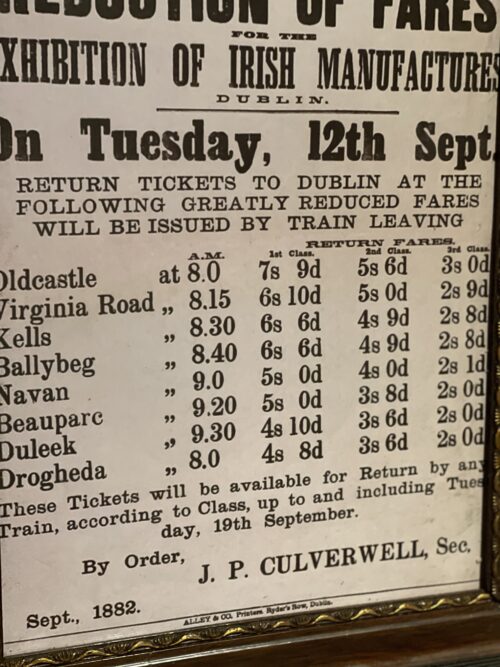
-

 30cm x 30cm ANOTHER great industry on the Scotch Hall site was the brewing firm of Cairnes Ltd, one of the original firms of Irish brewers dating back to 1772 with the foundation of the Castlebellingham Brewery at the picturesque Co Louth village of that name.In 1825, William Cairnes, who was related by marriage to the owners of the ’Bellingham brewery, founded the brewery at Marsh Road, Drogheda, which, for over 150 years, gave employment to almost 200 workers and the firm was famous for its ales and stout. In 1889 the interests of the two breweries were pooled, a public company being formed under the title of the Castlebellingham and Drogheda Breweries Ltd. This title was changed for brevity in 1933 to Cairnes Ltd. For a good many years subsequent to the merger, the breweries were worked independently, each supplying its own customers throughout Ireland and abroad. However, in 1923, it was considered advisable to concentrate brewing in Drogheda, owing to the more advantageous position of the town, and the brewing plant and premises there, were more extensive. Actually the plant at Drogheda was one of the most up-to-date in Ireland and compared very favourably with that of breweries in England and Wales. The supply of brewing water was obtained from a 400ft deep artesian well on the company’s premises. (I wonder if it is still there) and this water was used with the choicest hops and malt made from the best Irish barley obtainable. The hops used came chiefly from Kent and when obtainable, a percentage came from the USA. The process through which the barley went from its arrival in the brewery until it emerged as ale or stout, was extremely interesting and quaint. The barley was first dried to a consistent level of moisture content and then stored for a few weeks before being steeped. It was then ‘floored’ on lots which the brewery had, as well as lofts in Dominic Street and Wellington Quay. These have, in recent years, been converted into shops and a high rise apartment block. Here on these lofts the growing process of the barley in the ground was artificially repeated, the growth however being terminated at the desired stage. The barley was then kilned and cured before being ground and mashed with hot water and the liquid was drawn off. It was then run to built-in coppers, where hops was added, then boiled, the wort, as it was called, being subsequently strained from the hops, cooled and fermented. The final stage was when the beer was casked (in wooden barrels) and matured.
30cm x 30cm ANOTHER great industry on the Scotch Hall site was the brewing firm of Cairnes Ltd, one of the original firms of Irish brewers dating back to 1772 with the foundation of the Castlebellingham Brewery at the picturesque Co Louth village of that name.In 1825, William Cairnes, who was related by marriage to the owners of the ’Bellingham brewery, founded the brewery at Marsh Road, Drogheda, which, for over 150 years, gave employment to almost 200 workers and the firm was famous for its ales and stout. In 1889 the interests of the two breweries were pooled, a public company being formed under the title of the Castlebellingham and Drogheda Breweries Ltd. This title was changed for brevity in 1933 to Cairnes Ltd. For a good many years subsequent to the merger, the breweries were worked independently, each supplying its own customers throughout Ireland and abroad. However, in 1923, it was considered advisable to concentrate brewing in Drogheda, owing to the more advantageous position of the town, and the brewing plant and premises there, were more extensive. Actually the plant at Drogheda was one of the most up-to-date in Ireland and compared very favourably with that of breweries in England and Wales. The supply of brewing water was obtained from a 400ft deep artesian well on the company’s premises. (I wonder if it is still there) and this water was used with the choicest hops and malt made from the best Irish barley obtainable. The hops used came chiefly from Kent and when obtainable, a percentage came from the USA. The process through which the barley went from its arrival in the brewery until it emerged as ale or stout, was extremely interesting and quaint. The barley was first dried to a consistent level of moisture content and then stored for a few weeks before being steeped. It was then ‘floored’ on lots which the brewery had, as well as lofts in Dominic Street and Wellington Quay. These have, in recent years, been converted into shops and a high rise apartment block. Here on these lofts the growing process of the barley in the ground was artificially repeated, the growth however being terminated at the desired stage. The barley was then kilned and cured before being ground and mashed with hot water and the liquid was drawn off. It was then run to built-in coppers, where hops was added, then boiled, the wort, as it was called, being subsequently strained from the hops, cooled and fermented. The final stage was when the beer was casked (in wooden barrels) and matured. -
 47cm x 38cm The Great Northern Railway (Ireland) (GNR(I) or GNRI) was an Irish gauge (1,600 mm (5 ft 3 in)) railway company in Ireland. It was formed in 1876 by a merger of the Irish North Western Railway (INW), Northern Railway of Ireland, and Ulster Railway. The governments of Ireland and Northern Ireland jointly nationalised the company in 1953, and the company was liquidated in 1958: assets were split on national lines between the Ulster Transport Authority and Córas Iompair Éireann.
