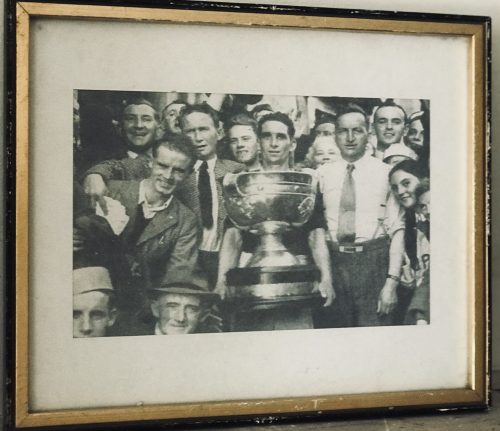
1934 All-Ireland Hurling Final
 Limerick 5-2 Dublin 2-6
D Clohessy 4-0, M Mackey 1-1, J O’Connell 0-1
Limerick 5-2 Dublin 2-6
D Clohessy 4-0, M Mackey 1-1, J O’Connell 0-1






 The 1938 All-Ireland Football Final Replay on October 23rd, 1938 ended in the most bizarre fashion imaginable when with 2 minutes left to play, Galway supporters, mistakenly believing the referee had blown for full-time, invaded the pitch, causing a 20 minute delay before the final minutes could be played out.
Even more dramatic was the fact that by the time the pitch was cleared, most of the Kerry players seemed to have disappeared.
The 1938 All-Ireland Football Final Replay on October 23rd, 1938 ended in the most bizarre fashion imaginable when with 2 minutes left to play, Galway supporters, mistakenly believing the referee had blown for full-time, invaded the pitch, causing a 20 minute delay before the final minutes could be played out.
Even more dramatic was the fact that by the time the pitch was cleared, most of the Kerry players seemed to have disappeared.
 The confusion all began with a free awarded to Kerry by referee Peter Waters of Kildare with Galway leading the defending champions, by 2-4 to 0-6.
The referee placed the ball and blew his whistle for the kick to be taken while running towards the Galway goals. He looked round just as Sean Brosnan was taking the kick and seeing a Galway player too close he blew for the kick to be retaken.
Thinking that he had blown for full-time the jubilant Galway supporters invaded the pitch.
The confusion all began with a free awarded to Kerry by referee Peter Waters of Kildare with Galway leading the defending champions, by 2-4 to 0-6.
The referee placed the ball and blew his whistle for the kick to be taken while running towards the Galway goals. He looked round just as Sean Brosnan was taking the kick and seeing a Galway player too close he blew for the kick to be retaken.
Thinking that he had blown for full-time the jubilant Galway supporters invaded the pitch.
 It took all of twenty minutes to clear the pitch but only then did the real problems come to light. Jerry O’Leary Chairman of the Kerry Selection Committee outlined their dilemma.
It took all of twenty minutes to clear the pitch but only then did the real problems come to light. Jerry O’Leary Chairman of the Kerry Selection Committee outlined their dilemma.

 Somehow or other Kerry managed to re-field even if the team which played out the remaining minutes bore little resemblance to the starting fifteen.
Somehow or other Kerry managed to re-field even if the team which played out the remaining minutes bore little resemblance to the starting fifteen.
 More remarkable again was the fact that Kerry went on to add another point to their total before the referee finally blew for full-time with Galway winners by 2-4 to 0-7.
It was generally agreed that the confusion was of the crowd’s and not the referee’s making but questions remained about the total number of players Kerry had been permitted to use in those final few minutes.
More remarkable again was the fact that Kerry went on to add another point to their total before the referee finally blew for full-time with Galway winners by 2-4 to 0-7.
It was generally agreed that the confusion was of the crowd’s and not the referee’s making but questions remained about the total number of players Kerry had been permitted to use in those final few minutes.
 The National and Provincial papers and indeed all available Records to this day list only those 16 Kerry players who were involved prior to the 20 minute interruption but now (80 years on) for the first time all the players who played for Kerry in that October 23rd, 1938 All-Ireland Final Replay can be given their rightful place in the Record Books.
KERRY’s 24:
The National and Provincial papers and indeed all available Records to this day list only those 16 Kerry players who were involved prior to the 20 minute interruption but now (80 years on) for the first time all the players who played for Kerry in that October 23rd, 1938 All-Ireland Final Replay can be given their rightful place in the Record Books.
KERRY’s 24:

 That night, in front of a 1,500 crowd, at a Gaelic League organised Siamsa Mór in the Mansion House in Dawson Street, Art McCann presented the Galway team with their winners’ medals.
That night, in front of a 1,500 crowd, at a Gaelic League organised Siamsa Mór in the Mansion House in Dawson Street, Art McCann presented the Galway team with their winners’ medals.
 The Kerry players meanwhile joined 300 of their suppoeters at a Ceilidhe hosted by the Kerrymen’s Social Club in Rathmines Town Hall.
The National Newspapers may not always have reported the facts to Galway’s satisfaction but there can be no questioning the support of Galway County Council.
The Kerry players meanwhile joined 300 of their suppoeters at a Ceilidhe hosted by the Kerrymen’s Social Club in Rathmines Town Hall.
The National Newspapers may not always have reported the facts to Galway’s satisfaction but there can be no questioning the support of Galway County Council.
 Needless to say the Galway players received an unprecedented welcome on their return to Galway having first been feted along the way in Mullingar, Streamstown, Moate and Athlone.
GALWAY – 1938 ALL-IRELAND SENIOR FOOTBALL CHAMPIONS
Needless to say the Galway players received an unprecedented welcome on their return to Galway having first been feted along the way in Mullingar, Streamstown, Moate and Athlone.
GALWAY – 1938 ALL-IRELAND SENIOR FOOTBALL CHAMPIONS
 Back (L-R) Bobby Beggs, Ralph Griffin, John Burke, Jimmy McGauran, Charlie Connolly, Brendan Nestor, Dinny Sullivan, Mick Connaire, Martin Kelly. Front (L-R) Frank Cunniffe, Jackie Flavin, Mick Higgins, John ‘Tull’ Dunne (Capt), Ned Mulholland, Mick Raftery.
Substitutes: (not in photograph) Mick Ryder and Pat McDonagh.
TIME ADDED ON:
Not far behind the controversy surrounding the last few minutes of 1938 All-Ireland Football Final Replay was the controversy surrounding the last few seconds of the drawn match played a month earlier.
Back (L-R) Bobby Beggs, Ralph Griffin, John Burke, Jimmy McGauran, Charlie Connolly, Brendan Nestor, Dinny Sullivan, Mick Connaire, Martin Kelly. Front (L-R) Frank Cunniffe, Jackie Flavin, Mick Higgins, John ‘Tull’ Dunne (Capt), Ned Mulholland, Mick Raftery.
Substitutes: (not in photograph) Mick Ryder and Pat McDonagh.
TIME ADDED ON:
Not far behind the controversy surrounding the last few minutes of 1938 All-Ireland Football Final Replay was the controversy surrounding the last few seconds of the drawn match played a month earlier.

