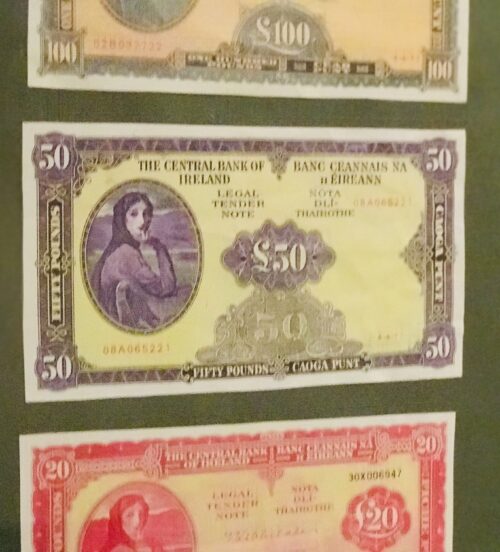
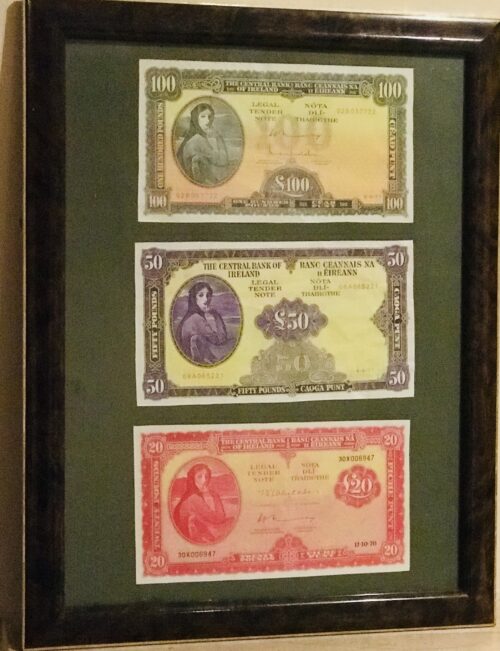
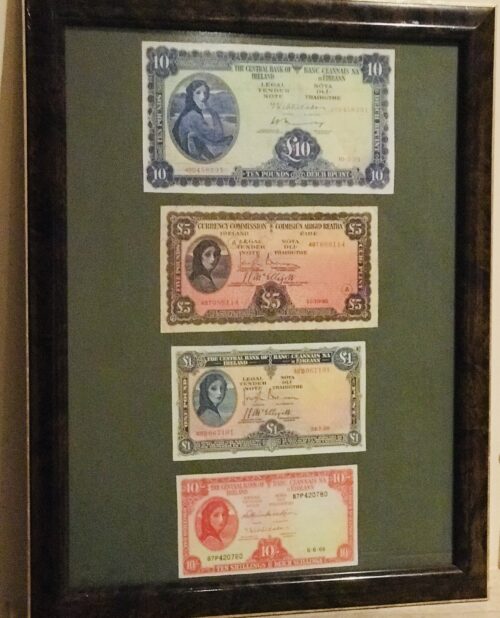
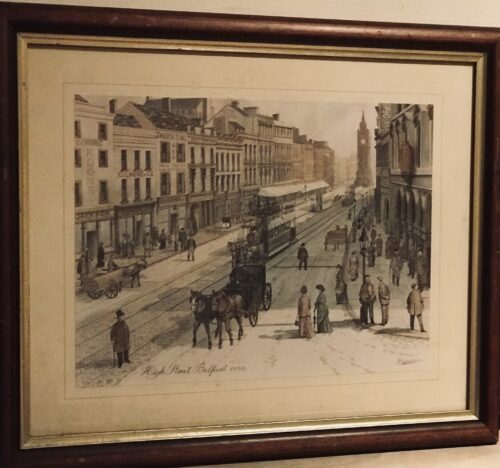Personal life










|
Bombay Sapphire was used in the video work Victoria Day (Bombay Sapphire), 2002 by contemporary artists Marina Roy and Abbas Akhavan. |

n 1863, Joseph Causton and his son, also named Joseph, developed the printing company which was to become the large and well known Joseph Causton & Sons Limited.
