-

 55cm x66cm Swords Co Dublin Experience the best of Ireland touring by car and golf at Portmarnock.Beautiful 1930s advertising print extolling the delights of visiting Ireland,drinking Jameson Whiskey and playing golf at the many wonderful courses in the country especially the famous links featured here,Portmarnock in North Co Dublin,presumably not all at the same time !The famous Jameson distillery in Bow Street in the heart of the city is also featured in this fine portrayal of that era in Dublin which is beautifully showcased in an ornate gold frame. The Jameson House, (‘St Marnock’s’) In the 1840s, the distiller, John Jameson acquired nearly 600 acres of land at Burrow, Portmarnock, buying out most of the small-holders there. He built a residence, which overlooked the ruins of the ancient church of St Marnock, after whom he named his house. Keenly interested in golf, he laid out a rudimentary course near the house. Following a fire in 1894, considerable renovation and extension was carried out. An inscription in stone over the original front-door of the house commemorates that work. Nearby was stabling for horses, coach-houses and farm buildings (in the area of the modern office park, ‘The Stables’). An avenue enclosed by iron railings, which survived until the late twentieth century, led from an entrance at South Lodge to the main house. Both gate lodges (‘North’ and ‘South’) have survived, with their distinctive design and (probably) local Plunkett brickwork. The amenities enjoyed by the Jamesons from their country mansion included sailing, shooting and horse-riding. The family’s considerable influence on Portmarnock included the establishment of the first local National School on Jameson land. The last of the family here, William George Jameson, was best known for his race-horses, his yachting prowess, and his association with high-society and royalty, including the future King Edward V11. After his death in1939, the house was sold and it has since been used as a hotel. Jameson and the fledging Irish Tourism Board partnered up in terms of selling both the country and a rising brand of Irish Whiskey from the 1930s onwards and a series of adverts ensued.This is a quaint and delightful reminder of times gone by. John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it maintained for four consecutive years.
55cm x66cm Swords Co Dublin Experience the best of Ireland touring by car and golf at Portmarnock.Beautiful 1930s advertising print extolling the delights of visiting Ireland,drinking Jameson Whiskey and playing golf at the many wonderful courses in the country especially the famous links featured here,Portmarnock in North Co Dublin,presumably not all at the same time !The famous Jameson distillery in Bow Street in the heart of the city is also featured in this fine portrayal of that era in Dublin which is beautifully showcased in an ornate gold frame. The Jameson House, (‘St Marnock’s’) In the 1840s, the distiller, John Jameson acquired nearly 600 acres of land at Burrow, Portmarnock, buying out most of the small-holders there. He built a residence, which overlooked the ruins of the ancient church of St Marnock, after whom he named his house. Keenly interested in golf, he laid out a rudimentary course near the house. Following a fire in 1894, considerable renovation and extension was carried out. An inscription in stone over the original front-door of the house commemorates that work. Nearby was stabling for horses, coach-houses and farm buildings (in the area of the modern office park, ‘The Stables’). An avenue enclosed by iron railings, which survived until the late twentieth century, led from an entrance at South Lodge to the main house. Both gate lodges (‘North’ and ‘South’) have survived, with their distinctive design and (probably) local Plunkett brickwork. The amenities enjoyed by the Jamesons from their country mansion included sailing, shooting and horse-riding. The family’s considerable influence on Portmarnock included the establishment of the first local National School on Jameson land. The last of the family here, William George Jameson, was best known for his race-horses, his yachting prowess, and his association with high-society and royalty, including the future King Edward V11. After his death in1939, the house was sold and it has since been used as a hotel. Jameson and the fledging Irish Tourism Board partnered up in terms of selling both the country and a rising brand of Irish Whiskey from the 1930s onwards and a series of adverts ensued.This is a quaint and delightful reminder of times gone by. John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it maintained for four consecutive years. -

 62cm x 62cm approx A real rarity here in the octagonal shape of a vintage Ireland Inland Waterways Cast-iron Sign denoting the river Shannon & Limerick.This most unusual find has been carefully restored and repainted and will make a most suitable exhibit for the most discerning Irish bar with Limerick /River Shannon affiliations.Please contact us directly at irishpubemporium@gmail.com or at 00353 878393200 to discuss.
62cm x 62cm approx A real rarity here in the octagonal shape of a vintage Ireland Inland Waterways Cast-iron Sign denoting the river Shannon & Limerick.This most unusual find has been carefully restored and repainted and will make a most suitable exhibit for the most discerning Irish bar with Limerick /River Shannon affiliations.Please contact us directly at irishpubemporium@gmail.com or at 00353 878393200 to discuss. -

 Very rare and much sought after Tullamore Dew advert featuring the greatest greyhound in racing history,Mick the Miller.Mick the Miller was bred in Co Offaly,the same county as the location of the Tullamore Dew distillery, hence the pride on the connection. 45cm x 90cm Banagher Co Offaly Tullamore D.E.W. is a brand of Irish whiskey produced by William Grant & Sons. It is the second largest selling brand of Irish whiskey globally, with sales of over 950,000 cases per annum as of 2015.The whiskey was originally produced in the Tullamore, County Offaly, Ireland, at the old Tullamore Distillery which was established in 1829. Its name is derived from the initials of Daniel E. Williams (D.E.W.), a general manager and later owner of the original distillery. In 1954, the original distillery closed down, and with stocks of whiskey running low, the brand was sold to John Powers & Son, another Irish distiller in the 1960s, with production transferred to the Midleton Distillery, County Cork in the 1970s following a merger of three major Irish distillers.In 2010, the brand was purchased by William Grant & Sons, who constructed a new distillery on the outskirts of Tullamore. The new distillery opened in 2014, bringing production of the whiskey back to the town after a break of sixty years.
Very rare and much sought after Tullamore Dew advert featuring the greatest greyhound in racing history,Mick the Miller.Mick the Miller was bred in Co Offaly,the same county as the location of the Tullamore Dew distillery, hence the pride on the connection. 45cm x 90cm Banagher Co Offaly Tullamore D.E.W. is a brand of Irish whiskey produced by William Grant & Sons. It is the second largest selling brand of Irish whiskey globally, with sales of over 950,000 cases per annum as of 2015.The whiskey was originally produced in the Tullamore, County Offaly, Ireland, at the old Tullamore Distillery which was established in 1829. Its name is derived from the initials of Daniel E. Williams (D.E.W.), a general manager and later owner of the original distillery. In 1954, the original distillery closed down, and with stocks of whiskey running low, the brand was sold to John Powers & Son, another Irish distiller in the 1960s, with production transferred to the Midleton Distillery, County Cork in the 1970s following a merger of three major Irish distillers.In 2010, the brand was purchased by William Grant & Sons, who constructed a new distillery on the outskirts of Tullamore. The new distillery opened in 2014, bringing production of the whiskey back to the town after a break of sixty years.Mick The Miller,as featured in this iconic advert, was the most famous greyhound of all time. He was born in 1926 in the village of Killeigh, County Offaly, Ireland at Millbrook House(only 5 miles from Tullamore), the home of parish curate, Fr Martin Brophy. When he was born Mick was the runt of the litter but Michael Greene, who worked for Fr Brophy, singled the little pup out as a future champion and insisted that he be allowed to rear him. With constant attention and regular exercise Mick The Miller developed into a racing machine. His first forays were on local coursing fields where he had some success but he showed his real talent on the track where he won 15 of his first 20 races.
.jpg)
In 1929 Fr Brophy decided to try Mick in English Greyhound Derby at White City, London. On his first trial-run, Mick equalled the track record. Then, in his first heat, he broke the world record, becoming the first greyhound ever to run 525 yards in under 30 seconds. Fr Brophy was inundated with offers and sold him to Albert Williams. Mick went on to win the 1929 Derby. Within a year he had changed hands again to Arundel H Kempton and won the Derby for a second time.
Over the course of his English career he won 36 of his 48 races, including the Derby (twice), the St Leger, the Cesarewitch, and the Welsh Derby. He set six new world records and two new track records. He was the first greyhound to win 19 races in a row. Several of his records went unbroken for over 40 years. He won, in total, almost £10,000 in prizemoney. But he also became the poster-dog for greyhound racing. He was a celebrity on a par with any sports person, muscisian or moviestar. The more famous he became, the more he attracted people to greyhound racing. Thousands thronged to watch him, providing a huge boost to the sport. It is said that he actually saved the sport of greyhound racing.
After retirement to stud his popularity continued. He starred in the film Wild Boy (based on his life-story) in 1934 which was shown in cinemas all across the UK. He was in huge demand on the celebrity circuit, opening shops, attending big races and even rubbing shoulder with royalty (such as the King and Queen) at charity events. When he died in 1939 aged 12, his owner donated his body to the British Natural History Museum in London. And Mick`s fame has continued ever since. In 1981 he was inducted into the American Hall of Fame (International Section). In 1990 English author Michael Tanner published a book, Mick The Miller - Sporting Icon Of the Depression. And in 2011 the people of Killeigh erected a monument on the village green to honour their most famous son. Mick The Miller is not just the most famous greyhound of all time but one of the most loved dogs that has ever lived.
-

 Real retro GAA hurling photo here of Kevin Hennessy of Cork & Conor Hayes of Galway marking each other in an All Ireland Final.Conor is wearing what appears to be a very old Cooper Ice hockey Head guard and it became his signature piece during his career as Galway Captain and Full Back. Kiltormer Co Galway 29cm x 23cm Conor Hayes was a three-time All-Star. He made his debut for the Galway senior hurlers during the 1979 championship and went on to play a key role for the Tribesmen for over a decade, winning three All-Irelands and two National Leagues. He was captain when Galway won back-to-back All-Ireland titles in 1987 and 1988. Conor is also an All-Ireland winner at club level, having achieved the highest honour in club hurling with Kiltormer in 1992. He is the holder of two Connacht club championships and three Galway hurling championships with Kiltormer and was named on the Galway Hurling Team of the Millennium. Kevin Hennessy (born 8 March 1961) is an Irish retired hurler who played as a left-corner forward for the Cork senior team. Born in Midleton, County Cork, Hennessy first arrived on the inter-county scene at the age of 18 when he first linked up with the Cork minor team, before later lining out with the under-21 side. He made his senior debut in the 1982 championship. Hennessy went on to play a key part for over a decade, and won three All-Ireland medals and seven Munster medals. He was an All-Ireland runner-up on three occasions. Hennessy represented the Munster inter-provincial team in the early stages of his career, winning two Railway Cup medals. At club level he won one All-Ireland medal, two Munster medals and four championship medals with Midleton. Throughout his career Hennessy made 22 championship appearances for Cork. He retired from inter-county hurling following the conclusion of the 1993 championship.
Real retro GAA hurling photo here of Kevin Hennessy of Cork & Conor Hayes of Galway marking each other in an All Ireland Final.Conor is wearing what appears to be a very old Cooper Ice hockey Head guard and it became his signature piece during his career as Galway Captain and Full Back. Kiltormer Co Galway 29cm x 23cm Conor Hayes was a three-time All-Star. He made his debut for the Galway senior hurlers during the 1979 championship and went on to play a key role for the Tribesmen for over a decade, winning three All-Irelands and two National Leagues. He was captain when Galway won back-to-back All-Ireland titles in 1987 and 1988. Conor is also an All-Ireland winner at club level, having achieved the highest honour in club hurling with Kiltormer in 1992. He is the holder of two Connacht club championships and three Galway hurling championships with Kiltormer and was named on the Galway Hurling Team of the Millennium. Kevin Hennessy (born 8 March 1961) is an Irish retired hurler who played as a left-corner forward for the Cork senior team. Born in Midleton, County Cork, Hennessy first arrived on the inter-county scene at the age of 18 when he first linked up with the Cork minor team, before later lining out with the under-21 side. He made his senior debut in the 1982 championship. Hennessy went on to play a key part for over a decade, and won three All-Ireland medals and seven Munster medals. He was an All-Ireland runner-up on three occasions. Hennessy represented the Munster inter-provincial team in the early stages of his career, winning two Railway Cup medals. At club level he won one All-Ireland medal, two Munster medals and four championship medals with Midleton. Throughout his career Hennessy made 22 championship appearances for Cork. He retired from inter-county hurling following the conclusion of the 1993 championship. -

