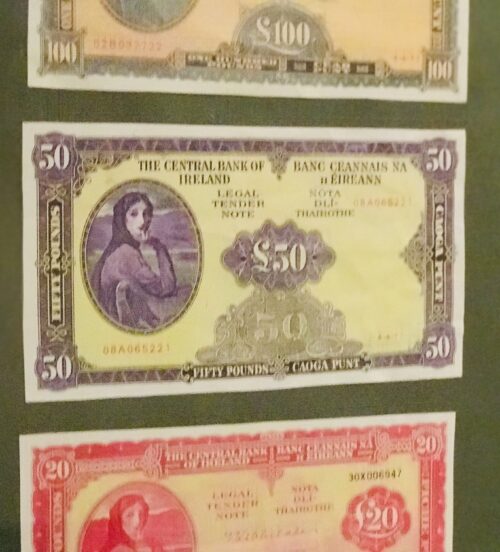
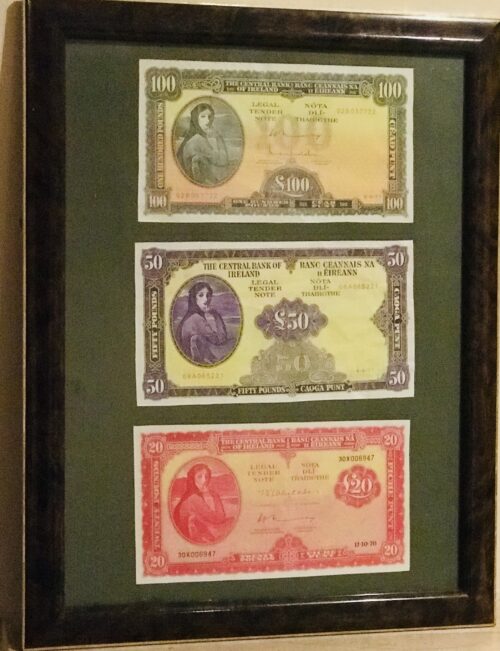
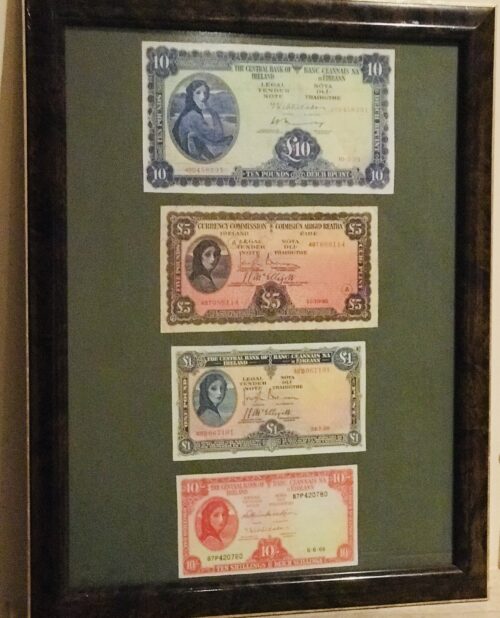
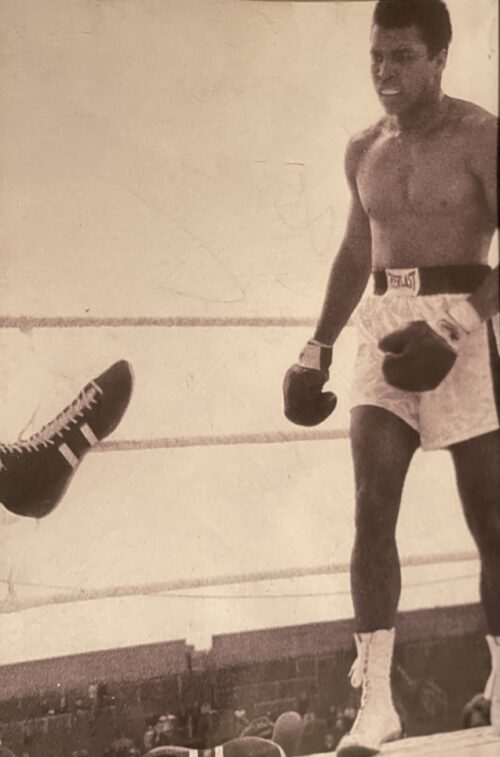
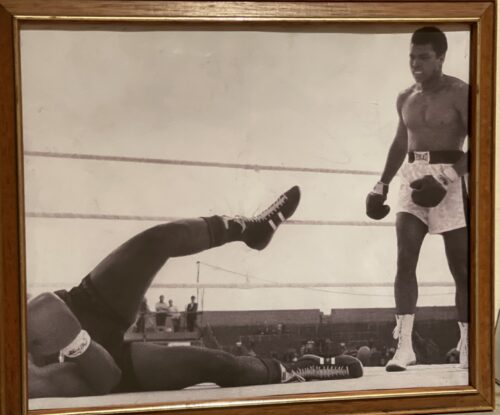
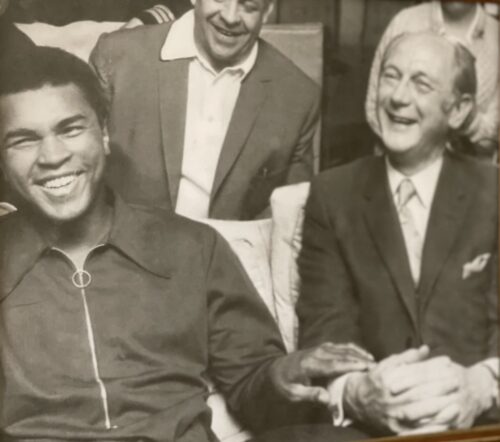
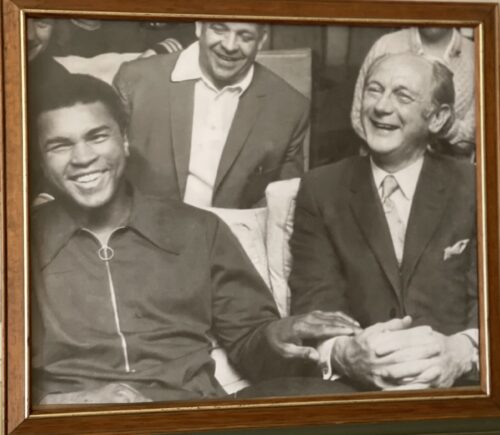
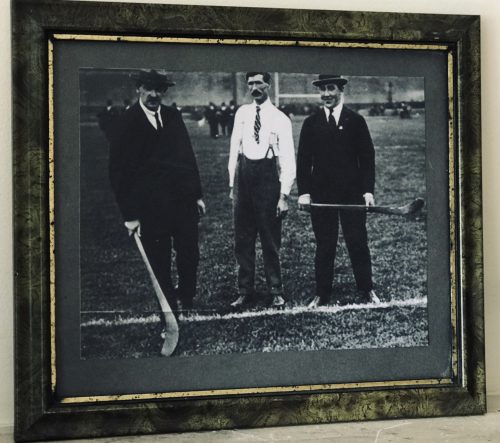
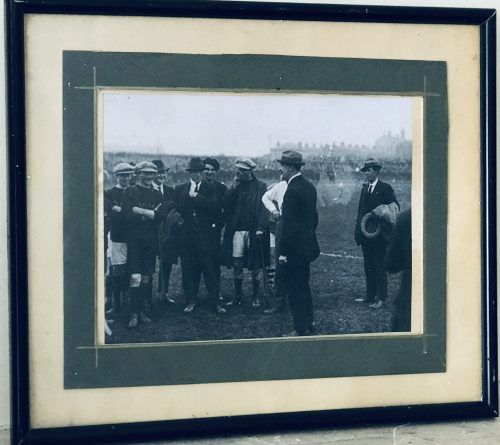
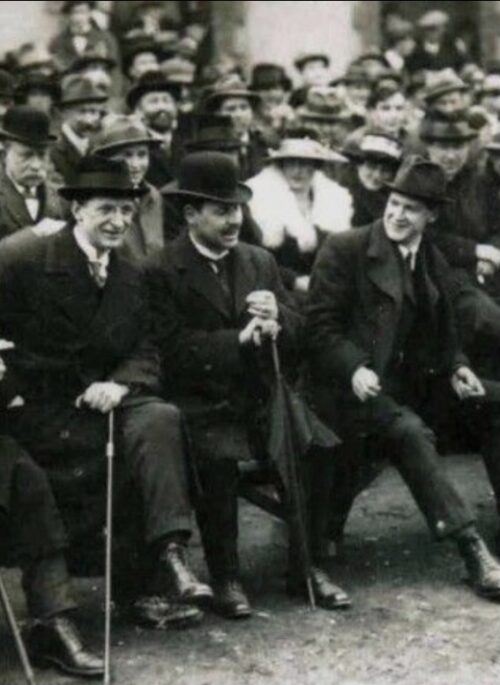
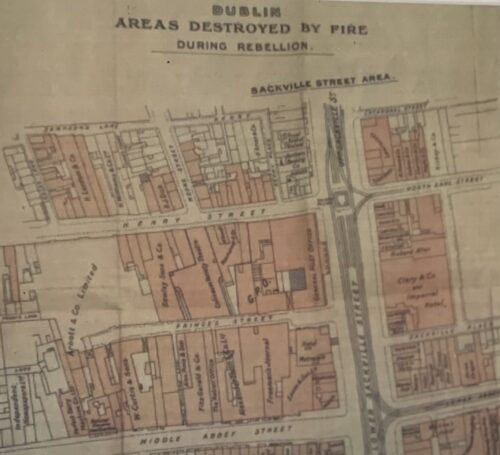
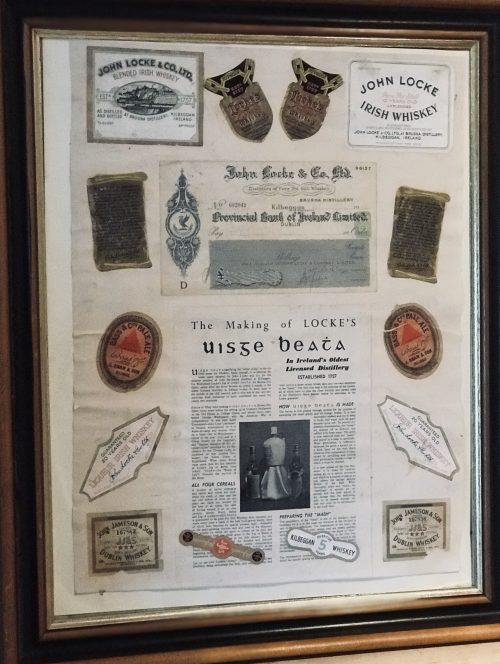
Fantastic display of Locke's Old Irish Whiskey Ephemera & Memorabilia including whiskey bottle labels, cheques,history of the distillery ,etc.
Origins: Kilbeggan Co Westmeath Dimensions:70cm x 60cm Unglazed
The Kilbeggan Distillery (formerly
Brusna Distillery and
Locke's Distillery) is an
Irish whiskey distillery situated on the
River Brosna in
Kilbeggan,
County Westmeath, Ireland. It is owned by
Beam Suntory.
A small
pot still distillery, the licence to distil dates to 1757, a copy of which can be seen in the distillery.
