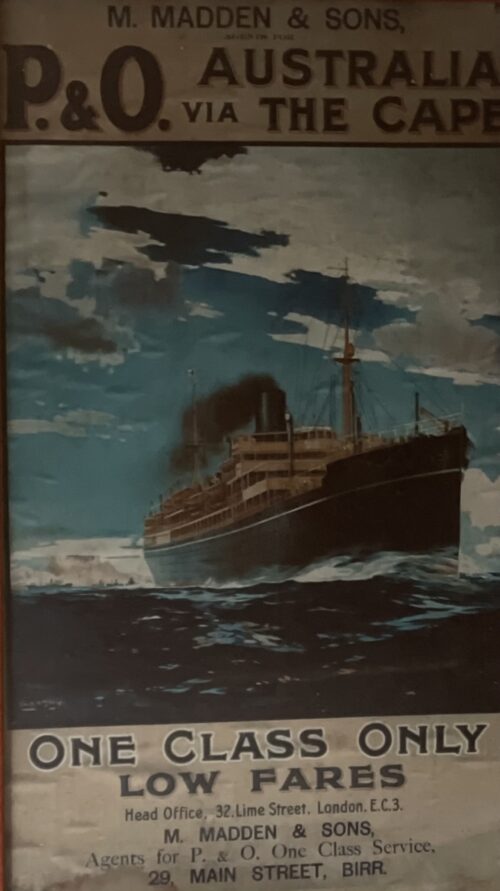
Early years and expansion: 1822–1900










There is nothing to prevent the other twenty-eight counties from calling into existence citizen forces to hold Ireland "for the Empire". It was precisely with this object that the Volunteers of 1782 were enrolled, and they became the instrument of establishing Irish self-government.After the article was published, Hobson asked The O'Rahilly to see MacNeill, to suggest to him that a conference should be called to make arrangements for publicly starting the new movement.The article "threw down the gauntlet to nationalists to follow the lead given by Ulster unionists."MacNeill was unaware of the detailed planning which was going on in the background, but was aware of Hobson's political leanings. He knew the purpose as to why he was chosen, but he was determined not to be a puppet.
| Portfolio | Name | Organisation | Political Party |
|---|---|---|---|
| Honorary Secretaries | Eoin Mac Néill | Gaelic League | |
| Laurence Kettle | Ancient Order of Hibernians | Irish Parliamentary Party | |
| Honorary Treasurers | The O'Rahilly | Gaelic League | Sinn Féin |
| John Gore | Ancient Order of Hibernians | Irish Parliamentary Party |
What if conscription be enforced on Ireland? What if a Unionist or a Coalition British Ministry repudiates the Home Rule Act? What if it be determined to dismember Ireland? The future is big with these and other possibilities.After the departure of Redmond and his followers, the Volunteers adopted a constitution, which had been drawn up by the earlier provisional committee, and was ratified by a convention of 160 delegates on 25 October 1914. It called for general council of fifty members to meet monthly, as well as an executive of the president and eight elected members. In December a headquarters staff was appointed, consisting of Eoin MacNeill as chief of staff, The O'Rahilly as director of arms, Thomas MacDonagh as director of training, Patrick Pearse as director of military organisation, Bulmer Hobson as quartermaster, and Joseph Plunkett as director of military operations. The following year they were joined by Éamonn Ceannt as director of communications and J.J. O'Connell as chief of inspection. This reorganisation put the IRB is a stronger position, as four important military positions (director of training, director of military organisation, director of military operations, and director of communications) were held by men who were, or would soon be, members of the IRB, and who later become four of the seven signatories of the Easter Proclamation. (Hobson was also an IRB member, but had a falling out with the leadership after he supported Redmond's appointees to the provisional council, and hence played little role in the IRB thereafter.)
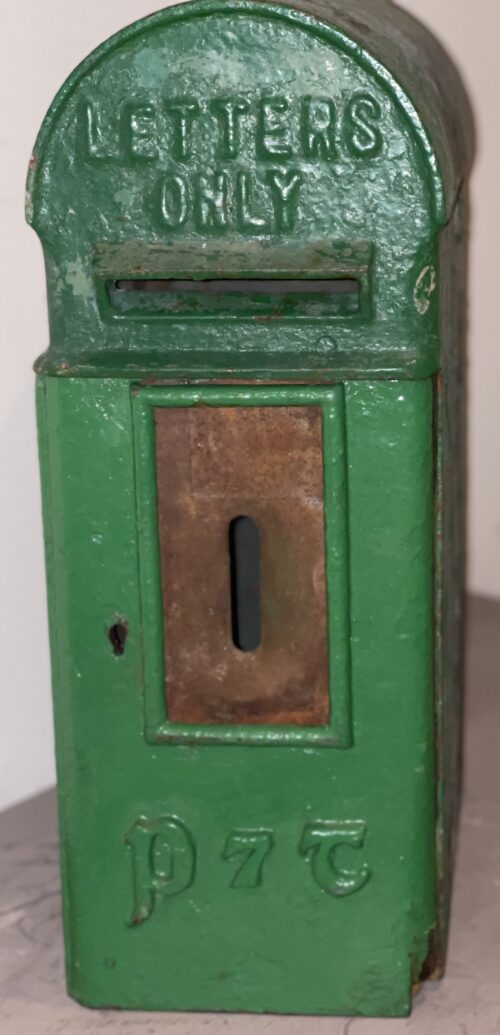






















The first act of the Irish Free State after independence was to paint all the post boxes throughout the country green. It was a brilliant stroke – royal red replaced by emerald green in one of the most visible and ubiquitous symbols of national administration.
