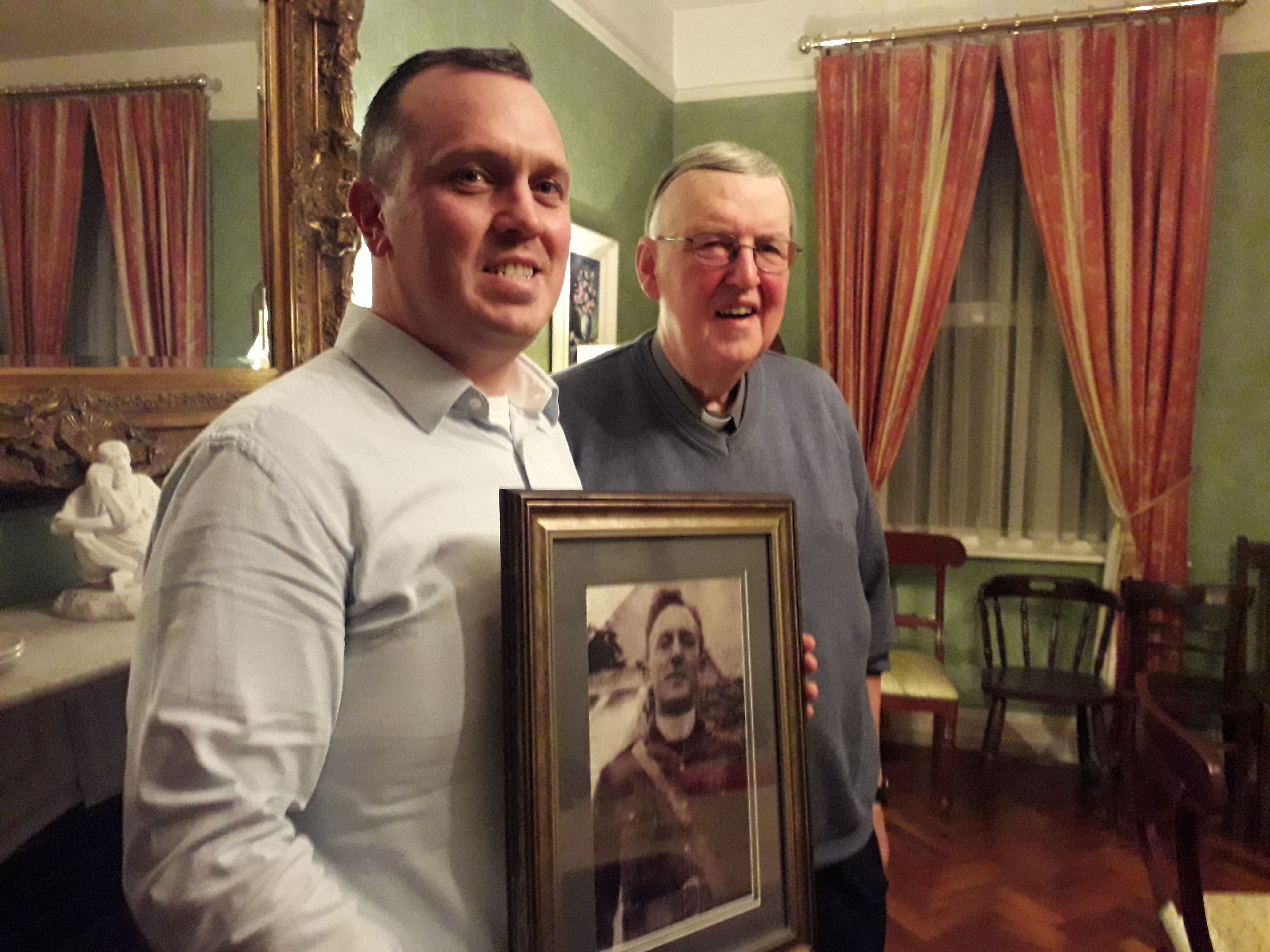
John Connolly and Fr Martin Downey, with a photo of Fr Griffin, courtesy of Ciaran Tierney Digital Storyteller.
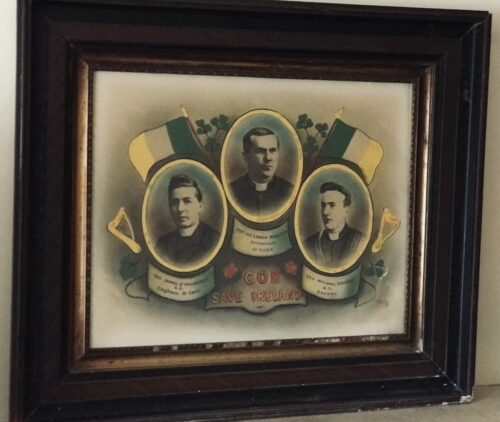



John Connolly and Fr Martin Downey, with a photo of Fr Griffin, courtesy of Ciaran Tierney Digital Storyteller.




