 45cm x 35cm " It was not until 1994 that the GAA decided that the football championship would benefit from bringing on a title sponsor in Bank of Ireland. Although an equivalent offer had been on the table for the hurling championship, Central Council pushed the plate away.Though the name of the potential sponsor wasn’t explicitly made public, everyone knew it was Guinness. More to the point, everyone knew why Central Council wouldn’t bite. As Mulvihill himself noted in his report to Congress, the offer was declined on the basis that “Central Council did not want an alcoholic drinks company associated with a major GAA competition”. As it turned out, Central Council had been deadlocked on the issue and it was the casting vote of then president Peter Quinn that put the kibosh on a deal with Guinness. Mulvihill’s disappointment was far from hidden, since he saw the wider damage caused by turning up the GAA nose at Guinness’s advances. “The unfortunate aspect of the situation,” he wrote, “is that hurling needs support on the promotion of the game much more than football.” Though it took the point of a bayonet to make them go for it, the GAA submitted in the end and on the day after the league final in 1995 , a three-year partnership with Guinness was announced. The deal would be worth £1 million a year, with half going to the sport and half going to the competition in the shape of marketing. That last bit was key. Guinness came up with a marketing campaign that fairly scorched across the general consciousness. Billboards screeched out slogans that feel almost corny at this remove but made a huge impact at the same time . This man can level whole counties in one second flat. This man can reach speeds of 100mph. This man can break hearts at 70 yards Its been Hell for Leather. Of course, all the marketing in the world can only do so much. Without a story to go alongside, the Guinness campaign might be forgotten now – or worse, remembered as an overblown blast of hot air dreamed up in some modish ad agency above in Dublin.Until the Clare hurlers came along and changed everything." Malachy Clerkin Irish Times GAA Correspondent Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.”
45cm x 35cm " It was not until 1994 that the GAA decided that the football championship would benefit from bringing on a title sponsor in Bank of Ireland. Although an equivalent offer had been on the table for the hurling championship, Central Council pushed the plate away.Though the name of the potential sponsor wasn’t explicitly made public, everyone knew it was Guinness. More to the point, everyone knew why Central Council wouldn’t bite. As Mulvihill himself noted in his report to Congress, the offer was declined on the basis that “Central Council did not want an alcoholic drinks company associated with a major GAA competition”. As it turned out, Central Council had been deadlocked on the issue and it was the casting vote of then president Peter Quinn that put the kibosh on a deal with Guinness. Mulvihill’s disappointment was far from hidden, since he saw the wider damage caused by turning up the GAA nose at Guinness’s advances. “The unfortunate aspect of the situation,” he wrote, “is that hurling needs support on the promotion of the game much more than football.” Though it took the point of a bayonet to make them go for it, the GAA submitted in the end and on the day after the league final in 1995 , a three-year partnership with Guinness was announced. The deal would be worth £1 million a year, with half going to the sport and half going to the competition in the shape of marketing. That last bit was key. Guinness came up with a marketing campaign that fairly scorched across the general consciousness. Billboards screeched out slogans that feel almost corny at this remove but made a huge impact at the same time . This man can level whole counties in one second flat. This man can reach speeds of 100mph. This man can break hearts at 70 yards Its been Hell for Leather. Of course, all the marketing in the world can only do so much. Without a story to go alongside, the Guinness campaign might be forgotten now – or worse, remembered as an overblown blast of hot air dreamed up in some modish ad agency above in Dublin.Until the Clare hurlers came along and changed everything." Malachy Clerkin Irish Times GAA Correspondent Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.” -
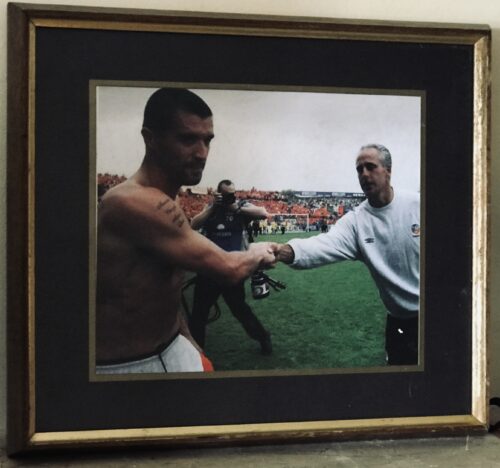
 Cork City 33cm x 38cm The Infamous Handshake between Roy Keane and Mick McCarthy that said it all
Cork City 33cm x 38cm The Infamous Handshake between Roy Keane and Mick McCarthy that said it all"Footballers are pragmatists. You play for the manager you have."
This is a quote from Roy Keane's autobiography [Page 76]. He was referring specifically to the Irish soccer players when Jack Charlton was the Republic of Ireland team manager, and to footballers in general. It would appear however that Keane had limits to his own pragmatism when it came to playing for Mick McCarthy as Irish manager.
The dynamics of the relationship between Roy Keane and Mick McCarthy are central to the whole Saipan incident. Clearly the two did not get on with each other. The question is - why? Keane and McCarthy are the only ones who can give a definitive answer to this but based upon the available evidence it appears to be primarily due to an intense dislike of McCarthy by Keane.
Roy Keane and Mick McCarthy Have a Row in Boston in 1992
Roy Keane and Mick McCarthy only played together for Ireland on two occasions, in September 1991 and May 1992. There are no generally known reports of any issues arising between the two men as players on the football pitch. However it was while Mick McCarthy was the Republic of Ireland team captain that the first instance of some discord between the two has been documented. During the fateful squad meeting, that led to the expulsion of Keane from the Irish World Cup squad, the Irish captain brought up an incident that had occurred a full ten years earlier. The now infamous Boston 1992 row.
It now seems that this otherwise innocuous event appears to have coloured the Keane and McCarthy relationship
from that time onward. A drunken 20 year old Keane had turned up late for the team bus at the end of a soccer tournament in the US. When the team captain Mick McCarthy challenged Keane about being late a heated row ensued. Roy Keane seems to have taken extreme exception to this. It is difficult to believe that such an event would even register the next day with Keane who seems to have spent his entire life going from one scrape to another. Keane admits in his autobiography that he has had hundreds or thousands of rows throughout his soccer career. Why should this one have been so significant to him?One possible explanation is that when Keane is drunk his, already low, tolerance levels become even lower. Any perceived slight is magnified disproportionately. Keane's autobiography is littered with stories about him getting into angry and violent situations when he was drunk. By his own admission there were many situations when he knew he should have walked away but his own sense of offence prevented him doing just that. These events seem to have made an indelible mark on his brain as they are recounted with real clarity in his book. It seems that a run of the mill, for footballers, exchange between McCarthy and Keane in 1992, magnified in intensity by his drunken state, soured Keane's view of McCarthy from that point on.
"Let Bygones be Bygones" - Roy Keane
There do not appear to have been any further meaningful interactions between the two until McCarthy was appointed as manager of the Republic of Ireland football team in 1996. In his autobiography [Page 246] Keane reveals an antipathy towards McCarthy that seems, to some extent, to be born out of Roy Keane's relationship with Jack Charlton. In his book Keane makes it clear that he had no time for Charlton "...I found it impossible to relate to him as a man or as a coach." [Page 54]. When commenting on McCarthy's appointment as Irish manager he said "McCarthy was part of the Charlton legend. Captain Fantastic...he didn't convince me. Still, when he got the job, I thought: let bygones be bygones." What bygones? Presumably the exchange between the pair in Boston six years earlier?
In his World Cup Diary McCarthy makes a case that he had gone to some lengths as manager of Ireland to accommodate Keane and his sensitivities. He had made Keane the captain of Ireland at the first opportunity. He allowed Keane to turn up later than the other players for international matches. Keane was the only player in the Irish squad that roomed alone. He also says that he put up "...with the odd tantrum from Keane here and there...". McCarthy contends that if he was holding a grudge towards Keane from 1992 he would not have gone to these lengths.
Roy Keane's first match for Ireland with Mick McCarthy as manager was an inauspicious occasion for the Manchester United player. Earning his 30th cap and wearing the captain's armband in place of the substituted Andy Townsend, Keane was sent off late in the match for kicking a Russian player.
Lack of Direct Communication Between Roy Keane & Mick McCarthy
The next notable point of conflict between Keane and McCarthy was on the occasion of a Republic of Ireland trip to the USA for an end of season international tournament in 1996. Keane decided that he didn't want to go as he was too tired after the season just ended. [Page 246]. Rather than contact McCarthy or anyone else in the Irish set up, Keane left it to someone at Old Trafford to inform the FAI. "As a result I got off to a bad start with McCarthy. He felt I should have spoken to him personally. He expressed this opinion, casting me in a bad light. What he didn't tell the media that if we had that sort of conversation on this occasion, it would have been our first." [Page 247]. This begs the question, why couldn't Keane contact McCarthy directly? Why would this have been the first such discussion between the two men as manager and team captain? It certainly doesn't suggest that Keane had, in reality, let bygones be bygones.
In his World Cup Diary McCarthy refers to the the 1996 USA trip. "I was never that bothered if he (Keane) went to America or not...it became a big media story...We have had a few chats to sort things out but it has all dragged on since then in the press." [Page 33].
In his autobiography Keane complains bitterly about the poor Republic of Ireland set up especially when compared to that of Manchester United. After the draw for the 2002 World Cup qualifiers was made Keane says that he met with McCarthy"...to level with him, to make the case for a reformed approach...We discussed the problems. He agreed with me...It was not and easy conversation - we're not not buddy-buddy...I thought we had a deal."[Page 250]. Interestingly this meeting took place at Keane's house in Manchester.
What is clear is that there was an unusual relationship between the Irish manager and his captain. Direct communication between McCarthy and Keane was kept to an absolute minimum. All of the available evidence is that was the way Keane wanted it. Keane admitted this in his interview with Tom Humphries in Saipan "I spoke to Mick Byrne, who's the middle man for me, really." For a man who has very admirable communication skills this is somewhat strange. Why would he need a middle man? The only possible explanation is that Roy Keane did not like Mick McCarthy and couldn't bear to be anywhere near him or have anything to do with him. During McCarthy's tenure as Irish manager Roy Keane took every opportunity to minimise his time with the Irish squad. "I dreaded the prospect of international weeks."[Page 250].
Conclusion
With the benefit of hindsight and with the insights afforded by Keane's autobiography it is clear that there was no way possible that Roy Keane could maintain an even keel while being away with Ireland for the duration of the World Cup campaign. All of his complaints about the crowded airport, the missing training gear, the poor training facilities, the goalkeeper row, were just symptoms. Clearly McCarthy and the FAI could have done better but the inescapable conclusion to be drawn is that even if conditions and facilities had been perfect Keane simply could not endure being in such close proximity to Mick McCarthy for such a protracted period of time. A Saipan incidentwas inevitable even before Roy Keane set foot on the plane to that Pacific island.
NOTE: Unless stated otherwise all quotations are from: Keane: The Autobiography; Roy Keane with Eamon Dunphy (2002); Michael Joseph Ltd
-
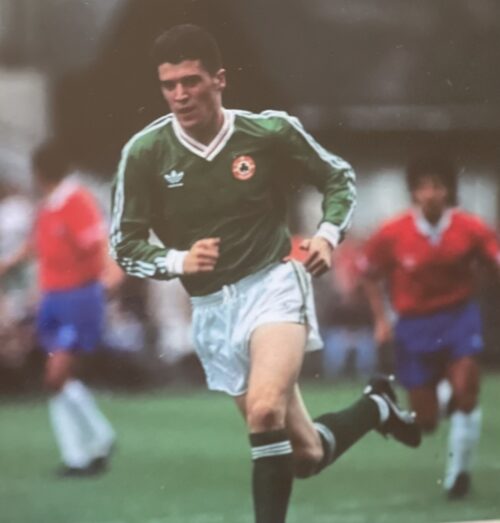
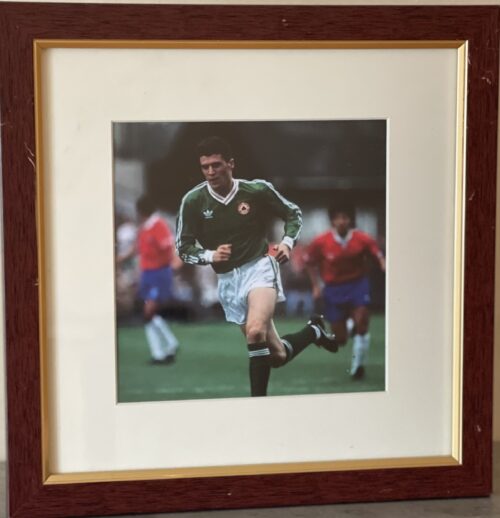
 I 30cm x 30cm Limerick Roy Maurice Keane (born 10 August 1971) is an Irish football manager and former professional player. He is the joint most successful Irish footballer of all time, having won 19 major trophies in his club career, 17 of which came during his time at English club Manchester United. He served as the assistant manager of the Republic of Ireland national teamfrom 2013 until 2018. Regarded as one of the best midfielders of his generation, he was named by Pelé in the FIFA 100 list of the world's greatest living players in 2004.Noted for his hardened and brash demeanour, he was ranked at No. 11 on The Times' list of the 50 "hardest" footballers in history in 2007. Keane was inducted into the Premier League Hall of Fame in 2021. In his 18-year playing career, Keane played for Cobh Ramblers, Nottingham Forest, and Manchester United, before ending his career at Celtic. He was a dominating box-to-box midfielder, noted for his aggressive and highly competitive style of play, an attitude that helped him excel as captain of Manchester United from 1997 until his departure in 2005. Keane helped United achieve a sustained period of success during his 12 years at the club. He then signed for Celtic, where he won a domestic double before he retired as a player in 2006. Keane played at the international level for the Republic of Ireland over 14 years, most of which he spent as captain. At the 1994 FIFA World Cup, he played in every Republic of Ireland game. He was sent home from the 2002 FIFA World Cup after a dispute with national coach Mick McCarthy over the team's training facilities. Keane was appointed manager of Sunderland shortly after his retirement as a player and took the club from 23rd position in the Football League Championship, in late August, to win the division title and gain promotion to the Premier League. He resigned in December 2008,and from April 2009 to January 2011, he was manager of Championship club Ipswich Town. In November 2013, he was appointed assistant manager of the Republic of Ireland national team by manager Martin O'Neill. Keane has also worked as a studio analyst for British channels ITV's and Sky Sportsfootball coverage.
I 30cm x 30cm Limerick Roy Maurice Keane (born 10 August 1971) is an Irish football manager and former professional player. He is the joint most successful Irish footballer of all time, having won 19 major trophies in his club career, 17 of which came during his time at English club Manchester United. He served as the assistant manager of the Republic of Ireland national teamfrom 2013 until 2018. Regarded as one of the best midfielders of his generation, he was named by Pelé in the FIFA 100 list of the world's greatest living players in 2004.Noted for his hardened and brash demeanour, he was ranked at No. 11 on The Times' list of the 50 "hardest" footballers in history in 2007. Keane was inducted into the Premier League Hall of Fame in 2021. In his 18-year playing career, Keane played for Cobh Ramblers, Nottingham Forest, and Manchester United, before ending his career at Celtic. He was a dominating box-to-box midfielder, noted for his aggressive and highly competitive style of play, an attitude that helped him excel as captain of Manchester United from 1997 until his departure in 2005. Keane helped United achieve a sustained period of success during his 12 years at the club. He then signed for Celtic, where he won a domestic double before he retired as a player in 2006. Keane played at the international level for the Republic of Ireland over 14 years, most of which he spent as captain. At the 1994 FIFA World Cup, he played in every Republic of Ireland game. He was sent home from the 2002 FIFA World Cup after a dispute with national coach Mick McCarthy over the team's training facilities. Keane was appointed manager of Sunderland shortly after his retirement as a player and took the club from 23rd position in the Football League Championship, in late August, to win the division title and gain promotion to the Premier League. He resigned in December 2008,and from April 2009 to January 2011, he was manager of Championship club Ipswich Town. In November 2013, he was appointed assistant manager of the Republic of Ireland national team by manager Martin O'Neill. Keane has also worked as a studio analyst for British channels ITV's and Sky Sportsfootball coverage. -
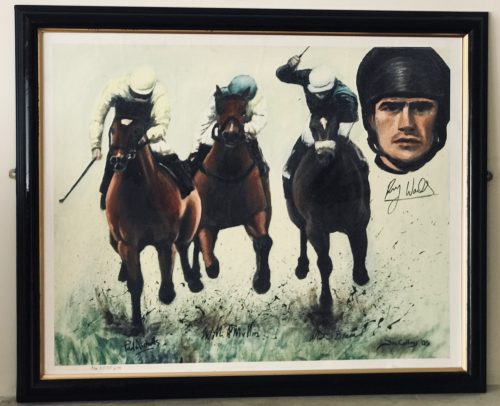 Superb limit edition artwork venerating the great Ruby Walsh,one of the greatest jump jockeys in history, signed by Ruby himself and champion trainers Paul Nicholls & Willie Mullins. Origins :Lismore Co Waterford Dimensions : 70cm x 85cm Rupert "Ruby" Walsh (born 14 May 1979 in Kill, County Kildare, Ireland) is an Irish former jockey. He is the second child, and eldest son, of former champion amateur jockey Ted Walsh and his wife Helen. Walsh is the third most prolific winner in British and Irish jump racing history behind only Sir Anthony McCoy and Richard Johnson.
Superb limit edition artwork venerating the great Ruby Walsh,one of the greatest jump jockeys in history, signed by Ruby himself and champion trainers Paul Nicholls & Willie Mullins. Origins :Lismore Co Waterford Dimensions : 70cm x 85cm Rupert "Ruby" Walsh (born 14 May 1979 in Kill, County Kildare, Ireland) is an Irish former jockey. He is the second child, and eldest son, of former champion amateur jockey Ted Walsh and his wife Helen. Walsh is the third most prolific winner in British and Irish jump racing history behind only Sir Anthony McCoy and Richard Johnson.Career
Showing talent from an early age, Walsh won the Irish amateur title twice, in 1996/97 (aged 18) and 1997/98, before turning professional. He won the English Grand National in 2000 at his first attempt, aged 20, on Papillon,a horse trained by his father and owned by Mrs J Maxwell Moran.Father and son then went on to win the Irish Grand National with Commanche Court the same year. In the 2004/05 season Walsh won three of the four Nationals: the Irish on the 2006 Grand National winner, Numbersixvalverde, the Welsh on subsequent 2007 Grand National winner Silver Birch, and the English on Hedgehunter. He rode Cornish Rebel in the Scottish, but was beaten a short head by Joe's Edge. However, he had earlier success in that race on Take Control in 2002 and following the retirement in 2015 of Tony McCoy, became the only jockey currently riding to have won all four Nationals. Walsh has one of the best Grand National records amongst current jockeys having won the race twice (2000, 2005), finished second once (2006), third once (2009) and fourth twice (2001, 2002). Walsh rode over 2500 winners including 59 winners at the Cheltenham Festival since his first win in 1998 on Alexander Banquet. These include the 2004 Queen Mother Champion Chase on Azertyuiop, the 2007 and 2009 Cheltenham Gold Cup on the favourite, Kauto Star and two subsequent Queen Mother successes in 2008 and 2009 on the brilliant Master Minded. He also won both the 2006 Tingle Creek Chase and the King George VI Chase on Kauto Star. He repeated the King George feat, again on Kauto Star, in 2007 (just days after returning from injury), 2008 and 2009 when Kauto Star won impressively by 36 lengths. He reclaimed the King George VI Chase in 2011 on board Kauto Star after Long Run won the race in 2010. He won the Hennessy Gold Cup twice, in 2003 on Strong Flow, and in more recent times, 2009 with Denman. He also won the Whitbread Gold Cup twice, in 2001 and 2003 (the latter when it was run as the Attheraces Gold Cup), both times on Ad Hoc. In 2007, Walsh won the inaugural British Horseracing Board Jockeys' Order of Merit award. Walsh was been Irish jump jockey champion twelve times – 1998/99, 2000/01, 2004/05, 2005/06, 2006/07, 2007/08, 2008/09, 2009/10, 2013/14, 2014/15, 2015/16 and 2016/17. Walsh's recent dominance of the jockeys' championship in Ireland is all the more remarkable given that for more than ten years he had a unique riding arrangement with two powerful stables, one on either side of the Irish Sea. Based in Calverstown, County Kildare, where he lives with his wife Gillian, he rode predominantly for Willie Mullins in Ireland. Formerly he also spent a substantial proportion of his time riding in England for Somerset-based champion trainer Paul Nicholls, the former trainer of Kauto Star. In January 2007, Walsh achieved the fastest ever century of winners in Irish jumps racing history aboard Bluestone Lad at Gowran Park. He ended the 2006/07 season with a combined total in Ireland and the UK of 198 winners, higher than any other jockey from either country that year. (This total was later increased to 200 on the disqualification of two horses for positive tests to banned substances. In both instances, Walsh had ridden the subsequently-promoted runners-up.) He repeated this feat in 2007/08, riding his 200th winner on Andreas at Sandown on his penultimate ride of the season. He rode his 1,000th Irish winner, Rare Article, at Sligo in May 2008. At the 2009 Cheltenham Festival Walsh rode a record-breaking seven winners over the four days. He equalled that record at the 2016 Cheltenham Festival. On the second day of the 2010 festival he rode Sanctuaire to victory in the Fred Winter Juvenile Novices Handicap Hurdle and therefore became the jockey with the most wins in the history of the Cheltenham festival. In March 2011, Walsh rode Hurricane Fly to victory in the Champion Hurdle at Cheltenham, finishing ahead of Peddlers Cross and Oscar Whisky. It was Walsh's first victory in the feature race of the opening day at the Cheltenham Festival. He won his 2,500 race on Au Quart De Tour at Gowran park on 20 January 2016. As of 2019, Walsh is the Festival's most successful rider with 59 wins and has won the leading rider's award eleven times within the last fourteen years. In August 2015 Walsh won the Australian Grand National on Bashboy. On 1 May 2019, Walsh announced his retirement from racing with immediate effect after a career spanning 24 years. The announcement was made after he rode Kemboy to victory in the Punchestown Gold Cup. It was the 213th Grade One win for Walsh -

