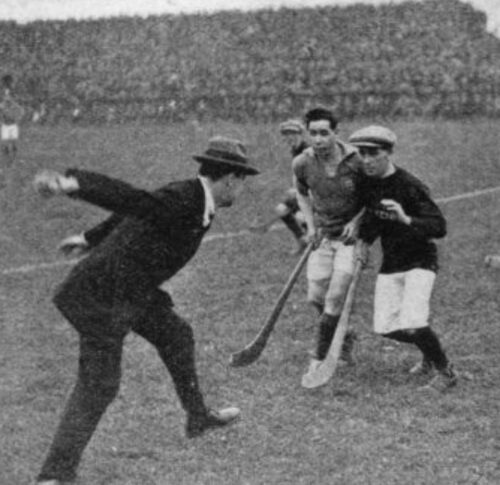
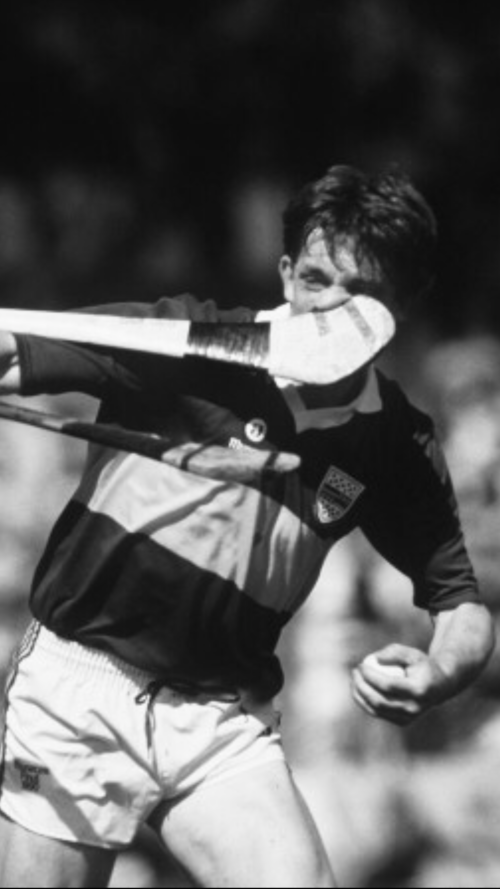
Marvellous photograph taken from the 1970s in a bar in Ballylongford Co Kerry as the locals celebrate the return of the magnificent Sam Maguire trophy,presenred to the winners of the All Ireland Football Championship every year.
25cm x 25cm Ballylongford Co Kerry
The
Sam Maguire Cup, often referred to as
Sam or
The Sam (
Irish:
Corn Sam Mhic Uidhir), is a trophy awarded annually by the
Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA) to the team that wins the
All-Ireland Senior Football Championship, the main competition in the
medieval sport of
Gaelic football. The Sam Maguire Cup was first presented to the winners of the
1928 All-Ireland Senior Football Championship Final. The original 1920s trophy was retired in the 1980s, with a new identical trophy awarded annually since 1988.
The GAA organises the series of games, which are played during the summer months. The All-Ireland Football Final was traditionally played on the third or fourth Sunday in September at
Croke Park in
Dublin. In 2018, the GAA rescheduled its calendar and since then the fixture has been played in early September
Old trophy
The original Sam Maguire Cup commemorates the memory of
Sam Maguire, an influential figure in the
London GAA and a former footballer.
A group of his friends formed a committee in
Dublin under the chairmanship of Dr
Pat McCartan from
Carrickmore,
County Tyrone, to raise funds for a permanent commemoration of his name. They decided on a cup to be presented to the GAA. The Association were proud to accept the Cup. At the time it cost £300. In today's terms that sum is equivalent to €25,392. The commission to make it was given to Hopkins and Hopkins, a jewellers and watchmakers of O'Connell Bridge, Dublin.
The silver cup was crafted, on behalf of Hopkins and Hopkins, by the silversmith Matthew J. Staunton of D'Olier Street, Dublin. Maitiú Standun, Staunton's son, confirmed in a letter printed in the Alive! newspaper in October 2003 that his father had indeed made the original Sam Maguire Cup back in 1928.
Matthew J. Staunton (1888–1966) came from a long line of silversmiths going back to the Huguenots, who brought their skills to Ireland in the 1600s. Matt, as he was known to his friends, served his time in the renowned Dublin silversmiths, Edmond Johnson Ltd, where the
Liam MacCarthy Hurling Cup was made in 1921.
The 1928 Sam Maguire Cup is a faithful model of the Ardagh Chalice. The bowl was not spun on a spinning lathe but hand-beaten from a single flat piece of silver. Even though it is highly polished, multiple hammer marks are still visible today, indicating the manufacturing process.
It was first presented in 1928 - to the
Kildare team that defeated
Cavan by one point in
that year's final.
It was the only time Kildare won old trophy. They have yet to win the new trophy, coming closest in
1998, when Galway defeated them by four points in that year's final.