Ironically, the post boxes themselves did not change, so the royal insignias were simply over-painted by the new colour. The result was a charming mixture of tradition and adaptation that serves as an ongoing reminder of the history of Ireland and its institutions.

The first post boxes were introduced to Ireland in the 1850s by the novelist Anthony Trollope, then a Surveyor for the Post Office. Trollope was happy in Ireland and wrote several novels and stories set here, although they are not the works for which he is most remembered.
One of the earliest models for a free-standing post box came to be known as the Penfold, after its designer, J W Penfold. They were manufactured and deployed from 1866 to 1879 and very few have survived in Ireland to this day – only six are known and of these only three are still in operation. Skibbereen has one of those, and very fine it is: one hundred and fifty years old and still in daily use!
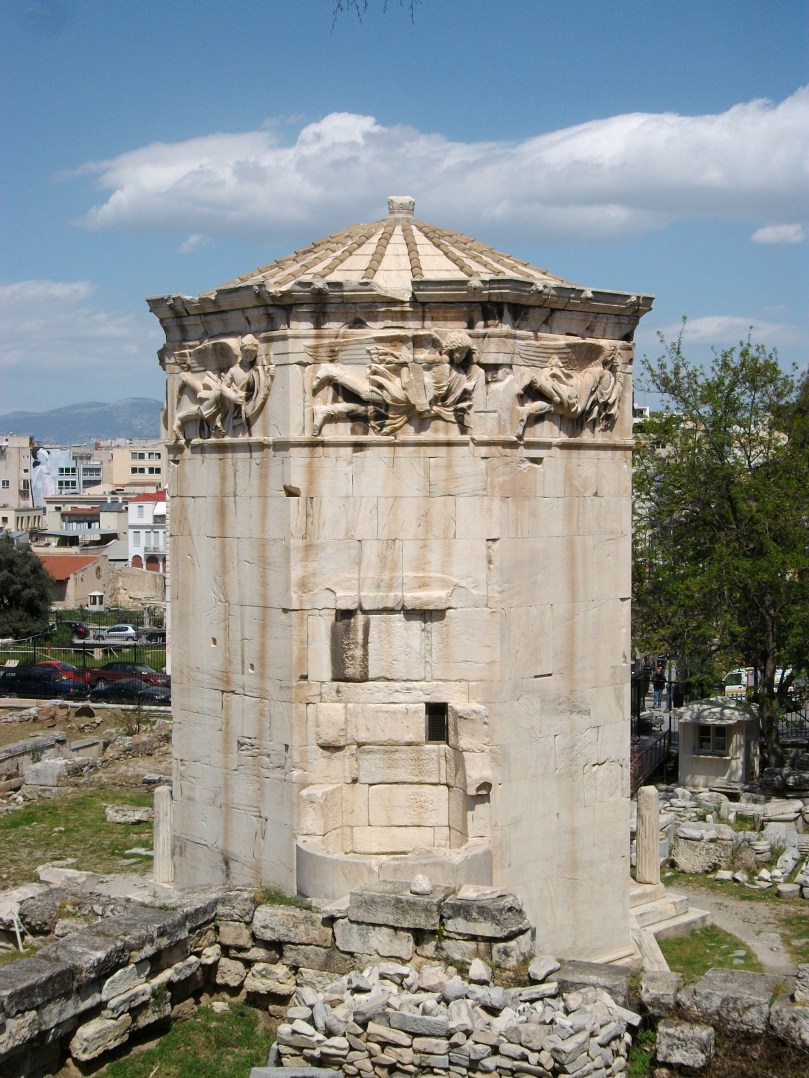
The hexagonal Penfold designed was apparently inspired by the Temple of the Winds in Athens (although the Temple is octagonal), with the addition of an acanthus leaf on the cap and a smart bud-shaped finial and beading.

Our Skibbereen Penfold is in excellent condition: note the royal insignia and the entwined VR for Victoria Regina.
The Penfolds were replaced by round pillar boxes because there were too many complaints that the hexagonal design caused letters to stick. These cylindrical boxes can be seen everywhere in Ireland still, although mostly in towns and cities. The one below is on Grand Parade in Cork.