 Marvellous photograph taken from the 1970s in a bar in Ballylongford Co Kerry as the locals celebrate the return of the magnificent Sam Maguire trophy,presenred to the winners of the All Ireland Football Championship every year. 25cm x 25cm Ballylongford Co Kerry The Sam Maguire Cup, often referred to as Sam or The Sam (Irish: Corn Sam Mhic Uidhir), is a trophy awarded annually by the Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA) to the team that wins the All-Ireland Senior Football Championship, the main competition in the medieval sport of Gaelic football. The Sam Maguire Cup was first presented to the winners of the 1928 All-Ireland Senior Football Championship Final. The original 1920s trophy was retired in the 1980s, with a new identical trophy awarded annually since 1988. The GAA organises the series of games, which are played during the summer months. The All-Ireland Football Final was traditionally played on the third or fourth Sunday in September at Croke Park in Dublin. In 2018, the GAA rescheduled its calendar and since then the fixture has been played in early September
Marvellous photograph taken from the 1970s in a bar in Ballylongford Co Kerry as the locals celebrate the return of the magnificent Sam Maguire trophy,presenred to the winners of the All Ireland Football Championship every year. 25cm x 25cm Ballylongford Co Kerry The Sam Maguire Cup, often referred to as Sam or The Sam (Irish: Corn Sam Mhic Uidhir), is a trophy awarded annually by the Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA) to the team that wins the All-Ireland Senior Football Championship, the main competition in the medieval sport of Gaelic football. The Sam Maguire Cup was first presented to the winners of the 1928 All-Ireland Senior Football Championship Final. The original 1920s trophy was retired in the 1980s, with a new identical trophy awarded annually since 1988. The GAA organises the series of games, which are played during the summer months. The All-Ireland Football Final was traditionally played on the third or fourth Sunday in September at Croke Park in Dublin. In 2018, the GAA rescheduled its calendar and since then the fixture has been played in early SeptemberOld trophy
The original Sam Maguire Cup commemorates the memory of Sam Maguire, an influential figure in the London GAA and a former footballer. A group of his friends formed a committee in Dublin under the chairmanship of Dr Pat McCartan from Carrickmore, County Tyrone, to raise funds for a permanent commemoration of his name. They decided on a cup to be presented to the GAA. The Association were proud to accept the Cup. At the time it cost £300. In today's terms that sum is equivalent to €25,392. The commission to make it was given to Hopkins and Hopkins, a jewellers and watchmakers of O'Connell Bridge, Dublin. The silver cup was crafted, on behalf of Hopkins and Hopkins, by the silversmith Matthew J. Staunton of D'Olier Street, Dublin. Maitiú Standun, Staunton's son, confirmed in a letter printed in the Alive! newspaper in October 2003 that his father had indeed made the original Sam Maguire Cup back in 1928. Matthew J. Staunton (1888–1966) came from a long line of silversmiths going back to the Huguenots, who brought their skills to Ireland in the 1600s. Matt, as he was known to his friends, served his time in the renowned Dublin silversmiths, Edmond Johnson Ltd, where the Liam MacCarthy Hurling Cup was made in 1921. The 1928 Sam Maguire Cup is a faithful model of the Ardagh Chalice. The bowl was not spun on a spinning lathe but hand-beaten from a single flat piece of silver. Even though it is highly polished, multiple hammer marks are still visible today, indicating the manufacturing process. It was first presented in 1928 - to the Kildare team that defeated Cavan by one point in that year's final. It was the only time Kildare won old trophy. They have yet to win the new trophy, coming closest in 1998, when Galway defeated them by four points in that year's final. Kerry won the trophy on the most occasions. They were also the only team to win it on four consecutive occasions, achieving the feat twice -first during the late-1920s and early-1930s (1929, 1930, 1931, 1932), and later during the late-1970s and early 1980s (1978, 1979, 1980, 1981). In addition, Kerry twice won the old trophy on three consecutive occasions, in the late 1930s and early-1940s (1939, 1940, 1941) and in the mid-1980s (1984, 1985, 1986). They also won it on two consecutive occasions in the late-1960s and early-1970s (1969, 1970). Galway won the old trophy on three consecutive occasions in the mid-1960s (1964, 1965, 1966). Roscommon won the old trophy on two consecutive occasions during the mid-1940s (1943, 1944), as did Cavan later that decade (1947, 1948). Mayo won the old trophy on two consecutive occasions during the early-1950s (1950, 1951), while Down did likewise in the early-1960s (1960, 1961). Offaly won the old trophy on two consecutive occasions during the early 1970s (1971, 1972), while Dublin did likewise later that decade (1976, 1977). Six men won the old trophy twice as captain: Joe Barrett of Kerry, Jimmy Murray of Roscommon, John Joe O'Reilly of Cavan, Seán Flanagan of Mayo, Enda Colleran of Galway and Tony Hanahoeof Dublin. The original trophy was retired in 1988 as it had received some damage over the years. It is permanently on display in the GAA Museum at Croke Park. Original 1928 Sam Maguire Cup on display in the GAA Museum at Croke Park
Original 1928 Sam Maguire Cup on display in the GAA Museum at Croke ParkNew trophy
The GAA commissioned a replica from Kilkenny-based silversmith Desmond A. Byrne and the replica is the trophy that has been used ever since. The silver for the new cup was donated by Johnson Matthey Ireland at the behest of Kieran D. Eustace Managing Director, a native of Newtowncashel Co. Longford . Meath's Joe Cassells was the first recipient of "Sam Óg". Meath have the distinction of being the last team to lift the old Sam Maguire and the first team to lift the new one following their back-to-back victories in 1987 and 1988. Cork won the new trophy on consecutive occasions in the late-1980s and early-1990s (1989, 1990), while Kerry did likewise during the mid-2000s (2006, 2007). Dublin are the only team to win the new trophy on more than two consecutive occasions, achieving a historic achievement of five-in-a-row during the second half of the 2010s (2015, 2016, 2017, 2018 and 2019). Stephen Cluxton of Dublin is the only captain to have won the new trophy six times as captain, doing so in 2013, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018 and 2019. No other person as ever won either the old or new trophy as captain more than twice. Two other men have won the new trophy twice as captain: Declan O'Sullivan of Kerry and Brian Dooher of Tyrone. In 2010, the GAA asked the same silversmith to produce another replica of the trophy (the third Sam Maguire Cup) although this was to be used only for marketing purposes.Winners
Old Trophy- Kerry – 1929, 1930, 1931, 1932, 1937, 1939, 1940, 1941, 1946, 1953, 1955, 1959, 1962, 1969, 1970, 1975, 1978, 1979, 1980, 1981, 1984, 1985, 1986
- Dublin – 1942, 1958, 1963, 1974, 1976, 1977, 1983
- Galway – 1934, 1938, 1956, 1964, 1965, 1966
- Cavan – 1933, 1935, 1947, 1948, 1952
- Meath – 1949, 1954, 1967, 1987
- Mayo – 1936, 1950, 1951
- Down – 1960, 1961, 1968
- Offaly – 1971, 1972, 1982
- Roscommon – 1943, 1944
- Cork – 1945, 1973
- Kildare – 1928
- Louth – 1957
-
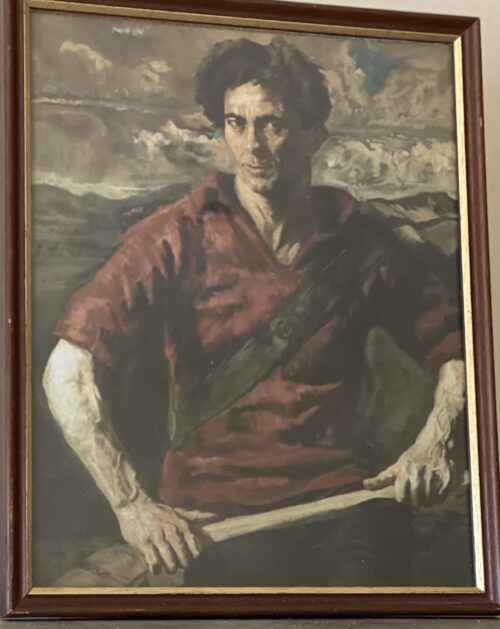
 Seán Keating (born John Keating, Limerick, 28 September 1889 – Dublin, 21 December 1977) was an Irish romantic-realist painter who painted some iconic images of the Irish War of Independence and of the early industrialization of Ireland. He spent two weeks or so each year during the late summer on the Aran Islands and his many portraits of island people depicted them as rugged heroic figures. However, he ceased to visit the Aran Islands in 1965.Seán Keating studied drawing at the Limerick Technical School before a scholarship arranged by William Orpen allowed him to go at the age of twenty to study at the Metropolitan School of Art in Dublin. Over the next few years, he spent time on the Aran Islands. In 1914 Keating won the RDS Taylor award with a painting titled The Reconciliation. The prize included £50 which allowed him to go to London to work as Orpen's studio assistant in 1915. In late 1915 or early 1916, he returned to Ireland where he documented the War of Independence and the subsequent Civil War. Examples include Men of the South (1921–22) which shows a group of IRA men ready to ambush a military vehicle and An Allegory (first exhibited in 1924), in which the two opposing sides in the Irish Civil War are seen to bury a tricolour-covered coffin amid the roots on an ancient tree. The painting includes a self-portrait of the artist.
Seán Keating (born John Keating, Limerick, 28 September 1889 – Dublin, 21 December 1977) was an Irish romantic-realist painter who painted some iconic images of the Irish War of Independence and of the early industrialization of Ireland. He spent two weeks or so each year during the late summer on the Aran Islands and his many portraits of island people depicted them as rugged heroic figures. However, he ceased to visit the Aran Islands in 1965.Seán Keating studied drawing at the Limerick Technical School before a scholarship arranged by William Orpen allowed him to go at the age of twenty to study at the Metropolitan School of Art in Dublin. Over the next few years, he spent time on the Aran Islands. In 1914 Keating won the RDS Taylor award with a painting titled The Reconciliation. The prize included £50 which allowed him to go to London to work as Orpen's studio assistant in 1915. In late 1915 or early 1916, he returned to Ireland where he documented the War of Independence and the subsequent Civil War. Examples include Men of the South (1921–22) which shows a group of IRA men ready to ambush a military vehicle and An Allegory (first exhibited in 1924), in which the two opposing sides in the Irish Civil War are seen to bury a tricolour-covered coffin amid the roots on an ancient tree. The painting includes a self-portrait of the artist. Men of the South, 1921–22, Crawford Art Gallery, Cork.Keating was elected an Associate of the Royal Hibernian Academy (RHA) in 1918, and a full member in 1923. One of the cardinal achievements of the Irish Free State in the 1920s was the building, in partnership with Siemens, of a hydro-electric power generator at Ardnacrusha, near Limerick. Between 1926 and 1927 Keating, at his own initiative, produced a considerable number of paintings related to this scheme. He exhibited several examples of the paintings in the RHA exhibitions in 1927 and 1928. Most are now in the collection of ESB Group. His work was also part of the art competitions at the 1924 Summer Olympics and the 1928 Summer Olympics. In 1936 a group of prominent Limerick politicians, artists and patrons established the first Limerick City Collection of Art, made up of various donations and bequests. Keating was part of this artist-led initiative to form a municipal art gallery in Limerick similar to those already in Dublin and Cork. As a pivotal member of the committee, Keating himself donated many works to the collection which was first exhibited in the Savoy Cinema, Limerick City, on 23 November 1937. It was not until 1948, however, that an extension to the rear of Limerick Free Library and Museum became the permanent home to the City Collection, acquiring the name of the Limerick Free Art Gallery. In 1985 the Library and Museum were transferred to larger buildings. In 1939 Keating was commissioned to paint a mural for the Irish pavilion at the New York World's Fair. He was President of the Royal Hibernian Academy from 1950 to 1962, and showed at the annual exhibition for 61 years from 1914 onwards. Keating was an intellectual painter in the sense that he consciously set out to explore the visual identity of the Irish nation, and his paintings show a very idealised realism. He feared that the modern movement would lead to a decline in artistic standards. Throughout his career, he exhibited nearly 300 works at the RHA, and also showed at the Oireachtas. Keating married political campaigner, May Walsh, in 1919. She was a frequent model for his paintings until her death in 1965. He died on 21 December 1977 at the Adelaide Hospital and was buried at Cruagh Cemetery, Rathfarnham. The 1978 RHA Exhibition featured a small memorial collection of his work. Posthumous exhibitions of his paintings were held by The Grafton Gallery, Dublin (1986) and the Electricity Supply Board (1987). Sean Keating – The Pilgrim Soul, a documentary presented and written by his son, the politician Justin Keating, aired on RTÉ in 1996.
Men of the South, 1921–22, Crawford Art Gallery, Cork.Keating was elected an Associate of the Royal Hibernian Academy (RHA) in 1918, and a full member in 1923. One of the cardinal achievements of the Irish Free State in the 1920s was the building, in partnership with Siemens, of a hydro-electric power generator at Ardnacrusha, near Limerick. Between 1926 and 1927 Keating, at his own initiative, produced a considerable number of paintings related to this scheme. He exhibited several examples of the paintings in the RHA exhibitions in 1927 and 1928. Most are now in the collection of ESB Group. His work was also part of the art competitions at the 1924 Summer Olympics and the 1928 Summer Olympics. In 1936 a group of prominent Limerick politicians, artists and patrons established the first Limerick City Collection of Art, made up of various donations and bequests. Keating was part of this artist-led initiative to form a municipal art gallery in Limerick similar to those already in Dublin and Cork. As a pivotal member of the committee, Keating himself donated many works to the collection which was first exhibited in the Savoy Cinema, Limerick City, on 23 November 1937. It was not until 1948, however, that an extension to the rear of Limerick Free Library and Museum became the permanent home to the City Collection, acquiring the name of the Limerick Free Art Gallery. In 1985 the Library and Museum were transferred to larger buildings. In 1939 Keating was commissioned to paint a mural for the Irish pavilion at the New York World's Fair. He was President of the Royal Hibernian Academy from 1950 to 1962, and showed at the annual exhibition for 61 years from 1914 onwards. Keating was an intellectual painter in the sense that he consciously set out to explore the visual identity of the Irish nation, and his paintings show a very idealised realism. He feared that the modern movement would lead to a decline in artistic standards. Throughout his career, he exhibited nearly 300 works at the RHA, and also showed at the Oireachtas. Keating married political campaigner, May Walsh, in 1919. She was a frequent model for his paintings until her death in 1965. He died on 21 December 1977 at the Adelaide Hospital and was buried at Cruagh Cemetery, Rathfarnham. The 1978 RHA Exhibition featured a small memorial collection of his work. Posthumous exhibitions of his paintings were held by The Grafton Gallery, Dublin (1986) and the Electricity Supply Board (1987). Sean Keating – The Pilgrim Soul, a documentary presented and written by his son, the politician Justin Keating, aired on RTÉ in 1996. An Allegory, 1924, National Gallery of Ireland.
An Allegory, 1924, National Gallery of Ireland. -

 Superb Smithwicks sponsored team photograph of the 1981 All Ireland Hurling Champions -Offaly.The authenticity of this print and its worn appearance makes for an excellent addition to any GAA wall collection. 32cm x 47cm. Birr Co Offaly The 1981 All Ireland Hurling Final was the 94th All-Ireland Final and the culmination of the 1981 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship, an inter-county hurling tournament for the top teams in Ireland. The match was held at Croke Park, Dublin, on 6 September 1981, between Galway and Offaly. The reigning champions lost to their Leinster opponents, who won their first ever senior hurling title, on a score line of 2-12 to 0-15. Johnny Flaherty scored a handpassed goal in this game; this was before the handpassed goal was ruled out of the game as hurling's technical standards improved.
Superb Smithwicks sponsored team photograph of the 1981 All Ireland Hurling Champions -Offaly.The authenticity of this print and its worn appearance makes for an excellent addition to any GAA wall collection. 32cm x 47cm. Birr Co Offaly The 1981 All Ireland Hurling Final was the 94th All-Ireland Final and the culmination of the 1981 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship, an inter-county hurling tournament for the top teams in Ireland. The match was held at Croke Park, Dublin, on 6 September 1981, between Galway and Offaly. The reigning champions lost to their Leinster opponents, who won their first ever senior hurling title, on a score line of 2-12 to 0-15. Johnny Flaherty scored a handpassed goal in this game; this was before the handpassed goal was ruled out of the game as hurling's technical standards improved. -