Kerry won the trophy on the most occasions. They were also the only team to win it on four consecutive occasions, achieving the feat twice -first during the late-1920s and early-1930s (1929, 1930, 1931, 1932), and later during the late-1970s and early 1980s (1978, 1979, 1980, 1981).
In addition, Kerry twice won the old trophy on three consecutive occasions, in the late 1930s and early-1940s (1939, 1940, 1941) and in the mid-1980s (1984, 1985, 1986). They also won it on two consecutive occasions in the late-1960s and early-1970s (1969, 1970).
Galway won the old trophy on three consecutive occasions in the mid-1960s (1964, 1965, 1966).
Roscommon won the old trophy on two consecutive occasions during the mid-1940s (1943, 1944), as did
Cavan later that decade (1947, 1948).
Mayo won the old trophy on two consecutive occasions during the early-1950s (1950, 1951), while
Down did likewise in the early-1960s (1960, 1961).
Offaly won the old trophy on two consecutive occasions during the early 1970s (1971, 1972), while
Dublin did likewise later that decade (1976, 1977).
Six men won the old trophy twice as
captain:
Joe Barrett of Kerry,
Jimmy Murray of Roscommon,
John Joe O'Reilly of Cavan,
Seán Flanagan of Mayo,
Enda Colleran of Galway and
Tony Hanahoeof Dublin.
The original trophy was retired in 1988 as it had received some damage over the years. It is permanently on display in the GAA Museum at Croke Park.

Original 1928 Sam Maguire Cup on display in the GAA Museum at
Croke Park
New trophy
The GAA commissioned a replica from Kilkenny-based silversmith Desmond A. Byrne and the replica is the trophy that has been used ever since. The silver for the new cup was donated by Johnson Matthey Ireland at the behest of Kieran D. Eustace Managing Director, a native of Newtowncashel Co. Longford .
Meath's Joe Cassells was the first recipient of "Sam Óg". Meath have the distinction of being the last team to lift the old Sam Maguire and the first team to lift the new one following their back-to-back victories in 1987 and 1988.
Cork won the new trophy on consecutive occasions in the late-1980s and early-1990s (1989, 1990), while Kerry did likewise during the mid-2000s (2006, 2007).
Dublin are the only team to win the new trophy on more than two consecutive occasions, achieving a historic achievement of five-in-a-row during the second half of the 2010s (2015, 2016, 2017, 2018 and 2019).
Stephen Cluxton of Dublin is the only captain to have won the new trophy six times as
captain, doing so in 2013, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018 and 2019. No other person as ever won either the old or new trophy as captain more than twice. Two other men have won the new trophy twice as captain:
Declan O'Sullivan of Kerry and
Brian Dooher of Tyrone.
In 2010, the GAA asked the same silversmith to produce another replica of the trophy (the third Sam Maguire Cup) although this was to be used only for marketing purposes.
Winners
Old Trophy
- Kerry – 1929, 1930, 1931, 1932, 1937, 1939, 1940, 1941, 1946, 1953, 1955, 1959, 1962, 1969, 1970, 1975, 1978, 1979, 1980, 1981, 1984, 1985, 1986
- Dublin – 1942, 1958, 1963, 1974, 1976, 1977, 1983
- Galway – 1934, 1938, 1956, 1964, 1965, 1966
- Cavan – 1933, 1935, 1947, 1948, 1952
- Meath – 1949, 1954, 1967, 1987
- Mayo – 1936, 1950, 1951
- Down – 1960, 1961, 1968
- Offaly – 1971, 1972, 1982
- Roscommon – 1943, 1944
- Cork – 1945, 1973
- Kildare – 1928
- Louth – 1957
New Trophy
- Dublin – 1995, 2011, 2013, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018, 2019
- Kerry – 1997, 2000, 2004, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2014
- Meath – 1988, 1996, 1999
- Cork – 1989, 1990, 2010
- Tyrone – 2003, 2005, 2008
- Down – 1991, 1994
- Donegal – 1992, 2012
- Galway – 1998, 2001
- Derry – 1993
- Armagh – 2002
 Toners won “Snug of the Year” 2010, a competition hosted by Powers Whiskey. 110 pubs across Ireland were shortlisted, and after counting the public’s votes Toners was announced the winner. A snug is a private area separated within a pub and is a timeless feature in a traditional Irish pub. Like the one in Toners, it typically has its own door, a rugged bench and is completely private. Back in the day it was where the likes of policemen, lovers and the Irish literati met up.
Toners won “Snug of the Year” 2010, a competition hosted by Powers Whiskey. 110 pubs across Ireland were shortlisted, and after counting the public’s votes Toners was announced the winner. A snug is a private area separated within a pub and is a timeless feature in a traditional Irish pub. Like the one in Toners, it typically has its own door, a rugged bench and is completely private. Back in the day it was where the likes of policemen, lovers and the Irish literati met up.