47cm x 38cm The Great Northern Railway (Ireland) (GNR(I) or GNRI) was an Irish gauge (1,600 mm (5 ft 3 in)) railway company in Ireland. It was formed in 1876 by a merger of the Irish North Western Railway (INW), Northern Railway of Ireland, and Ulster Railway. The governments of Ireland and Northern Ireland jointly nationalised the company in 1953, and the company was liquidated in 1958: assets were split on national lines between the Ulster Transport Authority and Córas Iompair Éireann.Foundation
The Ulster, D&D and D&BJct railways together formed the main line between Dublin and Belfast, with the D&BJct completing the final section in 1852 to join the Ulster at Portadown. The GNRI's other main lines were between Derry and Dundalk and between Omagh and Portadown. The Portadown, Dungannon and Omagh Junction Railway together with the Londonderry and Enniskillen Railway enabled GNRI trains between Derry and Belfast to compete with the Belfast and Northern Counties Railway, and both this and the Dundalk route gave connections between Derry and Dublin. These main lines supported the development of an extensive branch network serving the southwest half of Ulster and northern counties of Leinster. The GNRI became Ireland's most prosperous railway company and second largest railway network. In its early years the GNR(I) closely imitated the image of its English namesake, adopting an apple green livery for its steam locomotives and a varnished teak finish for its passenger coaches. Later the company adopted its famous pale blue livery for locomotives (from 1932), with the frames and running gear picked out in scarlet. Passenger vehicles were painted brown, instead of varnished. On 12 June 1889, a significant rail accident occurred when a passenger train stalled between Armagh and Newry. The train was divided, but during the uncoupling operation ten carriages ran away and collided with another passenger train. A total of 80 people were killed and 260 were injured in what was then the deadliest railway accident to have occurred in Europe. The accident remains the deadliest ever to have occurred on the island of Ireland.Growth and partition
In the early 20th century increasing traffic led the GNRI to consider introducing larger locomotives. The Great Southern & Western Railway had introduced express passenger locomotives with a 4-6-0 wheel arrangement, and the GNRI wanted to do the same. However, the lifting shop in the GNRI Dundalk works was too short to build or overhaul a 4-6-0, so the company persisted with 4-4-0 locomotives for even the heaviest and fastest passenger trains. This led to the GNRI to order a very modern and powerful class of 4-4-0's, the Class V three cylinder compound locomotives built by Beyer, Peacock & Company in 1932. This class has been compared with another notable V class, that introduced by the Southern Railway in England in 1930. The Partition of Ireland in 1921 created a border through the GNRI's territory. The new border crossed all three of its main lines and some of its secondary lines. The imposition of border controls caused some service disruption, with main line trains having to stop at both Dundalk and Goraghwood stations. This was not eased until 1947 when customs and immigration facilities for Dublin–Belfast expresses were opened at Dublin Amiens Street and Belfast Great Victoria Street stations.Nationalisation and division
A combination of the increasing road competition facing all railways and a change in patterns of economic activity caused by the Partition of Ireland reduced the GNRI's prosperity. The company modernised and reduced its costs by introducing modern diesel multiple units on an increasing number of services in the 1940s and 1950s and by making Dublin–Belfast expresses non-stop from 1948. In Dundalk at the GNR Works the railway engineers developed railbuses for use on sections of the rural network. Nevertheless, by the 1950s the GNRI had ceased to be profitable and in 1953 the company was jointly nationalised by the governments of the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland. The two governments ran the railway jointly under a Great Northern Railway Board until 1958.In May 1958, the Government of Northern Ireland's wish to close many lines led to the GNR(I) Board being dissolved and the assets divided between the two territories. At midnight on 30 September 1958, all lines entirely within Northern Ireland were transferred to the (nationalised) Ulster Transport Authority (UTA) and all lines entirely within the Republic of Ireland were transferred to Córas Iompair Éireann (CIÉ). CIÉ had been formed as a private company in 1945 but had been nationalised in 1950. In an attempt at fairness, all classes of locomotive and rolling stock were also divided equally between the transport operators of the two new owners.: 184–185 Most classes of GNRI locomotive had been built in small classes, so this division left both railways with an operational and maintenance difficulty of many different designs all in small numbers. The Government of Northern Ireland, which had a very anti-rail policy, rapidly closed most of the GNR(I) lines in Northern Ireland.Exceptions were the Belfast–Dundalk and Portadown–Derry main lines and the Newry–Warrenpoint and Lisburn–Antrim branches. It made the Lisburn–Antrim branch freight-only from 1960 and closed the Portadown–Derry and Newry–Warrenpoint lines to all traffic in 1965.The Republic of Ireland government tried briefly to maintain services on lines closed at the border by the Northern Ireland government, but this was impractical, and the Republic had to follow suit in closing most GNR(I) lines within the Republic. Since 1963, the Drogheda–Navan branch has survived for freight traffic only. The GNR's north western main line between Dundalk and Derry bypassed the small County Tyrone town of Fintona, which was instead served by a 1 mile (1.6 km) branch line from Fintona Junction station. The service was operated by the double-deck Fintona horse tram until the line's closure in 1957. CIÉ also acquired the Hill of Howth Tramway, in the northern suburbs of Dublin, in the 1958 dissolution of the GNRI Board. CIÉ closed the tramway about a year later. Today, the GNR routes remaining consist of the main line from Dublin to Belfast, the Howth branch, electrified for Dublin commuter services since 1984, the Drogheda - Navan (Tara Mines) line, which carries only freight traffic associated with that mine, passenger traffic having ceased with the closure of the line beyond there to Oldcastle in 1963, and the Lisburn to Antrim branch, now mothballed but retained in operational order for the time being. Preserved GNRI Class S no. 171 Slieve Gullion at Lisburn
Preserved GNRI Class S no. 171 Slieve Gullion at LisburnPreservation
Rolling stock
 No.85 taking on water on the former Northern Counties Committee line at Ballymena railway station.