In his book The Irish Post Box, which I gratefully acknowledge as the source of much of the information in this blog post, Stephen Ferguson describes the three main types of post boxes that have been developed for use in Ireland: pillar, wall and lamp. In rural areas, such as West Cork, wall and lamp boxes are the most common forms I have encountered.
Here’s a representative wall box in Skibbereen. Interestingly, it’s part of a mini-complex of historical markers including the plaque to the Clerke sisters (see my posts From Skibbereen to the Moon Part 1 and Part 2 for more about these remarkable women and their family) and signs for the Skibbereen heritage walking trail, all mounted together on the wall of what was the main bank in Skibbereen during the Famine period.
The box was manufactured by W T Allen and Co of London and bears the ornately scrolled insignia and crown of Edward the VII, which places it between 1901 to 1910.
Here’s another nice one in Bantry, a Victorian one, although this time the VR lettering is simpler than on the Penfold. This one has been painted so often that the embossed POST OFFICE on the protective hood has almost disappeared under the layers.
Lamp boxes were designed for remote areas where a suitable wall might not be readily available. Ferguson explains:
Lamp post boxes, based on a design used by the United States Postal Service, were first introduced in 1896 in London as a response to calls for more post boxes throughout the city. Affixed to a street lamp, the boxes were used at locations where the expense of a pillar or wall box could not be justified. In Ireland, however, they were often deployed in rural areas where, attached to a telegraph or specially erected pole by metal clips, they were very useful in extending postal collections to remote and sparsely populated regions. Tucked under hedges or used sometimes as a smaller version of a wall box, these post boxes were relatively cheap to make and easy to install and they symbolise…the extraordinary influence and reach of the Post Office as an institution at the height of its powers.
Driving or walking around rural Ireland, look out for ‘lamp’ boxes. Here’s one from the road near Barley Cove.
 A closer inspection reveals this one bears the P & T logo that was in use between 1939 and 1984, before it was replaced by the brand ‘An Post’. Sometimes the old royal initials were ground off the boxes, or sometimes the doors were replaced with new ones bearing the P&T lettering, but it seems that considerations of cost (always paramount with the careful Post Office) allowed many to simply remain in place as they were. In the early years of the new state, some were embossed with the Saorstát Éireann logo (even sharing the door with a VR insignia) but that practice was relatively short lived and I have found no examples to it yet in West Cork. The website Irish Postal History has this example from Washington Street in Cork.
A closer inspection reveals this one bears the P & T logo that was in use between 1939 and 1984, before it was replaced by the brand ‘An Post’. Sometimes the old royal initials were ground off the boxes, or sometimes the doors were replaced with new ones bearing the P&T lettering, but it seems that considerations of cost (always paramount with the careful Post Office) allowed many to simply remain in place as they were. In the early years of the new state, some were embossed with the Saorstát Éireann logo (even sharing the door with a VR insignia) but that practice was relatively short lived and I have found no examples to it yet in West Cork. The website Irish Postal History has this example from Washington Street in Cork.
If no lamp post or suitable pole existed, a simple stake was erected to which a box could be attached. Cape Clear Island didn’t get electricity until the 1970s, so this post box (above and below) must predate the advent of poles. The logo, however, is that of An Post, which was established as the new brand in 1984. Perhaps the poles were only erected island-wide after the submarine cable was laid in the 1990s.
Not all mail boxes have been retained for active use – so what happens to them? Many simply remain in situ, as a picturesque reminder of times when we actually wrote to each other instead of texting or emailing. The one below at Rossbrin, near Ballydehob, was once attached to the wall outside the old schoolhouse. The first photograph at the start of today’s post shows its location.
And this one, at Ahakista, has been repurposed as a wayside shrine.
But even if it’s still in use, sometimes a mail boxes can’t be used for its real purpose, but has more important work to do! I don’t know where this last photograph was taken or whose work this is – it was widely circulated on the internet – but I would be happy to credit the photographer if I knew who it was. Delighted to have this also as an example of a post box from the reign of George V, 1910 to 1936.


In a unique way, it has created a sense of community among Irish people both at home and abroad.The GAA provided enormous pleasure to millions of people of all generations. The Taoiseach reflects on the important role the GAA has played in Irish culture reflected in the way people live, work and play. The sports of hurling and football are a major strand in the culture of Ireland. The impact that the GAA has on Irish life is far stronger than politics.
No political event nowadays can assemble eighty thousand people filled with passion and excitement in one place.Garret FitzGerald describes hurling as the game of the heroic age and it is appropriate that the GAA Congress in the centenary year should be held in Cú Chulainn’s Ulster. A hundred years ago, Gaelic sports were under threat of dying out and the GAA turned this threat around by making the games an integral part of Irish life again. Nine years after the establishment of the GAA, Eoin MacNeill and Douglas Hyde followed in the footsteps of Michael Cusack and founded the Gaelic League in 1893. The establishment of both organisations ensured that both the Irish language and games survived. The Taoiseach applauds the thousands of volunteers who have made the work of the GAA possible.