In 1867 the company was described as being a wholesale stationer and printer with a large warehouse at Southwark Street, London.
Joseph Causton was also a politician. He became a Councillor for Billingsgate, East London in 1868 and later Sheriff for London and Middlesex. The pinnacle of his career came when Queen Victoria opened Blackfriars Bridge and Holburn Viaduct in 1869 and he was knighted at Windsor Castle to mark the event. The company name now became Sir Joseph Causton & Sons Limited. Sir Joseph died just two years later but his sons, Joseph, Richard and James continued as partners of the firm.
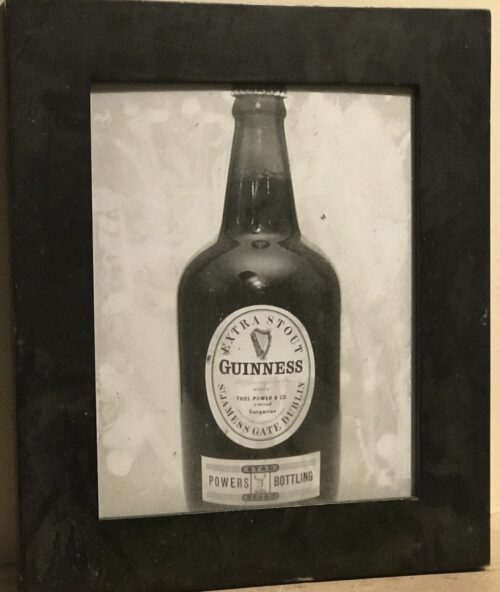
The company moved to a large new printing works in Eastleigh, Hampshire in the 1930s. The printing works made labels for household brands including Marmite and Guiness. During The Second World War they printed secret maps for the government in a specially bricked off part of the building.
By the end of the 1960s Sir Joseph Causton & Sons Limited fortunes were in decline. In the mid 1970s the company was losing money but it was not until 1984 that the firm was taken over by Norton Opex. They in turn were acquired by Bowater and Sir Joseph Causton and Sons ceased trading.
The Causton name has survived only as Causton Envelopes Limited and Causton Cartons, which is a subsidiary of the Bowater Group, manufacturing cartons for the pharmaceutical industry.
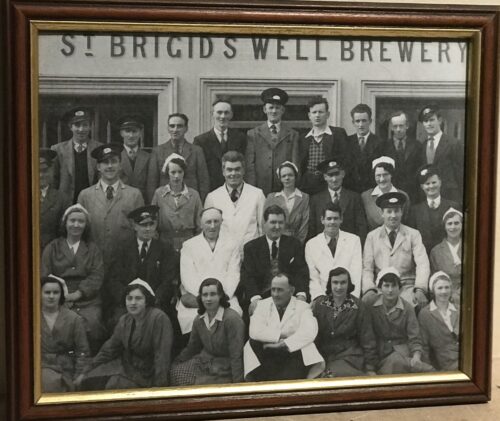
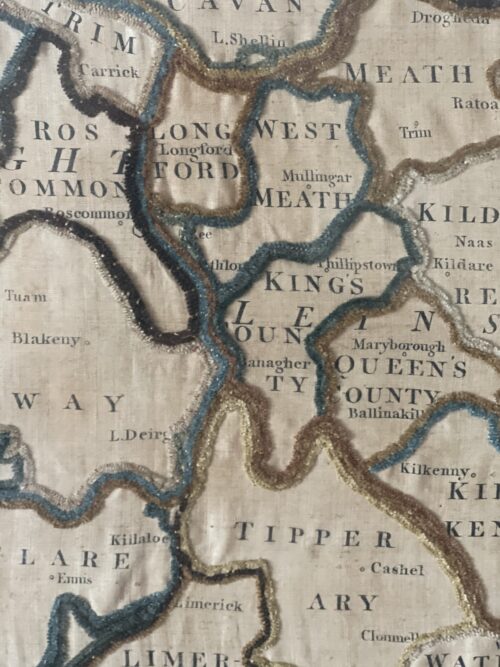
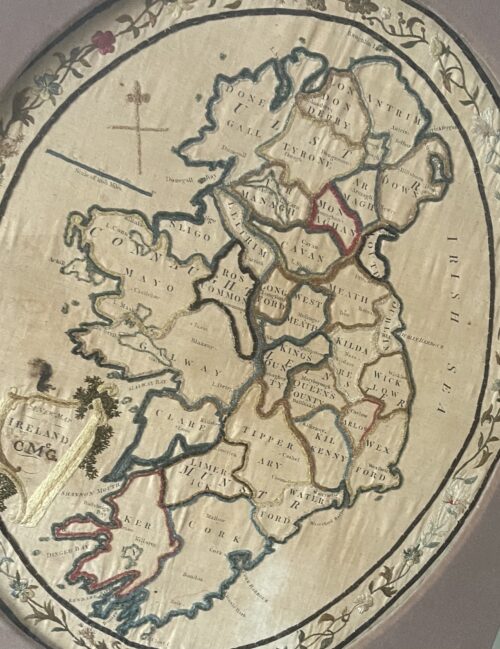




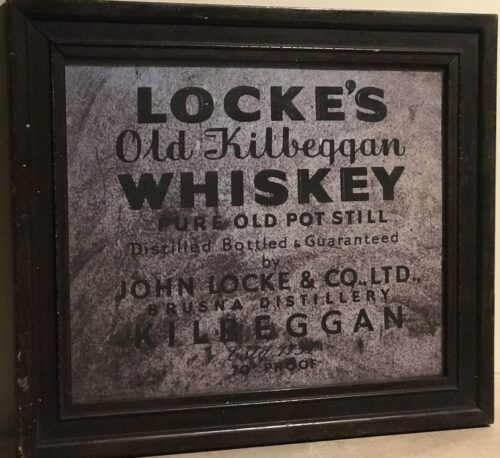
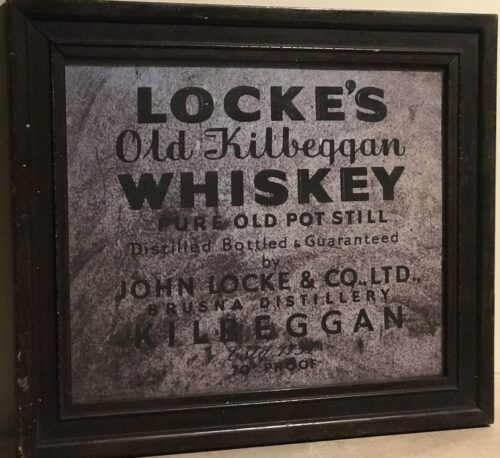
An Address from the People of Kilbeggan to John Locke, Esq. Dear Sir - Permit us, your fellow townsmen, to assure of our deep and cordial sympathy in your loss and disappointment from the accident which occurred recently in your Distillery. Sincerely as we regret the accident, happily unattended with loss of life, we cannot but rejoice at the long-wished-for opportunity it affords us of testifying to you the high appreciation in which we hold you for your public and private worth. We are well aware that the restrictions imposed by recent legislation on that particular branch of Irish industry, with which you have been so long identified, have been attended with disastrous results to the trade, as is manifest in the long list of Distilleries now almost in ruins, and which were a few years ago centres of busy industry, affording remunerative employment to thousands of hands; and we are convinced the Kilbeggan Distillery would have long since swelled the dismal catalogue had it fallen into less energetic and enterprising hands. In such an event we would be compelled to witness the disheartening scene of a large number of our working population without employment