No.85 taking on water on the former Northern Counties Committee line at Ballymena railway station. -
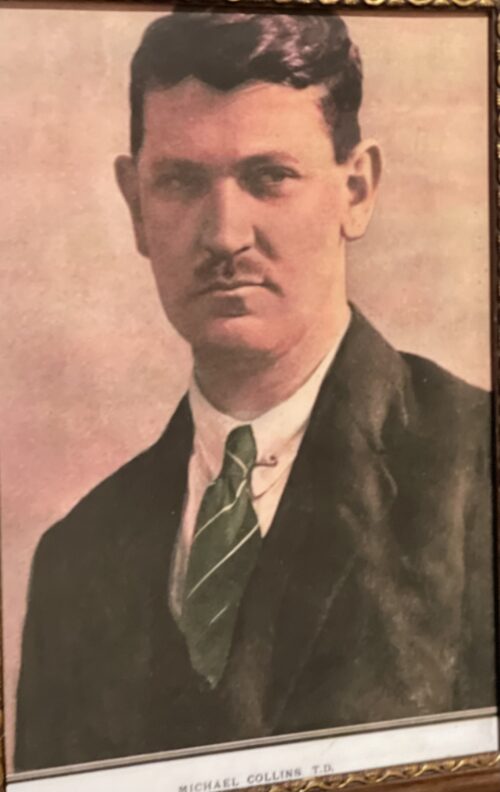
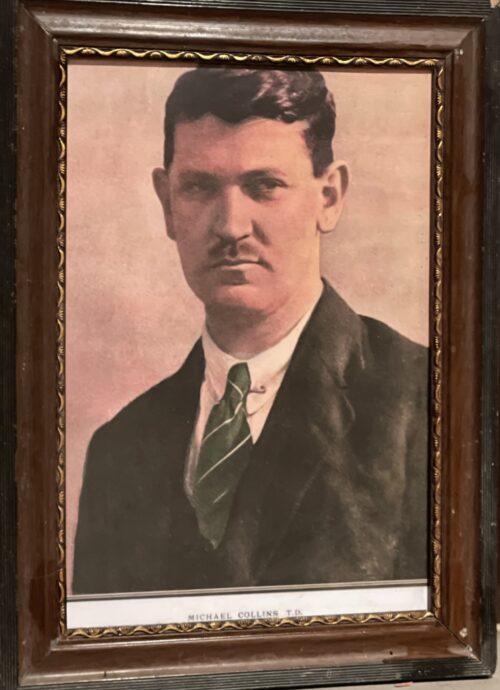
 40cm x 37cm Michael Collins (16 October 1890 – 22 August 1922) was an Irish revolutionary, soldier and politician who was a leading figure in the early-20th century struggle for Irish independence.During the War of Independence he was Director of Intelligence of the Irish Republican Army (IRA) and a government minister of the self-declared Irish Republic. He was then Chairman of the Provisional Government of the Irish Free State from January 1922 and commander-in-chief of the National Army from July until his death in an ambush in August 1922, during the Civil War. Collins was born in Woodfield, County Cork, the youngest of eight children. He moved to London in 1906 to become a clerk in the Post Office Savings Bank at Blythe House. He was a member of the London GAA, through which he became associated with the Irish Republican Brotherhood and the Gaelic League. He returned to Ireland in January 1916 and fought in the Easter Rising. He was taken prisoner and held in the Frongoch internment camp as a prisoner of war, but he was released in December 1916. Collins subsequently rose through the ranks of the Irish Volunteers and Sinn Féin. He was elected as a Teachta Dála for South Cork in December 1918. Sinn Féin's elected members formed an Irish parliament, the First Dáil, in January 1919 and declared the independence of the Irish Republic. Collins was appointed Minister for Finance. In the ensuing War of Independence, he was Director of Organisation and Adjutant General for the Irish Volunteers, and Director of Intelligence of the IRA. He gained fame as a guerrilla warfare strategist, planning many successful attacks on British forces together with 'the Squad', such as the "Bloody Sunday" assassinations of key British intelligence agents in November 1920. After the July 1921 ceasefire, Collins was one of five plenipotentiaries sent by the Dáil cabinet at the request of Éamon de Valera, to negotiate peace terms in London. The resulting Anglo-Irish Treaty, signed in December 1921, would establish the Irish Free State but depended on an oath of allegiance to the Crown. This was the clause in the treaty de Valera and other republican leaders found hardest to accept. Collins viewed the treaty as offering "the freedom to achieve freedom", and helped persuade a majority of the Dáil to ratify the treaty. A provisional government was formed under his chairmanship in early 1922. During this time he secretly provided support for an IRA offensive in Northern Ireland. It was soon disrupted by the Irish Civil War, in which Collins was commander-in-chief of the National Army. He was shot and killed in an ambush by anti-Treaty forces on 22 August 1922
40cm x 37cm Michael Collins (16 October 1890 – 22 August 1922) was an Irish revolutionary, soldier and politician who was a leading figure in the early-20th century struggle for Irish independence.During the War of Independence he was Director of Intelligence of the Irish Republican Army (IRA) and a government minister of the self-declared Irish Republic. He was then Chairman of the Provisional Government of the Irish Free State from January 1922 and commander-in-chief of the National Army from July until his death in an ambush in August 1922, during the Civil War. Collins was born in Woodfield, County Cork, the youngest of eight children. He moved to London in 1906 to become a clerk in the Post Office Savings Bank at Blythe House. He was a member of the London GAA, through which he became associated with the Irish Republican Brotherhood and the Gaelic League. He returned to Ireland in January 1916 and fought in the Easter Rising. He was taken prisoner and held in the Frongoch internment camp as a prisoner of war, but he was released in December 1916. Collins subsequently rose through the ranks of the Irish Volunteers and Sinn Féin. He was elected as a Teachta Dála for South Cork in December 1918. Sinn Féin's elected members formed an Irish parliament, the First Dáil, in January 1919 and declared the independence of the Irish Republic. Collins was appointed Minister for Finance. In the ensuing War of Independence, he was Director of Organisation and Adjutant General for the Irish Volunteers, and Director of Intelligence of the IRA. He gained fame as a guerrilla warfare strategist, planning many successful attacks on British forces together with 'the Squad', such as the "Bloody Sunday" assassinations of key British intelligence agents in November 1920. After the July 1921 ceasefire, Collins was one of five plenipotentiaries sent by the Dáil cabinet at the request of Éamon de Valera, to negotiate peace terms in London. The resulting Anglo-Irish Treaty, signed in December 1921, would establish the Irish Free State but depended on an oath of allegiance to the Crown. This was the clause in the treaty de Valera and other republican leaders found hardest to accept. Collins viewed the treaty as offering "the freedom to achieve freedom", and helped persuade a majority of the Dáil to ratify the treaty. A provisional government was formed under his chairmanship in early 1922. During this time he secretly provided support for an IRA offensive in Northern Ireland. It was soon disrupted by the Irish Civil War, in which Collins was commander-in-chief of the National Army. He was shot and killed in an ambush by anti-Treaty forces on 22 August 1922 -