Similar to many Irish distilleries, Kilbeggan endured financial difficulties during the early 20th century, and ceased operations in 1957. However, the distillery was later refurbished, with distilling recommencing on-site in 2007.
Noted devotees of the distillery's whiskeys include British Prime Minister
Sir Winston Churchill, and
Myles na gCopaleen, the Irish playwright.
Early years
The distillery was founded in 1757 by Matthew MacManus, who may have distilled elsewhere before founding Kilbeggan.
Although information about the early years of the distillery is scarce, documentation suggests that in its early years the distillery operated with a 232 gallon still, and an annual output of 1,500 gallons.
By the early 19th century, the distillery was being run by a John and William Codd.
In 1841, the distillery was put up for sale following the dissolution of the partnership between its then owners, William Codd and William Cuffee.
The distillery at the time consisted of a brew house, still house with three pot stills (wash still: 8,000 gallons; low wine still, no. 1; 2,000 gallons; low wine still, no. 2: 1,500 gallons), run-room with five receivers, malt house, corn stores capable of storing 5,000 barrels, and oat-meal mills.
Also listed in the sale were 400 tonnes of coal, and 10,000 boxes of turf - the latter reflecting the immense quantities of turf consumed at the distillery, so much so, that it was reported to have kept hundreds of poor people profitably employed in cutting, rearing, and drawing it to the town throughout the year.
Locke's Distillery
In 1843, the distillery was taken over by John Locke, under whose stewardship the distillery flourished.
Locke treated his staff well, and was held in high regard by both his workers and the people of the town. Informal records show that under Locke the distillery provided cottages for its employees, either for rent or purchase through a form of in-house mortgage scheme.