May your work prosper and may this dimension of Irish culture that you cherish be as full of vitality a century hence as it is in this centenary year.The GAA Centenary Taoiseach Special Message was broadcast on 22 April 1984.


 62cm x 45cm
An absolute once off piece of Irish Memorabilia .We at the Irish Pub Emporium were so lucky to acquire from a private collector .These superb castiron road signs were commissioned by the Irish Free State in the late 1940s post and were initially the responsibility of the newly formed Irish Tourism Organisation -Fógra Failte (later to become Bord Failte and then Failte Ireland).
"The former 'fingerpost' style of Irish directional signs can still be seen in many rural areas of the Republic of Ireland. These signs differ from their modern-day equivalent as they have black raised text on a white background. Destinations are in all caps (the placename in Irish was on top and in a smaller font than the one in English). Sometimes, the former route number ("T" for trunk road, "L" for link road) can be seen, and the former Bord Fáilte logo can be seen on some (they had responsibility for signs for a time), as well as occasionally a harp. Distances on these signs are in miles.
This style of sign has become a common feature of many tourist images of Ireland and can be seen in some Irish pubs. However, they can be easily rotated, and have been done so on occasion and therefore are not completely reliable. While most examples of these signs still in situ are rural finger-posts, the advance directional sign of this era can still very occasionally be seen: this has a grey background, with the destinations in outlined, white-background boxes linked together with black lines, and the text is not raised on these, unlike on fingerposts. These signs, rare even when the system was in use, can be seen in some areas of Dún Laoghaire and Drogheda. These signs were prescribed under various regulations, with the final design prescribed under the Road Traffic Signs (Regulations) 1962.
Despite the new sign style being introduced in 1977, the design change was never legislated for (apart from a reference to the change to italics in 1989) and the old designs were repealed only under the 1997 regulations, 20 years later.
62cm x 45cm
An absolute once off piece of Irish Memorabilia .We at the Irish Pub Emporium were so lucky to acquire from a private collector .These superb castiron road signs were commissioned by the Irish Free State in the late 1940s post and were initially the responsibility of the newly formed Irish Tourism Organisation -Fógra Failte (later to become Bord Failte and then Failte Ireland).
"The former 'fingerpost' style of Irish directional signs can still be seen in many rural areas of the Republic of Ireland. These signs differ from their modern-day equivalent as they have black raised text on a white background. Destinations are in all caps (the placename in Irish was on top and in a smaller font than the one in English). Sometimes, the former route number ("T" for trunk road, "L" for link road) can be seen, and the former Bord Fáilte logo can be seen on some (they had responsibility for signs for a time), as well as occasionally a harp. Distances on these signs are in miles.
This style of sign has become a common feature of many tourist images of Ireland and can be seen in some Irish pubs. However, they can be easily rotated, and have been done so on occasion and therefore are not completely reliable. While most examples of these signs still in situ are rural finger-posts, the advance directional sign of this era can still very occasionally be seen: this has a grey background, with the destinations in outlined, white-background boxes linked together with black lines, and the text is not raised on these, unlike on fingerposts. These signs, rare even when the system was in use, can be seen in some areas of Dún Laoghaire and Drogheda. These signs were prescribed under various regulations, with the final design prescribed under the Road Traffic Signs (Regulations) 1962.
Despite the new sign style being introduced in 1977, the design change was never legislated for (apart from a reference to the change to italics in 1989) and the old designs were repealed only under the 1997 regulations, 20 years later. 

 61cm x 69cm
An absolute once off piece of Irish Memorabilia .We at the Irish Pub Emporium were so lucky to acquire from a private collector who has moved overseas.These superb castiron road signs were commissioned by the Irish Free State in the late 1940s post and were initially the responsibility of the newly formed Irish Tourism Organisation -Fógra Failte (later to become Bord Failte and then Failte Ireland).
"The former 'fingerpost' style of Irish directional signs can still be seen in many rural areas of the Republic of Ireland. These signs differ from their modern-day equivalent as they have black raised text on a white background. Destinations are in all caps (the placename in Irish was on top and in a smaller font than the one in English). Sometimes, the former route number ("T" for trunk road, "L" for link road) can be seen, and the former Bord Fáilte logo can be seen on some (they had responsibility for signs for a time), as well as occasionally a harp. Distances on these signs are in miles.
This style of sign has become a common feature of many tourist images of Ireland and can be seen in some Irish pubs. However, they can be easily rotated, and have been done so on occasion and therefore are not completely reliable. While most examples of these signs still in situ are rural finger-posts, the advance directional sign of this era can still very occasionally be seen: this has a grey background, with the destinations in outlined, white-background boxes linked together with black lines, and the text is not raised on these, unlike on fingerposts. These signs, rare even when the system was in use, can be seen in some areas of Dún Laoghaire and Drogheda. These signs were prescribed under various regulations, with the final design prescribed under the Road Traffic Signs (Regulations) 1962.