 Framed Fight poster of Collins v Eubank at Millstreet 1995. 90cm x 68cm Co Cork Stephen Collins (born 21 July 1964) is an Irish former professional boxer who competed from 1986 to 1997. Known as the Celtic Warrior, Collins is the most successful Irish boxer in recent professional boxing history, having held the WBOmiddleweight and super-middleweight titles simultaneously and never losing a fight as champion. Collins' first nineteen professional fights all took place in the United States. In 1988 he won the Irish middleweight title, and the regional American USBA middleweight title the following year, defending the latter successfully in Atlantic City and Las Vegas. In his first two world championship challenges, both for the WBA middleweight title, Collins lost a unanimous decision to Mike McCallum in 1990 and a majority decision to Reggie Johnson in 1992. He also challenged unsuccessfully for the European middleweight title later in 1992, losing a split decision to Sumbu Kalambay in Italy. It was not until Collins reached his early 30s that he fulfilled his potential, becoming WBO middleweight champion in his third world title attempt with a fifth-round TKO victory over Chris Pyatt in 1994, before then moving up in weight to defeat the undefeated Chris Eubank and claim the WBO super-middleweight title in 1995. More success followed, as Collins successfully defended his title by winning the rematch against Eubank later in the year. Collins successfully defended his title another six times before pulling out of a proposed fight in October 1997 against rising Welsh star, Joe Calzaghe, and retiring from the sport, with Collins frustrated by his inability to get a fight against the pound for pound number one boxer of the time, Roy Jones Jr., who was then fighting in the light-heavyweight division. Having competed against some of the best boxers on both sides of the Atlantic during his career, Collins tends to be linked more to an era in the UK during which there was a notable rivalry between British boxers Chris Eubank and Nigel Benn, both of whom Collins fought and defeated twice.
Framed Fight poster of Collins v Eubank at Millstreet 1995. 90cm x 68cm Co Cork Stephen Collins (born 21 July 1964) is an Irish former professional boxer who competed from 1986 to 1997. Known as the Celtic Warrior, Collins is the most successful Irish boxer in recent professional boxing history, having held the WBOmiddleweight and super-middleweight titles simultaneously and never losing a fight as champion. Collins' first nineteen professional fights all took place in the United States. In 1988 he won the Irish middleweight title, and the regional American USBA middleweight title the following year, defending the latter successfully in Atlantic City and Las Vegas. In his first two world championship challenges, both for the WBA middleweight title, Collins lost a unanimous decision to Mike McCallum in 1990 and a majority decision to Reggie Johnson in 1992. He also challenged unsuccessfully for the European middleweight title later in 1992, losing a split decision to Sumbu Kalambay in Italy. It was not until Collins reached his early 30s that he fulfilled his potential, becoming WBO middleweight champion in his third world title attempt with a fifth-round TKO victory over Chris Pyatt in 1994, before then moving up in weight to defeat the undefeated Chris Eubank and claim the WBO super-middleweight title in 1995. More success followed, as Collins successfully defended his title by winning the rematch against Eubank later in the year. Collins successfully defended his title another six times before pulling out of a proposed fight in October 1997 against rising Welsh star, Joe Calzaghe, and retiring from the sport, with Collins frustrated by his inability to get a fight against the pound for pound number one boxer of the time, Roy Jones Jr., who was then fighting in the light-heavyweight division. Having competed against some of the best boxers on both sides of the Atlantic during his career, Collins tends to be linked more to an era in the UK during which there was a notable rivalry between British boxers Chris Eubank and Nigel Benn, both of whom Collins fought and defeated twice.Early years in Boston
Steve Collins won 26 Irish titles as an amateur before turning professional in Massachusetts, US in October 1986. Collins worked out of the Petronelli Brothers gym in Brockton, Massachusetts alongside Marvin Hagler. His debut fight was against Julio Mercado on the undercard of a bill that featured Irish Americans; his future trainer Freddie Roach and the future Fight of the Year winner Micky Ward. Collins beat Mercado by way of knockout in the third round. In Boston, Massachusetts in 1988, he defeated former Olympian and British Super Middleweight champion Sam Storey to win the Irish middleweight title, then defeated world No. 5, Kevin Watts to win the USBA middleweight title. After reaching 16–0, Collins stepped in as a substitute in a WBA middleweight title fight after Michael Watson was injured in training, and fought 12 rounds against Mike McCallum in Boston in 1990. Collins was supported by a large crowd of Irish Americans as he battled the champion McCallum, with the fight being close early on before McCallum started to tire as Collins gained momentum in the later stages to bring a close finish at the end of 12 exciting rounds. McCallum got the win by unanimous decision. In 1992, Collins lost a majority decision to Reggie Johnson in a closely contested slugfest for the vacant WBA middleweight title (which had been stripped from McCallum because he signed to fight IBF champion James Toney). Collins then lost by split decision to Sumbu Kalambay for the European title in Italy, before beating Gerhard Botes of South Africa to win the WBA Penta-Continental middleweight title in 1993.WBO middleweight champion
Collins then moved to Belfast under the management of Barney Eastwood before basing himself in England where he joined Barry Hearn's Matchroom Boxing. Alongside him was Paul "Silky" Jones, his sparring partner and good friend who later went on to become WBO light-middleweight title holder. Collins was trained by Freddie King in the Romford training camp. In May 1994, Collins finally won a world title by defeating Chris Pyatt by stoppage in five rounds to become the WBO middleweight champion. Early in 1995, Collins relinquished this title without a defence as he was having difficulty making the 160lbs middleweight limit. In March 1995, Chris Eubank (41-0-2) had been scheduled to have a third WBO super-middleweight title fight against Ray Close. Eubank and Close had two fights over the previous two years (their first fight a draw, and their second fight a narrow split decision win for Eubank), but Close was forced to withdraw from their scheduled third fight after failing an MRI brain scan. Collins then stepped into Close's place, moving up to super-middleweight to take on Eubank.WBO super-middleweight champion
Collins defeated the then unbeaten long-reigning champion Chris Eubank in Millstreet, County Cork, Ireland, in March 1995, by unanimous decision (115–111, 116–114, 114–113), to win the WBO super-middleweight title. Collins had enlisted the help of a guru, and they led the press to believe that Collins would be hypnotised for the fight, which noticeably unsettled Eubank. True to form, Collins sat in his corner and did not move, listening to headphones during Eubank's ring entrance. Collins knocked Eubank down in the eighth round, and was well ahead on the scorecards at the end of Round 9, but Eubank finished the fight strongly as he tried to save his unbeaten record and knocked Collins down in the tenth round, coming close to a stoppage. Eubank was unable to finish the job, and Collins held on for victory. In their September 1995 rematch in Cork, Collins performed brilliantly, changing his usual fighting style by adopting wild, brawling tactics throughout which Eubank really struggled to deal with. Despite most TV pundits and commentators giving Collins a wide points victory with scorecards in the region of 117–111 and 118–110, the three judges saw the fight very differently with Collins only winning by a close split decision, 115–113, 115–113 and 114–115. Collins successfully defended his WBO super-middleweight title seven times, including two fights against Nigel Benn in 1996. In the summer of 1997, Collins reportedly stated in the press that he had no motivation left, as he had spent the best part of his career chasing Roy Jones Jr. for a fight that had been promised to him many times. Collins is reported to have stated in Boxing World that he had spent so long chasing Roy Jones Jr. that money was no longer important; that he would "fight him in a phone box in front of two men and a dog". but the bout never materialised. A WBO super-middleweight title fight against Joe Calzaghe was agreed for October 1997, but Collins got injured 10 days before the scheduled fight, got stripped of his title by the WBO, with Collins then making a statement saying that fighting Calzaghe would do nothing to satisfy the desire he had for fighting Jones. Collins then added he wanted to retire on a high note with a good pay day, "Joe is a good up-and-coming kid, but he wouldn't fill a parish church". As Collins couldn't get the fight with Jones, Collins decided to retire. In 1999, Collins announced his decision to come out of retirement to fight Roy Jones Jr. Controversy surrounded the proposed fight, as WBC and WBA light heavyweight champion Jones decided to fight the IBF light heavyweight champion and old Collins foe Reggie Johnson (which Jones won by a shutout 120–106 on all three judges' scorecards), and it was revealed that Collins would have to fight Calzaghe before a showdown with Jones. Collins had accepted this and started to prepare to fight Calzaghe. In training, Collins collapsed during a sparring session with Howard Eastman. Although tests and a brain scan could not find any problems, Collins decided that it was a warning to make him stop boxing, and he retired for a second time. Collins retired in 1997, with a record of 39 fights, 36 wins (21 knockouts) and 3 losses. Collins has not entirely faded from the spotlight since his retirement. In 1998 he appeared in the film Lock, Stock and Two Smoking Barrels as a boxing gym bouncer. In 1999 he made a cameo appearance in "Sweetest Thing", a music video by U2. On 15 January 2013, at the age of 48, Collins announced plans to fight Roy Jones Jr.He went on to appear in a number of exhibition bouts in preparation for the proposed Jones fight. In 2017 Collins joined the Army Reserve's 253 Provost Company of the 4th Regiment Royal Military Police in London where he had been living for the previous 20 years. He gained promotion to Lance Corporal and qualified as an army boxing coach. His brother Roddy Collins is a former professional footballer and manager. His brother Paschal was a professional boxer and now a leading professional boxing coach plus manager. His eldest son Stevie Jnr is a retired rugby player and a retired professional boxer who now coaches and manages boxers His youngest son Luke is an active amateur boxer and qualified amateur boxing coach -

 34cm x 54cm Spectacular print of the Co Kildare Hunt in full cry including a stylish lady riding side saddle.The Kildare Hunt Club was formally born in 1804, with Sir Fenton Aylmer of Donadea as its first master. Hunting had flourished in the 17th century but became a more formal entity by 1726 when the Ponsonbys of Bishopscourt established what might well constitute the original ‘Kildare Hunt’. The Conollys of Castletown House and the Kennedy’s of Johnstown both had a private pack of foxhounds by the 1760s.There were also packs at Castlemartin, Ballynure, Castlewarden, Donadea and Straffan. The Leinster Harriers were established at Kilmorony House near Athy in 1812 while the Naas Harriers were kennelled at Jigginstown from 1920 until 2000. Another keen hunting family were the Burghs of Oldtown, Naas; TJ and Ulick Burgh both took part in the cavalry charge at the battle of Tel el Kebir in Egypt in 1882.In the early 19th century, hunt members simply ‘improvised some modest little meeting at which gentlemen and farmers alike could indulge their taste for riding over a typical bit of Kildare country’. And yet the sport transcended religion and class to such an extent that, in the diocese of Kildare and Leighlin, it was said that hunting amongst the Catholic clergy was widespread.
34cm x 54cm Spectacular print of the Co Kildare Hunt in full cry including a stylish lady riding side saddle.The Kildare Hunt Club was formally born in 1804, with Sir Fenton Aylmer of Donadea as its first master. Hunting had flourished in the 17th century but became a more formal entity by 1726 when the Ponsonbys of Bishopscourt established what might well constitute the original ‘Kildare Hunt’. The Conollys of Castletown House and the Kennedy’s of Johnstown both had a private pack of foxhounds by the 1760s.There were also packs at Castlemartin, Ballynure, Castlewarden, Donadea and Straffan. The Leinster Harriers were established at Kilmorony House near Athy in 1812 while the Naas Harriers were kennelled at Jigginstown from 1920 until 2000. Another keen hunting family were the Burghs of Oldtown, Naas; TJ and Ulick Burgh both took part in the cavalry charge at the battle of Tel el Kebir in Egypt in 1882.In the early 19th century, hunt members simply ‘improvised some modest little meeting at which gentlemen and farmers alike could indulge their taste for riding over a typical bit of Kildare country’. And yet the sport transcended religion and class to such an extent that, in the diocese of Kildare and Leighlin, it was said that hunting amongst the Catholic clergy was widespread. -
 Fantastic original Sweet Afton Virginia Cigarettes Advertising print with beautiful images of the two holy grails in Irish Sport-The Sam Maguire Cup for the All Ireland Gaelic football Champions and the Liam McCarthy Cup for the All Ireland Hurling Champions.A footballer from Cork and a hurler from Kilkenny are featured in this charming print. Also the winners and shorelines from All Irelands from 1887 to 1963 are included underneath.Acharming addition to any wall space Dimensions: 75cm x 55cm Origins;Aughrim Co Galway UnglazedOrigins : Co Kilkenny Dimensions : 48cm x 62cm
Fantastic original Sweet Afton Virginia Cigarettes Advertising print with beautiful images of the two holy grails in Irish Sport-The Sam Maguire Cup for the All Ireland Gaelic football Champions and the Liam McCarthy Cup for the All Ireland Hurling Champions.A footballer from Cork and a hurler from Kilkenny are featured in this charming print. Also the winners and shorelines from All Irelands from 1887 to 1963 are included underneath.Acharming addition to any wall space Dimensions: 75cm x 55cm Origins;Aughrim Co Galway UnglazedOrigins : Co Kilkenny Dimensions : 48cm x 62cm A 20-pack of Sweet Afton cigarettes with a text warning in both Irish and English stating "Smoking kills".
A 20-pack of Sweet Afton cigarettes with a text warning in both Irish and English stating "Smoking kills".Product type Cigarette Sweet Afton was an Irish brand of short, unfiltered cigarettes made with Virginia tobacco and produced by P.J. Carroll & Co., Dundalk, Ireland, now a subsidiary of British American Tobacco. The Sweet Afton brand was launched by Carroll's in 1919 to celebrate the link between Dundalk and the national poet of Scotland, Robert Burns. Burns' eldest sister, Agnes, lived in Dundalk from 1817 until her death in 1834 and was buried in the cemetery of St. Nicholas's Church in the town. Carroll's thought that the brand would only be successful in Scotland if the carton simply had an image of Burns, or Scottish name on the packet, so the people of Dundalk were canvassed and the name Sweet Afton was chosen. The name is taken from Burns' poem "Sweet Afton", which itself takes its title from the poem's first stanza: Flow gently, sweet Afton, amang thy green braes Flow gently, I’ll sing thee a song in thy praise My Mary’s asleep by they murmuring stream Flow gently, sweet Afton, disturb not her dream. A larger version of the cigarette was also marketed under the brand name Afton Major. This name served as inspiration for Carroll's later Majorbrand of tipped cigarettes. As of Autumn 2011, British American Tobacco no longer manufactures Sweet Afton cigarettes. The text "Thank you for your loyalty, unfortunately Sweet Afton will not be available in the future. However Major, our other Irish brand with similar tobacco will still be widely available for purchase." was written on a sticker that was put on the last line of packs, before it went out of production. The brand proved particularly popular with post World War II Rive Gauche Paris. It was reputed to be Jean-Paul Sartre's preferred cigarette, and also featured prominently in Louis Malle's film Le Feu Follet, as well as a number of other Nouvelle Vague films.Margot Tenenbaum (played by Gwyneth Paltrow) from Wes Anderson's 2001 film The Royal Tenenbaums also smokes Sweet Aftons. Thomas Shelby, in Peaky Blinders, smokes Sweet Aftons. They are also the favoured brand of Gerhard Selb, the eponymous private investigator in the trilogy by Bernhard SchlinkOld Afton advertisement on a pub in Wexford -
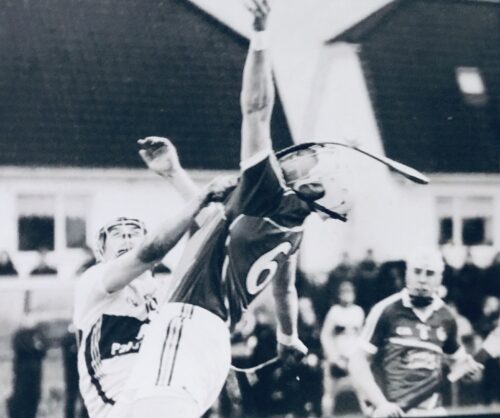