In addition, all staff received a wagon load of coal at the start of each winter, the cost of which was deducted from salaries retrospectively on a weekly basis.
Testimony of the respect with which he was held is offered by an incident in 1866. Following an accident on-site which had rendered a critical piece of equipment, the steam boiler, inoperable, the distillery had come to a standstill. With Locke unable to afford or obtain a loan to fund a replacement, the future of distillery lay in doubt.
However, in a gesture of solidarity, the people of Kilbeggan came together and purchased a replacement boiler, which they presented to John Locke, along with the following public letter of appreciation, which was printed in several local newspapers at the time:
An Address from the People of Kilbeggan to John Locke, Esq. Dear Sir - Permit us, your fellow townsmen, to assure of our deep and cordial sympathy in your loss and disappointment from the accident which occurred recently in your Distillery. Sincerely as we regret the accident, happily unattended with loss of life, we cannot but rejoice at the long-wished-for opportunity it affords us of testifying to you the high appreciation in which we hold you for your public and private worth. We are well aware that the restrictions imposed by recent legislation on that particular branch of Irish industry, with which you have been so long identified, have been attended with disastrous results to the trade, as is manifest in the long list of Distilleries now almost in ruins, and which were a few years ago centres of busy industry, affording remunerative employment to thousands of hands; and we are convinced the Kilbeggan Distillery would have long since swelled the dismal catalogue had it fallen into less energetic and enterprising hands. In such an event we would be compelled to witness the disheartening scene of a large number of our working population without employment during that period of the year when employment Is scarcest, and at the same time most essential to the poor. Independent then of what we owe you, on purely personal grounds, we feel we owe you a deep debt of gratitude for maintaining in our midst a manufacture which affords such extensive employment to our poor, and exercises so favourable an influence on the prosperity of the town. In conclusion, dear Sir, we beg your acceptance of a new steam boiler to replace the injured one, as testimony, inadequate though it is, of our unfeigned respect and esteems for you ; and we beg to present it with the ardent wish and earnest hope that, for many long years to come, it may contribute to enhance still more the deservedly high and increasing reputation of the Kilbeggan Distillery.
In a public response to mark the gift, also published in several newspapers, Locke thanked the people of Kilbeggan for their generosity, stating "...I feel this to be the proudest day of my life...".
A plaque commemorating the event hangs in the distillery's restaurant today.
In 1878, a fire broke out in the "can dip" (sampling) room of the distillery, and spread rapidly.
Although, the fire was extinguished within an hour, it destroying a considerable portion of the front of the distillery and caused £400 worth of damage.
Hundreds of gallons of new whiskey were also consumed in the blaze - however, the distillery is said to have been saved from further physical and financial ruin through the quick reaction of townsfolk who broke down the doors of the warehouses, and helped roll thousands of casks of ageing spirit down the street to safety.
In 1887, the distillery was visited by
Alfred Barnard, a British writer, as research for his book, "the Whiskey Distilleries of the United Kingdom".
By then, the much enlarged distillery was being managed by John's sons, John Edward and James Harvey, who told Barnard that the distillery's output had more than doubled during the preceding ten years, and that they intended to install electric lighting.
Barnard noted that the distillery, which he referred to as the "Brusna Distillery", named for the
nearby river, was said to be the oldest in Ireland.
According to Barnard, the distillery covered 5 acres, and employed a staff of about 70 men, with the aged and sick pensioned-off or assisted.
At the time of his visit, the distillery was producing 157,200 proof gallons per annum, though it had the capacity to produce 200,000.
The whiskey, which was sold primarily in Dublin, England, and "the Colonies", was
"old pot still", produced using four pot stills (two wash stills: 10,320 / 8,436 gallons; and two spirit stills: 6,170 / 6,080 gallons), which had been installed by Millar and Company, Dublin.
Barnard remarked that at the time of his visit over 2,000 casks of spirit were ageing in the distillery's bonded warehouses.
In 1893, the distillery ceased to be privately held, and was converted a limited stock company, trading as John Locke & Co., Ltd., with nominal capital of £40,000.
Decline and Closure
In the early part of the 20th century, Kilbeggan, like many Irish whiskey distilleries at the time, entered a period of decline. This was due to the combined effects of loss and hampering of market access - due to
prohibition in the United States, the
trade war with the British Empire, shipping difficulties during the world wars, and Irish Government export quotas; as well as competition from blended Scotch, and disruption to production during the
Irish war of Independence.