 The sides were level, Kerry 2-06 Galway 3-03, when Kerry’s J.J. Landers sent the ball between the Galway uprights for what looked like the winning point. However the thousands of celebrating Kerry supporters making for the Croke Park exits were soon stopped in their tracks.
The sides were level, Kerry 2-06 Galway 3-03, when Kerry’s J.J. Landers sent the ball between the Galway uprights for what looked like the winning point. However the thousands of celebrating Kerry supporters making for the Croke Park exits were soon stopped in their tracks.
 It was cruel luck on Kerry and while there were many who criticised the referee, Tom Culhane from Glin, County Limerick, for blowing the final whistle while John Joe Landers was it the act of shooting, Kerry’s County Board Chairman Denis J. Bailey wasn’t among them.
At the next Central Council meeting, in a remarkably generous response to the Referee’s Report being read he stated that ‘they in Kerry were quite satisfied with the result’ and ‘They wished to pay a tribute to Galway for their sporting spirit and also to the referee who, in their opinion, carried out his duties very well.’
The Central Council then awarded the two counties £300 each towards the costs of the two-week Collective Training Camps both counties had planned in the lead up to the Replay on October 23rd. Munster Council granted Kerry (pictured here in Collective Training) an additional £100.
It was cruel luck on Kerry and while there were many who criticised the referee, Tom Culhane from Glin, County Limerick, for blowing the final whistle while John Joe Landers was it the act of shooting, Kerry’s County Board Chairman Denis J. Bailey wasn’t among them.
At the next Central Council meeting, in a remarkably generous response to the Referee’s Report being read he stated that ‘they in Kerry were quite satisfied with the result’ and ‘They wished to pay a tribute to Galway for their sporting spirit and also to the referee who, in their opinion, carried out his duties very well.’
The Central Council then awarded the two counties £300 each towards the costs of the two-week Collective Training Camps both counties had planned in the lead up to the Replay on October 23rd. Munster Council granted Kerry (pictured here in Collective Training) an additional £100.
 Prior to that Central Council meeting, General Secretary, Pádraig Ó’Caoimh, received a telephone call from the New York GAA suggesting the replay take place in New York but the request (which was successfully repeated nine years later in 1947) was on this occasion turned down.
However doubts about the Replay even going ahead were immediately raised.
Prior to that Central Council meeting, General Secretary, Pádraig Ó’Caoimh, received a telephone call from the New York GAA suggesting the replay take place in New York but the request (which was successfully repeated nine years later in 1947) was on this occasion turned down.
However doubts about the Replay even going ahead were immediately raised.
 Satisfactory transport arrangements were eventually agreed and the match went ahead although the Kerry supporters who left Tralee on the so-called ‘ghost’ train at 1am on the morning of the October 23rd may still have felt hard done by.
Satisfactory transport arrangements were eventually agreed and the match went ahead although the Kerry supporters who left Tralee on the so-called ‘ghost’ train at 1am on the morning of the October 23rd may still have felt hard done by.
 In the lead-up to the game the Galway selectors expressed their delight at the success of their forwards short hand-passing game against the Kerry backs in the drawn match although there were some worries that not all their players had been able to attend the first week of Collective Training and of course there was Kerry’s Replay record to be considered.
Kerry had previously played in 4 All-Ireland Replays and won them all, a great source of encouragement to the Kerry supporters.
However amid some reports of disharmony within the Kerry camp, following a ‘trial match’ on the Sunday before the Replay, the Kerry selection Committee dropped a real bombshell.
Joe Keohane (Dublin Geraldines) who had been Kerry’s regular full-back for the previous two years and was one of the stars of their 1937 All-Ireland win over Cavan was replaced by young Paddy ‘Bawn’ Brosnan a member of the 1938 Kerry Junior team.
A back injury to Kerry’s best forward, J.J. Landers made him an extreme doubt for the Replay with Martin Regan on stand-by to take his place if required which is exactly what happened before that fateful free-kick, that infamous 20 minute delay and Kerry’s unprecedented use of 24 players.
Most definitely an All-Ireland Final and Final Replay never to be forgotten.
In the lead-up to the game the Galway selectors expressed their delight at the success of their forwards short hand-passing game against the Kerry backs in the drawn match although there were some worries that not all their players had been able to attend the first week of Collective Training and of course there was Kerry’s Replay record to be considered.
Kerry had previously played in 4 All-Ireland Replays and won them all, a great source of encouragement to the Kerry supporters.
However amid some reports of disharmony within the Kerry camp, following a ‘trial match’ on the Sunday before the Replay, the Kerry selection Committee dropped a real bombshell.
Joe Keohane (Dublin Geraldines) who had been Kerry’s regular full-back for the previous two years and was one of the stars of their 1937 All-Ireland win over Cavan was replaced by young Paddy ‘Bawn’ Brosnan a member of the 1938 Kerry Junior team.
A back injury to Kerry’s best forward, J.J. Landers made him an extreme doubt for the Replay with Martin Regan on stand-by to take his place if required which is exactly what happened before that fateful free-kick, that infamous 20 minute delay and Kerry’s unprecedented use of 24 players.
Most definitely an All-Ireland Final and Final Replay never to be forgotten.
 The Galway and Kerry players parade in front of the newly opened (1938) Cusack Stand
The Galway and Kerry players parade in front of the newly opened (1938) Cusack Stand

 The 1938 All-Ireland Football Final Replay on October 23rd, 1938 ended in the most bizarre fashion imaginable when with 2 minutes left to play, Galway supporters, mistakenly believing the referee had blown for full-time, invaded the pitch, causing a 20 minute delay before the final minutes could be played out.
Even more dramatic was the fact that by the time the pitch was cleared, most of the Kerry players seemed to have disappeared.
The 1938 All-Ireland Football Final Replay on October 23rd, 1938 ended in the most bizarre fashion imaginable when with 2 minutes left to play, Galway supporters, mistakenly believing the referee had blown for full-time, invaded the pitch, causing a 20 minute delay before the final minutes could be played out.
Even more dramatic was the fact that by the time the pitch was cleared, most of the Kerry players seemed to have disappeared.
 The confusion all began with a free awarded to Kerry by referee Peter Waters of Kildare with Galway leading the defending champions, by 2-4 to 0-6.
The referee placed the ball and blew his whistle for the kick to be taken while running towards the Galway goals. He looked round just as Sean Brosnan was taking the kick and seeing a Galway player too close he blew for the kick to be retaken.
Thinking that he had blown for full-time the jubilant Galway supporters invaded the pitch.
The confusion all began with a free awarded to Kerry by referee Peter Waters of Kildare with Galway leading the defending champions, by 2-4 to 0-6.
The referee placed the ball and blew his whistle for the kick to be taken while running towards the Galway goals. He looked round just as Sean Brosnan was taking the kick and seeing a Galway player too close he blew for the kick to be retaken.
Thinking that he had blown for full-time the jubilant Galway supporters invaded the pitch.
 It took all of twenty minutes to clear the pitch but only then did the real problems come to light. Jerry O’Leary Chairman of the Kerry Selection Committee outlined their dilemma.
It took all of twenty minutes to clear the pitch but only then did the real problems come to light. Jerry O’Leary Chairman of the Kerry Selection Committee outlined their dilemma.