 45cm x 38cm The Sunday Press was a weekly newspaper published in Ireland from 1949 until 1995. It was launched by Éamon de Valera's Irish Press group following the defeat of his Fianna Fáil party in the 1948 Irish general election. Like its sister newspaper, the daily The Irish Press, politically the paper loyally supported Fianna Fáil. The future Taoiseach Seán Lemass was the managing editor of the Irish Press who spearheaded the launch of the Sunday paper, with the first editor Colonel Matt Feehan. Many of the Irish Press journalists contributed to the paper. 'When I open the pages, I duck' was Brendan Behan's description of reading The Sunday Press, for the habit of published memoirs of veterans (usually those aligned to Fianna Fáil) of the Irish War of Independence. It soon built up a large readership, and overtook its main competitor the Sunday Independent, which tended to support Fine Gael. At its peak The Sunday Press sold up to 475,000 copies every week, and had a readership of over one million, around one third of the Irish population. Like the Evening Press, the paper's readership held up better over the years than that of the flagship title in the group, The Irish Press, and it might have survived as a stand-alone title had it been sold. However, with the collapse of the Irish Press Newspapers group in May 1995, all three titles ceased publication immediately. The launch of Ireland on Sunday in 1997 was initially interpreted by many observers as an attempt to appeal to the former readership of The Sunday Press, seen as generally rural, fairly conservative Catholic, and with a traditional Irish nationalist political outlook. When Christmas Day fell on Sunday in 1949, 1955, 1960, 1966, 1977, 1983, 1988 and 1994 the paper came out on the Saturday. Vincent Jennings at the age of 31 became editor of The Sunday Press in 1968, serving until December 1986, when he became manager of the Irish Press Group. Journalists who worked at the press include Stephen Collins served as political editor his father Willie Collins was deputy editor and Michael Carwood became sports editor of The Sunday Press in 1988 until its closure in 1995.
45cm x 38cm The Sunday Press was a weekly newspaper published in Ireland from 1949 until 1995. It was launched by Éamon de Valera's Irish Press group following the defeat of his Fianna Fáil party in the 1948 Irish general election. Like its sister newspaper, the daily The Irish Press, politically the paper loyally supported Fianna Fáil. The future Taoiseach Seán Lemass was the managing editor of the Irish Press who spearheaded the launch of the Sunday paper, with the first editor Colonel Matt Feehan. Many of the Irish Press journalists contributed to the paper. 'When I open the pages, I duck' was Brendan Behan's description of reading The Sunday Press, for the habit of published memoirs of veterans (usually those aligned to Fianna Fáil) of the Irish War of Independence. It soon built up a large readership, and overtook its main competitor the Sunday Independent, which tended to support Fine Gael. At its peak The Sunday Press sold up to 475,000 copies every week, and had a readership of over one million, around one third of the Irish population. Like the Evening Press, the paper's readership held up better over the years than that of the flagship title in the group, The Irish Press, and it might have survived as a stand-alone title had it been sold. However, with the collapse of the Irish Press Newspapers group in May 1995, all three titles ceased publication immediately. The launch of Ireland on Sunday in 1997 was initially interpreted by many observers as an attempt to appeal to the former readership of The Sunday Press, seen as generally rural, fairly conservative Catholic, and with a traditional Irish nationalist political outlook. When Christmas Day fell on Sunday in 1949, 1955, 1960, 1966, 1977, 1983, 1988 and 1994 the paper came out on the Saturday. Vincent Jennings at the age of 31 became editor of The Sunday Press in 1968, serving until December 1986, when he became manager of the Irish Press Group. Journalists who worked at the press include Stephen Collins served as political editor his father Willie Collins was deputy editor and Michael Carwood became sports editor of The Sunday Press in 1988 until its closure in 1995. -

 Art and craft classes were held at the Maze,Long Kesh Prison & prisons in the South as part of educational programmes, some by the prison authorities and some by the prisoners themselves. Prisoners could gain qualifications and formal courses in art history were also offered. In addition, arts and crafts were pursued at an informal level within the prison. Murals were painted on the walls of both the H-Blocks and the Nissen huts within the cages/ compounds. Handicrafts made in the prison could be sold on the ‘outside’, with proceeds going to prisoners’ families. In 1996 the Prison Arts Foundation (PAF) was founded, with the aim of providing access to the arts for all prisoners, ex-prisoners, young offenders and ex-young offenders in Northern Ireland. During the latter years of the Maze and Long Kesh Prison, the PAF promoted access to the arts by organising professional artist residencies and workshops in the H-Blocks. Security considerations placed constraints on materials permitted and the type of art and crafts that could be produced in the prison. For example, glass and ‘inflammable’ paint were not allowed. However, the availability of tools and materials varied across the site and over the years. And prisoners also improvised with materials to hand.