Despite the new sign style being introduced in 1977, the design change was never legislated for (apart from a reference to the change to italics in 1989) and the old designs were repealed only under the 1997 regulations, 20 years later.
61cm x 69cm
An absolute once off piece of Irish Memorabilia .We at the Irish Pub Emporium were so lucky to acquire from a private collector who has moved overseas.These superb castiron road signs were commissioned by the Irish Free State in the late 1940s post and were initially the responsibility of the newly formed Irish Tourism Organisation -Fógra Failte (later to become Bord Failte and then Failte Ireland).
"The former 'fingerpost' style of Irish directional signs can still be seen in many rural areas of the Republic of Ireland. These signs differ from their modern-day equivalent as they have black raised text on a white background. Destinations are in all caps (the placename in Irish was on top and in a smaller font than the one in English). Sometimes, the former route number ("T" for trunk road, "L" for link road) can be seen, and the former Bord Fáilte logo can be seen on some (they had responsibility for signs for a time), as well as occasionally a harp. Distances on these signs are in miles.
This style of sign has become a common feature of many tourist images of Ireland and can be seen in some Irish pubs. However, they can be easily rotated, and have been done so on occasion and therefore are not completely reliable. While most examples of these signs still in situ are rural finger-posts, the advance directional sign of this era can still very occasionally be seen: this has a grey background, with the destinations in outlined, white-background boxes linked together with black lines, and the text is not raised on these, unlike on fingerposts. These signs, rare even when the system was in use, can be seen in some areas of Dún Laoghaire and Drogheda. These signs were prescribed under various regulations, with the final design prescribed under the Road Traffic Signs (Regulations) 1962.
Despite the new sign style being introduced in 1977, the design change was never legislated for (apart from a reference to the change to italics in 1989) and the old designs were repealed only under the 1997 regulations, 20 years later. 

 55cm x 68cm
An absolute once off piece of Irish Memorabilia .We at the Irish Pub Emporium were so lucky to acquire from a private collector who has moved overseas.These superb castiron road signs were commissioned by the Irish Free State in the late 1940s post and were initially the responsibility of the newly formed Irish Tourism Organisation -Fógra Failte (later to become Bord Failte and then Failte Ireland).
"The former 'fingerpost' style of Irish directional signs can still be seen in many rural areas of the Republic of Ireland. These signs differ from their modern-day equivalent as they have black raised text on a white background. Destinations are in all caps (the placename in Irish was on top and in a smaller font than the one in English). Sometimes, the former route number ("T" for trunk road, "L" for link road) can be seen, and the former Bord Fáilte logo can be seen on some (they had responsibility for signs for a time), as well as occasionally a harp. Distances on these signs are in miles.
This style of sign has become a common feature of many tourist images of Ireland and can be seen in some Irish pubs. However, they can be easily rotated, and have been done so on occasion and therefore are not completely reliable. While most examples of these signs still in situ are rural finger-posts, the advance directional sign of this era can still very occasionally be seen: this has a grey background, with the destinations in outlined, white-background boxes linked together with black lines, and the text is not raised on these, unlike on fingerposts. These signs, rare even when the system was in use, can be seen in some areas of Dún Laoghaire and Drogheda. These signs were prescribed under various regulations, with the final design prescribed under the Road Traffic Signs (Regulations) 1962.
Despite the new sign style being introduced in 1977, the design change was never legislated for (apart from a reference to the change to italics in 1989) and the old designs were repealed only under the 1997 regulations, 20 years later.
55cm x 68cm
An absolute once off piece of Irish Memorabilia .We at the Irish Pub Emporium were so lucky to acquire from a private collector who has moved overseas.These superb castiron road signs were commissioned by the Irish Free State in the late 1940s post and were initially the responsibility of the newly formed Irish Tourism Organisation -Fógra Failte (later to become Bord Failte and then Failte Ireland).
"The former 'fingerpost' style of Irish directional signs can still be seen in many rural areas of the Republic of Ireland. These signs differ from their modern-day equivalent as they have black raised text on a white background. Destinations are in all caps (the placename in Irish was on top and in a smaller font than the one in English). Sometimes, the former route number ("T" for trunk road, "L" for link road) can be seen, and the former Bord Fáilte logo can be seen on some (they had responsibility for signs for a time), as well as occasionally a harp. Distances on these signs are in miles.
This style of sign has become a common feature of many tourist images of Ireland and can be seen in some Irish pubs. However, they can be easily rotated, and have been done so on occasion and therefore are not completely reliable. While most examples of these signs still in situ are rural finger-posts, the advance directional sign of this era can still very occasionally be seen: this has a grey background, with the destinations in outlined, white-background boxes linked together with black lines, and the text is not raised on these, unlike on fingerposts. These signs, rare even when the system was in use, can be seen in some areas of Dún Laoghaire and Drogheda. These signs were prescribed under various regulations, with the final design prescribed under the Road Traffic Signs (Regulations) 1962.