 Somehow or other Kerry managed to re-field even if the team which played out the remaining minutes bore little resemblance to the starting fifteen.
Somehow or other Kerry managed to re-field even if the team which played out the remaining minutes bore little resemblance to the starting fifteen.
 More remarkable again was the fact that Kerry went on to add another point to their total before the referee finally blew for full-time with Galway winners by 2-4 to 0-7.
It was generally agreed that the confusion was of the crowd’s and not the referee’s making but questions remained about the total number of players Kerry had been permitted to use in those final few minutes.
More remarkable again was the fact that Kerry went on to add another point to their total before the referee finally blew for full-time with Galway winners by 2-4 to 0-7.
It was generally agreed that the confusion was of the crowd’s and not the referee’s making but questions remained about the total number of players Kerry had been permitted to use in those final few minutes.
 The National and Provincial papers and indeed all available Records to this day list only those 16 Kerry players who were involved prior to the 20 minute interruption but now (80 years on) for the first time all the players who played for Kerry in that October 23rd, 1938 All-Ireland Final Replay can be given their rightful place in the Record Books.
KERRY’s 24:
The National and Provincial papers and indeed all available Records to this day list only those 16 Kerry players who were involved prior to the 20 minute interruption but now (80 years on) for the first time all the players who played for Kerry in that October 23rd, 1938 All-Ireland Final Replay can be given their rightful place in the Record Books.
KERRY’s 24:

 That night, in front of a 1,500 crowd, at a Gaelic League organised Siamsa Mór in the Mansion House in Dawson Street, Art McCann presented the Galway team with their winners’ medals.
That night, in front of a 1,500 crowd, at a Gaelic League organised Siamsa Mór in the Mansion House in Dawson Street, Art McCann presented the Galway team with their winners’ medals.
 The Kerry players meanwhile joined 300 of their suppoeters at a Ceilidhe hosted by the Kerrymen’s Social Club in Rathmines Town Hall.
The National Newspapers may not always have reported the facts to Galway’s satisfaction but there can be no questioning the support of Galway County Council.
The Kerry players meanwhile joined 300 of their suppoeters at a Ceilidhe hosted by the Kerrymen’s Social Club in Rathmines Town Hall.
The National Newspapers may not always have reported the facts to Galway’s satisfaction but there can be no questioning the support of Galway County Council.
 Needless to say the Galway players received an unprecedented welcome on their return to Galway having first been feted along the way in Mullingar, Streamstown, Moate and Athlone.
GALWAY – 1938 ALL-IRELAND SENIOR FOOTBALL CHAMPIONS
Needless to say the Galway players received an unprecedented welcome on their return to Galway having first been feted along the way in Mullingar, Streamstown, Moate and Athlone.
GALWAY – 1938 ALL-IRELAND SENIOR FOOTBALL CHAMPIONS
 Back (L-R) Bobby Beggs, Ralph Griffin, John Burke, Jimmy McGauran, Charlie Connolly, Brendan Nestor, Dinny Sullivan, Mick Connaire, Martin Kelly. Front (L-R) Frank Cunniffe, Jackie Flavin, Mick Higgins, John ‘Tull’ Dunne (Capt), Ned Mulholland, Mick Raftery.
Substitutes: (not in photograph) Mick Ryder and Pat McDonagh.
TIME ADDED ON:
Not far behind the controversy surrounding the last few minutes of 1938 All-Ireland Football Final Replay was the controversy surrounding the last few seconds of the drawn match played a month earlier.
Back (L-R) Bobby Beggs, Ralph Griffin, John Burke, Jimmy McGauran, Charlie Connolly, Brendan Nestor, Dinny Sullivan, Mick Connaire, Martin Kelly. Front (L-R) Frank Cunniffe, Jackie Flavin, Mick Higgins, John ‘Tull’ Dunne (Capt), Ned Mulholland, Mick Raftery.
Substitutes: (not in photograph) Mick Ryder and Pat McDonagh.
TIME ADDED ON:
Not far behind the controversy surrounding the last few minutes of 1938 All-Ireland Football Final Replay was the controversy surrounding the last few seconds of the drawn match played a month earlier.