during that period of the year when employment Is scarcest, and at the same time most essential to the poor. Independent then of what we owe you, on purely personal grounds, we feel we owe you a deep debt of gratitude for maintaining in our midst a manufacture which affords such extensive employment to our poor, and exercises so favourable an influence on the prosperity of the town. In conclusion, dear Sir, we beg your acceptance of a new steam boiler to replace the injured one, as testimony, inadequate though it is, of our unfeigned respect and esteems for you ; and we beg to present it with the ardent wish and earnest hope that, for many long years to come, it may contribute to enhance still more the deservedly high and increasing reputation of the Kilbeggan Distillery.In a public response to mark the gift, also published in several newspapers, Locke thanked the people of Kilbeggan for their generosity, stating "...I feel this to be the proudest day of my life...". A plaque commemorating the event hangs in the distillery's restaurant today. In 1878, a fire broke out in the "can dip" (sampling) room of the distillery, and spread rapidly. Although, the fire was extinguished within an hour, it destroying a considerable portion of the front of the distillery and caused £400 worth of damage. Hundreds of gallons of new whiskey were also consumed in the blaze - however, the distillery is said to have been saved from further physical and financial ruin through the quick reaction of townsfolk who broke down the doors of the warehouses, and helped roll thousands of casks of ageing spirit down the street to safety. In 1887, the distillery was visited by Alfred Barnard, a British writer, as research for his book, "the Whiskey Distilleries of the United Kingdom". By then, the much enlarged distillery was being managed by John's sons, John Edward and James Harvey, who told Barnard that the distillery's output had more than doubled during the preceding ten years, and that they intended to install electric lighting.Barnard noted that the distillery, which he referred to as the "Brusna Distillery", named for the nearby river, was said to be the oldest in Ireland. According to Barnard, the distillery covered 5 acres, and employed a staff of about 70 men, with the aged and sick pensioned-off or assisted. At the time of his visit, the distillery was producing 157,200 proof gallons per annum, though it had the capacity to produce 200,000. The whiskey, which was sold primarily in Dublin, England, and "the Colonies", was "old pot still", produced using four pot stills (two wash stills: 10,320 / 8,436 gallons; and two spirit stills: 6,170 / 6,080 gallons), which had been installed by Millar and Company, Dublin. Barnard remarked that at the time of his visit over 2,000 casks of spirit were ageing in the distillery's bonded warehouses. In 1893, the distillery ceased to be privately held, and was converted a limited stock company, trading as John Locke & Co., Ltd., with nominal capital of £40,000.












