-
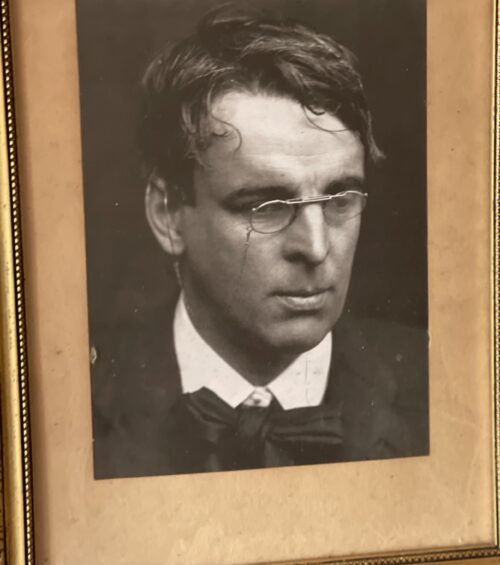
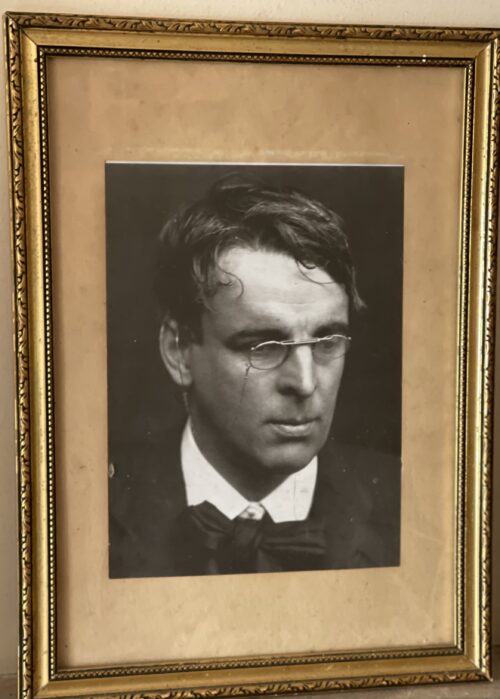
 40cm x 30cm Enniscrone Co Sligo William Butler Yeats(13 June 1865 – 28 January 1939) Irish poet, dramatist, prose writer and one of the foremost figures of 20th-century literature. A pillar of the Irish literary establishment, he helped to found the Abbey Theatre, and in his later years served two terms as a Senator of the Irish Free State. He was a driving force behind the Irish Literary Revival along with Lady Gregory, Edward Martyn and others. Yeats was born in Sandymount, Ireland, and educated there and in London. He was a Protestant and member of the Anglo-Irish community. He spent childhood holidays in County Sligo and studied poetry from an early age, when he became fascinated by Irish legends and the occult. These topics feature in the first phase of his work, which lasted roughly until the turn of the 20th century. His earliest volume of verse was published in 1889, and its slow-paced and lyrical poems display debts to Edmund Spenser, Percy Bysshe Shelley, and the poets of the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood. From 1900, his poetry grew more physical and realistic. He largely renounced the transcendental beliefs of his youth, though he remained preoccupied with physical and spiritual masks, as well as with cyclical theories of life. In 1923, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature.
40cm x 30cm Enniscrone Co Sligo William Butler Yeats(13 June 1865 – 28 January 1939) Irish poet, dramatist, prose writer and one of the foremost figures of 20th-century literature. A pillar of the Irish literary establishment, he helped to found the Abbey Theatre, and in his later years served two terms as a Senator of the Irish Free State. He was a driving force behind the Irish Literary Revival along with Lady Gregory, Edward Martyn and others. Yeats was born in Sandymount, Ireland, and educated there and in London. He was a Protestant and member of the Anglo-Irish community. He spent childhood holidays in County Sligo and studied poetry from an early age, when he became fascinated by Irish legends and the occult. These topics feature in the first phase of his work, which lasted roughly until the turn of the 20th century. His earliest volume of verse was published in 1889, and its slow-paced and lyrical poems display debts to Edmund Spenser, Percy Bysshe Shelley, and the poets of the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood. From 1900, his poetry grew more physical and realistic. He largely renounced the transcendental beliefs of his youth, though he remained preoccupied with physical and spiritual masks, as well as with cyclical theories of life. In 1923, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature. -
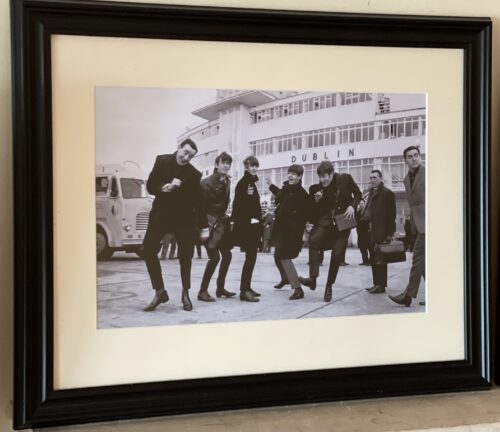
 Framed photo of an iconic moment as the Beatles arrive in Dublin,pistured outside the old Dublin Airport Terminal in 47cm x 60cm Dublin
Framed photo of an iconic moment as the Beatles arrive in Dublin,pistured outside the old Dublin Airport Terminal in 47cm x 60cm DublinNovember 7, 1963, one of the wildest phenomenons of the 20th century hit Dublin.... a Liverpudlian revolution named The Beatles!
All these years later, according to The Irish Times, a plaque will be placed at the site of the event, the Adelphi Cinema on Middle Abbey Street in Dublin. The tribute honors a world-changing British rock and roll group who the columnist Quidnunc in the Times described as “four hairy youngsters. [They] appeared onstage to be greeted with shrieks and whistles. Three of them walloped electric guitars which appeared to be amplified to the decibel limit, the fourth walloped a set of drums. “They all opened their mouths and made noises that sounded to me like: ‘Mew; Me-oh, me-ooh, me-ooh-ooh!’” The Beatles had come to town for two sold-out shows at the Adelphi. Ireland would never be quite the same again Fifteen days later JFK would be assassinated. The old innocent age drew to a close. The newspapers all reported on a strange phenomenon called Beatlemania. “It’s happening everywhere,” declared the Daily Mirrorworriedly. What was significant was that it was young girls who were screaming their heads off, crying, scratching to get near and touch the Beatles. Female sexuality was a completely new phenomenon in Holy Catholic Ireland, and their honors the bishops were not long in weighing in What happened in Dublin was a riot. The 3,000 pumped up crowd for the first show came streaming out only to run full tilt into the 3,000-second show patrons. Neither crowd gave way, and pushing and shoving ensued. Then it turned nasty. A commotion described as a riot took place. The Times lead ran"“Many arrested as city crowds run riot.”“Cars were overturned in Abbey Street and O’Connell Street, at least 50 people were treated for minor injuries, while three people were taken to hospital with fractured legs and arms.”
A young man was also hospitalized after being stabbed. Two hundred police and three fire brigades arrived. Buses and taxis were halted in the melee. Only the ringing of the fire bells seemed to settle down the crowd, but soon more crowds arrived and fights began anew. “One group of youths pushed a parked car into half a dozen policemen who were trying to get them out of the street,” reported the Times. “St John’s Ambulance men treated men and women on the footpaths while the crowds swirled around them.”The Beatles did not hang around. John, Paul, George, and Ringo escaped in a newspaper van to the nearby Gresham Hotel. Later, two of them went to Drumcondra to see relatives, the Times reported. The Times’ reviewer at the gig could hear nothing but the sound of “ecstatic, joyful, hysteric, demented” screams from Dublin teenagers. He wrote:“A pity, this, because the Beatles, in spite of their theatrical gimmicks, their long locks, and ‘with-it’ suits, have a great act…God knows, Dublin has never seen anything like the Beatles.”
Indeed they had not. Nor would they ever see their likes again. Despite their multiple Irish connections, the four lads would never be back, and more’s the pity. -
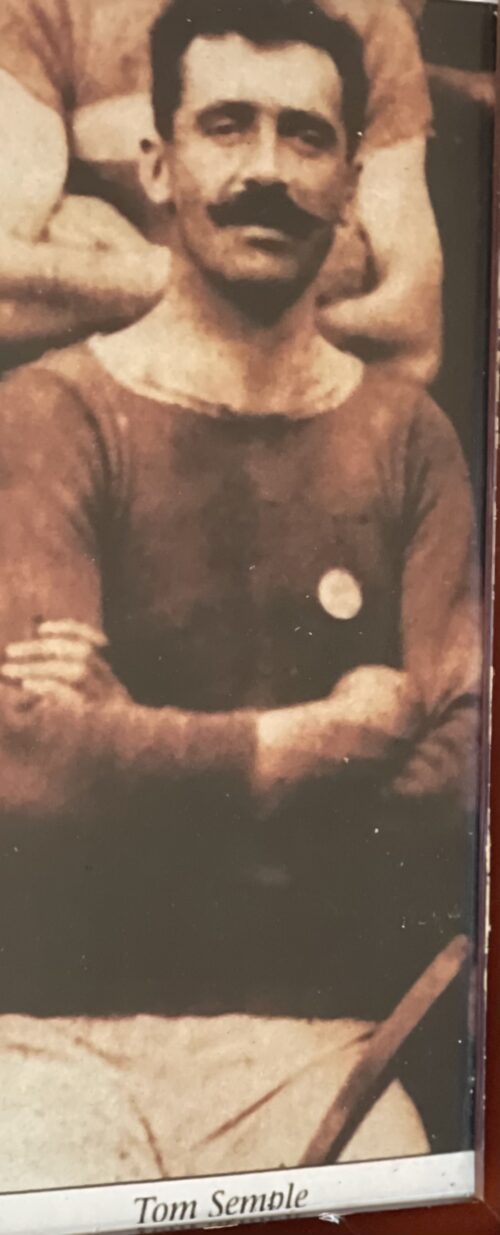

 Great portrait of Tipperary Hurling Legend Tom Semple of Thurles 47cm x 24cm Thurles Co Tipperary Thomas Semple (8 April 1879 – 11 April 1943) was an Irish hurler who played as a half-forward for the Tipperary senior team. Semple joined the panel during the 1897 championship and eventually became a regular member of the starting seventeen until his retirement after the 1909 championship. During that time he won three All-Ireland medals and four Munster medals. An All-Ireland runner-up on one occasion, Semple captained the team to the All-Ireland title in 1906 and in 1908. At club level Semple was a six-time county club championship medalist with Thurles. Semple played his club hurling with the local club in Thurles, the precursor to the famous Sarsfield's club. He rose through the club and served as captain of the team for almost a decade. In 1904 Semple won his first championship medal following a walkover from Lahorna De Wets. Thurles failed to retain their title, however, the team returned to the championship decider once again in 1906. A 4-11 to 3-6 defeat of Lahorna De Wets gave Semple his second championship medal as captain. It was the first of four successive championships for Thurles as subsequent defeats of Lahorna De Wets, Glengoole and Racecourse/Grangemockler brought Semple's medal tally to five. Five-in-a-row proved beyond Thurles, however, Semple's team reached the final for the sixth time in eight seasons in 1911. A 4-5 to 1-0 trouncing of Toomevara gave Semple his sixth and final championship medal as captain.