|




my purpose...is to shew the situation of every Citie and Shire-town only [within Great Britain]...I have separated...[with] help of the tables...any Citie, Towne, Borough, Hamlet, or Place of Note...[it] may be affirmed, that there is not any one Kingdome in the world so exactly described...as is...Great Britaine...In shewing these things, I have chiefly sought to give satisfaction to all.With maps as "proof impressions" and printed from copper plates, detail was engraved in reverse with writing having to be put on the map the correct way, while speed "copied, adapted and compiled the work of others", not doing much of the survey work on his own, which he acknowledged.The atlas was not above projections of his political opinions" Speed represented King James I as one who unified the "Kingdoms of the British isles". In 2016, the British Library published a book, introduced by former MP Nigel Nicolson and accompanied by commentaries by late medieval and early modern historian Alasdair Hawkyard, which reprinted this collection of maps on the British Isles, showing that Speed had drawn maps of areas ranging from Bedfordshire to Norfolk and Wales. Most, but not all, of the county maps have town plans on them; those showing a Scale of Passes being the places he had mapped himself. In 1627, two years before his death, Speed published Prospect of the Most Famous Parts of the World which was the first world atlas produced by an Englishman, costing 40 shillings, meaning that its circulation was limited to "richer customers and libraries", where many survive to this day. There is a fascinating text describing the areas shown on the back of the maps in English, although a rare edition of 1616 of the British maps has a Latin text – this is believed to have been produced for the Continental market. Much of the engraving was done in Amsterdam at the workshop of a Flemish man named Jodocus Hondius, with whom he collaborated with from 1598 until 1612, with Hondius's sudden death, a time period of 14 years.His maps of English and Welsh counties, often bordered with costumed figures ranging from nobility to country folk, are often found framed in homes throughout the United Kingdom. In 1611, he also published The genealogies recorded in the Sacred Scriptures according to euery family and tribe with the line of Our Sauior Jesus Christ obserued from Adam to the Blessed Virgin Mary, a biblical genealogy, reprinted several times during the 17th century. He also drew maps of the Channel Islands, Poland, and the Americas, the latter published only a few years before his death. On the year of his death, yet another collection of maps of Great Britain he had drawn the year before were published. Described as a "Protestant historian", "Puritan historian" or "Protestant propagandist" by some, Speed wrote about William Shakespeare, whom he called a "Superlative Monster" because of certain plays, Roman conquest, history of Chester, and explored "early modern concepts of national identity". As these writings indicate, he possibly saw Wales as English and not an independent entity. More concretely, there is evidence that Speed, in his chronicling of history, uses "theatrical metaphors" and his developed "historiographic skill" to work while he repeats myths from medieval times as part of his story.






“I'm a quarter Irish or half Irish or something, and long, long before the trouble started, I told Yoko that's where we're going to retire, and I took her to Ireland. We went around Ireland a bit and we stayed in Ireland and we had a sort of second honeymoon there. So, I was completely involved in Ireland” – John Lennon, 1971.James Paul McCartney was born on June 18, 1942 in Liverpool to Jim and Mary Patricia (Mahon) McCartney, and like many other Liverpool families descended from Irish immigrants. His mother’s father was born in Ireland, and was Roman Catholic, while his great-grandfather was an Irish native, and Protestant.













for the next seven years, within the countie of Colrane, otherwise called O Cahanes countrey, or within the territorie called Rowte, in Co. Antrim, by himselfe or his servauntes, to make, drawe, and distil such and soe great quantities of aquavite, usquabagh and aqua composita, as he or his assignes shall thinke fitt; and the same to sell, vent, and dispose of to any persons, yeeldinge yerelie the somme 13s 4d ...The Bushmills Old Distillery Company itself was not established until 1784 by Hugh Anderson.Bushmills suffered many lean years with numerous periods of closure with no record of the distillery being in operation in the official records both in 1802 and in 1822. In 1860 a Belfast spirit merchant named Jame McColgan and Patrick Corrigan bought the distillery; in 1880 they formed a limited company. In 1885, the original Bushmills buildings were destroyed by fire but the distillery was swiftly rebuilt. In 1890, a steamship owned and operated by the distillery, SS Bushmills, made its maiden voyage across the Atlantic to deliver Bushmills whiskey to America. It called at Philadelphia and New York City before heading on to Singapore, Hong Kong, Shanghai and Yokohama. In the early 20th century, the U.S. was a very important market for Bushmills (and other Irish Whiskey producers). American Prohibition in 1920 came as a large blow to the Irish Whiskey industry, but Bushmills managed to survive. Wilson Boyd, Bushmills' director at the time, predicted the end of prohibition and had large stores of whiskey ready to export. After the Second World War, the distillery was bought by Isaac Wolfson, and, in 1972, it was taken over by Irish Distillers, meaning that Irish Distillers controlled the production of all Irish whiskey at the time. In June 1988, Irish Distillers was bought by French liquor group Pernod Ricard. In June 2005, the distillery was bought by Diageo for £200 million. Diageo have also announced a large advertising campaign in order to regain a market share for Bushmills. In May 2008, the Bank of Ireland issued a new series of sterling banknotes in Northern Ireland which all feature an illustration of the Old Bushmills Distillery on the obverse side, replacing the previous notes series which depicted Queen's University of Belfast. In November 2014 it was announced that Diageo had traded the Bushmills brand with Jose Cuervo in exchange for the 50% of the Don Julio brand of tequila that Diageo did not already own.


The ballad is named after a crossroads between Ennis and Tulla in east Clare, the site of a centuries-old horse fair held every June. In 1870 a young man from the locality, Michael Considine, bade farewell to his sweetheart Mary McNamara and left for the US. He hoped to earn sufficient money to enable her to join him.