 Source: Photojoiner
EARLIER THIS YEAR, the controversial Cuban revolutionary Che Guevara appeared on an Irish stamp to commemorate 100 years since his birth.
As well as unearthing the debate around the divisive legacy of the Argentine who was pivotal in the struggle to overthrow Cuba’s dictatorship, it also brought to the fore a discussion of Guevara’s Irish links.
Che’s father, who’s full name is Ernesto Guevara Lynch, was proud of his Irish roots and the story of how his family built a business in Argentina after fleeing Ireland during Cromwell’s era.
Years later when Che was Cuba’s transport minister, he made an unscheduled stop off in Limerick, and wrote a letter to his father, who he thought would be pleased to hear that he was visiting a country of his ancestry, says Nathan Mannion, curator at Epic, the Irish emigration museum.
There’s another, non-familial link that Guevara has with the island of Ireland – the famous, ubiquitous two-tone print of Che was created by an Irish artist Jim Fitzpatrick, which was created using a photo by Cuban photographer Guerrillero Heroico.
Source: Photojoiner
EARLIER THIS YEAR, the controversial Cuban revolutionary Che Guevara appeared on an Irish stamp to commemorate 100 years since his birth.
As well as unearthing the debate around the divisive legacy of the Argentine who was pivotal in the struggle to overthrow Cuba’s dictatorship, it also brought to the fore a discussion of Guevara’s Irish links.
Che’s father, who’s full name is Ernesto Guevara Lynch, was proud of his Irish roots and the story of how his family built a business in Argentina after fleeing Ireland during Cromwell’s era.
Years later when Che was Cuba’s transport minister, he made an unscheduled stop off in Limerick, and wrote a letter to his father, who he thought would be pleased to hear that he was visiting a country of his ancestry, says Nathan Mannion, curator at Epic, the Irish emigration museum.
There’s another, non-familial link that Guevara has with the island of Ireland – the famous, ubiquitous two-tone print of Che was created by an Irish artist Jim Fitzpatrick, which was created using a photo by Cuban photographer Guerrillero Heroico.
 Source: Epic
After the stamp controversy earlier this year, Fitzpatrick told TheJournal.ie that he was used to the controversy around Guevara, dismissing the criticism and accusations levelled against him as “black propaganda”.
He added that he was “immensely proud” to have his artwork of the Irish-descendant revolutionary on an official Irish stamp.