 26cm x 33cm Not so much the clash of the ash as the bend of the ash in this unbelievable action photograph as Clare and Limerick Hurlers do battle in a challenge game in Sixmilebridge.The art of Hurley making & the raw materials used have not changed a lot since time immemorial as this article demonstrates ; Cad a dhéanfaimid feasta gan adhmaid, tá deireadh na gcoillte ar lár…” seems an appropriate opening to an article about hurley making, as we speak to Pat Cronin in his workshop overlooking the Comeragh Mountains in Kilcash, Tipperary. “Over 90% of the timber used in hurley-making now is foreign. Irish ash is very scarce, although Coillte are working to change this”, explained Pat. “I get most of my timber from Coillte in Dundrum (Tipperary). This comes from Denmark and Sweden”. Although some makers have produced hurleys from 14 year old ash Pat believes this is too soon. “You might only get two or three slabs out of a tree that young. If you left it another five or more years you’d get more than double that. It’d really take up to 25 years to get a decent return.” Pat’s uncle, Larry Welsh, made hurleys, but Pat didn’t realise this when he started out. “John Joe O’Brien in Cahir taught me. I used to call to him to get a few now and then and it went from there. I started about 25 years ago and gave up working with Eircom to go at it full time five years ago. I’m kept busy throughout the year.” Brian Dowling’s “Star Hurleys” workshop is in the heart of Kilkenny. Despite the fact that his son Mark is also in the business they’re under constant pressure to meet demand. Brian, who served his time to become a carpenter, has been making hurleys since 1980. His father Ramie was a well known maker, who started in the early 1960’s with Brian’s grandfather Tom Neary. It probably takes about thirty minutes to make a hurley, if you were to go at it from start to finish. However, neither Pat nor Brian make them in this way. Both use copying machines to rough cut “slabs” three or four at a time. Each then finishes the hurleys by hand, to meet specific requirements. “You get phases of popularity in styles”, explained Pat Cronin, “Because of the O’Connor’s of Cork for instance, big bosses are in favour now. But there’s also a trend towards shorter and lighter sticks. There’s a risk if the hurley is too light it’ll snap more easily. And you don’t get the same distance on a puck out.” Brian, recently in Italy looking at a replacement for his aging copying machine, only cuts 33 inch sticks and bigger this way. “I do the smaller ones entirely by hand”. The style of hurling has changed over the years and naturally the hurley changes to reflect this. “Demands for particular styles naturally reflect the styles of the successful teams of the time”. Certainly the demand for personalised sticks has grown. Brian, who supplies most of the Kilkenny senior team, explains that most of them have specific demands. Every hurley maker will advise you differently about how best to look after your stick! wever, you need good quality timber to start with. Pat Cronin suggests that when you get your new hurley you should put it away for a while. “Some people hang them, rather than prop them against a wall, so they won’t warp. There are those who put them in water until they get the right weight. Then they’ll varnish or linseed oil them to keep them at that weight. Like a good wine it should also be stored somewhere cool! You definitely shouldn’t keep them in the kitchen or in the boot of your car, or they will dry out.” Brian suggests that it’s better to buy the stick unbanded. “You need to allow a bit of time for timber to settle. You might also put five or six coats of linseed oil on, or even drop them into a barrel of linseed oil for a while, to get more penetration. You have to remember that this will add weight ‘though. But whether you oil them or not, you should leave them for a good week or so before banding them. And don’t keep them in the house!” There is a Hurley Makers Guild, which was formed almost ten years ago when ash became scarce. Makers felt the need to organise themselves to address the problem. There are about fifty active members these days. Both Pat Cronin and Brian Dowling are curious to see how Jack Carey – brother of the illustrious DJ – gets on with his plan to import finished hurleys from Eastern Europe. This could have quite an impact on what might be regarded as a quintessentially Irish cottage industry. However, time will tell. Just to set up a workshop and kit it out here in Ireland would probably cost about half a million Euro, according to both Pat and Brian. Not a cheap business to get into! Little wonder the notion of foreign manufactured hurleys doesn’t seem that strange… Two great Craftsmen, continuing the wonderful tradition of hurley-making.
26cm x 33cm Not so much the clash of the ash as the bend of the ash in this unbelievable action photograph as Clare and Limerick Hurlers do battle in a challenge game in Sixmilebridge.The art of Hurley making & the raw materials used have not changed a lot since time immemorial as this article demonstrates ; Cad a dhéanfaimid feasta gan adhmaid, tá deireadh na gcoillte ar lár…” seems an appropriate opening to an article about hurley making, as we speak to Pat Cronin in his workshop overlooking the Comeragh Mountains in Kilcash, Tipperary. “Over 90% of the timber used in hurley-making now is foreign. Irish ash is very scarce, although Coillte are working to change this”, explained Pat. “I get most of my timber from Coillte in Dundrum (Tipperary). This comes from Denmark and Sweden”. Although some makers have produced hurleys from 14 year old ash Pat believes this is too soon. “You might only get two or three slabs out of a tree that young. If you left it another five or more years you’d get more than double that. It’d really take up to 25 years to get a decent return.” Pat’s uncle, Larry Welsh, made hurleys, but Pat didn’t realise this when he started out. “John Joe O’Brien in Cahir taught me. I used to call to him to get a few now and then and it went from there. I started about 25 years ago and gave up working with Eircom to go at it full time five years ago. I’m kept busy throughout the year.” Brian Dowling’s “Star Hurleys” workshop is in the heart of Kilkenny. Despite the fact that his son Mark is also in the business they’re under constant pressure to meet demand. Brian, who served his time to become a carpenter, has been making hurleys since 1980. His father Ramie was a well known maker, who started in the early 1960’s with Brian’s grandfather Tom Neary. It probably takes about thirty minutes to make a hurley, if you were to go at it from start to finish. However, neither Pat nor Brian make them in this way. Both use copying machines to rough cut “slabs” three or four at a time. Each then finishes the hurleys by hand, to meet specific requirements. “You get phases of popularity in styles”, explained Pat Cronin, “Because of the O’Connor’s of Cork for instance, big bosses are in favour now. But there’s also a trend towards shorter and lighter sticks. There’s a risk if the hurley is too light it’ll snap more easily. And you don’t get the same distance on a puck out.” Brian, recently in Italy looking at a replacement for his aging copying machine, only cuts 33 inch sticks and bigger this way. “I do the smaller ones entirely by hand”. The style of hurling has changed over the years and naturally the hurley changes to reflect this. “Demands for particular styles naturally reflect the styles of the successful teams of the time”. Certainly the demand for personalised sticks has grown. Brian, who supplies most of the Kilkenny senior team, explains that most of them have specific demands. Every hurley maker will advise you differently about how best to look after your stick! wever, you need good quality timber to start with. Pat Cronin suggests that when you get your new hurley you should put it away for a while. “Some people hang them, rather than prop them against a wall, so they won’t warp. There are those who put them in water until they get the right weight. Then they’ll varnish or linseed oil them to keep them at that weight. Like a good wine it should also be stored somewhere cool! You definitely shouldn’t keep them in the kitchen or in the boot of your car, or they will dry out.” Brian suggests that it’s better to buy the stick unbanded. “You need to allow a bit of time for timber to settle. You might also put five or six coats of linseed oil on, or even drop them into a barrel of linseed oil for a while, to get more penetration. You have to remember that this will add weight ‘though. But whether you oil them or not, you should leave them for a good week or so before banding them. And don’t keep them in the house!” There is a Hurley Makers Guild, which was formed almost ten years ago when ash became scarce. Makers felt the need to organise themselves to address the problem. There are about fifty active members these days. Both Pat Cronin and Brian Dowling are curious to see how Jack Carey – brother of the illustrious DJ – gets on with his plan to import finished hurleys from Eastern Europe. This could have quite an impact on what might be regarded as a quintessentially Irish cottage industry. However, time will tell. Just to set up a workshop and kit it out here in Ireland would probably cost about half a million Euro, according to both Pat and Brian. Not a cheap business to get into! Little wonder the notion of foreign manufactured hurleys doesn’t seem that strange… Two great Craftsmen, continuing the wonderful tradition of hurley-making. -

 An extraordinary piece of Irish Rugby memorabilia .A team photo of the 'Blarney Boys-Irish International Rugby XV' taken by Jim Grier from Granard Co Longford,who was an RAF pilot incarcerated in Stalag VIIIB Prisoner of War Camp in Lamsdorf,East Germany from 1942 to 1945.This amazing photograph was taken by the resident German Camp Photographer and presented to Jim. 36cm x 50cm Jim captained the Irish Team which was assembled during the summer of 1943 when the prisoners organised their own international rugby tournament comprising of the various nationalities incarcerated there.The Irish Team were mainly Army men.Their coach was the remarkable 'Pop' Press -50 years old and a Great War Veteran and Royal Marine (seen in the photo back row on left ).All teams were assigned full playing kit by their hosts with their country's emblem emblazoned on each. Stalag 344 was a large German P.O.W Camp ,100 miles south of Breslau and held between 12 & 15000 British troops, most of them taken prisoner at Dunkirk in 1940,Canadian & RAF Aircrew. The competition was limited to 12 a side as the pitches were small.Not surprisingly ,a New Zealand team emerged victorious who competed against the Home Nations.
An extraordinary piece of Irish Rugby memorabilia .A team photo of the 'Blarney Boys-Irish International Rugby XV' taken by Jim Grier from Granard Co Longford,who was an RAF pilot incarcerated in Stalag VIIIB Prisoner of War Camp in Lamsdorf,East Germany from 1942 to 1945.This amazing photograph was taken by the resident German Camp Photographer and presented to Jim. 36cm x 50cm Jim captained the Irish Team which was assembled during the summer of 1943 when the prisoners organised their own international rugby tournament comprising of the various nationalities incarcerated there.The Irish Team were mainly Army men.Their coach was the remarkable 'Pop' Press -50 years old and a Great War Veteran and Royal Marine (seen in the photo back row on left ).All teams were assigned full playing kit by their hosts with their country's emblem emblazoned on each. Stalag 344 was a large German P.O.W Camp ,100 miles south of Breslau and held between 12 & 15000 British troops, most of them taken prisoner at Dunkirk in 1940,Canadian & RAF Aircrew. The competition was limited to 12 a side as the pitches were small.Not surprisingly ,a New Zealand team emerged victorious who competed against the Home Nations. -
Out of stock
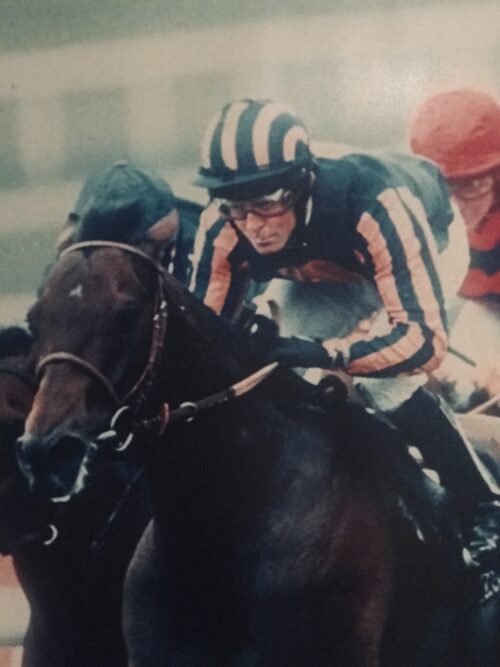

 Superb framed action photograph of a motionless Mick Kinane on board Montjeu showing a blistering turn of foot to win the Group 1 Tattersalls Gold Cup at the Curragh in 2000. 62cm x 80cm Cashel Co Tipperary Montjeu (4 April 1996 – 29 March 2012) was an Irish-bred, French-trained thoroughbred horse racing racehorse and sire. In a racing career which lasted from September 1998 to November 2000 he ran sixteen times and won eleven races. After winning twice as a juvenile, he was the outstanding European racehorse of 1999, winning the Prix du Jockey Club, the Irish Derby and the Prix de l'Arc de Triomphe. Four more victories in 2000 included the King George VI and Queen Elizabeth Stakes. He was then retired to stud where he proved to be an outstanding sire of winners. He died on 29 March 2012 at age 16 at Coolmore Stud from complications related to sepsis.
Superb framed action photograph of a motionless Mick Kinane on board Montjeu showing a blistering turn of foot to win the Group 1 Tattersalls Gold Cup at the Curragh in 2000. 62cm x 80cm Cashel Co Tipperary Montjeu (4 April 1996 – 29 March 2012) was an Irish-bred, French-trained thoroughbred horse racing racehorse and sire. In a racing career which lasted from September 1998 to November 2000 he ran sixteen times and won eleven races. After winning twice as a juvenile, he was the outstanding European racehorse of 1999, winning the Prix du Jockey Club, the Irish Derby and the Prix de l'Arc de Triomphe. Four more victories in 2000 included the King George VI and Queen Elizabeth Stakes. He was then retired to stud where he proved to be an outstanding sire of winners. He died on 29 March 2012 at age 16 at Coolmore Stud from complications related to sepsis.Background
Montjeu, a bay horse standing 16.1 hands high, was bred in Ireland by Sir James Goldsmith, who named him after his chateau outside Autun in France.Goldsmith died in 1997 before the colt began racing, and his ownership went to a holding company (Tsega Ltd) owned by Laure Boulay de la Meurthe, mother of two of Goldsmith's children. Montjeu was sired by the thirteen times British Champion Sire Sadler's Wells out of the Prix de Lutèce winner Floripedes. The colt was sent into training with John E. Hammond at Chantilly.Racing career
1998: two-year-old season[
Montjeu ran twice as a two-year-old in the autumn of 1998. On his racecourse debut he appeared in the Prix de la Maniguette over 1600 m at Chantilly and won "easily" from nine opponents.A month later, he was moved up to Listed class and won the Prix Isonomy by three quarters of a length from Spadoun. Montjeu's form was boosted two weeks later when Spadoun won the Group One Critérium de Saint-Cloud. At the end of the year, a half-share in Montjeu was sold to the Coolmore organization, represented by Michael Tabor and Susan Magnier.1999: three-year-old season
Montjeu began his three-year-old season by starting joint-favourite with the Aga Khan's colt Sendawar in the Group Two Prix Greffulhe over 2100 m at Longchamp in April. Ridden by Cash Asmussen, he was restrained in the early stages before finishing strongly to overtake Sendawar 50 m from the finish and win by a length. Sendawar went on to win the Poule d'Essai des Poulains the St. James's Palace Stakes and the Prix du Moulin de Longchamp before the end of the season. On his next start Montjeu was made 1/10 favourite for the Prix Lupin, but was beaten a length by Gracioso after hanging to the right in the closing stages of a slowly run race. Despite his defeat, Montjeu was made 7/5 favourite for the Prix du Jockey Club at Chantilly on 6 June. Asmussen held the colt up at the rear of the field before making his challenge in the straight. He took the lead 400 m from the finish and drew away from his opponents to win by four lengths from Nowhere To Exit, with Gracioso finishing nine lengths further back in sixth. Three weeks later, Montjeu was sent to the Curragh for the Irish Derby where his main rivals appeared to be the English-trained colts Daliapour and Beat All who had finished second and third respectively in The Derby. As at Chantilly, Montjeu was held up in the early running before moving smoothly through to dispute the lead in the straight. He took the lead a furlong from the finish and pulled clear to win by five lengths from Daliapour in "impressive" style.After the race, Asmussen claimed that he had "five kilos in hand". Montjeu was then given a planned break of more than two months before returning in the Prix Niel at Longchamp. Ridden for the first time by Mick Kinane, he was last of the four runners entering the straight but moved forward to take the lead in the closing stages and won "cleverly" by a head from Bienamado. In the Prix de l'Arc de Triomphe three weeks later, Montjeu started 6/4 favourite in a field of fourteen runners on unusually heavy ground. Kinane positioned Montjeu much closer to the lead on this occasion and he turned into the straight in fifth place before being switched to the outside. By this time however, the Japanese challenger El Condor Pasa had opened up a three-length lead, and Montjeu had to be driven out to catch him. Montjeu overtook El Condor Pasa 100 m from the finish and won by half a length, with a further six lengths back to Croco Rouge in third. The unplaced runners included Daylami and Fantastic Light. Immediately after the race, Kinane described Montjeu as "the best mile-and-a-half horse I have ever sat on." On his final start of the season, Montjeu started favourite for the Japan Cup on 28 November, but finished fourth behind Special Week, Indigenous and High-Rise.2000: four-year-old season
Montjeu stayed in training as a four-year-old and won his first four races. He began his season by moving down in distance to ten furlongs to win the Tattersalls Gold Cup at the Curragh by one and a half lengths from Greek Dance. On 2 July he won the Grand Prix de Saint-Cloud by five lengths from Daring Miss and the 1998 Arc de Triomphe winner Sagamix. Four weeks later he ran in Great Britain for the first time in his career when he contested the King George VI and Queen Elizabeth Stakes at Ascot. Montjeu showed signs of temperament in the preliminaries, as he refused to enter the paddock, but was never in danger in the race itself. Starting at odds of 1/3 he "cruised"into the lead in the straight and won very easily by one and three-quarter lengths from Fantastic Light. Brough Scott, of the Daily Telegraph described the performance as "devastating" and compared Montjeu to past champions such as Ribot, Nijinsky, Mill Reef and Shergar. Montjeu won the Prix Foy at odds of 1/10 and was then made odds-on favourite to win his second "Arc" in October. He failed to reproduce his best form however, and finished fourth to Sinndar. He returned to Britain two weeks later for the Champion Stakes and again started favourite, but was beaten half a length by Kalanisi. On his final racecourse appearance three weeks later he finished seventh behind Kalanisi in the Breeders' Cup Turf. At the end of 1999, Montjeu was voted that year's Cartier Three-Year-Old European Champion Colt and World Champion. Montjeu was given an official rating of 135 by the International Classification, making him the highest rated three-year-old of the season, although some, including the Racing Post, felt that the rating underestimated his achievements. Timeform concurred, giving him a mark of 137 in 1999 and 2000. Montjeu was known for his idiosyncratic temperament: Kinane explained that the horse had "a few issues", while Hammond called him "an eccentric genius". In 2001, Montjeu was retired to Coolmore Stud in Tipperary, Ireland. He was one of the top sires in the world and produced several noted champions, including four winners of the Epsom Derby – Motivator, Authorized, Pour Moi, and Camelot. -
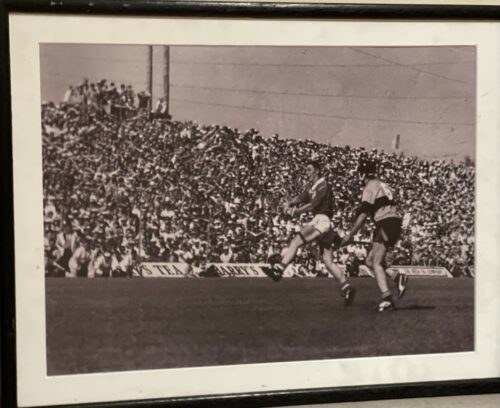
 47cm x 34cm In the relative cool of the Limerick dressing-room, cramped and pokey as it was beneath the Mackey Stand, Ger Loughnane addressed the victors. It was, the vanquished Clare manager told them, "the kind of game we hear about from our fathers and grandfathers" - adding that in all his time in hurling he had never been involved in anything like it. In the corner was Ciarán Carey, fresh from his wondrous individual point that had decided the game - it still remains one of hurling's greatest scores - parked on a slatted bench, pulling on a cigarette. The protein shakes were still a few years off. Loughnane would go on to savour many more tumultuous, spine-tingling days on the sideline with Clare, some of a higher standard than that particular scorching Sunday afternoon. For all the latest sports news, analysis and updates direct to your inbox, sign up to our newsletter. But that 1996 Munster semi-final was, as Anthony Daly put it in his autobiography many years later, "a day of days" - the most memorable game he had played in. Two things stood out on the way to the Gaelic Grounds that day - the heat and the crowds swarming on the Ennis Road, the tar squelching beneath each and every one. As far as the eye could see down both sides were people walking through a heat haze, so many white shirts peppered between green and saffron and blue. How, you thought, could anyone hurl in the conditions in little over an hour's time?ADVERTISEMENT
47cm x 34cm In the relative cool of the Limerick dressing-room, cramped and pokey as it was beneath the Mackey Stand, Ger Loughnane addressed the victors. It was, the vanquished Clare manager told them, "the kind of game we hear about from our fathers and grandfathers" - adding that in all his time in hurling he had never been involved in anything like it. In the corner was Ciarán Carey, fresh from his wondrous individual point that had decided the game - it still remains one of hurling's greatest scores - parked on a slatted bench, pulling on a cigarette. The protein shakes were still a few years off. Loughnane would go on to savour many more tumultuous, spine-tingling days on the sideline with Clare, some of a higher standard than that particular scorching Sunday afternoon. For all the latest sports news, analysis and updates direct to your inbox, sign up to our newsletter. But that 1996 Munster semi-final was, as Anthony Daly put it in his autobiography many years later, "a day of days" - the most memorable game he had played in. Two things stood out on the way to the Gaelic Grounds that day - the heat and the crowds swarming on the Ennis Road, the tar squelching beneath each and every one. As far as the eye could see down both sides were people walking through a heat haze, so many white shirts peppered between green and saffron and blue. How, you thought, could anyone hurl in the conditions in little over an hour's time?ADVERTISEMENT -