As a result, Kilbeggan was forced to cease production of new spirit for 7 years between 1924 and 1931, decimating the company's cash flow and finances.
Most of the staff at the distillery were let go, and the distillery slowly sold off its stocks of aged whiskey.
Distilling resumed in 1931, following the end of prohibition in the United States, and for a time the distillery's finances improved - with a loss of £83 in 1931, converted to a modest profit of £6,700 in 1939.
In the 1920s, both of John sons passed away, John in 1920, and James in 1927, and ownership of the distillery passed to Locke's granddaughters, Mary Evelyn and Florence Emily.
However, by then the distillery was in need to repair, with the turbulent economic conditions of the early 20th century having meant that no investment had been made in new plant since the 1890s.
In 1947, the Lockes decided to put the distillery was put up for sale as a going concern. Although run down, the distillery had valuable stocks of mature whiskey, a valuable commodity in post-war Europe.
An offer of £305,000 was received from a Swiss investor fronted by an Englishman, going by the name of Horace Smith.
Their unstated interest, was not the business itself, but the 60,000 gallons of whiskey stocks, which they hoped to sell on the black market in England at £11 a gallon - thus, more than doubling their investment overnight.
However, when they failed to come up with the deposit, the duo were arrested and promptly interrogated by
Irish police. The Englishman, it turned out, was an impostor named Maximoe, who was wanted by Scotland Yard.
]The Irish authorities placed Maximoe on a ferry back to England for extradition, but he jumped overboard and escaped with the help of unknown accomplices.
An Irish opposition politician,
Oliver J. Flanagan, subsequently alleged under
parliamentary privilege that members of the governing
Fianna Fáil political party were linked to the deal, accusing then
Irish Taoiseach Éamon de Valera and his son of having accepted gold watches from the Swiss businessman.
A
tribunal of inquiry discounted the allegations but the damage contributed to Fianna Fáil's defeat in the
1948 election.
In addition, as the scandal remained headline news in Ireland for several months, it discouraged interest from other investors in the distillery.
Thus with no buyer found, operations continued at the distillery, with production averaging between 120,000 - 150,000 proof gallons per annum, and consumption running at between 15,000 - 20,000 barrels of barrel.
In addition, although heavily indebted, investments were made in new plant and equipment.
However, the death knell for the distillery came in April 1952, when the Irish Government introduced a 28% hike in the excise duties on spirits, causing a drastic decline in domestic whiskey sales.
By November 1953, the distillery could not afford to pay the duty to release whiskey ordered for Christmas from bond, and production was forced to come to a halt.
Although distilling had stopped, the firm struggled on until 27 November 1958, when a debenture issued in 1953 fell due, which the distillery could not afford to pay, forcing the bank to call in the receivers. Thus, bringing to an end 201 years of distilling in the town.
In 1962, the distillery was purchased for £10,000 by Karl Heinz Moller, a German businessman, who owned a motor distribution company in Hamburg.
Moller made a substantial profit on the deal, by selling off the whiskey stocks (about 100,000 gallons - worth tens of thousands of pounds alone) and a rare Mercedes Benz owned by the distillery.
Much to the dismay of locals, Moller proceeded to convert the distillery into a pigsty, smashing thousands of Locke earthenware crocks (which would be worth a substantial amount at auction today) to create a hard-core base for the concrete floor.
In 1969, the distillery was sold to Powerscreen, a firm which sold Volvo loading shovels, and in the early 1970s, the stills and worms were removed and sold for scrap.
Distillery reopens
In 1982, almost thirty years after the distillery ceased operations, the Kilbeggan Preservation and Development Association was formed by locals in the town. Using funds raised locally, the Association restored the Distillery, and reopened it to the public as a whiskey distillery museum.
Then, in 1987, the newly opened
Cooley Distillery acquired the assets of Kilbeggan distillery, allowing Cooley to relaunch whiskeys under the Kilbeggan and Locke's Whiskey brands.
Cooley later also took over the running of the museum, and began the process of re-establishing a working distillery on-site. Cooley were aided in the process by the fact that since the distillery's closure, each subsequent owner had faithfully paid the £5 annual fee to maintain the distilling licence.
In 2007, the 250th anniversary of the distillery's founding, distillation recommenced at Kilbeggan. The official firing of the pot stills was witnessed by direct descendants of the three families, the McManuses, the Codds, and the Lockes, who had run the distillery during its 200 year distilling history.