 The sides were level, Kerry 2-06 Galway 3-03, when Kerry’s J.J. Landers sent the ball between the Galway uprights for what looked like the winning point. However the thousands of celebrating Kerry supporters making for the Croke Park exits were soon stopped in their tracks.
The sides were level, Kerry 2-06 Galway 3-03, when Kerry’s J.J. Landers sent the ball between the Galway uprights for what looked like the winning point. However the thousands of celebrating Kerry supporters making for the Croke Park exits were soon stopped in their tracks.
 It was cruel luck on Kerry and while there were many who criticised the referee, Tom Culhane from Glin, County Limerick, for blowing the final whistle while John Joe Landers was it the act of shooting, Kerry’s County Board Chairman Denis J. Bailey wasn’t among them.
At the next Central Council meeting, in a remarkably generous response to the Referee’s Report being read he stated that ‘they in Kerry were quite satisfied with the result’ and ‘They wished to pay a tribute to Galway for their sporting spirit and also to the referee who, in their opinion, carried out his duties very well.’
The Central Council then awarded the two counties £300 each towards the costs of the two-week Collective Training Camps both counties had planned in the lead up to the Replay on October 23rd. Munster Council granted Kerry (pictured here in Collective Training) an additional £100.
It was cruel luck on Kerry and while there were many who criticised the referee, Tom Culhane from Glin, County Limerick, for blowing the final whistle while John Joe Landers was it the act of shooting, Kerry’s County Board Chairman Denis J. Bailey wasn’t among them.
At the next Central Council meeting, in a remarkably generous response to the Referee’s Report being read he stated that ‘they in Kerry were quite satisfied with the result’ and ‘They wished to pay a tribute to Galway for their sporting spirit and also to the referee who, in their opinion, carried out his duties very well.’
The Central Council then awarded the two counties £300 each towards the costs of the two-week Collective Training Camps both counties had planned in the lead up to the Replay on October 23rd. Munster Council granted Kerry (pictured here in Collective Training) an additional £100.
 Prior to that Central Council meeting, General Secretary, Pádraig Ó’Caoimh, received a telephone call from the New York GAA suggesting the replay take place in New York but the request (which was successfully repeated nine years later in 1947) was on this occasion turned down.
However doubts about the Replay even going ahead were immediately raised.
Prior to that Central Council meeting, General Secretary, Pádraig Ó’Caoimh, received a telephone call from the New York GAA suggesting the replay take place in New York but the request (which was successfully repeated nine years later in 1947) was on this occasion turned down.
However doubts about the Replay even going ahead were immediately raised.
 Satisfactory transport arrangements were eventually agreed and the match went ahead although the Kerry supporters who left Tralee on the so-called ‘ghost’ train at 1am on the morning of the October 23rd may still have felt hard done by.
Satisfactory transport arrangements were eventually agreed and the match went ahead although the Kerry supporters who left Tralee on the so-called ‘ghost’ train at 1am on the morning of the October 23rd may still have felt hard done by.
 In the lead-up to the game the Galway selectors expressed their delight at the success of their forwards short hand-passing game against the Kerry backs in the drawn match although there were some worries that not all their players had been able to attend the first week of Collective Training and of course there was Kerry’s Replay record to be considered.
Kerry had previously played in 4 All-Ireland Replays and won them all, a great source of encouragement to the Kerry supporters.
However amid some reports of disharmony within the Kerry camp, following a ‘trial match’ on the Sunday before the Replay, the Kerry selection Committee dropped a real bombshell.
Joe Keohane (Dublin Geraldines) who had been Kerry’s regular full-back for the previous two years and was one of the stars of their 1937 All-Ireland win over Cavan was replaced by young Paddy ‘Bawn’ Brosnan a member of the 1938 Kerry Junior team.
A back injury to Kerry’s best forward, J.J. Landers made him an extreme doubt for the Replay with Martin Regan on stand-by to take his place if required which is exactly what happened before that fateful free-kick, that infamous 20 minute delay and Kerry’s unprecedented use of 24 players.
Most definitely an All-Ireland Final and Final Replay never to be forgotten.
In the lead-up to the game the Galway selectors expressed their delight at the success of their forwards short hand-passing game against the Kerry backs in the drawn match although there were some worries that not all their players had been able to attend the first week of Collective Training and of course there was Kerry’s Replay record to be considered.
Kerry had previously played in 4 All-Ireland Replays and won them all, a great source of encouragement to the Kerry supporters.
However amid some reports of disharmony within the Kerry camp, following a ‘trial match’ on the Sunday before the Replay, the Kerry selection Committee dropped a real bombshell.
Joe Keohane (Dublin Geraldines) who had been Kerry’s regular full-back for the previous two years and was one of the stars of their 1937 All-Ireland win over Cavan was replaced by young Paddy ‘Bawn’ Brosnan a member of the 1938 Kerry Junior team.
A back injury to Kerry’s best forward, J.J. Landers made him an extreme doubt for the Replay with Martin Regan on stand-by to take his place if required which is exactly what happened before that fateful free-kick, that infamous 20 minute delay and Kerry’s unprecedented use of 24 players.
Most definitely an All-Ireland Final and Final Replay never to be forgotten.
 The Galway and Kerry players parade in front of the newly opened (1938) Cusack Stand
The Galway and Kerry players parade in front of the newly opened (1938) Cusack Stand
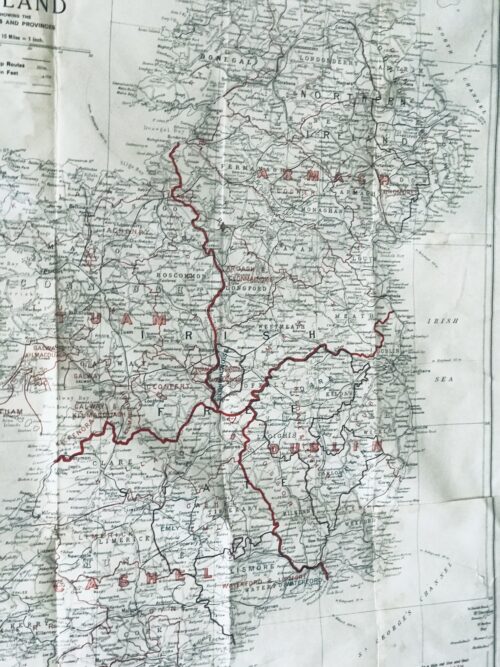

Fig.2 The chain and circumferentor were still the main tools of the trade in the 1750s. (Courtesy of the National Library of Ireland)
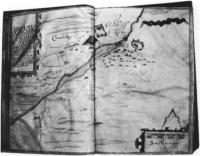
Fig.3 Carrickmacross, from Thomas Raven’s survey of Essex estate, County Monaghan 1634-5. Note the cluster of cabins, center right. (Courtesy of Marquis of Bath)
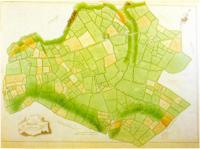
Fig.4 The manor of Tallow 1774 – part of Bernard Scale’s survey of County Waterford’s Devonshire estates. (Courtesy of the Trustees of the Chatsworth Settlement)
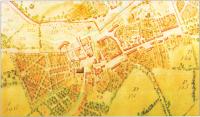
Fig.5 The town of Maynooth, County Kildare, from John Roque’s 1757 survey. (Courtesy of Patrick’s College, Maynooth)
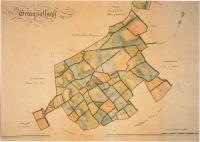
Fig.6 Graigsallagh, from a volume of maps of the ‘Manor of Maynooth'(1821) by Sherrard, Brassington and Green. (Courtesy of carton Desmesne)

All-Ireland football final day, 1949. Meath fans are en route to Croke Park by steam train, and will see their county win its first championship. They stop at Dunboyne. He hears their cheers fall through the billowing steam from the railway bridge. Five-year-old Seán Boylan knows something big is stirring.
Then he was simply a small boy kicking a ball around the family garden. The green and gold throng roared encouragement through fellowship and goodwill, buoyed by the occasion.
In later years he would give them good cause to cheer. Just a snapshot, but the moment seems to have acquired a near-cinematic resonance through what it prefigured. That railway bridge is now known locally as Boylan's bridge.
Around Dunboyne, there were local heroes to fire the imagination. His neighbours included Meath players like Jimmy Reilly, Bobby Ruske and 1949 All-Ireland-winning captain Brian Smyth.
"Brian Smyth was a great friend of my father's. I have a memory of kicking a ball around with him in the run-up to the 1954 All-Ireland final.
"He'd call out to the house on a Wednesday night to Daddy, getting the brews. Brian had a very famous dummy and he showed me how to do it. Of course, I practised it and used it all my life after."
He drew inspiration, too, from further afield. The great Gaelic names of his childhood were lent further mystique by Micheál O'Hehir's radio commentaries, which painted bold pictures in his head.
The legends were remote yet vividly present through the voice piercing the static.
"When he was doing matches you'd swear you were at the game. You were trying to be a John Dowling or a Seán Purcell or a Bobby or Nicky Rackard, a Christy Ring when you heard the way he described it."
Not that Gaelic games alone dominated his formative years. Motor races held in Dunboyne thrilled him as a youngster. Even now, his heart quickens a little at the vroom-vrooming of racing engines.
"I was always mad into motorsport, but most kids around Dunboyne were, because you had the racing which started in the '50s.
"It was outside your door so you followed the motorbikes and the cars. Of course, the only thing you could afford to do yourself was the go-karting. You'd go across to Monasterboice, where there was a track, or down to Askeaton in Limerick. The bug is still there."
At the age of nine, he was sent to Belvedere College. Rugby, of course, was on the sporting curriculum and he played with enthusiasm, once certain positional difficulties had been resolved.
"At the time the Ban was in but I played for a few years. In the first match I played I was put in the secondrow. At my height! I ended up in the backs afterwards, but it was very funny."
He chuckles at the thought of himself as a secondrow forward. In later years he was to meet Peter Stringer after an Ireland international. The scrumhalf greeted him warmly, announcing he was delighted to meet someone even smaller than himself.
His participation in rugby at Belvedere was never questioned, despite his GAA and republican family background. He was left to find his own course.
"My father, Lord be good to him, never tried to influence me in any way with regard to what I would play or what I became involved in. He wasn't that sort of man. And, well, in Belvedere, you're talking about the place where Kevin Barry went to school."
He took two of his boys in to see the old alma mater a few years back and was touched at the reception he received.
"I said I'd see if the then headmaster, Fr Leonard Moloney, was around. I hadn't been back in the place much but he invited us into his office. He went over to the press and took out two Club Lemons and two Mars bars for the lads. From then on that was the only school they wanted to go to and they're there now."
He hurled too at Belvedere, but his education in Gaelic games was to be furthered at Clogher Road Vocational School in Crumlin, which he attended after leaving Belvedere at 15. Moving from the privileged halls of Belvedere to the earthier environment of his new school was a jolt, but football and hurling helped smooth the transition.
In Crumlin, he would learn how to use his hands, within and without the classroom.
"The big thing there was the sport end of it. It was Gaelic and soccer we played. The PE instructor was Jim McCabe, who played centre-half back on the Cavan team that won the All-Ireland in 1952. He was still playing for Cavan at this stage. He was a lovely man and a terrific shooter."
He found himself spending Wednesday afternoons kicking a ball around with McCabe and another Cavan player, Charlie Gallagher. The latter's patiently rigorous application to practising his free-taking left a deep impression on the manager of the future.
While at Clogher Road, he represented Dublin Vocational Schools at centre-half back in both hurling and football. The goalkeeper on the football team was Pat Dunne, who would later play with Manchester United and Ireland.
He was on the move again at 16, switching to Warrenstown Agricultural College near Trim. His family background working with the land made the choice seem logical. Besides, the college did a nice sideline in cultivating footballers and hurlers. Again, he found an All-Ireland-winner circling prominently within his youthful orbit, foreshadowing his own relationship with Sam Maguire.
"The man who taught us veterinary was Séamus Murphy, who won five All-Irelands with Kerry in five different positions, an extraordinary record, from corner back to wing-half back to midfield to wing-half forward to corner forward. He brought a few of us from the college to Meath minor football trials."
Hurling, though, was the game at which he was most successful as a player. He broke into the Meath minor hurling panel while at Warrenstown. One day shortly after beginning there, he had another chance encounter which was to echo into the future. He was thumbing a lift home to Dunboyne, hurl slung over a shoulder, only to see a fawn-coloured Ford Anglia pull up. Its driver was Des "Snitchy" Ferguson. Thus began a long association. In later years, his two sons would win All-Irelands with Meath under Boylan's tutelage.
Back in his school days, though, nothing could top the feeling of making the Meath minor hurling panel. "The man who brought me for trials was the famous Brian Smyth. I'll never forget him coming to collect me for the trials. Here I was with Brian Smyth! Then when I got picked for Meath, it was just clover."



 Tom Moloughney, Jimmy Doyle, and Kieran Carey relax in the dressing room after Tipperary’s victory over Dublin in the 1961 All-Ireland final, a success that was to be repeated the following year. Picture from ‘The GAA — A People’s History’
Tom Moloughney, Jimmy Doyle, and Kieran Carey relax in the dressing room after Tipperary’s victory over Dublin in the 1961 All-Ireland final, a success that was to be repeated the following year. Picture from ‘The GAA — A People’s History’The 1962 All-Ireland hurling final wasn't the first time that the nation had been treated to live coverage of a game from Croke Park. That honour had been claimed by the Railway Cup hurling and football finals six months before when Clonmel's Mick Kennedy, playing for Leinster, had the honour of claiming the first ever score shown on live television. Dublin's Des Foley made his own entry into the annals by winning medals in both codes. Tipperary had seven players on the Munster hurling selection that particular St Patrick's Day. All of them would play again 24 hours later when the county side faced a Rest of Ireland selection in an exhibition in Thurles. Others to double up that same weekend were Christy Ring and Lar Foley. This was an era blessed with players whose talents would transcend time but Moloughney has no doubt that Jimmy Doyle's was the star that shone brightest. And still does.Roughly 500 people had arrived at Shannon Airport from the States and Canada on the morning of the match. A Swissair jet carrying 67 members of Toronto GAA Club was another visitor to Irish shores and these international waves were replicated on the ground. CIE laid on 25 special trains and road works on O'Connell Street made traffic jams inevitable.



| Pos. | Player | Team | Appearances | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GK | Kilkenny | 2 | "For his courageous defiance, his agility and trustworthiness making him the kind of goalkeeper that any player would be happy to have behind him." | |
| RCB | Kilkenny | 1 | "For his dependability in defence, which combines with his natural hurling skill to establish him as one of the great corner backs of today." | |
| FB | Limerick | 3 | "For his undiminished skill and dependability in a very demanding position where quite often brawn is substituted for hurling artistry." | |
| LCB | Limerick | 1 | "For his rare bravery and mobility: for the all-round splender of his contribution to Limerick's much-delayed return to championship honours." | |
| RWB | Wexford | 1 | "For his alertness and sense of judgement, for the crispness of his stroke which played such a sizeable part in regaining the National League title for his county." | |
| CB | Kilkenny | 1 | "For his sheer skill and obstinacy in defence, his tenacious approach and the devotion he continues to give to the game." | |
| LWB | Limerick | 1 | "For the fervour he brings to all facets of hurling, and particularly for his dedicated half-back play which contributed so much to Limerick's 1973 successes." | |
| MD | Kilkenny | 1 | "For his artistic stick-work which he has demonstrated with increasing regularity, and for establishing himself as one of the most elegant and energetic midfielders of recent times." | |
| MD | Limerick | 1 | "For the level-headedness he has so frequently shown in the tightest of situations and for his exceptionally high rate of scoring." | |
| RWF | Tipperary | 3 | "For his incisive intelligent running which so often splits opposing defences: for the remarkable consistency and accuracy of his marksmanship." | |
| CF | Kilkenny | 2 | "For highlighting just how vigorous play can be totally fair, particularly during his famous attacks towards the opposing goal." | |
| LWF | Limerick | 1 | "For his seemingly limitless energy and his desire to work all over the field: qualities which have made him a natural leader and a high scorer." | |
| RCF | Wexford | 1 | "For the wide range of his playing skills, his constancy of purpose and his obvious versatility." | |
| FF | Kilkenny | 1 | "For the out-and-out hard work he puts into the game. For his power of striking and his adaptability in attack." | |
| LCF | Kilkenny | 3 | "For his enormously successful scoring record, his fluency of stroke and his accurate passing which create so many chances for his team mates." |
| Pos. | Player | Team | Appearances |
|---|---|---|---|
| GK | Cork | 1 | |
| RCB | Cork | 1 | |
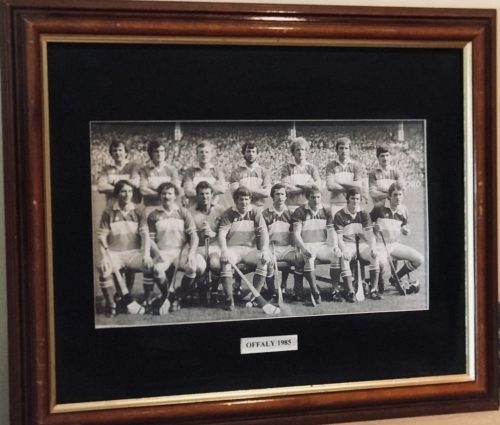
| FB | Offaly | 2 | |
| LCB | Cork | 1 | |
| RWB | Galway | 1 | |
| CB | Galway | 2 | |
| LWB | Cork | 2 | |
| MD | Kerry | 1 | |
| MD | Cork | 1 | |
| RWF | Offaly | 2 | |
| CF | Offaly | 2 | |
| LWF | Galway | 2 | |
| RCF | Cork | 1 | |
| FF | Cork | 2 | |
| LCF | Derry | 1 |


| Limerick | 1-21 – 1-14 | Kilkenny |
|---|---|---|
| R. Bennis (0-10), M. Dowling (1-1), É. Grimes (0-4), F. Nolan (0-2), N. Rea (0-2), B. Hartigan (0-1), J. McKenna (0-1). | C. Dunne (0-7), P. Delaney (1-1), M. Crotty (0-3), L. O'Brien (0-2), M. Brennan(0-1). |


| Clare | 1-17 – 0-11 | Limerick |
|---|---|---|
| J. O'Connor (0-6), P. J. Connell (0-4), D. FitzGerald (1-0), C. Clancy (0-2), S. McMahon (0-1), F. Tuohy (0-1), F. Hegarty (0-1), S. McNamara (0-1), G. O'Loughlin (0-1). | Report | G. Kirby (0-6), M. Galligan (0-3), P. Heffernan (0-1), F. Carroll (0-1). |

 |
|||||||
| Event | 1951 All-Ireland Senior Football Championship | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||
| Date | 23 September 1951 | ||||||
| Venue | Croke Park, Dublin | ||||||
| Attendance | 78,201 | ||||||
| Date | Performer(s) | Opening act(s) | Tour/Event | Attendance | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 29 June 1985 | U2 | In Tua Nua, R.E.M., The Alarm, Squeeze | The Unforgettable Fire Tour | 57,000 | First Irish act to have a headline concert. Part of the concert was filmed for the group's documentary Wide Awake in Dublin. |
| 28 June 1986 | Simple Minds | Once Upon A Time Tour | Guest appearance by Bono | ||
| 27 June 1987 | U2 | Light A Big Fire, The Dubliners, The Pogues, Lou Reed | The Joshua Tree Tour | 114,000 | |
| 28 June 1987 | Christy Moore, The Pretenders, Lou Reed, Hothouse Flowers | ||||
| 28 June 1996 | Tina Turner | Brian Kennedy | Wildest Dreams Tour | 40,000/40,000 | |
| 16 May 1997 | Garth Brooks | World Tour II | |||
| 18 May 1997 | |||||
| 29 May 1998 | Elton John & Billy Joel | Face to Face 1998 | |||
| 30 May 1998 | |||||
| 24 June 2005 | U2 | The Radiators from Space, The Thrills, The Bravery, Snow Patrol, Paddy Casey, Ash | Vertigo Tour | 246,743 | |
| 25 June 2005 | |||||
| 27 June 2005 | |||||
| 20 May 2006 | Bon Jovi | Nickelback | Have a Nice Day Tour | 81,327 | |
| 9 June 2006 | Robbie Williams | Basement Jaxx | Close Encounters Tour | ||
| 6 October 2007 | The Police | Fiction Plane | The Police Reunion Tour | 81,640 | Largest attendance of the tour. |
| 31 May 2008 | Celine Dion | Il Divo | Taking Chances World Tour | 69,725 | Largest attendance for a solo female act |
| 1 June 2008 | Westlife | Shayne Ward | Back Home Tour | 85,000 | Second Irish act to have a headline concert. Largest attendance of the tour. Part of the concert was filmed for the group's documentary and concert DVD 10 Years of Westlife - Live at Croke Park Stadium. |
| 14 June 2008 | Neil Diamond | ||||
| 13 June 2009 | Take That | The Script | Take That Present: The Circus Live | ||
| 24 July 2009 | U2 | Glasvegas, Damien Dempsey | U2 360° Tour | 243,198 | |
| 25 July 2009 | Kaiser Chiefs, Republic of Loose | ||||
| 27 July 2009 | Bell X1, The Script | The performances of "New Year's Day" and "I'll Go Crazy If I Don't Go Crazy Tonight" were recorded for the group's live album U22 and for the band's remix album Artificial Horizon and the live EP Wide Awake in Europe, respectively. | |||
| 5 June 2010 | Westlife | Wonderland, WOW, JLS, Jedward | Where We Are Tour | 86,500 | Largest attendance of the tour. |
| 18 June 2011 | Take That | Pet Shop Boys | Progress Live | 154,828 | |
| 19 June 2011 | |||||
| 22 June 2012 | Westlife | Jedward, The Wanted, Lawson | Greatest Hits Tour | 187,808[24] | The 23 June 2012 date broke the stadium record for selling out its tickets in four minutes. Eleventh largest attendance at an outdoor stadium worldwide. Largest attendance of the tour and the band's music career history. Part of the concert was filmed for the group's documentary and concert DVD The Farewell Tour - Live in Croke Park. |
| 23 June 2012 | |||||
| 26 June 2012 | Red Hot Chili Peppers | Noel Gallagher's High Flying Birds, The Vaccines | I'm with You World Tour | ||
| 23 May 2014 | One Direction | 5 Seconds of Summer | Where We Are Tour | 235,008 | |
| 24 May 2014 | |||||
| 25 May 2014 | |||||
| 20 June 2015 | The Script & Pharrell Williams | No Sound Without Silence Tour | 74,635 | ||
| 24 July 2015 | Ed Sheeran | x Tour | 162,308 | ||
| 25 July 2015 | |||||
| 27 May 2016 | Bruce Springsteen | The River Tour 2016 | 160,188 | ||
| 29 May 2016 | |||||
| 9 July 2016 | Beyoncé | Chloe x Halle, Ingrid Burley | The Formation World Tour | 68,575 | |
| 8 July 2017 | Coldplay | AlunaGeorge, Tove Lo | A Head Full of Dreams Tour[25] | 80,398 | |
| 22 July 2017 | U2 | Noel Gallagher's High Flying Birds | The Joshua Tree Tour 2017 | 80,901 | |
| 17 May 2018 | The Rolling Stones | The Academic | No Filter Tour | 64,823 | |
| 15 June 2018 | Taylor Swift | Camila Cabello, Charli XCX | Taylor Swift's Reputation Stadium Tour | 136.000 | Swift became the first woman headline two concerts in a row there. |
| 16 June 2018 | |||||
| 7 July 2018 | Michael Bublé | Emeli Sandé | |||
| 24 May 2019 | Spice Girls | Jess Glynne | Spice World - 2019 UK Tour | ||
| 5 July 2019 | Westlife | James Arthur Wild Youth | The 20 Touror The Twenty Tour | The 5 July 2019 date sold out its tickets in six minutes. Second date released were also sold out in under forty-eight hours. | |
| 6 July 2019 |





| An Garda Síochána | |
|---|---|

Shield of An Garda Síochána |
|
| Common name | Gardaí |
| Motto | Working with communities to protect and serve (Irish: Ag obair le Pobail chun iad a chosaint agus chun freastal orthu) |
| Agency overview | |
| Formed | 22 February 1922 |
| Preceding agencies | |
| Employees | 17,652 (total as of 2019) 14,250 sworn members 2,944 civilian staff 458 reserves |
| Annual budget | €1.426 billion (2015) |
| Jurisdictional structure | |
| National agency | Republic of Ireland |
| Operations jurisdiction | Republic of Ireland |
 |
|
| An Garda Síochána area of jurisdiction in dark blue | |
| Size | 70,273 km² |
| Population | 4,588,252 (2011) |
| General nature | |
| Headquarters | Garda Headquarters, Phoenix Park, Dublin |
| Officers | 14,708 incl. 458 reserves (2019) |
| Civilians | 2,944 (2019) |
| Elected officer responsible | |
| Agency executive | |
| Regions |
4
|
| Facilities | |
| Stations | 564 |
| Vehicles | 2,815 (2017) |
| Boats | Garda Water Unit |
| Aircraft | 2 helicopters 1 fixed-wing surveillance aircraft |
| Canines | Garda Dog Unit |
| Horses | Garda Mounted Unit |
| Website | |
| www.garda.ie | |
| ^ "Working with Communities to Protect and Serve" is described as mission statement rather than formal motto | |


| Name | From | Until | Reason |
|---|---|---|---|
| Michael Staines | February 1922 | September 1922 | resigned |
| Eoin O'Duffy | September 1922 | February 1933 | dismissed[note 2] |
| Eamon Broy | February 1933 | June 1938 | retired |
| Michael Kinnane | June 1938 | July 1952 | died |
| Daniel Costigan | July 1952 | February 1965 | resigned |
| William P Quinn | February 1965 | March 1967 | retired |
| Patrick Carroll | March 1967 | September 1968 | retired |
| Michael Wymes | September 1968 | January 1973 | retired |
| Patrick Malone | January 1973 | September 1975 | retired |
| Edmund Garvey | September 1975 | January 1978 | replaced[note 3] |
| Patrick McLaughlin | January 1978 | January 1983 | retired[note 4] |
| Lawrence Wren | February 1983 | November 1987 | retired |
| Eamonn Doherty | November 1987 | December 1988 | retired |
| Eugene Crowley | December 1988 | January 1991 | retired |
| Patrick Culligan | January 1991 | July 1996 | retired |
| Patrick Byrne | July 1996 | July 2003 | retired |
| Noel Conroy | July 2003 | November 2007 | retired |
| Fachtna Murphy | November 2007 | December 2010 | retired |
| Martin Callinan | December 2010 | March 2014 | resigned[47][48][note 5] |
| Nóirín O'Sullivan | March 2014(acting) November 2014 (permanent)[49] | September 2017 | retired[50][note 6] |
| Dónall Ó Cualáin | September 2017 (acting) | September 2018 | |
| Drew Harris | September 2018 | - |


"The An Post-GAA Team of the Millennium was unveiled at Croke Park yesterday. The selection which serves as the first 15 inductions into the GAA's new Hall of Fame has also been marked by an issue of 15 commemorative stamps by An Post. The stamps will be available in a variety of combinations from today. Next year, a similar exercise will take place to honour 15 hurlers.
There was some comment on the absence of Dublin's Brian Mullins and Jack O'Shea from Kerry but it seemed generally appreciated that there were only two centrefield slots on the team and someone had to lose out. Tommy Murphy, the Boy Wonder of the 1930s Laois team which won three Leinster titles in a row, who was included ahead of Mullins and O'Shea had the added distinction of being the only player honoured who had not won an All-Ireland medal.
Not surprisingly, Kerry - who top the All-Ireland roll of honour with 31 titles - lead the way on the team with six selections. Despite being clearly second behind Kerry with 22 All-Irelands, Dublin provide only one player, Kevin Heffernan at left corner forward. Galway and Mayo have two players each with one from Cavan, Down, Meath and Laois making up the balance.
Joe McDonagh, President of the GAA, described the project as a reflection "on the history and evolution of our association, its games and its central characters, the players who have left such giant footprints in the sands that is the chronicle of the GAA".
The Hall of Fame which is inaugurated by this team will be represented all through Croke Park, according the GAA director general Liam Mulvihill. He said that the Hall will be added to with a small number of inductions on an annual basis.
"We decided that this team would be the initial members of the Hall of Fame and we were planning to honour those selected around the main areas of the concourse of the re-developed stadium, in the bottom tier and the upper tier. We wanted those ordinary tiers where ordinary supporters gather as the most appropriate place to honour those players.
"The inductions will be in very small numbers, we're probably talking about two a year. Two footballers, two hurlers or one footballer and one hurler. It has to be made very, very special."
Paddy Downey, formerly GAA correspondent of The Irish Times, was one of the adjudicators and confirmed the widespread feeling that the task of selecting such a team wasn't an enviable one.
"It's nearly impossible because there's so many players, particularly in what you might call the big, central positions: midfield, centre-back, full back. Already people are saying to me: `why isn't Brian Mullins on, why isn't Paddy Kennedy of Kerry, Jack O'Shea - above all at the present time' and so on.
"We also had the problem of not picking a half-century team of people we had seen ourselves. You could also argue how could we pick someone we hadn't seen - Dick Fitzgerald, apparently one of the greatest players of all time, Paul Russell of Kerry, Jack Higgins of Kildare, from the earlier part of the century.
"I was conscious that we could have gone further back and taken the word of our predecessors in journalism who had praised these players and done so in print. Inevitably it came to be more a team of the second half of the century than the early years."
Martin O'Connell of Meath was the only player of what might roughly be called contemporary times - one whose career was largely after the selection of the 1984 Centenary Team - to earn a place.
"I was surprised," he said. "I didn't even know until I came up here. I arrived a bit late and Micheal O Muircheartaigh was just reading out the names. I was absolutely delighted."