 The Hurley Playerby Jack B Yeats in nice, offset frame. 33cm x 24cm Jack Butler Yeats RHA (29 August 1871 – 28 March 1957) was an Irish artist and Olympic medalist. W. B. Yeats was his brother. Butler's early style was that of an illustrator; he only began to work regularly in oils in 1906. His early pictures are simple lyrical depictions of landscapes and figures, predominantly from the west of Ireland—especially of his boyhood home of Sligo. Yeats's work contains elements of Romanticism. He later would adopt the style of Expressionism
The Hurley Playerby Jack B Yeats in nice, offset frame. 33cm x 24cm Jack Butler Yeats RHA (29 August 1871 – 28 March 1957) was an Irish artist and Olympic medalist. W. B. Yeats was his brother. Butler's early style was that of an illustrator; he only began to work regularly in oils in 1906. His early pictures are simple lyrical depictions of landscapes and figures, predominantly from the west of Ireland—especially of his boyhood home of Sligo. Yeats's work contains elements of Romanticism. He later would adopt the style of ExpressionismBiography
Yeats was born in London, England. He was the youngest son of Irish portraitist John Butler Yeats and the brother of W. B. Yeats, who received the 1923 Nobel Prize in Literature. He grew up in Sligo with his maternal grandparents, before returning to his parents' home in London in 1887. Early in his career he worked as an illustrator for magazines like the Boy's Own Paper and Judy, drew comic strips, including the Sherlock Holmes parody "Chubb-Lock Homes" for Comic Cuts, and wrote articles for Punch under the pseudonym "W. Bird".In 1894 he married Mary Cottenham, also a native of England and two years his senior, and resided in Wicklow according to the Census of Ireland, 1911. From around 1920, he developed into an intensely Expressionist artist, moving from illustration to Symbolism. He was sympathetic to the Irish Republican cause, but not politically active. However, he believed that 'a painter must be part of the land and of the life he paints', and his own artistic development, as a Modernist and Expressionist, helped articulate a modern Dublin of the 20th century, partly by depicting specifically Irish subjects, but also by doing so in the light of universal themes such as the loneliness of the individual, and the universality of the plight of man. Samuel Beckett wrote that "Yeats is with the great of our time... because he brings light, as only the great dare to bring light, to the issueless predicament of existence."The Marxist art critic and author John Berger also paid tribute to Yeats from a very different perspective, praising the artist as a "great painter" with a "sense of the future, an awareness of the possibility of a world other than the one we know". His favourite subjects included the Irish landscape, horses, circus and travelling players. His early paintings and drawings are distinguished by an energetic simplicity of line and colour, his later paintings by an extremely vigorous and experimental treatment of often thickly applied paint. He frequently abandoned the brush altogether, applying paint in a variety of different ways, and was deeply interested in the expressive power of colour. Despite his position as the most important Irish artist of the 20th century (and the first to sell for over £1m), he took no pupils and allowed no one to watch him work, so he remains a unique figure. The artist closest to him in style is his friend, the Austrian painter, Oskar Kokoschka. Besides painting, Yeats had a significant interest in theatre and in literature. He was a close friend of Samuel Beckett. He designed sets for the Abbey Theatre, and three of his own plays were also produced there. He wrote novels in a stream of consciousness style that Joyce acknowledged, and also many essays. His literary works include The Careless Flower, The Amaranthers (much admired by Beckett), Ah Well, A Romance in Perpetuity, And To You Also, and The Charmed Life. Yeats's paintings usually bear poetic and evocative titles. Indeed, his father recognized that Jack was a far better painter than he, and also believed that 'some day I will be remembered as the father of a great poet, and the poet is Jack'.He was elected a member of the Royal Hibernian Academy in 1916.He died in Dublin in 1957, and was buried in Mount Jerome Cemetery. Yeats holds the distinction of being Ireland's first medalist at the Olympic Games in the wake of creation of the Irish Free State. At the 1924 Summer Olympics in Paris, Yeats' painting The Liffey Swim won a silver medal in the arts and culture segment of the Games. In the competition records the painting is simply entitled Swimming.Works
In November 2010, one of Yeats's works, A Horseman Enters a Town at Night, painted in 1948 and previously owned by novelist Graham Greene, sold for nearly £350,000 at a Christie's auction in London. A smaller work, Man in a Room Thinking, painted in 1947, sold for £66,000 at the same auction. In 1999 the painting, The Wild Ones, had sold at Sotheby's in London for over £1.2m, the highest price yet paid for a Yeats painting. Adam's Auctioneers hold the Irish record sale price for a Yeats painting, A Fair Day, Mayo (1925), which sold for €1,000,000 in September 2011.Hosting museums
- The Hunt Museum, Limerick
- The National Gallery of Ireland, Dublin
- The Hugh Lane Gallery, Dublin
- Crawford Art Gallery, Cork
- Irish Museum of Modern Art, Dublin
- The National Gallery of Canada, Ottawa
- Walters Art Museum, Baltimore
- Model Arts and Niland Gallery, Sligo
- The Municipal Art Collection, Waterford
- Ulster Museum, Belfast
- The Snite Museum of Art, University of Notre Dame
The Geography of Hurling
Kevin Whelan Why is hurling currently popular in a compact region centred on east Munster and south Leinster, and in isolated pockets in the Glens of Antrim and in the Ards peninsula of County Down? The answer lies in an exploration of the interplay between culture, politics and environment over a long period of time. TWO VERSIONS By the eighteenth century it is quite clear that there were two principal, and regionally distinct,versions of the game. One was akin to modern field hockey, or shinty, in that it did not allow handling of the ball; it was played with a narrow, crooked stick; it used a hard wooden ball (the ‘crag’); it was mainly a winter game. This game, called camán (anglicised to ‘commons’), was confined to the northern half of the country; its southern limits were set sharply where the small farms of the drumlin belt petered out into the pastoral central lowlands. (Fig 1)
‘The Hurley Player’ by Jack B. Yeats
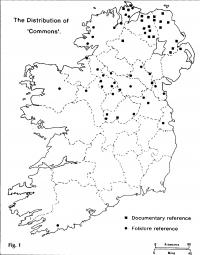 The second version of the game (iomán or báire) was of southern provenance. The ball could be handled or carried on the hurl, which was flat and round-headed; the ball (the sliothar) was soft and made of animal hair; the game was played in summer. Unlike commons, this form of hurling was patronised by the gentry, as a spectator and gambling sport, associated with fairs and other public gatherings, and involved a much greater degree of organisation (including advertising) than the more demotic ‘commons’. A 1742 advertisement for Ballyspellan Spa in Kilkenny noted that ‘horse racing, dancing and hurling will be provided for the pleasure of the quality at the spa’.
LANDLORD PATRONAGE
A number of factors determined the distribution of the southern game. (Fig. 2) The most important was the patronage of local gentry families, particularly those most closely embedded in the life of the local people. (Table 1) They picked the teams, arranged the hurling greens and supervised the matches, which were frequently organised as gambling events. The southern hurling zone coincides with the area where, in the late medieval period, the Norman and Gaelic worlds fused to produce a vigorous culture, reflected, for example, in the towerhouse as an architectural innovation. It coincides with well-drained, level terrain, seldom moving too far off the dry sod of limestone areas, which also happen to produce the best material for hurls – ash. It is closely linked to the distribution of big farms, where the relatively comfortable lifestyle afforded the leisure to pursue the sport.
Landlord patronage was essential to the well-being of the southern game; once it was removed, the structures it supported crumbled and the game collapsed into shapeless anarchy. The progressive separation of the manners and language of the élite from the common people was a pan-European phenomenon in the modern period. The gentry’s disengagement from immersion in the shared intimacies of daily life can be seen not just in hurling, but in other areas of language, music, sport and behaviour, as the gradual reception of metropolitan ideas eroded the older loyalties. As one hostile observer put it:
A hurling match is a scene of drunkenness, blasphemy and all kinds and manner of debauchery and faith, for my part, I would liken it to nothing else but to the idea I form of the Stygian regions where the daemonic inhabitants delight in torturing and afflicting each other.
DECLINE
By the mid nineteenth century, hurling had declined so steeply that it survived only in three pockets, around Cork city, in south-east Galway and in the area north of Wexford town. Amongst the reasons for decline were the withdrawal of gentry patronage in an age of political turbulence, sabbitudinarianism, modernisation and the dislocating impact of the Famine. Landlord, priest and magistrate all turned against the game. The older ‘moral economy’, which had linked landlord and tenant in bonds of patronage and deference, gave way to a sharper, adversarial relationship, especially in the 1790s, as the impact of the French Revolution in Ireland created a greater class-consciousness. Politicisation led to a growing anti-landlord feeling, which had been far more subdued in the heyday of gentry-sponsored hurling between the 1740s and 1760s.
The second version of the game (iomán or báire) was of southern provenance. The ball could be handled or carried on the hurl, which was flat and round-headed; the ball (the sliothar) was soft and made of animal hair; the game was played in summer. Unlike commons, this form of hurling was patronised by the gentry, as a spectator and gambling sport, associated with fairs and other public gatherings, and involved a much greater degree of organisation (including advertising) than the more demotic ‘commons’. A 1742 advertisement for Ballyspellan Spa in Kilkenny noted that ‘horse racing, dancing and hurling will be provided for the pleasure of the quality at the spa’.
LANDLORD PATRONAGE
A number of factors determined the distribution of the southern game. (Fig. 2) The most important was the patronage of local gentry families, particularly those most closely embedded in the life of the local people. (Table 1) They picked the teams, arranged the hurling greens and supervised the matches, which were frequently organised as gambling events. The southern hurling zone coincides with the area where, in the late medieval period, the Norman and Gaelic worlds fused to produce a vigorous culture, reflected, for example, in the towerhouse as an architectural innovation. It coincides with well-drained, level terrain, seldom moving too far off the dry sod of limestone areas, which also happen to produce the best material for hurls – ash. It is closely linked to the distribution of big farms, where the relatively comfortable lifestyle afforded the leisure to pursue the sport.
Landlord patronage was essential to the well-being of the southern game; once it was removed, the structures it supported crumbled and the game collapsed into shapeless anarchy. The progressive separation of the manners and language of the élite from the common people was a pan-European phenomenon in the modern period. The gentry’s disengagement from immersion in the shared intimacies of daily life can be seen not just in hurling, but in other areas of language, music, sport and behaviour, as the gradual reception of metropolitan ideas eroded the older loyalties. As one hostile observer put it:
A hurling match is a scene of drunkenness, blasphemy and all kinds and manner of debauchery and faith, for my part, I would liken it to nothing else but to the idea I form of the Stygian regions where the daemonic inhabitants delight in torturing and afflicting each other.
DECLINE
By the mid nineteenth century, hurling had declined so steeply that it survived only in three pockets, around Cork city, in south-east Galway and in the area north of Wexford town. Amongst the reasons for decline were the withdrawal of gentry patronage in an age of political turbulence, sabbitudinarianism, modernisation and the dislocating impact of the Famine. Landlord, priest and magistrate all turned against the game. The older ‘moral economy’, which had linked landlord and tenant in bonds of patronage and deference, gave way to a sharper, adversarial relationship, especially in the 1790s, as the impact of the French Revolution in Ireland created a greater class-consciousness. Politicisation led to a growing anti-landlord feeling, which had been far more subdued in the heyday of gentry-sponsored hurling between the 1740s and 1760s.
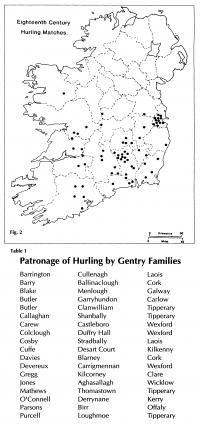 MICHAEL CUSACK & THE GAA
The model of élite participation in popular culture is a threefold process: first immersion, then withdrawal, and, finally rediscovery, invariably by an educated élite, and often with a nationalist agenda. ‘Rediscovery’ usually involves an invention of tradition, creating a packaged, homogenised and often false version of an idealised popular culture – as, for example, in the cult of the Highland kilt. The relationship of hurling and the newly established Gaelic Athletic Association in the 1880s shows this third phase with textbook clarity. Thus, when Michael Cusack set about reviving the game, he codified a synthetic version, principally modelled on the southern ‘iomán’ version that he had known as a child in Clare. Not surprisingly, this new game never caught on in the old ‘commons’ area, with the Glens of Antrim being the only major exception. Cusack and his GAA backers also wished to use the game as a nationalising idiom, a symbolic language of identity filling the void created by the speed of anglicisation. It had therefore to be sharply fenced off in organisational terms from competing ‘anglicised’ sports like cricket, soccer and rugby. Thus, from the beginning, the revived game had a nationalist veneer, its rules of association bristling like a porcupine with protective nationalist quills on which its perceived opponents would have to impale themselves. Its principal backers were those already active in the nationalist political culture of the time, classically the I.R.B. Its spread depended on the active support of an increasingly nationalist Catholic middle class – and as in every country concerned with the invention of tradition, its social constituency included especially journalists, publicans, schoolteachers, clerks, artisans and clerics. Thus, hurling’s early success was in south Leinster and east Munster, the very region which pioneered popular Irish nationalist politics – from the O’Connell campaign, to the devotional revolution in Irish Catholicism, from Fr. Matthews’ temperance campaign, to the Fenians, to the take-over of local government. The GAA was a classic example of the radical conservatism of this region – conservative in its ethos and ideology, radical in its techniques of organisation and mobilisation. The spread of hurling can be very closely matched to the spread of other radical conservative movements of this period – the diffusion of the indigenous Catholic teaching orders and the spread of co-operative dairying.
It would, however, be a mistake to see the spread of hurling under the aegis of the GAA solely in nationalist terms. The codification and success of gaelic games should be compared to the almost contemporaneous success in Britain of codified versions of soccer and rugby. All these were linked to rising spending power, a shortened working week (and the associated development of the ‘weekend’), improved and cheaper mass transport facilities which made spectator sports viable, expanded leisure time, the desire for organised sport among the working classes, and the commercialisation of leisure itself. The really distinctive feature of the GAA’s success was that it occurred in what was still a predominantly agrarian society. That success rested on the shrewd application of the principle of territoriality.
TERRITORIAL ALLEGIANCE
Irish rural life was essentially local life. Hurling was quintessentially a territorially based game – teams based on communities, parishes, counties, pitted one against the other. The painter Tony O’Malley has contrasted this tribal-territorial element in Irish sport to English attitudes:
If neighbours were playing like New Ross and Tullogher, there would be a real needle in it. When Carrickshock were playing, I once heard an old man shouting ‘come on the men that bate the tithe proctors’ and there was a tremor and real fervour in his voice. It was a battle cry, with hurleys as the swords, but with the same intensity.
Similar forces of territoriality have been identified behind the success of cricket in the West Indies and rugby in the Welsh valleys. The GAA tapped this deep-seated territorial loyalty, of the type which is beautifully captured in the rhetorical climax of the great underground classic of rural Ireland, Knocknagow or the Homes of Tipperary by Charles J. Kickham. Matt Donovan (Matt the Thrasher), the village hero, is competing against the outsider Captain French in a sledge-throwing contest. In the absence of steroids, Matt is pumping himself up before his throw:
Someone struck the big drum a single blow, as if by accident and, turning round quickly, the thatched roofs of the hamlet caught his eye. And, strange to say, those old mud walls and thatched roofs roused him as nothing else could. His breast heaved, as with glistening eyes, and that soft plaintive smile of his, he uttered the words, ‘For the credit of the little village!’ in a tone of the deepest tenderness. Then, grasping the sledge in his right hand, and drawing himself up to his full height, he measured the captain’s cast with his eye. The muscles of his arms seemed to start out like cords of steel as he wheeled slowly round and shot the ponderous hammer through the air. His eyes dilated as, with quivering nostrils, he watched its flight, till it fell so far beyond the best mark that even he himself started with astonishment. Then a shout of exultation burst from the excited throng; hands were convulsively grasped, and hats sent flying in the air; and in their wild joy they crushed around him and tried to lift him upon their shoulders.
The territorial allegiance and communal spirit celebrated and idealised by Kickham have died hard in Ireland. GAA club colours, for example were often drawn from old faction favours and, even now, an occasional faction slogan can still be heard. ‘If any man can, an Alley man can’. ‘Squeeze ‘em up Moycarkey and hang ‘em out to dry!’ Lingering animosities can sometimes surface in surprising ways: it is not unknown, for example, for an irate and disappointed Wexford hurling supporter (and what other kind of Wexford supporter is there?) to hurl abuse at Kilkenny, recalling an incident that occurred in Castlecomer to indignant Wexford United Irishmen: ‘Sure what good are they anyway? Didn’t they piss on the powder in ‘98?’ A possibly apocryphal incident occurred after a fiercely contested Cork-Tipperary match. Cork won but in Tipperary eyes that was solely due to a biased Limerick referee. When the disgruntled Tipperary supporters poured off the train at Thurles, they vented their frustrations on the only Limerick man they could find in the town – by tarring and feathering the statue of Archbishop Croke in the Square (presumably the only time in Irish history that a Catholic bishop has been tarred and feathered).
With the notable exception of Cork, the game has not been successfully transplanted into the cities. In Cork, close-knit working-class neighbourhoods like Blackrock and Gouldings Glen (home of Glen Rovers), and the strong antagonism between the hilly northside and the flat southside of the city, nourished the territoriality and community spirit so important to the game’s health. In Dublin, however, the modern suburbs, based on diversity, newness and mobility, have not proved hospitable receptacles of the game. Brendan Behan, brought up in the shadow of Croke Park, commented:
At home we played soccer in the street and sometimes a version of hurling, fast and sometimes savage, adapted from the long-pucking grace of Kilkenny and Tipperary to the crookeder, foreshortened, snappier brutality of the confines of a slum thoroughfare.
MICHAEL CUSACK & THE GAA
The model of élite participation in popular culture is a threefold process: first immersion, then withdrawal, and, finally rediscovery, invariably by an educated élite, and often with a nationalist agenda. ‘Rediscovery’ usually involves an invention of tradition, creating a packaged, homogenised and often false version of an idealised popular culture – as, for example, in the cult of the Highland kilt. The relationship of hurling and the newly established Gaelic Athletic Association in the 1880s shows this third phase with textbook clarity. Thus, when Michael Cusack set about reviving the game, he codified a synthetic version, principally modelled on the southern ‘iomán’ version that he had known as a child in Clare. Not surprisingly, this new game never caught on in the old ‘commons’ area, with the Glens of Antrim being the only major exception. Cusack and his GAA backers also wished to use the game as a nationalising idiom, a symbolic language of identity filling the void created by the speed of anglicisation. It had therefore to be sharply fenced off in organisational terms from competing ‘anglicised’ sports like cricket, soccer and rugby. Thus, from the beginning, the revived game had a nationalist veneer, its rules of association bristling like a porcupine with protective nationalist quills on which its perceived opponents would have to impale themselves. Its principal backers were those already active in the nationalist political culture of the time, classically the I.R.B. Its spread depended on the active support of an increasingly nationalist Catholic middle class – and as in every country concerned with the invention of tradition, its social constituency included especially journalists, publicans, schoolteachers, clerks, artisans and clerics. Thus, hurling’s early success was in south Leinster and east Munster, the very region which pioneered popular Irish nationalist politics – from the O’Connell campaign, to the devotional revolution in Irish Catholicism, from Fr. Matthews’ temperance campaign, to the Fenians, to the take-over of local government. The GAA was a classic example of the radical conservatism of this region – conservative in its ethos and ideology, radical in its techniques of organisation and mobilisation. The spread of hurling can be very closely matched to the spread of other radical conservative movements of this period – the diffusion of the indigenous Catholic teaching orders and the spread of co-operative dairying.
It would, however, be a mistake to see the spread of hurling under the aegis of the GAA solely in nationalist terms. The codification and success of gaelic games should be compared to the almost contemporaneous success in Britain of codified versions of soccer and rugby. All these were linked to rising spending power, a shortened working week (and the associated development of the ‘weekend’), improved and cheaper mass transport facilities which made spectator sports viable, expanded leisure time, the desire for organised sport among the working classes, and the commercialisation of leisure itself. The really distinctive feature of the GAA’s success was that it occurred in what was still a predominantly agrarian society. That success rested on the shrewd application of the principle of territoriality.
TERRITORIAL ALLEGIANCE
Irish rural life was essentially local life. Hurling was quintessentially a territorially based game – teams based on communities, parishes, counties, pitted one against the other. The painter Tony O’Malley has contrasted this tribal-territorial element in Irish sport to English attitudes:
If neighbours were playing like New Ross and Tullogher, there would be a real needle in it. When Carrickshock were playing, I once heard an old man shouting ‘come on the men that bate the tithe proctors’ and there was a tremor and real fervour in his voice. It was a battle cry, with hurleys as the swords, but with the same intensity.
Similar forces of territoriality have been identified behind the success of cricket in the West Indies and rugby in the Welsh valleys. The GAA tapped this deep-seated territorial loyalty, of the type which is beautifully captured in the rhetorical climax of the great underground classic of rural Ireland, Knocknagow or the Homes of Tipperary by Charles J. Kickham. Matt Donovan (Matt the Thrasher), the village hero, is competing against the outsider Captain French in a sledge-throwing contest. In the absence of steroids, Matt is pumping himself up before his throw:
Someone struck the big drum a single blow, as if by accident and, turning round quickly, the thatched roofs of the hamlet caught his eye. And, strange to say, those old mud walls and thatched roofs roused him as nothing else could. His breast heaved, as with glistening eyes, and that soft plaintive smile of his, he uttered the words, ‘For the credit of the little village!’ in a tone of the deepest tenderness. Then, grasping the sledge in his right hand, and drawing himself up to his full height, he measured the captain’s cast with his eye. The muscles of his arms seemed to start out like cords of steel as he wheeled slowly round and shot the ponderous hammer through the air. His eyes dilated as, with quivering nostrils, he watched its flight, till it fell so far beyond the best mark that even he himself started with astonishment. Then a shout of exultation burst from the excited throng; hands were convulsively grasped, and hats sent flying in the air; and in their wild joy they crushed around him and tried to lift him upon their shoulders.
The territorial allegiance and communal spirit celebrated and idealised by Kickham have died hard in Ireland. GAA club colours, for example were often drawn from old faction favours and, even now, an occasional faction slogan can still be heard. ‘If any man can, an Alley man can’. ‘Squeeze ‘em up Moycarkey and hang ‘em out to dry!’ Lingering animosities can sometimes surface in surprising ways: it is not unknown, for example, for an irate and disappointed Wexford hurling supporter (and what other kind of Wexford supporter is there?) to hurl abuse at Kilkenny, recalling an incident that occurred in Castlecomer to indignant Wexford United Irishmen: ‘Sure what good are they anyway? Didn’t they piss on the powder in ‘98?’ A possibly apocryphal incident occurred after a fiercely contested Cork-Tipperary match. Cork won but in Tipperary eyes that was solely due to a biased Limerick referee. When the disgruntled Tipperary supporters poured off the train at Thurles, they vented their frustrations on the only Limerick man they could find in the town – by tarring and feathering the statue of Archbishop Croke in the Square (presumably the only time in Irish history that a Catholic bishop has been tarred and feathered).
With the notable exception of Cork, the game has not been successfully transplanted into the cities. In Cork, close-knit working-class neighbourhoods like Blackrock and Gouldings Glen (home of Glen Rovers), and the strong antagonism between the hilly northside and the flat southside of the city, nourished the territoriality and community spirit so important to the game’s health. In Dublin, however, the modern suburbs, based on diversity, newness and mobility, have not proved hospitable receptacles of the game. Brendan Behan, brought up in the shadow of Croke Park, commented:
At home we played soccer in the street and sometimes a version of hurling, fast and sometimes savage, adapted from the long-pucking grace of Kilkenny and Tipperary to the crookeder, foreshortened, snappier brutality of the confines of a slum thoroughfare.
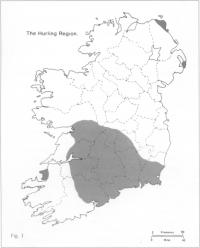 THE PRESENT HURLING REGION
If one looks at the present hurling core region, it is remarkably compact. It also exhibits striking continuity with the earlier ‘iomán’ region. (Fig. 3) The hurling heartland is focused on the three counties of Cork, Tipperary and Kilkenny, with a supporting cast of adjacent counties – Limerick, Clare, Galway, Offaly, Laois, Waterford and Wexford. In the hurling core, the game is king, and very closely stitched into the fabric of the community. Describing the situation in Rathnure, Billy Rackard claimed that in the absence of hurling, ‘the parish would commit suicide, if a parish could commit suicide!’ The boundaries of the hurling region are surprisingly well-defined. To the north, the midland bogs act, as in a way they have done throughout history, as a buffer zone, resolutely impervious to the spread of cultural influences from further south. The western edge of the hurling zone can be traced over a long distance. In County Galway, for example, its boundaries run along a line from Ballinasloe to the city; north of this line is the Tuam-Dunmore area, and west of it is Connemara, both footballing territories. In County Clare, the boundary runs from Tubber on the Galway border through Corofin and Kilmaley to Labasheeda on the Shannon estuary. Last summer, the tremendous achievement of Clare in winning a Munster football championship was most thoroughly relished in the footballing bastion of west Clare, from Kilkee and Doonbeg to Milltown Malbay. One could easily establish this pattern by looking at the thickening density of the forest of flags as one drove from east to west in August.
Across the Shannon in Limerick, the football-hurling divide runs clearly along the scarp dividing hilly west Limerick from the lush limestone lowlands of east Limerick. West of this is an enclave of hurling parishes in the footballing
kingdom of Kerry in the area north of Tralee, in Ardfert, Bally heigue, Causeway and Ballyduff. From Limerick, the hurling boundary loops through County Cork from Mallow to the city and then to the coast at Cloyne – home to the maestro Christy Ring, who famously expressed his strategy for promoting the game in Cork – by stabbing a knife through every football found east of that line. Outside this core region, there are only the hurling enclaves in the Glens of Antrim and on the tip of the Ards peninsula, where the clubs of Ballycran, Ballygalget and Portaferry backbone Down’s hurling revival.
The interesting question then is how these boundaries formed. In almost every case, that boundary divides big farm and small farm areas and marks the transition from fertile, drift-covered limestone lowland to hillier, hungrier, wetter shales, flagstones, grits and granites. In County Galway, for example, hurling has not put down roots in the bony granite outcrops of Connemara, and in Clare the poorly drained flagstone deposits are equally inhospitable. If ash is emblematic of hurling areas, the rush is the distinctive symbol of football territory.
CONCLUSION
This brief case study illustrates the interplay of what the French call la longue durée – the long evolution of history – and les évenements – the specific, precise incidents and personalities which intervene and alter that evolution. Hurling offers a classic Irish example, and the current game demonstrates that, beneath the superficial breaks, fractures and discontinuities, there are sometimes surprisingly stable, deep structures. If the idiom of the game has changed, its grammar stays the same.
THE PRESENT HURLING REGION
If one looks at the present hurling core region, it is remarkably compact. It also exhibits striking continuity with the earlier ‘iomán’ region. (Fig. 3) The hurling heartland is focused on the three counties of Cork, Tipperary and Kilkenny, with a supporting cast of adjacent counties – Limerick, Clare, Galway, Offaly, Laois, Waterford and Wexford. In the hurling core, the game is king, and very closely stitched into the fabric of the community. Describing the situation in Rathnure, Billy Rackard claimed that in the absence of hurling, ‘the parish would commit suicide, if a parish could commit suicide!’ The boundaries of the hurling region are surprisingly well-defined. To the north, the midland bogs act, as in a way they have done throughout history, as a buffer zone, resolutely impervious to the spread of cultural influences from further south. The western edge of the hurling zone can be traced over a long distance. In County Galway, for example, its boundaries run along a line from Ballinasloe to the city; north of this line is the Tuam-Dunmore area, and west of it is Connemara, both footballing territories. In County Clare, the boundary runs from Tubber on the Galway border through Corofin and Kilmaley to Labasheeda on the Shannon estuary. Last summer, the tremendous achievement of Clare in winning a Munster football championship was most thoroughly relished in the footballing bastion of west Clare, from Kilkee and Doonbeg to Milltown Malbay. One could easily establish this pattern by looking at the thickening density of the forest of flags as one drove from east to west in August.
Across the Shannon in Limerick, the football-hurling divide runs clearly along the scarp dividing hilly west Limerick from the lush limestone lowlands of east Limerick. West of this is an enclave of hurling parishes in the footballing
kingdom of Kerry in the area north of Tralee, in Ardfert, Bally heigue, Causeway and Ballyduff. From Limerick, the hurling boundary loops through County Cork from Mallow to the city and then to the coast at Cloyne – home to the maestro Christy Ring, who famously expressed his strategy for promoting the game in Cork – by stabbing a knife through every football found east of that line. Outside this core region, there are only the hurling enclaves in the Glens of Antrim and on the tip of the Ards peninsula, where the clubs of Ballycran, Ballygalget and Portaferry backbone Down’s hurling revival.
The interesting question then is how these boundaries formed. In almost every case, that boundary divides big farm and small farm areas and marks the transition from fertile, drift-covered limestone lowland to hillier, hungrier, wetter shales, flagstones, grits and granites. In County Galway, for example, hurling has not put down roots in the bony granite outcrops of Connemara, and in Clare the poorly drained flagstone deposits are equally inhospitable. If ash is emblematic of hurling areas, the rush is the distinctive symbol of football territory.
CONCLUSION
This brief case study illustrates the interplay of what the French call la longue durée – the long evolution of history – and les évenements – the specific, precise incidents and personalities which intervene and alter that evolution. Hurling offers a classic Irish example, and the current game demonstrates that, beneath the superficial breaks, fractures and discontinuities, there are sometimes surprisingly stable, deep structures. If the idiom of the game has changed, its grammar stays the same. -
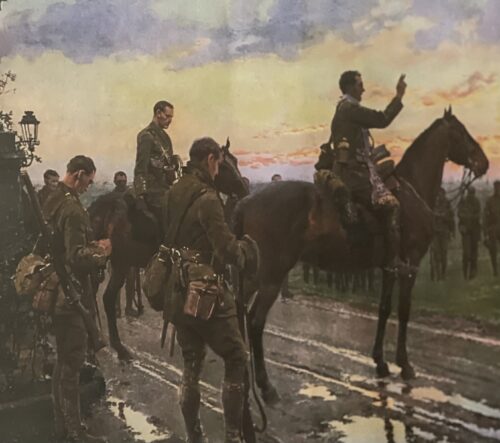
 57cm x 70cm Co Tipperary
57cm x 70cm Co TipperaryThe most haunting and poignant image of Irish involvement in the first World War is at the centre of an unsolved art mystery.
The Last General Absolution of the Munsters at Rue du Bois – a painting long presumed lost – depicts soldiers of the Royal Munster Fusiliers regiment receiving “general absolution” from their chaplain on the eve of battle in May 1915. Most of them died within 24 hours.
The painting, by Italian-born war artist Fortunino Matania, became one of the most famous images of the war when prints of it were published in illustrated weekly newspapers.
Copies hung in houses & pubs throughout Ireland, and especially Munster, but, as Irish public opinion towards the war changed, the picture gradually disappeared from view.A copy still hangs in the famous pub Larkins of Garrykennedy Co Tipperary to this day.
Centenary commemorations of the first World War have prompted renewed interest in the whereabouts of the original painting among art and military historians.
A widely held theory that the painting was lost when archives were destroyed in a fire during the blitz of London in 1940 is “very much” doubted by English historian Lucinda Gosling, who is writing a book about the artist.
She told The Irish Times there was no definitive proof to confirm this theory and it was possible the original painting was still “out there”.
The painting could, conceivably, be in private hands or, more improbably, be lying forgotten or miscatalogued in a museum’s storage area. Matania’s work occasionally turns up at art auctions, but there has been no known or publicly-documented sighting of the original Munsters painting.
Ms Gosling described Matania as an artist “able to work at great speed, producing pictures that were unnervingly photographic in their realism”.
His pictures, she said, had “reached and influenced millions” and “he combined skill and artistry with a strong streak of journalistic tenacity”.
Wayside shrine
The painting is based on an event that took place on Saturday evening, May 8th, 1915.Soldiers from the Second Battalion, Royal Munster Fusiliers, commanded by Lieut-Col Victor Rickard, paused beside a wayside shrine near the village of Rue du Bois in northwest France. The following day, they were due to go into battle, in what became known as the Battle of Aubers Ridge.The painting is imbued with a sense of impending doom.
In Catholic canon law, a priest may grant general absolution of sin to a gathering of the faithful where there is imminent danger of death and no time for individual confessions.
The ritual was used on September 11th, 2001, in New York to grant general absolution to police officers and firefighters about to enter the Twin Towers of the World Trade Centre.In the painting, the Irish chaplain Fr Francis Gleeson is shown blessing the men: “Misereatur vestri omnipotens Deus; et dimissis omnibus peccatis vestris, perducat vos Iesus Christus ad vitam aeternam” (May Almighty God have mercy on you, and having forgiven all your sins, may Jesus Christ bring you to life everlasting).
The men then sang the hymns Te Deum and Hail Glorious St Patrick.
The artist was not present at the scene but based his painting on a written account by Lieut- Col Rickard’s widow, Jessie, who is believed to have commissioned the painting in memory of her husband.
She had gathered eye-witness accounts from survivors and wrote: “There are many journeys and many stopping- places in the strange pilgrimage we call life, but there is no other such journey in the world as the journey up a road on the eve of battle, and no stopping- place more holy than a wayside shrine.”
She noted among the troops were “lads from Kerry and Cork, who, a year before, had never dreamed of marching in the ranks of the British army”.
After Fr Gleeson’s blessing, she wrote: “The regiment moved on, and darkness fell as the skirl of the Irish pipes broke out, playing a marching tune.“The Munsters were wild with enthusiasm; they were strong with the invincible strength of faith and high hope, for they had with them the vital conviction of success, the inspiration that scorns danger – which is the lasting heritage of the Irish; theirs still and theirs to remain when great armaments and armies and empires shall be swept away, because it is immovable as the eternal stars.”
Mown down
The following morning, Sunday May 9th, most of the Irish soldiers were mown down by German gunfire and shelling.
On a catastrophic day for the British army – over 11,000 casualties – the Royal Munster Fusiliers suffered dreadful losses. Exact estimates vary, but one account records 800 Munsters went into battle and only 200 assembled that evening.
Mrs Rickard concluded : “So the Munsters came back after their day’s work; they formed up again in the Rue du Bois, numbering 200 men and three officers. It seems almost superfluous to make any further comment.”
The Last General Absolution of the Munsters at Rue du Bois
The Painting
The Last General Absolution of the Munsters at Rue du Bois shows some of the hundreds of soldiers from the second battalion of the Royal Munster Fusiliers who gathered at a shrine near the village of Rue du Bois on the western front on Saturday, May 8th, 1915.
The image was published in the London illustrated weekly newspaper The Sphere in November 1916, and in 1917 in the Weekly Freeman’s, an Irish publication. There are copies of the print in various museums and in private ownership in Ireland and Britain.
The Artist
Fortunino Matania, (1881- 1963) was born in Naples and was a well-known artist and illustrator in Italy before moving to London in 1902. He worked for The Sphere – an illustrated weekly newspaper – and became famous for depicting the sinking of the Titanic in 1912.
He was an official war artist in the first World War and his graphic illustrations of trench warfare were highly renowned.
The Location
Rue du Bois is located near the village of Neuve Chapelle in the Nord-Pas-de-Calais region of France close to the border with Belgium. According to the Royal Munster Fusiliers Association, the original shrine has long gone.
The Chaplain
Depicted on horseback, with hand raised granting general absolution, is Fr Francis Gleeson, a native of Templemore, Co Tipperary. He was ordained a priest in Maynooth in 1910 and volunteered to serve as a chaplain in the army at the outbreak of the war. He was assigned to the Royal Munster Fusiliers and served with distinction. He survived the war and returned to Ireland where he worked as priest in Dublin and died in 1959.
The Commanding Officer
Lieut-Col Victor Rickard, the other man on horseback, was born in Englandto an Irish father and English mother.
He was the commander of the battalion. He died in action the next day, aged 40.
The Patron
Lieut-Col Rickard’s widow Jessie, who is believed to have commissioned the painting, was the daughter of a Church of Ireland clergyman who spent her youth in Mitchelstown, Co Cork. She became a well-known novelist and published some 40 books.
After the war she converted to Catholicism under the guidance of another former chaplain in the British army in the first World War – Fr Joseph Leonard, who later befriended Jackie Kennedy.
Mrs Rickard died at Montenotte, Cork, in 1963, aged 86.
-