In a fitting nod to the long history of distilling at Kilbeggan, one of the two pot stills installed in the refurbished distillery was a 180-year old pot still, which had originally been installed at the
Old Tullamore Distillery in the early 1800s.
] It is the oldest working pot still producing whiskey in the world today.
In 2010, with the installation of a mash tun and fermentation vats, Kilbeggan became a fully operational distillery once again.
Present day

Bottle of "Kilbeggan Finest Irish whiskey"
Today the distillery is known as
Kilbeggan Distillery, and includes a restaurant,
The Pantry Restaurant, and a 19th-century waterwheel that has been restored to working condition. The distillery can also be powered by a steam engine, which is in working condition but rarely used. It was installed to allow the distillery to continue operating in times of low water on the river.
Prior to the recommencement of operations of Kilbeggan, the three brands associated with the distillery—Kilbeggan, Locke's Blend and Locke's Malt were produced at the
Cooley Distillery in
County Louth, before being transported to Kilbeggan, where they were to stored in a 200 year old granite warehouse.
However, following recommencement of operations at Kilbeggan, new whiskey produced on-site has been sufficiently mature for market since around 2014.
Since reopening, the distillery has launched a Kilbeggan Small Batch Rye, the first whiskey to be 100% distilled and matured on-site since the restoration was completed. Double-distilled, the whiskey is produced from a mash of malt, barley, and about 30% rye, said to reflect the traditional practice of using rye, which was common at 19th century Irish distilleries, but has since virtually died out.
In late 2009, the distillery released small '3-pack' samples of its still-developing "new make spirit" at 1 month, 1 year, and 2 years of age (in Ireland, the spirit must be aged a minimum of three years before it can legally be called "whiskey").
The distillery's visitor centre was among the nominations in
Whisky Magazine's Icons of Whisky visitor attraction category in 2008.
Gallery
-
Machinery at the distillery
-
Historic view distillery buildings
-
Distillery buildings with roof sign
-
View of the distillery from the 1900s
 J Matterson & Sons operated out of Roches Street, while their rival company O’Mara’s operated across the road on the same street from 1839. Mattersons was established in 1816 by John Russell and J Matterson, who were brother-in-laws of a kind. Both men married a Mossop sister, Mary and Eleanor.
After the death of Joseph Matterson Snr in 1854, Joseph Matterson Jnr took over the Limerick aspect of the company. While Joseph Matterson Snr’s other son William Matterson, oversaw the London branch of the business. William Matterson died aged 71 in London in January 1903.
Not only was Joseph Matterson Jnr. a business owner in the city but he was also a key player in the community. He was vice president of the Protestant Young Mens Association which stained-glass window still remains in-situ in O’Connell Street.
Below are the funeral notices from the Limerick Chronicle, from the Limerick City Library Local Studies, for members of the Matterson Family.
J Matterson & Sons operated out of Roches Street, while their rival company O’Mara’s operated across the road on the same street from 1839. Mattersons was established in 1816 by John Russell and J Matterson, who were brother-in-laws of a kind. Both men married a Mossop sister, Mary and Eleanor.
After the death of Joseph Matterson Snr in 1854, Joseph Matterson Jnr took over the Limerick aspect of the company. While Joseph Matterson Snr’s other son William Matterson, oversaw the London branch of the business. William Matterson died aged 71 in London in January 1903.
Not only was Joseph Matterson Jnr. a business owner in the city but he was also a key player in the community. He was vice president of the Protestant Young Mens Association which stained-glass window still remains in-situ in O’Connell Street.
Below are the funeral notices from the Limerick Chronicle, from the Limerick City Library Local Studies, for members of the Matterson Family.
 In 1901 Joseph Matterson, Jnr aged 60 was living with his 46 year old wife Agnes and children Leopold (18), Vera Sunderland(9), Victor (7), Eva (5) and a seven various servants. Joseph Matterson Jnr and his wife Agnes had 12 children in total with 9 still living in 1911, married 33 years. After Joseph’s death in 1906, Agnes and family moved to the Ennis Road, her children Ian Gordon and Vera Sunderland were living with her in 1911.
The following also courtesy of Pat Mossop is a wonderful letter written by a Limerick lady in 1873: Eleanor McGhie, an article by Sharon Slater based on the letter was published in the Old Limerick Journal.
In 1901 Joseph Matterson, Jnr aged 60 was living with his 46 year old wife Agnes and children Leopold (18), Vera Sunderland(9), Victor (7), Eva (5) and a seven various servants. Joseph Matterson Jnr and his wife Agnes had 12 children in total with 9 still living in 1911, married 33 years. After Joseph’s death in 1906, Agnes and family moved to the Ennis Road, her children Ian Gordon and Vera Sunderland were living with her in 1911.
The following also courtesy of Pat Mossop is a wonderful letter written by a Limerick lady in 1873: Eleanor McGhie, an article by Sharon Slater based on the letter was published in the Old Limerick Journal.
 Shaw & Sons operated out of Mulgrave Street. It was founded in 1831 by William John Shaw, whose family originated in Co. Down. In 1892 Shaw’s factory was using electric lights, lifts, a mini-railway and even telephonic communications, the Shaw’s factory was well ahead of it’s time. It is now owned by the Kerry Group.
Below are the funeral notices from the Limerick Chronicle, from the Limerick City Library Local Studies, for members of the Shaw Family.
Shaw & Sons operated out of Mulgrave Street. It was founded in 1831 by William John Shaw, whose family originated in Co. Down. In 1892 Shaw’s factory was using electric lights, lifts, a mini-railway and even telephonic communications, the Shaw’s factory was well ahead of it’s time. It is now owned by the Kerry Group.
Below are the funeral notices from the Limerick Chronicle, from the Limerick City Library Local Studies, for members of the Shaw Family.
 Alexander William Shaw – 27 October 1847 – 29 November 1923Derravoher North Circular Road,bacon curer and local politician and the founder of Limerick and Lahinch golf clubs. He was born in County Limerick, the second son of John Shaw (son of WJ Shaw) of Willowbank, bacon merchant. The family firm was already thriving when he took it over, but under his astute management it grew to become one of the largest bacon curing businesses in Europe, and Shaw became one of the most prominent businessmen in the city.
Alexander William Shaw – 27 October 1847 – 29 November 1923Derravoher North Circular Road,bacon curer and local politician and the founder of Limerick and Lahinch golf clubs. He was born in County Limerick, the second son of John Shaw (son of WJ Shaw) of Willowbank, bacon merchant. The family firm was already thriving when he took it over, but under his astute management it grew to become one of the largest bacon curing businesses in Europe, and Shaw became one of the most prominent businessmen in the city.
 Denny’s and Sons operated out of 27 Upper William Street in in 1891 as well as Mulgrave Street. It was founded by Henry Denny in the 1870s and first operated as a Provision Merchants out of Newtown Mahon, Upper William Street. Denny operated out of Limerick, Cork and Waterford. Denny’s sausages make an appearance in James Joyce’s Ulysses, where Leopold Bloom watches a young girl in Dlugacz’s butcher’s shop buy a pound and a half of Denny’s sausages, as he waits to buy a pork kidney for his and wife Molly’s breakfast. Denny’s is now owned by the Kerry Food group, after they acquired it in 1982.
Dimensions :230cm x 10cm x 8cm
Denny’s and Sons operated out of 27 Upper William Street in in 1891 as well as Mulgrave Street. It was founded by Henry Denny in the 1870s and first operated as a Provision Merchants out of Newtown Mahon, Upper William Street. Denny operated out of Limerick, Cork and Waterford. Denny’s sausages make an appearance in James Joyce’s Ulysses, where Leopold Bloom watches a young girl in Dlugacz’s butcher’s shop buy a pound and a half of Denny’s sausages, as he waits to buy a pork kidney for his and wife Molly’s breakfast. Denny’s is now owned by the Kerry Food group, after they acquired it in 1982.
Dimensions :230cm x 10cm x 8cm







 45cm x 66cm
An absolute once off piece of Irish Memorabilia .We at the Irish Pub Emporium were so lucky to acquire from a private collector who has moved overseas.These superb castiron road signs were commissioned by the Irish Free State in the late 1940s post and were initially the responsibility of the newly formed Irish Tourism Organisation -Fógra Failte (later to become Bord Failte and then Failte Ireland).
"The former '
45cm x 66cm
An absolute once off piece of Irish Memorabilia .We at the Irish Pub Emporium were so lucky to acquire from a private collector who has moved overseas.These superb castiron road signs were commissioned by the Irish Free State in the late 1940s post and were initially the responsibility of the newly formed Irish Tourism Organisation -Fógra Failte (later to become Bord Failte and then Failte Ireland).
"The former '