Art and craft classes were held at the Maze,Long Kesh Prison & prisons in the South as part of educational programmes, some by the prison authorities and some by the prisoners themselves. Prisoners could gain qualifications and formal courses in art history were also offered. In addition, arts and crafts were pursued at an informal level within the prison. Murals were painted on the walls of both the H-Blocks and the Nissen huts within the cages/ compounds. Handicrafts made in the prison could be sold on the ‘outside’, with proceeds going to prisoners’ families. In 1996 the Prison Arts Foundation (PAF) was founded, with the aim of providing access to the arts for all prisoners, ex-prisoners, young offenders and ex-young offenders in Northern Ireland. During the latter years of the Maze and Long Kesh Prison, the PAF promoted access to the arts by organising professional artist residencies and workshops in the H-Blocks. Security considerations placed constraints on materials permitted and the type of art and crafts that could be produced in the prison. For example, glass and ‘inflammable’ paint were not allowed. However, the availability of tools and materials varied across the site and over the years. And prisoners also improvised with materials to hand. -

 67cm x 56cm
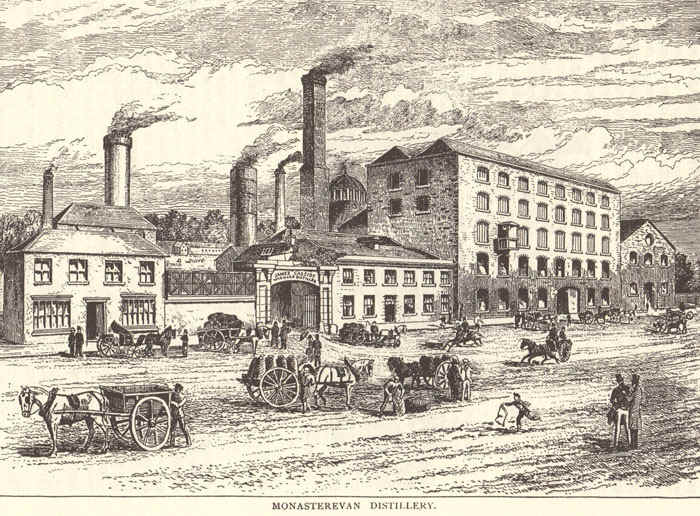
67cm x 56cmIn 1784 Monasterevin Distillery was opened by Mr. John Cassidy. A hundred years later, in 1884 the distillery was making 250,000 gallons of whiskey a year. It was said that the "Cassidy whiskey was the best whiskey in the country".
Some of the whiskey was exported to London. It was transported to Dublin on canal boats and then shipped to England from Dublin Port. A brewery for making beer was later opened in 1860. Cassidy's Distillery and Brewery closed in 1934.
The Cassidy Family lived in Monasterevin House. They were friendly with Gerard Manley Hopkins, the famous poet. He stayed with them when he visited Monasterevin.

-

 67cm x 56cm
67cm x 56cmDaniel O’Connnell Jr. had famously acquired the Phoenix Brewery in James’s street in 1831, which produced O’Connell’s Ale. It should be noted that O’Connell and the Guinness family were at times political rivals, something best captured by the 1841 ‘Repeal Election’, where O’Connell had stood against and defeated Arthur Guinness Jr. This period would see a sizeable boycott of Guinness, dubbed “Protestant Porter” by sections of the populace, though this was against the wishes of O’Connell himself.
John D’Arcy continued to brew O’Connell Ale after the family had ceased their role in brewing, and in time production moved to the Anchor Brewery in Usher Street. Watkins eventually took up the brewing of O’Connell Ale, and this advertisement was placed by them in the pages of leading newspapers in the 1930s.
While Arthur had failed to defeat O’Connell at the Ballot Box, I always wonder what O’Connell would think of the Guinness Empire today every time I see a Diaego truck pass his statue.
-

 74cm x 52cm ANOTHER great industry on the Scotch Hall site was the brewing firm of Cairnes Ltd, one of the original firms of Irish brewers dating back to 1772 with the foundation of the Castlebellingham Brewery at the picturesque Co Louth village of that name.In 1825, William Cairnes, who was related by marriage to the owners of the ’Bellingham brewery, founded the brewery at Marsh Road, Drogheda, which, for over 150 years, gave employment to almost 200 workers and the firm was famous for its ales and stout. In 1889 the interests of the two breweries were pooled, a public company being formed under the title of the Castlebellingham and Drogheda Breweries Ltd. This title was changed for brevity in 1933 to Cairnes Ltd. For a good many years subsequent to the merger, the breweries were worked independently, each supplying its own customers throughout Ireland and abroad. However, in 1923, it was considered advisable to concentrate brewing in Drogheda, owing to the more advantageous position of the town, and the brewing plant and premises there, were more extensive. Actually the plant at Drogheda was one of the most up-to-date in Ireland and compared very favourably with that of breweries in England and Wales. The supply of brewing water was obtained from a 400ft deep artesian well on the company’s premises. (I wonder if it is still there) and this water was used with the choicest hops and malt made from the best Irish barley obtainable. The hops used came chiefly from Kent and when obtainable, a percentage came from the USA. The process through which the barley went from its arrival in the brewery until it emerged as ale or stout, was extremely interesting and quaint. The barley was first dried to a consistent level of moisture content and then stored for a few weeks before being steeped. It was then ‘floored’ on lots which the brewery had, as well as lofts in Dominic Street and Wellington Quay. These have, in recent years, been converted into shops and a high rise apartment block. Here on these lofts the growing process of the barley in the ground was artificially repeated, the growth however being terminated at the desired stage. The barley was then kilned and cured before being ground and mashed with hot water and the liquid was drawn off. It was then run to built-in coppers, where hops was added, then boiled, the wort, as it was called, being subsequently strained from the hops, cooled and fermented. The final stage was when the beer was casked (in wooden barrels) and matured. Altogether there were approximately 200 people employed in the industry, for apart from the actual brewing of the beer there was a tremendous amount of activity, and the transport department built up a fine fleet of steam lorries, (I remember seeing Gerry McConville driving one of these down the Marsh Road), motor lorries and carts and Jemmy Early was in charge of town deliveries in a horse drawn wagon, from which he rolled the barrells into the pub. While catering for an extensive home market, Cairnes Ltd had, since May 1951, been engaged in the export of bottled stout to America. This stout was much stronger than anything of its kind on sale in Ireland and the venture steadily expanded in the new market. The metal caps of the export bottles had the imprint of the Star and Crescent, which is part of the Drogheda Coat of Arms, while the label carried three reproductions of miniature photographs of St Laurence Gate. And so one of Drogheda’s oldest industries was carrying the name of the town across the world. In Millmount museum there is a permanent exhibition of artifacts from Cairnes Brewery which were literally ‘rescued’ before and during the closing down of the brewery in 1965 when Guinness started buying out their competitors.Showcased are the various bottles with their beer labels – the famous ‘Stingo’, a most favoured ale at the time. There are also the large enamel advertising signs with ‘W Cairnes and Son. X Porter’ showing the brewery in its heyday, and a complete set of tools which were used by the cooper (wooden barrel maker), with a mythology of names like, the adze, draw knife, the buzz, the auger and chisel, the spokeshave and the coopers anvil. Note: A recent informant who wishes to remain anonymous, wrote the following about Cairnes Brewery: ‘The last brew was carried out in October 1960. The brew was mashed by Joseph Oliver Roche, head brewer and declared by Patrick (Paddy) Weldon. ‘In the break-up of the Brewery by Guinness, Roche was sent to Waterford, while Weldon was sent to Dundalk. Kevin Beatty was also sent to New Ross or was it Enniscorthy?’