However, he died in California in 1873. Before his death he wrote a poem dedicated to Mary which he posted to his six-year-old nephew, John, back home.
Seventy years later McMahon was given the words at a house party. His singing of the ballad was warmly received by those in attendance, who included the author’s nephew, then an elderly man.
Many singers have recorded the ballad, but McMahon insisted his was the authentic version. He told The Irish Times in 2006: “Nowadays the song is not sung correctly. Many singers put words that are not in it [at] all, singing stuff like ‘Johnny, I love you still’. There’s no ‘Johnny’ in that song.” The late writer Bryan MacMahon was an early admirer of his namesake’s talent and had high praise for his ability as a performer and entertainer.
Singer Maura O’Connell warmed to Robbie McMahon’s “great big personality”, and said that he made Spancil Hill his own.
Born in 1926, he was the third youngest of 11 children, one of whom died in childhood, and grew up on his father’s farm in Clooney, near Ennis. There was music in the family, and all the children sang. Young Robbie was something of a mischief-maker, hence the title of an album he recorded later in life – The Black Sheep.
He began singing in public at the age of 18, and went on to win 16 all-Ireland titles at fleadhanna around the country. In the 1950s, 1960s and 1970s he toured Britain and the US with a troupe of traditional musicians under the auspices of Comhaltas Ceoltóirí Éireann.
As a songwriter, he is best known for the Fleadh Down in Ennis, which celebrates the 1956 all-Ireland fleadh cheoil. Other compositions include Come on the Banner, the Red Cross Social and the Feakle Hurlers, in honour of the 1988 Clare county champions.
A lilter, he was renowned for his performance of the Mason’s Apron, in which he simulated the sound of both the fiddle and accompanying banjo.
Possessed of a store of jokes, ranging from the hilarious to the unprintable, he was as much a character as a singer and was more comfortable with the craic and banter of casual sessions than with formal concerts.
He was the subject of a film documentary Last Night As I Lay Dreaming. Clare County Council hosted a civic reception in his honour in 2010, and he was the recipient of the Fleadh Nua Gradam Ceoil in 2011.
He is survived by his wife Maura, daughters Fiona, Noleen and Dympna and son Donal.
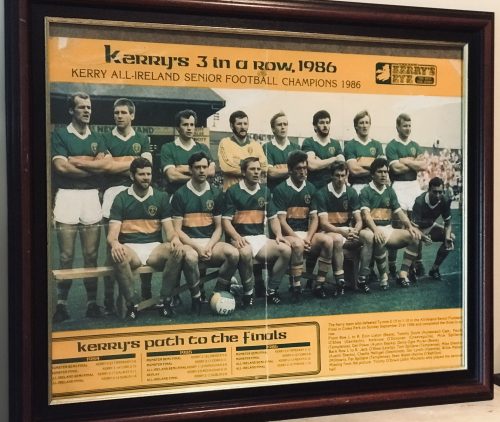









The 80s was a time when Ulster football was considered a distant cousin to the majesty of Kerry, even when the Kingdom's golden age was ending.
But such was Tyrone's initial dominance of the 1986 All-Ireland final against Kerry by half-time their fans began to panic about not having accommodation in Dublin that night. They needn't have worried as a seven-point lead turned into an eight-point pounding in the final 20 minutes.
The crucial moment was a Tyrone penalty, which was sent over the bar by Kevin McCabe. From the kick-out, Kerry whizzed downfield and Pat Spillane finished the move with a goal that reduced the arrears to four points. A Mikey Sheehy goal completed a nightmarish capitulation.
It was the last hurrah from a great Kerry team who had taken Sam Maguire home eight times in 12 years. An 11-year drought followed.
Moy's Plunkett Donaghy was Tyrone's class act back then but the loss of Eugene McKenna and John Lynch through injury coincided with the late collapse.
Moy send another marauding midfielder out against Kerry on Sunday in Seán Cavanagh along with clubmates Philip Jordan and Ryan Mellon.
KERRY: C Nelligan; P Ó Sé, S Walsh, M Spillane; T Doyle (captain), T Spillane, G Lynch; J O'Shea, A O'Donovan; W Maher, D Moran (0-2), P Spillane (1-4); M Sheehy (1-4, three points from frees), E Liston (0-2), G Power (0-1). Sub: T O'Dowd (0-2) for O'Donovan.
TYRONE: A Skelton; J Mallon, K McGarvey, J Lynch; K McCabe (0-1, from a penalty), N McGinn, P Ball; P Donaghy, H McClure; M McClure (0-1), E McKenna, S McNally (0-2); M Mallon (0-4, three frees), D O'Hagan (0-1), P Quinn (1-1). Subs: S Conway for Lynch, S Rice for McKenna, A O'Hagan for M Mallon.

 Source: Billy Stickland/INPHO
2. Sylvie Linnane (Gort)
Linnane was a teak tough corner back who took no prisoners.
A farmer who also hires out machinery, Linnane has dabbled in coaching and retains very strong links with his home club, Gort.
Sylvie’s three sons, Sylvie Óg, Tadhg and Darragh, won Galway senior club hurling medals with Gort last year.
Source: Billy Stickland/INPHO
2. Sylvie Linnane (Gort)
Linnane was a teak tough corner back who took no prisoners.
A farmer who also hires out machinery, Linnane has dabbled in coaching and retains very strong links with his home club, Gort.