Great portrait of Tipperary Hurling Legend Tom Semple of Thurles 47cm x 24cm Thurles Co Tipperary Thomas Semple (8 April 1879 – 11 April 1943) was an Irish hurler who played as a half-forward for the Tipperary senior team. Semple joined the panel during the 1897 championship and eventually became a regular member of the starting seventeen until his retirement after the 1909 championship. During that time he won three All-Ireland medals and four Munster medals. An All-Ireland runner-up on one occasion, Semple captained the team to the All-Ireland title in 1906 and in 1908. At club level Semple was a six-time county club championship medalist with Thurles. Semple played his club hurling with the local club in Thurles, the precursor to the famous Sarsfield's club. He rose through the club and served as captain of the team for almost a decade. In 1904 Semple won his first championship medal following a walkover from Lahorna De Wets. Thurles failed to retain their title, however, the team returned to the championship decider once again in 1906. A 4-11 to 3-6 defeat of Lahorna De Wets gave Semple his second championship medal as captain. It was the first of four successive championships for Thurles as subsequent defeats of Lahorna De Wets, Glengoole and Racecourse/Grangemockler brought Semple's medal tally to five. Five-in-a-row proved beyond Thurles, however, Semple's team reached the final for the sixth time in eight seasons in 1911. A 4-5 to 1-0 trouncing of Toomevara gave Semple his sixth and final championship medal as captain.Inter-county
Semple's skill quickly brought him to the attention of the Tipperary senior hurling selectors. After briefly joining the team in 1897, he had to wait until 1900 to become a regular member of the starting seventeen. That year a 6-11 to 1-9 trouncing of Kerry gave him his first Munster medal.Tipp later narrowly defeated Kilkenny in the All-Ireland semi-final before trouncing Galway in the "home" All-Ireland final. This was not the end of the championship campaign because, for the first year ever, the "home" finalists had to take on London in the All-Ireland decider. The game was a close affair with both sides level at five points with eight minutes to go. London then took the lead; however, they later conceded a free. Tipp's Mikey Maher stepped up, took the free and a forward charge carried the sliotar over the line. Tipp scored another goal following a weak puck out and claimed a 2-5 to 0-6 victory.It was Semple's first All-Ireland medal. Cork dominated the provincial championship for the next five years; however, Tipp bounced back in 1906. That year Semple was captain for the first time as Tipp foiled Cork's bid for an unprecedented sixth Munster title in-a-row. The score line of 3-4 to 0-9 gave Semple a second Munster medal. Tipp trounced Galway by 7-14 to 0-2 on their next outing, setting up an All-Ireland final meeting with Dublin. Semple's side got off to a bad start with Dublin's Bill Leonard scoring a goal after just five seconds of play. Tipp fought back with Paddy Riordan giving an exceptional display of hurling and capturing most of his team's scores. Ironically, eleven members of the Dublin team hailed from Tipperary. The final score of 3-16 to 3-8 gave victory to Tipperary and gave Semple a second All-Ireland medal. Tipp lost their provincial crown in 1907, however, they reached the Munster final again in 1908. Semple was captain of the side again that year as his team received a walkover from Kerry in the provincial decider. Another defeat of Galway in the penultimate game set up another All-Ireland final meeting with Dublin. That game ended in a 2-5 to 1-8 draw and a replay was staged several months later in Athy. Semple's team were much sharper on that occasion. A first-half goal by Hugh Shelly put Tipp well on their way. Two more goals by Tony Carew after the interval gave Tipp a 3-15 to 1-5 victory.It was Semple's third All-Ireland medal. 1909 saw Tipp defeat arch rivals Cork in the Munster final once again. A 2-10 to 1-6 victory gave Semple his fourth Munster medal. The subsequent All-Ireland final saw Tipp take on Kilkenny. The omens looked good for a Tipperary win. It was the county's ninth appearance in the championship decider and they had won the previous eight. All did not go to plan as this Kilkenny side cemented their reputation as the team of the decade. A 4-6 to 0-12 defeat gave victory to "the Cats" and a first final defeat to Tipperary. Semple retired from inter-county hurling following this defeat. Semple was born in Drombane, County Tipperary in 1879. He received a limited education at his local national school and, like many of his contemporaries, finding work was a difficult prospect. At the age of 16 Semple left his native area and moved to Thurles. Here he worked as a guardsman with the Great Southern & Western Railway. In retirement from playing Semple maintained a keen interest in Gaelic games. In 1910 he and others organised a committee which purchased the showgrounds in Thurles in an effort to develop a hurling playing field there. This later became known as Thurles Sportsfield and is regarded as one of the best surfaces for hurling in Ireland. In 1971 it was renamed Semple Stadium in his honour. The stadium is also lovingly referred to as Tom Semple's field. Semple also held the post of chairman of the Tipperary County Board and represented the Tipperary on the Munster Council and Central Council. He also served as treasurer of the latter organization. During the War of Independence Semple played an important role for Republicans. He organized dispatches via his position with the Great Southern & Western Railway in Thurles. Tom Semple died on 11 April 1943 Tipperary Hurling Team outside Clonmel railway station, August 26, 1910. Semple is in the centre of the middle row.
Tipperary Hurling Team outside Clonmel railway station, August 26, 1910. Semple is in the centre of the middle row. -
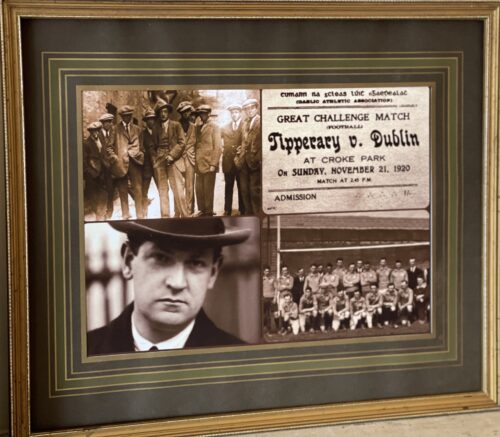
 35cm x 50cm Limerick
35cm x 50cm Limerickloody Sunday, 21st November 1920
In 1920 the War of Independence was ongoing in Ireland.
On the morning of November 21st, an elite assassination unit known as ‘The Squad’ mounted an operation planned by Michael Collins, Director of Intelligence of the Irish Republican Army (IRA). Their orders were clear – they were to take out the backbone of the British Intelligence network in Ireland, specifically a group of officers known as ‘The Cairo Gang’. The shootings took place in and around Dublin’s south inner city and resulted in fourteen deaths, including six intelligence agents and two members of the British Auxiliary Force. Later that afternoon, Dublin were scheduled to play Tipperary in a one-off challenge match at Croke Park, the proceeds of which were in aid of the Republican Prisoners Dependents Fund. Tensions were high in Dublin due to fears of a reprisal by Crown forces following the assassinations. Despite this a crowd of almost 10,000 gathered in Croke Park. Throw-in was scheduled for 2.45pm, but it did not start until 3.15pm as crowd congestion caused a delay.Eye-witness accounts suggest that five minutes after the throw-in an aeroplane flew over Croke Park. It circled the ground twice and shot a red flare - a signal to a mixed force of Royal Irish Constabulary (R.I.C.), Auxiliary Police and Military who then stormed into Croke Park and opened fire on the crowd. Amongst the spectators, there was a rush to all four exits, but the army stopped people from leaving the ground and this created a series of crushes around the stadium. Along the Cusack Stand side, hundreds of people braved the twenty-foot drop and jumped into the adjacent Belvedere Sports Grounds. The shooting lasted for less than two minutes. That afternoon in Croke Park, 14 people including one player (Michael Hogan from Tipperary), lost their lives. It is estimated that 60 – 100 people were injured.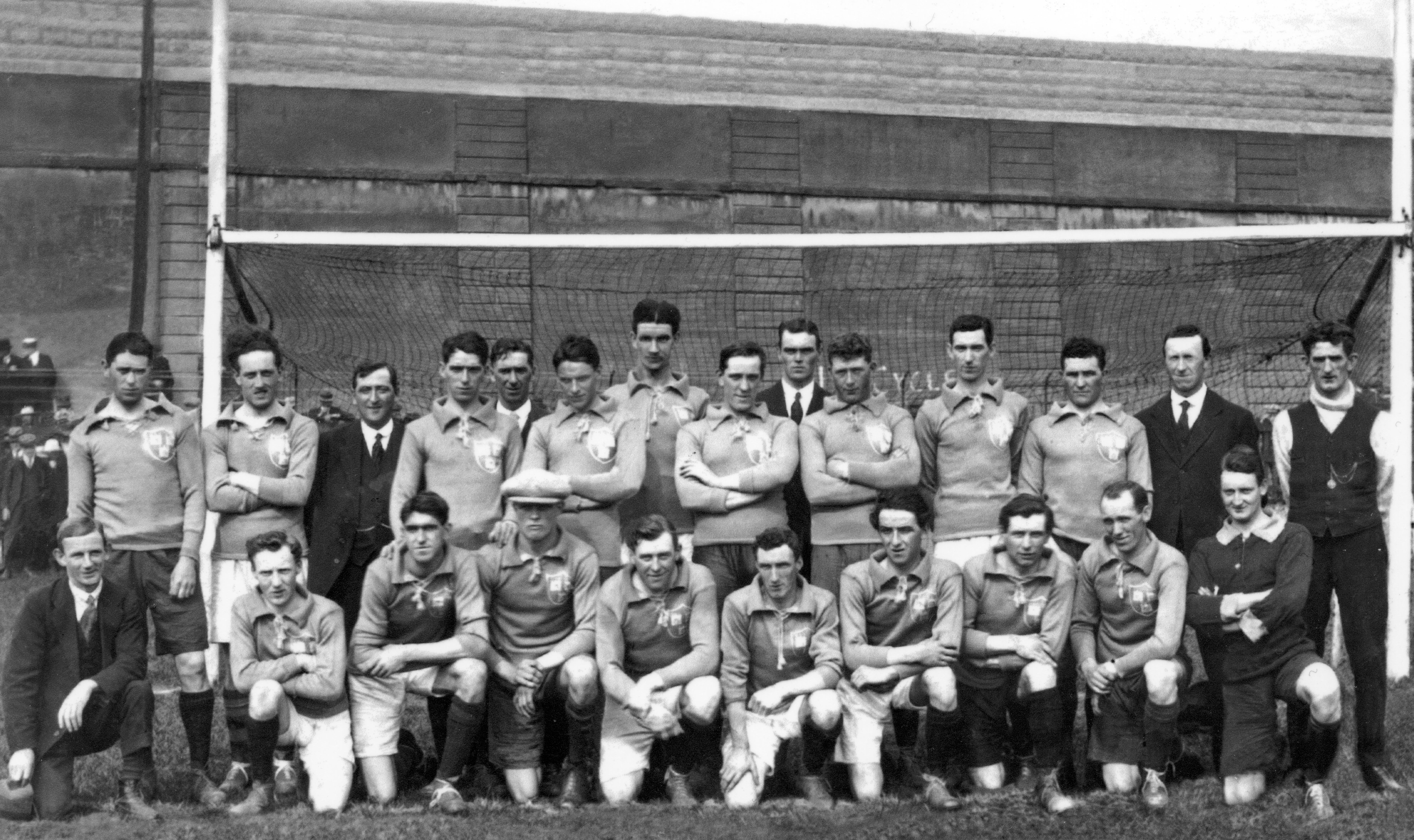 Dublin Team, Bloody Sunday 1920The names of those who died in Croke Park on Bloody Sunday 1920 were. James Burke, Jane Boyle, Daniel Carroll, Michael Feery, Michael Hogan, Thomas (Tom) Hogan, James Matthews, Patrick O’Dowd, Jerome O’Leary, William (Perry) Robinson, Tom Ryan, John William (Billy) Scott, James Teehan, Joseph Traynor. In 1925, the GAA's Central Council took the decision to name a stand in Croke Park after Michael Hogan. The 21st November 2020 marks one hundred years since the events of Bloody Sunday in Croke Park.