Despite the new sign style being introduced in 1977, the design change was never legislated for (apart from a reference to the change to italics in 1989) and the old designs were repealed only under the 1997 regulations, 20 years later. 

 45cm x 66cm
An absolute once off piece of Irish Memorabilia .We at the Irish Pub Emporium were so lucky to acquire from a private collector who has moved overseas.These superb castiron road signs were commissioned by the Irish Free State in the late 1940s post and were initially the responsibility of the newly formed Irish Tourism Organisation -Fógra Failte (later to become Bord Failte and then Failte Ireland).
"The former 'fingerpost' style of Irish directional signs can still be seen in many rural areas of the Republic of Ireland. These signs differ from their modern-day equivalent as they have black raised text on a white background. Destinations are in all caps (the placename in Irish was on top and in a smaller font than the one in English). Sometimes, the former route number ("T" for trunk road, "L" for link road) can be seen, and the former Bord Fáilte logo can be seen on some (they had responsibility for signs for a time), as well as occasionally a harp. Distances on these signs are in miles.
This style of sign has become a common feature of many tourist images of Ireland and can be seen in some Irish pubs. However, they can be easily rotated, and have been done so on occasion and therefore are not completely reliable. While most examples of these signs still in situ are rural finger-posts, the advance directional sign of this era can still very occasionally be seen: this has a grey background, with the destinations in outlined, white-background boxes linked together with black lines, and the text is not raised on these, unlike on fingerposts. These signs, rare even when the system was in use, can be seen in some areas of Dún Laoghaire and Drogheda. These signs were prescribed under various regulations, with the final design prescribed under the Road Traffic Signs (Regulations) 1962.
Despite the new sign style being introduced in 1977, the design change was never legislated for (apart from a reference to the change to italics in 1989) and the old designs were repealed only under the 1997 regulations, 20 years later.
45cm x 66cm
An absolute once off piece of Irish Memorabilia .We at the Irish Pub Emporium were so lucky to acquire from a private collector who has moved overseas.These superb castiron road signs were commissioned by the Irish Free State in the late 1940s post and were initially the responsibility of the newly formed Irish Tourism Organisation -Fógra Failte (later to become Bord Failte and then Failte Ireland).
"The former 'fingerpost' style of Irish directional signs can still be seen in many rural areas of the Republic of Ireland. These signs differ from their modern-day equivalent as they have black raised text on a white background. Destinations are in all caps (the placename in Irish was on top and in a smaller font than the one in English). Sometimes, the former route number ("T" for trunk road, "L" for link road) can be seen, and the former Bord Fáilte logo can be seen on some (they had responsibility for signs for a time), as well as occasionally a harp. Distances on these signs are in miles.
This style of sign has become a common feature of many tourist images of Ireland and can be seen in some Irish pubs. However, they can be easily rotated, and have been done so on occasion and therefore are not completely reliable. While most examples of these signs still in situ are rural finger-posts, the advance directional sign of this era can still very occasionally be seen: this has a grey background, with the destinations in outlined, white-background boxes linked together with black lines, and the text is not raised on these, unlike on fingerposts. These signs, rare even when the system was in use, can be seen in some areas of Dún Laoghaire and Drogheda. These signs were prescribed under various regulations, with the final design prescribed under the Road Traffic Signs (Regulations) 1962.
Despite the new sign style being introduced in 1977, the design change was never legislated for (apart from a reference to the change to italics in 1989) and the old designs were repealed only under the 1997 regulations, 20 years later. 
 61cm x 69cm
An absolute once off piece of Irish Memorabilia .We at the Irish Pub Emporium were so lucky to acquire from a private collector who has moved overseas.These superb castiron road signs were commissioned by the Irish Free State in the late 1940s post and were initially the responsibility of the newly formed Irish Tourism Organisation -Fógra Failte (later to become Bord Failte and then Failte Ireland).
"The former 'fingerpost' style of Irish directional signs can still be seen in many rural areas of the Republic of Ireland. These signs differ from their modern-day equivalent as they have black raised text on a white background. Destinations are in all caps (the placename in Irish was on top and in a smaller font than the one in English). Sometimes, the former route number ("T" for trunk road, "L" for link road) can be seen, and the former Bord Fáilte logo can be seen on some (they had responsibility for signs for a time), as well as occasionally a harp. Distances on these signs are in miles.
This style of sign has become a common feature of many tourist images of Ireland and can be seen in some Irish pubs. However, they can be easily rotated, and have been done so on occasion and therefore are not completely reliable. While most examples of these signs still in situ are rural finger-posts, the advance directional sign of this era can still very occasionally be seen: this has a grey background, with the destinations in outlined, white-background boxes linked together with black lines, and the text is not raised on these, unlike on fingerposts. These signs, rare even when the system was in use, can be seen in some areas of Dún Laoghaire and Drogheda. These signs were prescribed under various regulations, with the final design prescribed under the Road Traffic Signs (Regulations) 1962.