Sylvie’s three sons, Sylvie Óg, Tadhg and Darragh, won Galway senior club hurling medals with Gort last year.
 Source: James Crombie/INPHO
3. Conor Hayes (Kiltormer)
Hayes is the last Galway man to lift the Liam MacCarthy Cup on Galway’s behalf.
The Kiltmorer man was skipper of the 1987 and 1988 All-Ireland winning teams and was manager in 2005 when Galway lost the final to Cork.
He strongly believes that the Tribesmen can end a 27-year famine and shared his views with The42 in this piece.
Source: James Crombie/INPHO
3. Conor Hayes (Kiltormer)
Hayes is the last Galway man to lift the Liam MacCarthy Cup on Galway’s behalf.
The Kiltmorer man was skipper of the 1987 and 1988 All-Ireland winning teams and was manager in 2005 when Galway lost the final to Cork.
He strongly believes that the Tribesmen can end a 27-year famine and shared his views with The42 in this piece.
 Source: James Crombie/INPHO
4. Ollie Kilkenny (Kiltormer)
Kilkenny was a key member of the successful Kiltormer teams of the 1980s and 1990s, and won two All-Ireland senior medals with Galway in 1987 and 1988.
A psychiatric nurse by profession, Kilkenny formed one-third of a revered full-back line alongside clubmate Conor Hayes and Sylvie Linnane.
Ollie’s sons Jason and Keith won Nicky Rackard Cup medals with Roscommon this year.
Source: James Crombie/INPHO
4. Ollie Kilkenny (Kiltormer)
Kilkenny was a key member of the successful Kiltormer teams of the 1980s and 1990s, and won two All-Ireland senior medals with Galway in 1987 and 1988.
A psychiatric nurse by profession, Kilkenny formed one-third of a revered full-back line alongside clubmate Conor Hayes and Sylvie Linnane.
Ollie’s sons Jason and Keith won Nicky Rackard Cup medals with Roscommon this year.
 Source: James Crombie/INPHO
5. Peter Finnerty (Mullagh)
Part of one of the most revered half-back lines of all time, Finnerty went on to become a hurling analyst with RTÉ on The Sunday Game.
Involved in the Supermac’s franchise in Tuam, Finnerty was coach of the Mayo hurlers from 2007-2010.
On the eve of Sunday’s final, Finnerty will host a Bord Gáis Energy Legends Tour at Croke Park.
Source: James Crombie/INPHO
5. Peter Finnerty (Mullagh)
Part of one of the most revered half-back lines of all time, Finnerty went on to become a hurling analyst with RTÉ on The Sunday Game.
Involved in the Supermac’s franchise in Tuam, Finnerty was coach of the Mayo hurlers from 2007-2010.
On the eve of Sunday’s final, Finnerty will host a Bord Gáis Energy Legends Tour at Croke Park.
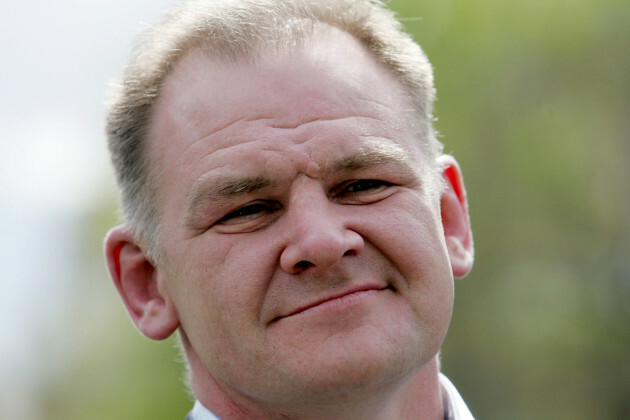 Source: James Crombie/INPHO
6. Tony Keady (Killimordaly)
Keady was a member of the Galway U21 backroom team this year, working alongside boss Johnny Kelly.
Currently caretaker at Calasanctius College in Oranmore, Keady coached the school to a first ever senior B title this year.
In 1989, the build-up to the All-Ireland semi-final against Tipperary was overshadowed by the ‘Tony Keady affair’, when the majestic centre back was suspended.
Source: James Crombie/INPHO
6. Tony Keady (Killimordaly)
Keady was a member of the Galway U21 backroom team this year, working alongside boss Johnny Kelly.
Currently caretaker at Calasanctius College in Oranmore, Keady coached the school to a first ever senior B title this year.
In 1989, the build-up to the All-Ireland semi-final against Tipperary was overshadowed by the ‘Tony Keady affair’, when the majestic centre back was suspended.
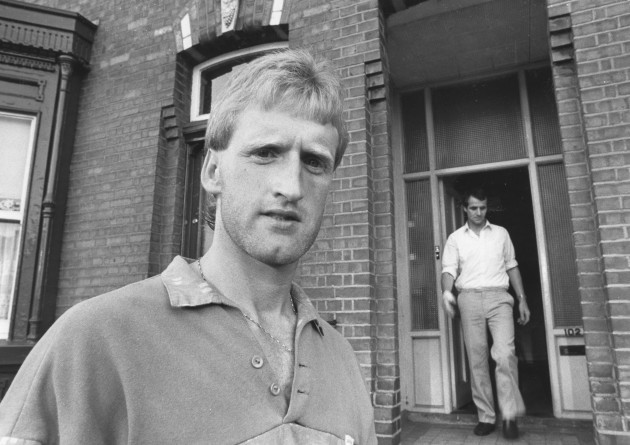 Source: Billy Stickland/INPHO
7. Gerry McInerney (Kinvara)
The man with the famous white boots now runs a sports shop in Oranmore.
McInerney is still involved in farming and his son, Gearóid, is a member of the Galway senior panel preparing for Sunday’s final.
Gearóid made his first championship start against Dublin in the drawn Leinster championship match at Croke Park this year.
Gerry played in a Galway senior hurling final for Kinvara as recently as 2007, when he was 42 years of age.
Source: Billy Stickland/INPHO
7. Gerry McInerney (Kinvara)
The man with the famous white boots now runs a sports shop in Oranmore.
McInerney is still involved in farming and his son, Gearóid, is a member of the Galway senior panel preparing for Sunday’s final.
Gearóid made his first championship start against Dublin in the drawn Leinster championship match at Croke Park this year.
Gerry played in a Galway senior hurling final for Kinvara as recently as 2007, when he was 42 years of age.
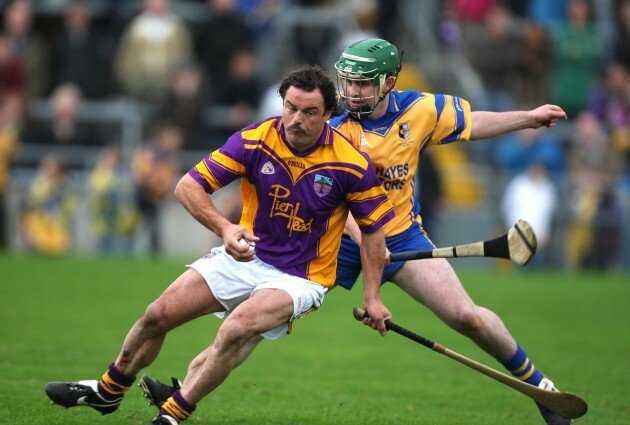 Source: Morgan Treacy/INPHO
8. Michael Coleman (Abbeyknockmoy)
Midfielder Coleman was involved in finance and qualified as a teacher.
Heavily involved in the juvenile ranks at Abbeyknockmoy, Coleman was the club’s hurling board delegate and manager of the U15 and U16 teams this year.
Michael was also the coach to the Leitrim senior hurlers in 2015 and his son, Dara, has been earmarked as one to watch in future years.
Source: Morgan Treacy/INPHO
8. Michael Coleman (Abbeyknockmoy)
Midfielder Coleman was involved in finance and qualified as a teacher.
Heavily involved in the juvenile ranks at Abbeyknockmoy, Coleman was the club’s hurling board delegate and manager of the U15 and U16 teams this year.
Michael was also the coach to the Leitrim senior hurlers in 2015 and his son, Dara, has been earmarked as one to watch in future years.
 Source: James Crombie/INPHO
9. Pat Malone (Oranmore-Maree)
Malone won All-Ireland medals in 1987 and 1988 and went on to become an Allstar in 1993.
A key member of Anthony Cunningham’s Galway senior backroom team, Malone is also involved with his home club Oranmore-Maree.
Coleman’s son, Ross, is a member of the Galway minor hurling panel.
Source: James Crombie/INPHO
9. Pat Malone (Oranmore-Maree)
Malone won All-Ireland medals in 1987 and 1988 and went on to become an Allstar in 1993.
A key member of Anthony Cunningham’s Galway senior backroom team, Malone is also involved with his home club Oranmore-Maree.
Coleman’s son, Ross, is a member of the Galway minor hurling panel.
 Source: Alan Betson/INPHO
10. Anthony Cunningham (St Thomas’)
Galway’s current senior hurling boss has made quite a name for himself in coaching since his playing days.
He enjoyed huge football success with Roscommon club side St Brigid’s and Garrycastle in Westmeath before guiding Galway’s U21 hurlers to All-Ireland glory in 2011.
He’s in his fourth season as the county’s senior hurling boss and hoping to mastermind a first Liam MacCarthy Cup success since 1988 on Sunday.
Source: Alan Betson/INPHO
10. Anthony Cunningham (St Thomas’)
Galway’s current senior hurling boss has made quite a name for himself in coaching since his playing days.
He enjoyed huge football success with Roscommon club side St Brigid’s and Garrycastle in Westmeath before guiding Galway’s U21 hurlers to All-Ireland glory in 2011.
He’s in his fourth season as the county’s senior hurling boss and hoping to mastermind a first Liam MacCarthy Cup success since 1988 on Sunday.
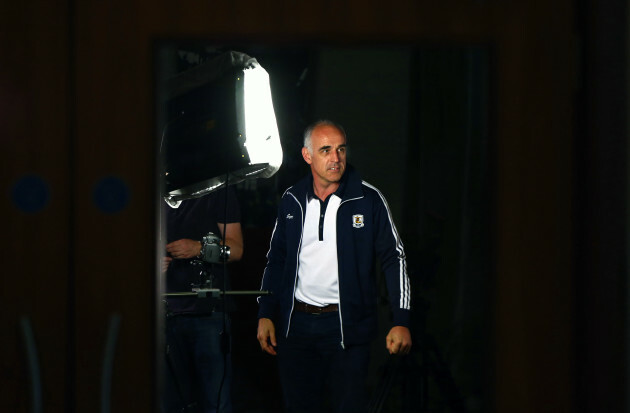 Source: Cathal Noonan/INPHO
11. Brendan Lynskey (Meelick-Eyrecourt)
Now running a restaurant in Athlone, Lynskey was a teak-tough centre forward who gave as good as he got.
Renowned as a shrewd business man with a penchant for succeeding in whatever he turns his hand to, Lynskey challenged Anthony Cunningham for the Galway senior hurling post last year.
Former Galway U21 boss Lynskey has developed a significant property portfolio in recent years, as a key leader with the Roebuck International group.
Source: Cathal Noonan/INPHO
11. Brendan Lynskey (Meelick-Eyrecourt)
Now running a restaurant in Athlone, Lynskey was a teak-tough centre forward who gave as good as he got.
Renowned as a shrewd business man with a penchant for succeeding in whatever he turns his hand to, Lynskey challenged Anthony Cunningham for the Galway senior hurling post last year.
Former Galway U21 boss Lynskey has developed a significant property portfolio in recent years, as a key leader with the Roebuck International group.
 Source: James Crombie/INPHO
12. Martin Naughton (Turloughmore)
Naughton is now self-employed with his own oil business in Claregalway.
Former manager of the Turloughmore senior club, Naughton is also a keen golfer and has played in the prestigious Pierce Purcell shield.
Naughton retired from intercounty hurling in 1992 after suffering cruciate knee ligament damage.
Source: James Crombie/INPHO
12. Martin Naughton (Turloughmore)
Naughton is now self-employed with his own oil business in Claregalway.
Former manager of the Turloughmore senior club, Naughton is also a keen golfer and has played in the prestigious Pierce Purcell shield.
Naughton retired from intercounty hurling in 1992 after suffering cruciate knee ligament damage.
 Source: Billy Stickland/INPHO
13. Michael McGrath (Sarsfields)
The man known as ‘Hopper’ scored two points against Tipperary in the 1988 decider.
Currently manager of the Sarsfields senior camogie team, he has three daughters involved in the county set-up – Niamh, Clodagh and Orlaith.
Michael’s wife Geraldine is a former Ireland hockey international and chair of the Galway camogie board.
Source: Billy Stickland/INPHO
13. Michael McGrath (Sarsfields)
The man known as ‘Hopper’ scored two points against Tipperary in the 1988 decider.
Currently manager of the Sarsfields senior camogie team, he has three daughters involved in the county set-up – Niamh, Clodagh and Orlaith.
Michael’s wife Geraldine is a former Ireland hockey international and chair of the Galway camogie board.
 Source: James Crombie/INPHO
14. Joe Cooney (Sarsfields)
Cooney is renowned as one of Galway’s all-time greats and he established the ‘Joe Cooney school of hurling’ in later years.
Now helping to maintain a school in Loughrea, Cooney has also enjoyed stints as coach of his local club Sarsfields.
Cooney, also a farmer, has a huge interest in Sunday’s All-Ireland finals, as two sons are involved.
Kevin is a sub on the Galway minor hurling panel and Joseph likewise for the seniors.
Joe’s daughter, Maria, is a key member of the county’s senior camogie team.
Source: James Crombie/INPHO
14. Joe Cooney (Sarsfields)
Cooney is renowned as one of Galway’s all-time greats and he established the ‘Joe Cooney school of hurling’ in later years.
Now helping to maintain a school in Loughrea, Cooney has also enjoyed stints as coach of his local club Sarsfields.
Cooney, also a farmer, has a huge interest in Sunday’s All-Ireland finals, as two sons are involved.
Kevin is a sub on the Galway minor hurling panel and Joseph likewise for the seniors.
Joe’s daughter, Maria, is a key member of the county’s senior camogie team.
 Source: Billy Stickland/INPHO
15. Éanna Ryan (Killimordaly)
Ryan was told that he might never play hurling again after suffering a serious head injury in a club game against Turloughmore in 1990.
But eight years later, he was back as a late sub for Killimordaly against Kinvara.
Ryan’s plight shocked the hurling world at the time but he’s made a good recovery and is currently working as a rep for a drinks company.
He’s also involved in underage coaching with Clarinbridge.
Source: Billy Stickland/INPHO
15. Éanna Ryan (Killimordaly)
Ryan was told that he might never play hurling again after suffering a serious head injury in a club game against Turloughmore in 1990.
But eight years later, he was back as a late sub for Killimordaly against Kinvara.
Ryan’s plight shocked the hurling world at the time but he’s made a good recovery and is currently working as a rep for a drinks company.
He’s also involved in underage coaching with Clarinbridge.
 Source: James Crombie/INPHO
Source: James Crombie/INPHO
 Source: Alan Betson/INPHO
Tony Kilkenny (Kiltormer)
Brother of corner back Ollie, Tony came on as a sub for Naughton with 13 minutes left.
A retired male nurse, Tony is now running a successful bus hire company.
Source: Alan Betson/INPHO
Tony Kilkenny (Kiltormer)
Brother of corner back Ollie, Tony came on as a sub for Naughton with 13 minutes left.
A retired male nurse, Tony is now running a successful bus hire company.
 Source: James Crombie/INPHO
Gerry Burke (Turloughmore)
In 1986, Burke scored all of Turloughmore’s nine points in the All-Ireland club semi-final defeat to eventual winners Kilruane MacDonagh’s of Tipperary.
He has been involved in coaching at club level with Turloughmore in more recent times.
Source: James Crombie/INPHO
Gerry Burke (Turloughmore)
In 1986, Burke scored all of Turloughmore’s nine points in the All-Ireland club semi-final defeat to eventual winners Kilruane MacDonagh’s of Tipperary.
He has been involved in coaching at club level with Turloughmore in more recent times.
 Source: James Crombie/INPHO
Phelim Murphy
Known as ‘the Godfather of Galway hurling’, Murphy was mastermind of the Turloughmore teams that dominated the county senior hurling championship in the 1960s.
He was club chairman and manager simultaneously when Turloughmore won six-in-a-row from 1961-66.
Murphy was selector in 1972 when Galway won the All-Ireland U21 hurling title and he went on to link up with Farrell from 1981 on.
Murphy served as secretary of the Galway hurling board from 1982-2004, and he was also Connacht chairman and vice-chairman during a lengthy administrative career.
Source: James Crombie/INPHO
Phelim Murphy
Known as ‘the Godfather of Galway hurling’, Murphy was mastermind of the Turloughmore teams that dominated the county senior hurling championship in the 1960s.
He was club chairman and manager simultaneously when Turloughmore won six-in-a-row from 1961-66.
Murphy was selector in 1972 when Galway won the All-Ireland U21 hurling title and he went on to link up with Farrell from 1981 on.
Murphy served as secretary of the Galway hurling board from 1982-2004, and he was also Connacht chairman and vice-chairman during a lengthy administrative career.
 Source: © Billy Stickland/INPHO
Bernie O’Connor
Another former Galway boss, O’Connor went on to become a successful administrator at board level.
O’Connor also hurled for Galway and he retains a keen interest in his local club Oranmore
Source: © Billy Stickland/INPHO
Bernie O’Connor
Another former Galway boss, O’Connor went on to become a successful administrator at board level.
O’Connor also hurled for Galway and he retains a keen interest in his local club Oranmore


 Origins:Kilmaley Co Clare Dimensions : Glazed
Origins:Kilmaley Co Clare Dimensions : Glazed 

Worldwide Duty Free selling is a $70 billion business, but it has its origins in the mind of one Clare man. And like many innovations, the concept of duty free, which first came to Shannon Airport in 1952, was born of necessity.Today the global travel retail business is a firm fixture at airports across the world, and the concept has made a lot of money for a lot of people.But not for Brendan O’Regan, the man with the idea.
He was born into “the first generation of free Irish men” in relatively well-off surroundings in Sixmilebridge, Co Clare in 1917. His father, James, was chairman of Clare County Council and a successful businessman. The family was in the hotel business, and for a time leased the renowned Falls Hotel in Ennistymon and the Old Ground in Ennis. Sent as a boarder to Blackrock College in Dublin in 1931, O’Regan enjoyed early renown when he requested that the college, which by then had given up on the camán, field a hurling team in the Leinster Colleges cup.
His next step after school was training in hotel management, an interest that brought him to Germany, France and the UK, before coming home to run The Falls. He then moved to the ailing St Stephen’s Green club in Dublin, before being appointed catering comptroller at Foynes flying boat base in Co Limerick, then a refuelling point for transatlantic seaplanes.
It was here his passion for travel took off, but it was his next move that sealed his legacy.
Rineanna on the Shannon estuary in Co Clare, chosen by then taoiseach Seán Lemass as the site for a new airport for both sea and land planes, opened in October 1945, when the first transatlantic commercial air service from Boston landed there. It soon became Europe’s most important transatlantic airport, handling more than 100,000 passengers in 1946, its first full year of operation.
When O’Regan joined the nascent airport, its future was by no means secure. The imminent arrival of jet planes, which meant US planes would no longer have to stop in Shannon to refuel, was of concern, while the political apparatus of the day favoured focusing efforts on one airport in Dublin.
Fearing “economic annihilation” for the new airport, O’Regan sought a new venture that would help secure its future. Inspiration struck when he was returning home by sea from a visit to the United States, arranged under the Marshall Plan to allow the Irish government to study US tourism.
As told in the recently published book Brendan O’Regan: Irish Innovator, Visionary and Peacemaker by Brian O’Connell and Cian O’Carroll, O’Regan had a “eureka” moment on board.
“I saw the shop that was selling duty-free goods and my brain said to me: “If they can do it when you are crossing the sea in a boat, you can surely be able to do [it] when you land for the first time.”
He had to convince the Department of Industry and Commerce and the Revenue Commissioners of the merits of forgoing tax on the sale of goods, while local traders also opposed the move.
Nonetheless, O’Regan got the go-ahead and by July 1950 he had set up an operation in a timber hut outside the terminal, selling whiskey for $1.50 a bottle. The following year, the first duty-free shop in the world opened, with a bottle of whiskey on sale for just 30s, compared with 10s 6d in a regular shop, while in 1954 a mail order service was included. It went on to become a vast operation, mailing to locations all around the world, quality items such as crystal, china, fashionable clothing and jewellery.
The concept soon caught on. In 1957 Amsterdam became the next airport to open a duty free, with the concept making its way across the Atlantic in 1962. Prince Philip was an early admirer of the concept, and he wanted it extended to all the UK’s international airports.
O’Regan also inspired philanthropist Chuck Feeney, who took the idea of duty free and galloped ahead with it, founding Duty Free Shoppers Group (DFS) in Hawaii in 1962, which later became the largest duty-free retailer in the world.