 30cm x 39cm Killenaule Co Tipperary
30cm x 39cm Killenaule Co TipperaryShowjumper helped transform the image of his sport in the 1960s but also attracted controversy
The showjumper Tommy Wade on his ''glorified'' Connemara pony, Dundrum, not only electrified audiences at the annual Horse Show in the RDS, Dublin in the 1960s but can be credited with popularising the sport of showjumping, then regarded as an elitist pursuit of the Anglo-Irish ascendency. Wade jumped a televised clear round in 1963 to clinch the Aga Khan trophy and the Nations Cup for Ireland in a thrilling conclusion to the annual Horse Show before an audience that included President Eamon De Valera. He had already created a sensation in 1961 by winning all five international classes at the show on Dundrum, described in some reports as "a former carthorse" that became a national celebrity and would inspire a later generation of horsemen like Eddie Macken and Paul Darragh. Shrouded in controversy, the outspoken Tipperary man arrived back in the RDS in 1967 vowing not to take part in any competitions, because of a dispute he was having with the Showjumping Association of Ireland over a show the previous week, where the judges had withheld the prize in a dispute with the riders. He relented when he was told that if he didn't take part in competition he would not be included in the Irish team. In the first round he incurred 22 penalty points and fell off his horse at the 11th fence. Due to the scores of his team-mates, Seamus Hayes, Billy Ringrose and Ned Campion, Ireland were still in contention at the end of the second round - but needed Wade and Dundrum to "go clear" to win. "Wade with icy calm and determination came into the ring," went one report of the event. "He and Dundrum approached each obstacle, willed on by an excited but tense and silent crowd. At a couple of fences the top pole trembled, but none fell. Finally, horse and rider sailed over the last jump for a clear round as wild cheering greeted the terse announcement of RDS secretary, John Whylie: 'Ireland have won the Aga Khan Cup.'" Wade said later: "He was like a little thoroughbred, he was all muscle, and he was a lovely horse to ride, strong and powerful." But within a couple of months Wade was suspended for a year from showjumping and was forced to take a job as a bookie at greyhound and race meetings around Munster. The suspension arose when he, his brother Ned and another rider Gerry Costelloe tied for first place at the Dungarvan Show in Co Waterford. They agreed to divide the €102 winner's purse, but the judges ordered them to jump again, which they felt would be hard on their horses going into the RDS the following week. Ned Wade came out, knocked the first fence and withdrew, Tommy went off before the starting bell and was eliminated and then Gerry Costelloe took the wrong course and was also eliminated. The judges were furious at what they believed was insubordination and refused to award the prize money. Wade demanded an apology and castigated what he insinuated were the Anglo-Irish ''bowler hat brigade'' who controlled the sport. "The showjumping crowd around Dublin are a rotten crowd, they're terrible jealous. The trouble with them is the trouble with Irish people generally: they're jealous of someone who gets to the top, Irish people still suffer from a peasant mentality," he said. Although he threatened to take his horses to northern England, near his friend Harvey Smith, peace was eventually made and Tommy Wade would later become Chef D'Equipe of the Irish showjumping team, claiming more than 30 Nations Cup victories at shows all over the world. Tommy Wade, who had earlier suffered a stroke, died last Monday aged 80 in the Bons Secours Hospital, Cork. Born at Gould's Cross at Camas, within sight of the Rock of Cashel, he went to school locally and later lived at Ballyroe House in Tipperary. His father was a local haulier and the family grew up in ''horse country'' steeped in racing and showjumping.Bred in the nearby village of Dundrum by Jack Ryan (Lar), the horse that made him famous had gone through several owners before Wade's father, Jimmy, spotted the gelding "hauling" goods for Tierney's hardware shop. Only five-and-a-half foot high, he began jumping at local shows before going to Manchester in 1957 where he won the North of England championship. "Tommy thought, dreamed and schemed about being first and usually was," said Michael Slavin in his book, Irish Showjumping Legends. It was an amateur sport at the time and he won a gold watch in Brussels, a gold tankard in Newcastle-upon-Tyne and a gold medal in Belfast - all trophies he treasured for the rest of his life. "I wasn't picked by the crowd here until I started getting invitations from England," he said, somewhat bitterly, later, when he was in dispute with the sports authorities. But they couldn't ignore him when Dundrum became Supreme Champion at the Wembley Horse of the Year Show and set a record clearing the seven foot two inches puissance wall. He was international Jumping Champion from 1959 to 1963. -
Out of stock