Despite the new sign style being introduced in 1977, the design change was never legislated for (apart from a reference to the change to italics in 1989) and the old designs were repealed only under the 1997 regulations, 20 years later.
61cm x 69cm
An absolute once off piece of Irish Memorabilia .We at the Irish Pub Emporium were so lucky to acquire from a private collector who has moved overseas.These superb castiron road signs were commissioned by the Irish Free State in the late 1940s post and were initially the responsibility of the newly formed Irish Tourism Organisation -Fógra Failte (later to become Bord Failte and then Failte Ireland).
"The former 'fingerpost' style of Irish directional signs can still be seen in many rural areas of the Republic of Ireland. These signs differ from their modern-day equivalent as they have black raised text on a white background. Destinations are in all caps (the placename in Irish was on top and in a smaller font than the one in English). Sometimes, the former route number ("T" for trunk road, "L" for link road) can be seen, and the former Bord Fáilte logo can be seen on some (they had responsibility for signs for a time), as well as occasionally a harp. Distances on these signs are in miles.
This style of sign has become a common feature of many tourist images of Ireland and can be seen in some Irish pubs. However, they can be easily rotated, and have been done so on occasion and therefore are not completely reliable. While most examples of these signs still in situ are rural finger-posts, the advance directional sign of this era can still very occasionally be seen: this has a grey background, with the destinations in outlined, white-background boxes linked together with black lines, and the text is not raised on these, unlike on fingerposts. These signs, rare even when the system was in use, can be seen in some areas of Dún Laoghaire and Drogheda. These signs were prescribed under various regulations, with the final design prescribed under the Road Traffic Signs (Regulations) 1962.
Despite the new sign style being introduced in 1977, the design change was never legislated for (apart from a reference to the change to italics in 1989) and the old designs were repealed only under the 1997 regulations, 20 years later. 





























| John Mary Lynch (15 August 1917 – 20 October 1999), known as Jack Lynch, was an Irish Fianna Fáil politician who served as Taoiseach from 1966 to 1973 and 1977 to 1979, Leader of Fianna Fáil from 1966 to 1979, Leader of the Opposition from 1973 to 1977, Minister for Finance from 1965 to 1966, Minister for Industry and Commerce from 1959 to 1965, Minister for Education 1957 to 1959, Minister for the Gaeltacht from March 1957 to June 1957, Parliamentary Secretary to the Minister for Lands and Parliamentary Secretary to the Government from 1951 to 1954. He served as a Teachta Dála (TD) from 1948 to 1981. | |






Born - March 11, 1858 Died - May 3, 1916
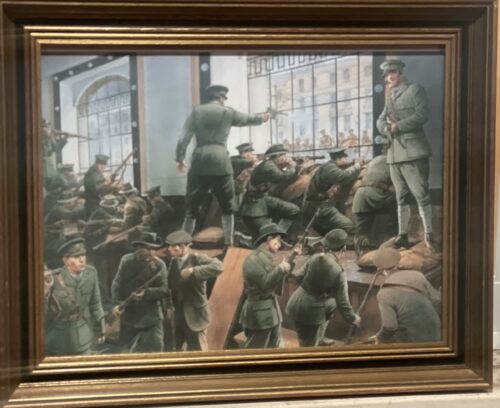
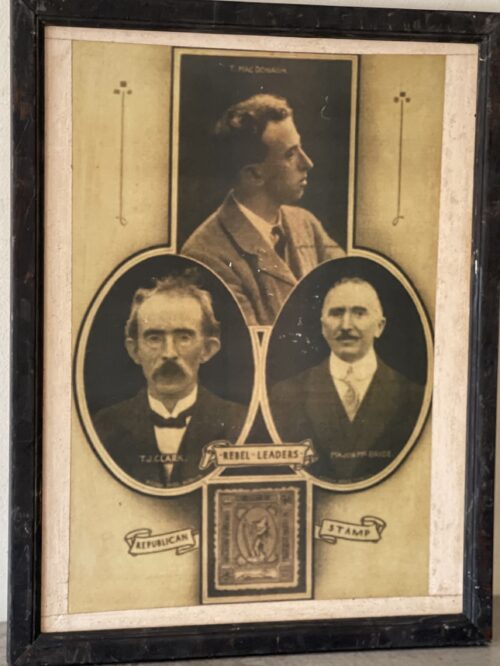
The first signatory on the 1916 Proclamation was Thomas Clarke, who joined the IRB, or the Fenians, in 1878 and with his protégé Seán Mac Diarmada effectively ran it in the run-up to the Rising. In 1915 they formed a Military Committee to plan a rebellion, later adding Pearse, Eamonn Ceannt, Joseph Mary Plunkett, Connolly and Thomas MacDonagh. Though three times the age of some Irish Volunteers, Clarke fought in the GPO throughout Easter Week. He was executed by firing squad on May 3rd, 1916, at the age of 59.Born - February 1, 1878 Died - May 3, 1916
Born in 1878 at Cloughjordan, Co Tipperary, MacDonagh attended Rockwell College and followed his parents into teaching. During a trip to the Aran Islands he met Pearse and the two became friends. A poet like Pearse, he became the first teacher on the staff of St Enda’s. With Joseph Plunkett he edited the Irish Review and helped Edward Martyn to found the Irish Theatre in 1914. He joined the Irish Volunteers in November 1913 and in 1915 the IRB. He was drafted on to the military council a few weeks before the Rising. He was in command of the Jacob’s factory garrison on Bishop Street (now the National Archives) during the Rising. A signatory of the Proclamation, he was executed on May 3rd 1916.Born - May 07, 1868 Died - May 05, 1916
“A drunken vainglorious lout,” is the poet William Butler Yeats’s famous description of Major John MacBride. Yeats may have been motivated by jealousy as MacBride had been married to Maud Gonne, the great love of the poet’s life. MacBride was a nationalist hero before the Easter Rising for his part in commanding the Irish Brigade which fought with the Boers in South Africa. He was not even supposed to be in the Rising, but chanced upon it while on his way to meet his brother. He was appointed second-in-command by Thomas MacDonagh at Jacob’s factory. Many historians believe he was executed not for his fairly minor part in the Rising, but for his actions with the Boers. His son, Séan MacBride, went on to win the Nobel Peace Prize.

