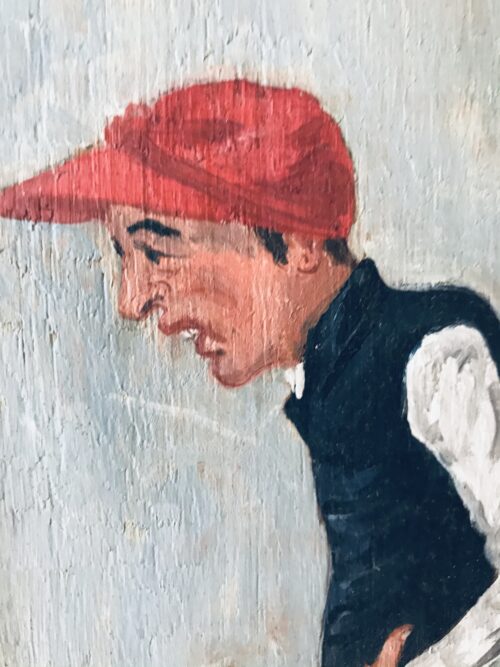
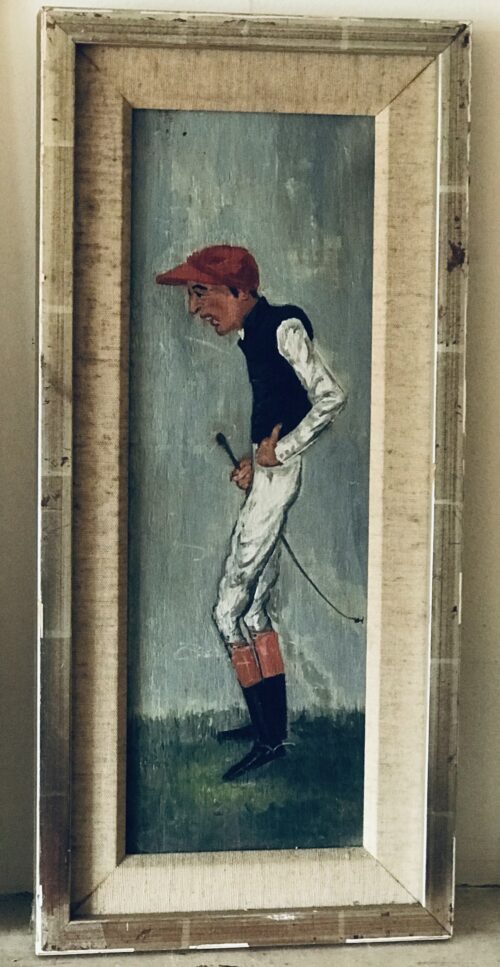
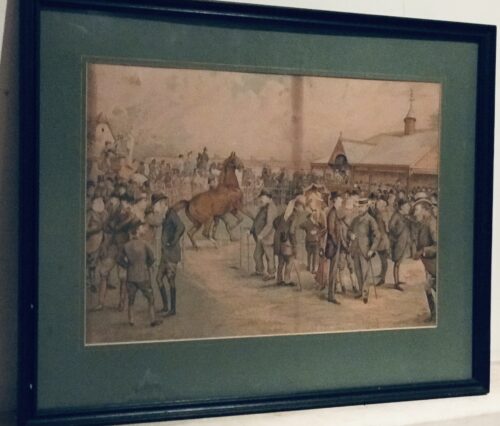
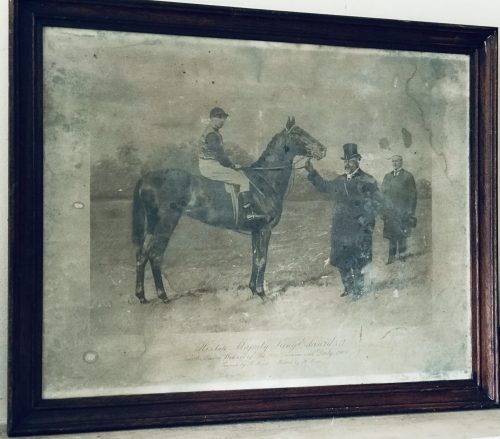
Real atmospheric original lithograph of Minoru,most famous for being the first Derby winner to be owned by a reigning British monarch.
45cm x 55cm Shanagolden Co Limerick
Minoru (1906 – circa 1917) was an Irish-bred, British-trained
Thoroughbred racehorse who won two
British Classic Races. In a career which lasted from June 1908 to April 1910 he ran thirteen times and won seven races. After showing moderate form as a two-year-old he improved to become one of the best colts in England in the early part of 1909. He won his first five races including the
2000 Guineas and
The Derby. His win at
Epsom Downs Racecourse made his owner
King Edward VII the first reigning British monarch to win a Derby and was greeted with unprecedented celebration. Minoru's bid to win the
British Triple Crown ended when he was beaten by
Bayardo in the
St Leger. He was retired to stud in 1910 and was soon afterwards exported to Russia, where he disappeared during the
Revolution in 1917.
A then popular game of chance, which simulates a horse race in miniature, had been named after Minoru.
Background
Minoru was a bay horse bred by
Colonel William Hall-Walker (later Lord Wavertree) at his
stud farm at Tully in
County Kildare which today is the
Irish National Stud.
Minoru was a son of
Cyllene, winner of the 1899
Ascot Gold Cup who sired three other
Epsom Derby winners, but was exported to
Argentina in January 1908, before his true quality as a stallion became evident. His dam was Mother Siegel, a daughter of the highly regarded multiple stakes winner, Friar's Balsam. The colt was leased by his breeder to
King Edward VII along with five other yearlings.
Minoru was trained by
Richard Marsh at his Egerton House stable at
Newmarket, Suffolk: Marsh was the established "Royal" trainer, having prepared both
Persimmon and
Diamond Jubilee to win the Derby for Edward when he was Prince of Wales.
Racing career
1908: two-year-old season
Minoru began his racing career impressively, by winning the five
furlong Great Surrey Foal Stakes at
Epsom, on 5 June, the day that
Signorinetta won
The Oaks.
His subsequent performances in 1908 were disappointing. He finished second to Louviers when strongly fancied for the
Coventry Stakes at
Royal Ascot in June and was second again to Battleaxe in the
July Stakes at
Newmarket.
After a break, Minoru returned to Newmarket in autumn for two further races. He finished third in the Hopeful Stakes, and third again in the New Nursery, a
handicap race for two-year-olds. In the Free Handicap, an end-of-season ranking of the best two-year-olds
Bayardo was ranked top with 126
pounds, while Minoru was unrated, meaning that he was at least twenty-two pounds behind the leader. At the end of the year he was considered "useful", but not top class. Marsh, however, thought highly of the colt: when asked to assess the six horses leased by the King from Colonel Hall-Walker, he commented, "I like Minoru best. He is a bit on the leg, but a fine and resolute goer.
1909: three-year-old season
Spring
During the winter of 1908–1909, Minoru made exceptional progress, and although the King's racing manager, Marcus Beresford, was initially sceptical, Marsh decided to train the colt for the
Classics. The cold weather early in the year delayed the preparation of many horses, including Bayardo, but the lightly-made Minoru took little work to reach peak fitness, giving him an advantage over most of his rivals.
After performing impressively in a private trial race, Minoru made his debut in the
Greenham Stakes at
Newbury on 31 March and won from Valens under top weight of 136
pounds.
In the
2000 Guineas at Newmarket on 28 April he started at odds of
4/1 against ten opponents and was regarded as the chief danger to the favourite Bayardo. Ridden by
Herbert Joneshe raced prominently before accelerating through a narrowing gap
in the closing stages and won easily from Phaleron and Louviers, with Bayardo fourth, in a race record time of 1:37.8. According to press reports the victory was greeted with "intense enthusiasm".
Minoru was given very little work by Marsh before his next run in the Derby.
Summer
At Epsom on 26 May, Minoru started at odds of 7/2 in a field of fifteen, with Bayardo and the American-bred
Sir Martin, who started favourite, being seen as his main rivals.
The crowd was smaller than usual on account of heavy rain on the morning of the race, but the King and
Queen were in attendance.
Minoru broke slowly on the inside but recovered quickly and by the beginning of the turn into the straight was in fourth place behind Louviers, Brooklands and Sir Martin, and just ahead of William the Fourth. At this point the race changed completely as Sir Martin, who had been traveling extremely well, stumbled in close quarters and lost his rider, badly interfering with William the Fourth.