Dublin Team, Bloody Sunday 1920The names of those who died in Croke Park on Bloody Sunday 1920 were. James Burke, Jane Boyle, Daniel Carroll, Michael Feery, Michael Hogan, Thomas (Tom) Hogan, James Matthews, Patrick O’Dowd, Jerome O’Leary, William (Perry) Robinson, Tom Ryan, John William (Billy) Scott, James Teehan, Joseph Traynor. In 1925, the GAA's Central Council took the decision to name a stand in Croke Park after Michael Hogan. The 21st November 2020 marks one hundred years since the events of Bloody Sunday in Croke Park. Tipperary Team, Bloody Sunday 1920
Tipperary Team, Bloody Sunday 1920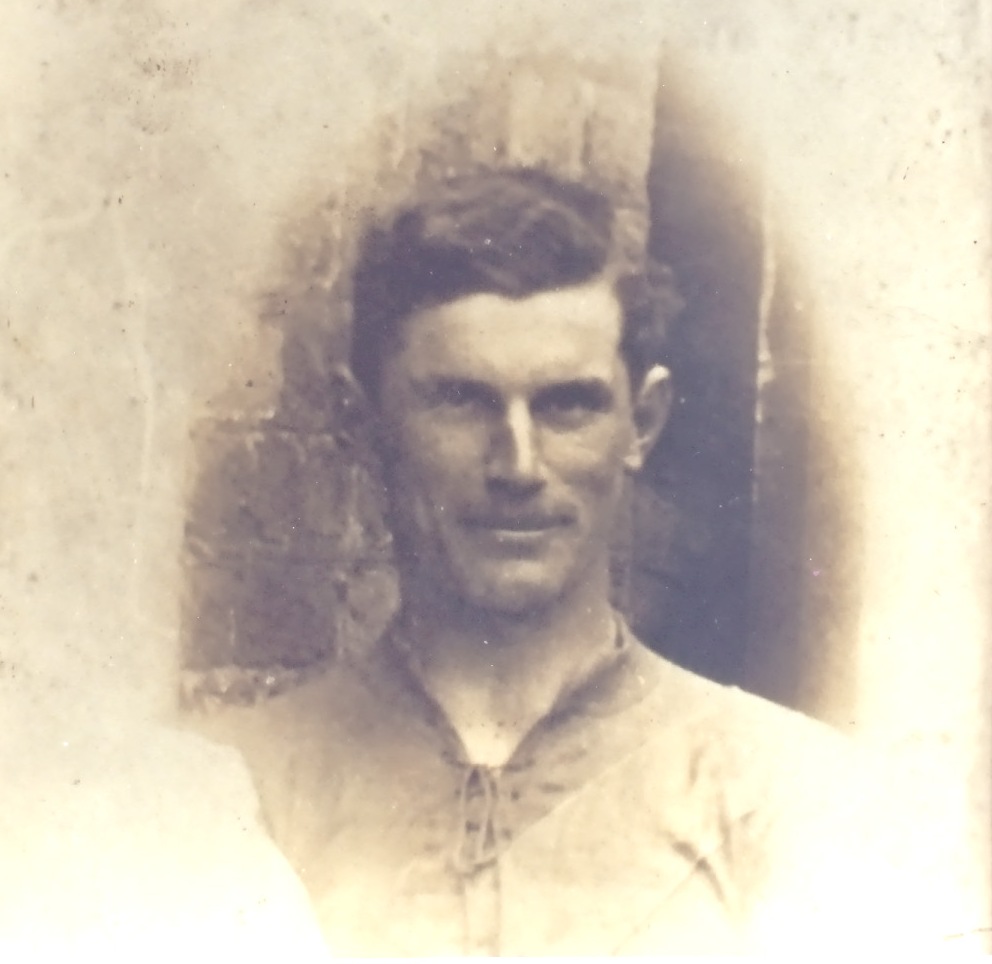 Michael Hogan
Michael Hogan -
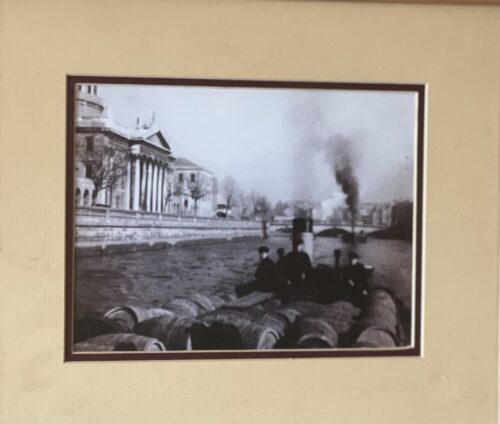
 Beautifully mounted & framed 30cm x 30cm Dublin Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.” Origins : Dublin Dimensions : 43cm x 35cm
Beautifully mounted & framed 30cm x 30cm Dublin Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.” Origins : Dublin Dimensions : 43cm x 35cm -

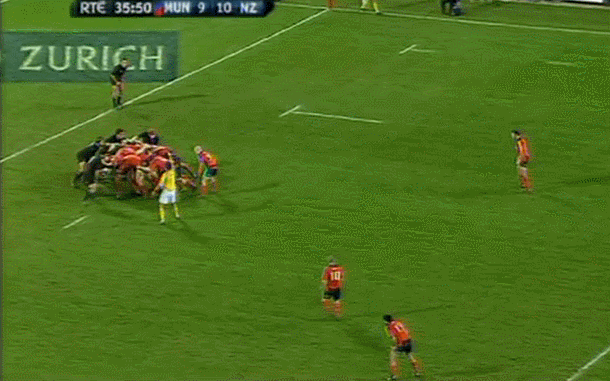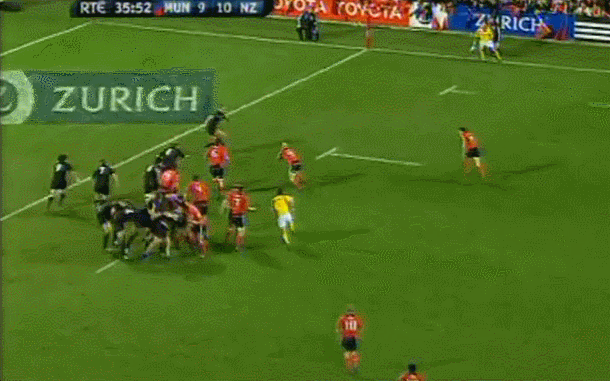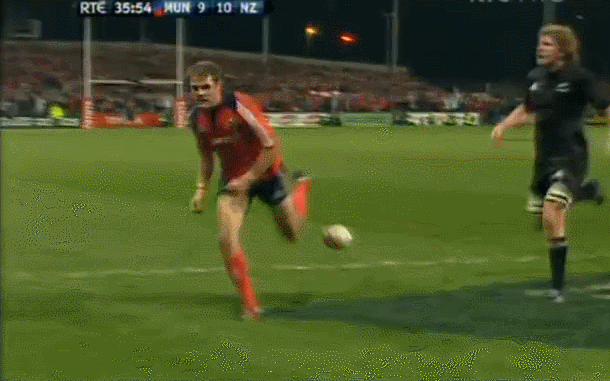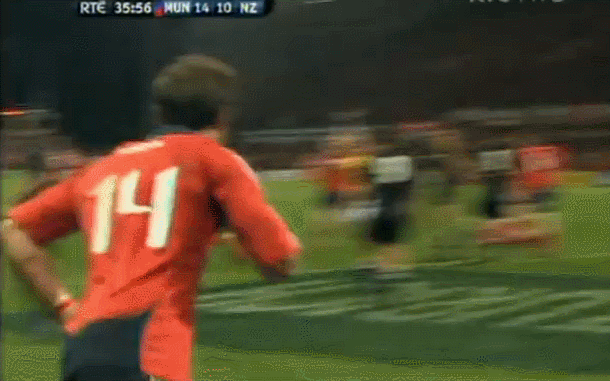
 Fantastic framed photo of the famous Munster Haka performed by the New Zealand contingent wearing red- Doug Howlett,Lifemi Mafi,Jeremy Manning & Rua Tipoki. Limerick 45cm x60cm WHAT DO YOU remember most about this game? 12 years have passed now but what sticks out is how low-key the build-up was until the moment of the famous response to the haka from Munster’s New Zealand contingent. Low-key in the sense that not a whole lot was expected from the game itself. The occasion was always going to be a bit of crack with all the players from the epic day in ’78 being wheeled out to give interviews about the time they slayed the giant from the land of the long white cloud. But after all the clips and interviews with Seamus Dennison and Tony Ward were over, was anyone seriously expecting a proper contest from the game? Sure, it was an All Blacks ‘B’ side (although at the time, their second-string consisted of Cory Jane, Liam Messam, Kieran Read and Hosea Gear) but it was also a weakened Munster team, with Denis Leamy the only first choice forward available due to international commitments. The state of the two line-ups meant that two of rugby’s most well-worn clichés were put head-to-head: ‘There is no such thing as an All Blacks B team’ vs ‘you can never count out Munster’. Given what followed, you would probably say it was a push. The first sense that the game might channel the spirit of ’78 rather than just pay tribute to it was obviously during the haka. This would have been the perfect sporting moment if you could have erased Jeremy Manning’s Village People moustache out of there. The Thomond Park crowd rarely needs any encouragement but the ground was heaving after that introduction. Then the game started and the untested members of the Munster pack were the most tigerish. James Coughlan was basically a 28-year-old club player at the time but his ferocious display of carrying earned him a proper professional career. Donnacha Ryan exploded out of POC and DOC’s shadow with an commanding performance and Munster were clinical early on. It helped that out-half Paul Warwick was in the form of his life. These monster drop goals were a regular sight during that 2008-09 season. The All Blacks hit back with a try from Stephen ‘Beaver’ Donald but right on half time, Munster took a six point lead after this Barry Murphy try. This was one of those classic moments during an upset when you turn to a mate, nod vigorously and say ‘It’s on now' Half time came a moment later and with it, this nice gesture from Cory Jane. For most Irish fans, this was the first time they had seen Jane in action and this moment, coupled with his strong attacking performance marked him as one of the good guys. I can’t speak for anyone else, but the only thing I remember about the second half is Joe Rokocoko’s try – probably because Munster didn’t score in the second 40. Munster held out for 76 minutes until Rokocoko got the ball directly against his old teammate Doug Howlett. Should Howlett have made the tackle? It is hard to stop Smokin’ Joe when he plants that foot. And that was it. There was no heroic win. Unknown players like prop Timmy Ryan didn’t get to join the heroes of ’78 as regulars on the after-dinner speech circuit. What made this such a memorable occasion was how unexpected it was. It was played on a Tuesday, sandwiched between two other November Tests and although the pageantry was always going to be good fun, the fact that it exploded into life in the way it did makes it one of the most exciting games in the history of Irish rugby. It’s been six years now, but the memory of ‘It’s on’ is one that will never go away. Munster: Howlett; B Murphy, Tipoki, Mafi, Dowling; Warwick, Stringer; Pucciariello, Sheahan, Ryan; M O’Driscoll (capt), Ryan; Coughlan, Ronan, Leamy. Replacements: Buckley for Ryan 40, Fogarty for Sheahan 63, Holland for Leamy 24, Manning for Tipoki 52. Not used: Melbourne, O’Sullivan, Prendergast New Zealand: Jane; H Gear, Tuitavake, Toeava, Rokocoko; Donald, Weepu (capt); Mackintosh, Flynn, Franks, Filipo, Eaton, Thomson, Waldrom, Messam. Replacements: Elliott for Flynn 65, Afoa for Franks 70, B Thorn for Filipo 71, Read for Thomson 60, Mathewson for Weepu 63, Muliaina for Tuitavake 71. Not used: Kahui,
Fantastic framed photo of the famous Munster Haka performed by the New Zealand contingent wearing red- Doug Howlett,Lifemi Mafi,Jeremy Manning & Rua Tipoki. Limerick 45cm x60cm WHAT DO YOU remember most about this game? 12 years have passed now but what sticks out is how low-key the build-up was until the moment of the famous response to the haka from Munster’s New Zealand contingent. Low-key in the sense that not a whole lot was expected from the game itself. The occasion was always going to be a bit of crack with all the players from the epic day in ’78 being wheeled out to give interviews about the time they slayed the giant from the land of the long white cloud. But after all the clips and interviews with Seamus Dennison and Tony Ward were over, was anyone seriously expecting a proper contest from the game? Sure, it was an All Blacks ‘B’ side (although at the time, their second-string consisted of Cory Jane, Liam Messam, Kieran Read and Hosea Gear) but it was also a weakened Munster team, with Denis Leamy the only first choice forward available due to international commitments. The state of the two line-ups meant that two of rugby’s most well-worn clichés were put head-to-head: ‘There is no such thing as an All Blacks B team’ vs ‘you can never count out Munster’. Given what followed, you would probably say it was a push. The first sense that the game might channel the spirit of ’78 rather than just pay tribute to it was obviously during the haka. This would have been the perfect sporting moment if you could have erased Jeremy Manning’s Village People moustache out of there. The Thomond Park crowd rarely needs any encouragement but the ground was heaving after that introduction. Then the game started and the untested members of the Munster pack were the most tigerish. James Coughlan was basically a 28-year-old club player at the time but his ferocious display of carrying earned him a proper professional career. Donnacha Ryan exploded out of POC and DOC’s shadow with an commanding performance and Munster were clinical early on. It helped that out-half Paul Warwick was in the form of his life. These monster drop goals were a regular sight during that 2008-09 season. The All Blacks hit back with a try from Stephen ‘Beaver’ Donald but right on half time, Munster took a six point lead after this Barry Murphy try. This was one of those classic moments during an upset when you turn to a mate, nod vigorously and say ‘It’s on now' Half time came a moment later and with it, this nice gesture from Cory Jane. For most Irish fans, this was the first time they had seen Jane in action and this moment, coupled with his strong attacking performance marked him as one of the good guys. I can’t speak for anyone else, but the only thing