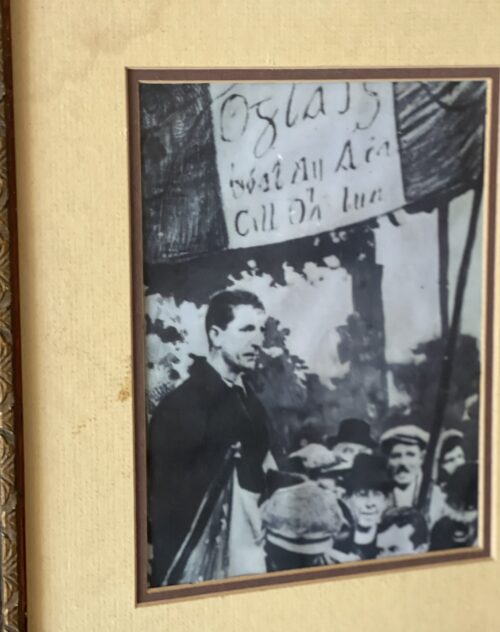
"...we took the action deliberately, having thought over the matter and talked it over between us. [Seán] Treacyhad stated to me that the only way of starting a war was to kill someone, and we wanted to start a war, so we intended to kill some of the police whom we looked upon as the foremost and most important branch of the enemy forces ... The only regret that we had following the ambush was that there were only two policemen in it, instead of the six we had expected..."During the conflict, the British put a £1,000 price on Breen's head, which was later raised to £10,000.He quickly established himself as a leader within the Irish Republican Army (IRA). He was known for his courage. On 13 May 1919, he helped rescue his comrade Seán Hogan at gunpoint from a heavily guarded train at Knocklong station in County Limerick. Breen, who was wounded, remembered how the battalion was "vehemently denounced as a cold-blooded assassins" and roundly condemned by the Catholic Church. After the fight, Seán Treacy, Séumas Robinson and Breen met Michael Collins in Dublin, where they were told to escape from the area. They agreed they would "fight it out, of course". Breen and Treacy shot their way out through a British military cordon in the northern suburb of Drumcondra (Fernside). They escaped, only for Treacy to be killed the next day. Breen was shot at least four times, twice in the lung. The British reaction was to make Tipperary a 'Special Military Area', with curfews and travel permits. Volunteer GHQ authorised enterprising attacks on barracks. Richard Mulcahy noted that British policy had "pushed rather turbulent spirits such as Breen and Treacy into the Dublin area". The inculcation of the principles of guerrilla warfare was to become an essential part of all training. They joined Collins' Squad of assassins, later known as the Dublin Guard, when Tipperary became "too hot for them". and Dublin was the centre of the war. Breen was present in December 1919 at the ambush in Ashtown beside Phoenix Park in Dublin where Martin Savage was killed while trying to assassinate the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland, Viscount French. The IRA men hid behind hedges and a dungheap as the convoy of vehicles came past. They had been instructed to ignore the first car, but this contained their target, Lord French. Their roadblock failed as a policeman removed the horse and cart intended to stop the car. Breen rejected the Anglo-Irish Treaty, which made him, like many others, angry and embittered:
I would never have handled a gun or fired a shot… to obtain this Treaty… writing on the second anniversary of Martin Savage's death, do you suppose that he sacrificed his life in attempting to kill one British Governor-General to make room for another British Governor-General?Regarding the continued existence of Northern Ireland from 1922, and an inevitable further war to conquer it to create a united Ireland, Breen commented: