- Bushmills Original – Irish whiskey blend sometimes called White Bush or Bushmills White Label. The grain whiskey is matured in American oak casks.
- Black Bush – A blend with a significantly greater proportion of malt whiskey than the white label. It features malt whiskey aged in casks previously used for Spanish Oloroso sherry.
- Red Bush – Like the Black Bush, this is a blend with a higher proportion of malt whiskey than the standard bottling, but in contrast the malt whiskey has been matured in ex-bourbon casks.
- Bushmills 10 year single malt – Combines malt whiskeys aged at least 10 years in American bourbon or Oloroso sherry casks.
- Bushmills Distillery Reserve 12 year single malt – exclusively available at the Old Bushmills Distillery, this 12 year aged single malt is matured in oak casks for a rich, complex flavour with notes of sherry, dark chocolate and spices.
- Bushmills 16 year single malt – Malt whiskeys aged at least 16 years in American bourbon barrels or Spanish Oloroso sherry butts are mixed together before finishing in Port pipes for a few months.
- Bushmills 21 year single malt – A limited number of 21 year bottles are made each year. After 19 years, bourbon-barrel-aged and sherry-cask-aged malt whiskeys are combined, which is followed by two years of finishing in Madeira drums.
- Bushmills 1608: Originally released as a special 400th Anniversary whiskey; since 2009 it will be available only in the Whiskey Shop at the distillery and at duty-free shops.
-

 Old Bushmills Irish Whiskey advert- depicting the Cheshire Hunt .Officially the worlds oldest whiskey distillery- when in 1608 King James I granted Sir Thomas Phillips,landowner and Governor of Co Antrim,Ireland - a licence to distill.It was in 1784 when Mr Hugh Anderson registered the Old Bushmills Distillery and the Pot Still became its registered trademark, which is still a mark of genuine distinction to this day. 50cm x 65cm Belfast The Bushmills area has a long tradition with distillation. According to one story, as far back as 1276, an early settler called Sir Robert Savage of Ards, before defeating the Irish in battle, fortified his troops with "a mighty drop of acqua vitae". In 1608, a licence was granted to Sir Thomas Phillips (Irish adventurer) by King James I to distil whiskey. The Bushmills Old Distillery Company itself was not established until 1784 by Hugh Anderson. Bushmills suffered many lean years with numerous periods of closure with no record of the distillery being in operation in the official records both in 1802 and in 1822. In 1860 a Belfast spirit merchant named Jame McColgan and Patrick Corrigan bought the distillery; in 1880 they formed a limited company. In 1885, the original Bushmills buildings were destroyed by fire but the distillery was swiftly rebuilt. In 1890, a steamship owned and operated by the distillery, SS Bushmills, made its maiden voyage across the Atlantic to deliver Bushmills whiskey to America. It called at Philadelphiaand New York City before heading on to Singapore, Hong Kong, Shanghai and Yokohama.In the early 20th century, the U.S. was a very important market for Bushmills (and other Irish Whiskey producers). American Prohibition in 1920 came as a large blow to the Irish Whiskey industry, but Bushmills managed to survive. Wilson Boyd, Bushmills' director at the time, predicted the end of prohibition and had large stores of whiskey ready to export. After the Second World War, the distillery was bought by Isaac Wolfson, and, in 1972, it was taken over by Irish Distillers, meaning that Irish Distillers controlled the production of all Irish whiskey at the time. In June 1988, Irish Distillers was bought by French liquor group Pernod Ricard.In June 2005, the distillery was bought by Diageo for £200 million. Diageo have also announced a large advertising campaign in order to regain a market share for Bushmills.In May 2008, the Bank of Ireland issued a new series of sterling banknotes in Northern Ireland which all feature an illustration of the Old Bushmills Distillery on the obverse side, replacing the previous notes series which depicted Queen's University of Belfast. In November 2014 it was announced that Diageo had traded the Bushmills brand with Jose Cuervo in exchange for the 50% of the Don Julio brand of tequila that Diageo did not already own.
Old Bushmills Irish Whiskey advert- depicting the Cheshire Hunt .Officially the worlds oldest whiskey distillery- when in 1608 King James I granted Sir Thomas Phillips,landowner and Governor of Co Antrim,Ireland - a licence to distill.It was in 1784 when Mr Hugh Anderson registered the Old Bushmills Distillery and the Pot Still became its registered trademark, which is still a mark of genuine distinction to this day. 50cm x 65cm Belfast The Bushmills area has a long tradition with distillation. According to one story, as far back as 1276, an early settler called Sir Robert Savage of Ards, before defeating the Irish in battle, fortified his troops with "a mighty drop of acqua vitae". In 1608, a licence was granted to Sir Thomas Phillips (Irish adventurer) by King James I to distil whiskey. The Bushmills Old Distillery Company itself was not established until 1784 by Hugh Anderson. Bushmills suffered many lean years with numerous periods of closure with no record of the distillery being in operation in the official records both in 1802 and in 1822. In 1860 a Belfast spirit merchant named Jame McColgan and Patrick Corrigan bought the distillery; in 1880 they formed a limited company. In 1885, the original Bushmills buildings were destroyed by fire but the distillery was swiftly rebuilt. In 1890, a steamship owned and operated by the distillery, SS Bushmills, made its maiden voyage across the Atlantic to deliver Bushmills whiskey to America. It called at Philadelphiaand New York City before heading on to Singapore, Hong Kong, Shanghai and Yokohama.In the early 20th century, the U.S. was a very important market for Bushmills (and other Irish Whiskey producers). American Prohibition in 1920 came as a large blow to the Irish Whiskey industry, but Bushmills managed to survive. Wilson Boyd, Bushmills' director at the time, predicted the end of prohibition and had large stores of whiskey ready to export. After the Second World War, the distillery was bought by Isaac Wolfson, and, in 1972, it was taken over by Irish Distillers, meaning that Irish Distillers controlled the production of all Irish whiskey at the time. In June 1988, Irish Distillers was bought by French liquor group Pernod Ricard.In June 2005, the distillery was bought by Diageo for £200 million. Diageo have also announced a large advertising campaign in order to regain a market share for Bushmills.In May 2008, the Bank of Ireland issued a new series of sterling banknotes in Northern Ireland which all feature an illustration of the Old Bushmills Distillery on the obverse side, replacing the previous notes series which depicted Queen's University of Belfast. In November 2014 it was announced that Diageo had traded the Bushmills brand with Jose Cuervo in exchange for the 50% of the Don Julio brand of tequila that Diageo did not already own. -

 Great picture of a recuperating Arkle getting his lunch washed down by one of his two daily bottles of Guinness by the managing director of Kempton Park Racecourse Henry Hyde. Ratoath Co Meath. 45cm x 75cm Arkle (19 April 1957 – 31 May 1970) was an Irish Thoroughbred racehorse. A bay gelding by Archive out of Bright Cherry, he was the grandson of the unbeaten (in 14 races) flat racehorse and prepotent sire Nearco. Arkle was born at Ballymacoll Stud, County Meath, by Mrs Mary Alison Baker of Malahow House, near Naul, County Dublin. He was named after the mountain Arkle in Sutherland, Scotland that bordered the Duchess of Westminster’s Sutherland estate. Owned by Anne Grosvenor, Duchess of Westminster, he was trained by Tom Dreaper at Greenogue, Kilsallaghan in County Meath, Ireland, and ridden during his steeplechasing career by Pat Taaffe. At 212, his Timeform rating is the highest ever awarded to a steeplechaser. Only Flyingbolt, also trained by Dreaper, had a rating anywhere near his at 210. Next on their ratings are Sprinter Sacre on 192 and then Kauto Star and Mill House on 191. Despite his career being cut short by injury, Arkle won three Cheltenham Gold Cups, the Blue Riband of steeplechasing, and a host of other top prizes. On 19th April, 2014 a magnificent 1.1 scale bronze statue was unveiled in Ashbourne, County Meath in commemoration of Arkle.In the 1964 Cheltenham Gold Cup, Arkle beat Mill House (who had won the race the previous year) by five lengths to claim his first Gold Cup at odds of 7/4. It was the last time he did not start as the favourite for a race. Only two other horses entered the Gold Cup that year. The racing authorities in Ireland took the unprecedented step in the Irish Grand National of devising two weight systems — one to be used when Arkle was running and one when he was not. Arkle won the 1964 race by only one length, but he carried two and half stones more than his rivals. The following year's Gold Cup saw Arkle beat Mill House by twenty lengths at odds of 3/10. In the 1966 renewal, he was the shortest-priced favourite in history to win the Gold Cup, starting at odds of 1/10. He won the race by thirty lengths despite a mistake early in the race where he ploughed through a fence. However, it did not stop his momentum, nor did he ever look like falling. Arkle had a strange quirk in that he crossed his forelegs when jumping a fence. He went through the season 1965/66 unbeaten in five races. Arkle won 27 of his 35 starts and won at distances from 1m 6f up to 3m 5f. Legendary Racing commentator Peter O'Sullevan has called Arkle a freak of nature — something unlikely to be seen again. Besides winning three consecutive Cheltenham Gold Cups (1964, 1965, 1966) and the 1965 King George VI Chase, Arkle triumphed in a number of other important handicap chases, including the 1964 Irish Grand National (under 12-0), the 1964 and 1965 Hennessy Gold Cups (both times under 12-7), the 1965 Gallagher Gold Cup (conceding 16 lb to Mill House while breaking the course record by 17 seconds), and the 1965 Whitbread Gold Cup(under 12-7). In the 1966 Hennessy, he failed by only half a length to give Stalbridge Colonist 35 lb. The scale of the task Arkle faced is shown by the winner coming second and third in the two following Cheltenham Gold Cups, while in third place was the future 1969 Gold Cup winner, What A Myth. In December 1966, Arkle raced in the King George VI Chase at Kempton Park but struck the guard rail with a hoof when jumping the open ditch, which resulted in a fractured pedal bone; despite this injury, he completed the race and finished second. He was in plaster for four months and, though he made a good enough recovery to go back into training, he never ran again. He was retired and ridden as a hack by his owner and then succumbed to what has been variously described as advanced arthritis or possibly brucellosis and was put down at the early age of 13. Arkle became a national legend in Ireland. His strength was jokingly claimed to come from drinking 2 pints of Guinness a day. At one point, the slogan Arkle for President was written on a wall in Dublin. The horse was often referred to simply as "Himself", and he supposedly received items of fan mail addressed to 'Himself, Ireland'. The Irish government-owned Irish National Stud, at Tully, Kildare, Co. Kildare, Ireland, has the skeleton of Arkle on display in its museum. A statue in his memory was erected in Ashbourne Co Meath in 2004. Dimensions : 55cm x 60cm
Great picture of a recuperating Arkle getting his lunch washed down by one of his two daily bottles of Guinness by the managing director of Kempton Park Racecourse Henry Hyde. Ratoath Co Meath. 45cm x 75cm Arkle (19 April 1957 – 31 May 1970) was an Irish Thoroughbred racehorse. A bay gelding by Archive out of Bright Cherry, he was the grandson of the unbeaten (in 14 races) flat racehorse and prepotent sire Nearco. Arkle was born at Ballymacoll Stud, County Meath, by Mrs Mary Alison Baker of Malahow House, near Naul, County Dublin. He was named after the mountain Arkle in Sutherland, Scotland that bordered the Duchess of Westminster’s Sutherland estate. Owned by Anne Grosvenor, Duchess of Westminster, he was trained by Tom Dreaper at Greenogue, Kilsallaghan in County Meath, Ireland, and ridden during his steeplechasing career by Pat Taaffe. At 212, his Timeform rating is the highest ever awarded to a steeplechaser. Only Flyingbolt, also trained by Dreaper, had a rating anywhere near his at 210. Next on their ratings are Sprinter Sacre on 192 and then Kauto Star and Mill House on 191. Despite his career being cut short by injury, Arkle won three Cheltenham Gold Cups, the Blue Riband of steeplechasing, and a host of other top prizes. On 19th April, 2014 a magnificent 1.1 scale bronze statue was unveiled in Ashbourne, County Meath in commemoration of Arkle.In the 1964 Cheltenham Gold Cup, Arkle beat Mill House (who had won the race the previous year) by five lengths to claim his first Gold Cup at odds of 7/4. It was the last time he did not start as the favourite for a race. Only two other horses entered the Gold Cup that year. The racing authorities in Ireland took the unprecedented step in the Irish Grand National of devising two weight systems — one to be used when Arkle was running and one when he was not. Arkle won the 1964 race by only one length, but he carried two and half stones more than his rivals. The following year's Gold Cup saw Arkle beat Mill House by twenty lengths at odds of 3/10. In the 1966 renewal, he was the shortest-priced favourite in history to win the Gold Cup, starting at odds of 1/10. He won the race by thirty lengths despite a mistake early in the race where he ploughed through a fence. However, it did not stop his momentum, nor did he ever look like falling. Arkle had a strange quirk in that he crossed his forelegs when jumping a fence. He went through the season 1965/66 unbeaten in five races. Arkle won 27 of his 35 starts and won at distances from 1m 6f up to 3m 5f. Legendary Racing commentator Peter O'Sullevan has called Arkle a freak of nature — something unlikely to be seen again. Besides winning three consecutive Cheltenham Gold Cups (1964, 1965, 1966) and the 1965 King George VI Chase, Arkle triumphed in a number of other important handicap chases, including the 1964 Irish Grand National (under 12-0), the 1964 and 1965 Hennessy Gold Cups (both times under 12-7), the 1965 Gallagher Gold Cup (conceding 16 lb to Mill House while breaking the course record by 17 seconds), and the 1965 Whitbread Gold Cup(under 12-7). In the 1966 Hennessy, he failed by only half a length to give Stalbridge Colonist 35 lb. The scale of the task Arkle faced is shown by the winner coming second and third in the two following Cheltenham Gold Cups, while in third place was the future 1969 Gold Cup winner, What A Myth. In December 1966, Arkle raced in the King George VI Chase at Kempton Park but struck the guard rail with a hoof when jumping the open ditch, which resulted in a fractured pedal bone; despite this injury, he completed the race and finished second. He was in plaster for four months and, though he made a good enough recovery to go back into training, he never ran again. He was retired and ridden as a hack by his owner and then succumbed to what has been variously described as advanced arthritis or possibly brucellosis and was put down at the early age of 13. Arkle became a national legend in Ireland. His strength was jokingly claimed to come from drinking 2 pints of Guinness a day. At one point, the slogan Arkle for President was written on a wall in Dublin. The horse was often referred to simply as "Himself", and he supposedly received items of fan mail addressed to 'Himself, Ireland'. The Irish government-owned Irish National Stud, at Tully, Kildare, Co. Kildare, Ireland, has the skeleton of Arkle on display in its museum. A statue in his memory was erected in Ashbourne Co Meath in 2004. Dimensions : 55cm x 60cm -
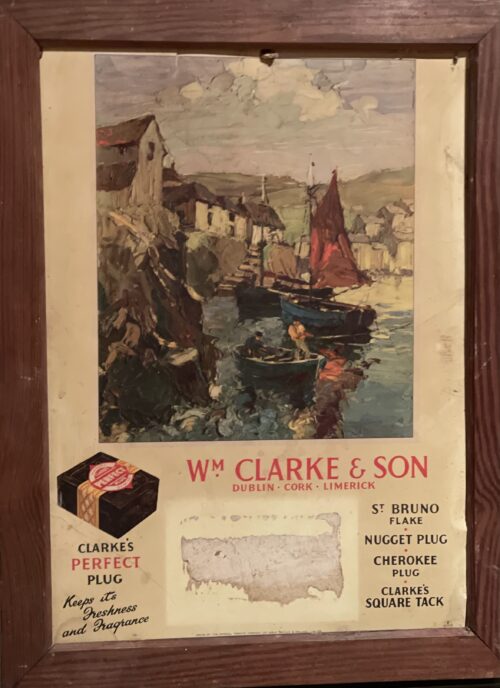
 49cm x 38cm William Clarke & Son was a tobacco company that was founded in 1830 at South Main Street, Cork, Ireland. In January 1924, following the formation of the Irish Free State, the United Kingdom trade of William Clarke & Son was transferred to Dublin and taken over by Ogden's.
49cm x 38cm William Clarke & Son was a tobacco company that was founded in 1830 at South Main Street, Cork, Ireland. In January 1924, following the formation of the Irish Free State, the United Kingdom trade of William Clarke & Son was transferred to Dublin and taken over by Ogden's.William Clarke & Son, Dublin
William Clarke was founded in 1830 at South Main Street in Cork, however by 1870 the manufacturing side of the business had all been transferred to Hare Place, Scotland Road, Liverpool, with only depots remaining in Ireland. Following the formation of the Irish Free State in 1926, the Liverpool based operation was taken over by Ogden’s, while a new factory was set up at South Circular Road in Dublin to produce tobacco and snuff under the William Clarke & Son brand. In 1929 William Clarke was amalgamated with Wills’s Irish branch, which resulted in Wills’s Irish production being integrated into the new South Circular Road factory in Dublin, though senior management were based in Wills’s Bristol operations and the Irish entity ultimately reported back into Bristol. -

 Framed Fight poster of Collins v Eubank at Millstreet 1995. 90cm x 68cm Co Cork Stephen Collins (born 21 July 1964) is an Irish former professional boxer who competed from 1986 to 1997. Known as the Celtic Warrior, Collins is the most successful Irish boxer in recent professional boxing history, having held the WBOmiddleweight and super-middleweight titles simultaneously and never losing a fight as champion. Collins' first nineteen professional fights all took place in the United States. In 1988 he won the Irish middleweight title, and the regional American USBA middleweight title the following year, defending the latter successfully in Atlantic City and Las Vegas. In his first two world championship challenges, both for the WBA middleweight title, Collins lost a unanimous decision to Mike McCallum in 1990 and a majority decision to Reggie Johnson in 1992. He also challenged unsuccessfully for the European middleweight title later in 1992, losing a split decision to Sumbu Kalambay in Italy. It was not until Collins reached his early 30s that he fulfilled his potential, becoming WBO middleweight champion in his third world title attempt with a fifth-round TKO victory over Chris Pyatt in 1994, before then moving up in weight to defeat the undefeated Chris Eubank and claim the WBO super-middleweight title in 1995. More success followed, as Collins successfully defended his title by winning the rematch against Eubank later in the year. Collins successfully defended his title another six times before pulling out of a proposed fight in October 1997 against rising Welsh star, Joe Calzaghe, and retiring from the sport, with Collins frustrated by his inability to get a fight against the pound for pound number one boxer of the time, Roy Jones Jr., who was then fighting in the light-heavyweight division. Having competed against some of the best boxers on both sides of the Atlantic during his career, Collins tends to be linked more to an era in the UK during which there was a notable rivalry between British boxers Chris Eubank and Nigel Benn, both of whom Collins fought and defeated twice.
Framed Fight poster of Collins v Eubank at Millstreet 1995. 90cm x 68cm Co Cork Stephen Collins (born 21 July 1964) is an Irish former professional boxer who competed from 1986 to 1997. Known as the Celtic Warrior, Collins is the most successful Irish boxer in recent professional boxing history, having held the WBOmiddleweight and super-middleweight titles simultaneously and never losing a fight as champion. Collins' first nineteen professional fights all took place in the United States. In 1988 he won the Irish middleweight title, and the regional American USBA middleweight title the following year, defending the latter successfully in Atlantic City and Las Vegas. In his first two world championship challenges, both for the WBA middleweight title, Collins lost a unanimous decision to Mike McCallum in 1990 and a majority decision to Reggie Johnson in 1992. He also challenged unsuccessfully for the European middleweight title later in 1992, losing a split decision to Sumbu Kalambay in Italy. It was not until Collins reached his early 30s that he fulfilled his potential, becoming WBO middleweight champion in his third world title attempt with a fifth-round TKO victory over Chris Pyatt in 1994, before then moving up in weight to defeat the undefeated Chris Eubank and claim the WBO super-middleweight title in 1995. More success followed, as Collins successfully defended his title by winning the rematch against Eubank later in the year. Collins successfully defended his title another six times before pulling out of a proposed fight in October 1997 against rising Welsh star, Joe Calzaghe, and retiring from the sport, with Collins frustrated by his inability to get a fight against the pound for pound number one boxer of the time, Roy Jones Jr., who was then fighting in the light-heavyweight division. Having competed against some of the best boxers on both sides of the Atlantic during his career, Collins tends to be linked more to an era in the UK during which there was a notable rivalry between British boxers Chris Eubank and Nigel Benn, both of whom Collins fought and defeated twice.Early years in Boston
Steve Collins won 26 Irish titles as an amateur before turning professional in Massachusetts, US in October 1986. Collins worked out of the Petronelli Brothers gym in Brockton, Massachusetts alongside Marvin Hagler. His debut fight was against Julio Mercado on the undercard of a bill that featured Irish Americans; his future trainer Freddie Roach and the future Fight of the Year winner Micky Ward. Collins beat Mercado by way of knockout in the third round. In Boston, Massachusetts in 1988, he defeated former Olympian and British Super Middleweight champion Sam Storey to win the Irish middleweight title, then defeated world No. 5, Kevin Watts to win the USBA middleweight title. After reaching 16–0, Collins stepped in as a substitute in a WBA middleweight title fight after Michael Watson was injured in training, and fought 12 rounds against Mike McCallum in Boston in 1990. Collins was supported by a large crowd of Irish Americans as he battled the champion McCallum, with the fight being close early on before McCallum started to tire as Collins gained momentum in the later stages to bring a close finish at the end of 12 exciting rounds. McCallum got the win by unanimous decision. In 1992, Collins lost a majority decision to Reggie Johnson in a closely contested slugfest for the vacant WBA middleweight title (which had been stripped from McCallum because he signed to fight IBF champion James Toney). Collins then lost by split decision to Sumbu Kalambay for the European title in Italy, before beating Gerhard Botes of South Africa to win the WBA Penta-Continental middleweight title in 1993.WBO middleweight champion
Collins then moved to Belfast under the management of Barney Eastwood before basing himself in England where he joined Barry Hearn's Matchroom Boxing. Alongside him was Paul "Silky" Jones, his sparring partner and good friend who later went on to become WBO light-middleweight title holder. Collins was trained by Freddie King in the Romford training camp. In May 1994, Collins finally won a world title by defeating Chris Pyatt by stoppage in five rounds to become the WBO middleweight champion. Early in 1995, Collins relinquished this title without a defence as he was having difficulty making the 160lbs middleweight limit. In March 1995, Chris Eubank (41-0-2) had been scheduled to have a third WBO super-middleweight title fight against Ray Close. Eubank and Close had two fights over the previous two years (their first fight a draw, and their second fight a narrow split decision win for Eubank), but Close was forced to withdraw from their scheduled third fight after failing an MRI brain scan. Collins then stepped into Close's place, moving up to super-middleweight to take on Eubank.WBO super-middleweight champion
Collins defeated the then unbeaten long-reigning champion Chris Eubank in Millstreet, County Cork, Ireland, in March 1995, by unanimous decision (115–111, 116–114, 114–113), to win the WBO super-middleweight title. Collins had enlisted the help of a guru, and they led the press to believe that Collins would be hypnotised for the fight, which noticeably unsettled Eubank. True to form, Collins sat in his corner and did not move, listening to headphones during Eubank's ring entrance. Collins knocked Eubank down in the eighth round, and was well ahead on the scorecards at the end of Round 9, but Eubank finished the fight strongly as he tried to save his unbeaten record and knocked Collins down in the tenth round, coming close to a stoppage. Eubank was unable to finish the job, and Collins held on for victory. In their September 1995 rematch in Cork, Collins performed brilliantly, changing his usual fighting style by adopting wild, brawling tactics throughout which Eubank really struggled to deal with. Despite most TV pundits and commentators giving Collins a wide points victory with scorecards in the region of 117–111 and 118–110, the three judges saw the fight very differently with Collins only winning by a close split decision, 115–113, 115–113 and 114–115. Collins successfully defended his WBO super-middleweight title seven times, including two fights against Nigel Benn in 1996. In the summer of 1997, Collins reportedly stated in the press that he had no motivation left, as he had spent the best part of his career chasing Roy Jones Jr. for a fight that had been promised to him many times. Collins is reported to have stated in Boxing World that he had spent so long chasing Roy Jones Jr. that money was no longer important; that he would "fight him in a phone box in front of two men and a dog". but the bout never materialised. A WBO super-middleweight title fight against Joe Calzaghe was agreed for October 1997, but Collins got injured 10 days before the scheduled fight, got stripped of his title by the WBO, with Collins then making a statement saying that fighting Calzaghe would do nothing to satisfy the desire he had for fighting Jones. Collins then added he wanted to retire on a high note with a good pay day, "Joe is a good up-and-coming kid, but he wouldn't fill a parish church". As Collins couldn't get the fight with Jones, Collins decided to retire. In 1999, Collins announced his decision to come out of retirement to fight Roy Jones Jr. Controversy surrounded the proposed fight, as WBC and WBA light heavyweight champion Jones decided to fight the IBF light heavyweight champion and old Collins foe Reggie Johnson (which Jones won by a shutout 120–106 on all three judges' scorecards), and it was revealed that Collins would have to fight Calzaghe before a showdown with Jones. Collins had accepted this and started to prepare to fight Calzaghe. In training, Collins collapsed during a sparring session with Howard Eastman. Although tests and a brain scan could not find any problems, Collins decided that it was a warning to make him stop boxing, and he retired for a second time. Collins retired in 1997, with a record of 39 fights, 36 wins (21 knockouts) and 3 losses. Collins has not entirely faded from the spotlight since his retirement. In 1998 he appeared in the film Lock, Stock and Two Smoking Barrels as a boxing gym bouncer. In 1999 he made a cameo appearance in "Sweetest Thing", a music video by U2. On 15 January 2013, at the age of 48, Collins announced plans to fight Roy Jones Jr.He went on to appear in a number of exhibition bouts in preparation for the proposed Jones fight. In 2017 Collins joined the Army Reserve's 253 Provost Company of the 4th Regiment Royal Military Police in London where he had been living for the previous 20 years. He gained promotion to Lance Corporal and qualified as an army boxing coach. His brother Roddy Collins is a former professional footballer and manager. His brother Paschal was a professional boxer and now a leading professional boxing coach plus manager. His eldest son Stevie Jnr is a retired rugby player and a retired professional boxer who now coaches and manages boxers His youngest son Luke is an active amateur boxer and qualified amateur boxing coach -
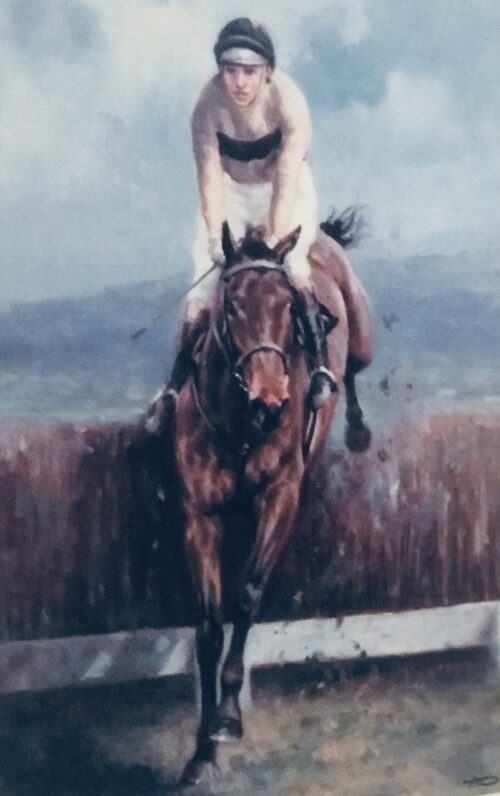

 Beautiful tribute print to the great Arkle with list of major career victories undeneath.The Legendary gelding is pictured successfully negotiating a fence at Cheltenham with regular jockey Pat Taafe on board wearing the distinctive yellow and black silks of Arkle's owner Anne,Duchess of Westminster. 70cm x 50cm Kilcock Co Kildare Arkle (19 April 1957 – 31 May 1970) was an Irish Thoroughbred racehorse. A bay gelding by Archive out of Bright Cherry, he was the grandson of the unbeaten (in 14 races) flat racehorse and prepotent sire Nearco. Arkle was born at Ballymacoll Stud, County Meath, by Mrs Mary Alison Baker of Malahow House, near Naul, County Dublin. He was named after the mountain Arkle in Sutherland, Scotland that bordered the Duchess of Westminster’s Sutherland estate. Owned by Anne Grosvenor, Duchess of Westminster, he was trained by Tom Dreaper at Greenogue, Kilsallaghan in County Meath, Ireland, and ridden during his steeplechasing career by Pat Taaffe. At 212, his Timeform rating is the highest ever awarded to a steeplechaser. Only Flyingbolt, also trained by Dreaper, had a rating anywhere near his at 210. Next on their ratings are Sprinter Sacre on 192 and then Kauto Star and Mill House on 191. Despite his career being cut short by injury, Arkle won three Cheltenham Gold Cups, the Blue Riband of steeplechasing, and a host of other top prizes. On 19th April, 2014 a magnificent 1.1 scale bronze statue was unveiled in Ashbourne, County Meath in commemoration of Arkle. In the 1964 Cheltenham Gold Cup, Arkle beat Mill House (who had won the race the previous year) by five lengths to claim his first Gold Cup at odds of 7/4. It was the last time he did not start as the favourite for a race. Only two other horses entered the Gold Cup that year. The racing authorities in Ireland took the unprecedented step in the Irish Grand National of devising two weight systems — one to be used when Arkle was running and one when he was not. Arkle won the 1964 race by only one length, but he carried two and half stones more than his rivals. The following year's Gold Cup saw Arkle beat Mill House by twenty lengths at odds of 3/10. In the 1966 renewal, he was the shortest-priced favourite in history to win the Gold Cup, starting at odds of 1/10. He won the race by thirty lengths despite a mistake early in the race where he ploughed through a fence. However, it did not stop his momentum, nor did he ever look like falling. Arkle had a strange quirk in that he crossed his forelegs when jumping a fence. He went through the season 1965/66 unbeaten in five races. Arkle won 27 of his 35 starts and won at distances from 1m 6f up to 3m 5f. Legendary Racing commentator Peter O'Sullevan has called Arkle a freak of nature — something unlikely to be seen again. Besides winning three consecutive Cheltenham Gold Cups (1964, 1965, 1966) and the 1965 King George VI Chase, Arkle triumphed in a number of other important handicap chases, including the 1964 Irish Grand National (under 12-0), the 1964 and 1965 Hennessy Gold Cups (both times under 12-7), the 1965 Gallagher Gold Cup (conceding 16 lb to Mill House while breaking the course record by 17 seconds), and the 1965 Whitbread Gold Cup(under 12-7). In the 1966 Hennessy, he failed by only half a length to give Stalbridge Colonist 35 lb. The scale of the task Arkle faced is shown by the winner coming second and third in the two following Cheltenham Gold Cups, while in third place was the future 1969 Gold Cup winner, What A Myth. In December 1966, Arkle raced in the King George VI Chase at Kempton Park but struck the guard rail with a hoof when jumping the open ditch, which resulted in a fractured pedal bone; despite this injury, he completed the race and finished second. He was in plaster for four months and, though he made a good enough recovery to go back into training, he never ran again. He was retired and ridden as a hack by his owner and then succumbed to what has been variously described as advanced arthritis or possibly brucellosis and was put down at the early age of 13. Arkle became a national legend in Ireland. His strength was jokingly claimed to come from drinking 2 pints of Guinness a day. At one point, the slogan Arkle for President was written on a wall in Dublin. The horse was often referred to simply as "Himself", and he supposedly received items of fan mail addressed to 'Himself, Ireland'. The Irish government-owned Irish National Stud, at Tully, Kildare, Co. Kildare, Ireland, has the skeleton of Arkle on display in its museum. A statue in his memory was erected in Ashbourne Co. Meath in April 2014.
Beautiful tribute print to the great Arkle with list of major career victories undeneath.The Legendary gelding is pictured successfully negotiating a fence at Cheltenham with regular jockey Pat Taafe on board wearing the distinctive yellow and black silks of Arkle's owner Anne,Duchess of Westminster. 70cm x 50cm Kilcock Co Kildare Arkle (19 April 1957 – 31 May 1970) was an Irish Thoroughbred racehorse. A bay gelding by Archive out of Bright Cherry, he was the grandson of the unbeaten (in 14 races) flat racehorse and prepotent sire Nearco. Arkle was born at Ballymacoll Stud, County Meath, by Mrs Mary Alison Baker of Malahow House, near Naul, County Dublin. He was named after the mountain Arkle in Sutherland, Scotland that bordered the Duchess of Westminster’s Sutherland estate. Owned by Anne Grosvenor, Duchess of Westminster, he was trained by Tom Dreaper at Greenogue, Kilsallaghan in County Meath, Ireland, and ridden during his steeplechasing career by Pat Taaffe. At 212, his Timeform rating is the highest ever awarded to a steeplechaser. Only Flyingbolt, also trained by Dreaper, had a rating anywhere near his at 210. Next on their ratings are Sprinter Sacre on 192 and then Kauto Star and Mill House on 191. Despite his career being cut short by injury, Arkle won three Cheltenham Gold Cups, the Blue Riband of steeplechasing, and a host of other top prizes. On 19th April, 2014 a magnificent 1.1 scale bronze statue was unveiled in Ashbourne, County Meath in commemoration of Arkle. In the 1964 Cheltenham Gold Cup, Arkle beat Mill House (who had won the race the previous year) by five lengths to claim his first Gold Cup at odds of 7/4. It was the last time he did not start as the favourite for a race. Only two other horses entered the Gold Cup that year. The racing authorities in Ireland took the unprecedented step in the Irish Grand National of devising two weight systems — one to be used when Arkle was running and one when he was not. Arkle won the 1964 race by only one length, but he carried two and half stones more than his rivals. The following year's Gold Cup saw Arkle beat Mill House by twenty lengths at odds of 3/10. In the 1966 renewal, he was the shortest-priced favourite in history to win the Gold Cup, starting at odds of 1/10. He won the race by thirty lengths despite a mistake early in the race where he ploughed through a fence. However, it did not stop his momentum, nor did he ever look like falling. Arkle had a strange quirk in that he crossed his forelegs when jumping a fence. He went through the season 1965/66 unbeaten in five races. Arkle won 27 of his 35 starts and won at distances from 1m 6f up to 3m 5f. Legendary Racing commentator Peter O'Sullevan has called Arkle a freak of nature — something unlikely to be seen again. Besides winning three consecutive Cheltenham Gold Cups (1964, 1965, 1966) and the 1965 King George VI Chase, Arkle triumphed in a number of other important handicap chases, including the 1964 Irish Grand National (under 12-0), the 1964 and 1965 Hennessy Gold Cups (both times under 12-7), the 1965 Gallagher Gold Cup (conceding 16 lb to Mill House while breaking the course record by 17 seconds), and the 1965 Whitbread Gold Cup(under 12-7). In the 1966 Hennessy, he failed by only half a length to give Stalbridge Colonist 35 lb. The scale of the task Arkle faced is shown by the winner coming second and third in the two following Cheltenham Gold Cups, while in third place was the future 1969 Gold Cup winner, What A Myth. In December 1966, Arkle raced in the King George VI Chase at Kempton Park but struck the guard rail with a hoof when jumping the open ditch, which resulted in a fractured pedal bone; despite this injury, he completed the race and finished second. He was in plaster for four months and, though he made a good enough recovery to go back into training, he never ran again. He was retired and ridden as a hack by his owner and then succumbed to what has been variously described as advanced arthritis or possibly brucellosis and was put down at the early age of 13. Arkle became a national legend in Ireland. His strength was jokingly claimed to come from drinking 2 pints of Guinness a day. At one point, the slogan Arkle for President was written on a wall in Dublin. The horse was often referred to simply as "Himself", and he supposedly received items of fan mail addressed to 'Himself, Ireland'. The Irish government-owned Irish National Stud, at Tully, Kildare, Co. Kildare, Ireland, has the skeleton of Arkle on display in its museum. A statue in his memory was erected in Ashbourne Co. Meath in April 2014. -
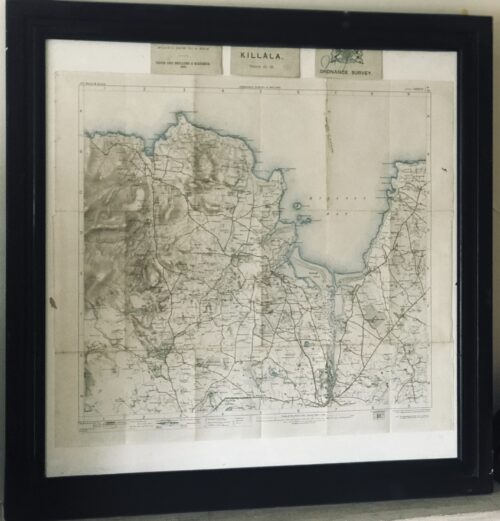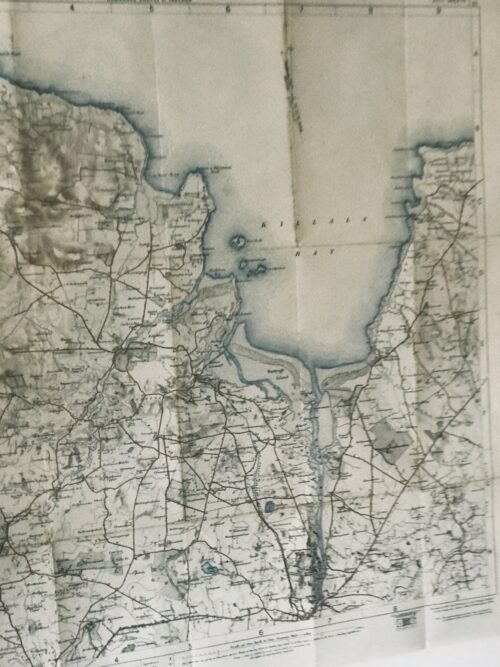
 Original ordnance survey map from 19 of Killala Bay Co Mayo in superb frame. Westport Co Mayo 65cm x 65cm Killala is a quiet seaside resort but the harbour warehouses show that it was once a busy port. This remote little town enjoys a place of disproportionate importance in the history of Ireland, as it was here that the French first halted when they invaded in 1798. The 1798 French invasion of Ireland On August 6, 1798, General Humbert’s “Army of Ireland” set sail from La Rochelle destined for Killala, Co. Mayo …
Original ordnance survey map from 19 of Killala Bay Co Mayo in superb frame. Westport Co Mayo 65cm x 65cm Killala is a quiet seaside resort but the harbour warehouses show that it was once a busy port. This remote little town enjoys a place of disproportionate importance in the history of Ireland, as it was here that the French first halted when they invaded in 1798. The 1798 French invasion of Ireland On August 6, 1798, General Humbert’s “Army of Ireland” set sail from La Rochelle destined for Killala, Co. Mayo …
La Rochelle’s harbour.
On July 19, 1798, the French Directory authorises the sending of three expeditions to Ireland and gives command of the first one to General Humbert.
On August 6, 1798, General Humbert’s Army of Ireland sailed from La Rochelle in three frigates La Concorde, La Franchise, La Médée, carrying 1,025 French troops, 3 light field cannons, 3,000 muskets, and 400 sabres.
There were also a number of Irish among Humbert’s command. These included Bartholomew Teeling and Fr. Henry O Kane. This tiny force, together with its Irish allies, was to conduct an extraordinary campaign that shook the British Empire.During 16 days they sailed taking a circuitous route to avoid detection by the British navy. The mission of this little French expeditionary force was to provide military assistance to the Irish rebels of the “Rising of ’98” – sometimes referred to as “Bliadhan na bhFrancach” or “The Year of the French” – in their attempt to free Ireland from English domination.
The fleet had originally planned to land in Co. Donegal, but due to storm and no doubt influenced by the presence of Fr. O Kane who was a native of Killala the fleet sailed into Killala Bay.

Kilcumminn head, Co. Mayo
On the 22nd of August, 1798, the three frigates landed at Kilcummin flying the English colours.
Edwin and Arthur Stock, sons of the Protestant Bishop of Killala, who had sailed out to meet them, greeted them. The two were captured, the English flag taken down and the French flag hoisted.
One of the first to disembark was Fr. O Kane who spoke to the locals in Irish which was the native tongue of most of the Irish at that time. Word soon filtered to native Irish throughout Mayo and Sligo.
Kilcumminn strand,landing-place of the French
Bishop Stock also heard of the arrival and he sent messages to the local gentry among them the Jacksons, the Knoxs, Binghams, Palmers and Kirkwoods. Into the relative quiescence of northwest Ireland, the French expeditionary force fell like a thunderbolt. By about 7pm the landing was complete.

General Humbert
Young Général Jean-Joseph-Amable Humbert (the landing occurred on his 31st birthday), a canny veteran of irregular warfare against the insurgents of the Vendée, was well aware of the odds against him in a conventional military showdown, but also of the multiplying effects of surprise and speed.
He was also keenly aware of the importance of early victory for exciting the morale of the Irish insurgents and dismaying the ill-trained loyalist militia.
The first military confrontation occurred on the afternoon of 22 August, when Colonel Jean Sarrazin led a group of French Grenadiers south to the nearby village of Killala.

Killala, viewed from the north.
The garrison of 200 men included a handful of regulars of the 17th Foot (Leicestershire Regiment), but was mostly composed of the Yeomanry, an ill-trained part-time paramilitary constabulary.
With a portion of Sarrazin’s force circling around the British left flank and the remainder pressing a frontal attack with the bayonet, the unnerved Loyalists fired one ragged volley and then fled in terror towards Ballina.
Three Frenchmen were slightly wounded, bishop Stock’s palace was taken over as Humbert’s H.Q. and several of the yeomen were taken prisoner.

Ireland forever – l’Irlande pour toujours
A French soldier then climbed to the top of the palace and removed the British flag, which was replaced by a green and gold flag bearing the inscription ‘Erin Go Bragh’ (Ireland forever).

General Humbert statue in Killala.
LIBERTY, EQUALITY, FRATERNITY, UNION “After several unsuccessful attempts behold at last Frenchmen arrived amongst you . . . “Brave Irishmen, our cause is common. Like you we hold as indefeasible the right of all nations to liberty. Like you we are persuaded that the peace of the world shall ever be troubled as long as the British ministry is suffered to make with impunity a traffic of the industry and blood of the people . . . “Union, Liberty, the Irish Republic! Such is our shout. Let us march. Our hearts are devoted to you; our glory is in your happiness.”
From General Humbert’s Proclamation of 22nd August, 1798. (This last sentence of Humbert’s Proclamation became our pub’s motto!)

Mémorial de Ballina
This initial humbling of their oppressors had the desired effect on the local population, bringing forward thousands of eager, though ignorant and ill-disciplined Irish volunteers who were hastily equipped and formed into companies. Muskets were issued to some, but as in the uprisings elsewhere in Ireland that year, most of the insurgents were armed with crude pikes, scythes, and hay-forks.
On the 24th of August, having captured Killala, Humbert sent two groups under Sarrazin (provisionally promoted to Général de Brigade by Humbert on 23 August) and Adjudant-General Fontaine to capture Ballina.That night a fight took place between Sarrazin’s troops and the British at Rosserk. The English eventually retreated in confusion. The next morning the French/Irish troops captured Ballina under cover of darkness. The Irish peasants lit bundles of straw to show them their way. This approach road to Ballina has since been known as Bothair na Sop. They took Ballina without much resistance. The English for the most part fled towards Foxford where they would have their forces waiting for the French advance on Castlebar.

Humbert – Windy Gap Pass
The British commander in County Mayo, General Hutchinson, expected Humbert to continue south along the only decent road out of Ballina toward Castlebar, the commercial and strategic center of the region.
Where the road crosses the River Moy at Foxford, Hutchinson placed a strong blocking force with ample artillery. Clashes of French and British patrols along the Ballina-Foxford road appeared to confirm British expectations.Humbert, closely questioning the locals, learned that there was an alternative route to Castlebar, a barely-practicable goat-trail that ran west of Lough Conn, over the Windy Gap pass, and then south to the town. He resolved to take this route.
To further the deception, the Franco-Irish forces marched out of Ballina along the Foxford road at sunset on August 26 with ostentatious noise and shouted boasts of expected victory at Foxford, then doubled back in silence and darkness to the west of Loch Conn. At midnight, Humbert’s army was in Lahardane.
“Tour D’Humbert” signposts in Lahardane
The local priest, Father Andrew Conroy, was fluent in French from his time at seminary in Nantes.
He gave precious directions to the French officers and marshalled the people to provide food and assistance to the troops. In the aftermath of the campaign, Father Conroy was arrested, tried, and executed by the vengeful British.After a rigorous night-march of 40 km (25 miles), Humbert’s 800 French, 600 Irish, and 1 laboriously manhandled gun reached Castlebar on 27 August.
Sion Hill (now built-up)
A yeoman farmer who had been tending to his cattle had spotted the French/Irish advance party. He immediately fled to Castlebar to warn the British commander of the eminent arrival of the French/Irish forces.
The English forces took up position at Sion Hill just outside the town. Humbert approached and took account of the English position.
Batlle of Castlebar known as “Races of Castlebar”.
Following a number of attacks in which they were hit by British cannon, Humbert decided to regroup and divided his troops, splitting them to the left and right so as to attack the English flanks. The Irish drove a herd of cattle ahead of them causing confusion in the English rank. The French/Irish made an effective bayonet charge through the centre.

Castlebar Memorial
The English retreated down Staball Hill. Another attack occurred at Main St. Bridge. The English defended the bridge for some time using forces from the Longford and Kilkenny militias and Fraser Fencibles (a Scottish regiment).
There was confused fighting in the town as knots of the more stalwart British, notably the Fraser Fencibles and Roden’s Dragoons, attempted to make a stand.
The bulk of the redcoat forces, abandoning all guns, standards, and baggage, ran in headlong flight down the road to Tuam, 54 km (34 miles) to the southeast; some apparently did not stop until reaching Athlone, a further 68 km (42 miles) away. General Lake’s army being dissolved.
The event has since become mockingly known among the Irish as “The Castlebar Races.” In all the attack only lasted six hours from 6a.m. to 12 noon and has been described by Thomas Pakenham in The Year of Liberty as one of the most ignominious defeats in British military history. Following this brilliant victory, Humbert spent the next few days resting and reorganizing his army, absorbing many hundreds of new Irish volunteers including some 250 deserters from the Longford and Kilkenny Militias.The “Republic of Connaught” was proclaimed and a makeshift revolutionary government installed.Army of Ireland – Liberty, Equality
Head quarters at Castlebar, 14th Fructidor, sixth Year of the French Republic, One and Indivisible. General Humbert, Commander in Chief of the Army of Ireland, desirous of organizing with the least possible delay, an administrative power for the Province of Connaught, decrees as follows:
1. The Government of the Province of Connaught shall reside at Castlebar till further orders. 2. The Government shall be composed of twelve members, who shall be named by the General-in-chief of the French Army. 3. Citizen JOHN MOORE is named President of the Government of the Province of Connaught, he is specially entrusted with the nomination and reunion of the members of the Government. 4. The Government shall occupy itself immediately in organizing the Military power of the Province of Connaught, and with providing subsistence for the French and Irish Armies. 5. There shall be organized eight regiments of infantry, each of twelve hundred men, and four regiments of cavalry, each of six hundred men. 6. The Government shall declare rebels and traitors to the country all those who having received clothing and arms, shall not join the army within four and twenty hours. 7. Every individual from sixteen years of age to forty, inclusive, is REQUIRED in the name of the Irish Republic, to betake himself instantly to the French Camp, to march in a mass against the common enemy. The General Commanding-in-Chief HUMBERT.Lord Cornwallis (the same who had surrendered to Washington at Yorktown), now the Viceroy and Commander-in-Chief in Ireland, moved west from Dublin to take personal command of the campaign.It was obvious that after the fiasco of Castlebar, the Crown forces in Ireland would marshal every possible resource to crush Humbert.
Lord Cornwallis
By the 2nd of September, Cornwallis had 7,800 men, including two reliable Scottish regiments (the Sutherland and Rehy Fencibles) concentrated at Tuam, organized into four brigades under Generals Hunter, Campbell, Hutchinson, and Moore (later the hero of Corunna), and a further 2,800 at Boyle.
Cornwallis advanced from Tuam on the 4th of September, but on arriving at Castlebar on the 5th found only a small Franco-Irish rearguard. Aware of the impossibility of defeating the well-equipped and far more numerous Crown forces, and with no sign of reinforcements from France, Humbert had marched off to the east on 4 September, under cover of darkness, taking his army, now totalling 3,000 men, towards Sligo, covering 58 miles in 36 hours. The long march had begun. Some Irish troops under French officers remained to protect Killala and receive the expected reinforcements.
Collooney, Co. Sligo
On the morning of the 5th of September, an English army from Sligo under Col Vereker attacks the Franco-Irish army at Collooney with its left protected by the Ballysadare River and its right anchored on a steep, wooded hill. Humbert again outmanoeuvres them.
In what may be one of the greatest feats of individual bravery in the long history of the Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, Colonel Bartholomew Teeling, a United Irishman holding a French commission, galloped forward alone to the British line, pistolled the enemy gunner at point-blank range, and rode back unscathed under a hail of musket-fire. Inspired by his example, the Irish and French surged forward and routed the Loyalists. The English retreated with heavy losses as far as Ballyshannon, County Donegal.Cornwallis has now divided his army in two, one half under General Lake to pursue the enemy and the other half, under his own personal command, to protect the line of the river Shannon.
Ballinamuck pikeman
The French and Irish “must not cross”. Meanwhile, the United Irishmen of Longford and Westmeath have assembled. They capture Wilson’s Hospital near Mullingar but fail to take the town of Granard. Humbert, on hearing of the midlands rising decides to link up with the insurgents there.He is now near Manorhamilton but changes and goes straight for Granard. He abandons some of the heavier guns so as to make more speed. So far he has eluded the cordon closing in around him. With some luck he hopes to slip past the net, reach Granard and then strike for Dublin which is virtually unprotected as most of the garrison have been moved to Connacht. The Franco-Irish army reaches Drumkeerin in the evening of September 6. An envoy from Lord Cornwallis offers terms for surrender but they are rejected.On September 7, shortly before noon Humbert’s army crosses the Shannon at Ballintra Bridge just south of Loch Allen, but they fail in an attempt to demolish the bridge behind them.
His army shows signs of fatigue and skirmishes with the English advance guard become more frequent. The race for Granard quickens.
The Franco-Irish army reaches Cloone, in South Leitrim, while Cornwallis, with 15,000 men is at Mohill, five miles away. Humbert gets news that he is surrounded and outnumbered but decides to push on even if the best he can now do is to make a token resistance before surrender.On September 8, 1798, near the small village of Ballinamuck, County Longford, Humbert drew up his 859 French troops in line of battle. There could be little doubt of the outcome.
Behind Humbert was Cornwallis blocking Humbert’s way to Dublin. In front was Lake’s 6000 men. The battle which lasted but half an hour commenced with Colonel Crawford’s dragoons cutting through the Irish rebels. When the British grand assault poured up the hill from three sides, in overwhelming numbers, Humbert gave the order to surrender.
Humbert surrenders in Ballinamuck
The French officers followed their general’s signal and ordered their men to lay down their muskets. A second body of British cavalry had reined in seeing the signs of surrender, but Colonel Teeling, an Irish officer in the French army, had not signaled surrender so British infantry advanced on them. Crawford attacked a large contingent of Irishmen with his dragoons, their sabres sparing only those with officers insignia, hanging to be their fate.
Later testimonies reveal that on arresting Humbert, General Lake could not conceal his astonishment: “Where is your army?” Lake demanded “This is it all” Humbert replied, indicating his soldiers. “And what were you planning to do with this lot?” Lake asked. “We were going to Dublin to break the irons of a nation that suffers under your yoke” Humbert said. “That is an idea that could only be born in a Frenchman’s brains!” Lake declared.
Humbert surrenders in Ballinamuck
Humbert and the French prisoners were conducted to Dublin and treated with all the consideration that could be given to gallant prisoners after an honorable defeat.
Not so the Irish. Accounts vary, but it appears that many of the Irish were cut down where they stood, or driven into the bog south of the hill where they were hunted down and slaughtered. Captured Irish officers, even those bearing legitimate commissions in the French army, were seized and hanged as traitors. Such was Bartholomew Teeling, Matthew Tone and Gunner James Magee’s fate.“After having obtained the greatest successes and made the arms of the French Republic triumph during my stay in Ireland, I have at length been obliged to submit to a superior force of 30,000 troops.” General Humbert’s Report to the French Directory after Ballinamuck.
‘A SHORT BUT VERY FATIGUING CAMPAIGN’
English historians have always treated General Humbert’s expedition to Ireland with ridicule, but Brian O hUiginn was fond of quoting Plowden the military correspondent of the London Times who held a different view. This expert wrote some years ago:
“In these operations described by Cornwallis to the Duke of Portland as a short but very fatiguing campaign, a raiding party of 1000 French landed in Ireland without opposition, after sixteen days of navigation, unobserved by the British Navy; defeated and drove back the British troops opposing them on four separate occasions; routed a force of second line troops of at least double its strength; captured eleven British guns; held the field for seventeen days; entirely occupied the attention of all the available troops of a garrison of Ireland 150,000 strong; penetrated almost to the centre of the island, and compelled the Lord Lieutenant to send an urgent requisition to London for ‘as great a reinforcement as possible.’ “
This was a fine tribute to General Humbert and his troops.- In Humbert’s footsteps 2013 – Killala & Castlebar
- In Humbert’s footsteps 2013 – Killala & Castlebar
- In Humbert’s footsteps 2013 – Killala & Castlebar
- In Humbert’s footsteps 2013 – Killala & Castlebar
The Charentais of the expedition.
Many Charentais took part in the expedition. Among them: Daniel Savary, who was born in Salles sur Mer (17), was in command of the naval division charged with transporting the expedition from La Rochelle to Killala. François Babin, born in Péré (17), became Commander of the Castlebar battalion. Jean Jobit, born in Chateauneuf en Charente (16), was a Commander on the Castlebar battlefield in Castlebar. Jean-Paul Leugerat, born in Barbezières (16), died during the battle of Castlebar. -
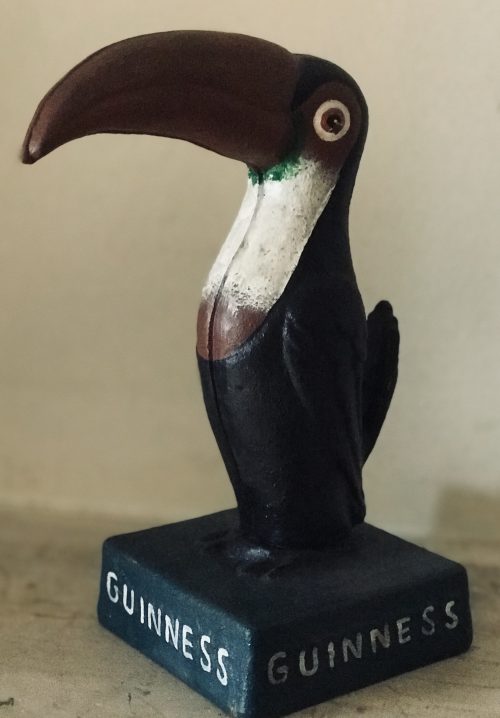 Very well manufactured Castiron Toucan replica. Dimensions :20cm x 10cm x 8cm 1.5kg The legendary Guinness Toucan goes back to 1935 and the advertising firm S.H. Benson. Artist John Gilroy had been recently hired, and Dorothy Sayers, a famous crime writer and playwright, wrote advertising copy for the company. For nearly two centuries of existence, the brewery had almost no need to formally advertise, allowing word-of-mouth to sell the beer, and sell it did. By the late 19th century, Guinness was one of the top three breweries between Britain and Ireland. In 1862, the company adopted an Irish harp as their logo and trademarked it in 1875. However, by the late 1920s, sales were declining, and in 1929, Rupert Guinness, then chair of the company, ran the first-ever Guinness print ad with the slogan “Guinness is good for you.” The very next year, the brewery hired advertising firm S.H. Benson. It was then, in 1930, that the story of the Guinness toucan began. The man responsible for the iconic bird and his animal companions is the English illustrator and draftsman John Gilroy. He was born in 1898 in Newcastle upon Tyne into a family of eight children, and his father, William, was a landscape painter. From a young age, Gilroy began copying the drawings in magazines, and it was quickly evident he would follow in his father’s professional footsteps. By 15, he was a cartoonist for the local newspaper. He won a scholarship to art school, and although World War I interrupted his studies, he entered London’s Royal College of Art in 1919. While he was still a student, he received his first commission for commercial art—a promotional pamphlet for the Hydraulic Engineering Co. Not long after graduating, Gilroy began working for S.H. Benson, where he would eventually work on Guiness.Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.His first work with the firm was on campaigns for Skipper Sardines and Virol (a brand of malt extract). In his early years at Benson, he and his colleagues created clever characters to make their designs memorable: Baron de Beef, Signor Spaghetti, Miss Di Gester. All these playful characters likely primed Gilroy for the fun and whimsical designs he would eventually draw for Guinness in his 35 years working with the company. In the early 1930s S.H. Benson boasted an impressive staff of creatives beyond John Gilroy; the aforementioned Dorothy Sayers, now famous as a crime writer and poet, wrote copy for the agency. When Guinness approached the firm, they had an interesting request: the final advertising campaign should not be too much to do with beer, despite the fact that it was advertising—well—beer. They thought it would be vulgar. Instead, they preferred something that appealed to families and that highlighted the purported health benefits of the brew. They asked Gilroy to draft an ad showing a family drinking Guinness, but no one could seem to agree on what the family should look like, nor how they should be presented. Luckily, it was precisely family that led Gilroy to the particular idea that eventually spawned Guinness’s most famous ad campaigns. The artist had recently taken his son to the circus, recounts Guinness archive manager Fergus Brady, and had watched a sea lion balancing a ball on its nose. He realized how fun it would be to draw a sea lion balancing a pint of Guinness on its nose, and pitched the idea to Guinness. From there the series expanded to an entire menagerie. Gilroy drew ostriches, bears, pelicans, kangaroos, and of course, the toucan. Paired with Sayers’s inventive copy, the ads took off. In her most clever ad, she plays on the toucan / two-can homophone and on the idea that drinking Guinness offers a range of health benefits: “If he can say as you can / Guinness is good for you / How grand to be a Toucan — / Just think what Toucan do.” The illustration features a smiling toucan perched next to two shining pint glasses full of Guinness stout.
Very well manufactured Castiron Toucan replica. Dimensions :20cm x 10cm x 8cm 1.5kg The legendary Guinness Toucan goes back to 1935 and the advertising firm S.H. Benson. Artist John Gilroy had been recently hired, and Dorothy Sayers, a famous crime writer and playwright, wrote advertising copy for the company. For nearly two centuries of existence, the brewery had almost no need to formally advertise, allowing word-of-mouth to sell the beer, and sell it did. By the late 19th century, Guinness was one of the top three breweries between Britain and Ireland. In 1862, the company adopted an Irish harp as their logo and trademarked it in 1875. However, by the late 1920s, sales were declining, and in 1929, Rupert Guinness, then chair of the company, ran the first-ever Guinness print ad with the slogan “Guinness is good for you.” The very next year, the brewery hired advertising firm S.H. Benson. It was then, in 1930, that the story of the Guinness toucan began. The man responsible for the iconic bird and his animal companions is the English illustrator and draftsman John Gilroy. He was born in 1898 in Newcastle upon Tyne into a family of eight children, and his father, William, was a landscape painter. From a young age, Gilroy began copying the drawings in magazines, and it was quickly evident he would follow in his father’s professional footsteps. By 15, he was a cartoonist for the local newspaper. He won a scholarship to art school, and although World War I interrupted his studies, he entered London’s Royal College of Art in 1919. While he was still a student, he received his first commission for commercial art—a promotional pamphlet for the Hydraulic Engineering Co. Not long after graduating, Gilroy began working for S.H. Benson, where he would eventually work on Guiness.Arthur Guinness started brewing ales in 1759 at the St James Gate Brewery,Dublin.On 31st December 1759 he signed a 9,000 year lease at £45 per annum for the unused brewery.Ten years later, on 19 May 1769, Guinness first exported his ale: he shipped six-and-a-half barrels to Great Britain before he started selling the dark beer porter in 1778. The first Guinness beers to use the term were Single Stout and Double Stout in the 1840s.Throughout the bulk of its history, Guinness produced only three variations of a single beer type: porter or single stout, double or extra and foreign stout for export. “Stout” originally referred to a beer’s strength, but eventually shifted meaning toward body and colour.Porter was also referred to as “plain”, as mentioned in the famous refrain of Flann O’Brien‘s poem “The Workman’s Friend”: “A pint of plain is your only man.” Already one of the top-three British and Irish brewers, Guinness’s sales soared from 350,000 barrels in 1868 to 779,000 barrels in 1876.In October 1886 Guinness became a public company, and was averaging sales of 1,138,000 barrels a year. This was despite the brewery’s refusal to either advertise or offer its beer at a discount. Even though Guinness owned no public houses, the company was valued at £6 million and shares were twenty times oversubscribed, with share prices rising to a 60 per cent premium on the first day of trading. The breweries pioneered several quality control efforts. The brewery hired the statistician William Sealy Gosset in 1899, who achieved lasting fame under the pseudonym “Student” for techniques developed for Guinness, particularly Student’s t-distribution and the even more commonly known Student’s t-test. By 1900 the brewery was operating unparalleled welfare schemes for its 5,000 employees. By 1907 the welfare schemes were costing the brewery £40,000 a year, which was one-fifth of the total wages bill. The improvements were suggested and supervised by Sir John Lumsden. By 1914, Guinness was producing 2,652,000 barrels of beer a year, which was more than double that of its nearest competitor Bass, and was supplying more than 10 per cent of the total UK beer market. In the 1930s, Guinness became the seventh largest company in the world. Before 1939, if a Guinness brewer wished to marry a Catholic, his resignation was requested. According to Thomas Molloy, writing in the Irish Independent, “It had no qualms about selling drink to Catholics but it did everything it could to avoid employing them until the 1960s.” Guinness thought they brewed their last porter in 1973. In the 1970s, following declining sales, the decision was taken to make Guinness Extra Stout more “drinkable”. The gravity was subsequently reduced, and the brand was relaunched in 1981. Pale malt was used for the first time, and isomerized hop extract began to be used. In 2014, two new porters were introduced: West Indies Porter and Dublin Porter. Guinness acquired the Distillers Company in 1986.This led to a scandal and criminal trialconcerning the artificial inflation of the Guinness share price during the takeover bid engineered by the chairman, Ernest Saunders. A subsequent £5.2 million success fee paid to an American lawyer and Guinness director, Tom Ward, was the subject of the case Guinness plc v Saunders, in which the House of Lords declared that the payment had been invalid. In the 1980s, as the IRA’s bombing campaign spread to London and the rest of Britain, Guinness considered scrapping the Harp as its logo. The company merged with Grand Metropolitan in 1997 to form Diageo. Due to controversy over the merger, the company was maintained as a separate entity within Diageo and has retained the rights to the product and all associated trademarks of Guinness.His first work with the firm was on campaigns for Skipper Sardines and Virol (a brand of malt extract). In his early years at Benson, he and his colleagues created clever characters to make their designs memorable: Baron de Beef, Signor Spaghetti, Miss Di Gester. All these playful characters likely primed Gilroy for the fun and whimsical designs he would eventually draw for Guinness in his 35 years working with the company. In the early 1930s S.H. Benson boasted an impressive staff of creatives beyond John Gilroy; the aforementioned Dorothy Sayers, now famous as a crime writer and poet, wrote copy for the agency. When Guinness approached the firm, they had an interesting request: the final advertising campaign should not be too much to do with beer, despite the fact that it was advertising—well—beer. They thought it would be vulgar. Instead, they preferred something that appealed to families and that highlighted the purported health benefits of the brew. They asked Gilroy to draft an ad showing a family drinking Guinness, but no one could seem to agree on what the family should look like, nor how they should be presented. Luckily, it was precisely family that led Gilroy to the particular idea that eventually spawned Guinness’s most famous ad campaigns. The artist had recently taken his son to the circus, recounts Guinness archive manager Fergus Brady, and had watched a sea lion balancing a ball on its nose. He realized how fun it would be to draw a sea lion balancing a pint of Guinness on its nose, and pitched the idea to Guinness. From there the series expanded to an entire menagerie. Gilroy drew ostriches, bears, pelicans, kangaroos, and of course, the toucan. Paired with Sayers’s inventive copy, the ads took off. In her most clever ad, she plays on the toucan / two-can homophone and on the idea that drinking Guinness offers a range of health benefits: “If he can say as you can / Guinness is good for you / How grand to be a Toucan — / Just think what Toucan do.” The illustration features a smiling toucan perched next to two shining pint glasses full of Guinness stout.
John Gilroy, illustrator of some of Guinness’s most well-known advertisements.
Gilroy even created toucan ads specifically for the American market with the birds flying over landmarks like the Statue of Liberty, Mount Rushmore, and the Golden Gate Bridge—always carrying two pints on their beaks. Sadly, Guinness never approved and ran the ads. Over the years, Gilroy created nearly 100 advertisements and 50 poster designs for Guinness. Though he left S.H. Benson as an in-house artist in the 1940s, he continued to freelance for them and continued to create the beloved Guinness zoo ads, crafting new scenarios for his Guinness-loving animals and their beleaguered zookeeper. Other vintage Guinness ads from the time feature simpler jingles and catchphrases. “My goodness—my Guinness” often features an animal stealing a man’s pint in comical fashions—an ostrich swallows it, a kangaroo hides the bottle in its pouch, a crocodile holds the pint between his massive jaws, and so on. In another, a smirking tortoise carries a pint on its back under the text, “Have a Guinness when you’re tired.” A man pulls a cart while his horse relaxes and goes for a ride—“Guinness for strength.” There is a playfulness to all of them. Even the ad in which a man is being chased by a lion feels funny—of course, the lion is chasing the man not to eat him, but to steal his beer. The lion is smiling, his tongue lolling out of his mouth as he runs, and we’re in on the joke: he’ll get the Guinness in the end, and the man is panicking not to save his skin, but to save his beer.
With John Gilroy’s illustrations and Dorothy Sayers’s copy, the Guinness toucan ads were an immediate hit. (Guinness)
The ads ran primarily in the U.K. and in the 1930s and 1940s were immensely popular—likely the cheerful, cheeky animals and bright colors provided a small antidote to the horrors going on in Europe at the time. In 1939, all troops in the British Expeditionary Force in France received a bottle of Guinness with their Christmas dinner. The company remained committed to adding a touch of whimsy to their generally solid and forward-thinking business practices. To celebrate Guinness’s bicentennial in 1959, the company dropped 150,000 embossed bottles containing Guinness-related information and paraphernalia into the Atlantic Ocean. It is the same year, as well, that Guinness employed scientists to create the Guinness Draft we know today by pairing nitrogen gas and carbon dioxide—it is that combination that gives the beer its prized silky texture. In in 1963 and 1965, Guinness opened breweries in Nigeria and Malaysia, respectively, cementing the company’s global reach and impact. As the company modernized, so too did their advertising strategies. In 1982, the Guinness brewery switched ad firms and stopped running the zoo-themed ads—the toucan and its friends were no longer considered effective advertising techniques. However, nostalgia for the Guinness toucan remained, and the company has released limited-edition cans and merchandise featuring the original Gilroy drawings. In 2017, the 200th anniversary of Guinness in America, they released a number of decorative itemsimprinted with the image of the two-pint-touting toucans flying over Mount Rushmore. The image of Gilroy’s toucan still immediately brings Guinness to mind, and it remains an immensely memorable mascot of the world’s premier dark beer.
Guinness coasters featuring the menagerie of John Gilroy’s advertisements. (Guinness)
The Guinness brewery in Park Royal, London closed in 2005. The production of all Guinness sold in the UK and Ireland was moved to St. James’s Gate Brewery, Dublin. Guinness has also been referred to as “that black stuff”. Guinness had a fleet of ships, barges and yachts. The Irish Sunday Independent newspaper reported on 17 June 2007 that Diageo intended to close the historic St James’s Gate plant in Dublin and move to a greenfield site on the outskirts of the city.This news caused some controversy when it was announced.The following day, the Irish Daily Mail ran a follow-up story with a double page spread complete with images and a history of the plant since 1759. Initially, Diageo said that talk of a move was pure speculation but in the face of mounting speculation in the wake of the Sunday Independent article, the company confirmed that it is undertaking a “significant review of its operations”. This review was largely due to the efforts of the company’s ongoing drive to reduce the environmental impact of brewing at the St James’s Gate plant. On 23 November 2007, an article appeared in the Evening Herald, a Dublin newspaper, stating that the Dublin City Council, in the best interests of the city of Dublin, had put forward a motion to prevent planning permission ever being granted for development of the site, thus making it very difficult for Diageo to sell off the site for residential development. On 9 May 2008, Diageo announced that the St James’s Gate brewery will remain open and undergo renovations, but that breweries in Kilkenny and Dundalk will be closed by 2013 when a new larger brewery is opened near Dublin. The result will be a loss of roughly 250 jobs across the entire Diageo/Guinness workforce in Ireland.Two days later, the Sunday Independent again reported that Diageo chiefs had met with Tánaiste Mary Coughlan, the deputy leader of the Government of Ireland, about moving operations to Ireland from the UK to benefit from its lower corporation tax rates. Several UK firms have made the move in order to pay Ireland’s 12.5 per cent rate rather than the UK’s 28 per cent rate. Diageo released a statement to the London stock exchange denying the report.Despite the merger that created Diageo plc in 1997, Guinness has retained its right to the Guinness brand and associated trademarks and thus continues to trade under the traditional Guinness name despite trading under the corporation name Diageo for a brief period in 1997. In November 2015 it was announced that Guinness are planning to make their beer suitable for consumption by vegetarians and vegans by the end of 2016 through the introduction of a new filtration process at their existing Guinness Brewery that avoids the need to use isinglass from fish bladders to filter out yeast particles.This went into effect in 2017, per the company’s FAQ webpage where they state: “Our new filtration process has removed the use of isinglass as a means of filtration and vegans can now enjoy a pint of Guinness. All Guinness Draught in keg format is brewed without using isinglass. Full distribution of bottle and can formats will be in place by the end of 2017, so until then, our advice to vegans is to consume the product from the keg format only for now. Guinness stout is made from water, barley, roast malt extract, hops, and brewer’s yeast. A portion of the barley is roasted to give Guinness its dark colour and characteristic taste. It is pasteurisedand filtered. Until the late 1950s Guinness was still racked into wooden casks. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, Guinness ceased brewing cask-conditioned beers and developed a keg brewing system with aluminium kegs replacing the wooden casks; these were nicknamed “iron lungs”.Until 2016 the production of Guinness, as with many beers, involved the use of isinglass made from fish. Isinglass was used as a fining agent for settling out suspended matter in the vat. The isinglass was retained in the floor of the vat but it was possible that minute quantities might be carried over into the beer. Diageo announced in February 2018 that the use of isinglass in draught Guinness was to be discontinued and an alternative clarification agent would be used instead. This has made draught Guinness acceptable to vegans and vegetarians. Arguably its biggest change to date, in 1959 Guinness began using nitrogen, which changed the fundamental texture and flavour of the Guinness of the past as nitrogen bubbles are much smaller than CO2, giving a “creamier” and “smoother” consistency over a sharper and traditional CO2 taste. This step was taken after Michael Ash – a mathematician turned brewer – discovered the mechanism to make this possible. Nitrogen is less soluble than carbon dioxide, which allows the beer to be put under high pressure without making it fizzy. High pressure of the dissolved gas is required to enable very small bubbles to be formed by forcing the draught beer through fine holes in a plate in the tap, which causes the characteristic “surge” (the widget in cans and bottles achieves the same effect). This “widget” is a small plastic ball containing the nitrogen. The perceived smoothness of draught Guinness is due to its low level of carbon dioxide and the creaminess of the head caused by the very fine bubbles that arise from the use of nitrogen and the dispensing method described above. “Foreign Extra Stout” contains more carbon dioxide, causing a more acidic taste. Contemporary Guinness Draught and Extra Stout are weaker than they were in the 19th century, when they had an original gravity of over 1.070. Foreign Extra Stout and Special Export Stout, with abv of 7.5% and 9% respectively, are perhaps closest to the original in character.Although Guinness may appear to be black, it is officially a very dark shade of ruby. The most recent change in alcohol content from the Import Stout to the Extra Stout was due to a change in distribution through North American market. Consumer complaints have influenced recent distribution and bottle changes. Studies claim that Guinness can be beneficial to the heart. Researchers found that “‘antioxidantcompounds’ in the Guinness, similar to those found in certain fruits and vegetables, are responsible for the health benefits because they slow down the deposit of harmful cholesterol on the artery walls.”Guinness ran an advertising campaign in the 1920s which stemmed from market research – when people told the company that they felt good after their pint, the slogan, created by Dorothy L. Sayers–”Guinness is Good for You”. Advertising for alcoholic drinks that implies improved physical performance or enhanced personal qualities is now prohibited in Ireland.Diageo, the company that now manufactures Guinness, says: “We never make any medical claims for our drinks.” -

 Excellent Bass Showcard advert circa 1960s.
Excellent Bass Showcard advert circa 1960s.The former beer of choice of An Taoiseach Bertie Ahern,the Bass Ireland Brewery operated on the Glen Road in West Belfast for 107 years until its closure in 2004.But despite its popularity, this ale would be the cause of bitter controversy in the 1930s as you can learn below.
Founded in 1777 by William Bass in Burton-upon-Trent, Staffordshire, England.The main brand was Bass Pale Ale, once the highest-selling beer in the UK.By 1877, Bass had become the largest brewery in the world, with an annual output of one million barrels.Its pale ale was exported throughout the British Empire, and the company's distinctive red triangle became the UK's first registered trade mark. In the early 1930s republicans in Dublin and elsewhere waged a campaign of intimidation against publicans who sold Bass ale, which involved violent tactics and grabbed headlines at home and further afield. This campaign occurred within a broader movement calling for the boycott of British goods in Ireland, spearheaded by the IRA. Bass was not alone a British product, but republicans took issue with Colonel John Gretton, who was chairman of the company and a Conservative politician in his day.In Britain,Ireland and the Second World War, Ian Woods notes that the republican newspaper An Phoblacht set the republican boycott of Bass in a broader context , noting that there should be “No British ales. No British sweets or chocolate. Shoulder to shoulder for a nationwide boycott of British goods. Fling back the challenge of the robber empire.”
In late 1932, Irish newspapers began to report on a sustained campaign against Bass ale, which was not strictly confined to Dublin. On December 5th 1932, The Irish Times asked:
Will there be free beer in the Irish Free State at the end of this week? The question is prompted by the orders that are said to have been given to publicans in Dublin towards the end of last week not to sell Bass after a specified date.
The paper went on to claim that men visited Dublin pubs and told publicans “to remove display cards advertising Bass, to dispose of their stock within a week, and not to order any more of this ale, explaining that their instructions were given in furtherance of the campaign to boycott British goods.” The paper proclaimed a ‘War on English Beer’ in its headline. The same routine, of men visiting and threatening public houses, was reported to have happened in Cork.
It was later reported that on November 25th young men had broken into the stores owned by Bass at Moore Lane and attempted to do damage to Bass property. When put before the courts, it was reported that the republicans claimed that “Colonel Gretton, the chairman of the company, was a bitter enemy of the Irish people” and that he “availed himself of every opportunity to vent his hate, and was an ardent supporter of the campaign of murder and pillage pursued by the Black and Tans.” Remarkably, there were cheers in court as the men were found not guilty, and it was noted that they had no intention of stealing from Bass, and the damage done to the premises amounted to less than £5.
A campaign of intimidation carried into January 1933, when pubs who were not following the boycott had their signs tarred, and several glass signs advertising the ale were smashed across the city. ‘BOYCOTT BRITISH GOODS’ was painted across several Bass advertisements in the city.
Throughout 1933, there were numerous examples of republicans entering pubs and smashing the supply of Bass bottles behind the counter. This activity was not confined to Dublin,as this report from late August shows. It was noted that the men publicly stated that they belonged to the IRA.
September appears to have been a particularly active period in the boycott, with Brian Hanley identifying Dublin, Tralee, Naas, Drogheda and Waterford among the places were publicans were targetted in his study The IRA: 1926-1936. One of the most interesting incidents occurring in Dun Laoghaire. There, newspapers reported that on September 4th 1933 “more than fifty young men marched through the streets” before raiding the premises of Michael Moynihan, a local publican. Bottles of Bass were flung onto the roadway and advertisements destroyed. Five young men were apprehended for their role in the disturbances, and a series of court cases nationwide would insure that the Bass boycott was one of the big stories of September 1933.
The young men arrested in Dun Laoghaire refused to give their name or any information to the police, and on September 8th events at the Dublin District Court led to police baton charging crowds. The Irish Times reported that about fifty supporters of the young men gathered outside the court with placards such as ‘Irish Goods for Irish People’, and inside the court a cry of ‘Up The Republic!’ led to the judge slamming the young men, who told him they did not recognise his court. The night before had seen some anti-Bass activity in the city, with the smashing of Bass signs at Burgh Quay. This came after attacks on pubs at Lincoln Place and Chancery Street. It wasn’t long before Mountjoy and other prisons began to home some of those involved in the Boycott Bass campaign, which the state was by now eager to suppress.

An undated image of a demonstration to boycott British goods. Credit: http://irishmemory.blogspot.ie/
This dramatic court appearance was followed by similar scenes in Kilmainham, where twelve men were brought before the courts for a raid on the Dead Man’s Pub, near to Palmerstown in West Dublin. Almost all in their 20s, these men mostly gave addresses in Clondalkin. Their court case was interesting as charges of kidnapping were put forward, as Michael Murray claimed the men had driven him to the Featherbed mountain. By this stage, other Bass prisoners had begun a hungerstrike, and while a lack of evidence allowed the men to go free, heavy fines were handed out to an individual who the judge was certain had been involved.
The decision to go on hungerstrike brought considerable attention on prisoners in Mountjoy, and Maud Gonne MacBride spoke to the media on their behalf, telling the Irish Press on September 18th that political treatment was sought by the men. This strike had begun over a week previously on the 10th, and by the 18th it was understood that nine young men were involved. Yet by late September, it was evident the campaign was slowing down, particularly in Dublin.
The controversy around the boycott Bass campaign featured in Dáil debates on several occasions. In late September Eamonn O’Neill T.D noted that he believed such attacks were being allowed to be carried out “with a certain sort of connivance from the Government opposite”, saying:
I suppose the Minister is aware that this campaign against Bass, the destruction of full bottles of Bass, the destruction of Bass signs and the disfigurement of premises which Messrs. Bass hold has been proclaimed by certain bodies to be a national campaign in furtherance of the “Boycott British Goods” policy. I put it to the Minister that the compensation charges in respect of such claims should be made a national charge as it is proclaimed to be a national campaign and should not be placed on the overburdened taxpayers in the towns in which these terrible outrages are allowed to take place with a certain sort of connivance from the Government opposite.
Another contribution in the Dáil worth quoting came from Daniel Morrissey T.D, perhaps a Smithwicks man, who felt it necessary to say that we were producing “an ale that can compare favourably with any ale produced elsewhere” while condemning the actions of those targeting publicans:
I want to say that so far as I am concerned I have no brief good, bad, or indifferent, for Bass’s ale. We are producing in this country at the moment—and I am stating this quite frankly as one who has a little experience of it—an ale that can compare favourably with any ale produced elsewhere. But let us be quite clear that if we are going to have tariffs or embargoes, no tariffs or embargoes can be issued or given effect to in this country by any person, any group of persons, or any organisation other than the Government elected by the people of the country.
Tim Pat Coogan claims in his history of the IRA that this boycott brought the republican movement into conflict with the Army Comrades Association, later popularly known as the ‘Blueshirts’. He claims that following attacks in Dublin in December 1932, “the Dublin vitners appealed to the ACA for protection and shipments of Bass were guarded by bodyguards of ACA without further incident.” Yet it is undeniable there were many incidents of intimidation against suppliers and deliverers of the product into 1933.
Not all republicans believed the ‘Boycott Bass’ campaign had been worthwhile. Patrick Byrne, who would later become secretary within the Republican Congress group, later wrote that this was a time when there were seemingly bigger issues, like mass unemployment and labour disputes in Belfast, yet:
In this situation, while the revolution was being served up on a plate in Belfast, what was the IRA leadership doing? Organising a ‘Boycott Bass’ Campaign. Because of some disparaging remarks the Bass boss, Colonel Gretton, was reported to have made about the Irish, some IRA leaders took umbrage and sent units out onto the streets of Dublin and elsewhere to raid pubs, terrify the customers, and destroy perfectly good stocks of bottled Bass, an activity in which I regret to say I was engaged.
Historian Brian Hanley has noted by late 1933 “there was little effort to boycott anything except Bass and the desperation of the IRA in hoping violence would revive the campaign was in fact an admission of its failure. At the 1934 convention the campaign was quietly abandoned.”
Interestingly, this wasn’t the last time republicans would threaten Bass. In 1986 The Irish Times reported that Bass and Guinness were both threatened on the basis that they were supplying to British Army bases and RUC stations, on the basis of providing a service to security forces.
Origins : Co Limerick
Dimensions:35 cm x 45cm
-
Out of stock