 Beautiful print of three all time great National Hunt Horses : Arkle,Red Rum and Desert Orchid by the artist SL Crawford 60cmx 85cm Lucan Co Dublin
Beautiful print of three all time great National Hunt Horses : Arkle,Red Rum and Desert Orchid by the artist SL Crawford 60cmx 85cm Lucan Co Dublin -

 45cm x 35cm Thurles Co Tipperary Thomas Semple (8 April 1879 – 11 April 1943) was an Irish hurler who played as a half-forward for the Tipperary senior team. Semple joined the panel during the 1897 championship and eventually became a regular member of the starting seventeen until his retirement after the 1909 championship. During that time he won three All-Ireland medals and four Munster medals. An All-Ireland runner-up on one occasion, Semple captained the team to the All-Ireland title in 1906 and in 1908. At club level Semple was a six-time county club championship medalist with Thurles.
45cm x 35cm Thurles Co Tipperary Thomas Semple (8 April 1879 – 11 April 1943) was an Irish hurler who played as a half-forward for the Tipperary senior team. Semple joined the panel during the 1897 championship and eventually became a regular member of the starting seventeen until his retirement after the 1909 championship. During that time he won three All-Ireland medals and four Munster medals. An All-Ireland runner-up on one occasion, Semple captained the team to the All-Ireland title in 1906 and in 1908. At club level Semple was a six-time county club championship medalist with Thurles.Playing career
Club
Semple played his club hurling with the local club in Thurles, the precursor to the famous Sarsfield's club. He rose through the club and served as captain of the team for almost a decade. In 1904 Semple won his first championship medal following a walkover from Lahorna De Wets. Thurles failed to retain their title, however, the team returned to the championship decider once again in 1906. A 4-11 to 3-6 defeat of Lahorna De Wets gave Semple his second championship medal as captain. It was the first of four successive championships for Thurles as subsequent defeats of Lahorna De Wets, Glengoole and Racecourse/Grangemockler brought Semple's medal tally to five. Five-in-a-row proved beyond Thurles, however, Semple's team reached the final for the sixth time in eight seasons in 1911. A 4-5 to 1-0 trouncing of Toomevara gave Semple his sixth and final championship medal as captain.Inter-county
Semple's skill quickly brought him to the attention of the Tipperary senior hurling selectors. After briefly joining the team in 1897, he had to wait until 1900 to become a regular member of the starting seventeen. That year a 6-11 to 1-9 trouncing of Kerry gave him his first Munster medal.Tipp later narrowly defeated Kilkenny in the All-Ireland semi-final before trouncing Galway in the "home" All-Ireland final. This was not the end of the championship campaign because, for the first year ever, the "home" finalists had to take on London in the All-Ireland decider. The game was a close affair with both sides level at five points with eight minutes to go. London then took the lead; however, they later conceded a free. Tipp's Mikey Maher stepped up, took the free and a forward charge carried the sliotar over the line. Tipp scored another goal following a weak puck out and claimed a 2-5 to 0-6 victory. It was Semple's first All-Ireland medal. Cork dominated the provincial championship for the next five years; however, Tipp bounced back in 1906. That year Semple was captain for the first time as Tipp foiled Cork's bid for an unprecedented sixth Munster title in-a-row. The score line of 3-4 to 0-9 gave Semple a second Munster medal. Tipp trounced Galway by 7-14 to 0-2 on their next outing, setting up an All-Ireland final meeting with Dublin. Semple's side got off to a bad start with Dublin's Bill Leonardscoring a goal after just five seconds of play. Tipp fought back with Paddy Riordan giving an exceptional display of hurling and capturing most of his team's scores. Ironically, eleven members of the Dublin team hailed from Tipperary. The final score of 3-16 to 3-8 gave victory to Tipperary and gave Semple a second All-Ireland medal. Tipp lost their provincial crown in 1907, however, they reached the Munster final again in 1908. Semple was captain of the side again that year as his team received a walkover from Kerry in the provincial decider. Another defeat of Galway in the penultimate game set up another All-Ireland final meeting with Dublin. That game ended in a 2-5 to 1-8 draw and a replay was staged several months later in Athy. Semple's team were much sharper on that occasion. A first-half goal by Hugh Shelly put Tipp well on their way. Two more goals by Tony Carew after the interval gave Tipp a 3-15 to 1-5 victory.It was Semple's third All-Ireland medal. 1909 saw Tipp defeat arch rivals Cork in the Munster final once again. A 2-10 to 1-6 victory gave Semple his fourth Munster medal. The subsequent All-Ireland final saw Tipp take on Kilkenny. The omens looked good for a Tipperary win. It was the county's ninth appearance in the championship decider and they had won the previous eight. All did not go to plan as this Kilkenny side cemented their reputation as the team of the decade. A 4-6 to 0-12 defeat gave victory to "the Cats" and a first final defeat to Tipperary. Semple retired from inter-county hurling following this defeat. Tipperary Hurling Team outside Clonmel railway station, August 26, 1910. Semple is in the centre of the middle row.
Tipperary Hurling Team outside Clonmel railway station, August 26, 1910. Semple is in the centre of the middle row.Personal life
Semple was born in Drombane, County Tipperary in 1879. He received a limited education at his local national school and, like many of his contemporaries, finding work was a difficult prospect. At the age of 16 Semple left his native area and moved to Thurles. Here he worked as a guardsman with the Great Southern & Western Railway. In retirement from playing Semple maintained a keen interest in Gaelic games. In 1910 he and others organised a committee which purchased the showgrounds in Thurles in an effort to develop a hurling playing field there. This later became known as Thurles Sportsfield and is regarded as one of the best surfaces for hurling in Ireland. In 1971 it was renamed Semple Stadium in his honour. The stadium is also lovingly referred to as Tom Semple's field. Semple also held the post of chairman of the Tipperary County Board and represented the Tipperary on the Munster Council and Central Council. He also served as treasurer of the latter organization. During the War of Independence Semple played an important role for Republicans. He organized dispatches via his position with the Great Southern & Western Railway in Thurles. Tom Semple died on 11 April 1943.