74cm x 52cm ANOTHER great industry on the Scotch Hall site was the brewing firm of Cairnes Ltd, one of the original firms of Irish brewers dating back to 1772 with the foundation of the Castlebellingham Brewery at the picturesque Co Louth village of that name.In 1825, William Cairnes, who was related by marriage to the owners of the ’Bellingham brewery, founded the brewery at Marsh Road, Drogheda, which, for over 150 years, gave employment to almost 200 workers and the firm was famous for its ales and stout. In 1889 the interests of the two breweries were pooled, a public company being formed under the title of the Castlebellingham and Drogheda Breweries Ltd. This title was changed for brevity in 1933 to Cairnes Ltd. For a good many years subsequent to the merger, the breweries were worked independently, each supplying its own customers throughout Ireland and abroad. However, in 1923, it was considered advisable to concentrate brewing in Drogheda, owing to the more advantageous position of the town, and the brewing plant and premises there, were more extensive. Actually the plant at Drogheda was one of the most up-to-date in Ireland and compared very favourably with that of breweries in England and Wales. The supply of brewing water was obtained from a 400ft deep artesian well on the company’s premises. (I wonder if it is still there) and this water was used with the choicest hops and malt made from the best Irish barley obtainable. The hops used came chiefly from Kent and when obtainable, a percentage came from the USA. The process through which the barley went from its arrival in the brewery until it emerged as ale or stout, was extremely interesting and quaint. The barley was first dried to a consistent level of moisture content and then stored for a few weeks before being steeped. It was then ‘floored’ on lots which the brewery had, as well as lofts in Dominic Street and Wellington Quay. These have, in recent years, been converted into shops and a high rise apartment block. Here on these lofts the growing process of the barley in the ground was artificially repeated, the growth however being terminated at the desired stage. The barley was then kilned and cured before being ground and mashed with hot water and the liquid was drawn off. It was then run to built-in coppers, where hops was added, then boiled, the wort, as it was called, being subsequently strained from the hops, cooled and fermented. The final stage was when the beer was casked (in wooden barrels) and matured. Altogether there were approximately 200 people employed in the industry, for apart from the actual brewing of the beer there was a tremendous amount of activity, and the transport department built up a fine fleet of steam lorries, (I remember seeing Gerry McConville driving one of these down the Marsh Road), motor lorries and carts and Jemmy Early was in charge of town deliveries in a horse drawn wagon, from which he rolled the barrells into the pub. While catering for an extensive home market, Cairnes Ltd had, since May 1951, been engaged in the export of bottled stout to America. This stout was much stronger than anything of its kind on sale in Ireland and the venture steadily expanded in the new market. The metal caps of the export bottles had the imprint of the Star and Crescent, which is part of the Drogheda Coat of Arms, while the label carried three reproductions of miniature photographs of St Laurence Gate. And so one of Drogheda’s oldest industries was carrying the name of the town across the world. In Millmount museum there is a permanent exhibition of artifacts from Cairnes Brewery which were literally ‘rescued’ before and during the closing down of the brewery in 1965 when Guinness started buying out their competitors.Showcased are the various bottles with their beer labels – the famous ‘Stingo’, a most favoured ale at the time. There are also the large enamel advertising signs with ‘W Cairnes and Son. X Porter’ showing the brewery in its heyday, and a complete set of tools which were used by the cooper (wooden barrel maker), with a mythology of names like, the adze, draw knife, the buzz, the auger and chisel, the spokeshave and the coopers anvil. Note: A recent informant who wishes to remain anonymous, wrote the following about Cairnes Brewery: ‘The last brew was carried out in October 1960. The brew was mashed by Joseph Oliver Roche, head brewer and declared by Patrick (Paddy) Weldon. ‘In the break-up of the Brewery by Guinness, Roche was sent to Waterford, while Weldon was sent to Dundalk. Kevin Beatty was also sent to New Ross or was it Enniscorthy?’ -

 68cm x 56cmWith a history dating back generations it is inevitable that many myths and legends about Kinahans whiskey steeped into storytelling. But the origins of the L.L. mark have been well documented. In 1807, the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland (the head of state), Charles Lennox, was so impressed with the whiskeys made by Kinahans that he ordered all stocks at the Kinahans Dublin vaults to be taken exclusively for his private use, marking each cask with “L.L.”. The news, which were highly advertised, led to Kinahans becoming one of the most sought after whiskeys both, domestically and in neighbouring countries.In 1819, the popularity of the Kinahans brand allowed to set up its own four story headquarters, at the corner of Burgh Quay and D’Olier Street, Dublin, Named the Carlisle Building, to resonate with nearby Carlisle Bridge, the premises were built as part of the re-development of the city being overseen by the city's Wide Street Commissioners. By the middle of 20th Century the historic building has been taken down.As Kinahans popularity grew, London became a natural base for the company in 1800s wishing to expand into international markets. On 31 December 1841, Kinahans appointed Mr. George Smyth as its first agent in the city of London, with an address at no.1 White Hart Court, London, UK. For over half a century the company's London base has formed the centre of a great volume of export trade to the Continent, China, India, Australia and all the foreign markets.
68cm x 56cmWith a history dating back generations it is inevitable that many myths and legends about Kinahans whiskey steeped into storytelling. But the origins of the L.L. mark have been well documented. In 1807, the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland (the head of state), Charles Lennox, was so impressed with the whiskeys made by Kinahans that he ordered all stocks at the Kinahans Dublin vaults to be taken exclusively for his private use, marking each cask with “L.L.”. The news, which were highly advertised, led to Kinahans becoming one of the most sought after whiskeys both, domestically and in neighbouring countries.In 1819, the popularity of the Kinahans brand allowed to set up its own four story headquarters, at the corner of Burgh Quay and D’Olier Street, Dublin, Named the Carlisle Building, to resonate with nearby Carlisle Bridge, the premises were built as part of the re-development of the city being overseen by the city's Wide Street Commissioners. By the middle of 20th Century the historic building has been taken down.As Kinahans popularity grew, London became a natural base for the company in 1800s wishing to expand into international markets. On 31 December 1841, Kinahans appointed Mr. George Smyth as its first agent in the city of London, with an address at no.1 White Hart Court, London, UK. For over half a century the company's London base has formed the centre of a great volume of export trade to the Continent, China, India, Australia and all the foreign markets.