Irish roots
Patrick Lynch was born and raised in 1715 to parents from two of the main tribes of Galway. But after defeats at the hands of Cromwell’s forces, and later those of William of Orange, he fled to Bilbao in the Basque region of northern Spain, and then to Rio de la Plata, which would later become Argentina.
“He became a prominent figure in the Spanish government, a leading civil servant,” Nathan told TheJournal.ie.
After travelling to Buenos Aires in 1749 to work as a captain in the Milicias, he married a wealthy heiress. The valuable lands he gathered over the years were then passed on to his son, who followed into his father’s line of business.
In the century that followed, one of Patrick Lynch’s descendants would set up a shipping company, fight in the Argentine army and Chilean navy, write novels and short stories, paint and found a movement for rural libraries in Argentina.
It’s hard not to see how that family history didn’t impact on young Che, who was athletic and political, as well as passionate about poetry.
But it was while Che Guevara toured South America during his 20s that the spark of political activism was lit – it was during this time that he also penned a book of his own – The Motorcycle Diaries, (which decades later was turned into a film of the same name).
Source: Epic
After the stamp controversy earlier this year, Fitzpatrick told TheJournal.ie that he was used to the controversy around Guevara, dismissing the criticism and accusations levelled against him as “black propaganda”.
He added that he was “immensely proud” to have his artwork of the Irish-descendant revolutionary on an official Irish stamp.
Irish roots
Patrick Lynch was born and raised in 1715 to parents from two of the main tribes of Galway. But after defeats at the hands of Cromwell’s forces, and later those of William of Orange, he fled to Bilbao in the Basque region of northern Spain, and then to Rio de la Plata, which would later become Argentina.
“He became a prominent figure in the Spanish government, a leading civil servant,” Nathan told TheJournal.ie.
After travelling to Buenos Aires in 1749 to work as a captain in the Milicias, he married a wealthy heiress. The valuable lands he gathered over the years were then passed on to his son, who followed into his father’s line of business.
In the century that followed, one of Patrick Lynch’s descendants would set up a shipping company, fight in the Argentine army and Chilean navy, write novels and short stories, paint and found a movement for rural libraries in Argentina.
It’s hard not to see how that family history didn’t impact on young Che, who was athletic and political, as well as passionate about poetry.
But it was while Che Guevara toured South America during his 20s that the spark of political activism was lit – it was during this time that he also penned a book of his own – The Motorcycle Diaries, (which decades later was turned into a film of the same name).
 Source: Epic
Referring to Che’s “restless” nature, his father declared “the first thing to note is that in my son’s veins flowed the blood of the Irish rebels”.
“Half a million, to a million of the Argentinian population claim to be of Irish descent. But there are problems with identifying people of Irish descent, because when the Irish arrived during that era, they were recorded as ‘British’, so it’s a little bit problematic identifying who was Irish and who wasn’t.
“So the ancestry of Guevara is quite exceptional – as they emigrated to Argentina long before most Irish people did, during the latter half of the 19th century, coming up to the Great Famine.”
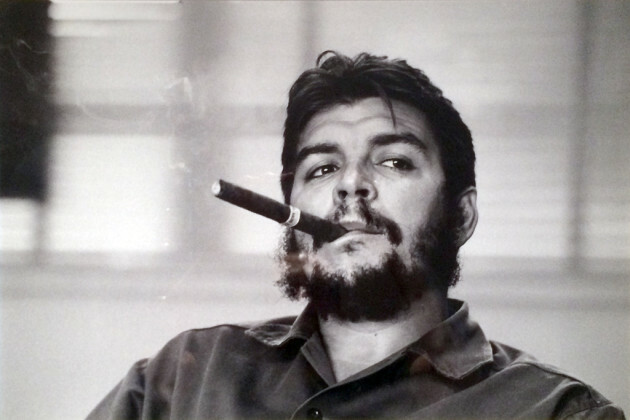
Jim Fitzpatrick (born James Fitzpatrick in 1944) is an Irish artist. He is best known for elaborately detailed work inspired by the Irish Celtic artistictradition. However, his most famous single piece is rather different in style, his iconic two-tone portrait of Che Guevara created in 1968, based on a photo by Alberto Korda.
Jim Fitzpatrick was born in December 1944 to James and Elizabeth Fitzpatrick (née O'Connor). His parents had married in the north Dublin suburb of Cabra in June 1943. During a period of childhood sickness, Fitzpatrick read and drew in bed, as well as his mother and great-aunt telling him stories of the Tuatha Dé Danann, Cú Chulainn and Fionn MacCumhaill. He was educated at the Franciscan College Gormanston, County Meath, just north of Dublin. His father was a photo-journalist and he is a grandson of political cartoonist Thomas Fitzpatrick.
Fitzpatrick's earliest work was the graphic portrait of Che Guevara, which was based on the photograph by Alberto Korda, entitled Guerrillero Heroico, was taken on 5 March 1960. Fitzpatrick met Guevara 5 years earlier in Kilkee during Guevara's visit to trace his Irish ancestry. Having initially tried to distribute the poster himself, Fitzpatrick chose to remove copyright from the image so that is could be used freely by left wing groups, stating that "I literally wanted it to breed like rabbits. I wanted it to spread."
In 1978, he wrote and illustrated a book called The Book of Conquests, the retelling of a cycle of Irish myths, the Lebor Gabála Érenn. The book is a retelling of the legends of the coming of the Tuatha dé Dannan to Ireland and their fight with the Fir Bolg. The illustrations include intricate Celtic scroll work and knotwork, for which Fitzpatrick has become known. A second book, The Silver Arm, is based on the deeds of Nuada of the Silver Arm and Lugh in their fight with the Formor.
Fitzpatrick has produced artwork for bands such as Thin Lizzy including their Jailbreak album in 1976, for Sinéad O'Connor's 2000 album Faith and Courage, for The Darkness' 2003 single "Christmas Time (Don't Let the Bells End)",Norwegian black metal band Darkthrone's 2013 album cover The Underground Resistance, and took the photograph for the cover of Louise Patricia Crane's 2020 album Deep Blue.He was commissioned by CityJet in 2007 to create images reflecting Ireland's culture, mythology, history and landscapes.
In 2011, Fitzpatrick announced that he intended to copyright the iconic red and black Che Guevara graphic. He cited "crass commercial" use of the image for his decision and planned to hand over the copyright and all rights, in perpetuity, to the family of Guevara in Cuba. The image remains available for free through Fitzpatrick's website for non-commercial usage. An Post released a stamp featuring Fitzpatrick's image of Guevara in 2017 to mark 50 years since its publication.
Source: Epic
Referring to Che’s “restless” nature, his father declared “the first thing to note is that in my son’s veins flowed the blood of the Irish rebels”.
“Half a million, to a million of the Argentinian population claim to be of Irish descent. But there are problems with identifying people of Irish descent, because when the Irish arrived during that era, they were recorded as ‘British’, so it’s a little bit problematic identifying who was Irish and who wasn’t.
“So the ancestry of Guevara is quite exceptional – as they emigrated to Argentina long before most Irish people did, during the latter half of the 19th century, coming up to the Great Famine.”
Jim Fitzpatrick (born James Fitzpatrick in 1944) is an Irish artist. He is best known for elaborately detailed work inspired by the Irish Celtic artistictradition. However, his most famous single piece is rather different in style, his iconic two-tone portrait of Che Guevara created in 1968, based on a photo by Alberto Korda.
Jim Fitzpatrick was born in December 1944 to James and Elizabeth Fitzpatrick (née O'Connor). His parents had married in the north Dublin suburb of Cabra in June 1943. During a period of childhood sickness, Fitzpatrick read and drew in bed, as well as his mother and great-aunt telling him stories of the Tuatha Dé Danann, Cú Chulainn and Fionn MacCumhaill. He was educated at the Franciscan College Gormanston, County Meath, just north of Dublin. His father was a photo-journalist and he is a grandson of political cartoonist Thomas Fitzpatrick.
Fitzpatrick's earliest work was the graphic portrait of Che Guevara, which was based on the photograph by Alberto Korda, entitled Guerrillero Heroico, was taken on 5 March 1960. Fitzpatrick met Guevara 5 years earlier in Kilkee during Guevara's visit to trace his Irish ancestry. Having initially tried to distribute the poster himself, Fitzpatrick chose to remove copyright from the image so that is could be used freely by left wing groups, stating that "I literally wanted it to breed like rabbits. I wanted it to spread."