 Lovely and rarely encountered John Gilroy farm scene advertising print in its original aged frame. John Gilroy was a polymath of the painting world, with a mind unlike those of his peers. Because of this, the Guinness® campaigns he brought to life from 1928 to the 1960s remain as distinctive now as they were back then. It was Gilroy's colourful artwork that moved our advertising forward. One of the most memorable was born of his creative interpretation of a performing sea lion that caught his eye at the zoo. That animal, Gilroy mused, would be smart enough to balance a glass of Guinness on its nose. This concept became one of the longest living advertising campaigns in history: "My Goodness, My Guinness."
Lovely and rarely encountered John Gilroy farm scene advertising print in its original aged frame. John Gilroy was a polymath of the painting world, with a mind unlike those of his peers. Because of this, the Guinness® campaigns he brought to life from 1928 to the 1960s remain as distinctive now as they were back then. It was Gilroy's colourful artwork that moved our advertising forward. One of the most memorable was born of his creative interpretation of a performing sea lion that caught his eye at the zoo. That animal, Gilroy mused, would be smart enough to balance a glass of Guinness on its nose. This concept became one of the longest living advertising campaigns in history: "My Goodness, My Guinness."“One of the most memorable was born of his creative interpretation of a performing sea lion that caught his eye at the zoo.”
![]()
 The hapless zookeeper, a caricature of Gilroy himself, presented the family of unruly animals. From an ostrich swallowing a Guinness, glass and all, to a pelican with a beak full of bottles. A bounding lion, a thieving bear. A crocodile, kangaroo, and penguin. And, of course, most famous of all, the toucan. This evolved, via the toucan, into the "Guinness-a-day" campaign. That fans still adorn their walls with this poster today is a testament to the creative relationship between Gilroy and Guinness.
The hapless zookeeper, a caricature of Gilroy himself, presented the family of unruly animals. From an ostrich swallowing a Guinness, glass and all, to a pelican with a beak full of bottles. A bounding lion, a thieving bear. A crocodile, kangaroo, and penguin. And, of course, most famous of all, the toucan. This evolved, via the toucan, into the "Guinness-a-day" campaign. That fans still adorn their walls with this poster today is a testament to the creative relationship between Gilroy and Guinness. Origins : Co GalwayDimensions : 46cm x 36cm 4kg
Origins : Co GalwayDimensions : 46cm x 36cm 4kg -

 Extremely rare,interesting print of the Irish Benches of the Irish Parliamentary Party in the House of Commons in 1885,with all members identified by name and number. Gort Co Galway 45 cm x 60cm The Irish Parliamentary Party or more commonly called the Irish Party or the Home Rule Party) was formed in 1874 by Isaac Butt, the leader of the Nationalist Party, replacing the Home Rule League, as official parliamentary party for Irish nationalist Members of Parliament (MPs) elected to the House of Commons at Westminster within the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland up until 1918. Its central objectives were legislative independence for Ireland and land reform. Its constitutional movement was instrumental in laying the groundwork for Irish self-government through three Irish Home Rule bills.Instrumental to the party's rise and fall was the iconic statesman,Charles Stewart Parnell.
Extremely rare,interesting print of the Irish Benches of the Irish Parliamentary Party in the House of Commons in 1885,with all members identified by name and number. Gort Co Galway 45 cm x 60cm The Irish Parliamentary Party or more commonly called the Irish Party or the Home Rule Party) was formed in 1874 by Isaac Butt, the leader of the Nationalist Party, replacing the Home Rule League, as official parliamentary party for Irish nationalist Members of Parliament (MPs) elected to the House of Commons at Westminster within the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland up until 1918. Its central objectives were legislative independence for Ireland and land reform. Its constitutional movement was instrumental in laying the groundwork for Irish self-government through three Irish Home Rule bills.Instrumental to the party's rise and fall was the iconic statesman,Charles Stewart Parnell. -

 Lovely Irish Mist Pub Mirror-the Worlds Most Luxurious Liqueur Pub Mirror . Edenderry Co Offaly. 60cm x 50cm Irish Mist is a brown Whiskey Liqueur produced in Dublin, Ireland, by the Irish Mist Liqueur Company Ltd. In September 2010 it was announced that the brand was being bought by Gruppo Campari from William Grant, only a few months after Grants had bought it from the C&C Group. It is made from aged Irish whiskey, heather and clover honey, aromatic herbs, and other spirits, blended to an ancient recipe claimed to be 1,000 years old.Though it was once 80 US proof (40% alcohol per volume), Irish Mist is now 35% or 70 US proof. The bottle shape has also been changed from a “decanter” style to a more traditional whiskey bottle shape. It is currently available in more than 40 countries. Irish Mist was the first liqueur to be produced in Ireland when commercial production began in 1947 at Tullamore, County Offaly. Tullamore is the hometown of the Williams family who were the original owners of Irish Mist. The company history goes back to 1829 when the Tullamore Distillery was founded to produce Irish whiskey. In the mid-1940s Desmond E. Williams began the search for an alternative yet related product, eventually deciding to produce a liqueur based on the ancient beverage known as heather wine.In 1985 the Cantrell & Cochrane Group purchased the Irish Mist Liqueur Company from the Williams family. In the summer of 2010 Irish Mist and the entire spirit division of C&C was bought by William Grant of Scotland. In September 2010 they in turn sold Irish Mist to Gruppo Campari.Irish Mist is typically served straight up or on ice, but also goes with coffee, vodka, or cranberry juice. Per the makers, Irish Mist’s most popular recipe is Irish Mist with Cola and Lime. A Rusty Mist is an ounce of Irish Mist with an ounce of Drambuie Scotch whisky liqueur.A Black Nail is made from equal parts Irish Mist and Irish whiskey.
Lovely Irish Mist Pub Mirror-the Worlds Most Luxurious Liqueur Pub Mirror . Edenderry Co Offaly. 60cm x 50cm Irish Mist is a brown Whiskey Liqueur produced in Dublin, Ireland, by the Irish Mist Liqueur Company Ltd. In September 2010 it was announced that the brand was being bought by Gruppo Campari from William Grant, only a few months after Grants had bought it from the C&C Group. It is made from aged Irish whiskey, heather and clover honey, aromatic herbs, and other spirits, blended to an ancient recipe claimed to be 1,000 years old.Though it was once 80 US proof (40% alcohol per volume), Irish Mist is now 35% or 70 US proof. The bottle shape has also been changed from a “decanter” style to a more traditional whiskey bottle shape. It is currently available in more than 40 countries. Irish Mist was the first liqueur to be produced in Ireland when commercial production began in 1947 at Tullamore, County Offaly. Tullamore is the hometown of the Williams family who were the original owners of Irish Mist. The company history goes back to 1829 when the Tullamore Distillery was founded to produce Irish whiskey. In the mid-1940s Desmond E. Williams began the search for an alternative yet related product, eventually deciding to produce a liqueur based on the ancient beverage known as heather wine.In 1985 the Cantrell & Cochrane Group purchased the Irish Mist Liqueur Company from the Williams family. In the summer of 2010 Irish Mist and the entire spirit division of C&C was bought by William Grant of Scotland. In September 2010 they in turn sold Irish Mist to Gruppo Campari.Irish Mist is typically served straight up or on ice, but also goes with coffee, vodka, or cranberry juice. Per the makers, Irish Mist’s most popular recipe is Irish Mist with Cola and Lime. A Rusty Mist is an ounce of Irish Mist with an ounce of Drambuie Scotch whisky liqueur.A Black Nail is made from equal parts Irish Mist and Irish whiskey.