The Royal Warrants

1845
Throughout 1800s Kinahans continued to offer the highest level of differentiated taste and craftsmanship, for which Queen Victoria awarded it a Royal Warrant in 1845. With major accolades in hand, the recruitment of the agents and retail outlets continued.
The Preferred Whiskey Of Jerry Thomas

1862
With popularity in the British Isles, by the middle of 19th century Kinahans whiskey came to be the notice of many American authors and connoisseurs. In 1860s Kinahans came to the attention of the legendary Jerry Thomas. Also known as "the father of American mixology", Jerry Thomas was a revolutionary character, who due to his creativity and showmanship transformed the image of the bartender as a creative professional. In his 1862 "Guide on How to Mix Drinks", Jerry Thomas featured Kinahans in one of his book's recipes. The Bartender's "Guide on How to Mix Drinks" was the first drinks and mixology book ever published in the United States and can be counted amongst very few most influential drinks publications to date.
Protected Trademark

1863
Since its rise to popularity Kinahans faced hazardous times. Because of the brand's accolades, unscrupulous merchants publicans and others were restless in using the Kinahans bottles, labels and brand marks in order to sell their own products. In 1863, the activities of William Bolton, a grocer in Dublin's Westmoreland Street, led to the final and landmark case of legal redress. In the Irish case of Kinahan v. Bolton, the Irish Courts granted an injunction to restrain others from invading the Kinahans L.L. mark.
A Household Name

1881
The terms “Kinahans” and “Kinahans L.L.” is by 1881 a household name, becoming widely accepted as shorthand for a whisky of a specific price, quality and reputation. Confirmation for this is found in the 1881 Edition of Brewer's Dictionary of Phrases and Fables, in which the origin of L.L. trademark is also described. It is against this background that familiarity with the Kinahans brand name found expression in books written by countless British and American authors.
Decline Of The Irish Whiskey Industry

1902-1911
The new century began favourably. However, nothing could shield the company from the tribulations that were about to unfold. One of the key family members, George Kinahan died in 1903 and with him ended the family's long association with Dublin civic life as well as the prestige and opportunities which would have created. As the longest serving director, he took with him an intimate knowledge of the company's history as well as a wealth of practical business experience. Additionally, his long directorship at the Bank of Ireland would also have been of great practical value, not least because at various times his fellow directors at the bank included senior members of the Jameson whiskey family. On top of the departure of George Kinahan, the company had to cope with changing and more difficult economy in Ireland. Overall Irish whiskey exports declined spectacularly between 1900 and 1914. In Ireland itself both consumption and production fell, aided by increase of almost a third in spirit duty, as proposed by Lloyd George in his 1909 budget.
Transfer Of The Brand
 In June 1911 Kinahans business operations were being transferred to Bagot & Hutton, another long established Dublin wine and spirit enterprise. This company bottled and distributed Kinahans L.L. whiskey up until the time of Prohibition in the United States in 1920.In November 1920, following the Prohibition in the United States, an economic decline and a forthcoming Civil War in Ireland, the two spirit houses combined and were registered as Bagot Hutton & Kinahan. This arrangement continued until October 1988, when the shareholders decided to take a long break for one of Dublin's most prominent business houses, until better times.
In June 1911 Kinahans business operations were being transferred to Bagot & Hutton, another long established Dublin wine and spirit enterprise. This company bottled and distributed Kinahans L.L. whiskey up until the time of Prohibition in the United States in 1920.In November 1920, following the Prohibition in the United States, an economic decline and a forthcoming Civil War in Ireland, the two spirit houses combined and were registered as Bagot Hutton & Kinahan. This arrangement continued until October 1988, when the shareholders decided to take a long break for one of Dublin's most prominent business houses, until better times. -

 58cm x 58cm Jameson did not bottle our own whiskey until 1963. The first Jameson whiskey bottled at Bow Street was launched as Crested Ten. Back then, Jameson was available in 68 markets worldwide, exporting 15,000 cases annually to the United States. During the 19th century Irish distillers did not bottle and sell their own whiskey. They simply produced the spirit, put it in casks and then sold it on to retailers directly, who would then supply the public as they wished. These spirits merchants were known as bonders, from the practice of holding whiskey “in bond” (i.e. without duties paid on it) in their specialised bonded warehouses. Many pubs also doubled as bonders, which meant they could, supply their patrons with whiskey of which they were assured the provenance. Provenance and dishonesty were the main problem with this system as distilleries had no control over what happened to their whiskey after it left their premises. This lead some of the more unscrupulous proprietors to adulterate the whiskey coming from the cask or lie about how old it was, meaning that a distillery might end up with a bad name for their product through no fault of their own. However, some whiskey bonders of the era were renowned for their dedication to the art of maturing and blending, such that their names and products have today become some of the most important in Irish whiskey.Though beginning life in 1805 as a tea shop and confectionary business, it was in 1887 that the Mitchell family made their mark on Irish spirit history. That was the year they decided to go into the whiskey bonding, following a period as solely wine merchants. The ingenious idea must have seemed quite obvious, they had lots of empty wine and sherry casks so why not send them across the river to Jameson’s Bow Street distillery to be filled with new make single pot still whiskey. Once in the bonded warehouse the casks were given a coloured dash or spot, depending on how long they were due to be aged for, blue for seven years, green for 10, yellow for 12 and red for 15. This led to its renown as “Spot Whiskey” which became hugely popular with the high society of the time and had no lesser proponent than Samuel Beckett, who would order casks to be delivered to his Parisian literary atelier. Thankfully, Mitchell and Son are still going strong, and aged single pot still whiskey from Midleton, in the form of Green and Yellow Spot is widely available. John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it