Unfortunately for H.P. Bulmer, it wasn’t long before the company again changed hands. Coming out on the losing end of a legal dispute with the creators of Babycham sparkling perry over a competing product, they were forced to sell Bulmers Clonmel during the 1960s. Having become part of the C&C Group – a soft drinks and cider company then jointly owned by Guinness and Allied Breweries – production of Irish Bulmers was moved five years later to a modern complex at Annerville, outside Clonmel.

With the Tipperary cider greatly exceeding sales expectations in Ireland, the C&C Group sought during the late 1990s to sell it outside of its home country, particularly in the burgeoning international Irish bar market. But as H.P. Bulmer still owned the rights to that name everywhere other than Ireland, they decided to call the brand after its original owner when exporting it – bringing Magners Irish cider first to Spain, then to Germanyand the UK. In spite of the the differing name, the two products are identical.
Still produced at Annerville, today Irish Bulmers and Magners are made from 17 different kinds of apples, left to ferment and mature for up to two years. Continuing to grow in popularity, the cider can now be found in bars throughout Europe, Asia, North America, Australia and New Zealand.






 |
|
 |
|
| Introduced | 1879, renamed as Paddy in 1912 |
|---|---|



| Desert Orchid | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Sire | Grey Mirage |
| Grandsire | Double-U-Jay |
| Dam | Flower Child |
| Damsire | Brother |
| Sex | Gelding |
| Foaled | 11 April 1979 in Goadby, Leicestershire, England. |
| Country | Great Britain |
| Colour | Grey |
| Breeder | James Burridge |
| Owner | James Burridge, Midge Burridge, Richard Burridge, Simon Bullimore |
| Trainer | David Elsworth at Whitsbury Manor Racing Stables, Fordingbridge, Wiltshire |
| Record | 70: 34-11-8 |
| Earnings | £654,066 |
| Major wins | |
| Tolworth Hurdle (1984) Kingwell Hurdle (1984) Hurst Park Novices' Chase (1985) King George VI Chase (1986, 1988, 1989, 1990) Gainsborough Chase (1987, 1989, 1991) Martell Cup (1988) Whitbread Gold Cup (1988) Tingle Creek Chase (1988) Victor Chandler Chase (1989) Cheltenham Gold Cup (1989) Racing Post Chase (1990) Irish Grand National (1990) | |
| Awards | |
| Timeform rating: 187 | |
| Honours | |
| The Desert Orchid Chase at Wincanton Desert Orchid Chase at Kempton Park Racecourse Statue, ashes, headstone - Kempton Park Racecourse | |







"The An Post-GAA Team of the Millennium was unveiled at Croke Park yesterday. The selection which serves as the first 15 inductions into the GAA's new Hall of Fame has also been marked by an issue of 15 commemorative stamps by An Post. The stamps will be available in a variety of combinations from today. Next year, a similar exercise will take place to honour 15 hurlers.
There was some comment on the absence of Dublin's Brian Mullins and Jack O'Shea from Kerry but it seemed generally appreciated that there were only two centrefield slots on the team and someone had to lose out. Tommy Murphy, the Boy Wonder of the 1930s Laois team which won three Leinster titles in a row, who was included ahead of Mullins and O'Shea had the added distinction of being the only player honoured who had not won an All-Ireland medal.
Not surprisingly, Kerry - who top the All-Ireland roll of honour with 31 titles - lead the way on the team with six selections. Despite being clearly second behind Kerry with 22 All-Irelands, Dublin provide only one player, Kevin Heffernan at left corner forward. Galway and Mayo have two players each with one from Cavan, Down, Meath and Laois making up the balance.
Joe McDonagh, President of the GAA, described the project as a reflection "on the history and evolution of our association, its games and its central characters, the players who have left such giant footprints in the sands that is the chronicle of the GAA".
The Hall of Fame which is inaugurated by this team will be represented all through Croke Park, according the GAA director general Liam Mulvihill. He said that the Hall will be added to with a small number of inductions on an annual basis.
"We decided that this team would be the initial members of the Hall of Fame and we were planning to honour those selected around the main areas of the concourse of the re-developed stadium, in the bottom tier and the upper tier. We wanted those ordinary tiers where ordinary supporters gather as the most appropriate place to honour those players.
"The inductions will be in very small numbers, we're probably talking about two a year. Two footballers, two hurlers or one footballer and one hurler. It has to be made very, very special."
Paddy Downey, formerly GAA correspondent of The Irish Times, was one of the adjudicators and confirmed the widespread feeling that the task of selecting such a team wasn't an enviable one.
"It's nearly impossible because there's so many players, particularly in what you might call the big, central positions: midfield, centre-back, full back. Already people are saying to me: `why isn't Brian Mullins on, why isn't Paddy Kennedy of Kerry, Jack O'Shea - above all at the present time' and so on.
"We also had the problem of not picking a half-century team of people we had seen ourselves. You could also argue how could we pick someone we hadn't seen - Dick Fitzgerald, apparently one of the greatest players of all time, Paul Russell of Kerry, Jack Higgins of Kildare, from the earlier part of the century.
"I was conscious that we could have gone further back and taken the word of our predecessors in journalism who had praised these players and done so in print. Inevitably it came to be more a team of the second half of the century than the early years."
Martin O'Connell of Meath was the only player of what might roughly be called contemporary times - one whose career was largely after the selection of the 1984 Centenary Team - to earn a place.
"I was surprised," he said. "I didn't even know until I came up here. I arrived a bit late and Micheal O Muircheartaigh was just reading out the names. I was absolutely delighted."


“I'm a quarter Irish or half Irish or something, and long, long before the trouble started, I told Yoko that's where we're going to retire, and I took her to Ireland. We went around Ireland a bit and we stayed in Ireland and we had a sort of second honeymoon there. So, I was completely involved in Ireland” – John Lennon, 1971.James Paul McCartney was born on June 18, 1942 in Liverpool to Jim and Mary Patricia (Mahon) McCartney, and like many other Liverpool families descended from Irish immigrants. His mother’s father was born in Ireland, and was Roman Catholic, while his great-grandfather was an Irish native, and Protestant.