In 1978, he wrote and illustrated a book called The Book of Conquests, the retelling of a cycle of Irish myths, the Lebor Gabála Érenn. The book is a retelling of the legends of the coming of the Tuatha dé Dannan to Ireland and their fight with the Fir Bolg. The illustrations include intricate Celtic scroll work and knotwork, for which Fitzpatrick has become known. A second book, The Silver Arm, is based on the deeds of Nuada of the Silver Arm and Lugh in their fight with the Formor.
Fitzpatrick has produced artwork for bands such as Thin Lizzy including their Jailbreak album in 1976, for Sinéad O'Connor's 2000 album Faith and Courage, for The Darkness' 2003 single "Christmas Time (Don't Let the Bells End)",Norwegian black metal band Darkthrone's 2013 album cover The Underground Resistance, and took the photograph for the cover of Louise Patricia Crane's 2020 album Deep Blue.He was commissioned by CityJet in 2007 to create images reflecting Ireland's culture, mythology, history and landscapes.
In 2011, Fitzpatrick announced that he intended to copyright the iconic red and black Che Guevara graphic. He cited "crass commercial" use of the image for his decision and planned to hand over the copyright and all rights, in perpetuity, to the family of Guevara in Cuba. The image remains available for free through Fitzpatrick's website for non-commercial usage. An Post released a stamp featuring Fitzpatrick's image of Guevara in 2017 to mark 50 years since its publication.


"The An Post-GAA Team of the Millennium was unveiled at Croke Park yesterday. The selection which serves as the first 15 inductions into the GAA's new Hall of Fame has also been marked by an issue of 15 commemorative stamps by An Post. The stamps will be available in a variety of combinations from today. Next year, a similar exercise will take place to honour 15 hurlers.
There was some comment on the absence of Dublin's Brian Mullins and Jack O'Shea from Kerry but it seemed generally appreciated that there were only two centrefield slots on the team and someone had to lose out. Tommy Murphy, the Boy Wonder of the 1930s Laois team which won three Leinster titles in a row, who was included ahead of Mullins and O'Shea had the added distinction of being the only player honoured who had not won an All-Ireland medal.
Not surprisingly, Kerry - who top the All-Ireland roll of honour with 31 titles - lead the way on the team with six selections. Despite being clearly second behind Kerry with 22 All-Irelands, Dublin provide only one player, Kevin Heffernan at left corner forward. Galway and Mayo have two players each with one from Cavan, Down, Meath and Laois making up the balance.
Joe McDonagh, President of the GAA, described the project as a reflection "on the history and evolution of our association, its games and its central characters, the players who have left such giant footprints in the sands that is the chronicle of the GAA".
The Hall of Fame which is inaugurated by this team will be represented all through Croke Park, according the GAA director general Liam Mulvihill. He said that the Hall will be added to with a small number of inductions on an annual basis.
"We decided that this team would be the initial members of the Hall of Fame and we were planning to honour those selected around the main areas of the concourse of the re-developed stadium, in the bottom tier and the upper tier. We wanted those ordinary tiers where ordinary supporters gather as the most appropriate place to honour those players.
"The inductions will be in very small numbers, we're probably talking about two a year. Two footballers, two hurlers or one footballer and one hurler. It has to be made very, very special."
Paddy Downey, formerly GAA correspondent of The Irish Times, was one of the adjudicators and confirmed the widespread feeling that the task of selecting such a team wasn't an enviable one.
"It's nearly impossible because there's so many players, particularly in what you might call the big, central positions: midfield, centre-back, full back. Already people are saying to me: `why isn't Brian Mullins on, why isn't Paddy Kennedy of Kerry, Jack O'Shea - above all at the present time' and so on.
"We also had the problem of not picking a half-century team of people we had seen ourselves. You could also argue how could we pick someone we hadn't seen - Dick Fitzgerald, apparently one of the greatest players of all time, Paul Russell of Kerry, Jack Higgins of Kildare, from the earlier part of the century.
"I was conscious that we could have gone further back and taken the word of our predecessors in journalism who had praised these players and done so in print. Inevitably it came to be more a team of the second half of the century than the early years."
Martin O'Connell of Meath was the only player of what might roughly be called contemporary times - one whose career was largely after the selection of the 1984 Centenary Team - to earn a place.
"I was surprised," he said. "I didn't even know until I came up here. I arrived a bit late and Micheal O Muircheartaigh was just reading out the names. I was absolutely delighted."




The ballad is named after a crossroads between Ennis and Tulla in east Clare, the site of a centuries-old horse fair held every June. In 1870 a young man from the locality, Michael Considine, bade farewell to his sweetheart Mary McNamara and left for the US. He hoped to earn sufficient money to enable her to join him.
However, he died in California in 1873. Before his death he wrote a poem dedicated to Mary which he posted to his six-year-old nephew, John, back home.
Seventy years later McMahon was given the words at a house party. His singing of the ballad was warmly received by those in attendance, who included the author’s nephew, then an elderly man.
Many singers have recorded the ballad, but McMahon insisted his was the authentic version. He told The Irish Times in 2006: “Nowadays the song is not sung correctly. Many singers put words that are not in it [at] all, singing stuff like ‘Johnny, I love you still’. There’s no ‘Johnny’ in that song.” The late writer Bryan MacMahon was an early admirer of his namesake’s talent and had high praise for his ability as a performer and entertainer.
Singer Maura O’Connell warmed to Robbie McMahon’s “great big personality”, and said that he made Spancil Hill his own.
Born in 1926, he was the third youngest of 11 children, one of whom died in childhood, and grew up on his father’s farm in Clooney, near Ennis. There was music in the family, and all the children sang. Young Robbie was something of a mischief-maker, hence the title of an album he recorded later in life – The Black Sheep.
He began singing in public at the age of 18, and went on to win 16 all-Ireland titles at fleadhanna around the country. In the 1950s, 1960s and 1970s he toured Britain and the US with a troupe of traditional musicians under the auspices of Comhaltas Ceoltóirí Éireann.
As a songwriter, he is best known for the Fleadh Down in Ennis, which celebrates the 1956 all-Ireland fleadh cheoil. Other compositions include Come on the Banner, the Red Cross Social and the Feakle Hurlers, in honour of the 1988 Clare county champions.
A lilter, he was renowned for his performance of the Mason’s Apron, in which he simulated the sound of both the fiddle and accompanying banjo.
Possessed of a store of jokes, ranging from the hilarious to the unprintable, he was as much a character as a singer and was more comfortable with the craic and banter of casual sessions than with formal concerts.
He was the subject of a film documentary Last Night As I Lay Dreaming. Clare County Council hosted a civic reception in his honour in 2010, and he was the recipient of the Fleadh Nua Gradam Ceoil in 2011.
He is survived by his wife Maura, daughters Fiona, Noleen and Dympna and son Donal.


|
|



n 1863, Joseph Causton and his son, also named Joseph, developed the printing company which was to become the large and well known Joseph Causton & Sons Limited.
In 1867 the company was described as being a wholesale stationer and printer with a large warehouse at Southwark Street, London.
Joseph Causton was also a politician. He became a Councillor for Billingsgate, East London in 1868 and later Sheriff for London and Middlesex. The pinnacle of his career came when Queen Victoria opened Blackfriars Bridge and Holburn Viaduct in 1869 and he was knighted at Windsor Castle to mark the event. The company name now became Sir Joseph Causton & Sons Limited. Sir Joseph died just two years later but his sons, Joseph, Richard and James continued as partners of the firm.
The company moved to a large new printing works in Eastleigh, Hampshire in the 1930s. The printing works made labels for household brands including Marmite and Guiness. During The Second World War they printed secret maps for the government in a specially bricked off part of the building.
By the end of the 1960s Sir Joseph Causton & Sons Limited fortunes were in decline. In the mid 1970s the company was losing money but it was not until 1984 that the firm was taken over by Norton Opex. They in turn were acquired by Bowater and Sir Joseph Causton and Sons ceased trading.
The Causton name has survived only as Causton Envelopes Limited and Causton Cartons, which is a subsidiary of the Bowater Group, manufacturing cartons for the pharmaceutical industry.