58cm x 58cm Jameson did not bottle our own whiskey until 1963. The first Jameson whiskey bottled at Bow Street was launched as Crested Ten. Back then, Jameson was available in 68 markets worldwide, exporting 15,000 cases annually to the United States. During the 19th century Irish distillers did not bottle and sell their own whiskey. They simply produced the spirit, put it in casks and then sold it on to retailers directly, who would then supply the public as they wished. These spirits merchants were known as bonders, from the practice of holding whiskey “in bond” (i.e. without duties paid on it) in their specialised bonded warehouses. Many pubs also doubled as bonders, which meant they could, supply their patrons with whiskey of which they were assured the provenance. Provenance and dishonesty were the main problem with this system as distilleries had no control over what happened to their whiskey after it left their premises. This lead some of the more unscrupulous proprietors to adulterate the whiskey coming from the cask or lie about how old it was, meaning that a distillery might end up with a bad name for their product through no fault of their own. However, some whiskey bonders of the era were renowned for their dedication to the art of maturing and blending, such that their names and products have today become some of the most important in Irish whiskey.Though beginning life in 1805 as a tea shop and confectionary business, it was in 1887 that the Mitchell family made their mark on Irish spirit history. That was the year they decided to go into the whiskey bonding, following a period as solely wine merchants. The ingenious idea must have seemed quite obvious, they had lots of empty wine and sherry casks so why not send them across the river to Jameson’s Bow Street distillery to be filled with new make single pot still whiskey. Once in the bonded warehouse the casks were given a coloured dash or spot, depending on how long they were due to be aged for, blue for seven years, green for 10, yellow for 12 and red for 15. This led to its renown as “Spot Whiskey” which became hugely popular with the high society of the time and had no lesser proponent than Samuel Beckett, who would order casks to be delivered to his Parisian literary atelier. Thankfully, Mitchell and Son are still going strong, and aged single pot still whiskey from Midleton, in the form of Green and Yellow Spot is widely available. John Jameson was originally a lawyer from Alloa in Scotland before he founded his eponymous distillery in Dublin in 1780.Prevoius to this he had made the wise move of marrying Margaret Haig (1753–1815) in 1768,one of the simple reasons being Margaret was the eldest daughter of John Haig, the famous whisky distiller in Scotland. John and Margaret had eight sons and eight daughters, a family of 16 children. Portraits of the couple by Sir Henry Raeburn are on display in the National Gallery of Ireland. John Jameson joined the Convivial Lodge No. 202, of the Dublin Freemasons on the 24th June 1774 and in 1780, Irish whiskey distillation began at Bow Street. In 1805, he was joined by his son John Jameson II who took over the family business that year and for the next 41 years, John Jameson II built up the business before handing over to his son John Jameson the 3rd in 1851. In 1901, the Company was formally incorporated as John Jameson and Son Ltd. Four of John Jameson’s sons followed his footsteps in distilling in Ireland, John Jameson II (1773 – 1851) at Bow Street, William and James Jameson at Marrowbone Lane in Dublin (where they partnered their Stein relations, calling their business Jameson and Stein, before settling on William Jameson & Co.). The fourth of Jameson's sons, Andrew, who had a small distillery at Enniscorthy, Co. Wexford, was the grandfather of Guglielmo Marconi, inventor of wireless telegraphy. Marconi’s mother was Annie Jameson, Andrew’s daughter. John Jameson’s eldest son, Robert took over his father’s legal business in Alloa. The Jamesons became the most important distilling family in Ireland, despite rivalry between the Bow Street and Marrowbone Lane distilleries. By the turn of the 19th century, it was the second largest producer in Ireland and one of the largest in the world, producing 1,000,000 gallons annually. Dublin at the time was the centre of world whiskey production. It was the second most popular spirit in the world after rum and internationally Jameson had by 1805 become the world's number one whiskey. Today, Jameson is the world's third largest single-distillery whiskey. Historical events, for a time, set the company back. The temperance movement in Ireland had an enormous impact domestically but the two key events that affected Jameson were the Irish War of Independence and subsequent trade war with the British which denied Jameson the export markets of the Commonwealth, and shortly thereafter, the introduction of prohibition in the United States. While Scottish brands could easily slip across the Canada–US border, Jameson was excluded from its biggest market for many years. The introduction of column stills by the Scottish blenders in the mid-19th-century enabled increased production that the Irish, still making labour-intensive single pot still whiskey, could not compete with. There was a legal enquiry somewhere in 1908 to deal with the trade definition of whiskey. The Scottish producers won within some jurisdictions, and blends became recognised in the law of that jurisdiction as whiskey. The Irish in general, and Jameson in particular, continued with the traditional pot still production process for many years.In 1966 John Jameson merged with Cork Distillers and John Powers to form the Irish Distillers Group. In 1976, the Dublin whiskey distilleries of Jameson in Bow Street and in John's Lane were closed following the opening of a New Midleton Distillery by Irish Distillers outside Cork. The Midleton Distillery now produces much of the Irish whiskey sold in Ireland under the Jameson, Midleton, Powers, Redbreast, Spot and Paddy labels. The new facility adjoins the Old Midleton Distillery, the original home of the Paddy label, which is now home to the Jameson Experience Visitor Centre and the Irish Whiskey Academy. The Jameson brand was acquired by the French drinks conglomerate Pernod Ricard in 1988, when it bought Irish Distillers. The old Jameson Distillery in Bow Street near Smithfield in Dublin now serves as a museum which offers tours and tastings. The distillery, which is historical in nature and no longer produces whiskey on site, went through a $12.6 million renovation that was concluded in March 2016, and is now a focal part of Ireland's strategy to raise the number of whiskey tourists, which stood at 600,000 in 2017.Bow Street also now has a fully functioning Maturation Warehouse within its walls since the 2016 renovation. It is here that Jameson 18 Bow Street is finished before being bottled at Cask Strength. In 2008, The Local, an Irish pub in Minneapolis, sold 671 cases of Jameson (22 bottles a day),making it the largest server of Jameson's in the world – a title it