These years also saw the invention of Irish coffee, after O’Regan asked chef Joe Sheridan to “come up with something special” to warm up transatlantic passengers tired and cold after their trip.
But duty free was only part of the equation. O’Regan’s big dream was to position Shannon as the European manufacturing basis for US companies, and to bring employment and prosperity to the region.

Shaped by the devastating impact poverty and emigration had on the county of his birth, O’Regan often repeated his father’s maxim, that “the most important thing about life is to create work for others, if you can”.
In the 1950s, the post-war boom that lifted the US, Europe and the UK had missed Ireland, and emigration was running at the highest level since independence.
So O’Regan didn’t stop at the duty free.
In 1951, he established the Shannon College of Hotel Management, which is still operating today and the graduates of which have managed the world’s top hotels, while he also leveraged the area’s potential as a tourist hub. He identified the potential of Bunratty Castle as a tourist attraction and, with the co-operation of its owner, Lord Gort, it was renovated and opened to the public in 1960, with the first medieval banquet held shortly thereafter. O’Regan later chaired Bord Fáilte.
“He was very much a leader and innovative in the sense that he thought up ideas himself,” recalls O’Carroll, who worked alongside O’Regan as estates manager in the Shannon Free Airport Development Company Limited (SFADCO). “He would work very intensively until the project was launched, and then he would go on to the next project”.
It was a time of “brainstorming picnics”, and consultancy reports, to try and hit on a new idea.
“They were great times,” says O’Carroll. “If an idea came up, and it was any way worthwhile, it would stand a very good chance of implementation.”
The big move came in the establishment of the Shannon Free Zone, the world’s first free trade zone, in 1959, overseen by SFADCO. It operated a licensing system, offering qualifying companies a corporation tax rate of just 10 per cent; a model that would later be taken up by the IFSC.
O’Regan’s idea, inspired by the Free Zone in Colon, Panama, was greeted with much scepticism initially, but his ability to build good relationships, particularly with those in government, helped secure the initiative.
“He had the ability to short-circuit a lot of things in terms of procedures in getting approval,” says O’Carroll, adding that “this clearly annoyed civil servants at the time.”
Indeed his initials, BOR, in Shannon came to mean “Bash on regardless”.
So, on an “if you build it they will come” ambition, SFADCO set about building factories – without any tenants. A Dutch piano manufacturer owned by Johan J Rippen was the first real enterprise to come to Shannon, followed by Sony, and diamond company De Beers in 1960.
O’Regan also ramped up the region’s renown as a tourist destination, using his tools of persuasion to garner investment.
When Bernard McDonough, a wealthy Irish-American industrialist pulled out of a planned ball-bearing factory in the Shannon Free Zone, O’Regan told him about a nearby castle that was for sale. He took the bait and bought it; in 1963 Dromoland Castle opened as a five-star hotel. McDonough would later open a further three hotels in the area.
When he heard of a plan by German investors to acquire the land leading to the Cliffs of Moher, he rang then Clare county manager Joe Boland, who subsequently got the county council to buy it.
During the 1970s he moved away from his formal roles in Shannon, and turned his attention to the peace process, founding Co-operation North (now Co-operation Ireland) in 1979. He died in 2008, and a bronze bust sculpture was unveiled at Shannon Airport in May 2017 to mark the centenary of his birth.
A man of his time – as O’Carroll recalls, an “infinitely simpler” time – he nonetheless left a significant legacy.
As described when receiving an honorary degree from the National University of Ireland in 1978: “Rare is the man of whom it can be justly said that he transformed the social, economic and industrial life of a whole region”
The Shannon project was not just about creating jobs; it was also about providing homes for the workers who flocked there.
By the late 1950s the housing issue, which had plagued the development of the hub since the early days, was becoming a crisis. So, in 1960, a proposal was tabled for the creation of a new town; an innovation without precedent in post-war Ireland.
Inspired by the British new towns that arose after the war, including Crawleyin Sussex and Stevenage in Hertfordshire, Brendan O’Regan and his team sought to build a new hub for workers of the airport and the industrial zone.
The creation of the first new town in the history of the State was not without challenges; there were political ructions as to who would oversee the project – the government or SFADCO – while residents of nearby Limerick city accused Brendan O’Regan of “empire building”, as they rued the fact that the development did not happen in Limerick instead.
Nonetheless, by 1962 the first residents were moving in, all of whom were tenants of SFADCO and who had to work either in the airport or industrial area to qualify for affordable housing.
As SFADCO estates manager Cian O’Carroll recalls, building the houses so close to a place of huge employment was key, as was the fact that units were small – but even larger families were catered for.
“We often let them two houses and knocked them together,” he says.
Also key to its success was the fact that housing was affordable, and graded and related to people’s incomes. After some time a tenant purchase scheme was introduced, allowing people to buy their homes outright.
Today the town is home to some 10,000 residents, and remains one of the few examples of a new planned town in Ireland.
“It hasn’t grown as much as people might have expected, but it has its own social and economic viability,” says O’Carroll.
As to why subsequent governments haven’t looked to emulate the success of Shannon – particularly given our housing shortages – O’Carroll suggests it’s due to an ideological shift away from the State doing things directly themselves, instead encouraging the private sector to do the same through tax incentives and other methods.
“It’s a shame,” he says.







 antr
antr



 |
|
 |
|
| Introduced | 1879, renamed as Paddy in 1912 |
|---|---|