I remember about the second half is Joe Rokocoko’s try – probably because Munster didn’t score in the second 40. Munster held out for 76 minutes until Rokocoko got the ball directly against his old teammate Doug Howlett. Should Howlett have made the tackle? It is hard to stop Smokin’ Joe when he plants that foot. And that was it. There was no heroic win. Unknown players like prop Timmy Ryan didn’t get to join the heroes of ’78 as regulars on the after-dinner speech circuit. What made this such a memorable occasion was how unexpected it was. It was played on a Tuesday, sandwiched between two other November Tests and although the pageantry was always going to be good fun, the fact that it exploded into life in the way it did makes it one of the most exciting games in the history of Irish rugby. It’s been six years now, but the memory of ‘It’s on’ is one that will never go away. Munster: Howlett; B Murphy, Tipoki, Mafi, Dowling; Warwick, Stringer; Pucciariello, Sheahan, Ryan; M O’Driscoll (capt), Ryan; Coughlan, Ronan, Leamy. Replacements: Buckley for Ryan 40, Fogarty for Sheahan 63, Holland for Leamy 24, Manning for Tipoki 52. Not used: Melbourne, O’Sullivan, Prendergast New Zealand: Jane; H Gear, Tuitavake, Toeava, Rokocoko; Donald, Weepu (capt); Mackintosh, Flynn, Franks, Filipo, Eaton, Thomson, Waldrom, Messam. Replacements: Elliott for Flynn 65, Afoa for Franks 70, B Thorn for Filipo 71, Read for Thomson 60, Mathewson for Weepu 63, Muliaina for Tuitavake 71. Not used: Kahui, -
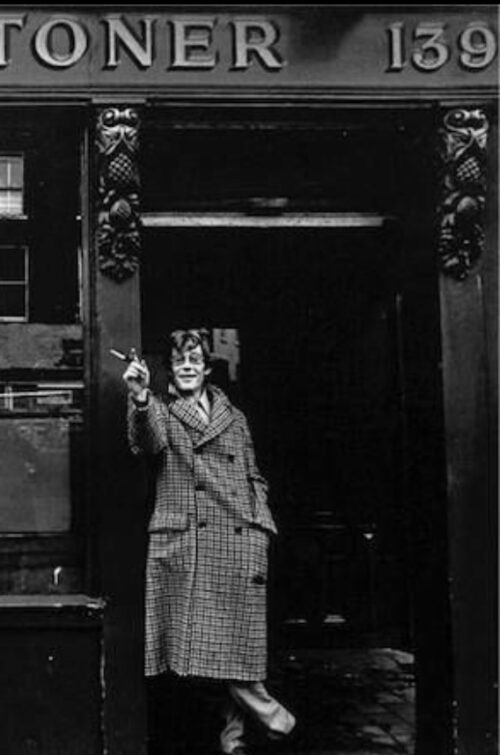

 45cm x 35cm. Dublin Iconic b&w photograph of legendary Actor & Bon Viveur Peter O'Toole outside one of his favourite Dublin Watering Hole's-Toners of Baggott Street. Peter Seamus O'Toole ( 2 August 1932 – 14 December 2013) was a British stage and film actor of Irish descent. He attended the Royal Academy of Dramatic Art and began working in the theatre, gaining recognition as a Shakespearean actor at the Bristol Old Vic and with the English Stage Company. In 1959 he made his West End debut in The Long and the Short and the Tall, and played the title role in Hamlet in the National Theatre’s first production in 1963. Excelling on the London stage, O'Toole was known as a "hellraiser" off it. Making his film debut in 1959, O'Toole achieved international recognition playing T. E. Lawrence in Lawrence of Arabia (1962) for which he received his first nomination for the Academy Award for Best Actor. He was nominated for this award another seven times – for playing King Henry II in both Becket (1964) and The Lion in Winter (1968), Goodbye, Mr. Chips (1969), The Ruling Class (1972), The Stunt Man (1980), My Favorite Year (1982), and Venus (2006) – and holds the record for the most Academy Award nominations for acting without a win. In 2002, O'Toole was awarded the Academy Honorary Award for his career achievements. He was additionally the recipient of four Golden Globe Awards, one BAFTA Award for Best British Actor and one Primetime Emmy Award. Brought up in Leeds, England in a Yorkshire Irish family, O'Toole has appeared on lists of greatest actors from publications in England and Ireland. In 2020, he was listed at number 4 on The Irish Times list of Ireland's greatest film actors. Situated on Baggot Street, Toners is one of Dublin’s oldest and most famous traditional pubs. To prove this, we were the overall winners of “Best Traditional Pub” in the National Hospitality Awards 2014. In September 2015 we also won Dublin Bar of the Year at the Sky Bar of the Year Awards. Original features in the pub take visitors back in time, including the old stock drawers behind the bar from when Toners first opened in 1818 as a bar and grocery shop. The interior details like the glazed cabinets filled with curio, elaborate mirrors, the brass bar taps and flagstone floors to mention a few, makes you feel like you are stepping in to a museum… A museum in which you can drink in! Frequented by many of Ireland’s literary greats, including Patrick Kavanagh, the pub was also a favourite spot of W.B. Yeats and the snug is said to be the only place he would drink when he took an occasional tipple.
45cm x 35cm. Dublin Iconic b&w photograph of legendary Actor & Bon Viveur Peter O'Toole outside one of his favourite Dublin Watering Hole's-Toners of Baggott Street. Peter Seamus O'Toole ( 2 August 1932 – 14 December 2013) was a British stage and film actor of Irish descent. He attended the Royal Academy of Dramatic Art and began working in the theatre, gaining recognition as a Shakespearean actor at the Bristol Old Vic and with the English Stage Company. In 1959 he made his West End debut in The Long and the Short and the Tall, and played the title role in Hamlet in the National Theatre’s first production in 1963. Excelling on the London stage, O'Toole was known as a "hellraiser" off it. Making his film debut in 1959, O'Toole achieved international recognition playing T. E. Lawrence in Lawrence of Arabia (1962) for which he received his first nomination for the Academy Award for Best Actor. He was nominated for this award another seven times – for playing King Henry II in both Becket (1964) and The Lion in Winter (1968), Goodbye, Mr. Chips (1969), The Ruling Class (1972), The Stunt Man (1980), My Favorite Year (1982), and Venus (2006) – and holds the record for the most Academy Award nominations for acting without a win. In 2002, O'Toole was awarded the Academy Honorary Award for his career achievements. He was additionally the recipient of four Golden Globe Awards, one BAFTA Award for Best British Actor and one Primetime Emmy Award. Brought up in Leeds, England in a Yorkshire Irish family, O'Toole has appeared on lists of greatest actors from publications in England and Ireland. In 2020, he was listed at number 4 on The Irish Times list of Ireland's greatest film actors. Situated on Baggot Street, Toners is one of Dublin’s oldest and most famous traditional pubs. To prove this, we were the overall winners of “Best Traditional Pub” in the National Hospitality Awards 2014. In September 2015 we also won Dublin Bar of the Year at the Sky Bar of the Year Awards. Original features in the pub take visitors back in time, including the old stock drawers behind the bar from when Toners first opened in 1818 as a bar and grocery shop. The interior details like the glazed cabinets filled with curio, elaborate mirrors, the brass bar taps and flagstone floors to mention a few, makes you feel like you are stepping in to a museum… A museum in which you can drink in! Frequented by many of Ireland’s literary greats, including Patrick Kavanagh, the pub was also a favourite spot of W.B. Yeats and the snug is said to be the only place he would drink when he took an occasional tipple.History of Toners Pub
- Acquired first License by Andrew Rogers 1818 – 1859.
- William F. Drought 1859 – 1883, Grocer, Tea, Wine & Spirit Merchant
- John O’Neill 1883 – 1904, Tea, Wine & Spirit Merchant
- James M Grant 1904 – 1923, Grocer, Tea, Wine & Spirit Merchant
- James Toner 1923 – 1970, Grocer, Tea, Wine & Spirit Merchant
- Joe Colgan Solicitor 1970 – 1976
- Ned & Patricia Dunne & Partner Tom Murphy 1976 – 1987
- Frank & Michael Quinn 1987 – Present
Snug of the Year 2010
 Toners won “Snug of the Year” 2010, a competition hosted by Powers Whiskey. 110 pubs across Ireland were shortlisted, and after counting the public’s votes Toners was announced the winner. A snug is a private area separated within a pub and is a timeless feature in a traditional Irish pub. Like the one in Toners, it typically has its own door, a rugged bench and is completely private. Back in the day it was where the likes of policemen, lovers and the Irish literati met up.
Toners won “Snug of the Year” 2010, a competition hosted by Powers Whiskey. 110 pubs across Ireland were shortlisted, and after counting the public’s votes Toners was announced the winner. A snug is a private area separated within a pub and is a timeless feature in a traditional Irish pub. Like the one in Toners, it typically has its own door, a rugged bench and is completely private. Back in the day it was where the likes of policemen, lovers and the Irish literati met up.
Toners Yard
Since Toners opened its doors to the yard in 2012 it has been a very popular spot with both locals and tourists. The beer garden is ideal for sunny days as it gets the sun from morning until evening, and if it is a bit chillier the heaters will keep you warm.Mumford & Sons – Arthurs Day 2012 in Toners Yard
Arthurs Day, the annual celebration of all things Guinness, has been hugely successful since it launched in 2009. Diageo launched a “vote for your local” competition for Arthurs Day 2012. The public got a chance to vote and help bring a headline artist to their local pub. Toners, serving the best pint of Guinness in Dublin, got so much support from everyone and ended up being one of the winning pubs. The winning pubs were kept a secret until the night of Arthurs Day and to everyone’s delight, Mumford & Sons walked in to Toners Yard and played an amazing set. -
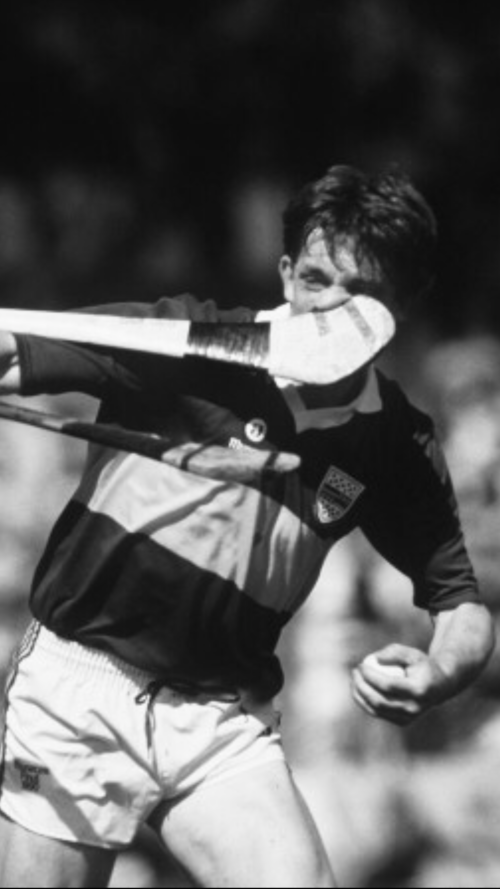

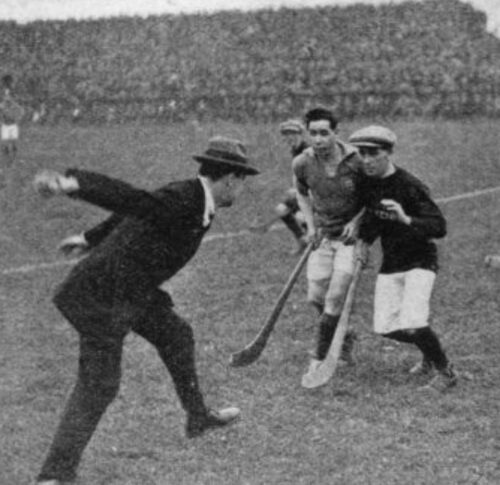
 45cm x 35cm. Thurles Co Tipperary Very interesting action shot of Denis Walsh of Cork getting very up close and personal with Nicky English of Tipperary during the 1990 Munster Final,in the era before the wearing of protective helmets became mandatory.
45cm x 35cm. Thurles Co Tipperary Very interesting action shot of Denis Walsh of Cork getting very up close and personal with Nicky English of Tipperary during the 1990 Munster Final,in the era before the wearing of protective helmets became mandatory. Canon Michael O’Brien had taken the managerial reigns while Cork’s 1966 All-Ireland winning captain Gerald McCarthy had taken over the coaching duties.In the pre-match build-up Tipperary’s coach Babs Keating had riled Cork supporters with his infamous quote, ‘You don’t win derbies with donkeys’. It was a statement that to this day he has lived to regret although it must be said that nobody has more respect for Cork hurling than Babs Keating has.
Canon Michael O’Brien had taken the managerial reigns while Cork’s 1966 All-Ireland winning captain Gerald McCarthy had taken over the coaching duties.In the pre-match build-up Tipperary’s coach Babs Keating had riled Cork supporters with his infamous quote, ‘You don’t win derbies with donkeys’. It was a statement that to this day he has lived to regret although it must be said that nobody has more respect for Cork hurling than Babs Keating has. Cork's Mark Foley scores on the stroke of half time against Tipperary in the 1990 Munster final at Semple Stadium. He banged in a brace of goals, rifled over seven points, all from play, he was simply unstoppable on that July afternoon in Semple Stadium.
Cork's Mark Foley scores on the stroke of half time against Tipperary in the 1990 Munster final at Semple Stadium. He banged in a brace of goals, rifled over seven points, all from play, he was simply unstoppable on that July afternoon in Semple Stadium.

-
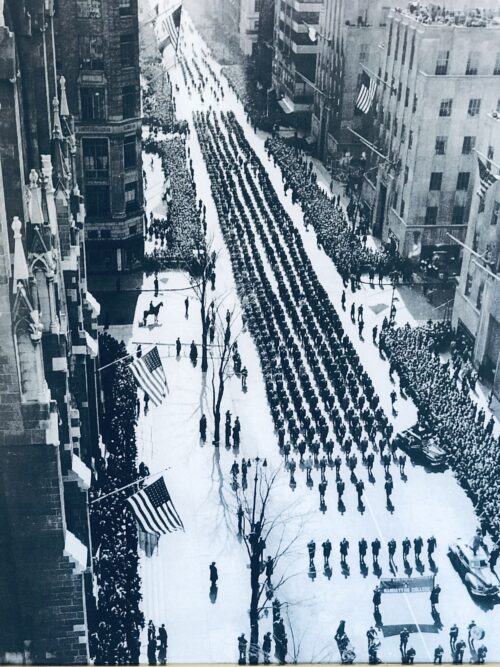

 36cm x 30cm New York Wonderful elevated shot of the 1950 New York St Patricks Day Parade from high above 5th Avenue as the procession passes St Patricks Cathedral. The St. Patrick’s Day Parade is one of New York City’s greatest traditions. On this day, everyone is Irish in the Big Apple! The Parade marched for the first time on March 17, 1762 – fourteen Years before the Declaration of Independence was adopted and today it is the largest Parade in the World. This annual parade has been held for the past 257 years in honor of the Patron Saint of Ireland and the Archdiocese of New York. The Parade is reviewed from the steps of Saint Patrick’s Cathedral by His Eminence, Timothy Cardinal Dolan, Archbishop of New York in the same manner as the Archbishop of New York did in the early days of the Parade at the Old St. Patrick’s Cathedral in Lower Manhattan before the new St Patrick’s was built on Fifth Avenue. Often regarded as the most popular parade in New York City, the Parade is the largest and most famous of the many parades held in the city each year. The Parade starts at 44th Street at 11 am and is held every March 17th except when March 17th falls on a Sunday; it is celebrated the day before, Saturday the 16th, because of religious observances. The parade marches up Fifth Avenue past St. Patrick’s Cathedral at 50th Street all the way up 79th Street, where the parade finishes around 4:30 – 5:00 pm To this day, the St. Patrick’s Day Parade remains true to its roots as a true marchers Parade by not allowing floats, automobiles and other commercial aspects in the Parade. Every year the Parade Committee hosts the 150,000- 250,000 marchers, along with many great bands; bagpipes, high school bands and the ever-present politicians in front of the approx 2 million spectators lining Fifth Avenue. The Parade is televised for four hours on WNBC Channel Four to over half a million households and was web streamed live for the first time in 2008. Today, the coverage has expanded to seven additional internet based platforms and can easily be viewed on mobile devices. The first St. Patrick’s Day Parade in New York was held on lower Broadway in 1762 by a band of homesick Irish ex-patriots and Irish military serving with the British Army stationed in the American colonies in New York City. This was a time when the wearing of green was a sign of Irish pride and was banned in Ireland. The parade participants reveled in the freedom to speak Irish, wear green, sing Irish songs and play the pipes to Irish tunes that were very meaningful to the Irish immigrants who had fled their homeland. For the first few years of its existence, the parade was organized by military units. After the war of 1812, the Irish fraternal and benevolent societies took over the duties of hosting and sponsoring the event. Originally, the Irish societies joined together at their respective meeting places and moved in a procession toward Old St. Patrick’s Cathedral in Lower Manhattan on Mott & Prince Streets where the Archbishop of New York would then address the crowd before revelers dispersed to celebrate. Around 1851 the individual societies merged under a single grand marshal and the size of the parade grew sharply. This was when the “Irish” 69th Regiment began to lead the marchers and the Ancient Order of Hibernians became the official sponsor. In the early 90’s, the Parade was attacked for its traditional values and in the resulting lawsuits the organizers rights were up held all the way to the US Supreme court. In 1992 the National AOH directed all AOH organizations to form separate corporations to run events such as the Parade. The Parade is run today by members of the AOH under a separate corporation, St Patrick’s Day Parade Inc. Since the first Parade, 257 years ago, the Parade today is still escorted by a unit of soldiers; and for the past 165 years “The Irish Infantry” National Guard 69th Regiment have led the Parade up Fifth Avenue, and they are followed by the various Irish societies of the city, the thirty two Irish county societies, and various schools, colleges, Emerald Societies, Irish-language, and Nationalist Societies. The 2002 parade was dedicated to the ‘Heroes of 9/11, ‘ honoring the police, fire and all rescue workers. At midday, the entire parade paused for two minutes, the Parade at that time stretched one and a half miles and the entire Parade turned around and faced South towards the “TWIN TOWERS” as the Cardinal said a prayer for all the victims of 9/11. This was the first time in history, in the City that never sleeps, one could hear a pin drop on Fifth Avenue, a fitting tribute to the men and women who lost their lives on that fateful day in 2001. The 2002 Parade was the largest Parade to date with an estimated 300,000 marchers and three million spectators lining Fifth Avenue. This was the first time in history; the President of Ireland reviewed a St. Patrick’s Day Parade outside Ireland on March 17th.
36cm x 30cm New York Wonderful elevated shot of the 1950 New York St Patricks Day Parade from high above 5th Avenue as the procession passes St Patricks Cathedral. The St. Patrick’s Day Parade is one of New York City’s greatest traditions. On this day, everyone is Irish in the Big Apple! The Parade marched for the first time on March 17, 1762 – fourteen Years before the Declaration of Independence was adopted and today it is the largest Parade in the World. This annual parade has been held for the past 257 years in honor of the Patron Saint of Ireland and the Archdiocese of New York. The Parade is reviewed from the steps of Saint Patrick’s Cathedral by His Eminence, Timothy Cardinal Dolan, Archbishop of New York in the same manner as the Archbishop of New York did in the early days of the Parade at the Old St. Patrick’s Cathedral in Lower Manhattan before the new St Patrick’s was built on Fifth Avenue. Often regarded as the most popular parade in New York City, the Parade is the largest and most famous of the many parades held in the city each year. The Parade starts at 44th Street at 11 am and is held every March 17th except when March 17th falls on a Sunday; it is celebrated the day before, Saturday the 16th, because of religious observances. The parade marches up Fifth Avenue past St. Patrick’s Cathedral at 50th Street all the way up 79th Street, where the parade finishes around 4:30 – 5:00 pm To this day, the St. Patrick’s Day Parade remains true to its roots as a true marchers Parade by not allowing floats, automobiles and other commercial aspects in the Parade. Every year the Parade Committee hosts the 150,000- 250,000 marchers, along with many great bands; bagpipes, high school bands and the ever-present politicians in front of the approx 2 million spectators lining Fifth Avenue. The Parade is televised for four hours on WNBC Channel Four to over half a million households and was web streamed live for the first time in 2008. Today, the coverage has expanded to seven additional internet based platforms and can easily be viewed on mobile devices. The first St. Patrick’s Day Parade in New York was held on lower Broadway in 1762 by a band of homesick Irish ex-patriots and Irish military serving with the British Army stationed in the American colonies in New York City. This was a time when the wearing of green was a sign of Irish pride and was banned in Ireland. The parade participants reveled in the freedom to speak Irish, wear green, sing Irish songs and play the pipes to Irish tunes that were very meaningful to the Irish immigrants who had fled their homeland. For the first few years of its existence, the parade was organized by military units. After the war of 1812, the Irish fraternal and benevolent societies took over the duties of hosting and sponsoring the event. Originally, the Irish societies joined together at their respective meeting places and moved in a procession toward Old St. Patrick’s Cathedral in Lower Manhattan on Mott & Prince Streets where the Archbishop of New York would then address the crowd before revelers dispersed to celebrate. Around 1851 the individual societies merged under a single grand marshal and the size of the parade grew sharply. This was when the “Irish” 69th Regiment began to lead the marchers and the Ancient Order of Hibernians became the official sponsor. In the early 90’s, the Parade was attacked for its traditional values and in the resulting lawsuits the organizers rights were up held all the way to the US Supreme court. In 1992 the National AOH directed all AOH organizations to form separate corporations to run events such as the Parade. The Parade is run today by members of the AOH under a separate corporation, St Patrick’s Day Parade Inc. Since the first Parade, 257 years ago, the Parade today is still escorted by a unit of soldiers; and for the past 165 years “The Irish Infantry” National Guard 69th Regiment have led the Parade up Fifth Avenue, and they are followed by the various Irish societies of the city, the thirty two Irish county societies, and various schools, colleges, Emerald Societies, Irish-language, and Nationalist Societies. The 2002 parade was dedicated to the ‘Heroes of 9/11, ‘ honoring the police, fire and all rescue workers. At midday, the entire parade paused for two minutes, the Parade at that time stretched one and a half miles and the entire Parade turned around and faced South towards the “TWIN TOWERS” as the Cardinal said a prayer for all the victims of 9/11. This was the first time in history, in the City that never sleeps, one could hear a pin drop on Fifth Avenue, a fitting tribute to the men and women who lost their lives on that fateful day in 2001. The 2002 Parade was the largest Parade to date with an estimated 300,000 marchers and three million spectators lining Fifth Avenue. This was the first time in history; the President of Ireland reviewed a St. Patrick’s Day Parade outside Ireland on March 17th. -
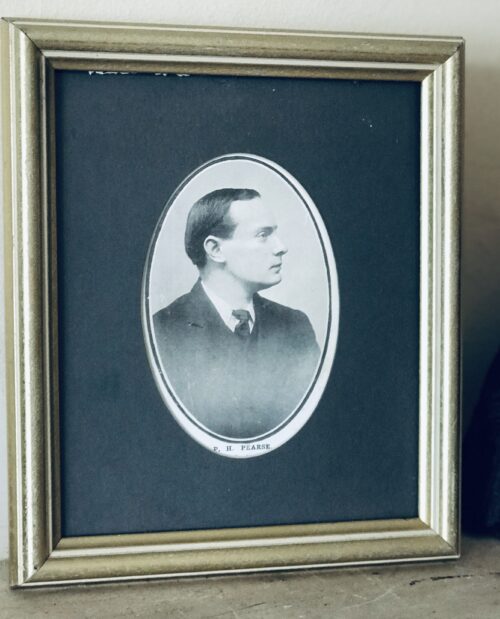
 Beautiful and poignant collection of four of the 1916 Easter Rising Rebel Leaders who were executed by the British Crown Forces at Kilmainham Jail a few weeks later.Featured here are Padraig Pearse,Thomas Clarke,James Connolly,Thomas Kent. Patrick Pearse, in full Patrick Henry Pearse, Patrick also spelled in Irish Pádraic, (born November 10, 1879, Dublin, Ireland—died May 3, 1916, Dublin), Irish nationalist leader, poet, and educator. He was the first president of the provisional government of the Irish republic proclaimed in Dublin on April 24, 1916, and was commander in chief of the Irish forces in the anti-British Easter Rising that began on the same day.The son of an English sculptor and his Irish wife, Pearse became a director of the Gaelic League (founded 1893 for the preservation of the Irish language) and edited (1903–09) its weekly newspaper, An Claidheamh Soluis (“The Sword of Light”). To further promote the Irish language as a weapon against British domination, he published tales from old Irish manuscripts and a collection (1914) of his own poems in the modern Irish idiom. He founded St. Enda’s College (1908), near Dublin, as a bilingual institution with its teaching based on Irish traditions and culture. On the formation of the Irish Volunteers (November 1913) as a counterforce against the Ulster Volunteers (militant supporters of the Anglo-Irish union), Pearse became a member of their provisional committee, and he contributed poems and articles to their newspaper, The Irish Volunteer. In July 1914 he was made a member of the supreme council of the Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB). After the Irish Volunteers split (September 1914), he became a leader of the more extreme nationalist section, which opposed any support for Great Britain in World War I. He came to believe that the blood of martyrs would be required to liberate Ireland, and on that theme he delivered a famous oration in August 1915 at the burial of Jeremiah O’Donovan, known as O’Donovan Rossa, a veteran of Sinn Féin.Pearse’s Collected Works appeared in 1917–22 (3 vol.) and again in 1924 (5 vol.), and his Political Writings and Speeches appeared in 1952.
Beautiful and poignant collection of four of the 1916 Easter Rising Rebel Leaders who were executed by the British Crown Forces at Kilmainham Jail a few weeks later.Featured here are Padraig Pearse,Thomas Clarke,James Connolly,Thomas Kent. Patrick Pearse, in full Patrick Henry Pearse, Patrick also spelled in Irish Pádraic, (born November 10, 1879, Dublin, Ireland—died May 3, 1916, Dublin), Irish nationalist leader, poet, and educator. He was the first president of the provisional government of the Irish republic proclaimed in Dublin on April 24, 1916, and was commander in chief of the Irish forces in the anti-British Easter Rising that began on the same day.The son of an English sculptor and his Irish wife, Pearse became a director of the Gaelic League (founded 1893 for the preservation of the Irish language) and edited (1903–09) its weekly newspaper, An Claidheamh Soluis (“The Sword of Light”). To further promote the Irish language as a weapon against British domination, he published tales from old Irish manuscripts and a collection (1914) of his own poems in the modern Irish idiom. He founded St. Enda’s College (1908), near Dublin, as a bilingual institution with its teaching based on Irish traditions and culture. On the formation of the Irish Volunteers (November 1913) as a counterforce against the Ulster Volunteers (militant supporters of the Anglo-Irish union), Pearse became a member of their provisional committee, and he contributed poems and articles to their newspaper, The Irish Volunteer. In July 1914 he was made a member of the supreme council of the Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB). After the Irish Volunteers split (September 1914), he became a leader of the more extreme nationalist section, which opposed any support for Great Britain in World War I. He came to believe that the blood of martyrs would be required to liberate Ireland, and on that theme he delivered a famous oration in August 1915 at the burial of Jeremiah O’Donovan, known as O’Donovan Rossa, a veteran of Sinn Féin.Pearse’s Collected Works appeared in 1917–22 (3 vol.) and again in 1924 (5 vol.), and his Political Writings and Speeches appeared in 1952. -
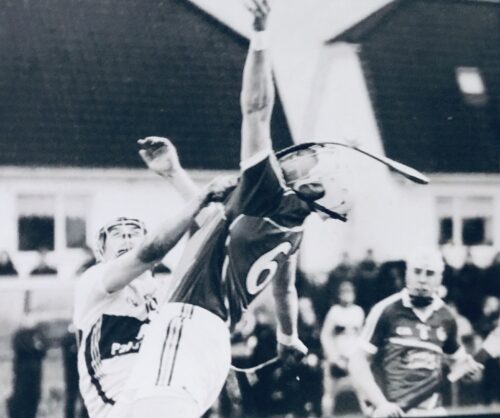

 26cm x 33cm Not so much the clash of the ash as the bend of the ash in this unbelievable action photograph as Clare and Limerick Hurlers do battle in a challenge game in Sixmilebridge.The art of Hurley making & the raw materials used have not changed a lot since time immemorial as this article demonstrates ; Cad a dhéanfaimid feasta gan adhmaid, tá deireadh na gcoillte ar lár…” seems an appropriate opening to an article about hurley making, as we speak to Pat Cronin in his workshop overlooking the Comeragh Mountains in Kilcash, Tipperary. “Over 90% of the timber used in hurley-making now is foreign. Irish ash is very scarce, although Coillte are working to change this”, explained Pat. “I get most of my timber from Coillte in Dundrum (Tipperary). This comes from Denmark and Sweden”. Although some makers have produced hurleys from 14 year old ash Pat believes this is too soon. “You might only get two or three slabs out of a tree that young. If you left it another five or more years you’d get more than double that. It’d really take up to 25 years to get a decent return.” Pat’s uncle, Larry Welsh, made hurleys, but Pat didn’t realise this when he started out. “John Joe O’Brien in Cahir taught me. I used to call to him to get a few now and then and it went from there. I started about 25 years ago and gave up working with Eircom to go at it full time five years ago. I’m kept busy throughout the year.” Brian Dowling’s “Star Hurleys” workshop is in the heart of Kilkenny. Despite the fact that his son Mark is also in the business they’re under constant pressure to meet demand. Brian, who served his time to become a carpenter, has been making hurleys since 1980. His father Ramie was a well known maker, who started in the early 1960’s with Brian’s grandfather Tom Neary. It probably takes about thirty minutes to make a hurley, if you were to go at it from start to finish. However, neither Pat nor Brian make them in this way. Both use copying machines to rough cut “slabs” three or four at a time. Each then finishes the hurleys by hand, to meet specific requirements. “You get phases of popularity in styles”, explained Pat Cronin, “Because of the O’Connor’s of Cork for instance, big bosses are in favour now. But there’s also a trend towards shorter and lighter sticks. There’s a risk if the hurley is too light it’ll snap more easily. And you don’t get the same distance on a puck out.” Brian, recently in Italy looking at a replacement for his aging copying machine, only cuts 33 inch sticks and bigger this way. “I do the smaller ones entirely by hand”. The style of hurling has changed over the years and naturally the hurley changes to reflect this. “Demands for particular styles naturally reflect the styles of the successful teams of the time”. Certainly the demand for personalised sticks has grown. Brian, who supplies most of the Kilkenny senior team, explains that most of them have specific demands. Every hurley maker will advise you differently about how best to look after your stick! wever, you need good quality timber to start with. Pat Cronin suggests that when you get your new hurley you should put it away for a while. “Some people hang them, rather than prop them against a wall, so they won’t warp. There are those who put them in water until they get the right weight. Then they’ll varnish or linseed oil them to keep them at that weight. Like a good wine it should also be stored somewhere cool! You definitely shouldn’t keep them in the kitchen or in the boot of your car, or they will dry out.” Brian suggests that it’s better to buy the stick unbanded. “You need to allow a bit of time for timber to settle. You might also put five or six coats of linseed oil on, or even drop them into a barrel of linseed oil for a while, to get more penetration. You have to remember that this will add weight ‘though. But whether you oil them or not, you should leave them for a good week or so before banding them. And don’t keep them in the house!” There is a Hurley Makers Guild, which was formed almost ten years ago when ash became scarce. Makers felt the need to organise themselves to address the problem. There are about fifty active members these days. Both Pat Cronin and Brian Dowling are curious to see how Jack Carey – brother of the illustrious DJ – gets on with his plan to import finished hurleys from Eastern Europe. This could have quite an impact on what might be regarded as a quintessentially Irish cottage industry. However, time will tell. Just to set up a workshop and kit it out here in Ireland would probably cost about half a million Euro, according to both Pat and Brian. Not a cheap business to get into! Little wonder the notion of foreign manufactured hurleys doesn’t seem that strange… Two great Craftsmen, continuing the wonderful tradition of hurley-making.
26cm x 33cm Not so much the clash of the ash as the bend of the ash in this unbelievable action photograph as Clare and Limerick Hurlers do battle in a challenge game in Sixmilebridge.The art of Hurley making & the raw materials used have not changed a lot since time immemorial as this article demonstrates ; Cad a dhéanfaimid feasta gan adhmaid, tá deireadh na gcoillte ar lár…” seems an appropriate opening to an article about hurley making, as we speak to Pat Cronin in his workshop overlooking the Comeragh Mountains in Kilcash, Tipperary. “Over 90% of the timber used in hurley-making now is foreign. Irish ash is very scarce, although Coillte are working to change this”, explained Pat. “I get most of my timber from Coillte in Dundrum (Tipperary). This comes from Denmark and Sweden”. Although some makers have produced hurleys from 14 year old ash Pat believes this is too soon. “You might only get two or three slabs out of a tree that young. If you left it another five or more years you’d get more than double that. It’d really take up to 25 years to get a decent return.” Pat’s uncle, Larry Welsh, made hurleys, but Pat didn’t realise this when he started out. “John Joe O’Brien in Cahir taught me. I used to call to him to get a few now and then and it went from there. I started about 25 years ago and gave up working with Eircom to go at it full time five years ago. I’m kept busy throughout the year.” Brian Dowling’s “Star Hurleys” workshop is in the heart of Kilkenny. Despite the fact that his son Mark is also in the business they’re under constant pressure to meet demand. Brian, who served his time to become a carpenter, has been making hurleys since 1980. His father Ramie was a well known maker, who started in the early 1960’s with Brian’s grandfather Tom Neary. It probably takes about thirty minutes to make a hurley, if you were to go at it from start to finish. However, neither Pat nor Brian make them in this way. Both use copying machines to rough cut “slabs” three or four at a time. Each then finishes the hurleys by hand, to meet specific requirements. “You get phases of popularity in styles”, explained Pat Cronin, “Because of the O’Connor’s of Cork for instance, big bosses are in favour now. But there’s also a trend towards shorter and lighter sticks. There’s a risk if the hurley is too light it’ll snap more easily. And you don’t get the same distance on a puck out.” Brian, recently in Italy looking at a replacement for his aging copying machine, only cuts 33 inch sticks and bigger this way. “I do the smaller ones entirely by hand”. The style of hurling has changed over the years and naturally the hurley changes to reflect this. “Demands for particular styles naturally reflect the styles of the successful teams of the time”. Certainly the demand for personalised sticks has grown. Brian, who supplies most of the Kilkenny senior team, explains that most of them have specific demands. Every hurley maker will advise you differently about how best to look after your stick! wever, you need good quality timber to start with. Pat Cronin suggests that when you get your new hurley you should put it away for a while. “Some people hang them, rather than prop them against a wall, so they won’t warp. There are those who put them in water until they get the right weight. Then they’ll varnish or linseed oil them to keep them at that weight. Like a good wine it should also be stored somewhere cool! You definitely shouldn’t keep them in the kitchen or in the boot of your car, or they will dry out.” Brian suggests that it’s better to buy the stick unbanded. “You need to allow a bit of time for timber to settle. You might also put five or six coats of linseed oil on, or even drop them into a barrel of linseed oil for a while, to get more penetration. You have to remember that this will add weight ‘though. But whether you oil them or not, you should leave them for a good week or so before banding them. And don’t keep them in the house!” There is a Hurley Makers Guild, which was formed almost ten years ago when ash became scarce. Makers felt the need to organise themselves to address the problem. There are about fifty active members these days. Both Pat Cronin and Brian Dowling are curious to see how Jack Carey – brother of the illustrious DJ – gets on with his plan to import finished hurleys from Eastern Europe. This could have quite an impact on what might be regarded as a quintessentially Irish cottage industry. However, time will tell. Just to set up a workshop and kit it out here in Ireland would probably cost about half a million Euro, according to both Pat and Brian. Not a cheap business to get into! Little wonder the notion of foreign manufactured hurleys doesn’t seem that strange… Two great Craftsmen, continuing the wonderful tradition of hurley-making. -

 26cm x 33cm Ferns Co Wexford An anxious looking Wexford defence prepare as Christy Ring takes a in the 1956 All Ireland Hurling Final.The result would be forever known simply as " The Save ". Art Foley, who died on Monday last in New York, will be remembered for a save he made in the closing stages of the 1956 All-Ireland hurling final that had seismic and far-reaching consequences. It formed an instrumental part of a metamorphic sequence of play in a terrific contest with Cork, leading to one of the game's most epic finales. With three minutes left the ever-threatening Christy Ring gained possession and made for the Wexford goal. The finer points of what happened next are still in dispute. The main thread of the narrative is not. Ring let fly and the diminutive Foley in Wexford's goal was equal to it. He needed to be. His side led by two points, and a goal, especially one by Ring, would surely have inspired a Cork victory. Ring would have had his ninth medal. Wexford hurling might not be the beguiling and romanticised entity it is today.In the game's pivotal moment, the ball quickly travelled down the other end where Tom Ryan sent a raking handpass to Nickey Rackard. In a piece of perfect casting, the greatest name in Wexford hurling landed the deathblow, netting with a low shot to the corner. Wexford were already champions, having defeated Galway in the final a year before to end a 45-year wait. But to beat Cork gave them a status they'd never attained before and wrote them into everlasting legend. The death of Foley at 90 ended a significant chapter for that storied era, he being the last surviving member of the team that won the final in '56 and which started the '55 decider, giving hope to all counties outside the traditional fold. In a decade often depicted as repressive and severe, with heavy emigration, Wexford brought an abundance of novelty and glamour and dauntless expression which made them huge crowd-pullers and popular all over the country. A jazzy addition to the traditional acts. The previous six All-Irelands before Wexford's breakthrough in '55 were shared between Cork and Tipperary. "Why are all these massive crowds following Wexford?" asks Liam Griffin. "The Wexford support base for hurling grew with the rise of the Wexford teams of the 1950s. There was a romantic connection between them and all hurling people. Why? Because they came up to challenge the dominant counties." At the time Wexford looked more likely to prosper in football than hurling. The 1950s, led by the Rackards, changed all that. Only a few survivors remain from the '56 panel: Ted Morrissey, Oliver Gough and Pat Nolan. Morrissey played in the Leinster final before losing his place and had also been on the squad in '51 when Wexford reached the All-Ireland final. Nolan was Art Foley's goalkeeping deputy in '56, later winning All-Ireland medals over a long career in '60 and '68. Gough came on in the '55 final. In a way the loop that began the most famous end-to-end move in Wexford hurling history, starting with Foley's save and concluding with Rackard's goal, was replicated in life itself. The first of that celebrated '56 team to die was Rackard, in April, 1976, at the age of 54 after succumbing to cancer. When the team was celebrating its silver jubilee in 1981, Foley came home from the US for the occasion, having emigrated with his wife Anne and their three young children at 27 in the late 1950s. By the time of the silver jubilee of the '56 win, only Rackard was missing. Gradually over the years the numbers diminished. Ned Wheeler went this year. Billy Rackard was the last of that famous band of brothers to die ten years ago. Now, Foley, literally the last one standing, has gone too. The deeds, though, remain timeless and immortal. The save which made Foley famous followed him around all his days. "The big story of Art Foley is that save because it is the seminal moment of that time," as Liam Griffin puts it. It is also probably the most enigmatic save in the history of the game - the Mona Lisa of hurling saves, such has been the variety of interpretations. Even Ring seems to have offered contradictory accounts. Raymond Smith has an account from John Keane, the former Waterford great, who was umpiring that day. He recalled Ring shooting from 25 yards and the ball moving "so fast that the thought flashed through my mind, this must be a goal . . . and I couldn't believe my eyes when I saw that he'd saved it." One newspaper referred to "a powerful close-in shot" and another to a "piledriver" which was one of "several miracle saves" made by Foley on the day. Val Dorgan, Ring's biographer, reported a "vicious strike" that was saved just under the cross bar and he also used the word "miraculous".It wasn't until the next decade that All-Ireland finals began to be televised, leaving iconic moments like this shrouded in some mystery. Speaking to the Irish Echo in 2011, Foley himself gave this account: "Well, he shot and I blocked it straight up in the air. This is where they always get it wrong. They always say I caught it and cleared it, straight to Nickey [Rackard] and he scored the goal. But I blocked it out and Pat Barry [Cork] doubled on it, and it hit the outside of the net. "I pucked it out to Jim English and he passed it to Tom Ryan, and he got it to Nickey and Nickey got the goal, and we went on to win." It was in keeping with Foley's personality to play down the save's merits. In an interview in 2014, Ned Wheeler referred to Foley as "a gentlemen of few words". They stayed in touch regularly on the phone up to shortly before Wheeler's death. Ted Morrissey was another in frequent contact, a player who moved to Enniscorthy to work and joined the St Aidan's club which Foley played for. "I used to ring him every couple of weeks until recently," says Morrissey, now 89. "I rang him recently and he had fallen, the wife told me he was in the nursing home. "He was very clear, he had a great memory, could tell me all the people who lived on the street where he was. He worked as a lorry driver, that's what he was doing before he left. I suppose he thought there was a better life over there." What did they talk about? "About hurling and old times and the people he knew and he'd be asking me about the people around Enniscorthy. Unfortunately, by the last few conversations there weren't many left that he knew." Foley was just 5'6" at a time when there were marauding full-forwards aplenty and the goalkeeper didn't have the protection in the rulebook he has now. He was dropped after conceding six goals in the 1951 National League final and didn't play in the All-Ireland final later that year against Tipperary when Wexford suffered a heavy loss. Wexford opted for a novice 'keeper, something Billy Rackard later said had been a mistake. When he made the save in '56 Foley was given an appreciative and sporting hand-shake from Ring. The Cloyne man was notoriously competitive but often commented on the sportsmanship of Wexford and specifically his marker Bobby Rackard. At the end of the '56 final Nick O'Donnell and Rackard chaired Ring off the field which is another lasting and remarkable feature of that final. Foley spoke of that moment to Ted Morrissey. "Nicko (O'Donnell) came to Arty and says, 'we'll shoulder him off the field'. And Arty says to him, 'how the hell will we do that, you are 6'2 and I am 5'6 . . . go and get Bobby with you'. So Nicko and Bobby shouldered him off and Arty was a back-up man, giving them a push from behind." Ring stated after the '54 final when Cork defeated Wexford that Cork had never defeated a cleaner team. Perhaps the very different experience he had against Galway in the previous year's final had something to do with that, but the relationship between the counties at the time was cordial and warm. Ring being chaired off the field was its Olympian moment. At a time when hurling was notoriously rough and macho, these displays of sportsmanship were notably different from the norm. It deepened Wexford's unique appeal. Tony Dempsey, the former Wexford county chairman, and former senior hurling manger, met Foley and his wife and some of the family over lunch in Long Island a few years ago, where they made a presentation to him for his services to the county. They spoke of that decision to carry off Ring. "He told me Bobby caught Ring like a doll and lifted him up," said Dempsey, noting the power for which he was renowned. Foley survived in spite of his height limitations, helped by having O'Donnell in front of him. He left school at 13, like many others who were obliged to at the time, and followed his father Tommy, a truck driver, into employment at Davis's Mills in Enniscorthy. He told Dempsey in New York how he routinely carried 12-stone bags of flour up and down ladders at 14. "He took out a photo album and showed a photo of himself jumping for the ball," says Dempsey, "and proportionate to his body he had massive muscles, massive quads and massive thighs." In New York he ended up in long-term employment for TWA, spending 34 years as a crew chief. He came home occasionally, sometimes for reunions. After winning the '56 final, and entering legend, Wexford's victorious players began the triumphant journey home on the Monday night, stopping off in the Market Square in Enniscorthy. A Mr Browne from the county board introduced the players individually. "The greatest ovation was reserved for the goalkeeper Arty Foley whose brilliance in the net contributed much to Wexford's victory," the Irish Independent reported. Forty three years after they laid Nickey Rackard to rest in Bunclody, the first of that special team, Art Foley has gone to his eternal resting place in New York. Their deaths took place decades and thousands of miles apart. But their spirits will remain inseparable.Later, Ring claimed in conversations with Dorgan that he was off balance after being impeded by Paddy Barry and didn't get sufficient power in the shot. Yet Ring himself is quoted in The Irish Press after the match as follows: "It was one of the best saves I ever saw. I thought it was all over when I went through."
26cm x 33cm Ferns Co Wexford An anxious looking Wexford defence prepare as Christy Ring takes a in the 1956 All Ireland Hurling Final.The result would be forever known simply as " The Save ". Art Foley, who died on Monday last in New York, will be remembered for a save he made in the closing stages of the 1956 All-Ireland hurling final that had seismic and far-reaching consequences. It formed an instrumental part of a metamorphic sequence of play in a terrific contest with Cork, leading to one of the game's most epic finales. With three minutes left the ever-threatening Christy Ring gained possession and made for the Wexford goal. The finer points of what happened next are still in dispute. The main thread of the narrative is not. Ring let fly and the diminutive Foley in Wexford's goal was equal to it. He needed to be. His side led by two points, and a goal, especially one by Ring, would surely have inspired a Cork victory. Ring would have had his ninth medal. Wexford hurling might not be the beguiling and romanticised entity it is today.In the game's pivotal moment, the ball quickly travelled down the other end where Tom Ryan sent a raking handpass to Nickey Rackard. In a piece of perfect casting, the greatest name in Wexford hurling landed the deathblow, netting with a low shot to the corner. Wexford were already champions, having defeated Galway in the final a year before to end a 45-year wait. But to beat Cork gave them a status they'd never attained before and wrote them into everlasting legend. The death of Foley at 90 ended a significant chapter for that storied era, he being the last surviving member of the team that won the final in '56 and which started the '55 decider, giving hope to all counties outside the traditional fold. In a decade often depicted as repressive and severe, with heavy emigration, Wexford brought an abundance of novelty and glamour and dauntless expression which made them huge crowd-pullers and popular all over the country. A jazzy addition to the traditional acts. The previous six All-Irelands before Wexford's breakthrough in '55 were shared between Cork and Tipperary. "Why are all these massive crowds following Wexford?" asks Liam Griffin. "The Wexford support base for hurling grew with the rise of the Wexford teams of the 1950s. There was a romantic connection between them and all hurling people. Why? Because they came up to challenge the dominant counties." At the time Wexford looked more likely to prosper in football than hurling. The 1950s, led by the Rackards, changed all that. Only a few survivors remain from the '56 panel: Ted Morrissey, Oliver Gough and Pat Nolan. Morrissey played in the Leinster final before losing his place and had also been on the squad in '51 when Wexford reached the All-Ireland final. Nolan was Art Foley's goalkeeping deputy in '56, later winning All-Ireland medals over a long career in '60 and '68. Gough came on in the '55 final. In a way the loop that began the most famous end-to-end move in Wexford hurling history, starting with Foley's save and concluding with Rackard's goal, was replicated in life itself. The first of that celebrated '56 team to die was Rackard, in April, 1976, at the age of 54 after succumbing to cancer. When the team was celebrating its silver jubilee in 1981, Foley came home from the US for the occasion, having emigrated with his wife Anne and their three young children at 27 in the late 1950s. By the time of the silver jubilee of the '56 win, only Rackard was missing. Gradually over the years the numbers diminished. Ned Wheeler went this year. Billy Rackard was the last of that famous band of brothers to die ten years ago. Now, Foley, literally the last one standing, has gone too. The deeds, though, remain timeless and immortal. The save which made Foley famous followed him around all his days. "The big story of Art Foley is that save because it is the seminal moment of that time," as Liam Griffin puts it. It is also probably the most enigmatic save in the history of the game - the Mona Lisa of hurling saves, such has been the variety of interpretations. Even Ring seems to have offered contradictory accounts. Raymond Smith has an account from John Keane, the former Waterford great, who was umpiring that day. He recalled Ring shooting from 25 yards and the ball moving "so fast that the thought flashed through my mind, this must be a goal . . . and I couldn't believe my eyes when I saw that he'd saved it." One newspaper referred to "a powerful close-in shot" and another to a "piledriver" which was one of "several miracle saves" made by Foley on the day. Val Dorgan, Ring's biographer, reported a "vicious strike" that was saved just under the cross bar and he also used the word "miraculous".It wasn't until the next decade that All-Ireland finals began to be televised, leaving iconic moments like this shrouded in some mystery. Speaking to the Irish Echo in 2011, Foley himself gave this account: "Well, he shot and I blocked it straight up in the air. This is where they always get it wrong. They always say I caught it and cleared it, straight to Nickey [Rackard] and he scored the goal. But I blocked it out and Pat Barry [Cork] doubled on it, and it hit the outside of the net. "I pucked it out to Jim English and he passed it to Tom Ryan, and he got it to Nickey and Nickey got the goal, and we went on to win." It was in keeping with Foley's personality to play down the save's merits. In an interview in 2014, Ned Wheeler referred to Foley as "a gentlemen of few words". They stayed in touch regularly on the phone up to shortly before Wheeler's death. Ted Morrissey was another in frequent contact, a player who moved to Enniscorthy to work and joined the St Aidan's club which Foley played for. "I used to ring him every couple of weeks until recently," says Morrissey, now 89. "I rang him recently and he had fallen, the wife told me he was in the nursing home. "He was very clear, he had a great memory, could tell me all the people who lived on the street where he was. He worked as a lorry driver, that's what he was doing before he left. I suppose he thought there was a better life over there." What did they talk about? "About hurling and old times and the people he knew and he'd be asking me about the people around Enniscorthy. Unfortunately, by the last few conversations there weren't many left that he knew." Foley was just 5'6" at a time when there were marauding full-forwards aplenty and the goalkeeper didn't have the protection in the rulebook he has now. He was dropped after conceding six goals in the 1951 National League final and didn't play in the All-Ireland final later that year against Tipperary when Wexford suffered a heavy loss. Wexford opted for a novice 'keeper, something Billy Rackard later said had been a mistake. When he made the save in '56 Foley was given an appreciative and sporting hand-shake from Ring. The Cloyne man was notoriously competitive but often commented on the sportsmanship of Wexford and specifically his marker Bobby Rackard. At the end of the '56 final Nick O'Donnell and Rackard chaired Ring off the field which is another lasting and remarkable feature of that final. Foley spoke of that moment to Ted Morrissey. "Nicko (O'Donnell) came to Arty and says, 'we'll shoulder him off the field'. And Arty says to him, 'how the hell will we do that, you are 6'2 and I am 5'6 . . . go and get Bobby with you'. So Nicko and Bobby shouldered him off and Arty was a back-up man, giving them a push from behind." Ring stated after the '54 final when Cork defeated Wexford that Cork had never defeated a cleaner team. Perhaps the very different experience he had against Galway in the previous year's final had something to do with that, but the relationship between the counties at the time was cordial and warm. Ring being chaired off the field was its Olympian moment. At a time when hurling was notoriously rough and macho, these displays of sportsmanship were notably different from the norm. It deepened Wexford's unique appeal. Tony Dempsey, the former Wexford county chairman, and former senior hurling manger, met Foley and his wife and some of the family over lunch in Long Island a few years ago, where they made a presentation to him for his services to the county. They spoke of that decision to carry off Ring. "He told me Bobby caught Ring like a doll and lifted him up," said Dempsey, noting the power for which he was renowned. Foley survived in spite of his height limitations, helped by having O'Donnell in front of him. He left school at 13, like many others who were obliged to at the time, and followed his father Tommy, a truck driver, into employment at Davis's Mills in Enniscorthy. He told Dempsey in New York how he routinely carried 12-stone bags of flour up and down ladders at 14. "He took out a photo album and showed a photo of himself jumping for the ball," says Dempsey, "and proportionate to his body he had massive muscles, massive quads and massive thighs." In New York he ended up in long-term employment for TWA, spending 34 years as a crew chief. He came home occasionally, sometimes for reunions. After winning the '56 final, and entering legend, Wexford's victorious players began the triumphant journey home on the Monday night, stopping off in the Market Square in Enniscorthy. A Mr Browne from the county board introduced the players individually. "The greatest ovation was reserved for the goalkeeper Arty Foley whose brilliance in the net contributed much to Wexford's victory," the Irish Independent reported. Forty three years after they laid Nickey Rackard to rest in Bunclody, the first of that special team, Art Foley has gone to his eternal resting place in New York. Their deaths took place decades and thousands of miles apart. But their spirits will remain inseparable.Later, Ring claimed in conversations with Dorgan that he was off balance after being impeded by Paddy Barry and didn't get sufficient power in the shot. Yet Ring himself is quoted in The Irish Press after the match as follows: "It was one of the best saves I ever saw. I thought it was all over when I went through." -

 26cm x 33cm Fantastic shot of the most westerly GAA pitch in Ireland and prob in Western Europe-the pitch on Care Island where the resourceful locals have mangaged to produce a decent playing surface on the only flat patch of land on the island ! Inishturk (Inis Toirc in Irish, meaning Wild Boar Island) is an inhabited island of County Mayo, in Ireland.
26cm x 33cm Fantastic shot of the most westerly GAA pitch in Ireland and prob in Western Europe-the pitch on Care Island where the resourceful locals have mangaged to produce a decent playing surface on the only flat patch of land on the island ! Inishturk (Inis Toirc in Irish, meaning Wild Boar Island) is an inhabited island of County Mayo, in Ireland.Geography
The island lies about 15 km (9 mi) off the coast; its highest point reaches 189.3 m (621.1 ft) above sea level. Between Inisturk and Clare Island lies Caher Island. It has a permanent population of 58 people.There are two main settlements, both on the more sheltered eastern end of the island, Ballyheer and Garranty. Bellavaun and Craggy are abandoned settlements. The British built a Martello tower on the western coast during the Napoleonic Wars. Inisturk has the highest per capita donation rate towards the RNLI in the whole of Ireland.History
Inishturk has been inhabited on and off since 4,000 BCE and has been inhabited permanently since at least 1700. Some of the more recent inhabitants are descended from evacuees from Inishark to the southwest. The social club Mountain Common is situated on the hill that separates the two settlements.Recent history
In 1993 Inishturk Community centre was opened, this community centre doubles as a library and a pub. In June 2014 the ESB commissioned three new Broadcrown BCP 110-50 100kVA diesel generators to supply electricity to the island The ESB have operated a diesel power station on the island since the 1980s Inishturk gained international attention in 2016 after a number of websites claimed that the island would welcome any American "refugees" fleeing a potential Donald Trump presidency.These claims were used as one example of the type of "fake news" that arose during the 2016 US presidential election campaign. As of November 2016, no changes to inward migration have been reported. The island is home to a primary school on the island which in 2011 had only 3 pupils, this believed to be the smallest primary school in IrelandDemographics
The table below reports data on Inisturk's population taken from Discover the Islands of Ireland (Alex Ritsema, Collins Press, 1999) and the Censusof Ireland.Historical population Year Pop. ±% 1841 577 — 1851 174 −69.8% 1861 110 −36.8% 1871 112 +1.8% 1881 116 +3.6% 1891 135 +16.4% 1901 135 +0.0% 1911 132 −2.2% 1926 101 −23.5% Year Pop. ±% 1936 107 +5.9% 1946 125 +16.8% 1951 123 −1.6% 1956 110 −10.6% 1961 108 −1.8% 1966 92 −14.8% 1971 83 −9.8% 1979 85 +2.4% 1981 76 −10.6% Year Pop. ±% 1986 90 +18.4% 1991 78 −13.3% 1996 83 +6.4% 2002 72 −13.3% 2006 58 −19.4% 2011 53 −8.6% 2016 51 −3.8% Source: Central Statistics Office. "CNA17: Population by Off Shore Island, Sex and Year". CSO.ie. Retrieved October 12, 2016. Transport[edit]
Prior to 1997 there was no scheduled ferry service and people traveled to and from the islands using local fishing boats. Since then a ferry service operates from Roonagh Quay, Louisburgh, County Mayo.[13] The pier was constructed during the 1980s by the Irish government, around this time the roads on the island were paved.[14]