In the straight the race developed into a match between Minoru and Louviers who raced together throughout the last two furlongs, with first one and then the other appearing to have the advantage. The two colts crossed the line together, just ahead of William the Fourth who finished very strongly after recovering from the earlier incident, and looked an unlucky loser.
After a long delay, the judge announced Minoru as the winner by a short head from Louviers, many of whose supporters were convinced that he had won.
Valens finished fourth and Bayardo fifth. The victory for the "Royal" colt provoked "the wildest scenes of enthusiasm ever known in England",
including a mass rendition of
the National Anthem as the King led his horse to the winner's enclosure.
Minoru himself was "swallowed up" by a crowd of supporters, several of whom attempted to obtain souvenirs by pulling hairs from his mane and tail,
while his owner was informally congratulated with cries of "Good for you old sport!" and "Well done Teddy!".
Minoru's victory was the first in the Derby for a reigning British monarch.
The King received many congratulatory
telegrams, his favourite reportedly being one which arrived from
Argentina and read: "Minoru, England. Congratulations from your father– Cyllene."
Minoru followed up his win at Epsom by running in the
St. James's Palace Stakes over one mile at
Royal Ascot, in which he started at odds of 1/3 and won from The Story and Blankney II.
Minoru was then sent to
Goodwood on 29 July for the
Sussex Stakes, another one mile race which at that time was restricted to three-year-olds. Minoru carried 134 pounds and won very easily from his two opponents, Prester Jack and Verney.
Autumn
On 8 September Minoru attempted to complete the
British Triple Crown in the
St Leger at
Doncaster. Bayardo had meanwhile won four successive races including an easy win over Louviers at
Sandown. Minoru started second favourite and finished fourth of the seven runners, six lengths behind Bayardo, who won from Valens and Mirador.
Minoru had little luck in running, being unable to obtain a clear run along the rails, but appeared to have been well beaten on merit.
Herbert Jones offered no excuses, and admitted that in view of Bayardo's superiority, Minoru had been "a lucky animal" to win the 2000 Guineas and Derby.
On his final start of the season, he was sent to Newmarket in October for the Free Handicap, in which he defeated the filly Electra, the winner of the
1000 Guineas and
Epsom Oaks, by a neck. As Jones had been injured the previous day,
Minoru was ridden on this occasion by
Danny Maher, who was presented by the King with a jewelled
scarf-pin in recognition of his success.
Minoru's performances in 1909 was the key factor in his sire Cyllene being the 1909
Leading sire in Great Britain & Ireland. His prize money of £15,246 placed him second to Bayardo on the list of leading British money-winners.
1910: four-year-old season
Minoru was kept in training as a four-year-old with the
Ascot Gold Cup as his principal target,
but began to develop problems with his eyes. He made his debut in the City and Suburban Handicap at Epsom on 26 April and started 3/1 favourite, but finished seventh of the fourteen runners behind
Bachelor's Double.
Shortly after Minoru's disappointing run at Epsom the King died and the ownership of the colt was returned to Colonel Hall-Walker.
The King's death resulted in the cancellation of all sporting events, including a meeting at
Kempton Park Racecourse, where Minoru had been entered in the Jubilee Stakes.
The decision was made not to persevere with the horse and he was retired to stud.
Assessment
When a new racecourse was opened on
Lulu Island,
Richmond, British Columbia in 1909 it was named "Minoru Park" in honour of the Derby winner. The track was later renamed Brighouse Park and closed in 1941,
although the name lives on in playing fields and an ice rink on the site under the name of "Minoru Park".
In their book A Century of Champions, Tony Morris and John Randall rated Minoru an average winner of the 2000 Guineas and an inferior winner of the Derby.
Stud record
Minoru stood as a stallion at Hall-Walker's Tully Stud in
County Kildare, Ireland at an initial fee of 98 guineas., Minoru produced the excellent
broodmare Serenissima before being sold in 1913 to a breeding operation in
Russia. Serenissima's foals included:
Minoru disappeared during the turmoil of the 1917
Russian Revolution along with his racecourse rival Louviers and the 1913 Derby winner
Aboyeur. Although there was speculation that he survived after being smuggled to Serbia, no trace of him was ever actually found.